Изучение кишечных микробных профилей Equus ferus caballus методом NGS-секвенирования
Автор: Алексеева Е.И., Дубровин А.В., Лаптев Г.Ю., Йылдырым Е.А., Ильина Л.А., Бражник Е.А., Филиппова В.А., Новикова Н.И., Тюрина Д.Г., Дуняшев Т.П., Тарлавин Н.В.
Журнал: Сельскохозяйственная биология @agrobiology
Рубрика: Микробиомы
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.55, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Симбиотический микробиом желудочно-кишечного тракта животных играет жизненно важную роль в переваривании и усвоении питательных веществ кормов, становлении иммунитета, устойчивости к заболеваниям, расщеплении токсинов. Нарушения микробного сообщества кишечника могут становиться причиной метаболических расстройств, таких как ацидоз, снижение переваримости компонентов рациона (прежде всего клетчатки), болезней копыт и т.д. Пищеварительная система Equus ferus caballus имеет ряд уникальных особенностей по сравнению с другими млекопитающими. В настоящей работе впервые в России было показано разнообразие состава микробиома кишечника лошадей с применением метода 16S-метагеномики. В составе микрофлоры выявлено значительное количество микроорганизмов, связанных с процессами переваривания кормов, прежде всего клетчатки, а также ряд микроорганизмов, которые могут сопутствовать возникновению различных заболеваний - колик, ацидозов, ламинитов. Целью исследования была оценка структуры микробиомов содержимого прямой кишки лошадей (с учетом их возраста, пола, породы и рациона) с применением высокопроизводительного секвенирования. Эксперимент проводили в летний период 2017 года в Крестьянско-фермерском хозяйстве «Маланичевых» (пос. Гришкино, Ленинградская обл., Тосненский р-н) на лошадях, специализированных для верховой езды и ипподромных испытаний. Отбирали пробы объемом 10-50 г (в 3 повторностях) из прямой кишки трех жеребцов ганноверской породы (возраст 3 года), кобылы (6 лет) и жеребца (7 лет) тракененской породы. За 5 сут до отбора проб кобыла ожеребилась. Рационы жеребцов и кобылы различались. Рацион жеребцов включал траву (20 кг), сено (9 кг), морковь (1 кг), овес (3 кг), поваренную соль (29 г). Рацион кобыл состоял из травы (26 кг), моркови (1 кг), плющеного овса (2,5 кг), поваренной соли (27 г). Тотальную ДНК из образцов выделяли с использованием набора Genomic DNA Purification Kit («Fermentas Inc.», Литва). Амплификацию для последующего проведения NGS-секвенирования проводили на ДНК-амплификаторе Verity («Life Technologies, Inc.», США) с помощью эубактериальных праймеров (IDT) 343F (5'-CTCCTACGGRRSGCAGCAG-3') и 806R (5'-GGACTACNVGGGTWTCTAAT-3'), фланкирующих участок V1V3 гена 16S рРНК. Метагеномное секвенирование осуществляли на приборе MiSeq («Illumina, Inc.», США). Таксономическую принадлежность микроорганизмов до рода определяли с применением программы RDP Classifier (https://rdp.cme.msu.edu/classifier/classifier.jsp). У исследованных особей E. ferus caballus были выявлены довольно сходные микробиомные профили кишечника вне зависимости от типа питания, физиологического статуса, возраста, пола и породы. Высокие значения экологических индексов Шеннона и Симпсона свидетельствовали о биоразнообразии содержимого кишечника лошадей. В составе содержимого прямой кишки обнаружили 25 филумов микроорганизмов. Доминирующими филумами оказались Firmicutes (содержание колебалось от 32±1,9 до 40±3,8 %) и Bacteroidetes (от 34±2,1 до 40±4,7 %). В составе микрофлоры детектировали значительное количество микроорганизмов, связанных с процессами переваривания кормов, прежде всего клетчатки. Так, доля бактерий, синтезирующих целлюлазы, достигала значительных величин: Bacteroidales - до 23,8±1,30 %, Lachnospiraceae - до 14,7±2,80 %, Ruminococcaceae - до 10,2±3,30 %, Clostridiaceae - до 6,6±0,6 %. Присутствовали микроорганизмы, которых выявляют при ряде заболеваний - при коликах, ацидозах, ламинитах. Например, во всех образцах содержимого прямой кишки были обнаружены нежелательные представители отряда Lactobacillales , такие как Streptococcusequinus и Str. bovis , которых связывают с возникновением ацидозов и ламинитов лошадей. Выявлены бактерии рода Treponema (от 2,2±0,22 до 6,5±0,40 %), которые ассоциированы с возникновением периодонтита у лошадей. Обнаружены энтеробактерии родов Enterobacter , Serratia , Escherichia , среди которых нередко встречаются возбудители гастроэнтеритов. Дальнейшее изучение профилей кишечной микробиоты будет способствовать совершенствованию методов диагностики и лечения заболеваний у лошадей.
