Исламские геометрические орнаменты, их история и способы построения
Автор: Щетников А.
Журнал: Schole. Философское антиковедение и классическая традиция @classics-nsu-schole
Рубрика: Публикации
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.18, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В данной статье рассматривается искусство геометрического орнамента, широко распространенное во всем исламском мире. Это искусство появилось в начале XI века в Хорасане и Трансоксании, бурно развивалось в последующие два столетия до монгольского нашествия, отсюда перешло в Дамаск, Каир и далее в страны Магриба, а затем вновь расцвело в империи Тимуридов, когда к сложной геометрии звездчатых многоугольников добавились многоцветные решения. Мы рассматриваем различные принципы построения этих узоров, уделяя особое внимание так называемой "полигональной технике".
Архитектурный орнамент, исламский геометрический дизайн, гирих, соприкасающиеся многоугольники, полигональная техника
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147244491
IDR: 147244491 | DOI: 10.25205/1995-4328-2024-18-1-427-468
Текст научной статьи Исламские геометрические орнаменты, их история и способы построения
Непосредственным поводом для написания этой статьи стала наша поездка в Узбекистан, где я своими глазами увидел великолепные геометрические и растительные орнаменты, украшающие медресе, мечети, мавзолеи и минареты Хивы, Бухары и Самарканда. Искусство построения столь сложных орнаментов не могло обойтись без знания геометрии, и мне захотелось понять, какая геометрия тут была задействована, и как она воплощалась в работе мастеров, придумывавших и изготавливавших эти узоры. Я купил в Бухаре альбом и цветные карандаши, циркуль и линейку, и начал рисовать, чертить и размышлять. Вернувшись домой, стал читать обширную литературу по этому вопросу и продолжил разбираться с проблемами, возникающими при построении таких орнаментов. Результаты своих изысканий изложил в четырёх популярных видеороликах для канала GetAClass . А теперь настало время собрать их в статье — для пользы всех, кто интересуется связями, возникающими между наукой и искусством в их долгой истории. Статья будет носить
по преимуществу обзорный характер, будучи в значительной мере основанной на многочисленных книгах и статьях по данной теме. Однако я изложу в ней и некоторые результаты своих собственных наблюдений, реконструкций и размышлений. И ещё: хотя созерцание сложных орнаментов подводит нас к рассмотрению в первую очередь геометрической стороны дела, следует держать в уме и то, что у этих орнаментов была своя история, что они создавались мастерами этого искусства, а какие-то сложные конструкции могли быть придуманы и геометрами прошлого, — и рассматривая эти орнаменты сегодня, мы можем погрузиться в это прошлое, в мир искусства и человеческой мысли, если будем задавать себе правильные вопросы.
Предварительные сведения из истории
Геометрические орнаменты, составленные из ломаных линий, многоугольников и многоконечных звёзд, распространены по всему мусульманскому Востоку, от Средней Азии, Северной Индии, Афганистана и Ирана до Марокко и Гранады. Такой орнамент называют персидским словом «гирих» (ге-рех, герих), что значит «узел».
Геометрические орнаменты Средней Азии, дошедшие до наших дней, по большей части созданы после монгольского нашествия в 13 веке и наступившего за ним почти векового запустения и упадка. Радующие глаз своей лазурной синевой самаркандские орнаменты, выложенные поливной терракотой, полихромной мозаикой и глазурованными плитками, созданы при жизни Тимура (вторая половина 14 века), сделавшего этот вновь отстроенный город своей столицей, и его внука Улугбека (первая половина 15 века). В эту пору были построены многие мавзолеи комплекса Шахи Зинда, мечеть Биби-Ханым, мавзолей Гур-Эмир, в котором погребены Тимур и Улугбек, и медресе
Улугбека на площади Регистан; а завершённый вид ансамбль этой площади принял в середине 17 века со строительством ещё двух медресе Шердор и Тилля-Кари. Орнаменты Бухары — несколько более поздние по времени; первой постройкой послемонгольской эпохи здесь является медресе Улугбека, а большая часть архитектурного декора бухарских медресе и мечетей относится к 16 веку. Орнаменты Хивы, в которых геометрический орнамент «гирих» умопомрачительным образом сплетается с растительным орнаментом «ислими», по времени самые поздние, они созданы в 19 веке — а от архитектурных орнаментов древнего Хорезма почти ничего не сохранилось. Орнаменты, продолжающие древнюю геометрическую традицию, создаются в городах Средней Азии и в наши дни, как при реконструкции памятников архитектуры, так и при строительстве новых зданий и архитектурных ансамблей. Что касается реконструкции, надо понимать, что часть воссозданных орнаментов — это также творения современных мастеров; ведь там, где часть здания была обрушена полностью, узнать, как она была изначально украшена, уже невозможно, а оставить при восстановлении кирпичную стену без украшения — значит сделать её непривлекательной, мало отличающейся от других кирпичных стен, что конечно неправильно.
В Средней Азии сохранилось не так много построек домонгольского периода. Одной из самых ранних является мавзолей Саманидов в Бухаре, построенный в начале 10 века. Этот прекрасно сохранившийся памятник архитектуры украшен узорной кладкой обожжённого тёсаного кирпича, и классические гирихи с переплетающимися геометрическими фигурами и звёздами в его декоре отсутствуют. На этом основании можно предположить, что развитой системы гирихов среднеазиатские мастера в это время ещё не знали, хотя простые орнаменты из шестиконечных звёзд и шестиугольников, равно как и из восьмиконечных звёзд и квадратов, могли использоваться в качестве архитектурного декора и раньше.
Судя по немногим дошедшим до наших дней постройкам и находкам археологов, гирихи появляются в архитектурном декоре Средней Азии в 10 веке. В селении Тим в сотне километров к юго-западу от Самарканда находится мавзолей Араб-Ата, постройка которого по надписи на нём датируется 978 годом (Пугаченкова 1963). Это самый ранний архитектурный памятник Средней Азии, в котором система гириха предстает в развитом виде. Стрельчатая ниша его портала украшена изящным орнаментом, построенным на сетке равносторонних треугольников (Рис. 1). Он выполнен в технике резьбы по ганчу — материалу из гипса и глины. Концом 10 века также датируется мавзолей Мир-Сеид Бахрам в Кермине, близ Навои. Здесь в обрамлении пор- тала использован орнамент из кирпичной решётки на квадратной сетке, в ко- тором крестовые солярные знаки чередуются с пересекающимися по диагонали квадратами.
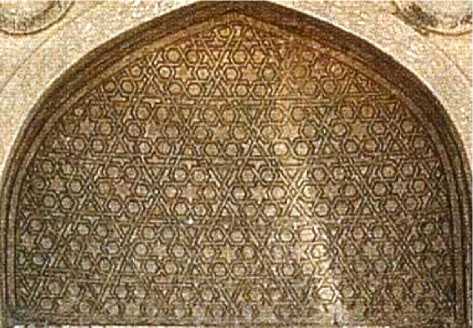
Рис. 1. Ганчевая панель мавзолея Араб-Ата в Тиме.
Первой половиной 11 века принято датировать башню Бурана́ — сохранившуюся нижнюю часть минарета в Чуйской долине (Бернштам 1950, с. 40–45). Она опоясана пятью орнаментальными кольцами кирпичной кладки, причём орнаменты во всех этих кольцах разные. Все кирпичи в узоре выложены по горизонтали либо по вертикали простой «текстильной» кладкой, однако сами орнаменты устроены здесь весьма замысловато — видно, что простыми узорами мысль их авторов уже не удовлетворялась, и они искали схемы, способные поразить наше зрение и воображение (Рис. 2).
Рис. 2. Структура кирпичной кладки первого пояса башни Бурана́ в Чуйской долине.
Следующим 12 веком датируются гирихи, сохранившиеся на нескольких среднеазиатских постройках эпохи Караханидов. Узоры из переплетающихся и восьмиконечных звёзд можно видеть в обрамлении южного портала мечети Магоки-Аттари в Бухаре. Терракотовые плитки с шестиконечными и восьмиконечными звёздами украшают мавзолей Айша-Биби близ города Тараза в Казахстане. Кирпичные и терракотовые узоры с различными геометрическими фигурами и изящными растительными орнаментами сохранились на трёх мавзолеях и стоящем рядом с ними минарете, построенных во второй половине 12 века в Узгене — городе в восточной части Ферганской долины на территории Кыргызстана (Бернштам 1950, с. 46–85; Булатов 1988, с. 278–282).
Геометрические орнаменты применялись в эту эпоху не только во внешнем декоре построек, но и в их внутреннем убранстве. Относительно простые в геометрическом плане узоры с шестиконечными звёздами, выполненные в технике резьбы по ганчу, найдены при раскопках дворца Саманидов в Афро-сиабе — древнем домонгольском Самарканде; эти узоры принято датировать второй половиной 10 века (Рис. 3) .

Рис. 3. Ганчевая панель из дворца Саманидов, хранящаяся в Музее истории основания Самарканда.
Особый интерес представляют геометрические орнаменты, обнаруженные археологической экспедицией музея культур Востока при раскопках дворца правителей Термеза (Веймарн 1936, Денике 1939, Термезская экспедиция 1941, Ремпель 1961). Сам дворец был построен ок. 1130, украшающие его приёмный зал ганчевые панели датируются второй половиной 12 века. На этих панелях встречаются сложные геометрические орнаменты, отличающиеся исключительным разнообразием мотивов и требующие искусного согласования элементов между собой.

Рис. 4. Ганчевая панель из Нишапура, хранящаяся в Метрополитен-музее в Нью-Йорке (40.170.442).
