Использование продуктов микроволновой аминолитической деструкции полиэтилентерефталата в резинах на основе хлоропренового каучука
Автор: М.А. Вохмянин, Р.Л. Веснин, А.Д. Краев, В.А. Седых
Журнал: Вестник Воронежского государственного университета инженерных технологий @vestnik-vsuet
Рубрика: Химическая технология
Статья в выпуске: 3 (89), 2021 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В данной работе рассмотрен метод утилизации отходов полиэтилентерефталата (ПЭТ) смесью аминоспиртов – моноэтаноламином и триэтаноламином, взятых в определенном соотношении. В результате реакции деструкции образуется диамид терефталевой кислоты (N, N'-бис (2-гидроксиэтил) терефталамид). Для ускорения процесса деструкции было использовано микроволновое излучение различной мощности. Определены оптимальные условия разложения ПЭТ: время и мощность микроволнового излучения с выходом целевого продукта (диамида терефталевой кислоты) 80-85%. Процесс деструкции проводился без применения катализаторов и при атмосферном давлении. Продукт аминолитической деструкции ПЭТ (диамид терефталевой кислоты) был использован в качестве мономера в реакции поликонденсации при получении нового олигомера. Полученный олигомер и продукт деструкции ПЭТ исследовались в качестве новых компонентов в резинах на основе трех марок хлоропренового каучука различной скорости кристаллизации. Выявлено ускоряющее действие новых ингредиентов на процесс серной вулканизации резин на основе хлоропренового каучука. Продемонстрировано, что введение олигомера на основе продукта деструкции ПЭТ снижает вязкость резиновых смесей на 25-35%. Рассмотрено влияние на упруго-прочностные свойства полученных резин до и после термического старения. Показано, что диамид терефталевой кислоты и олигомер на его основе оказывают влияние на упруго-прочностные свойства исследуемых резин до и после термического старения. В дальнейшем планируется более подробное рассмотрение влияния новых полученных ингредиентов в резинах на основе полярных каучуков и термопластов на физико-химические и физико-механические параметры.
Аминолиз, отходы полиэтилентерефталата, микроволновое излучение, хлоропреновый каучук
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140259879
IDR: 140259879 | УДК: 678 | DOI: 10.20914/2310-1202-2021-3-182-190
Use of microwave aminolytic destruction products of polyethylene terephthalate in rubbers based on chloroprene rubber
In this paper, a method of recycling polyethylene terephthalate (PET) waste with a mixture of amino-alcohols - mo-noethanolamine and triethanolamine, taken in a certain ratio, is considered. As a result, of the degradation reaction, terephthalic acid diamide (N, N'-bis (2-hydroxyethyl) terephthalamide) is formed. To accelerate the destruction process, microwave radiation of various powers was used. The optimal conditions for PET decomposition have been determined: the time and power of microwave radiation with the yield of the target product (terephthalic acid diamide) 80-85%. The destruction process was carried out without the use of catalysts and at atmospheric pressure. The aminolytic degradation product of PET (terephthalic acid diamide) was used as a monomer in the polycondensation reaction to obtain a new oligomer. The obtained oligomer and the PET degradation product were investigated as new components in rubbers based on three grades of chloroprene rubber with different crystallization rates. The accelerating effect of new ingredients on the process of sulfur vulcanization of rubbers based on chloroprene rubber has been revealed. It has been demonstrated that the introduction of an oligomer based on a PET degradation product reduces the viscosity of rubber compounds by 25-35%. The effect on the elastic-strength properties of the obtained rubbers be-fore and after thermal aging is considered. It is shown that terephthalic acid diamide and oligomer based on it have an effect on the elastic-strength properties of the studied rubbers before and after thermal aging. In the future, a more detailed consideration of the effect of the new obtained ingredients in rubbers based on polar rubbers and thermoplastics on the physicochemical and physicomechanical parameters is planned.
Текст научной статьи Использование продуктов микроволновой аминолитической деструкции полиэтилентерефталата в резинах на основе хлоропренового каучука
Переработка бытовых, либо промышленных твердых отходов полиэтилентерефталата (ПЭТ) с каждым годом привлекает к себе все больше внимания. Это связано не только со стремлением к снижению экологической нагрузки на окружающую среду, но и с тем, что продукты переработки ПЭТ могут быть использованы в различных отраслях промышленности [1].
