Исследование Advance 20 лет спустя
Автор: Кобалава Ж.Д., Колесник Э.Л.
Журнал: Евразийский кардиологический журнал @eurasian-cardiology-journal
Рубрика: Обзоры
Статья в выпуске: 3, 2021 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Наблюдательные и интервенционные исследования показали, что интенсивный контроль артериального давления может принести пользу пациентам с сахарным диабетом. Международное рандомизированное, контролируемое, клиническое исследование ADVANCE (Action in Diabetes and Vascular Disease: Preterax and Diarnicron MR Controlled Evaluation) стартовало в 2001 году. По результатам исследования риск основных микро- и макрососудистых событий (первичная конечная точка) достоверно снизился на 9%, при этом риски сердечно-сосудистой смерти и смерти от любой причины снизились, соответственно, на 18% и 14%. Было зарегистрировано снижение рисков микрососудистых осложнений - любого почечного события, появления или ухудшения нефропатии и появления микроальбуминурии на 21%, 18% и 21%, соответственно.Результаты антигипертензивной части исследования ADVANCE дополнили расширяющуюся доказательную базу и послужили основой для изменения клинических рекомендаций по ведению пациентов с АГ и сахарным диабетом. Согласно обновленным объединенным рекомендациям Европейского общества кардиологов/Европейской ассоциации по изучению диабета (ESC/EASD) целевые уровни систолического/диастолического артериального давления должны составлять 130/80 мм рт.ст., с некоторыми исключениями, а фиксированная комбинация блокатора РААС с диуретиком или антагонистом кальция предлагается в качестве терапии первой линии.По результатам наблюдательного исследования ADVANCE-ON, в котором приняли участие 8494 пациента из 11 140 пациентов, рандомизированных в исследование ADVANCE, был обнаружен эффект памяти, или «наследования», при котором интенсивный контроль артериального давления в ходе исследования оказывал благоприятное влияние на различные исходы после его прекращения. Эти данные подчеркивают важность достижения и сохранения оптимального контроля артериального давления для снижения риска микро- и макрососудистых осложнений.
Артериальная гипертония, сахарный диабет 2 типа, комбинированная антигипертензивная терапия, интенсивный контроль артериального давления (ад), интенсивный контроль гликемии
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143178174
IDR: 143178174 | DOI: 10.38109/2225-1685-2021-3-36-45
Текст научной статьи Исследование Advance 20 лет спустя
Authors’ contributions. All authors meet the ICMJE criteria for authorship, participated in the preparation of the article, the collection of material and its processing.
Conflict of Interest. Manuscript was prepared with the Servier pharmaceutical company informational and financial support that didn’t impact on author’s opinion.
For quotation: Zhanna D. Kobalava, Eteri L. Kolesnik ADVANCE research 20 years later. Eurasian heart journal. 2021;(3):36-45 (In Russ.).
Received: 10.07.2021 | Revision Received: 18.08.2021 | Accepted: 02.08.2021
ВСТУПЛЕНИЕ
Артериальная гипертония (АГ) занимает лидирующее место среди основных факторов, определяющих общую смертность в мире в настоящее время [1]. На основании офисных значений артериального давления (АД) установлено, что в 2015 г. число больных АГ в мире составляло 1,13 млрд [2]. Для многих развитых стран в последние годы наблюдаются общие процессы, которые способствуют еще большему увеличению распространенности АГ во всем мире: постарение населения, прогрессирующая распространенность сидячего образа жизни и увеличение массы тела. Согласно прогнозам, к 2025 году число больных АГ увеличится на 15-20%, достигнув почти 1,5 млрд [2]. В России, по данным многоцентрового наблюдательного исследования ЭССЕ-РФ, распространенность АГ остается одной из самых высоких в Европе и составляет 33,8% [3].
Трудности в лечении АГ связаны со многими факторами, среди которых важное значение имеют возраст пациентов, приверженность к лечению, а также коморбидные состояния – метаболические нарушения, сахарный диабет 2 типа (СД2) и хроническая болезнь почек (ХБП) [4]. В мире в возрастной группе 20-79 лет распространенность СД2 в 2019 году составила 9,3%, а в России по данным эпидемиологического исследования NATION – 5,4% [5, 6]. АГ у пациентов с СД встречается в 1,5-3 раза чаще, чем у пациентов без нарушений углеводного обмена. Так, распространенность АГ среди лиц с СД2 составила 58,8%, у пациентов с преддиабетом – 34,2% и у лиц с нормогликемией – 23,8% [2]. В исследовании M. Nowakowska и соавт. АГ была наиболее частым состоянием среди сопутствующих заболеваний у пациентов с СД, ее распространенность составила 45,8% среди женщин и 42,8% – среди мужчин [3].
АГ у пациентов с СД2 может присутствовать в момент диагностики нарушений углеводного обмена или задолго до их обнаружения [7]. Это подтверждает наличие общих патогенетических механизмов указанных заболеваний и сопровождается развитием сходных метаболических и сосудистых нарушений.
Сочетание СД и АГ повышает риск развития кардиальной смерти, ишемической болезни сердца, сердечной недостаточности, церебральных осложнений и заболеваний периферических сосудов [7]. Больные с АГ и СД 1 и 2 типов относятся к категориям очень высокого (риск сердечно-сосудистой смертности ≥ 10%) или высокого (сердечно-сосудистая смертность 5-10%) 10-летнего сердечно-сосудистого риска [2]. У пациентов СД 2-го типа АГ является дополнительным фактором риска развития атеросклероза и сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний (ССЗ), что обуславливает повышение общей смертности в 4-7 раз по сравнению с пациентами без АГ и СД [8].
Течение АГ на фоне СД2 имеет ряд клинических особенностей. Для пациентов с СД характерны изолированная систолическая АГ и маскированная АГ, появление ортостатической гипотензии и АГ в положении лежа на фоне развивающейся полинейропатии, высокая солечувствительность [9, 10]. Проведение суточного мониторирования АД в течение 24 часов у пациентов с АГ и СД2 позволяет выявить нарушения суточного профиля АД (недостаточное снижение АД во время сна – нон-диппер, ночная АГ – найт-пикер), высокую вариабельность АД вследствие ортостатических и пост-прандиальных колебаний АД, утреннюю АГ даже на фоне лечения [11–13]. Эти изменения способствуют раннему формированию поражения органов-мишеней: гипертрофии левого желудочка, микроальбуминурии, увеличению ригидности артерий [9, 10].
По данным Фремингемского исследования, для лиц 40-70 лет увеличение АД на каждые 20/10 мм рт.ст. удваивает риск ССЗ в диапазоне АД от 115/75 до 185/115 мм рт.ст. [14]. Наблюдательное исследование, проведенное Стамлером и соавт. (Stamler et al. 1993), показало, что при одинаковом уровне АД абсолютный сердечно-сосудистый риск в 3 раза выше у лиц с СД, чем у лиц без СД. Таким образом, можно рассчитать, что при одном и том же снижении АД, польза будет в 3 раза большей у лиц с СД, чем у лиц без этого заболевания [15].