Кишечный микробиом, ngs-секвенирование, биотроф, молекулярно-биологические методы
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142226326
IDR: 142226326 | УДК: 636.1:579.6:577.2 | DOI: 10.15389/agrobiology.2020.4.671rus
Текст научной статьи Изучение кишечных микробных профилей Equus ferus caballus методом NGS-секвенирования
Симбиотический микробиом желудочно-кишечного тракта животных играет жизненно важную роль в переваривании и усвоении питательных веществ кормов, становлении иммунитета, устойчивости к заболеваниям, расщеплении токсинов. Нарушения микробного сообщества кишечника могут становиться причиной метаболических расстройств, таких как ацидоз, снижение переваримости компонентов рациона (прежде всего клетчатки), болезней копыт и т.д. Пищеварительная система Equus ferus caballus имеет ряд уникальных особенностей по сравнению с другими млекопитающими. В настоящей работе впервые в России было показано разнообразие состава микробиома кишечника лошадей с применением метода 16S-метагеномики. В составе микрофлоры выявлено значительное количество микроорганизмов, связанных с процессами переваривания кормов, прежде всего клетчатки, а также ряд микроорганизмов, которые могут сопутствовать возникновению различных заболеваний — колик, ацидозов, ламинитов. Целью исследования была оценка структуры микробиомов содержимого прямой кишки лошадей (с учетом их возраста, пола, породы и рациона) с применением высокопроизводительного секвенирования. Эксперимент проводили в летний период 2017 года в Крестьянско-фермерском хозяйстве «Маланичевых» (пос. Гришкино, Ленинградская обл., Тосненский р-н) на лошадях, специализированных для верховой езды и ипподромных испытаний. Отбирали пробы объемом 10-50 г (в 3 повторностях) из прямой кишки трех жеребцов ганноверской породы (возраст 3 года), кобылы (6 лет) и жеребца (7 лет) тракененской породы. За 5 сут до отбора проб кобыла ожеребилась. Рационы жеребцов и кобылы различались. Рацион жеребцов включал траву (20 кг), сено (9 кг), морковь (1 кг), овес (3 кг), поваренную соль (29 г). Рацион кобыл состоял из травы (26 кг), моркови (1 кг), плющеного овса (2,5 кг), поваренной соли (27 г). Тотальную ДНК из образцов выделяли с использованием набора Genomic DNA Purification Kit («Fermentas Inc.», Литва). Амплификацию для последующего проведения NGS-секвенирования проводили на ДНК-амплификаторе Verity («Life Technologies, Inc.», США) с помощью эубактериальных праймеров (IDT) 343F (5′-CTCCTACGGRRSGCAGCAG-3′) и 806R (5′-GGACTACNVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′), фланкирующих участок V1V3 гена 16S рРНК. Метагеном-ное секвенирование осуществляли на приборе MiSeq («Illumina, Inc.», США). Таксономическую принадлежность микроорганизмов до рода определяли с применением программы RDP Classifier . У исследованных особей E. ferus caballus были выявлены довольно сходные микробиомные профили кишечника вне зависимости от типа питания, физиологического статуса, возраста, пола и породы. Высокие значения экологических индексов Шеннона и Симпсона свидетельствовали о биоразнообразии содержимого кишечника лошадей. В составе содержимого прямой кишки обнаружили 25 филумов микроорганизмов. Доминирующими филумами оказались Firmicutes (содержание колебалось от 32±1,9 до 40±3,8 %) и Bac-teroidetes (от 34±2,1 до 40±4,7 %). В составе микрофлоры детектировали значительное количество микроорганизмов, связанных с процессами переваривания кормов, прежде всего клетчатки. Так, доля бактерий, синтезирующих целлюлазы, достигала значительных величин: Bacteroidales — до 23,8±1,30 %, Lachnospiraceae — до 14,7±2,80 %, Ruminococcaceae — до 10,2±3,30 %, Clostridiaceae — до 6,6±0,6 %. Присутствовали микроорганизмы, которых выявляют при ряде заболеваний — при коликах, ацидозах, ламинитах. Например, во всех образцах содержимого прямой кишки были обнаружены нежелательные представители отряда Lactobacillales, такие как Streptococcus equinus и Str. bovis, которых связывают с возникновением ацидозов и ламинитов лошадей. Выявлены бактерии рода Treponema (от 2,2±0,22 до 6,5±0,40 %), которые ассоциированы с возникновением периодонтита у лошадей. Обнаружены энтеробактерии родов Enterobacter, Serratia, Escherichia, среди которых нередко встречаются возбудители гастроэнтеритов. Дальнейшее изучение профилей кишечной микробиоты будет способствовать совершенствованию методов диагностики и лечения заболеваний у лошадей.