В настоящее время существуют несколько основных методов переработки отходов ПЭТ: захоронение на полигонах, механическая переработки (измельчение и повторное использование), химическая переработка и сжигание. Среди вышеупомянутых методов рециркуляции наиболее важным является химический метод ввиду того, что он позволяет получать и производить сырье, которое в дальнейшем может использоваться в различных отраслях промышленности, в частности и для повторного синтеза полимеров [2–5].
Химическая переработка – один из методов переработки путем химической модификации или деконструкции полимерных макромолекул. Существует несколько сольволитических методов, эффективных для деконструкции ПЭТ. Такими методами являются: алкоголиз (реакция со спиртом) [6–11]; аминолиз (реакция с аминами) [12–15]; аммонолиз (реакция с аммиаком) и гидролиз (реакция с водой) [16–19]. Общим для этих методов утилизации является механизм нуклеофильной атаки карбонильного атома углерода в ПЭТ нуклеофильными реагентами. В результате этого происходит образование сложных эфиров, диамидов терефталевой кислоты, сложных эфиров терефталевой кислоты или терефталевой кислоты соответственно. Полученные соединения могут быть использованы в качестве добавок в асфальты и битумы [20–22]; в качестве модифицирующей, либо сшивающей добавки в эпоксидные смолы [23–25], для получения защитных покрытий [26–28]; в качестве одного из компонентов полиуретанов [29–31] и так далее.
Сольвотические методы деструкции ПЭТ могут протекать при различных условиях, с применением катализаторов и без них [33–37]. Особый интерес вызывают методы деструкции при использовании микроволнового излучения, вместо конвективного нагрева. Микроволновое излучение позволяет проводить процессы деструкции в несколько раз быстрее, чем при конвективном нагреве. В первую очередь это связано с тем, что все реагирующие компоненты при реакциях деструкции ПЭТ являются полярными соединениями [38–42].
Ввиду большого разнообразия возможных методов химической утилизации отходов ПЭТ для дальнейшего изучения был выбран аминолиз, как один из методов, который позволяет получить большое разнообразие продуктов, а также из-за возможности регулирования условий проведения реакции деструкции в широких диапазонах (время, температура, соотношение компонентов).
Цель работы – изучение процесса аминолитической деструкции отходов ПЭТ при микроволновом излучении различной мощности. Изучение влияния продуктов аминолитической деструкции ПЭТ и их производных на серную вулканизацию и упруго-прочностные свойства резин на основе хлоропренового каучука.
Материалы и методы
Для проведения процесса деструкции ПЭТ использовалась смесь аминоспиртов – моноэта-ноламин (МЭА) технический (ТУ 2423–159– 00203335–2004) и триэтаноламин (ТЭА) (ТУ 2423–168–00203335–2007) производства ПАО "Казаньоргсинтез". Отходы ПЭТ представляли собой измельченные пластиковые бутылки без этикетки, с размером частиц 5 x 5 мм.
Исследование влияние продукта деструкции ПЭТ и его производных проводилось в рецептурах на основе хлоропренового каучука трех марок различной скорости кристаллизации (регулированные меркаптанами) СR121, СR232 и СR244, производства Китай, Shanxi Synthetic Rubber Group Co. Ltd. Рецептуры модельных резиновых смесей представлены в таблице 1.
Таблица 1.
Рецептура модельной резиновой смеси
Table 1.
Model rubber compounding
|
Ингредиенты Ingredients |
Массовые части на 100 массовых частей каучука, масс. ч. Mass parts per 100 mass parts of rubber, mass.p. |
||
|
1 (СR232) |
2 (СR244) |
3 (СR121) |
|
|
Каучук | Rubber |
100 |
100 |
100 |
|
Оксид магния Magnesium oxide |
4 |
4 |
4 |
|
Оксид цинка | Zinc oxide |
5 |
5 |
5 |
|
Сера | Sulfur |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
ТМТД (Тетраметилтиурамдисульфид) Tetramethylthiuram disulfide |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
ДФГ (Дифенилгуанидин) Diрhеnуlguаnidinе |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
Технический углерод (П 803) Carbon black (P 803) |
40 |
40 |
40 |
|
Итого | Total |
160 |
100 |
80 |
За базовые были приняты три смеси с различными марками каучуков, различающихся скоростью кристаллизации.