Конец ХХ и начало ХХІ столетий в гипертензиологии были ознаменованы глобальной переоценкой основного критерия диагностики АГ – уровня АД. Принципы доказательной медицины легли в основу этого переосмысления [16]. Именно в этот период на стыке двух столетий были продемонстрированы впервые у пациентов с СД2 преимущества усиленного контроля АД в исследовании UKPDS (The UK Prospective Diabetes Study) [17]. Уровень систолического АД (САД)/диастолического АД (ДАД) в группе интенсивного антигипертензивного контроля был на 10 мм рт.ст./5 мм рт.ст. ниже, чем в группе сравнения, соответственно (р=0,0001). Стратегия интенсивной антигипертензивной терапии (АГТ) сразу продемонстрировала убедительные преимущества в снижении на 24% всех осложнений, связанных с СД, на 37% – смертей от СД и на 44% – от мозговых инсультов (все различия статистически значимы) [17].
В исследовании НОТ (Hypertension Optimal Treatment) изучали оптимальный целевой уровень ДАД. Достижение уровня ДАД 80 мм рт.ст. у больных с СД приводило к снижению в 23 раза риска сердечно-сосудистых осложнений (ССО) и смертности [18]. Во многих сравнительных исследованиях было продемонстрировано достоверное снижение риска развития инсульта, коронарной патологии, нефропатии и ретинопатии у больных СД на фоне приема ингибиторов АПФ и блокаторов рецепторов ангиотензина II [18–26]. Однако, несмотря на это, в 2000 году перед исследователями и экспертами оставались нерешенные вопросы (таблица 1).
Таблица 1. Нерешенные вопросы гипертензиологии в 2000 году Table 1. Unresolved issues of hypertension in 2000 year
Возможно ли получить дополнительные преимущества при снижении САД ниже 140 мм рт. ст.?
Можно ли получить преимущества для пациентов с АГ и без АГ на фоне приема фиксированной комбинации периндоприла и индапамида?
Проявятся ли благоприятные последствия снижения АД на фоне лечения фиксированной комбинацией периндоприла и индапамида, назначенной в дополнение к другим гипотензивным и кардиопротективным препаратам?
Будут ли взаимодополняющими последствия снижения АД и интенсивного контроля гликемии?
Для ответов на эти вопросы, адекватной оценки эффективности, безопасности и возможных негативных эффектов предлагаемой стратегии интенсивного контроля АД, гликемии и дислипидемии требовалось проведение масштабных рандомизированных, плацебо контролируемых клинических исследований.
Международное рандомизированное, контролируемое, клиническое исследование ADVANCE (Action in Diabetes and Vascular Disease: Preterax and Diarnicron MR Controlled Evaluation) стартовало в 2001 году. Исследователи ставили перед собой цель выяснить, будет ли более интенсивное снижение АД (без обозначения целевых цифр АД) и уровня глюкозы уменьшать риск основной комбинированной конечной точки и ее компонентов. В качестве первичных конечных точек исследования были выбраны нефатальный инсульт, нефатальный острый коронарный синдром и сердечно-сосудистая смерть, а также впервые выявленная нефропатия или ретинопатия либо значительное ухудшение их течения. Вторичные конечные точки включали в себя различные варианты цереброваскулярной и коронарной патологии, сердечную недостаточность, патологию периферических сосудов, микроальбуминурию, ухудшение зрения, нейропатию, деменцию и общую смертность.
Основной задачей исследования была оценка влияния жесткого контроля АД и уровня гликемии на частоту развития макро- и микрососудистых осложнений у больных СД 2 типа, относящихся к группе высокого риска с или без АГ.
В исследовании приняли участие 215 центров из 20 стран Австралии, Азии, Северной Америки и Европы. Рандомизация 11140 пациентов, включенных в исследование, проводилась централизованно с использованием 2x2 факторного дизайна. В антигипертензивной части пациенты получали лечение фиксированной комбинацией ингибитора ангиотензин-превращающего фермента (АПФ) периндоприла и тиазидоподобного диуретика индапамида (2,0/0,625 – 4,0/1,25 мг/сут) либо плацебо, тогда как в сахароснижающей части сравнивали лечение препаратом суль-фонилмочевины гликлазидом МВ (30-120 мг/сут) в сочетании с другими сахароснижающими препаратами, направленное на достижение целевого уровня гликированного гемоглобина (HbA1c) ≤ 6,5% (48 ммоль/моль), со стандартным контролем гликемии (рис. 1).
В исследование были включены больные СД2 в возрасте 55 лет и старше, имевшие не менее одного дополнительного фактора риска сердечно-сосудистых осложнений: анамнез микро- или ма-крососудистой патологии, возраст 65 лет и старше, давность диабета 10 лет и более до старта исследования; микроальбуминурия; диабетическая ретинопатия на поздних стадиях; курение; дислипидемия. Критериями исключения были: уровень HbA1c ≤ 6,5% (48 ммоль/моль), определенное показание или противопоказание к назначению любого из изучаемых препаратов, определенное показание к долгосрочной терапии инсулином, одновременное участие в другом клиническом исследовании. Критериев включения по уровню АД не было [27].
Различий между группами по характеристикам участников, факторам риска, приему сопутствующих препаратов и лабораторным показателям не было. Средний возраст включенных в исследование участников составил 66 лет, 42,5% пациентов были женского пола. Приблизительно у трети пациентов имелось диагностированное ССЗ, 15% участников были активными курильщиками. Средняя давность сахарного диабета по группам составила 8 лет. Средний уровень САД/ДАД составил 145/81 мм рт.ст., практически 70% участников получали антигипертензивную терапию. Половина участников получала ингибитор АПФ или антагонист рецепторов ангиотензина (АРА) 2 типа, несколько реже – антагонисты кальция (30%) и b-адреноблокаторы (24%). Всех пациентов, получавших ингибиторы АПФ или АРА ІІ типа, переводили на периндоприл. Около трети больных получали липидснижаюшую терапию и почти половина – антитромботические препараты [30]. Более 90% получали сахароснижающие препараты; из них 60% получали метформин, 72% – производное сульфонилмочевины и всего 1% лечились инсулином [27].
На исходном этапе средняя расчетная скорость клубочковой фильтрации (СКФ) составила 76 мл/мин, а среднее отношение альбумин/креатинин (ОАК) в моче составило 15 мг/г. Более чем у 50% участников не было признаков ХБП, тогда как ХБП стадии 1, 2, 3, 4 и 5 имелась у 7%, 15%, 19%, 0,5% и <0,1% пациентов, соответственно. Приблизительно у 25% участников имелась микроальбуминурия и 4% – макроальбуминурия.