Украшение построек сложными геометрическими узорами из резного обожжённого кирпича, предполагающее высокую геометрическую изощрённость, известно в 11 веке на территории северного Ирана. Две башни-мавзолея в Харракане (1067 и 1093) по всем своим граням украшены разнообразными орнаментами, выказывающими высокую геометрическую осведомлённость их автора (Bier 2002, Makovicky 2023b).
В тимпанах северо-восточного купола Пятничной мечети в Исфахане, построенного в 1089 году, имеются орнаменты с разнообразной геометрической структурой, в том числе и самый ранний из дошедших до наших дней и впоследствии исключительно часто воспроизводившийся орнамент из 10-конечных звёзд, а также весьма изощрённый орнамент, основанный на делении прямого угла на семь равных частей (Bonner 2012, 2016). Создание таких орнаментов требует тонкого геометрического воображения, и участие крупных математиков в этом процессе представляется несомненным; было высказано предположение, что эти орнаменты связаны со знаменитым математиком и поэтом Омаром Хайямом, который в это время как раз жил в Исфахане (Özdural 1995).
В Иране и в Афганистане имеются и другие украшенные резным кирпичом постройки этой эпохи, чаще с простыми, но иногда и с весьма сложными орнаментами. Среди богатых кирпичными украшениями памятников 12 века на территории северного Афганистана можно назвать минарет Мас’уда III в Газне (до 1115), руины мавзолея в Чишти Шариф (1167), руины медресе Шах-и Машад (1176), минарет в Джаме (1194), портал Гуридов в пятничной мечети в Герате (ок. 1200).
В целом можно сказать, что искусство гириха складывается и открывает всё новые и новые геометрические схемы в домонгольский период, будучи воплощённым как во внутреннем ганчевом декоре, так и в отделке построек резным обожжённым кирпичом и терракотовой плиткой, обычно неокрашенными, и лишь иногда и в некоторых деталях — с голубой глазурью. Здесь я хочу особо подчеркнуть, что весь период 11–12 вв. в плане создания гирихов следует считать не ремесленным, но творческим, ведь само разнообразие геометрических схем на не слишком многочисленных дошедших до нас памятниках этой эпохи говорит о том, что их авторы постоянно стремились к тому, чтобы придумывать нечто новое, чтобы изобретённые ими орнаменты были такими, каких никто до сих пор не придумывал.
Письменные свидетельства
Как уже было сказано выше и будет показано ниже, начиная с некоторого уровня сложности геометрических орнаментов просто невозможно представить, чтобы они были построены без опоры на соответствующий уровень геометрических знаний. Базовая геометрия построений с помощью циркуля и линейки содержится в Началах Евклида, где рассматривается в том числе и построение правильного пятиугольника.
Некоторые более специальные знания содержатся в Книге духовных искусных приемов и природных тайн о тонкостях геометрических фигур , написанной в 933 году Абу Насром Мухаммедом ал-Фараби (870–950). Эта книга в редакции Абу-л-Вафы ал-Бузджани (940–998), добавившего к ней раздел, посвящённый чертёжным инструментам, получила характерное название О том, что необходимо ремесленнику из геометрических построений . Среди прочего здесь описывается метод трисекции угла с помощью подвижной линейки (так называемый «метод вставки»), основанный на нём метод построения правильного девятиугольника, а также приближённый метод построения правильного семиугольника. Однако в целом это сочинение не выглядит книгой, напрямую помогающей при изобретении гирихов.
В приложении к персидскому переводу трактата Абу-л-Вафы, хранящемуся в Парижской национальной библиотеке, имеется написанное на фарси анонимное Введение в учение о подобных и соответственных фигурах . Это единственная средневековая рукопись, в которой содержатся приёмы построения гирихов. Её принято датировать приблизительно 1300 годом, поскольку её цитирует живший в это время Абу Бакр ал-Халил, хотя возможно, её исходный вариант был написан и раньше. Рукопись представляет собой собрание чертежей с конспективными комментариями, по большей части не слишком внятными из-за их краткости. Перевод А. Б. Вильдановой опубликован в приложении к книге М. С. Булатова (1988) и проанализирован там же. К этой рукописи также имеются комментарии Chorbachi 1989, Özdural 1996, 2000, Bonner 2016.
Кроме письменных текстов, до нас дошло несколько свитков с чертежами — своеобразных «альбомов» с образцами гирихов. Самый известный из них — это датируемый концом 15 века свиток из стамбульского дворца Топкапы размером 33 см на 29,5 м, содержащий 114 орнаментов, в том числе и весьма изощрённых (см. Necipoğlu 1996, Rogers 1997, Cromwell 2010). Опубликовано также описание бухарских свитков, использовавшихся местными мастерами (Бакланов 1947, Андреев 1956, Хмельницкий 1959).
Математики и архитекторы этой эпохи
Естественно предполагать, что изобретение сложных гирихов не обошлось без участия математиков, однако кто именно приложил руку к этому делу, мы не знаем. Назовём некоторых математиков мусульманского Востока по поколениям, с 9 по 12 век. На первую половину 9 века приходится деятельность ал-Хорезми (ок. 783 – ок. 850), работавшего в багдадском «Доме мудрости» — академии, учреждённой халифом ал-Мамуном. Во второй половине 9 века там же в Багдаде работали братья Бану Муса, Сабит ибн Корра, ал-Баттани и другие математики. Создание первых гирихов предположительно датируется второй половиной 10 века; в Багдаде в это время работали упомянутые выше ал-Фараби и Абу-л-Вафа. Крупнейший математик первой половины 11 века — это Абу Рейхан ал-Бируни (973–1048), а во второй половине 11 века жил Омар Хайям (1048–1131).
Название книги Абу-л-Вафы / ал-Фараби О том, что необходимо ремесленнику из геометрических построений говорит о том, что геометры, знатоки Евклида и Архимеда, не избегали общения с теми, кто занимался проектированием архитектурных построек и их декора. Вот что говорит Абу-л-Вафа в предисловии к этой книге:
Я установил смысл того, что упоминалось в присутствии его величества из области геометрических построений, так как часто применялось ремесленниками; при этом я отвлекался от причин и доказательств. Это облегчит ремесленникам применение этих построений и проложит дорогу к ним.
Из предисловия следует, что некие «ремесленники» обсуждали практику геометрических построений не где-нибудь, но в высоком собрании в присутствии шахиншаха. Стало быть, и статус этих «ремесленников» был достаточно высоким, и в геометрии они разбирались неплохо, хотя и не на таком уровне, как профессиональные геометры, не слишком утруждая себя разбором геометрических доказательств, поскольку практика построений интересовала их гораздо больше. Как сказал ал-Фараби в главе 10 «О разделении квадратов»,
Многие геометры и ремесленники ошибались в построениях этих квадратов в их составлении, геометры — в силу недостаточной практики, а ремесленники — из-за того, что им не хватало знаний о доказательствах. Так как геометры не знают практических методов построений, с помощью доказательств на линиях им трудно найти правильные способы приближённых построений. Что же касается ремесленников, когда они находят приближённое построение, они получают то, что мы ощущаем и видим, не обращая внимания на доказательства с помощью линий и на геометров.
Кем же были эти «ремесленники», обсуждавшие с геометрами свои задачи? Надо думать, не каменщиками, плотниками и резчиками по дереву, но теми, кто создавал проекты, по которым потом работали эти люди, то есть архитекторами. Вопросу об общественном положении и образованности средневековых архитекторов посвящён специальный раздел в книге М. С. Булатова (1988). Архитектор, умеющий создавать чертежи, модели и сметы, являлся человеком двора, и входил в один класс придворных с врачами и астрономами. Он получал образование в медресе, изучая адаб — комплекс наук, включавший в себя арифметику, геометрию, астрономию, философию, поэтику, медицину, фармакологию. Его имя фиксировалось на постройке, как знак авторства, и этим он отличался от безымянных строителей. И если он в своей практике и не обращался к доказательствам Евклида, поскольку они относятся к теоретической части геометрии, то построениями с помощью циркуля, линейки и угольника он безусловно владел, поскольку строительство невозможно без проекта, а проект должен быть воплощён в чертежах. Чертежами мы дальше и займёмся.
Метод мелкой сетки
Этот метод построения гирихов — самый простой; и он хорошо работает для простых орнаментов на основе квадратной либо изогональной (состоящей из равносторонних треугольников) сетки. Орнамент на квадратной сетке, удобный для выкладывания его рядами кирпичей, мы уже видели на Рис. 2; теперь же рассмотрим орнамент из шестиконечных звёзд, соприкасающихся друг с другом концами лучей по две либо по три; промежутки между звёздами соответственно будут правильными шестиугольниками либо ромбами. Два таких орнамента из комплекса мавзолеев Шахи-Зинда в Самарканде изображены на Рис. 5. В обоих случаях внутрь больших шестиконечных звёзд, составляющих основу орнамента, встроены с поворотом на 30° малые шестиконечные звёзды, делающие узор более богатым.

Рис. 5. Два орнамента на изогональной сетке. Иллюстрации из комплекса Шахи-Зинда в Самарканде.
Ещё один способ переплетения шестиугольников можно видеть на резной панели по ганчу из Нишапура (Рис. 6) . (Здесь я сделаю техническое замечание: слова «иллюстрация собрана на основе…» в описании этого и многих следующих рисунков означает следующее: я взял фотографию реального орнамента, вырезал из неё прямоугольный фрагмент и многократно его размножил, чтобы заполнить этим орнаментом достаточно большой прямоугольный участок плоскости.)