Резиновые смеси были изготовлены на лабораторном микросмесителе с объёмом загрузочной камеры 0,1 л (производства ООО Полимермаш Групп).
Снятие вулканизационных характеристик осуществлялось на оборудовании Moving Die Rheometer, фирмы Prescott Instruments Ltd. Вязкость по Муни определялась на ротационном вискозиметре Mooneyline MV Variable Speed, фирмы Prescott Instruments Ltd. Определение упруго-прочностных свойств было произведено на разрывной машине AG-X 5 kN, фирмы Shimadzu.
Исследования изготовленных резин осуществлялись по стандартным методикам в соответствии с ГОСТ: снятие вулканизационных характеристик резиновых смесей (ГОСТ 12535–84), определение вязкости сырой резиновой смеси по Муни на ротационном вискозиметре (ГОСТ 10722–76), упругопрочностные свойства (ГОСТ 270–75), твердость резин по Шору А (ГОСТ 263–75), испытания на ускоренное старение и теплостойкость (ГОСТ ISO 188–2013).
Результаты
Кинетика аминолитической деструкции полиэтилентерефталата при микроволновом излучении
За основу лабораторной установки для аминолитической деструкции ПЭТ была взята бытовая микроволновая печь с возможностью регулирования мощности микроволнового излучения (рисунок 1). Основным из главных изменений в конструкции является возможность присоединения обратного холодильника к реакционной колбе, находящейся внутри микроволновой печи.
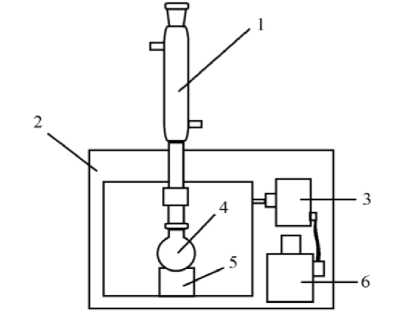
Рисунок 1. Схема лабораторной установки для проведения деструкции ПЭТ при микроволновом излучении (1 – обратный холодильник; 2 – корпус установки; 3 – магнетрон; 4 – реакционная колба; 5 – подставка; 6 – трансформатор)
Figure 1.Schematic of a laboratory setup for PET destruction under microwave radiation (1 – reverse cooler; 2 – installation body; 3 – magnetron; 4 – reaction flask; 5 – stand; 6 – transformer)
Аминолитическая деструкция частиц ПЭТ проводилась в смеси аминоспиртов, при соотношениях 1:4:5 и 1:3:4 соответственно для ПЭТ: МЭА:ТЭА. Выбор данных соотношений аминоспиртов обусловлен необходимостью достаточного количества аминоспиртов для разложения частиц ПЭТ. Кинетика деструкции ПЭТ при различной мощности микроволнового излучения (220, 540 и 700 ватт) и двух соотношениях компонентов приведена на рисунках 2 и 3.
К у tt "О о о
X
m
700 Вт
2 4 6 8 10
Время, мин
Time, min
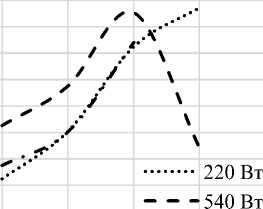
Рисунок 2. Кинетика деструкции ПЭТ при соотношении компонентов 1:4:5 (ПЭТ: МЭА:ТЭА)
Figure 2. Kinetics of PET destruction at a component ratio of 1: 4 : 5 (PET: MEA : TEA)
Time, min
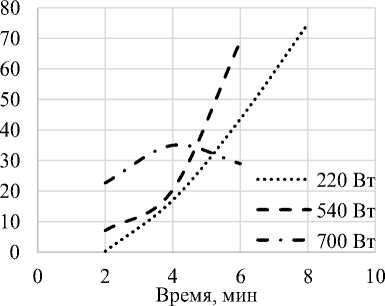
Рисунок 3. Кинетика деструкции ПЭТ при соотношении компонентов 1:3:4 (ПЭТ: МЭА:ТЭА)
Figure 3. Kinetics of PET destruction at a component ratio of 1: 3 : 4 (PET: MEA : TEA)
Получение олигомера на основе продукта деструкции ПЭТ.
Продукт деструкции ПЭТ (диамид терефталевой кислоты) был использован в качестве мономера в реакции поликонденсации с получением олигомера. Реакция проводилась в диапазоне температур от 200 до 215 °С, при вакуумировании для удаления побочных продуктов реакции (этаноламина). В качестве катализатора использовалась фосфорная кислота.
