Исследование влияния ультразвукового воздействия на растворы полимеров при получении биоразлагаемых упаковочных материалов
Автор: Астахов В.А., Губанова М.И.
Журнал: Вестник Воронежского государственного университета инженерных технологий @vestnik-vsuet
Рубрика: Химическая технология
Статья в выпуске: 3 (97) т.85, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Одним из вариантов улучшения структуры и свойств пленок получаемых из растворов полимеров является ультразвуковое воздействие на растворы различной химической природы. Использование данного влияния на растворы полимеров с разными добавками и агентами, показало не только улучшение физико-механических свойств, но и антибактериальных, что способствовало увеличению срока хранения пищевых продуктов. Основными компонентами композиций исследования которых представлены в научных статьях являлись: поливиниловый спирт, белки и пуллулан, их смешивали с различными добавками и агентами, с разной длительностью воздействия ультразвуковой обработки растворов. Исследуемые композиции имели следующие составы: поливиниловый спирт и гемицеллюлоза с антиоксидантным агентом чая; поливиниловый спирт, натрий-карбоксиметилцеллюлоза, наночастицы оксида цинка, а также многослойные графеновые нанопластины; поливиниловый спирт и хитозан; коллаген рыбьей чешуи, поливиниловый спирт и сорбат калия; яичный белок; белок киноа и хитозан; белок гороха; гидролизат рисового белка и хитозан; гидролизат сывороточного белка; водный экстракт сои с пчелиным воском и эфирном маслом гвоздики; овсяный белок с пуллуланом и низином; пуллулан с добавлением наноэмульсии с эфирным маслом корицы; пуллулан и трегалоза с насыщением полифенолами чая. Некоторые изготовленные пленки из данных составов тестировались на пищевых продуктах, таких как клубника, яблоко, груша и кексы. Исходя из рассмотренных научных данных можно сделать вывод, что для улучшения свойств пленок из растворов полимеров необходимо, оптимальное время воздействия ультразвука на растворы, так как более длительное ультразвуковое воздействие может ухудшить физико-механические свойства, а именно снизить прочность на растяжение и удлинение при разрыве, в отличии от умеренного воздействия.
Ультразвук, растворы полимеров, поливиниловый спирт, биоразлагаемые материалы, белок, пуллулан
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140303237
IDR: 140303237 | УДК: 66.084.8 | DOI: 10.20914/2310-1202-2023-3-180-186
Текст научной статьи Исследование влияния ультразвукового воздействия на растворы полимеров при получении биоразлагаемых упаковочных материалов
Полимерная упаковка постоянно используется в современной жизни. В пищевом производстве в основном используют упаковку из синтетических полимеров, которую трудно переработать. В результате увеличивается поток пластика в океаны, который может привести к глобальной проблеме с окружающей средой [1]. Поэтому упаковка из биоразлагаемых полимеров Для цитирования
набирает популярность в пищевой отрасли. В большинстве случаев в состав биоразлагаемой упаковки входит несколько полимеров, а также добавки, которые могут увеличить срок годности продуктов питания при хранении и транспортировке. Такую упаковку можно дополнить различными агентами и добавками, выделенными из отходов производств пищевой промышленности [2]. Антиоксидантные агенты
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License могут увеличить срок хранения продуктов питания, тем самым превращая обычную биоразлагаемую упаковку в антимикробную, такая упаковка называется активной упаковкой.
Для изготовления упаковки применяют природное сырье в виде крахмалов [3], целлюлозы, белков и подобных пленкообразующих веществ [4]. Производство активной упаковки из растворов биополимеров с различными агентами требует хорошего смешения компонентов и однородности, что не всегда можно достичь за счет физико-механического воздействия. Для улучшения совмещения компонентов исследователи начали использовать ультразвуковую обработку растворов, которая улучшает однородность структуры для изготовления пленки. В данном обзоре рассмотрим информацию о влиянии ультразвука на свойства растворов полимеров при изготовлении упаковки из растительных и синтетических биоразлагаемых растворов полимеров.
Цель работы – обобщить и проанализировать найденные данные и оценить влияние ультразвуковой обработки полимерных растворов.