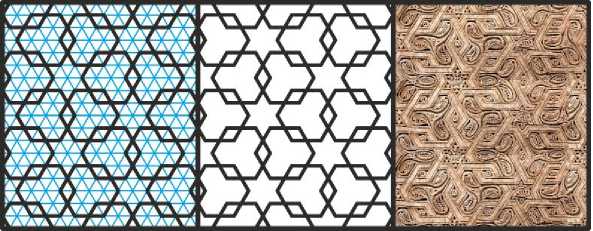
Рис. 6. Орнамент на мелкой изогональной сетке. Иллюстрация собрана на основе орнамента по ганчу, найденного на раскопках близ Нишапура.
Теперь посмотрим, как на такой же сетке строится более изощрённый орнамент из мавзолея Араб-Ата в Тиме (Рис. 7). Построим на сетке шестиконечную звезду в обрамлении шестиугольников, и окружим её ещё одним внешним шестиугольником, отодвинув его стороны на один шаг сетки; этот элемент выделен красным цветом. Этот фрагмент распространим по сетке так, чтобы внешние шестиугольники перекрывали друг друга, примыкая углами к малым шестиугольникам соседних фрагментов, создавая в обрамлении характерные фигуры «корабликов».
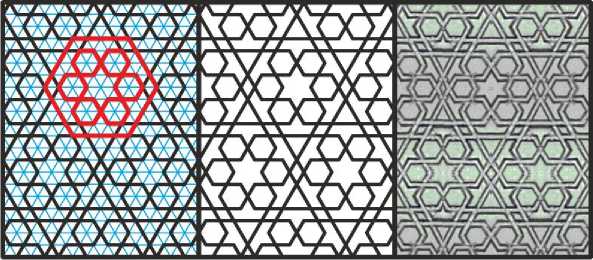
Рис. 7. Орнамент на мелкой изогональной сетке. Иллюстрация собрана на основе орнамента из мавзолея Араб-ата в Тиме.
В качестве следующей вариации этой же темы рассмотрим гирих, вырезанный на деревянном кенотафе из мавзолея Сайф ад-Дина Бахарзи в Бухаре (Немцова 2003, фото 26; кенотаф находится в музее «Тарикат Накшбандия» близ Бухары). Здесь снова встречается мотив шестиконечной звезды в обрамлении шестиугольников и корабликов, но теперь стороны фигур имеют длины как в 2, так и в 3 единицы сетки (Рис. 8).
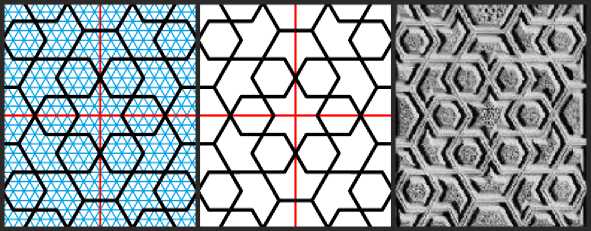
Рис. 8. Орнамент на боковой панели кенотафа Сайф ад-Дина Бахарзи в Бухаре, построенный на мелкой изогональной сетке.
Сразу же отметим один важный для построения гирихов момент. При построении большого орнамента на плоскости весьма неудобно расчерчивать мелкой сеткой всю плоскость. Удобнее построить на бумаге или другом материале раппорт — повторяющийся прямоугольный фрагмент орнамента, выделенный на Рис. 8 красным цветом. Такой раппорт копируется на рабочую поверхность, каждый раз зеркально перевёрнутый в соседнем прямоугольнике.
Гирихи на крупной квадратной сетке
Если в геометрических орнаментах имеются элементы, которые не получается вписать в узлы однородной мелкой сетки, приходится переходить к крупной сетке. Простейший пример такого рода являет собой широко распространённый орнамент на квадратной сетке, составленный из примыкающих друг к другу концами лучей восьмиконечных звёзд (Рис. 9). Его построение на мелкой сетке невозможно, поскольку здесь по одному направлению чередуются шаги, соотносящиеся друг с другом как сторона и диагональ квадрата, а это отношение является иррациональным.
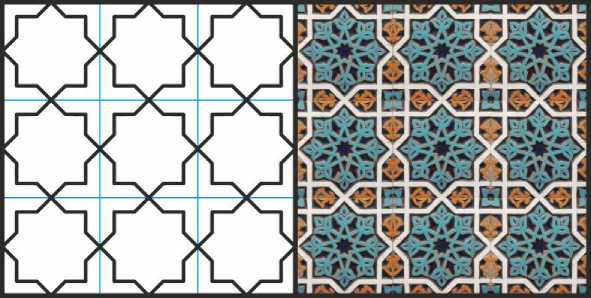
Рис. 9. Орнамент из восьмиконечных звёзд. Иллюстрация собрана на основе орнамента из Пятничной мечети Хазрат Имам в Ташкенте.
Ещё один простой орнамент на квадратной сетке составлен из примыкаю- щих друг к другу правильных восьмиугольников и квадратов (Рис. 10, а). Если всю эту структуру наложить на себя со сдвигом, образуется орнамент, который часто встречается в деревянных или ганчевых резных решётках — пан-джарах (Рис. 10, б).
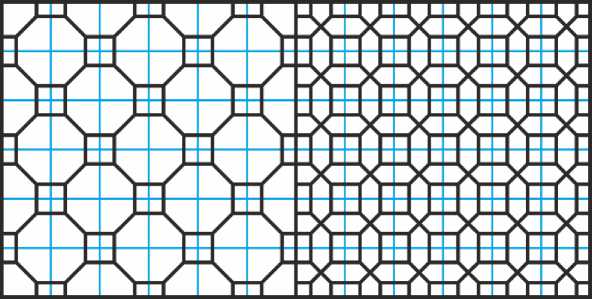
Рис. 10. Два простых орнамента из восьмиугольников и квадратов.
Добавим к этим орнаментам ещё два мотива из перекрывающихся восьмиугольников (Рис. 11) , чтобы показать, как одна простая геометрическая фигура порождает целый набор изящных решений.
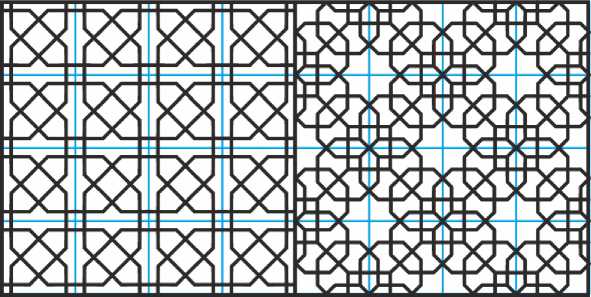
Рис. 11. Ещё два орнамента из перекрывающихся восьмиугольников.
Гирихи на крупной изогональной сетке
Теперь рассмотрим несколько орнаментов, построенных на крупной изогональной сетке. Когда шестиконечные звёзды стыкованы друг с другом концами лучей, каждую звезду можно удвоить и повернуть на 30°, в результате чего получится орнамент из примыкающих друг к другу 12-конечных звёзд (Рис. 12).
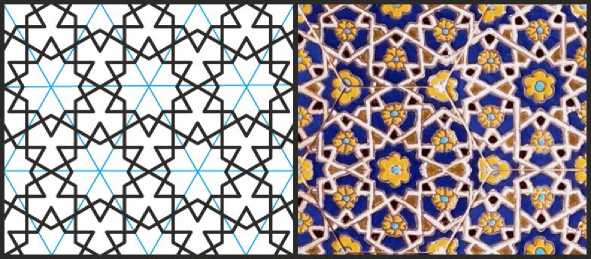
Рис. 12. Орнамент из 12-конечных звёзд. Иллюстрация собрана на основе орнамента из комплекса Шахи-Зинда в Самарканде.
В качестве повторяющегося элемента следующего орнамента взят 12-угольник с центром в узле сетки; его размер подобран так, чтобы соседние 12-угольники пересекались в серединах сторон (Рис. 13, верхний ряд). На ещё одной вариации этого орнамента 12-угольники заменены на 12-конечные звёзды, образованные пересечением двух шестиугольников; при этом соседние 12-угольники пересекаются в изломах границы (Рис. 13, нижний ряд). Этот же орнамент читается и как составленный из шестиугольных звёзд и правильных шестиугольников, примыкающих друг к другу вершинами.
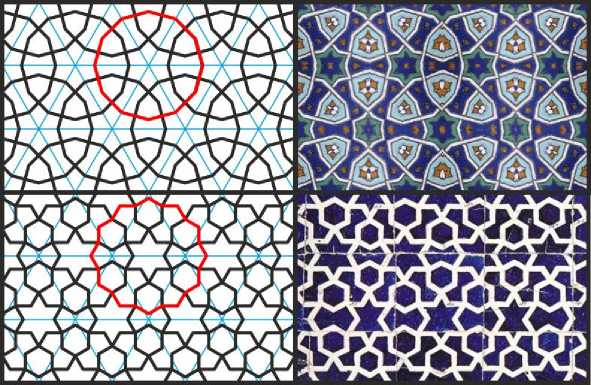
Рис. 13. Орнаменты на изогональной сетке. Иллюстрации собраны на основе орнаментов из из комплекса Шахи-Зинда в Самарканде и медресе Мухаммада Рахим-хана в Хиве.
Следующий орнамент также построен на изогональной сетке, которую, впрочем, удобнее превратить в сетку правильных шестиугольников. Он образован перекрывающимися квадратами, середины противоположных сторон которых расположены в соседних вершинах этих шестиугольников (Рис. 14). Шесть квадратов обрамляют правильный шестиугольник, внутри каждого квадрата появляется «кувшинчик», а при встрече трёх квадратов в узле гексагональной сетки возникает «цветок» с тремя четырёхугольными лепестками.