Вохмянин М.А. и др.Вестник ВГУИТ, 2021, Т. 83, №. 3, С.
Изготовление резиновых смесей на основе хлоропренового каучука
Резиновые смеси на основе трех видов хлоропреновых каучуков различной скорости кристаллизации были изготовлены в соответствии с рецептурами, приведенными в таблице 2.
Таблица 2.
Рецептуры резиновых смесей на основе хлоропренового каучука
Table 2.
Chloroprene rubber based rubber formulations
|
Ингредиенты Ingredients |
Резиновая смесь, масс. части The rubber compound of the masses. part |
|
|
4 5 6 7 8 9 |
||
|
Каучук | Rubber |
100 |
|
|
Оксид магния | Magnesium oxide |
4 |
|
|
Оксид цинка | Zinc oxide |
5 |
|
|
Сера | Sulfur |
1 |
|
|
ТМТД (Тетраметилтиурамдисульфид) Tetramethylthiuram disulfide |
1 |
|
|
ДФГ (Дифенилгуанидин) Diрhеnуlguаnidinе |
1 |
|
|
Технический углерод (П 803) Carbon black (P 803) |
39 |
|
|
БГЭТФА* | BHETA |
1 |
– |
|
оАТФК** | оАТРА |
– |
1 |
|
Итого | Total |
152 |
|
Примечание: * БГЭТФА – продукт аминолитической деструкции ПЭТ ** оАТФК – олигомер на основе продукта деструкции ПЭТ
Note: *BHETA is a product of aminolytic degradation of PET ** оАТРА – oligomer based on PET degradation product
Резиновые смеси 4 и 7 сделаны на основе каучука СR232; смеси 5 и 8 – СR244; смеси 6 и 9 – СR121.
В первую очередь рассматривалось влияние диамида терефталевой кислоты и олигомера на его основе на кинетику серной вулканизации резиновых смесей. В таблице 3 представлены данные по ключевым вулканизационным характеристикам серной вулканизации исследуемых резин Т 10 , Т 50 и Т 90 .
|
Таблица 3. Продолжительность периодов вулканизации резиновых смесей Table 3. The duration of the periods of vulcanization of rubber compounds |
|||||||||
|
Смесь | |
Соmроund |
||||||||
|
Модельные Modeling |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
|||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
|||||||
|
Т 10% , сек Т 10% , sec |
87 |
57 |
74 |
91 |
60 |
84 |
93 |
84 |
69 |
|
Т 50% , сек Т 50% , sec |
220 |
226 |
148 |
265 |
229 |
149 |
278 |
242 |
158 |
|
Т 90% , сек Т 90% , sec |
1107 |
967 |
833 |
1082 |
953 |
797 |
1094 |
961 |
723 |
Упруго-прочностные свойства полученных резин
В дальнейшем исследовалась вязкость сырых резиновых смесей, а также упругопрочностные характеристики вулканизатов. Вулканизация резин происходила в оптимуме вулканизации при температуре 160 °С в течение 15–17 минут.
Кроме этого, помимо основных упругопрочностных свойств резин, оценивалось влияние диамида терефталевой кислоты и олигомера на его основе на процессы старения резин. В таблице 4 приведены данные по вязкости сырых резиновых смесей, а также некоторые показатели упруго-прочностных свойств резин до и после термического старения в течение 24 часов.
Таблица 4.
Упруго-прочностные показатели вулканизатов до и после термического старения
Table 4.
