Использование мобильного телефона (smartphone) в точном земледелии
Автор: Личман Г.И., Смирнов И.Г., Беленков А.И.
Журнал: Фермер. Черноземье @vfermer-chernozemye
Рубрика: Вести из Тимирязевки
Статья в выпуске: 1 (1), 2017 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В настоящее время смартфоны стали полезным инструментом в сельском хозяйстве благодаря их мобильности и доступной стоимости. Их вычислительная мощность позволяет решать различные практические задачи, возникающие при внедрении систем точного земледелия. Кроме того, смартфоны в настоящее время оснащены различными типами физических датчиков и сенсоров, которые делают их перспективным инструментом для оказания помощи в решении разнообразных сельскохозяйственных задач. В статье рассмотрены различные возможности использования встроенных в смартфоны датчиков для решения возникающих задач.
Точное земледелие, смартфон, получение данных, мониторинг урожайности, состояние посевов
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/170177260
IDR: 170177260
Текст научной статьи Использование мобильного телефона (smartphone) в точном земледелии
В статье рассмотрены различные возможности использования встроенных в смартфоны датчиков для решения возникающих задач.Введение в сельскохозяйственное производство точного земледелия и, в частности, технологий дифференцированного применения средств химизации требует большого объема информации о состоянии поля и растений. Для ее получения необходимо использовать специальное технологическое оборудование и получать услуги, такие, например, как системы мониторинга урожайности, позиционирования GPS, математическое обеспечение (GIS) для сбора информации о параметрах плодородия поля, состоянии посевов, хранения, обработки и принятия оптимальных управленческих решений.
Для принятия управленческих решений о дозах и сроках дифференцированного применения средств химизации необходимо знать характер распределения основных агрохимических показателей плодородия поля. К таким показателям в первую очередь следует отнести кислотность, содержание фосфора, калия, нитратного азота, органического вещества и микроэлементов. Количество параметров, которые необходимо измерять, зависит от моделей или алгоритмов используемых для определения дифференцированных доз внесения. Получение избыточной информации, которая не будет применена для решения конкретной задачи, не целесообразно.
В результате выполненного анализа разработана структурная схема наиболее распространенных способов получения данных о состоянии поля (рис. 1).
При разработке технологий дифференцированного применения удобрений необходимо, прежде всего, знать количество элементов питания, содержащихся в почве, и характер их распределения. Анализ и моделирование пространственных данных о пестроте параметров плодородия поля требует применения комплексного подхода и различных методов, характеризующих ту или иную особенность явления. Сложность такого анализа обусловлена несколькими факторами: наличием большого объема количественной и качественной информации о параметрах плодородия поля, многомасштаб-ностью и многопеременностью, наличием различных факторов влияния.
По мере развития информационно коммуникационных систем (ИКТ) появляются новые способы получения информации о состоянии поля, растений и окружающей среды такие, например, как цифровые фотографические методы, полусферическая фотография, стереозрение (StereoVision), световые сенсоры, кинетические сенсоры (Kinect sensor), сенсоры LIDAR, термография, спектроскопия в видимом диапазоне VIS/NIR, системы электронного носа и другие. Среди них особое место занимают смартфоны [1].
Среди технологий, изобретенных в последние несколько десятилетий, смартфоны приобрели большие доли рынка среди различных секторов пользователей по причине их полезности, простоты в использовании и доступности. Количество новых пользователей смартфонов продолжает расти. Предполагается, что, к 2017году число пользователей будет более 2 миллиардов человек во всем мире [2].
Один фактор, который повышает способность смартфонов помочь пользователям выполнять различные задачи, являются многочисленные встроенные датчики
Рис. 1. Способы получения данных о состоянии системы «почва + растение»
(например, датчики позиционирования, датчики движения, камеры и микрофоны). Многие отрасли народного хозяйства используют смартфоны для облегчения их работы, такие, например, как здравоохранение [3 ,4] и образование[5,6].
Недорогой смартфон, оснащенный различными датчиками, открывает новые возможности для сельских фермеров, которые ранее имели ограниченный доступ к последней сельскохозяйственной информации (например, о рынке, погоде и болезнях растений) и помощи со стороны специалистов сельского хозяйства и государственных служащих. Между тем, фермеры, крупные хозяйства, которые уже используют информационные технологии, теперь могут использовать смартфон с различными датчиками для повышения производительности и облегчения решения различных задач на протяжении всего сельскохозяйственного цикла.