Детальная характеристика пациентов представлена в таблице 2.
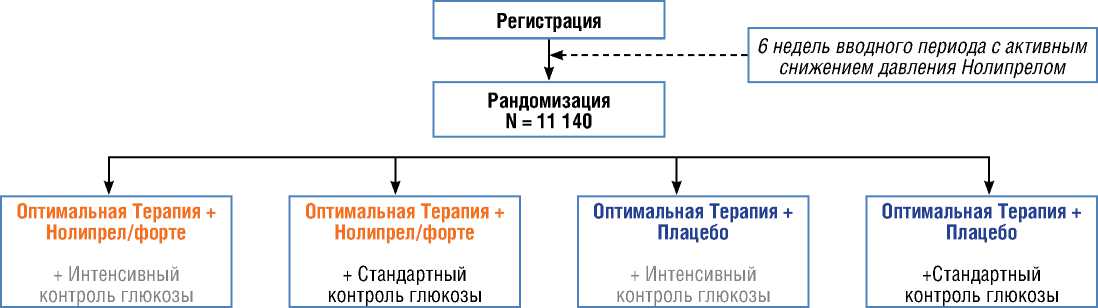
Рисунок 1. Дизайн исследования ADVANCE
Figure 1. ADVANCE Study Design
Таблица 2. Исходная характеристика рандомизированных больных (n=11140)
Table 2. Baseline characteristics of randomized patients (n = 11140)
|
Показатели |
Значения |
|
Средний возраст, лет |
66 |
|
Мужчины, % |
57,5 |
|
Возраст в момент установления диагноза СД, лет |
58 |
|
Средний уровень АД, мм рт. ст. |
145/81 |
|
HbAlc, % |
7,5 |
|
Анамнез, % |
|
|
макрососудистая патология |
33 |
|
микрососудистая патология |
11 |
|
макро- или микрососудистая патология |
40 |
|
Другие факторы риска (критерии включения),% |
|
|
возраст >65 лет |
59 |
|
анамнез сахарного диабета >10 лет |
37 |
|
курение |
14 |
|
общий холестерин >6,0 ммоль/л |
11 |
|
ЛВП<1,0 ммоль/л |
21 |
|
микроальбуминурия |
25 |
Выбор фиксированной низкодозовой комбинации периндопри-ла и индапамида (Нолипрел) в качестве базового антигипертензивного препарата был аргументирован доказанной безопасностью, хорошей переносимостью и эффективностью сочетанного применения ингибиторов АПФ и диуретиков, обладающих различными механизмами действия и взаимодополняющих друг друга. Кроме того, низкие дозы компонентов препарата снижают риск развития нежелательных эффектов, а возможность принимать препарат один раз в сутки повышает приверженность больных к лечению [19–21].
Данные исследований PROGRESS, PREMIER, PICxEL, EUROPA и ASCOT-BPLA продемонстрировали эффективность периндопри-ла как в виде монотерапии, так и в комбинации с другими препаратами, в том числе с индапамидом, в качестве гипотензивного средства, а также его положительное влияние на риск развития сосудистых осложнений СД [28-32].
Контроль уровня АД в исследовании ADVANCE
Исследование ADVANCE было спланировано таким образом, чтобы выявить статистически значимое снижение относительного риска развития каждой конечной точки в результате активной терапии не менее, чем на 16%. Предполагалось, что ежегодная частота конечных точек в контрольной группе превысит 3%, как в исследованиях НОРЕ и UKPDS. Ожидалось также, что снижение САД в группе больных, получающих периндоприл/индапамид составит как минимум 6 мм рт. ст., что приведет к уменьшению частоты макро- и микрососудистых событий в данной группе на 15-20%. Целевое различие уровней гликированного гемоглобина между группами интенсивного и стандартного контроля глюкозы предполагалось довести до 1% или более, в результате чего число микро- и макрососудистых событий должно снизиться на 25% и 16%, соответственно.
Поскольку за время исследования ежегодная частота конечных точек составила примерно 2,5%, а разница уровней HbAlc между группами не достигла запланированного 1%, было принято решение о продлении двойной слепой части исследования (контроль артериального давления) на 6 месяцев, а открытой части (контроль гликемии) – на 12 месяцев.
По результатам исследования ADVANCE были получены данные, подтверждающие благоприятное влияние снижения АД у пациентов с СД2, в отношении основных макро- и микрососуди-стых осложнений СД, а также смертности. Доказано также, что на фоне антигипертензивной терапии больных СД2 существенно уменьшается частота развития терминальной почечной недостаточности, ретинопатии и альбуминурии [2].
Исходно в исследовании ADVANCE средний уровень АД составил 145/81 мм рт.ст. В среднем через 4,3 года наблюдений в группе активной терапии величина САД/ДАД снизилась до 135/75 мм рт.ст., а в группе плацебо – до 140/77 мм рт.ст., что оказалось существенно ниже, чем в группах «более жесткого» и «менее жесткого» контроля АД в исследовании UKPDS (144/82 и 154/87 мм рт.ст., соответственно) [7].
Риск основных микро- и макрососудистых событий (первичная конечная точка) снизился на 9%, при этом риски сердечно-сосудистой смерти и смерти от любой причины снизились, соответственно, на 18% и 14%. Полученные результаты не зависели от исходного уровня АД, сопутствующего использования других препаратов или любого другого состояния на начальном этапе и воспроизводимы во всех подгруппах исследования (рис. 2) [33].
Также зарегистрировано достоверное снижение рисков микро-сосудистых осложнений: любого почечного события – на 21%, появления или ухудшения нефропатии – на 18% и появления микроальбуминурии – на 21% [33].