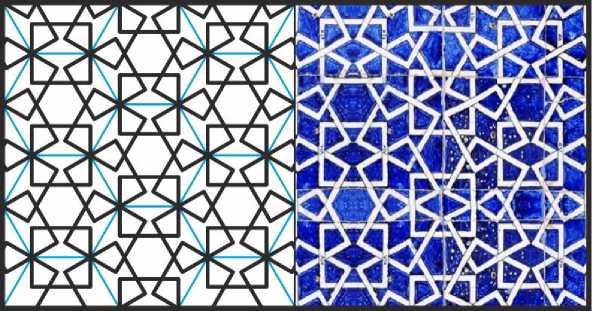
Рис. 14. Орнамент из квадратов на изогональной сетке. Иллюстрация собрана на основе орнамента из дворца Таш-Хаули в Хиве.
У всех рассмотренных выше орнаментов есть важная особенность, касающаяся их зрительного восприятия. Орнамент на квадратной сетке можно повернуть на 45°, а орнамент на изогональной сетке — на 30° (или, что то же самое, на 90°), и, оставаясь структурно теми же самыми, они будут восприниматься совсем иначе, поскольку задающие основу восприятия горизонтальные и вертикальные ряды повторяющихся фигур теперь окажутся выстроены в ином порядке. Читатель может попрактиковаться в такой перестройке восприятия самостоятельно.
Звёзды с 10 и 5 лучами в вершинах ромбической сетки
В гирихах на основе квадратной сетки в качестве базовых фигур участвуют квадраты и восьмиугольники, на основе изогональной сетки — шести- и 12-угольники. В Началах Евклида показано, как с помощью циркуля и линейки построить правильные пяти- и десятиугольник. И естественно, именно эти две фигуры оказались кандидатами на роль основы для следующих геометрических орнаментов.
Однако если квадратами и правильными шестиугольниками можно замостить плоскость, то правильными пятиугольниками сделать этого не получается: угол при вершине пятиугольника равен 108°, и три пятиугольника с общей вершиной не добирают до 360°, а четыре в сумме дают слишком много. Угол при вершине правильного 10-угольника равен 144°, и вместе с углами двух пятиугольников он даёт нужные 360°. Поэтому вокруг 10-угольника можно расположить десять пятиугольников с такими же по длине сторонами, образовав розетку; однако такую розетку нельзя распространить на всю плоскость.
Выход из этого затруднения был найден в том, чтобы слить вместе два пятиугольника и образовать из них выпуклую шестиугольную фигуру («бочку»), которая вместе с десятиугольниками и пятиугольниками позволяет создать регулярное замощение плоскости (Рис. 15, а ). Наряду с этим замощением используется и второй его вариант, когда правильные десятиугольники непосредственно примыкают друг к другу сторонами, а промежутки между ними заполняются невыпуклыми шестиугольными фигурами («бабочками»). Стороны многоугольников обоих замощений, наложенных друг на друга, делят друг друга под прямым углом пополам (Рис. 15, б ). Одни и те же гирихи, как мы увидим ниже, могут строиться и на первом, и на втором замощении.
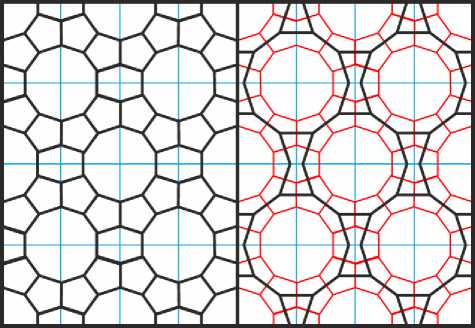
Рис. 15. Два варианта регулярного замощения плоскости для построения гирихов c 10-конечными звёздами.
Дальше делается ключевой шаг, с помощью которого строятся многие орнаменты с многоконечными звёздами. Через середины всех сторон проводятся два отрезка под одним и тем же углом к стороне, а потом эти отрезки соединяются внутри многоугольников замощения. Этот метод построения первым из исследователей гирихов переоткрыл и стал применять Эрнст Ханкин (Hankin 1905). Метод Ханкина замечателен тем, что в нём гирих не собирается из мелких деталей, но мысль при его изобретении движется от цельного образа к мелкой деталировке, которая этому образу всецело подчинена. Усвоение этого метода является ключевым и для анализа гирихов, и для их построения, проясняя геометрию, лежащую в их основе (Bonner 2016, Bonner 2017, Majewsky 2020, Cromwell 2014, 2021).
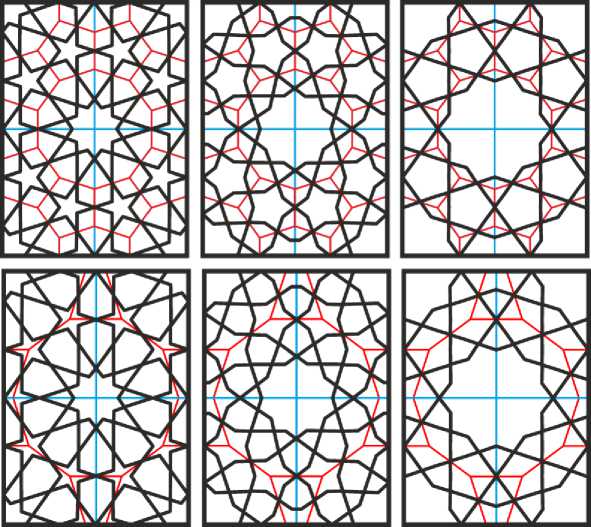
Рис. 16. Построение «острой», «средней» и «тупой» разновидности орнамента с 10- и 5-конечными звёздами на двух вариантах базового замощения.
На Рис. 16 показаны три основных варианта построения раппорта для гири-хов с 10- и 5-конечными звёздами, когда углы при вершинах всех этих звёзд равны 36°, 72°, 104°; эти варианты принято называть «острым», «средним» и «тупым» соответственно. В верхнем ряду подложкой для гирихов служит замощение из десятиугольников, пятиугольников и бочек, в нижнем — из десятиугольников и бабочек. В «тупом» варианте гириха в пятиугольники базового замощения вписаны уже не пятиконечные звёзды, но пятиугольники, которые визуально сами теперь оказываются центрами перекрывающихся пятиконечных звёзд со срезанными концами лучей.
В качестве примера «острой» схемы взята орнаментальная решётка из мавзолея Тадж-Махал в Агре, в которой мы можем видеть не только звёзды, но и исходное замощение плоскости многоугольниками (Рис. 17).
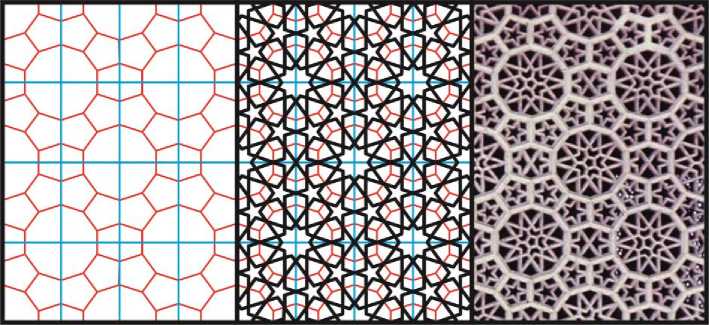
Рис. 17. Орнамент с 10-конечными звёздами, «острая» разновидность. Для иллюстрации взята решётка из мавзолея Тадж-Махал.
Зато орнаменты на основе второй схемы в Самарканде и Бухаре распространены очень широко, и ими оформлены порталы многих мечетей и медресе. В качестве примера взят орнамент из мечети Калян в Бухаре (Рис. 18).
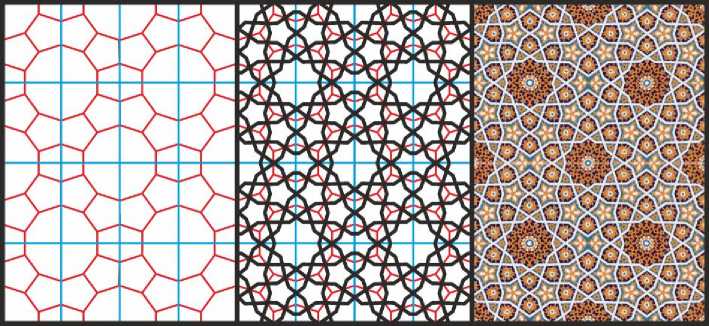
Рис. 18. Орнамент с 10-конечными звёздами, «средняя» разновидность. Иллюстрация собрана на основе орнамента из мечети Калян в Бухаре.
Гирих на основе третьей схемы с подчёркнутым заплетением лент находится на стене дворца Таш-Хаули в Хиве (Рис. 19). Для прояснения структуры этого гириха удобно воспользоваться замощением с десятиугольниками и бабочками.
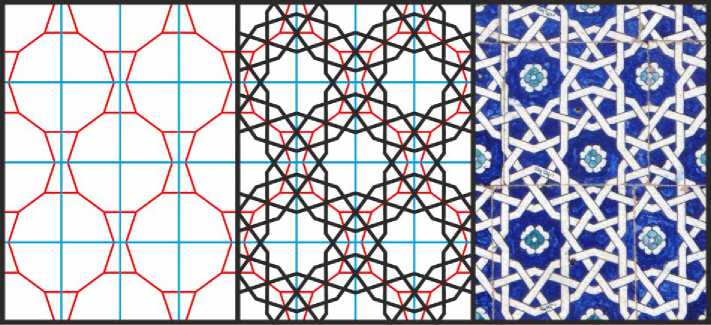
Рис. 19. Орнамент с 10-конечными звёздами, «тупая» разновидность. Иллюстрация представлена орнаментом из дворца Таш-Хаули в Хиве.