Материалы и методы
В обзор были включены статьи, монографии, опубликованные на английском и русском языках электронных баз данных ScienceDirect Scopus, Web of Science, cyberleninka.ru и elibrary.ru. Поиск был ограничен периодом с 2019 по 2023 год; В центре внимания были статьи, опубликованные в научных журналах, прошедшие процедуру рецензирования, подтверждающую ее качество.
Результаты
Композитные биоразлагаемые пленки, изготовленные физико-механическим путём при помощи обычного смешения компонентов, не всегда имеют однородную структуру. Таким образом, исследование получения упаковки из поливинилового спирта и гемицеллюлозы с антиоксидантным агентом чая, показывает, что включение антиоксидантного агента чая в композитные пленки путем физического смешения может привести к плохой дисперсии антиоксидантного агента в матрице пленки. Так как в большинстве случаев, пленки, изготовленные из растительных пленкообразователей, имеют вязкую структуру с множеством микропузырьков. Для однородной структуры пленки с антиоксидантом чая использовали ультразвук, который влиял на микропузырьки, разбивая их на мелкие частицы, превращая все компоненты в однородную массу. При помощи ультразвуковой обработки, множественное скопление используемого агента распределилось по всему раствору пленкообразующего состава, благодаря этому, исследование показало, что поверхности образцов обработанных ультразвуком в течении 45 минут получились гладкими с хорошим поверхностным сцеплением и с минимальным значением шероховатости в пределах 22–24 нм (рисунок 1), в отличии от необработанных образцов, что показывает положительное воздействие на однородность структуры [5].
s 40
0 0 45
Время обработки ультразвуком, мин
-
□ПВС/ГМЦ/TP 1% □ПВС/ГМЦ/TP 10%
Рисунок 1. Влияние ультразвуковой обработки на шероховатость поверхности: ПВС – поливиниловый спирт; ГМЦ – гемицеллюлоза; ТР – антиоксидантный агент чая
-
Figure 1. The effect of ultrasonic treatment on a rough surface: PVA – polyvinyl alcohol; HMC – hemicellulose; TP – antioxidant agent of tea
Другими исследователями проводилось аналогичное исследование с изготовлением композитной пленки. В качестве пленкообразо-вателя использовали поливиниловый спирт с добавлением антиоксидантного агента чая, в разном соотношении с воздействием ультразвуковой обработки в временном диапазоне от 0 до 40 минут. Данные образцы пленок были сделаны методом литья на ленту, результаты исследования показали, что обработка ультразвуком повысила барьерные свойства, но при длительной обработке свыше 30 минут физикомеханические свойства стали ухудшаться, а именно снизился предел прочности на растяжение и удлинение при разрыве [6].
Кроме использования полифенолов чая с поливиниловым спиртом, исследователи Китая изготовили упаковку для продолжительного хранения клубники, которая увеличила срок хранения, а также способствовала уменьшению потери веса образцов клубники. В данном эксперименте композитные пленки были с разным составом в который входил поливиниловый спирт, натрий-карбоксиметилцеллюлоза, наночастицы оксида цинка, а также многослойные графеновые нанопластины с обработкой ультразвуком. Для эксперимента брали разные сочетания компонентов. В ходе проведенных исследований было выявлено, что добавление наночастиц оксида цинка и графеновых нанопластин в состав поливинилового спирта, натрий-карбоксиметилцеллюлозы уменьшило прочность полученной пленки, но увеличило ее антибактериальные свойства против грамположительных и грамотрицательных патогенных пищевых бактерий. Наиболее эффективная упаковка для хранения клубники получилась со следующим составом: поливиниловый спирт, натрий-карбоксиметилцеллюлоза, наночастицы оксида цинка, многослойные графеновые нанопластины в соотношении (7:3). Данное исследование доказало, что обработка пленкообразующих растворов при помощи ультразвука улучшило механические свойства пленки [7].