В исследованиях по изучению различий между более или менее интенсивным снижением АД у пациентов с СД2 было показано, что активное лечение приводит к снижению сердечно-сосудистой заболеваемости и смертности при достижении САД/ДАД 144/82 мм рт.ст. в исследовании UKPDS, 144/81 мм рт.ст. в исследовании НОТ и 140/77 мм рт.ст. в исследовании МIСRО-НОРЕ [19]. Таким образом, благоприятный эффект достижения уровня ДАД в пределах 77-82 мм рт.ст. не вызывает сомнения. В то же время в этих исследованиях уровень САД оставался выше 140 мм рт.ст. Только в двух наблюдениях АВСD удалось достигнуть снижения АД 132/78 мм рт.ст. (АВСD-HТ) и 128/75 мм рт.ст. (АВСD-NТ), но при этом в обоих исследованиях положительный эффект снижения
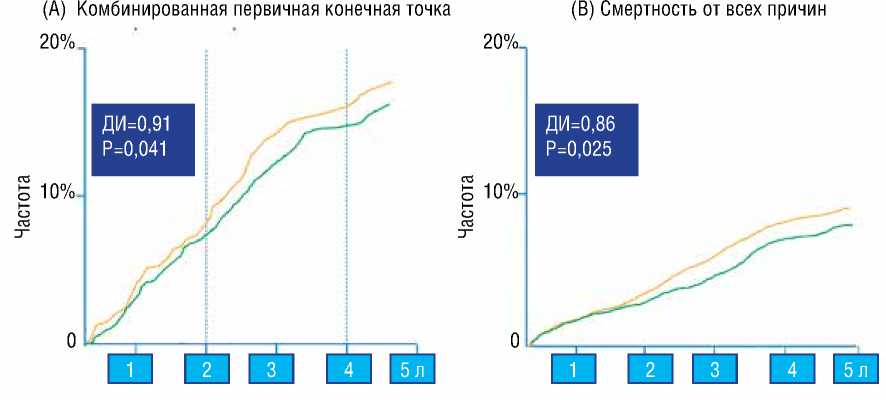
ОР = 0,91, 95% ДИ 0,81-1,00 р = 0,041 HR = 0.91, 95% CI 0.81-1.00 p = 0.041
ОР = 0,86, 95% ДИ 0,75-0,98 р = 0,025 HR = 0.86, 95% CI 0.75-0.98 p = 0.025
Рисунок 2. (A) Влияние фиксированной комбинации периндоприла/индапамида на частоту первичной конечной точки (комбинация микро-и макрососудистых событий), и (B) общая смертность в антигипертензивной части исследования ADVANCE. Зеленые линии – комбинация периндоприла/индапамида, красные линии – плацебо. Адаптировано из работы Патель и соавт. (Patel et al) [33]. ОР: отношение рисков Figure 2. (A) Impact of fixed-combination perindopril/indapamide on (A) incidence of the primary outcome (combined microvas-cular and macrovascular events), and (B) all-cause mortality in the blood pressure arm of the ADVANCE study. Green lines indicate perindopril/indapamide, and red lines indicate placebo. Adapted from Patel et al [33]. HR, hazard ratio
АД не был таким впечатляющим (значимое снижение только общей смертности в исследовании АВСD-НТ и количества инсультов в исследовании АВСD-NТ) [34, 35]. И, наконец, в проспективном наблюдении по программе UКРDS продемонстрирована значимая связь между уровнем САД и частотой развития макро- и микросо-судистых осложнений у пациентов с СД (количество осложнений увеличивалось при САД выше 120 мм рт.ст.) [17].
Результаты антигипертензивной части исследования ADVANCE дополнили расширяющуюся доказательную базу и легли в основу обновленных объединенных рекомендаций Европейского общества кардиологов/Европейской ассоциации по изучению диабета (ESC/EASD). В них отмечается, что целевой уровень САД должен составлять 130 мм рт.ст. и <130 мм рт.ст. (с небольшими вариациями в зависимости от возраста и сопутствующих заболеваний), а фиксированная комбинация блокатора РААС с диуретиком или антагонистом кальция предлагается в качестве терапии первой линии [36].
КОНТРОЛЬ ГЛИКЕМИИ В ИССЛЕДОВАНИИ ADVANCE
Повышенные уровни глюкозы в крови ассоциируются с широким рядом сосудистых осложнений [7]. В связи с этим, нормализация уровня глюкозы в крови остается важной частью многофакторного подхода к лечению пациентов с СД2. По мере увеличения длительности СД2 обычно возникает потребность в интенсификации терапии и одного препарата часто оказывается недостаточно для снижения уровня гликированного гемоглобина (HbA1c) до оптимальных значений.
За предыдущие три десятилетия в четырех крупных многоцентровых рандомизированных клинических исследованиях у пациентов с СД2 (UKPDS, ADVANCE, ACCORD и VADT) были изучены различные подходы к достижению близких к нормальным уровней гликемии [37-40]. Каждое из этих исследований планировалось на основе международных и национальных руководств, рекомендующих достижение целевого уровня гликемии 6,5% или менее для предотвращения диабетических осложнений. В совокупности эти клинические исследования позволили получить убедительные доказательства потенциальных сосудистых выгод и снижения рисков, связанных с более интенсивным контролем гликемии, по сравнению с менее интенсивным контролем, и достичь критически важного понимания того, как использовать такие методы лечения на практике.
В исследовании ADVANCE режим интенсивного контроля уровня глюкозы был основан на приеме гликлазида с модифицированным высвобождением (МВ), производном сульфонилмоче-вины 3-го поколения в дозе 30-120 мг/сут в виде монотерапии или в комбинации с другими пероральными сахароснижаюшими препаратами и/или инсулином. К преимуществам гликлазида MB следует отнести безопасность, эффективность и его хорошую переносимость, низкий риск развития эпизодов гипогликемии и возможность приема всей дозы один раз в сутки [41].
Средний уровень HbA1c в начале исследования составил 7,5%, и более 90% пациентов уже принимали один или несколько пероральных препаратов [39]. В конце периода наблюдения в группах интенсивного и стандартного контроля гликлазид МВ (в дозе 70% от максимальной) или другие препараты сульфонилмочеви-ны получали, соответственно, 92% и 59% пациентов, метформин получали 74% и 67% пациентов, тиазолидиндионы получали 17% и 11%, и на терапии инсулином были 40% и 24% пациентов [39].
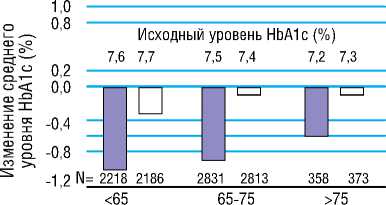
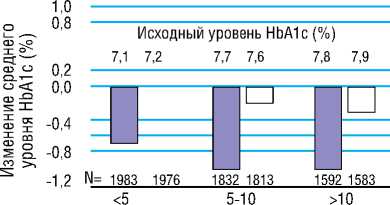
В группе интенсивного контроля гликемии уровень HbA1c постепенно снижался в течение 36 месяцев, а затем поддерживался стабильным в среднем на протяжении 5 лет, в результате чего средний уровень HbA1c составил 6,5%, по сравнению с 7,3% в группе стандартного контроля [39]. Похожее по величине снижение уровня HbA1c также наблюдалось в других подгруппах, сформированных в зависимости от возраста, пола, давности СД2, ИМТ, уровня HbA1c или лечения на исходном этапе (Рисунок 3) [39].
Как и следовало ожидать, пропорции пациентов с достижением целевых уровней HbA1c ≤ 7,0% и <6,5% были значимо больше в группе интенсивного контроля (81% и 65%, соответственно), чем в группе стандартного контроля гликемии (50% и 29%, соответственно) [39, 42]. Эффекты лечения были одинаковыми в разных регионах мира [43].