Замечу ещё, что в этой статье я рассматриваю орнаменты так, словно они заполняют бесконечную плоскость. Однако не следует забывать, что реальные орнаменты всегда расположены на ограниченной части плоскости. Очень часто из них выбирается полоса шириной в один или два раппорта, расположенная на обрамлении портала, в оконной решётке или в дверной панели. Столь же характерным является встраивание орнамента в тимпан портала. Обычно это делается таким образом, чтобы в верхних прямых углах тимпана располагались центры двух звёзд. Это условие задаёт требование на размеры сетки, и поэтому построение гириха начинается с вычерчивания раппорта, по которому дальше собирается мозаика или изготавливаются плитки.
Выше мы рассмотрели базовое замощение плоскости, возникающее на основе деления прямого угла на пять равных частей, и возникающие на его основе гирихи. Теперь будем усложнять само базовое замощение и смотреть, что при этом получается. В орнаменте на Рис. 20 каждый десятиугольник базового замощения соприкасается с шестью пятиугольниками и четырьмя «бочками». Между четырьмя пятиугольниками в замощении образуется узкий ромб с углом 36° при вершине. На гирихе этому ромбу соответствует возникающая вокруг него фигура в виде кувшинчика. Угол раствора при конце луча звезды в этом построении взят равным 108°; понятно, что здесь возможны также «острый» и «средний» варианты орнамента.
Рис. 20. «Тупая» разновидность орнамента с 10-конечными звёздами, появление «кувшинчиков». Иллюстрация собрана на основе орнамента из мавзолея Гур-Эмир в Самарканде.
В базовом замощении следующего орнамента участвуют те же детали, что и в предыдущем (Рис. 21). Здесь пояс из пятиугольников удвоен параллельным переносом, за счёт чего горизонтальные ряды десятиугольников и бочек ото- двинулись друг от друга.
Рис. 21. «Тупая» разновидность орнамента с 10-конечными звёздами, появление пояса «кувшинчиков». Иллюстрация собрана на основе орнамента из мечети Туман-ака в комплексе Шахи-Зинда в Самарканде.
Конструктор гирихов
Выше мы увидели, что разные гирихи, содержащие 10- и 5-конечные звёзды, могут строиться на основе замощений, содержащих небольшое число элементов, таких как десятиугольники, пятиугольники, бочки и ромбы. Отсюда возникает мысль о наборе элементов, которые могут быть использованы при построении гирихов, относящихся к той или иной системе. Рассмотрению таких наборов посвящён рад статей Джея Боннера, и итоговая для этого круга исследований книга Bonner 2017.
Для гирихов пятилучевой системы такой набор составляют восемь многоугольников с равными сторонами и углами, кратными 36° (Рис. 22) . Это (1) правильный десятиугольник; (2) правильный пятиугольник; (3) «бочка», получаемая пересечением двух пятиугольников; (4) «веретено» с острым углом 72°; (5) ромб с острым углом 72°; (6) ромб с острым углом 36°; (7) «бабочка»; (8) восьмиугольник. Нетрудно видеть, что веретено, ромб с углом 36° и восьмиугольник получаются пересечением двух десятиугольников, бочка образуется объединением двух пятиугольников, ромб с углом 72° — пересечением двух пятиугольников, и бабочка — вычитанием двух ромбов с углом 36° из бочки. Восьмиугольник в построениях гирихов встречается очень редко, но следуя Боннеру, я привожу его для полноты картины.
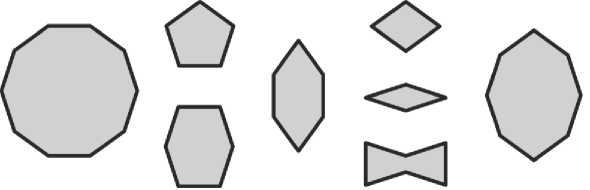
Рис. 22. Набор плиток замощения для построения гирихов пятилучевой системы.
В плитки замощения встраиваются линии будущего орнамента, образуя наборы для гирихов «острой», «средней» и «тупой» разновидностей. На Рис. 23 показаны плитки для «средней» разновидности, когда отрезки, проводимые из середин сторон плиток, образуют с этими сторонами углы в 54°, а между собой — угол в 72°. Наборы плиток для двух других разновидностей пятилучевого гириха строятся аналогичным образом.
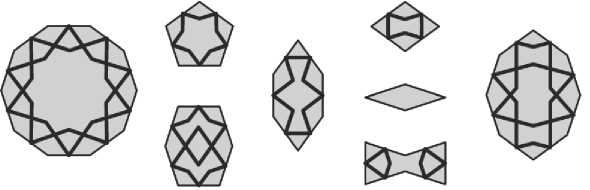
Рис. 23. Набор плиток замощения для построения «средней» разновидности гириха пятилучевой системы.
На основе такого набора можно строить гирихи пятилучевой системы, не содержащие ни 10-конечных, ни 5-конечных звёзд. Простой, и при этом богатый вариантами прочтения вариант такого гириха, в замощении которого использованы только бочки и веретёна, показан на Рис. 24. Структуры такого рода замечательны тем, что их происхождение от правильного десятиугольника сокрыто на двух уровнях: во-первых, на переходе от десятиугольника к фигурам, из которых строится базовое замощение плоскости, во-вторых, на переходе от этого замощения к самому орнаменту.

Рис. 24. Гирих пятилучевой системы, построенный на основе замощения из бочек и веретён.
Звёзды с 12 и 9 лучами в вершинах изогональной сетки
Когда гирихи с 10- и 5-конечными звёздами уже освоены, возникает вопрос: а какие ещё звёзды можно приставлять друг к другу концами лучей, чтобы образовать регулярный орнамент? Чтобы все звёзды были правильными, должны быть правильными и многоугольники в порождающем эти звёзды замощении. Посмотрим, к чему ведёт мысль использовать в орнаменте 12-конечные звёзды. Угол между лучами таких звёзд равен 30°; ему кратен и угол в 60°, характерный для изогональной сетки, и угол в 90°, характерный для квадратной сетки.
Мы начнём с изогональной сетки, и рассмотрим замощение из правильных 12- и 9-угольников, в котром каждый 12-угольник окружён шестью 9-угольниками с бабочками между ними. В соответствующем гирихе будут присутствовать 12- и 9-конечные звёзды (Рис. 25). (Заметим попутно, что разделить окружность на 9 равных частей с помощью циркуля и линейки невозможно. Алгебраически эта задача сводится к кубическому уравнению, а геометрически она решается с помощью конических сечений либо методом вставки.)
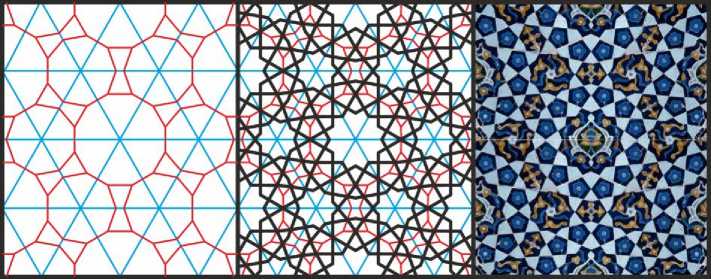
Рис. 25. «Тупой» вариант орнамента с 12- и 9-конечными звёздами,. Иллюстрация собрана на основе орнамента из Пятничной мечети в Исфахане.
Перейдём теперь к «среднему» варианту этого же орнамента. В этом случае базовое замощение удобнее составлять из многоугольников, пятиугольников и бочек. Получающийся при этом орнамент изображён на Рис. 26.
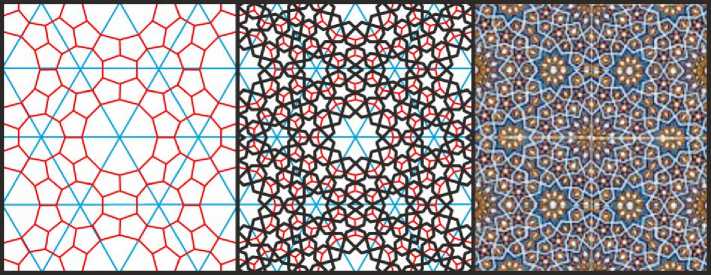
Рис. 26. «Средний» вариант орнамента с 12- и 9-конечными звёздами. Иллюстрация собрана на основе орнамента из медресе Улугбека в Самарканде.
Прямоугольный раппорт этого орнамента, показанный на Рис. 27, содержится в ташкентском свитке, хранящимся в Институте востоковедения Узбекистана. Его детальному анализу посвящена статья Bodner 2012. Нетрудно показать, что получающиеся в этом построении пятиконечные звёзды являются неправильными, поскольку углы между их лучами не равны 72°: тупой угол в закрашенном треугольнике равен 145° (180° за вычетом 15° и 20°), что на 1° отличается от «правильных» 144°. Однако это отклонение от правильности столь мало, что оно никак не заметно глазу. Эта идея «незаметных глазу неправильностей», постижимых только в рассуждении, присутствует и во многих других орнаментах.