Elastic-strength characteristics of vulcanizates before and after thermal aging
|
Показатель резиновая смесь Indicator rubber compound |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
|
Вязкость, ед. Муни | Viscosity, units Muni |
69,67 |
90,33 |
79,00 |
70,67 |
83,33 |
75,33 |
70,00 |
79,00 |
72,67 |
|
Твердость, Шор А | Hardness, Shore A |
88,86 |
- |
51,05 |
102,5 |
- |
32,05 |
76,7 |
- |
38,89 |
|
fp, Мпа |
20,07 |
24,74 |
18,83 |
20,65 |
23,53 |
18,09 |
21,69 |
25,95 |
18,87 |
|
e,% |
336 |
214 |
241 |
310 |
236 |
293 |
352 |
281 |
313 |
|
Напряжение при 100%, Мпа | Voltage at 100%, MPa |
4,30 |
12,78 |
7,18 |
5,24 |
10,76 |
5,64 |
4,55 |
9,84 |
5,13 |
|
Напряжение при 200%, Мпа z | Voltage at 200%, MPa |
10,70 |
22,38 |
16,31 |
12,96 |
21,54 |
12,5 |
11,25 |
21,02 |
11,74 |
|
После старения (24 часа при 100 градусах Цельсия) After aging (24 hours at 100 degrees Celsius) |
|||||||||
|
fp, Мпа |
19,13 |
21,71 |
16,64 |
20,25 |
24,00 |
17,75 |
20,09 |
21,54 |
17,86 |
|
e,% |
295 |
217 |
264 |
358 |
301 |
261 |
307 |
270 |
266 |
Обсуждение
Кинетика аминолитической деструкции полиэтилентерефталата
Из данных, представленных на рисунке 1, видно, что максимальный выход продукта, 85%, достигается при времени реакции 6 минут и мощности микроволнового излучения 540 Вт. При более длительном времени воздействия микроволнового излучения в данных условиях выход продукта снижается ввиду значительного испарения реакционной массы (смеси аминоспиртов) и нахождения её в месте соединения обратного холодильника и реакционной колбы в виде паров.
При использовании мощности 220 Вт наибольший выход продукта (84–86%) достигается при 8 минутах реакции, что связано с медленным разогревом реакционной массы и снижением скорости испарения смеси аминоспиртов.
Использование мощности излучения 700 Вт нецелесообразно ввиду слишком быстрого разогрева, закипания и испарения реакционной массы. Время контакта смеси аминоспиртов с частицами ПЭТ мало, что приводит к меньшему выходу продукта (до 74%).
При соотношении компонентов 1:3:4 наблюдается общее снижение выхода целевого продукта при всех используемых мощностях (рисунок 2). В данном случае максимальный выход продукта достигает лишь 74%. Снижение выхода продукта обусловлено недостатком смеси аминоспиртов, которая при микроволновом излучении, в особенности при мощности в 700 Вт, очень быстро испаряется и не успевает полностью конденсироваться, при попадании в обратный холодильник.
Олигомер на основе продукта деструкции ПЭТ .
В результате реакции получено светложелтое смолообразное вещество, кристаллизующееся при остывании, с небольшим запахом аминоспиртов. Цвет и запах полученного продукта обусловлен неполным удалением побочных продуктов поликонденсации диамида терефталевой кислоты, а именно моноэтаноламина.
Полученный олигомер растворим в высокопо-лярных растворителях – диметилсульфоксиде и диметилформамиде; обладает хорошей способностью вытягиваться в волокна (до нескольких метров) в тёплом и горячем состоянии. Температура плавления полученного продукта находится в диапазоне от 75 до 80 °С.
Кинетика вулканизации резиновых смесей
По данным таблицы 3 видно, что ускоряющее действие на процесс серной вулканизации наблюдалось практически во всех случаях с добавлением диамида терефталевой кислоты и олигомера на его основе, что особенно наглядно видно по параметру Т 90 . В смесях с добавлением продукта деструкции ПЭТ Т 90 сократилось на 1,5–4%, а в смесях с добавлением олигомера на основе диамида терефталевой кислоты Т 90 сократилось на 0,5–13%. Наиболее сильное сокращение Т 90 наблюдалось в смеси 9 – на 13,2% (сокращение времени вулканизации на 2 минуты).
Такое ускоряющее влияние на процесс серной вулканизации может быть обусловлено тем, что вводимые ингредиенты (диамид терефталевой кислоты и олигомер на его основе) имеют щелочной характер.
В случае параметров Т 10 и Т 50 наблюдалось незначительное (в пределах 5%) замедление процесса, что приводит к увеличению индукционного периода вулканизации.
Упруго-прочностные показатели исследуемых резин
Из данных таблицы 4 (исследование упруго-прочностных свойств) видно, что при добавлении диамида терефталевой кислоты значительных изменений в условной прочности при разрыве не наблюдалось, данный показатель остался на уровне базовых смесей сравнения. Однако, добавление данного компонента оказало влияние на удлинение при разрыве: увеличение данного показателя наблюдалось у смесей 5 и 6, особенно в случае последней смеси увеличение составило более 50%.