В работе [1] авторы подразделяют возможные приложения смартфо-нов в сельском хозяйстве на четыре категории: сельское хозяйство, управленческие функции, информационное обеспечение, а также взаимодействие со службами распространения знаний. Сельскохозяйственными приложениями являются те, которые помогают в сельскохозяйственной деятельности, например, с целью выявления болезней и определения норм применения пестицидов. Приложения для управления хозяйством облегчают пользователям лучше управлять ресурсами и сельскохозяйственной деятельностью более эффективно и в целях получения большей прибыли и повышения продуктивности сельского хозяйства. Информационная система включают в себя системы, которые предоставляют необходимую информацию для фермеров, в том, числе информацию о хозяйстве, окружающей среде и о рынке. Система по взаимодействию со службами распространения знаний обеспечивает доступ к экспертам для получения консультаций необходимых для более эффективного ведения хозяйства.
Датчики, включенные в смартфоны, могут быть классифицированы на три категории: датчики дви- жения, экологические датчики, и датчики положения (Таблица 1).
Первая категория, датчики движения, обеспечивает измерение ускорения и вращающей силы. Примерами датчиков движения являются акселерометры, гироскопы, датчики силы тяжести, вращательные векторные датчики.
Вторая категория – это экологические датчики, обеспечивающие измерение состояния окружающей среды. Температура воздуха измеряется термометром, давление барометром, а освещенность - фотометром.
Третья категория – датчики положения определяют физическое положение устройства. Такие датчики включают GPS, и датчики ориентации [7].
Недавний рост популярности смартфонов привлек внимание исследователей к изучению возможности использования датчиков смартфона в своей работе. Многие датчики были применены успешно во многих областях. Спутниковая система навигации встроенная в смартфон (GPS), позволяет определять текущее местоположение устройства. Помимо прямого использования местоположения в приложениях (например, карты), данные GPS также используются для определения траектории движения агрегатов. [8].
Акселерометры, измеряющие силу ускорения, вызванную либо движением смартфона, либо изменением силы тяжести земли по 3-м осям, могут быть использованы в качестве датчиков [3] распознавания активности [9], вождения [10] и так далее. Встроенные камеры (передние и задние камеры) смартфонов значительно улучшились за последние годы. Разрешающая способность их сопоставима со специальными карманными фотоаппаратами. Поэтому получаемые при помощи смартфона изображения и видео после их обработки с использованием специальных компьютерных алгоритмов могут быть использованы в точном земледелии наряду с информацией, получаемой посредством систем технического зрения[11]. !►
Таблица 1. Общие датчики смартфона [11, 12]
|
Сенсор |
Описание |
Использование |
|
Акселерометр |
Определяет ускорение в м/с2 |
Обнаружение движения и ориентации смартфона |
|
Гироскоп |
Определяет частоту вращение в рад/ сек вокруг осей x,y,z |
Обнаружение вращения, поворотов |
|
Световой сенсор |
Определяет уровень освещенности в Люксах |
Контроль освещенности |
|
Барометр |
Измерение атмосферного давления в Па |
Измерение изменения давления |
|
Бесконтактный датчик |
Измеряет расстояние до объекта |
- |
|
Датчик влажности |
Измеряет влажность окружающей среды, (%) |
Определение точки росы, абсолютной и относительной влажности |
|
Глобальная Система Позиционирования (GPS) |
Определяет координаты смартфона |
Определение координат, наблюдаемого объекта |
|
Датчик изображения (камера) |
Фиксирует изображение и видео |
Получение фотографии объекта или видеофильма |
|
Аудиосенсор |
Преобразует звуковой сигнал в электрический. |
Запись голоса |
|
Датчик идентичности отпечатка пальца |
Определяет отпечаток пальца пользователя |
Определение пользователя по отпечатку пальца |
ВЕСТИ ИЗ ТИМИРЯЗЕВКИ
Таблица 2. Сравнение использования в сельском хозяйстве сенсоров смартфона и традиционных методов
|
Функции |
Традиционные методы |
Преимущества смартфона |
|
Растениеводство |
||
|
Определение болезни растений |
||
|
Пользователь делает снимки пораженных болезнью листьев и отсылает их в лабораторию для дальнейшей диагностики Пользователь получает сообщение о типе болезни и совет по борьбе с ней. |
|
|
|
Калькулятор удобрений |
||
|
Используя изображение листьев растения, приложение смартфона анализирует содержание хлорофилла и количество необходимых азотных удобрений. |
|
( а) Они могут быть более точными и более надежными, чем визуальная инспекция (б) Они дешевле, чем СПАД анализаторы |
|
Оценка потребности растений в воде |
||
|