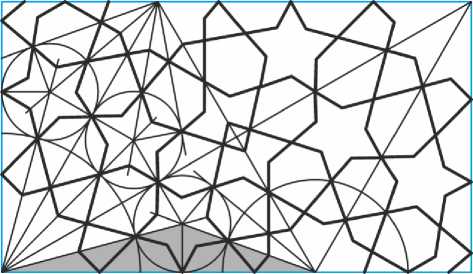
Рис. 27. Раппорт для «среднего» варианта орнамента с 12- и 9-конечными звёздами.
Звёзды с 12 и 8 лучами в вершинах квадратной сетки
Рассмотрим теперь часто встречающийся в Средней Азии орнамент, в котором 12- и 8-конечные звёзды расположены в узлах квадратной сетки, а в промежутках между ними встроены пятиконечные звёзды и «птичьи лапки» (Рис. 28) . Такой орнамент естественно строится на базовом замощении, в котором прокладками между правильными 12- и 8-угольниками служат пятиугольники и бочки.
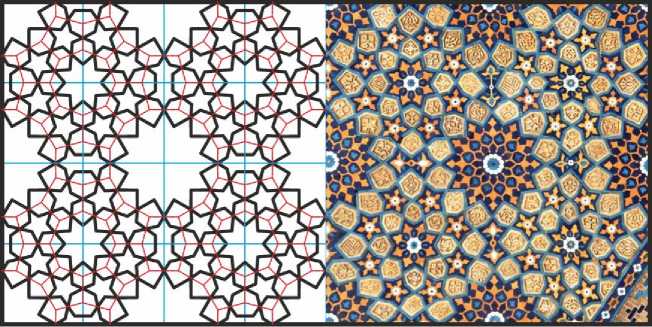
Рис. 28. «Средняя» версия орнамента с 12- и 8-конечными звёздами. Иллюстрация собрана на основе орнамента из мечети Биби-Ханым в Самарканде
В этом орнаменте есть одна тонкость, которая почти не заметна для глаза, но обнаруживается при подсчёте суммы углов в закрашенном внутри раппорта треугольнике (Рис. 29). Острый угол со стороны 12-конечной звезды равен 1/6 прямого, то есть 15°. Острый угол со стороны 8-конечной звезды равен 1/4 прямого, то есть 22,5°. Таким образом, на тупой угол между лучами пятиконечной звезды остаётся 142,5°; однако в правильной пятиконечной звезде этот угол составляет 144°. Разница невелика, но она существует, и потому пятиконечные звёзды в этом орнаменте несколько отличаются от правильных. Если провести к концам лучей пять отрезков из центра окружности, описанной вокруг такой звезды, два угла между этими отрезками со стороны восьмиконечной звезды будут равны 67,5°, а остальные три угла равны 75° — разница существенна, но для глаза не слишком заметна.
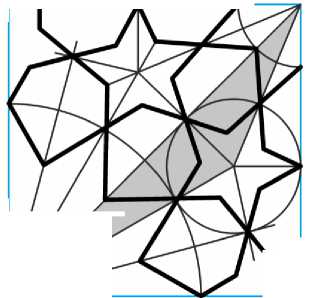
Рис. 29. Раппорт «среднего» варианта орнамента с 12- и 8-конечными звёздами.
Ещё один вариант орнамента с 12- и 8-конечными звёздами в узлах квадратной сетки показан на Рис. 30. Отличие от предыдущего орнамента здесь состоит в том, что теперь восьмиконечная звезда развёрнута лучами вдоль линий сетки, так что обе звезды смотрят своими лучами друг на друга. Такой орнамент удобно строить, предварительно замостив плоскость 12- и 8-угольниками, с бабочками между ними.
Рис. 30. «Тупой» вариант орнамента с 12- и 8-конечными звёздами. Иллюстрация собрана на основе орнамента из мечети Биби-Ханым в Самарканде
Восьмиконечные звёзды в вершинах квадратной сетки
Следующим рассмотрим гирих на квадратной сетке с восьмиконечными звёздами в её узлах и пятиконечными звёздами в промежутках между ними (Рис. 31) . Этот орнамент строится на базовом замощении из правильных восьмиугольников и неправильных пятиугольников. Для примера взята ещё одна решётка из Агры, в которой присутствуют как звёзды, так и линии многоугольников исходного замощения.
Рис. 31. «Острый» вариант орнамента с 8-конечными звёздами.
Для иллюстрации взята решётка из мавзолея Тадж-Махал в Агре.
Пятиконечные звёзды в этом орнаменте очевидно не являются правильными. В закрашенном прямоугольном треугольнике на Рис. 32 острый угол в с вершиной в центре восьмиугольника равен 22,5°, поэтому второй острый угол равен 67,5°, что заметно меньше 72° между соседними лучами правильной пятиконечной звезды. Тем самым четыре угла между лучами пятиконечной звезды равны 67,5°, и на долю пятого угла остаётся 90°: это прямой угол в квадрате, соединяющем центры окружностей, описанных вокруг четырёх соседних пятиконечных звёзд.
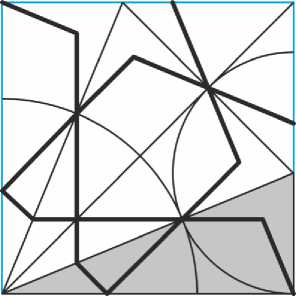
Рис. 32. Раппорт «острого» варианта орнамента с 8-конечными звёздами
Наращивание сложности орнамента за счёт добавления новых деталей в базовое замощение работает и здесь. К примеру, объединив вместе два пятиугольника, образуем шестиугольную бочку; окружив восьмиугольник бочками со всех сторон, мы получаем орнамент, который можно видеть на мимбаре мечети Ибн Тулуна в Каире (Рис. 33) .
Рис. 33. Орнамент на мимбаре мечети Ибн Тулуна в Каире.
Звёзды с 11 и 9 лучами
Орнаменты из 11- и 9-конечных звёзд в среднеазиатском архитектурном декоре похоже что не встречаются; я построил их в качестве упражнения, чтобы убедиться, что принцип построения таких орнаментов мной усвоен. «Тупая» версия орнамента строится на базовом замощении, составленном из правильных 11-угольников, непосредственно примыкающих к ним неправильных 9-угольников, у которых семь сторон равны между собой, а две другие от них отличаются, и двух различающихся между собой разновидностей «бабочек» (Рис. 34) .
Рис. 34. «Тупой» вариант орнамента с 11- и 9-конечными звёздами.
Для «средней» версии, как это было и раньше, удобнее использовать другое базовое замощение, составленное из правильных 11-угольников и неправильных 9-угольников, между которыми располагаются пятиугольники и бочки (Рис. 35). Пятиугольники ограничены стороной 11-угольника, двумя лучами, выходящими из центра 11-угольника, и ещё двумя сторонами, параллельными соседним сторонам 11-угольника; бочка получается объединением двух пятиугольников.
Рис. 35. «Средний» вариант орнамента с 11- и 9-конечными звёздами.
Замощение из квадратов и треугольников
Вернёмся теперь к сетке квадратов и рассмотрим замощение, элементами которого служат квадраты и равносторонние треугольники (Рис. 36, а ). В каждой его вершине встречаются два квадрата (2 по 90°) и три треугольника (3
по 60°), в сумме как раз 360°. Соединив отрезками центры квадратов с центрами соседних треугольников, мы получим замощение, дуальное к данному.
Оно образовано из пятиугольников с тремя углами по 120° и двумя углами по 90°; эти углы сходятся в вершинах замощения соответственно по три или по четыре (Рис. 36, б). Орнаменты в нижнем ряду на этом рисунке в своей основе имеют ту же структуру, что и орнаменты верхнего ряда.
Рис. 36. Орнаменты на основе простейшей сетки из квадратов и равносторонних треугольников.
Построим на квадратной сетке ещё один орнамент из квадратов и правильных треугольников (Рис. 37, а ). В нём присутствуют также правильные 6- и 12-угольники, и размеры последних можно принять за основу раппорта. Сочетая 12-уольники иным образом, преобразуем этот орнамент в родственный ему, построенный уже не на квадратной, а на изогональной сетке (Рис. 37, б ).
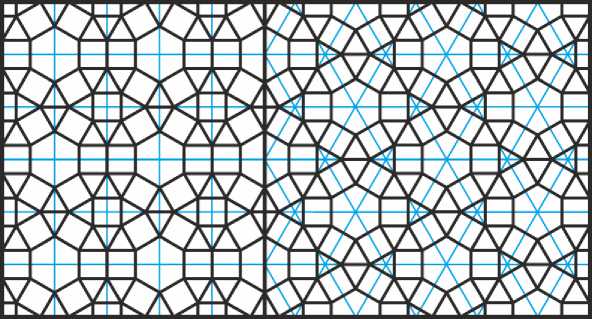
Рис. 37. Орнамент из квадратов, треугольников и шестиугольников
(а) на квадратной сетке, (б) на изогональной сетке.
В следующем замощении на квадратной сетке, родственном только что рассмотренным, участвуют повёрнутые относительно сетки квадраты, треугольники и пятиугольники (Рис. 38) . И уже в который раз может показаться, что все фигуры здесь правильные. Но в таком случае сумма углов при общей вершине была бы равна 366°, что несколько больше, чем 360°. Поэтому квадраты, в силу их симметричного положения, оставлены правильными, а треугольники и пятиугольники несколько деформированы, с сохранением одной оси симметрии. В принципе, одну из этих фигур, треугольник либо пятиугольник, можно было бы оставить правильной, но тогда деформация другой фигуры оказалась бы более заметной. Нижний орнамент на Рис. 38 построен из первого проведением отрезков, соединяющих условные «центры» фигур замощения, и добавлением к ним контуров уменьшенных пятиугольников. Этот орнамент выложен из кирпичей на тимпане западной башни в Харра-кане (Bier 2012).
