Исследование влияния природного антоциана дельфинидина на продолжительность жизни Drosophila melanogaster
Автор: Платонова Е.Ю., Голубев Д.А., Патов С.А., Некрасова П.С., Шапошников М.В., Москалев А.А.
Журнал: Известия Коми научного центра УрО РАН @izvestia-komisc
Рубрика: Научные статьи
Статья в выпуске: 9 (75), 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Антоцианы - это ярко окрашенные в розовый, красный, синий или фиолетовый цвет пигменты, растворенные в вакуолярном соке эпидермальных тканей цветов, плодов, листьев и стеблей. Дельфинидин - один из наиболее распространенных антоцианов, обладающий геропротекторным потенциалом. В данной работе мы изучили влияние дельфинидина на продолжительность жизни особей обоих полов Drosophila melanogaster. Наши результаты показали, что концентрация дельфинидина в 10 мкМ приводит к статистически значимому снижению медианной продолжительности жизни самцов Drosophila melanogaster на 5 %, в то время как у самок наблюдается увеличение медианной продолжительности жизни на 4 %. Однако механизм воздействия дельфинидина на организм еще недостаточно изучен, что ограничивает наше понимание его геропротекторных свойств. В этом контексте изучение эффектов дельфинидина на стрессоустойчивость, показатели жизнеспособности и уровень экспрессии, связанных со старением генов у Drosophila melanogaster, представляется перспективным направлением для дальнейшего изучения. Такие исследования способны пролить свет на механизмы геропротекции и старения, а также на то, как природные антоцианы, такие как дельфинидин, могут быть использованы для улучшения здоровья и продолжительности жизни человека.
Антоцианы, дельфинидин, геропротекторы, drosophila melanogaster, продолжительность жизни
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/149147257
IDR: 149147257 | УДК: 57.047 | DOI: 10.19110/1994-5655-2024-9-92-97
Текст научной статьи Исследование влияния природного антоциана дельфинидина на продолжительность жизни Drosophila melanogaster
Антоцианы – это водорастворимые гликозиды из класса флавоноидов, которые ответственны за красный, фиолетовый и синий цвета многих растений, фруктов, овощей и цветов [1, 2]. Помимо их участия в регуляции роста и развития растений, антоцианы обладают биологическими свойствами, влияющими на клетки живых организмов. Они проявляют мощные антиоксидантные свойства, что помогает защищать клетки от окислительного стресса и повреждения, вызванного свободными радикалами [1]. Это, в свою очередь, может снизить риск развития различных заболеваний, таких как рак, сердечно-сосудистые и ней-родегенеративные заболевания [1]. Антоцианы также способствуют улучшению зрения, поддерживают здоровье сосудов и обладают противовоспалительным действием [2]. Основными представителями антоцианов являются цианидин, дельфинидин, пеларгонидин, пеонидин, пету-нидин и мальвидин [2, 3].
Как известно, экстракты многих плодовых растений содержат большое количество биологически активных веществ (полифенолы, фенольные кислоты, флавоноиды, антоцианы и проантоцианидины), которые обладают ге-ропротекторным потенциалом [4]. Наибольшее количество антоцианов содержится в таких ягодах, как черноплодная рябина (Aronia melanocarpa) [5], черника (Vaccinium ashei) [6], ежевика (Rubus fruticosus L. ) , вишня (Prunus cera-sus L. ) , черешня (Prunus avium L. ) , бузина (Sambucus nigra L. ) [7], виноград (Vitis spp.) , черная смородина (Ribes nigrum), слива (Prunus spp.) , жимолость (Lonicera caerulea) , клюква (Vaccinium macrocarpon) , клубника (Fragaria spp.) [1, 8, 9], клубнях картофеля (Solanum tuberosum) и батата (Ipomoea batatas L. ) , корнеплоде черной моркови (Daucus carota L. ssp. sativus var. atrorubens Alef.) [10], а также в томатах (Solanum lycopersicum) [11] и черных соевых бобах (Glycine max (L.) Merr) [12].