Толстый кишечник лошадей хорошо сформирован, составляет приблизительно 64 % объема ЖКТ и включает три отдела: слепую, ободочную и прямую кишку (5). Слепая кишка у лошадей (длина около 1 м, объем 3035 л) считается аналогом рубца жвачных, поскольку здесь переваривается 40-50 % всей клетчатки и до 40 % белка (6, 7) при участии разнообразной симбиотической микрофлоры: бактерий, архей, микромицетов, простейших, бактериофагов (1). Микроорганизмы обладают разнообразной функциональной активностью, необходимой для содействия перевариванию кормов, например гемицеллюлолитической и целлюлолитической, амилолитической, протеолитической, могут утилизировать лактат (1). Пищеварительная система E. ferus caballus по сравнению с таковой у диких сородичей испытывает жесткий антропогенный прессинг, что имеет отрицательные последствия для здоровья. Например, повышенное количество сухого вещества в кормах служит дополнительным фактором, провоцирующим возникновение колик, поскольку существенно замедляет прохождение химуса по слепым отросткам кишечника в связи с их анатомическими особенностями (1). Дисбиотические нарушения микрофлоры слепых отростков кишечника, принимающей активное участие в пищеварении, на фоне несбалансированных рационов усиливают риск возникновения симптомоком-плекса колики (1).
В состав рациона лошадей, специализированных для верховой езды, в ряде случаев (например, перед участием в выставках) вводят значительные количества крахмала. По аналогии с подобными процессами у крупного рогатого скота (8) это приводит к увеличению содержания в ЖКТ, прежде всего в толстом кишечнике, амилолитических бактерий, которые вырабатывают молочную кислоту, что, в свою очередь, вызывает снижение рН и запуск последующих каскадных механизмов (1). Падает численность целлюлозолитических форм, которые чувствительны к значениям рН, нарушаются процессы усвоения клетчатки в слепой кишке, что становится провокационным фактором для возникновения колик (1).
В настоящей работе впервые в России показано разнообразие состава микробиома кишечника лошадей с применением метода 16S-метаге-номики. В составе микрофлоры выявлено значительное количество микроорганизмов, связанных с процессами переваривания кормов, прежде всего клетчатки, а также ряд микроорганизмов, которые могут сопутствовать возникновению различных заболеваний — колик, ацидозов, ламинитов.
Целью исследования была оценка микробиомов содержимого прямой кишки лошадей (с учетом их возраста, пола, породы и рациона) с применением высокопроизводительного секвенирования.
Методика. Эксперимент проводили в летний период 2017 года в Крестьянско-фермерском хозяйстве «Маланичевых» (пос. Гришкино, Ленинградской обл., Тосненский р-н) на лошадях, специализированных для 672
верховой езды и ипподромных испытаний.
Пробы объемом 10-50 г (в 3 повторностях) из прямой кишки трех жеребцов ганноверской породы (возраст 3 года), кобылы (6 лет) и жеребца (7 лет) тракененской породы отбирали с соблюдением условий асептики вручную с использованием стерильных резиновых перчаток. За 5 сут до отбора проб кобыла ожеребилась.
Рационы жеребцов и кобылы различались. Рацион жеребцов включал траву (20 кг), сено (9 кг), морковь (1 кг), овес (3 кг), поваренную соль (29 г). Содержание энергетических кормовых единиц (ЭКЕ) составляло 9,89. Рацион кобыл состоял из травы (26 кг), моркови (1 кг), плющеного овса (2,5 кг), поваренной соли (27 г); содержание ЭКЕ — 9,87.
Тотальную ДНК из образцов выделяли с использованием набора Genomic DNA Purification Kit («Fermentas, Inc.», Литва) согласно прилагаемой инструкции. Амплификацию для NGS-секвенирования проводили на ДНК-амплификаторе Verity («Life Technologies, Inc.», США) с помощью эубактериальных праймеров (IDT) 343F (5'-CTCCTACGGRRSGCAGC-AG-3') и 806R (5'-GGACTACNVGGGTWTCTAAT-3'), фланкирующих участок V1V3 гена 16S рРНК. Использовали следующий режим амплификации: 3 мин при 95 °С (1 цикл); 30 с при 95 °С, 30 с при 55 °С, 30 с при 72 °С (25 циклов); 5 мин при 72 °С (1 цикл).