В случае использования олигомера на основе диамида терефталевой кислоты условная прочность смесей на основе хлоропреновых каучуков СR232 и СR244 увеличилась, а в случае каучука СR121 осталась соизмеримой с базовой смесью. Относительное удлинение при разрыве исследуемых смесей во всех трех случаях увеличилось на величину от 20 до 70%, что указывает на пластифицирующее действие полученного олигомера.
Кроме этого, пластифицирующее действие полученного олигомера подтверждаются данными по вязкости резиновых смесей. Вязкость сырых резиновых смесей 7 и 9 снижается на 13 и 24% соответственно.
Сравнивая упруго-прочностные параметры полученных вулканизатов до и после старения, можно сказать, что в некоторых случаях (смесь 4 и 5 с добавлением диамида терефталевой кислоты) наблюдалось увели- чение относительного удлинения при разрыве вулкнизатов после старения на 49 и 65% соответственно.
Условная прочность при разрыве после старения у вулканизатов с добавлением димида терефталевой кислоты снизилась в меньшей степени по сравнению с модельными смесями: снижение условной прочности при разрыве у модельных смесей порядка 13%, у смесей с добавлением диамида терефталевой кислоты 2%. Это может быть связано с тем, что диамид терефталевой кислоты выступает в качестве ингибитора термоокислительного процесса хлоропренового каучука за счет наличия амидной группы.
Заключение
Изучен процесс аминолитической деструкции отходов полиэтилентерефталата при микроволновом излучении различной мощности и при различном соотношении компонентов. Выявлены наиболее оптимальные условия деструкции ПЭТ при микроволновом излучении с выходов продукта 82–85% и временем деструкции 4–6 минут.
Рассмотрена возможность использования продукта аминолитической деструкции ПЭТ и его олигомера в качестве новых ингредиентов в резинах на основе хлоропренового каучука. Показаны некоторые упруго-прочностные характеристики и характер их изменения с добавлением новых полученных ингредиентов. Выявлено, что новые ингредиенты немного ускоряют процесс серной вулканизации резин на основе хлоропреновых каучуков; оказывают пластифицирующее действие на исследуемые вулканизаты, а также могут выступать в качестве ингибиторов термоокислительных процессов.
В дальнейшем планируется более подробное рассмотрение влияния новых полученных ингредиентов в резинах на основе полярных каучуков и термопластов на физико-химические и физико-механические параметры.
Исследование выполнено при финансовой поддержке РФФИ в рамках научного проекта № 20–33–90115
Список литературы Использование продуктов микроволновой аминолитической деструкции полиэтилентерефталата в резинах на основе хлоропренового каучука
- Yun X., Xin-Yi Y., Dun-Hong G., Yong-Bo D. et al. Preparation and characterization of waterborne alkyd-amino baking coatings based on waste polyethylene terephthalate // Royal Society open science. 2020. V. 7. №. 1. P. 191447. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.191447
- Веснин Р.Л., Алалыкин А.А., Вохмянин М.А. Технология утилизации отходов полиэтилентерефталата с получением амида терефталевой кислоты // Известия высших учебных заведений. Серия «Химия и химическая технология». 2020. № 2. С. 99-104.
- Al-Sabagh A.M., Yehia F.Z., Eshaq G., Rabie A.M. et al. Greener routes for recycling of polyethylene terephthalate // Egyptian Journal of Petroleum. 2016. V. 25. №. 1. P. 53-64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpe.2015.03.001
- Jamdar V., Kathalewar M., Sabnis A. Depolymeriza-tion study of PET waste using aminoethylethanolamine and recycled product application as polyesteramide synthesis // Journal of Polymers and the Environment. 2018. V. 26. №. 6. P. 2601-2618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-017-1149-4
- Логинова А.В., Тишин Д.Е., Касьянова О.В. Современные способы переработки вторичного полиэтилентерефталата и области применения полученных материалов // Глобализация экологических проблем: прошлое, настоящее и будущее. 2017. С. 221-221.