Например, антоциановый экстракт клюквы (V. macro-carpon Ait.) в концентрации 20 мг/мл увеличивал среднюю продолжительность жизни Drosophila melanogaster на 10 % [13]. Экстракт терпкой вишни (Prunus cerasus), добавляемый в пищу с третьего дня жизни червей N2 дикого типа Caenorhabditis elegans, на протяжении всей жизни в концентрациях 6 и 12 мкг/мл увеличивал среднюю продолжительность жизни [14]. Экстракт пурпурного сладкого батата (Ipomoea batatas L.) в концентрации 0,5 мг/мл увеличивал среднюю продолжительность жизни самцов D. melanogaster на 2,8 %, а 2,0 мг/мл – на 14,5 % [15]. Добавление в питательную среду взрослым (с четвертой по шестую недели) мухам D. melanogaster этанольного экстракта черноплодной рябины (×Sorbaronia mitschurinii) в концентрациях 0,1 и 5 мг/мл увеличивало максимальную продолжительность жизни самцов на 9 % [16]. Ацетоновый экстракт аронии черноплодной (Aronia melanocarpa) в концентрации 2,5 мг/мл увеличил на 18 % среднюю продолжительность жизни самцов D. melanogaster [17]. Метанольный экстракт пурпурной пшеницы (Triticum aestivum), богатый антоцианами, продлил среднюю продолжительность жизни C. elegans на 10,5 % [18]. Сок красной капусты (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata L. f. Rubra) в различных концентрациях: 1 % (5 %), 2 (8), 3 (9) и 5 % (21 %) увеличива- ет среднюю продолжительность жизни C. elegans [19]. Экстракт черники (Vaccinium spp.) увеличил среднюю и максимальную продолжительность жизни самцов дрозофил дикого типа Oregon-RC на 5 % [20].
Более того, исследования показали, что отдельные биологически активные вещества, содержащиеся в растениях, также могут оказывать положительное влияние на продолжительность жизни модельных организмов. Например, антоциан цианидин-3-глюкозид (C3G) в концентрациях 10 и 100 мкМ увеличивает максимальную продолжительность жизни самцов на 3 и 8 % соответственно у D. melanogaster [21]. Пеонидин-3-глюкозид в концентрации 50 мкг/мл увеличивал продолжительность жизни C. elegans на 14 %. Кроме того, этот антоциан повышал устойчивость червя к неблагоприятным условиям внешней среды, таким как ультрафиолетовое излучение (UVA), гипертермия и перекись водорода. При воздействии UVA и термическом стрессе устойчивость червя повышалась на 25 %, а при окислительном стрессе – на 48 % [22].
Антоцианы представляют собой большой класс соединений, которые мы регулярно употребляем с пищей, и изучение вызываемых ими биологических эффектов является важным шагом для определения потенциальных геропро-текторов, которые могут быть использованы для разработки целевых стратегий улучшения здоровья и продления жизни. В настоящем исследовании мы предложили гипотезу о том, что природный антоциан дельфинидин обладает высоким потенциальным геропротекторным эффектом, и проверили ее в исследовании на модельном организме Drosophila melanogaster.
Материалы и методы
Выделение природного антоциана из плодов. Выделение дельфинидина-3-О-глюкозида проводили из плодов жимолости Палласа (Lonícera pallacii L. ). Для получения экстракта жимолости Палласа 10 г размороженных ягод были раздавлены стеклянной палочкой и помещены в коническую колбу объемом 250 мл. Далее к ним был добавлен раствор 10%-ной соляной кислоты с 5%-ным этиловым спиртом (100 мл). Экстракцию сырья осуществляли три раза, обрабатывая ягодную массу раствором 10%-ной соляной кислоты в соотношении 10 частей раствора на 1 часть сырья. Экстракцию проводили в темном месте при температуре +25 ºС в течение суток. Полученные элюаты отфильтровывали, объединяли и упаривали на роторном испарителе (Heidolph, Германия) при температуре 35–40 °C до консистенции густого сиропа, после чего лиофильно высушивали. Полученный сухой экстракт представлял аморфное порошкообразное вещество темно-красного цвета.