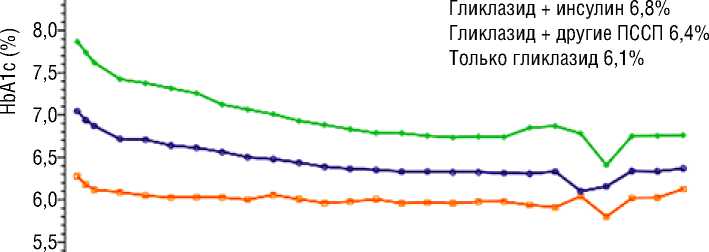
Снижение среднего уровня HbA1c было таким же впечатляющим у тех, кто получал гликлазид МВ как в виде монотерапии, так и в комбинации с другой пероральной терапией и/или инсулином (Рисунок 4) [42]. Среднее время до назначения базального инсу-
1,0
0,8
0,2
0,0
-0,4
-0,8
-1,2
Возраст на исходном этапе (годы)
Длительность сахарного диабета на исходном этапе (годы)
Рисунок 3. Изменение среднего уровня гликированного гемоглобина (HbA1c) за период наблюдения в зависимости от основных характеристик пациентов [42]
Figure 3. Mean change in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels during follow-up by key patient characteristics [42]
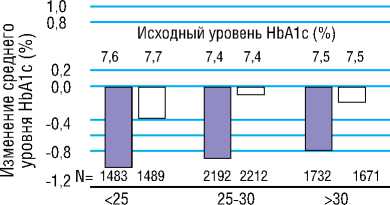
Индекс массы тела (кг/м2)
ОБЗОР
ИССЛЕДОВАНИЕ ADVANCE 20 ЛЕТ СПУСТЯ лина составило 44 месяца, что значительно больше, чем требовалось первоначально для достижения среднего целевого уровня HbA1c 6,5% (36 месяцев) [42, 44]
Медленное снижение гликемии на фоне применения гликла-зида МВ привело к достоверному снижению на 10% риска составного исхода – макро- и микрососудистых событий – за весь период наблюдения в исследовании ADVANCE [39].
Полученные результаты спасли научный мир от ложного предположения о том, что снижение гликемии могло быть опасным, учитывая данные исследования ACCORD.
В исследовании ACCORD (Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes) проверяли эффективность двух стратегий контроля гликемии: интенсивного лечения с достижением целевого уровня HbA1c <6,0% и стандартного лечения с достижением целевого уровня HbA1c от 7,0% до 7,9% [38]. Пациенты с сердечно-сосудистым заболеванием или высоким риском его развития были включены в группу с достижением уровня HbA1c ≥ 7,5%. В группе интенсивного контроля уровни использования метформина, ПСМ, тиазолидиндионов и инсулина были очень высокими и составили 95%, 87%, 92% и 77%, соответственно. Это привело к быстрому снижению уровня HbA1c с достижением медианы 6,4% в группе интенсивного контроля, по сравнению с медианой 7,5% в группе стандартного контроля [45]. По прошествии в среднем 3,5 лет интенсивное лечение с целью контроля гликемии было преждевременно прекращено в связи с выявлением повышенных рисков смерти от любой причины и сердечно-сосудистой смерти [45]. Интересно отметить, что риск нефатального инфаркта миокарда уменьшился на 24% при интенсивном контроле глюкозы, при этом различий по частоте первичного составного сердечнососудистого исхода не было [45].
В исследовании UKPDS изучали вопрос: «Уменьшает ли раннее интенсивное управление гликемией частоту диабетических осложнений у пациентов с впервые выявленным СД2?» [46, 47]. Пациенты случайным образом были распределены в группу с начальной терапией производным сульфонилмочевины (ПСМ) или инсулином с целью достижения уровня глюкозы в плазме натощак <6 ммоль/л или в группу стандартного контроля гликемии
[46]. При необходимости добавляли и другие препараты. При таком подходе в группе интенсивного контроля гликемии была достигнута медиана HbA1c 7,0% против 7,9% в группе стандартного лечения [46]. Цели гликемии были достигнуты постепенно и не могли сохраняться стабильными в течение длительного периода времени. Так, уровни HbA1c возрастали в периоде наблюдения в обеих группах, но оставались более низкими в группе интенсивного контроля (спустя первые и вторые 5 лет медиана HbA1c составила, соответственно, 6,6% и 7,5% в группе интенсивного контроля против 7,4% и 8,4% в группе стандартного контроля). Это привело к снижению риска микрососудистых событий на 25% и риска любого клинического исхода, связанного с диабетом, на 12% [46]. Достоверного снижения риска инфаркта миокарда выявлено не было [46]. В отдельной выборке из 1704 пациентов с ожирением участники были распределены на лечение метформином или ПСМ/инсулином в группе интенсивного контроля [47]. В результате была достигнута медиана HbA1c 7,4% в группе интенсивного лечения метформином, по сравнению с 8,0% в группе стандартного лечения [47]. Это привело к значительному снижению рисков любого клинического исхода, связанного с СД, смерти, связанной с СД, и инфаркта миокарда на 32, 42% и 39%, соответственно [47].
В исследовании VADT (Veteran Affairs Diabetes Trial) изучали эффекты интенсивного контроля гликемии у пациентов с плохо контролируемым СД 2 типа (средний уровень HbA1c на исходном этапе 9,4%) [40]. Все участники исследования были рандомизированы в группу интенсивного контроля глюкозы с целевым уровнем HbA1c <6% или в группу стандартного контроля гликемии (целевой уровень HbA1c <9%) [40]. На исходном этапе у пациентов с индексом массы тела (ИМТ) ≥ 27 кг/м 2 была начата терапия метформином плюс розиглитазоном, тогда как у пациентов с ИМТ <27 кг/м 2 была начата терапия глимепиридом плюс розиглитазоном. В группе интенсивного контроля лечение начинали с пероральных препаратов в половинных дозах, а инсулин добавляли, если уровень HbA1c оставался выше 6%. В группе стандартного контроля лечение также начинали с пероральных препаратов в половинных дозах, а инсулин добавляли, если уро-
10,0
9,5
9,0
Гликлазид + инсулин (независимо от применения других ПССП)
Гликлазид + любые другие ПССП, кроме инсулина
Только гликлазид
HbA1c в конце исследования
8,5
5,0 ' I I I I I I I I 1 T — I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I R3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30 33 36 39 42 45 48 51 54 57 60 63 T1 69 T2
Период наблюдения (месяцы)
Примечание/Note: ПССП – пероральные сахароснижающие препараты (oral glucose lowering drugs).