- Woortman, A.J.J.; Loos, K.; Popovic, I.G. High Performance Alkyd Resins Synthesized from Postconsumer PET Bottles // RSC Advances. 2015. V. 5. №. 76. P. 62273-62283. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA11777A
- Scremin D.M., Miyazaki D.Y., Lunelli C.E., Silva S.A. et al. PET recycling by alcoholysis using a new heterogeneous catalyst: study and its use in polyurethane adhesives preparation // Macromolecular Symposia. 2019. V. 383. №. 1. P. 1800027. https://doi.org/10.1002/masy.201800027
- Zhou L., Lu X., Ju Z., Liu B. et al. Alcoholysis of polyethylene terephthalate to produce dioctyl terephthalate using choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents as efficient catalysts // Green Chemistry. 2019. V. 21. №. 4. P. 897-906.
- Zhou X., Wang C., Fang C., Yu R. et al. Structure and thermal properties of various alcoholysis products from waste poly (ethylene terephthalate) // Waste management. 2019. V. 85. P. 164-174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.12.032
- Li Y., Li M., Lu J., Li X. et al. Decoloration of waste PET alcoholysis liquid by an electrochemical method // Water Science and Technology. 2018. V. 77. №. 10. P. 2463-2473. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2018.191
- Linlin D.Y.M.Y.Z. Study on the chemical recycling technologies on hydrolysis and alcoholysis of PET waste [J] // Plastics Manufacture. 2011. V. 7.
- Teotia M., Tarannum N., Soni R.K. Depolymerization of PET waste to potentially applicable aromatic amides: Their characterization and DFT study // Journal of Applied Polymer Science. 2017. № 31. P. 45153.
- Панфилов Д.А., Дворко И.М. Химическая деструкция вторичного полиэтилентерефталата как метод получения смол-модификаторов полимеров // Научный альманах. 2018. №. 3-2. С. 183-186.
- Tawfik M.E., Eskander S.B. Chemical Recycling of Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) Waste Using Ethanolamine. Sorting of the End Products // Polymer Degradation and Stability. 2010. V. 95. №. 2. P. 187-194.
- Parab Y.S., Shukla S.R. Novel synthesis, characterization of N1, N1, N4, N4-tetrakis (2-hydroxyethyl) terephthalamide (THETA) and terephthalic Acid (TPA) by depolymerization of PET bottle waste using diethanolamine // Journal of Macromolecular Science, Part A. 2013. V. 50. №. 11. P. 1149-1156. https://doi.org/10.1080/10601325.2013.830004
- Aguado A., Mart?nez L., Becerra L., Arieta-Araunabe?a M. et al. Chemical depolymerisation of PET complex waste: hydrolysis vs. glycolysis // Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management. 2014. V. 16. №. 2. P. 201-210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-013-0177-y
- Malik N., Kumar P., Shrivastava S., Ghosh S.B. An overview on PET waste recycling for application in packaging // International Journal of Plastics Technology. 2017. V. 21. №. 1. P. 1-24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12588-016-9164-1
- Sinha V., Patel M.R., Patel J.V. PET waste management by chemical recycling: a review // Journal of Polymers and the Environment. 2010. V. 18. №. 1. P. 8-25.
- Singh S., Sharma S., Umar A., Mehta S.K. et al. Recycling of waste poly (ethylene terephthalate) bottles by alkaline hydrolysis and recovery of pure nanospindle-shaped terephthalic acid // Journal of nanoscience and nanotechnology. 2018. V. 18. №. 8. P. 5804-5809. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2018.15363
- Sreeram A., Leng Z., Padhan R.K., Qu X. Eco-friendly paving materials using waste PET and reclaimed asphalt pavement // HKIE Transactions. 2018. V. 25. №. 4. P. 237-247. https://doi.org/10.1080/1023697X.2018.1534617
- Padhan R.K., Mohanta C., Sreeram A., Gupta A. Rheological evaluation of bitumen modified using antistripping additives synthesised from waste polyethylene terephthalate (PET) // International Journal of Pavement Engineering. 2020. V. 21. №. 9. P. 1083-1091. https://doi.org/10.1080/10298436.2018.1519192
- Merkel D.R., Kuang W., Malhotra D., Petrossian G. et al. Waste PET chemical processing to terephthalic amides and their effect on asphalt performance // ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering. 2020. V. 8. №. 14. P. 5615-5625. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c00036
- D?bska B., Licho?ai L. The effect of the type of curing agent on selected properties of epoxy mortar modified with PET glycolisate // Construction and Building Materials. 2016. V. 124. P. 11-19.
- D?bska B., Licho?ai L. The selected mechanical properties of epoxy mortar containing PET waste // Construction and Building materials. 2015. V. 94. P. 579-588.