Получение дельфинидин-3-О-глюкозида. Для разделения суммарного экстракта антоцианов жимолости колонку, заполненную сорбентом с обращенной фазой Диа-сорб 130С16Т, промывали начальным элюентом – 10%-ным раствором дегазированной муравьиной кислоты. После чего вносили экстракт массой 1 г, растворенный в 10%-ном растворе муравьиной кислоты, и проводили хроматографическое разделение на фракции растворами ацетонитрила в воде (10%-ный раствор муравьиной кислоты) в соотношениях 0:100, 2:98, 4:96, 6:94, 8:92, 10:90, 12:88. В ходе разделения суммарного экстракта получены: дельфини-дин-3-О-глюкозид. Структуры выделенных веществ были доказаны физико-химическими методами исследования (ЯМР, ВЭЖХ-МС). Полученный дельфинидин был передан для биохимического испытания. В дальнейших экспериментах с применением дельфинидина-3-О-глюкозида и его различных концентраций в качестве разбавителя использовали дистиллированную воду.
Условия содержания Drosophila melanogaster. В экспериментах использовали линию Drosophila melanogaster дикого типа Canton-S (#64349, Блумингтон, США). Мух содержали в камере постоянного климата Binder KBF720-ICH (Binder, Германия) при температуре +25 °C и относительной влажности 60 %, с режимом освещения 12 ч свет: 12 ч темнота. Питательная среда, на которой жили мухи, содержала воду – 1 л, кукурузную муку – 92 г, сухие дрожжи – 32,1 г, агар-агар – 5,2 г, глюкозу – 136,9 г. Для предотвращения роста плесени и бактерий на 1 л среды добавляли 10 мл 10%-ного раствора нипагина (метил 4-гидроксибензоат, Merck, США) в этаноле и 10 мл 50%-ной пропионовой кислоты (Merck, США). Водные растворы дельфинидина в концентрациях 1, 10 и 100 мкМ наносили непосредственно на поверхность свежей застывшей питательной среды в объеме 30 мкл. На поверхность питательной среды контрольных вариантов наносили 30 мкл воды. Далее поверхность среды просушивали под вентилятором.
Анализ продолжительности жизни. Для анализа продолжительности жизни (далее – ПЖ) имаго разделяли по полу, на каждый вариант эксперимента отбирали по 150 особей, помещая по 30 особей в каждую пробирку. Самцов и самок содержали раздельно. Эксперименты проводили в двух независимых повторностях. Рассчитывали медианную и максимальную (возраст 90 % смертности особей) продолжительности жизни.
Статистический анализ полученных результатов. Для анализа статистических различий в функциях выживаемости между контрольной и экспериментальной группой использовали модифицированный критерий Колмогорова-Смирнова. Критерии Гехана-Бреслоу-Вилкоксона и Мантеля-Кокс применяли для анализа статистической значимости различий по медианной продолжительности жизни. Для оценки различий в возрасте 90 % смертности использовали тест Ванг-Эллисона [23]. Статистический анализ данных был выполнен с использованием программного обеспечения R, версии 2.15.1 (The R Foundation, США), Excel (Microsoft, США) и OASIS 2 (Online Application for Survival Analysis 2) [24].
Результаты и их обсуждение
Известно, что старение происходит планомерно, но при воздействии различных неблагоприятных факторов продолжительность жизни может резко сократиться за счет активации внутренних воспалительных процессов и накопления повреждений ДНК, приводящих к усугублению разнообразных заболеваний [25]. Поэтому для улучшения и продления здорового состояния организма применяют биологически активные вещества, обладающие геро-протекторным потенциалом . К основным критериям геропротекторов относят: положи- тельный эффект на продолжительность жизни модельных организмов, улучшение биомаркеров старения и качества жизни, низкую токсичность и минимальные побочные эффекты [26]. В качестве дополнительных критериев ге-ропротекторов рассматривают эволюционно консервативные механизмы эффектов, воспроизводимые на различных моделях, способность отсрочивать развитие возрастных заболеваний и повышать устойчивость организма к неблагоприятным факторам окружающей среды [26].