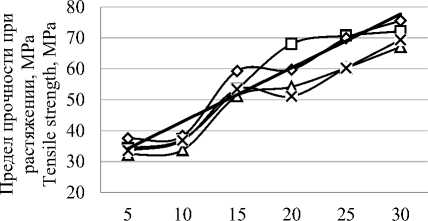
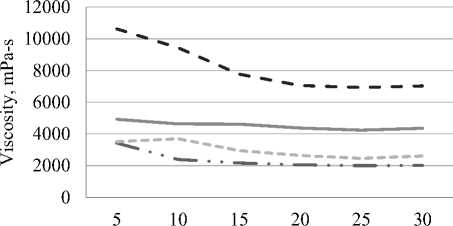
Также можно привести пример изготовления двухслойной пленки на основе поливинилового спирта и хитозана для упаковки клубники. Поливиниловый спирт и хитозан брали в разном соотношении и с разным временем обработки от 0–30 минут. Наилучший эффект получился при обработке в 25 минут, что показывает, то что увеличение времени обработки ультразвуком не всегда улучшает качество пленки. Образец с 25 минутной ультразвуковой обработкой получился с однородной структурой, также данный метод изготовления увеличил предел прочности при растяжении (рисунок 2) и уменьшил вязкость готового раствора полимеров (рисунок 3), что позволяет создать наиболее тонкое покрытие. Благодаря данному смешению компонентов, у пленки появились антибактериальные свойства, что хорошо повлияло на эксперимент с увеличением срока годности клубники в период низкотемпературного хранения [8].
Время обработки ультразвуком, мин Ultrasonic treatment time, min
ПВС ПВС/ХС 2%
ПВС/ХС 2.5% —X— ПВС/ХС 3%
^^^^^^^^^^^ Линейная (ПВС/ХС 2%)
Время обработки ультразвуком, мин Ultrasonic treatment time, min
ПВС
ПВС/ХС 2.5%
ПВС/ХС 2%
ПВС/ХС 3%
Рисунок 2. Влияние ультразвуковой обработки на предел прочности при растяжении: ПВС – поливиниловый спирт; ХС – хитозан
-
Figure 2. Effect of ultrasonic treatment on ultimate tensile strength: PVA – polyvinyl alcohol; CS – chitosan
Рисунок 3. Влияние ультразвуковой обработки на вязкость пленкообразующего раствора: ПВС – поливиниловый спирт; ХС – хитозан
-
Figure 3. Influence of ultrasonic treatment on the viscosity of the film-forming solution: PVA – polyvinyl alcohol; CS, chitosan
В качестве пленкообразователей с поливиниловым спиртом можно использовать коллаген рыбьей чешуи, который улучшает свойства упаковки с ультразвуковой обработкой, что показали исследователи Xue Liang, Shiyi Feng, Saeed Ahmed и другие. Они изготовили композитную пленку на основе коллагена рыбьей чешуи, поливинилового спирта и сорбата калия в роли антибактериального агента. Проанализировав данные, можно сделать вывод, что добавление коллагена рыбьей чешуи снизило светопропускание композитной пленки, в то время, как сорбат калия не оказал существенного влияния на данный показатель. Также обработка ультразвуком снизила паропроницаемость, улучшила прочность на разрыв и удлинение при разрыве (рисунок 4).
Кроме того, пленка проявила антибактериальные свойства в отношении Escherichia coli и Staphylococcus aureus. Пленка с содержанием коллагена рыбьей чешуи, поливинилового спирта и сорбата калия 9% с ультразвуковой обработкой в 45 минут, показала лучшие показатели паропро-ницаемости в отличие от аналогичной пленки обрабатываемой ультразвуком 60 минут. Таким образом, увеличение времени обработки ультразвуком повлекло за собой уменьшение предела прочности при растяжении и удлинение при разрыве, а паропроницаемость увеличилась. Это доказывает, что увеличение времени обработки может ухудшить свойства, из-за разрыва большого количества химических связей, что повлияло на ухудшение формирования сетчатой структуры пленки. Подобную пленку можно использовать в качестве антимикробной упаковки для пищевых продуктов [9].