Рисунок 4. Динамика среднего уровня гликированного гемоглобина HbA1c (%) в исследовании ADVANCE в зависимости от лечения в периоде наблюдения [42]
Figure 4. Mean change in glycated hemoglobin HbA1c by treatment during follow-up in the ADVANCE study [42]
42 ЕВРАЗИЙСКИЙ КАРДИОЛОГИЧЕСКИЙ ЖУРНАЛ, 3, 2021
вень HbA1c оставался выше 9%. По усмотрению лечащих врачей могли быть добавлены другие препараты. Интенсивный контроль гликемии привел к быстрому улучшению уровней глюкозы с уменьшением уровня HbA1c через 3 месяца и его стабилизацией через 6 месяцев, при этом к концу периода наблюдения была достигнута медиана HbA1c 6,9% в группе интенсивного контроля, по сравнению с 8,4% в группе стандартного контроля [40]. Тем не менее, интенсивный контроль гликемии не снизил риск первичного составного сердечно-сосудистого исхода, включавшего инфаркт миокарда, инсульт, сердечно-сосудистую смерть, сердечную недостаточность, хирургическую операцию по поводу сосудистого заболевания, неоперабельную ишемическую болезнь сердца и ампутацию в связи с ишемической гангреной [40].
Стратегию быстрой интенсификации терапии в исследованиях ACCORD и VADT, с внедрением режимов с использованием множества пероральных сахароснижающих препаратов и инсулина, сравнивали со стратегией гораздо более осторожного наращивания терапии с назначением гликлазида МВ и других препаратов в исследовании ADVANCE [38, 40]. Более агрессивные подходы к лечению характеризовались значительно более высокой долей пациентов, получавших инсулин и тиазолидиндионы в исследованиях ACCORD и VADT, чем в исследовании ADVANCE [40, 45]. Как следствие, снижение HbA1c происходило намного быстрее (в течение 3-6 месяцев в ACCORD и VADT по сравнению с 2 годами в исследовании ADVANCE). Это привело к значительной прибавке массы тела у пациентов в группах интенсивного контроля гликемии в исследованиях ACCORD (3,5 кг) и VADT (8,4 кг), но не в исследовании ADVANCE (0,1 кг) [39, 40, 45]. Кроме того, частота тяжелой гипогликемии (при использовании аналогичных определений) в исследованиях ACCORD и VADT была в 6 раз выше, чем в исследовании ADVANCE [39, 40, 45]. Эти различия, вероятно, снижают оценку безопасности усиления терапии и должны учитываться при стремлении к достижению целевых уровней гликемии, близких к нормальным.
По результатам первоначального мета-анализа с объединением табличных данных из исследований ADVANCE, ACCORD, VADT и UKPDS интенсивный контроль уровня глюкозы уменьшил риск основных сердечно-сосудистых событий на скромные 10%, главным образом, за счет снижения риска инфаркта миокарда на 15% (Рисунок 5) [48].
Уровни общей и сердечно-сосудистой смертности достоверно не различались при сравнении двух режимов контроля гликемии [48]. При последующем мета-анализе с объединением данных для отдельных пациентов из исследований ADVANCE, ACCORD, VADT и UKPDS было выявлено снижение рисков основных почечных событий и ретинопатии на 20% и 13%, соответственно, но не риска нейропатии, что подтверждает важную роль контроля гликемии в профилактике микрососудистых осложнений [49].
|
Исследования |
Более интенсивный |
Менее интенсивный |
D HbA 1c (%) |
В пользу более интенсивного |
В пользу менее интенсивного |
|
Основные сердечно-сосудистые события |
|||||
|
ACCORD |
352(2.11) |
371 (2.29) |
-1.01 |
||
|
ADVANCE |
557 (2.15) |
590 (2.28) |
-0.72 |
1 |
|
|
UKPDS |
169 (1.30) |
87 (1.60) |
-0.66 |
---■—1— 1 |
|
|
VADT |
116 (2.68) |
128 (2.98) |
-1.16 |
—*- |
|
|
Overall |
1.194 |
1.176 |
-0.88 |
||
|
Инсульт фатальный/нефатальный |
1 |
||||
|
ACCORD |
73 (0,43) |
70 (0,42) |
-1,01 |
----II— |
— |
|
ADVANCE |
238 (0,91) |
246 (0,94) |
-0,72 |
||
|
UKPDS |
35 (0,26) |
17 (0,31) |
-0,66 |
----------■—'-- 1 |
|
|
VADT |
32 (0,71) |
37 (0,82) |
-1,16 |
---------■—1-- 1 |
|
|
Overall |
378 |
370 |
-0,88 |
||
|
Инфаркт миокарда фатальный/нефатальный |
|||||
|
ACCORD |
198 (1,18) |
245 (1,15) |
-1,01 |
||
|
ADVANCE |
310 (1,18) |
337 (1,28) |
-0,72 |
||
|
UKPDS |
150 (1,20) |
76 (1,40) |
-0,66 |
-----■-- |
|
|
VADT |
72 (1,65) |
87 (1,99) |
-1,16 |
----■-- |
|
|
Overall |
730 |
745 |
-0,88 |
||
|
1 0.5 1.0 |
2.0 |
||||
Отношение рисков (95% ДИ)
Отношение рисков(95% ДИ)
0.90 (.78-1.04)
0.94 (0.84-1.06)
0.80 (0.62-1.04)
0.90 (0.70-1.16)
0.91 (0.84-0.99)
(Q=1.32, p=0.72, I2=0.0%)
1,00(0,72-1,39)
0,97 (0,81-1,16)
0,85 (0,48-1,52)
0,87 (0,54-1,39)
0,96 (0,83-1,10)
(Q=0.40, p=0.94, I2=0.0%)
0,77 (0,64-0,93)
0,92 (0,79-1,07)
0,81 (0,62-1,07)
0,83 (0,61-1,13)
0,85 (0,76-0,94)
(Q=2.25, p=0.52, I2=0.0%)
Рисунок 5. Объединенные эффекты более интенсивного контроля гликемии, по сравнению с менее интенсивным контролем, в основных клинических исследованиях. Черные прямоугольники = точечные оценки (их площадь пропорциональна числу событий); горизонтальные линии = 95%-ные доверительные интервалы [48].
Figure 5. Pooled effects of more versus less intensive glucose control in major clinical trials. Black squares = point estimates (with area proportional to number of events); horizontal lines = 95% confidence interval [48].
Важным выводом стало то, что постепенное снижение уровня гликемии (снижение HbA1c с 7,5% до 6,5% в течение 5 лет) ассоциируется со значительным уменьшением риска составного исхода, главным образом за счет достоверно меньшей частоты почечных осложнений.
Первые сообщения о наблюдаемом более низком риске ма-крососудистых событий после завершения исследований у пациентов с СД2 были опубликованы по итогам исследования EDIC (Epidemiology of Diabetes Intervention and Complications), продленного периода наблюдения участников исследования DCCT (Diabetes Intervention and Complications Trial;) у молодых пациентов с СД 1 типа в 2005 г., в котором также сообщалось о сохраняющейся пользе рандомизированного лечения в улучшении микрососуди-стых осложнений [50]. Вслед за этим, в 2008 году последовали сообщения из исследования UKPDS «Проспективное исследование диабета в Великобритании»), в котором были выявлены благоприятные эффекты более интенсивного контроля глюкозы в отношении сердечно-сосудистых событий и смертности у пациентов с СД 2 типа, но не более интенсивного контроля АД, через 10 лет после прекращения рандомизированного лечения [51, 52].