Нами установлено, что природный антоциан дельфинидин вызывает статистически значимое снижение медианной продолжительности жизни самцов на 5 и 4 % при концентрациях 10 и 100 мкМ соответственно, что отображается сдвигом кривых влево по отношении к контрольной линии (рисунок А, таблица). При этом, дельфинидин в концентрации 10 мкМ увеличивал медианную продолжительность жизни самок на 4 %, в подтверждение этому отмечен сдвиг кривой смертности данного варианта эксперимента вправо по отношению к контрольной кривой (рисунок Б, таблица).
Ранее обнаружено, что дельфинидин-3-глюкозид увеличивает среднюю продолжительность жизни и улучшает состояние здоровья (увеличение средней скорости сокращений глоточного насоса) C. elegans , даже в условиях окислительного стресса, вызванного H2O2 [27]. А также выявлено, что дельфинидин-3-рутинозид, выделенный из плодов черной смородины (Ribes nigrum), облегчает расслабление цилиарной мышцы, тем самым отсрочивая
A
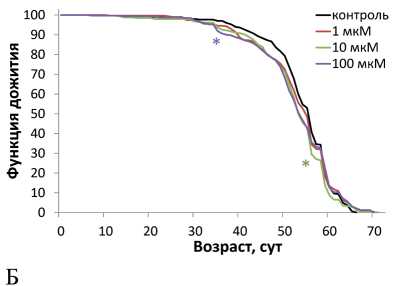
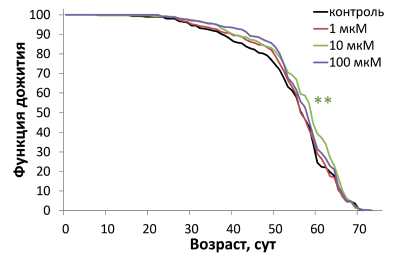
Рисунок. Влияние природного антоциана дельфинидина на продолжительность жизни самцов (А) и самок (Б) Drosophila melanogaster .
Условные обозначения. Критерий Колмогорова-Смирнова для кривых выживаемости: *p < 0,05; **p < 0,01.
Figure. Influence of the natural anthocyanin delphinidin on the lifespan of male (A) and female (Б) Drosophila melanogaster .
Keys: the Kolmogorov-Smirnov criterion for survival curves at * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01.
Влияние природного антоциана дельфинидина на продолжительность жизни Drosophila melanogaster
Influence of the natural anthocyanin delphinidin on the lifespan of Drosophila melanogaster
|
Концентрация |
Пол |
М сут |
dM % |
90% сут |
d90 % |
пол |
М сут |
dM % |
90% сут |
d90 % |
|
Контроль |
$ |
56 |
61 |
$ |
57 |
66 |
||||
|
1 мкМ |
$ |
55 |
-1.8 |
63 |
3.3 |
$ |
56 |
-1.8 |
66 |
0 |
|
10 мкМ |
$ |
54 |
-4.5*# |
60 |
-1.6 |
$ |
59 |
3.5*# |
67 |
1.5 |
|
100 мкМ |
$ |
54 |
-3.6*# |
63 |
-3.3 |
$ |
58 |
1.8 |
66 |
0 |
Условные обозначения. M – медианная продолжительность жизни; 90 % – возраст 90 % смертности (максимальная продолжительность жизни); dM – разница в медианной продолжительности жизни; d90 % - разница смертности в возрасте 90 %; $ - самцы; $ - самки; *p<0,05 критерий Мантеля-Кокс;
#p<0,05 критерий Гехана-Бреслоу-Вилкоксона для медианной ПЖ.
Keys: M – median lifespan; 90 % – 90 % mortality age (maximum lifespan); dM – difference in median lifespan; d90 % – difference in mortality at 90 % age;
$ - males; $ - females. * p < 0.05 - the Mantel-Cox criterion; # p < 0.05 - the Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon criterion for median lifespan.