|
100 |
|||
|
80 |
А 0 0 |
||
|
60 |
д __ |
Д Д____д |
|
|
А |
|||
|
40 |
|||
|
20 |
Q— - |
||
|
0 |
1 А А' X |
||
|
0 |
15 |
30 45 60 |
—X- TS: предел прочности при растяжении (MPa) ^^^^^^^^^™ EAB: удлинение при разрыве
T: прозрачность
AT: средняя толщина
Рисунок 4. Свойства пленки, полученной с использованием ультразвуковой обработки композитной пленки с содержанием коллагена рыбьей чешуи, поливинилового спирта и сорбата калия 9%
Figure 4. Properties of a film obtained using ultrasonic treatment of a composite film containing fish scale collagen, polyvinyl alcohol and potassium sorbate 9%
Хорошим пленкообразователем является белок, в данном случае яичный. На его основе изготавливали пищевые пленки с улучшенными свойствами, которые модифицировали при помощи высокоинтенсивного звукового излучения. Свойства пленок изменились в лучшую сторону, а именно: повысилась термическая стабильность, увеличилось количество гидрофобных групп и межмолекулярных водородных связей, а также и сшивка между белками. В результате пленка стала наиболее гибкой с лучшими физическими качествами. Данное улучшение свойств наблюдалось при 10 минутной обработке высокоинтенсивным звуковым излучением, в отличие от более длительной обработки, при которой ухудшались свойства пленки [10]. Как, и в исследовании с изготовлением пленки из поливинилового спирта и хитозана, чрезмерная обработка ухудшает свойства пленки [8].
Кроме белков животного происхождения используют растительные белки для изготовления биоразлагаемого упаковочного материала. Комбинированное воздействие высокоинтенсивного ультразвука с воздействием трансглю-таминазой с включением наночастиц улучшает барьерные и физико-механические свойства пищевых пленок на основе белка киноа и хитозана. Данное комбинированное воздействие увеличило толщину пленки и прочность на растяжение, уменьшив процент удлинения [11].
Одним из видов растительного белка является белок гороха. Который был изучен Американскими учеными из университета штата Флорида. Исследователи использовали изолят горохового белка для изготовления пленок на белковой основе под влиянием высокой интенсивности ультразвука. Учеными было обнаружено, что ультразвук изменяет структуру белка, что вызывает появление гидрофобных групп в большем количестве на поверхности при снижении электростатического отталкивания. Также ультразвук улучшает структуру пленки устраняя трещины и уменьшая белковые скопления на ее поверхности. Кроме этого, ультразвуковая обработка не повлияла на толщину пленки и удлинение при разрыве. Эти структурные изменения были подтверждением улучшения свойств пленки из изолята горохового белка [12].
Изолят горохового белка имеет плохую растворимость и эмульгирование. Исследования показали, что при комбинированной обработке ультразвуком и изменение рН, растворимость и эмульгирование значительно улучшаются, особенно при мощности ультразвуковой обработки 500 Вт [13].
Кроме исследований изолятов белка также в качестве эксперимента проводились исследования с использованием гидролизата рисового белка, но так как гидролизат рисового белка не способен образовывать пленку, в качестве модификатора добавляли хитозан под действием ультразвука. Результаты исследований показали хорошее смешение компонентов за счет уменьшения размера частиц и вязкости пленкообразующих растворов. Также увеличилось удлинение при разрыве. Ультразвуковая обработка улучшила водородные связи и ковалентные взаимодействия, за счет чего образовалась пленка [14].
Комбинированная обработка ультразвуком микробной трансглютаминазы способна модифицировать структуру концентрата сывороточного белка. Данные комбинации показали, что ультразвуковая обработка пленкообразующих растворов сывороточного белка способствовала уменьшению паропроницаемости, толщины пленки и увеличению устойчивости к механическим воздействиям, а добавление микробной трансглютаминазы в растворы обработанные ультразвуком не повлияли на свойства, кроме их цвета. Проницаемость пленок, обработанных ультразвуком, была ниже, чем у пленок, обработанных термообработкой. Пленки из термообработанных растворов показали лучшие механические свойства [15].
Ультразвук за счет акустического эффекта способен совместить водный экстракт сои, пчелиный воск и эфирное масло гвоздики превращая данные компоненты в пленку, а в дальнейшем в упаковку для продукции. Как показывают проведенные исследования ультразвук улучшил совмещение компонентов, повысив барьерные и механические свойства пленки. Данная упаковка из этой пленки тестировалась на продолжительности срока годности кексов и показала, что эта упаковка способна сохранить влажность и внешний вид кексов до 6 дней в условиях окружающей среды. Качественный тест пленки показал, что пленка разлагается в течении 12 дней, что делает ее экологичной [16].