Исследования ADVANCE и ADVANCE-ON
Из 11 140 пациентов, рандомизированных в исследование ADVANCE, 8494 было включено в последующее наблюдательное исследование ADVANCE-ON [49]. Перед рандомизацией характеристики всей когорты исследования ADVANCE и подгруппы ADVANCE-ON, предоставившей дополнительные данные в ходе последующего наблюдения, были похожими, о чем сообщалось в финальном отчете для продленного периода наблюдения. Медианы периодов наблюдения в основном, дополнительном исследованиях и в целом составили, соответственно, 4,4, 5,9 и 9,9 лет в группе с оценкой антигипертензивной терапии и 5,0, 5,4 и 9,9 лет в группе с оценкой сахароснижающей терапии. Разница по среднему уровню САД и ДАД (5,6 и 2,2 мм рт.ст.), достигнутая за период рандомизированного лечения, исчезла через 6 месяцев, как было установлено на финальном визите в рандомизированной фазе в сахароснижающей части, и затем уровни АД оставались похожими на всем протяжении продленного периода наблюдения.
По результатам 5-летнего периода наблюдения после исследования был обнаружен эффект памяти, или «наследования», при котором интенсивный контроль АД в ходе исследования оказывал благоприятное влияние на различные исходы после его прекращения [53]. Хотя уровни АД были выровнены между группами в конце исследования, преимущества такого контроля сохранялись еще 5,9 лет – отношение рисков [ОР] смерти от любой причины составило 0,91 (p = 0,03), а ОР сердечно-сосудистой смерти – 0,88 (p = 0,04). Таким образом, для снижения риска микро - и макрососудистых осложнений важен оптимальный контроль АД, который необходимо удерживать для сохранения достигнутого положительного результата.
В недавно опубликованном крупномасштабном метаанализе 48 рандомизированных исследований было установлено, что снижение уровня САД на 5 мм рт.ст. позволяет уменьшить риск серьезных СС событий примерно на 10% [54]. Эти данные свидетельствуют о том, что фиксированная степень фармакологического снижения АД одинаково эффективна для первичной и вторичной профилактики серьезных ССЗ, даже при уровнях АД, которые в настоящее время не рассматриваются для лечения [55].
Разница по среднему уровню гликированного гемоглобина (HbA1c; 0,67%), достигнутая за период рандомизированного лечения, исчезла к моменту первого визита в рамках продленного периода, в среднем через 2,9 года (0,08%, р = 0,29), и далее уровни HbA1c оставались похожими до конца этого периода (7,2% и 7,4%, соответственно).
У пациентов с давно имеющимся СД2 антигипертензивная терапия периндоприлом и индапамидом в среднем на протяжении 4,5 лет обеспечила слабую, но достоверную пользу на долгосрочном этапе в снижении рисков смерти от любой причины и сердечнососудистой смерти, тогда как интенсивный контроль гликемии в среднем на протяжении 5 лет не обеспечил долгосрочной пользы в отношении рисков смерти или развития основных макрососуди-стых событий. Отмечалась стойкая польза интенсивного контроля гликемии в виде снижения риска достижения терминальной стадии заболевания почек. Эти наблюдения подчеркивают важность продолжения антигипертензивной терапии и поддержания оптимального контроля глюкозы у пациентов данной категории.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Долгосрочные исследования с оценкой исходов являются дорогостоящими и трудоемкими. Они требуют многолетней приверженности пациентов и врачей к решению возникающих проблем.
Исследование ADVANCE значительно улучшило наше понимание лечения пациентов с АГ и СД и показало, вне всякого сомнения, что АД можно и нужно контролировать, и что контролируемое и устойчивое снижение уровня глюкозы крови также способно увеличить продолжительность жизни.
Результаты антигипертензивной части исследования ADVANCE послужили основой для разработки клинических рекомендаций по ведению пациентов с АГ и СД2. Они поддержали и укрепили убежденность в том, что контроль АД при помощи фиксированной комбинации блокатора РААС с тиазидоподобным диуретиком является терапией первой линии у таких пациентов.
Исследование ADVANCE бесспорно занимает почетное место в анналах изысканий в области сахарного диабета.
Список литературы Исследование Advance 20 лет спустя
- GBD 2019 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2020;396(10258):1223-49.
- Williams B., Mancia G., Spiering W. et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2018;39(33):3021-104.
- Муромцева Г.А., Концевая А.В., Константинов В.В. и др. Распространенность факторов риска неинфекционных заболеваний в российской популяции в 2012-2013 гг. Результаты исследования ЭССЕ-РФ. Кардиоваскулярная терапия и профилактика. 2014;13(6):4-11.
- Gu Q., Burt V.L., Dillon C.F., Yoon S. Trends in Antihypertensive Medication Use and Blood Pressure Control Among United States Adults With Hypertension. Circulation. 2012;126(17):2105-14.
- IDF Diabetes Atlas 9th edition 2019. https://www.diabetesatlas.org/en (31 May 2021).
- Дедов И.И., Шестакова М.В., Галстян Г.Р. Распространенность сахарного диабета 2 типа у взрослого населения России (исследование NATION). Сахарный диабет. 2016;19(2):104-12.
- Кобалава Ж.Д., Котовская Ю.В., Моисеев В.С. Артериальная гипертония. Ключи к диагностике и лечению: Серия «Библиотека врачаспециалиста». Москва: ГЭОТАР-Медиа; 2009. 864 p.
- Чазова И.Е., Шестакова М.В., Жернакова Ю.В. и др. Рекомендации по ведению больных артериальной гипертонией с метаболическими нарушениями и сахарным диабетом 2-го типа. Системные Гипертензии. 2020;17(1).
- Kocemba J., Kawecka-Jaszcz K., Gryglewska B., Grodzicki T. Isolated systolic hypertension: pathophysiology, consequences and therapeutic benefits. J Hum Hypertens. 1998;12(9):621-6.
- Alsuwaida A., Parkes R., So J. et al. High prevalence of masked hypertension in treated hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2006;17(3):326-37.
- Cuspidi C., Meani S., Lonati L. et al. Short-term reproducibility of a non-dipping pattern in type 2 diabetic hypertensive patients. J Hypertens. 2006;24(4):647-53.
- Sowers J.R., Haffner S. Treatment of cardiovascular and renal risk factors in the diabetic hypertensive. Hypertension. 2002;40(6):781-8.
- Kuriyama S., Otsuka Y., Iida R. et al. Morning blood pressure predicts hypertensive organ damage in patients with renal diseases: effect of intensive antihypertensive therapy in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Intern Med. 2005;44(12):1239-46.