развитие близорукости у крупного рогатого скота [28]. У мышей, получавших диету с высоким содержанием жиров одновременно с цианидином и дельфинидином в дозе 40 мг/кг в условиях окислительного стресса, повышались уровни экспрессии белков, участвующих в регуляции процессов воспаления (NF-κB), апоптоза (JNK) и метаболизма (PTP1B). Кроме того, у самцов мышей цианидин и дельфинидин улучшали показатели дислипидемии и инсулино-резистентности на диете с высоким содержанием жиров [29]. Дельфинидин и цианидин оказывали цитотоксическое действие на клетки линий колоректального рака LoVo и LoVo/ADR. При этом дельфинидин вызывал незначительное повышение, а цианидин – снижение количества активных форм кислорода (далее – АФК) в клетках [30]. Было показано, что дельфинидин оказывает антипроли-феративное действие в отношении различных видов рака (простаты, колоректального рака, рака яичников, кожи, молочной железы, мочевого пузыря, первичной опухоли головного мозга и остеосаркомы) [31].
Перечисленные, а также полученные нами результаты подчеркивают необходимость дальнейших исследований для понимания механизмов, лежащих в основе различных биологических эффектов дельфинидина и выяснения возможностей его потенциального применения в терапии возраст-зависимых заболеваний.
Заключение
Таким образом, в нашем исследовании мы обнаружили достоверный разнонаправленный эффект природного антоциана дельфинидина на медианную продолжительность жизни особей обоих полов Drosophila melanogaster .
Наблюдаемое у самок дрозофил увеличение продолжительности жизни после кормления дельфинидин-3-глюко-зидом подчеркивает его потенциал в качестве натуральной добавки для замедления старения. Однако необходимы дальнейшие исследования влияния дельфинидина на связанные со старением параметры жизнеспособности организма, такие как стрессоустойчивость и двигательная активность на модели Drosophila melanogaster. Также необходимо провести анализ изменения экспрессии генов (таких как Sirt1, Keap1, NRF2, Sod1, HIF1,Clk, per ), чтобы выяснить молекулярные механизмы, лежащие в основе наблюдаемых эффектов.
Список литературы Исследование влияния природного антоциана дельфинидина на продолжительность жизни Drosophila melanogaster
- Chemistry, pharmacology and health benefits of anthocyanins / A. Smeriglio [et al.]. – Phytotherapy Research. – 2016. – № 30 (8). – P. 1265–86.
- Anthocyanins: promising natural products with diverse pharmacological activities / J. Liu [et al.]. – Molecules. – 2021. – № 26 (13).
- Anthocyanins: a comprehensive review of their chemical properties and health effects on cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases / R. Mattioli [et al.]. – Molecules. – 2020. – № 25 (17).
- Polyphenols as potential geroprotectors / E. Proshkina [et al.]. – Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. – 2024. – № 40 (7–9). – P. 564–593.
- Kulling, S. E. Chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) – a review on the characteristic components and potential health effects / S. E. Kulling, H. M. Rawel. – Planta Medica. – 2008. – № 74 (13). – P. 1625–34.
- Optimization and application of HPLC for simultaneous separation of six well-known major anthocyanins in blueberry / Y. Zhou [et al.]. – Preparative Biochemistry and Biotechnology. – 2021. – № 51 (10). – P. 961–970.
- Total content of phenols and anthocyanins in edible fruits from Bosnia / Z. Rimpapa [et al.]. – Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences. – 2007. – № 7 (2). – P. 117–20.
- Classification of fruits based on anthocyanin types and relevance to their health effects / J. Fang. – Nutrition. – 2015. – № 31 (11–12). – P. 1301–6.
- Berry derived constituents in suppressing viral infection: potential avenues for viral pandemic management / P. Shahagadkar [et al.]. – Clinical Nutrition ESPEN. – 2021. – № 46. – P. 14–20.
- Zaim, M. Black carrot anthocyanins exhibit neuroprotective effects against MPP+ induced cell death and cytotoxicity via inhibition of oxidative stress mediated apoptosis / M. Zaim, I. Kara, A. Muduroglu. – Cytotechnology. – 2021. – № 73 (6). – P. 827–840.
- Anthocyanin-rich vegetables for human consumption – focus on potato, sweetpotato and tomato / A. K. Mattoo [et al.]. – International Journal of Molecular Sciences. – 2022. – № 23 (5). – P. 2634.
- Cyanidin-3-glucoside derived from black soybeans ameliorate type 2 diabetes through the induction of differentiation of preadipocytes into smaller and insulin-sensitive adipocytes / T. Matsukawa [et al.]. – The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry. – 2015. – № 26 (8). – P. 860–7.