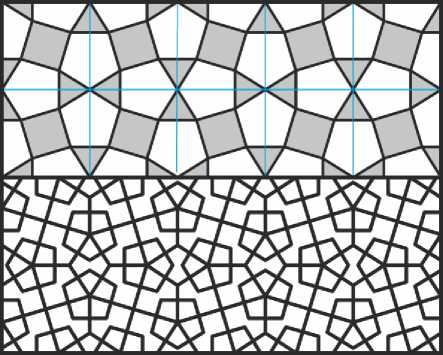
Рис. 38. Замощение из квадратов, треугольников и пятиугольников, и орнамент на его основе.
Появление семиугольников
В комплексе Шахи-Зинда в Самарканде находится орнамент редкого типа с семиугольниками и семиконечными звёздами, не совсем правильными. Сам орнамент, как это часто бывает, расположен на ограниченной части плоскости так, что его полная структура просматривается не сразу (Рис. 39) .
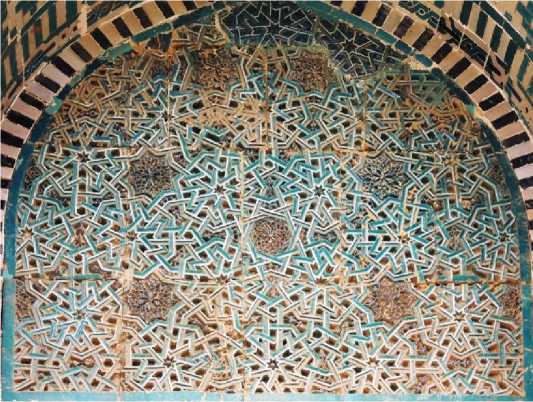

Рис. 39. Щипец портальной ниши мавзолея Ходжи Ахмада (комплекс Шахи-Зинда) в Самарканде.
Анализ показывает, что этот орнамент выстроен на сетке из квадратов и треугольников, уже рассмотренной выше (Рис. 37, а). Помимо звёзд с семью концами, в его структуре имеются также восьмиконечные и шестиконечные звёзды, причём последние в формат щипца не вписались и выстраиваются лишь в реконструкции (Рис. 40).
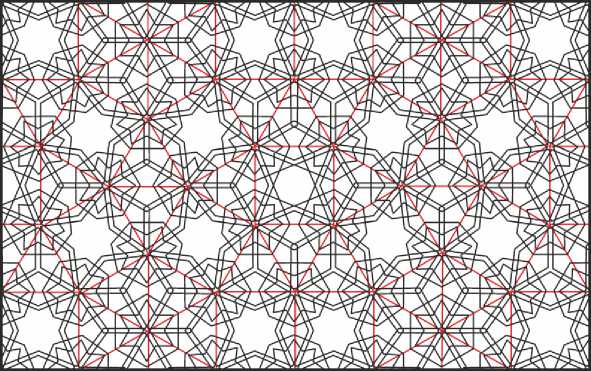
Рис. 40. Схема орнамента с семиконечными звёздами из мавзолея Ходжи Ахмада в Самарканде.
Замощение из равносторонних неравноугольных шестиугольников
В основе следующего орнамента (Рис. 41) лежит деление прямого угла на 7 равных частей (это построение невыполнимо с помощью циркуля и линейки) и замощение плоскости равносторонними шестиугольниками двух типов. Шестиугольники первого типа имеют четыре угла в 5/7 и два угла в 4/7 от развёрнутого. Четырёхугольники второго типа имеют четыре угла в 4/7 и два угла в 6/7 от развёрнутого. Острые углы всех встроенных в шестиугольники фигур составляют 2/7 от развёрнутого. Дополнительное требование построения состоит в том, чтобы семиугольники, примыкающие по бокам к фигурам, встроенным в шестиугольники первого типа, были правильными. Этот орнамент можно видеть на одном из тимпанов северо-восточного купола Пятничной мечети в Исфахане (Bonner 2016, fig 34).
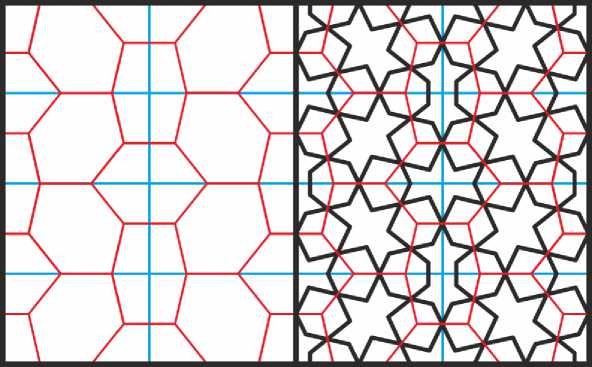
Рис. 41. Орнамент на основе замощения из шестиугольников, все углы которых кратны 1/7 части прямого угла.
Чтобы увидеть, как этот орнамент организуется на основе деления прямого угла на семь равных частей (заметим попутно, что эта операция, невыполнима с помощью циркуля и линейки), полезно показать, как его замощение образуется на основе структуры из равных правильных семиугольников. На Рис. 42 в каждом таком семиугольнике четыре стороны проведены синим цветом, а три другие стороны — чёрным цветом.
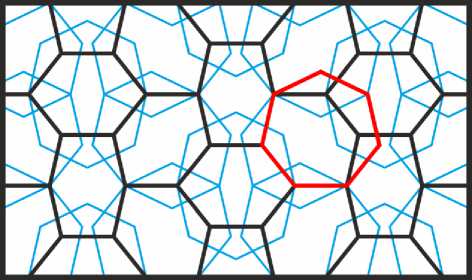
Рис. 42. Структура из правильных семиугольников, порождающая замощение рассмотренного орнамента; один из таких семиугольников выделен красным.
Вторым исторически известным примером этого орнамента является раппорт из Введения в учение о подобных и соответственных фигурах , изображённый на Рис. 43. Построение этого раппорта является весьма непростым делом, в чём читатель может убедиться самостоятельно.
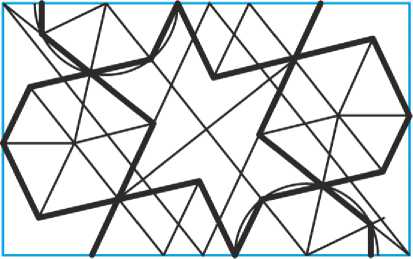
Рис. 43. Раппорт орнамента, основанного на делении прямого угла на семь равных частей.
Как анализировать гирихи
В завершение статьи я хочу выразить надежду на то, что читатель до некоторой степени уже готов самостоятельно анализировать гирихи по их фотографиям или въявь. В качестве примера проведём анализ гириха из мавзолея Буайн-Кули-хана в Бухаре (Немцова 2003, фото 54), датируемого примерно 1360 годом (Рис. 44) .
При анализе гириха лучше всего действовать в следующем порядке: (1)
внимательно осмотреть его и выделить «атомы» мозаики, ограниченные прямолинейными отрезками; (2) найти структуру, которая повторяется параллельным переносом; (3) перевести «атомы» мозаики в дуальные по отношению к ним «атомы» базового замощения; (4) наметить линии гириха внутри «атомов» базового замощения; (5) выделить раппорт орнамента и наметить порядок его построения.

Рис. 44. Гирих в мавзолее Буайн-Кули-хана в Бухаре.
Начнём с того, что выделим основные «атомы» рассматриваемого орнамента. На уровне «атомов» мозаики, ограниченных прямыми линиями, это пятиугольники, «кувшинчики», «бабочки» (Рис. 45, а ) — все эти фигуры нам знакомы по предыдущему анализу, и по их набору сразу можно сказать, что все углы в этом гирихе кратны 18°.
Теперь найдём структуру, которая повторяется параллельным переносом. Это шестиугольная фигура, внутри которой находится горизонтально ориентированный кувшинчик, над ним и под ним два пятиугольника и воздушный змей (Рис. 45, б ). По бокам от кувшинчика к этой фигуре присоединены два пятиугольника. Между шестиугольными фигурами на одной с ними вертикали находятся бабочки, к которым примыкают наклонные кувшинчики.
Рис. 45. Первые этапы анализа гириха: (а) выделение «атомов» мозаики; (б) выделение повторяющейся «молекулы»; (в) установление соответствия между «атомами» мозаики и «атомами» порождающего замощения.
Теперь нам надо вспомнить алфавит, превращающий невидимое базовое замощение в «атомы» мозаики, и обратно, ставящее в соответствие «атомам» мозаики «атомы» базового замощения. С пятиугольником связан описанный около него пятиугольник, с бабочкой — бочкообразный шестиугольник, который получается объединением двух пятиугольников, с кувшинчиком — ромб с углом при вершине 18°, и все эти выпуклые пятиугольники имеют равные стороны (Рис. 45, в ).
Рис. 46. Построение орнамента из мавзолея Буайн-Кули-хана на основе базового замощения.
На следующем шаге анализа мы можем, имея в виду исходный орнамент, сложить базовое замощение из этих фигур (Рис. 46) . А сложив его, внутрь пятиугольников мы впишем пятиугольники, внутрь бочек — бабочки, а внутрь узких ромбов ничего не впишем — и гирих восстановлен!
Осталось построить прямоугольный раппорт, зеркальным отражением которого гирих распространяется по плоскости (Рис. 47) . Противоположные углы раппорта я выбрал находящимися в центрах двух бочек.