- Lewington S., Clarke R., Qizilbash N. et al. Prospective Studies Collaboration. Age-specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: a meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet. 2002;360(9349):1903-13.
- Stamler J., Vaccaro O., Neaton JD., Wentworth D. Diabetes, other risk factors, and 12-yr cardiovascular mortality for men screened in the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial. Diabetes Care. 1993;16(2):434-44.
- Дзяк Г.В., Колесник Т.В., Погорецкий Ю.Н. Суточное мониторирование артериального давления. Днепропетровск: Пороги; 2005. 200 c.
- Group BMJP. Tight blood pressure control and risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes: UKPDS 38. BMJ. 1998;317(7160):703-13.
- Hansson L., Zanchetti A., Carruthers S.G., et al. Effects of intensive blood-pressure lowering and low-dose aspirin in patients with hypertension: principal results of the Hypertension Optimal Treatment (HOT) randomised trial. HOT Study Group. Lancet. 1998;351(9118):1755-62.
- Effects of ramipril on cardiovascular and microvascular outcomes in people with diabetes mellitus: results of the HOPE study and MICRO-HOPE substudy. Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation Study Investigators. Lancet. 2000;355(9200):253-9.
- The EUCLID Study Group. Randomised placebo-controlled trial of lisinopril in normotensive patients with insulin-dependent diabetes and normoalbuminuria or microalbuminuria. Lancet. 1997;349(9068):1787-92.
- Chan J.C., Ko G.T., Leung D.H. et al. Long-term effects of angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibition and metabolic control in hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients. Kidney Int. 2000;57(2):590-600.
- Estacio R.O., Jeffers B.W., Gifford N., Schrier RW. Effect of blood pressure control on diabetic microvascular complications in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2000;23 Suppl 2:B54-64.
- Brenner B.M., Cooper M.E., de Zeeuw D. et al. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(12):861-9.
- Lewis E.J., Hunsicker L.G., Clarke W.R. et al. Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(12):851-60.
- Parving H.H., Lehnert H., Bröchner-Mortensen J. et al. The effect of irbesartan on the development of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(12):870-8.
- Strippoli G.F.M, Craig M., Deeks JJ., et al. Effects of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists on mortality and renal outcomes in diabetic nephropathy: systematic review. BMJ. 2004;329(7470):828.
- ADVANCE Management Committee. Study rationale and design of ADVANCE: action in diabetes and vascular disease--preterax and diamicron MR controlled evaluation. Diabetologia. 2001 Sep;44(9):1118-20.
- Dahlöf B., Gosse P., Guéret P., et al. Perindopril/indapamide combination more effective than enalapril in reducing blood pressure and left ventricular mass: the PICXEL study. J Hypertens. 2005; 23 (11): 2063-2070.
- PROGRESS Collaborative Group. Randomised trial of a perindopril-based blood-pressure-lowering regimen among 6,105 individuals with previous stroke or transient ischaemic attack. Lancet. 2001;358(9287):1033-41.
- Effects of PREMIER Lifestyle Modifications on Participants With and Without the Metabolic Syndrome Hypertension https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/hypertensionaha.107.089458 (5 Aug 2021).
- Fox KM, EURopean trial On reduction of cardiac events with Perindopril in stable coronary Artery disease Investigators. Efficacy of perindopril in reduction of cardiovascular events among patients with stable coronary artery disease: randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial (the EUROPA study). Lancet. 2003;362(9386):782-8.
- Meurin P. The ASCOT trial: clarifying the role of ACE inhibition in the reduction of cardiovascular events in patients with hypertension. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2006;6(5):327-34.
- Patel A., ADVANCE Collaborative Group, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, Neal B, Woodward M, et al. Effects of a fixed combination of perindopril and indapamide on macrovascular and microvascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (the ADVANCE trial): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2007;370(9590):829-40.
- Estacio R.O., Jeffers B.W., Hiatt W.R., et al. The effect of nisoldipine as compared with enalapril on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes and hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1998;338(10):645-52.
- Schrier R.W., Estacio R.O., Esler A., Mehler P. Effects of aggressive blood pressure control in normotensive type 2 diabetic patients on albuminuria, retinopathy and strokes. Kidney Int. 2002;61(3):1086-97.
- Cosentino F, Grant PJ, Aboyans V, Bailey CJ. 2019 ESC Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD. Eur Heart J. 2019;41(2):255-323.
- Dluhy R.G., McMahon G.T. Intensive glycemic control in the ACCORD and ADVANCE trials. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(24):2630-3.
- ACCORD Study Group, Buse J.B., Bigger J.T., et al. Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) trial: design and methods. Am J Cardiol. 2007;99(12A):21i-33i.
- ADVANCE Collaborative Group, Patel A., MacMahon S., et al. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(24):2560-72.
- Duckworth W., Abraira C., Moritz T., et al. Glucose Control and Vascular Complications in Veterans with Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(2):129-39.
- Schernthaner G., Grimaldi A., Di Mario U., et al. GUIDE study: double-blind comparison of once-daily gliclazide MR and glimepiride in type 2 diabetic patients. Eur J Clin Invest. 2004;34(8):535-42.
- Zoungas S., Chalmers J., Kengne AP., et al. The efficacy of lowering glycated haemoglobin with a gliclazide modified release-based intensive glucose lowering regimen in the ADVANCE trial. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010;89(2):126-33.
- Woodward M., Patel A., Zoungas S. et al. Does glycemic control offer similar benefits among patients with diabetes in different regions of the world? Results from the ADVANCE trial. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(12):2491-5.
- Van Dieren S., Kengne A.P., Chalmers J., et al. Intensification of medication and glycaemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes - the ADVANCE trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014;16(5):426-32.
- Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group, Gerstein H.C., Miller M.E., et al. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(24):2545-59.
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet. 1998;352(9131):837-53.
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). Lancet. 1998;352(9131):854-65.
- Control Group, Turnbull F.M., Abraira C., Anderson R.J., et al. Intensive glucose control and macrovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2009;52(11):2288-98.
- Zoungas S., Arima H., Gerstein H.C., et al. Effects of intensive glucose control on microvascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised controlled trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5(6):431-7.
- Nathan D.M., Cleary P.A., Backlund J.-Y.C., et al. Intensive diabetes treatment and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(25):2643-53.
- Holman R.R., Paul S.K., Bethel M.A. et al. 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(15):1577-89.
- Holman R.R., Paul S.K., Bethel M.A. et al. Long-term follow-up after tight control of blood pressure in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(15):1565-76.
- Zoungas S., Chalmers J., Neal B., Billot L., Li Q., Hirakawa Y., et al. Follow-up of blood-pressure lowering and glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(15):1392-406.
- Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration. Pharmacological blood pressure lowering for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease across different levels of blood pressure: an individual participant-level data meta-analysis. Lancet. 2021;397(10285):1625-36.