- Cranberry anthocyanin extract prolongs lifespan of fruit flies / L. Wang [et al.]. – Experimental Gerontology. – 2015. – № 69. – P. 189–95.
- Tart cherry increases lifespan in caenorhabditis elegans by altering metabolic signaling pathways / S. Jayarathne [et al.]. – Nutrients. – 2020. – № 12 (5).
- Purple sweet potato extract extends lifespan by activating autophagy pathway in male Drosophila melanogaster / Y. Han [et al.]. – Experimental Gerontology. – 2021. – № 144. – P. 111190.
- Geroprotective effects of ×Sorbaronia mitschurinii fruit extract on Drosophila melanogaster / E. Platonova [et al.]. – Journal of Berry Research. – 2021. – № 12. – P. 1–19.
- Effects of aronia extract on lifespan and age-related oxidative stress in Drosophila melanogaster / A. R. Jo, J. Y. Imm. – Food Science and Biotechnology. – 2017. – № 26 (5). – P. 1399–1406.
- Anthocyanin-rich purple wheat prolongs the life span of Caenorhabditis elegans probably by activating the DAF-16/FOXO transcription factor / W. Chen [et al.]. – Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. – 2013. – № 61 (12). – P. 3047–53.
- Red cabbage rather than green cabbage increases stress resistance and extends the lifespan of Сaenorhabditis elegans / N. Zhang, S. Jiao, P. Jing. – Antioxidants (Basel). – 2021. – № 10 (6).
- Blueberry extract prolongs lifespan of Drosophila melanogaster / C. Peng [et al.]. – Experimental Gerontology. – 2012. – № 47 (2). – P. 170–8.
- Honeysuckle extract (Lonicera pallasii L.) exerts antioxidant properties and extends the lifespan and healthspan of Drosophila melanogaster / D. Golubev [et al.]. – Biogerontology. – 2022. – № 23 (2). – P. 215–235.
- Nas, J. S. Peonidin-3-glucoside extends the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans and enhances its tolerance to heat, UV, and oxidative stresses / J. S. Nas, R. V. Manalo, P. M. Medina. – ScienceAsia. – 2021. – № 47. – P. 457.
- Exploring the neuroprotective effects of chokeberry (×Sorbaronia mitschurinii) extract on Drosophila melanogaster model of Alzheimer’s disease / N. V. Zemskaya [et al.]. – Proceedings of the Komi Science Centre of the Ural Division of the Russian Academy of Sciences. – 2023. – № (0). – P. 7.
- OASIS portable: user-friendly offline suite for secure survival analysis / S. K. Han [et al.]. – Molecules and Cells. – 2024. – № 47 (2). – P. 100011.
- Nutrient-response pathways in healthspan and lifespan regulation / A. Dabrowska, J. Kumar, C. Rallisю – Cells. – 2022. – № 11 (9).
- Developing criteria for evaluation of geroprotectors as a key stage toward translation to the clinic / A. Moskalev [et al.]. – Aging Cell. – 2016. – № 15 (3). – P. 407–415.
- Nas, J. S. Delphinidin-3-glucoside prolongs lifespan and healthspan in Caenorhabditis elegans with and without environmental stress / J. S. Nas, P. Medina. – Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science. – 2023.
- Delphinidin-3-rutinoside relaxes the bovine ciliary smooth muscle through activation of ETB receptor and NO/cGMP pathway / H. Matsumoto [et al.]. – Experimental Eye Research. – 2005. – № 80 (3). – P. 313–22.
- Cyanidin and delphinidin modulate inflammation and altered redox signaling improving insulin resistance in high fat-fed mice / E. Daveri [et al.]. – Redox Biology. – 2018. – № 18. – P. 16–24.
- Oxidative stress-based cytotoxicity of delphinidin and cyanidin in colon cancer cells / J. Cvorovic [et al.]. – Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. – 2010. – № 501 (1). – P. 151–7.
- Delphinidin and its glycosides’ war on cancer: preclinical perspectives / A. Sharma [et al.]. – International Journal of Molecular Sciences. – 2021. – № 22 (21).