Овсяный белок также используют в качестве пленкообразователей вместе с пуллуланом с использованием воздействия ультразвука для улучшения различных свойств пленок. Результаты исследований с изготовлением такой пленки показали уменьшение коэффициента пропускания света, проницаемости водяного пара и кислорода, а также увеличение однородности. Кроме этого данный состав изменяли и добавляли низин. Добавление низина сопровождалось снижением прозрачности и влажности пленки, а также уменьшением общего содержания растворимых веществ. Тем самым ультразвуковая обработка по сравнению с обычным смешением повлияла на данный состав пленки увеличив удлинение при разрыве и прозрачность, а также усиление межмолекулярных связей, тем самым превращая в однородную поверхность [17].
В другом исследовании для изготовления антибактериальной пленки из пуллулана была добавлена наноэмульсия эфирного масла корицы при ультразвуковой обработке. За счет ультразвуковой эмульгации удалось совместить наноэмульсию масла с пуллуланом получив антибактериальную пленку с улучшенными свойствами. Ультразвук значительно уменьшил размер капель масла и превратил раствор в однородную структуру. Пленка, изготовленная из данных компонентов показала наименьшую паропроницаемость и максимальное удлинение при разрыве за счет пластифицирующего действия наноэмульсии [18].
Упаковка на основе пуллулана [19] испытывалась на свежесрезанных яблоках и грушах, но уже с иным составом. Она изготавливалась из пуллулана и трегалозы с насыщением полифенолами чая. Под действием ультразвука данный состав значительно увеличил удлинение при разрыве, прочность на растяжение, а также повысил барьерные свойства композитной пленки по отношению к ультрафиолету, воде и кислороду. Кроме того, пленка показала хорошие антибактериальные свойства в отношении Escherichia coli и Staphylococcus aureus . Таким образом, ультразвук оказался эффективным воздействием для улучшения качества упаковочных пленок для пищевых продуктов с широким спектром применения [20].
Заключение
Ультразвук улучшает структуру различных растворов биополимеров, воздействуя на микропузырьки разбивая их, тем самым улучшая смешение компонентов с дополнительными антиоксидантными и противомикробными агентами. Полученные покрытия становятся более эластичными, приобретают однородную структуру, уменьшается шероховатость полученных пленок из растворов биоразлагаемых полимеров различной химической природы. Данные пленки исходя из исследований, показали хорошие результаты по продолжительности сохранения товарного вида различных продуктов питания. Ультразвуковая обработка растворов биополимеров является перспективным направлением для развития по исследованию различных материалов в связке с различными противомикробными и антиоксидантными агентами для изготовления активных упаковок. Данные упаковки могут не только помочь сохранять экологию всей планеты, благодаря своей биоразлагаемости и экологичности, но и также увеличивать срок годности продуктов при хранении и транспортировке. Метод ультразвуковой обработки актуален, потому, что за счет данного воздействия на растворы полимеров, можно улучшить их свойства и изготовить новую активную модифицированную упаковку.
Список литературы Исследование влияния ультразвукового воздействия на растворы полимеров при получении биоразлагаемых упаковочных материалов
- Талипова Г.А., Галяветдинов Н.Р. Разработка биоразлагаемых композиционных материалов из полимера и растительного наполнителя // Актуальные проблемы биологии и экологии: материалы международной научно-практической конференции. 2019. С. 235-240.
- Espinosa E., Rincón E., Morcillo-Martín R., Rabasco-Vílchez L. et al. Orange peel waste biorefinery in multi-component cascade approach: Polyphenolic compounds and nanocellulose for food packaging // Industrial Crops and Products. 2022. V. 187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.115413
- Тверитникова И.С., Кирш И.А., Безнаева О.В., Банникова О.А. и др. Разработка упаковочных материалов с антими-кробными свойствами и способностью к биоразложению // Вестник Технологического университета. 2021. № 7. С. 78-83.