Датчик изображения смартфона используется для мониторинга яркости света, отражаемого растениями, приложение PocketLAI определяет индекс площади листьев (LAI), который является ключевым фактором для расчета требований сельскохозяйственных культур в воде. Приложение RaGPS вычисляет солнечное излучение и эквивалентное испарение от положения солнца с помощью GPS смартфона |
|
Смартфоны в настоящее время являются весьма доступными
|
|
Анализ зрелости урожая |
||
|
Светочувствительные матрицы смартфона позволяют измерять степень зрелости плодов |
|
Это - неразрушающий метод, который является идеальным для сохранения фруктов |

Исследуемая часть растения
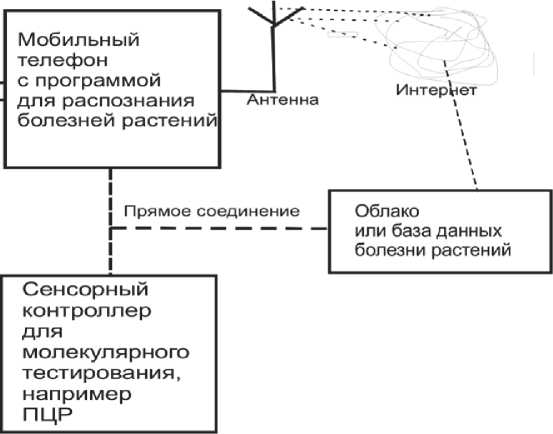
Рисунок 2. Схема работы системы определения болезни растений с использованием смартфона
Среди технологий, изобретенных в последние несколько десятилетий, смартфоны приобрели большие доли рынка среди различных секторо пользователей по причине их полезности, простоты в использовании и доступности․
Применение смартфона для получения информации о состоянии сельскохозяйственных культур обладают рядом преимуществ по сравнению с традиционными методами (Таблица 2)
В работе [12] рассмотрен способ определения болезни растений с использованием смартфона. Установленное на мобильный телефон программное обеспечение позволяет сфотографировать пораженную болезнью часть растения, например лист, немедленно проанализировать фотографию и принять необходимые меры для подтверждения потенциального заболевания и принятия соответствующих действий по устранению болезни.
Предложенный способ не нуждается в сложных алгоритмах и дорогом оборудовании для обработки изображений и поэтому может быть легко реализован с использованием языков программирования Java или С.
К сожалению, еще мало смартфонов с набором перечисленных в статье датчиков. Например, Смартфон Nokia 6 оснащен 4 ГБ оперативной памяти LPDDR3 и встроенным накопителем на 64 ГБ. Слот под карты памяти microSD позволяет расширить память до 128 ГБ. В наличии также весь традиционный набор интерфейсов, выключая 3,5мм аудио, MicroUSB, акселерометр, электронный компас, гироскоп, датчик освещенности и сенсор приближения.
Cмартфон Samsung Galaxy A7 имеет оперативную память – 2 ГБ; встроенную – 16 ГБ (11,2 ГБ доступно); слот для карт памяти micro SD/HC/XC (до 64 ГБ), cенсоры: акселерометр, датчики приближения и освещенности, датчик Холла. Но даже со смартфоном, у которого есть система GPS и фотокамера можно решать многие задачи точного земледелия.
Список литературы Использование мобильного телефона (smartphone) в точном земледелии
- Applications of Smartphone-Based Sensors in Agriculture: A Systematic Review of Research Suporn Pongnumkul, Pimwadee Chaovalit, and Navaporn Surasvadi. Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Sensors Volume 2015, Article ID 195308, 18 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/195308.
- “2 billion consumers worldwide to get smart(phones) by 2016,” 2014, http://www.emarketer.com/Article/2-Billion- Consumers-Worldwide-Smartphones-by-2016/1011694.
- M. Mosa A. S., Yoo I., and Sheets L., “A systematic review of healthcare applications for smartphones,” BMC Medical Informatics & Decision Making, vol. 12, no. 1, article 67, 2012.
- Habib M. A., Mohktar M. S., Kamaruzzaman S. B., Lim K. S., Pin T. M., and Ibrahim F., “Smartphone-based solutions for fall detection and prevention: challenges and open issues,” Sensors,vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 7181–7208, 2014.
- Cheung W. S. and Hew K. F. A review of research methodologies used in studies on mobile handheld devices in K-12 and higher education settings, Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, vol. 25, no. 2, pp. 153–183, 2009.
- Milrad M.and Spikol D., Anytime, anywhere learning supported by smart phones: experiences and results from the musis project,” Educational Technology and Society, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 62–70, 2007.
- Sensors overview—android developers, 2015, http: // developer.android. com/guide/topics/sensors/sensors overview.html.
- Gong H., Chen C., Bialostozky E., and Lawson C. T., A GPS/ GIS method for travel mode detection in New York City, Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, vol. 36, no. 2, pp. 131–139, 2012.]
- Anjum A.and Ilyas M. U., Activity recognition using smartphone sensors, in Proceedings of the IEEE 10th Consumer Communications and Networking Conference (CCNC ’13), pp. 914–919, IEEE, January 2013.
- Chaovalit P., Saiprasert C., and Pholprasit T., A method for driving event detection using sax with resource usage exploration on smartphone platform, EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, vol. 2014, no. 1, article 135, 2014.