- D?bska B., Licho?ai L., Szyszka J. Innovative compo-site on the basis of an aerogel mat with an epoxy resin modified with PET waste and PCM // E3S Web of Conferences. EDP Sciences, 2018. V. 44. P. 31.
- More A., Mhaske S. Epoxy-based anticorrosive coating developed with modified poly (o-anisidine) and depolymerized product of PET waste // Iranian Polymer Journal. 2018. V. 27. №. 6. P. 359-370.
- Saidi N.M., Shafaamri A.S., Ma I.A.W., Kasi R. et al. Development of anti-corrosion coatings using the disposable waste material // Pigment & Resin Technology. 2018. V. 47. №. 6. P. 478-484. https://doi.org/10.1108/PRT-03-2018-0030
- Yun X., Xin-Yi Y., Dun-Hong G., Yong-Bo D. et al. Preparation and characterization of waterborne alkyd-amino baking coatings based on waste polyethylene terephthalate // Royal Society open science. 2020. V. 7. №. 1. P. 191447. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.191447
- Sadeghi G.M.M., Shamsi R., Sayaf M. From aminolysis product of PET waste to novel biodegradable polyurethanes // Journal of Polymers and the Environment. 2011. V. 19. №. 2. P. 522-534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-011-0283-7
- Sadeghi G.M., Sayaf M. From PET waste to novel polyurethanes // Material Recycling-Trends and Perspectives. 2012. P. 357-390.
- Cakic S.M., Risti? I.S., Milena M., Nikoli? N.?. et al. Glycolyzed products from PET waste and their application in synthesis of polyurethane dispersions // Progress in Organic Coatings. 2012. V. 74. №. 1. P. 115-124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2011.11.024
- Luo X., Li Y. Synthesis and characterization of polyols and polyurethane foams from PET waste and crude glycerol // Journal of Polymers and the Environment. 2014. V. 22. №. 3. P. 318-328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-014-0649-8
- Palekar V.S., Shah R.V., Shukla S.R. Ionic liquid?catalyzed aminolysis of poly (ethylene terephthalate) waste // Journal of applied polymer science. 2012. V. 126. №. 3. P. 1174-1181. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.36878
- Shojaei B., Abtahi M., Najafi M. Chemical recycling of PET: A stepping?stone toward sustainability // Polymers for Advanced Technologies. 2020. V. 31. №. 12. P. 2912-2938. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.5023
- Fukushima K., Lecuyer J.M., Wei D.S., Horn H.W. et al. Advanced chemical recycling of poly (ethylene terephthalate) through organocatalytic aminoly-sis // Polymer Chemistry. 2013. V. 4. №. 5. P. 1610-1616.
- Wang Y., Zhang Y., Song H., Wang Y. et al. Zinc-catalyzed ester bond cleavage: Chemical degradation of polyethylene terephthalate // Journal of Cleaner Production. 2019. V. 208. P. 1469-1475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.117
- Delle Chiaie K.R. et al. Dual-catalytic depolymerization of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) // Polymer Chemistry. 2020. V. 11. №. 8. P. 1450-1453.
- B?ckstr?m E., Odelius K., Hakkarainen M. Ultrafast microwave assisted recycling of PET to a family of functional precursors and materials // European Polymer Journal. 2021. V. 151. P. 110441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2021.110441
- Achilias D.S., Tsintzou G.P., Nikolaidis A.K., Bikiaris D.N. et al. Aminolytic depolymerization of poly (ethylene terephthalate) waste in a microwave reactor // Polymer International. 2011. V. 60. №. 3. P. 500-506. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.2976
- Parab Y.S., Pingale N.D., Shukla S.R. Aminolytic depolymerization of poly (ethylene terephthalate) bottle waste by conventional and microwave irradiation heating // Journal of applied polymer science. 2012. V. 125. №. 2. P. 1103-1107. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.34855
- Shah R.V., Borude V.S., Shukla S.R. Recycling of PET waste using 3?amino?1?propanol by conventional or microwave irradiation and synthesis of bis?oxazin there from // Journal of Applied Polymer Science. 2013. V. 127. №. 1. P. 323-328. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.37900
- Park R., Sridhar V., Park H. Taguchi method for optimization of reaction conditions in microwave glycolysis of waste PET // Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management. 2020. V. 22. №. 3. P. 664-672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-019-00958-7