- Shima J., Seid M.J., Ali S., Abdorreza M.N. et al. Biodegradable green packaging with antimicrobial functions based on the bioactive compounds from tropical plants and their by-products. // Trends in Food Science & Technology. 2020. V. 100. P. 262-277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.04.017
- Wang Y., Li J., Guo X., Wang H. et al. Active Biodegradable Polyvinyl Alcohol-Hemicellulose/Tea Polyphenol Films with Excellent Moisture Resistance Prepared via Ultrasound Assistance for Food Packaging. // Coatings. 2021. V. 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11020219
- Yaowen L., Shuyao W., Weijie L., Wen Q. Development of ultrasound treated polyvinyl alcohol/tea polyphenol composite films and their physicochemical properties // Ultrasonics Sonochemistry. 2019. V. 51. P. 386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.07.043
- Ji T., Zhang R., Dong X., Sameen D.E. et al. Effects of Ultrasonication Time on the Properties of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose/Nano-ZnO/Multilayer Graphene Nanoplatelet Composite Films // Nanomaterials. 2020. V. 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091797
- Ding J., Zhang R., Ahmed S., Liu Y. et al. Effect of Sonication Duration in the Performance of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Chitosan Bilayer Films and Their Effect on Strawberry Preservation // Molecules. 2019. V. 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071408
- Liang X., Feng S., Ahmed S., Qin W. et al. Effect of Potassium Sorbate and Ultrasonic Treatment on the Properties of Fish Scale Collagen/Polyvinyl Alcohol Composite Film // Molecules. 2019. V. 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132363
- Wanqing D., Qiong X., Xiaoxian H., Long S. Structure and properties of egg white protein films modified by high-intensity ultrasound: An effective strategy // Food Research International. 2022. V. 157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111264
- Antonia V., Cristian T., Lilian A. Effect of high-intensity ultrasound treatment in combination with transglutaminase and nanoparticles on structural, mechanical, and physicochemical properties of quinoa proteins/chitosan edible films // International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 2020. V. 144. P. 536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.12.120
- Jingjing C., Leqi C. Effects of high-intensity ultrasound on the structural, optical, mechanical and physicochemical properties of pea protein isolate-based edible film // Ultrasonics Sonochemistry. 2021. V. 80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105809
- Jingnan Z., Qian L., Qian C., Fangda S. et al. Synergistic modification of pea protein structure using high-intensity ultrasound and pH-shifting technology to improve solubility and emulsification // Ultrasonics Sonochemistry. 2022. V. 88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2022.106099
- Lingling W., Jian D., Yong F., Xin P. et al. Effect of ultrasonic power on properties of edible composite films based on rice protein hydrolysates and chitosan // Ultrasonics Sonochemistry. 2020. V. 65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105049
- Karen C.-D., Ángel C., María E.F.-V., Olga D. et al. Characterization of edible films from whey proteins treated with heat, ultrasounds and/or transglutaminase. Application in cheese slices packaging // Food Packaging and Shelf Life. 2019. V. 22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2019.100397
- Kumar V.A., Pravitha M., Yadav A., Pandiselvam R. et al. Influence of ultrasonic application on soybean aqueous extract based composite edible film: Characterization and their food application // Food Hydrocolloids. 2023. V. 135. P. 108210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.108210
- Lixin K., Qiufang L., Huanxin C., Qiusuo Z. et al. Insights into ultrasonic treatment on the properties of pullulan/oat protein/nisin composite film:mechanical, structural and physicochemical properties // Food Chemistry. 2023. V. 402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134237
- Yifu C., Weiwei C., Xiao F., Chengcheng G. et al. Fabrication, structure and properties of pullulan-based active films incorporated with ultrasound-assisted cinnamon essential oil nanoemulsions // Food Packaging and Shelf Life. 2020. V. 25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2020.100547
- Ben N., Ping S., Hangjun C., Peilong S. Structural and physiochemical characterization of novel hydrophobic packaging films based on pullulan derivatives for fruits preservation // Carbohydrate Polymers. 2019. V. 208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.12.070
- Lixin K., Qiufang L., Arif R., Abdul Q. et al. Ultrasound-assisted development and characterization of novel polyphenol-loaded pullulan/trehalose composite films for fruit preservation // Ultrasonics Sonochemistry. 2023. V. 92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2022.106242