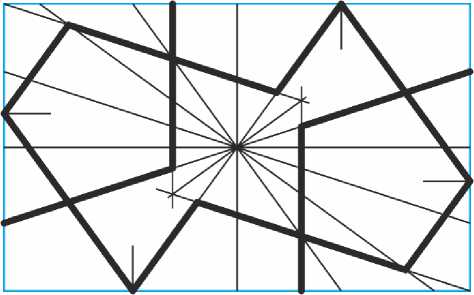
Рис. 47. Раппорт рассмотренного орнамента.
Мы прошли сейчас по пути многократной перефокусировки зрения, соответствующей разным уровням организации орнамента. Более подробно с вопросами реконструкции построения гирихов и их зрительного восприятия можно ознакомиться в препринтах Cromwell 2018, 2021.
Список литературы Исламские геометрические орнаменты, их история и способы построения
- Абу-л-Вафа ал-Бузджани. “Книга о том, что необходимо ремесленнику из геометрических построений”. Пер. С. А. Красновой. Физико-математические науки в странах Востока. Вып. I (IV), М.: Наука, 1966, с. 56–130.
- Аль-Фараби. Математические трактаты. 1972, Алма-Ата: Наука.
- Андреев М. С. (1956) “Старинные свитки альбомы из Бухары с образцами архитектурного орнамента”. Изв. отд. общ. наук АН Тадж. ССР, 10, 121–136.
- Аноним. “Введение в учение о подобных и соответственных фигурах”. Пер. А. Б. Вильдановой. Приложение к кн: Булатов М. С. (1988), 315–340.
- Бакланов Н. Б. (1947) “Герих. Геометрический орнамент Средней Азии и методы его построения”. Советская археология, №9, 101–120.
- Бернштам А. Н. (1950) Архитектурные памятники Киргизии. М.–Л.: АН СССР.
- Булатов М. С. (1988) Геометрическая гармонизация в архитектуре Средней Азии IX– XV вв. М.: Наука.
- Веймарн Б. (1936) “Орнаментация дворца XII века в Древнем Термезе”. Искусство, №8, 104–113.
- Гаганов Г. И. (1958) “Геометрический орнамент Средней Азии”. Архитектурное наследство, 11, 181–208.
- Денике Б. П. (1939) Архитектурный орнамент Средней Азии. М.-Л.: Изд-во Академии архитектуры.
- Немцова Н. Б. (2003) Ханака Сайф ад-Дина Бахарзи в Бухаре (к истории архитектурного комплекса). Бухара: изд-во «Бухоро».
- Немцова Н. Б. (2019) Ансамбль Шахи-Зинда: история-археология-архитектура XI—XXI вв. Самарканд.
- Нильсен В. А, Манакова В. Н. (1974) Архитектурный декор памятников Узбекистана. Л.: Стройиздат.
- Прибыткова А. М. (1973) “Архитектурный орнамент IX–X вв. в Средней Азии”. Архитектурное наследство, 21, 121–134.
- Пугаченкова Г. А. (1963) Мавзолей Араб-Ата (из истории архитектуры Мавераннахра IX–X вв.) Ташкент, Изд-во Академии наук.
- Ремпель Л. И. (1957) Панджара: архитектурные решётки и их построение. Ташкент: Худ. лит.
- Ремпель Л. И. (1961) Архитектурный орнамент Узбекистана: история развития и теория построения. Ташкент: Худ. лит.
- Термезская археологическая комплексная экспедиция 1936 г. (1941) Ташкент: УзФАН.
- Хмельницкий С. Г. (1959) “Свиток из Бухары”. Декоративное искусство СССР, № 1, 29–32.
- Bier C. (2002) “Geometric patterns and the interpretation of meaning: two monuments in Iran”. Bridges: Mathematical Connections in Art, Music, and Science, 67–78.
- Bier C. (2012). “The decagonal tomb tower at Maragha and its architectural context: lines of mathematical thought”. Nexus Network Journal, 14, 251–273.
- Bier C. (2015) “Geometry in Islamic art”. Encyclopaedia of the History of Science, Technology, and Medicine in Non-Western Cultures, 1–21.
- Bodner B. L. (2008) “Hankin’s ‘polygons in contact’grid method for recreating a decagonal star polygon design”. Bridges: Mathematics, Music, Art, Architecture, Culture, 21–28.
- Bodner B. L. (2012) “From Sultaniyeh to Tashkent Scrolls: euclidean constructions of two nine-and twelve-pointed interlocking star polygon designs”. Nexus Network Journal, 14, 307–332.
- Bonner J. F., Pelletier M. (2012) “A 7-fold system for creating Islamic geometric patterns I: historical antecedents”. Bridges: Mathematics, Music, Art, Architecture, Culture, 141–148.
- Bonner J. F. (2016) “The historical significance of the geometric designs in the northeast dome chamber of the Friday mosque at Isfahan”. Nexus Network Journal, 18(1), 55–103.
- Bonner J. F. (2017) Islamic geometric patterns. Springer.
- Broug E. (2019) Islamic geometric patterns. London: Themes & Hudson.
- Critchlow K. (1976) Islamic patterns: an analytical and cosmological approach. L.: Thames & Hudson.
- Cromwell P. R. (2010) “Islamic geometric designs from the Topkapi scroll I: unusual arrangements of stars”. Journal of Mathematics and the Arts, 4, 73–85.
- Cromwell P. R. (2010) “Islamic geometric designs from the Topkapi scroll II: a modular design system”. Journal of Mathematics and the Arts, 4, 119–136.
- Cromwell P. R. (2014) “Reverse engineering of Islamic geometric patterns: a scientific approach to art history”. https://girih.wordpress.com
- Cromwell P. R. (2018) “Islamic geometric ornament from twelfth-century architecture in Azerbaijan”. https://girih.wordpress.com
- Cromwell P. R. (2021) “Looking at Islamic patterns I: the perception of order”. https://girih.wordpress.com
- Cromwell P. R. (2021) “Looking at Islamic patterns II: making sense of geometry”. https://girih.wordpress.com
- Degeorge G., Porter Y. (2002) The art of the Islamic tile. Paris: Flammarion.
- Dimand M. S. (1938) “Samanid stucco decoration from Nishapur”. Journal of the American Oriental Society, 58, 258–261.
- Embi M. R., Abdullahi Y. (2012) “Evolution of Islamic geometrical patterns”. Global Journal Al-Thaqafah, 2, 27-39.
- Eriksson L. (2021) “The short tiles category”. Bridges: Mathematical Connections in Art, Music, and Science, 127–134.
- Hankin E. H. (1905) “On some discoveries of the methods of design employed in Mohammedan Art”. Society of Arts Journal, 53, 461–477.
- Hankin E. H. (1925) “The drawing of geometric patterns in Saracenic art”. Memoirs of the Archaeological Survey of India, 15, 25 pages and XIV plates, Calcutta, Government of India Central Publication Branch.
- Hauser W. (1937) “The plaster dado from Sabz Pūshān”. Bulletin of the Metropolitan Museum of Art, 32, 23–36.
- Lee A. J. (1987) “Islamic star patterns”. Muqarnas, 4, 182–197.
- Lu P. J., Steinhardt P. J. (2007). “Decagonal and quasi-crystalline tilings in medieval Islamic architecture”. Science, 315, 1106–1110.
- Majewski M. (2020) “Understanding geometric pattern and its geometry (part 1)”. Electronic Journal of Mathematics & Technology, 14.
- Makovicky E. (1989) “Ornamental brickwork: theoretical and applied symmetrology and classification of patterns”. Symmetry 2. Pergamon, 955–999.
- Makovicky E. (1992) “800-year-old pentagonal tiling from Maragha, Iran, and the new varieties of aperiodic tiling it inspired”. Fivefold symmetry. World Scientific, 67–86.
- Makovicky E. (2016) “On the Kond style of Islamic tiling: a study in practical Islamic geometry”. Rendiconti Lincei, 28, 35–51.
- Makovicky E. (2023a) “Quasicrystals and art: interesting new facts”. Rendiconti Lincei, 34, 321–331.
- Makovicky E. (2023b) “Tomb towers and minarets: analysis of symmetries and geometries of Iranian geometrical ornaments of the Seljuq era. Pictorial requiem for the Kharraqan towers”. Rendiconti Lincei, 35, 1–18.
- McClary R. P. (2015) “From Nakhchivan to Kemah: the western extent of brick Persianate funerary architecture in the sixth/twelfth century AD”. Iran, 53, 119–142.
- Necipoğlu G. (1992) “Geometric design in Timurid/Turkmen architectural practice: thoughts on a recently discovered scroll and its late Gothic parallels”. Timurid Art and Culture, Iran and Central Asia in the Fifteenth Century. Brill.
- Necipoğlu G. (1996). The Topkapi scroll: geometry and ornament in Islamic architecture. Getty Publications.
- Özdural A. (1995) “Omar Khayyam, mathematicians, and conversazioni with artisans”. Journal of the Society of Architectural Historians, 54, 54–71.
- Özdural A. (1996) “On Interlocking Similar or Corresponding Figures and ornamental patterns of cubic equations”. Muqarnas, 13, 191–211.
- Özdural A. (2000) “Mathematics and arts: connections between theory and practice in the medieval Islamic world”. Historia Mathematica, 27, 171–201.
- Sarhangi R. (2012) “Interlocking star polygons in Persian architecture: the special case of the decagram in mosaic designs”. Nexus Network Journal, 14, 345–372.
- Sutton D. (2007) Islamic design: genius for geometry. NY: Walker & Company.
- Wade D. (1976) Pattern in Islamic art. NY: Overlook press.
- Wichmann B., Wade D. (2017) Islamic design: a mathematical approach. Birkhäuser.