Метагеномное секвенирование (MiSeq, «Illumina, Inc.», США) осуществляли с набором MiSeq Reagent Kit v3 («Illumina, Inc.», США). Максимальная длина полученных последовательностей составила 2½300 п.н. Химерные последовательности исключали из анализа с помощью программы USEARCH 7.0 . Полученные риды 2½300 п.н. обрабатывали с применением биоинформатической платформы CLC Bio GW 7.0 («Qiagen», Нидерланды), процессинг включал перекрывание, фильтрацию по качеству (quality value, QV > 15), триммирование праймеров. Таксономическую принадлежность микроорганизмов до рода определяли с применением программы RDP Classifier .
Математическую и статистическую обработку результатов проводили, используя программные пакеты Microsoft Office Excel 2003, PASТ, R-Studio (Version 1.1.453) (PASТ, 2011, (9, 10). Результаты статистического анализа считались значимыми при p < 0,05. Числовые данные представлены в виде средних значений (M) и стандартных ошибок среднего (±SEM). Рассчитывали также индексы биоразнообразия Chao1, Шеннона (Н), Симпсона (D) (11).
Результаты. При сравнении параметров а-биоразнообразия, рассчитанных по результатам изучения микробного сообщества кишечника лошадей методом NGS-секвенирования, мы не обнаружили различий между животными (табл. 1). Значения индексов видового разнообразия Шеннона и Симпсона оказались достаточно высокими по сравнению с показателями, установленными для крупного рогатого скота. Так, для бычков на откорме, получавших различные рационы, индекс Шеннона микробиоты рубца варьировал от 7,43±0,66 до 8,48±0,28, индекс Симпсона — от 0,975±0,002 до 0,985±0,001 (12). Известно, что условия в рубце оптимальны для развития разнообразной микрофлоры, при этом корм задерживается здесь на 24-48 ч, что способствует созданию благоприятных условий для микробиологических процессов и определяет высокую степень биоразнообразия (13). Тем не менее значения индекса Chao1, свидетельствующего о видовом богатстве микробиома, при анализе микробиоты кишечника лошадей были в среднем в 5 раз ниже, чем при исследовании рубца крупного рогатого скота (12).
Индексы α -разнообразия микрофлоры прямой кишки лошадей ( Equus ferus caballus ) разного возраста, пола и породы, получавших неодинаковый рацион, по данным NGS-секвенирования ( M ±SEM, пос. Гришкино, Ленинградская обл., Тосненский р-н, 2017 год)
|
Образец |
Индекс Chao1 Индекс Шеннона (H) Индекс Симпсона (D) |
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
255,6±18,235 7,5±0,68 0,99±0,063 259,5±12,442 7,6±0,44 0,99±0,073 341,8±16,329 7,9±0,42 0,99±0,047 324,1±15,321 7,9±0,39 0,99±0,054 224,3±12,637 7,3±0,53 0,99±0,068 |
П р и м еч а ни е. 1 — жеребец тракененской породы (7 лет), 2 — кобыла тракененской породы (6 лет), 3, 4, 5 — жеребцы ганноверской породы (3 года). Описание рациона для жеребцов и кобылы см. в разделе «Методика».
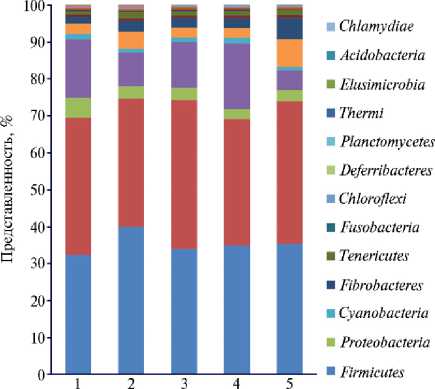
В составе микробиома прямой кишки обследованных особей E. ferus caballus было выявлено 25 филумов микроорганизмов (рис. 1). Доминирующими оказались Firmicutes (содержание колебалось от 32±1,9 до 40±3,8 %) и Bacteroidetes (от 34±2,1 до 40±4,7%), достаточно широко были представлены Verrucomicrobia , Proteobacteria , Spirochaetes , Fibrobacteres , остальные фи-лумы оказались минорными. Ранее другими исследователями отмечалось преобладание филума Firmicutes в кале здоровых лошадей на фоне снижения содержания представителей Bacteroidetes (14). В то же время снижение процентной доли представителей филума Firmicutes при повышении доли бактерий филума Verrucomicrobia имело связь с ламинитами лошадей (15, 16). Снижение доли филума Firmicutes также наблюдалось у лошадей с колитом и у особей с симптомами диареи. В работе P.K. Morrison с соавт. (17) продемонстрировано, что в фекалиях здоровых лошадей в процентном отношении преобладали бактерии филума Bacteroidetes , в меньшей степени были представлены Firmicutes и Fibrobacteres .
-
■ Chrysiogenetes
-
■ Chlorobi
-
■ Thermodesulfobacteria
Caldithrix
-
■ Thermotogae
-
■ Euryarchaeota
-
■ Nitrospirae
-
■ Synergistetes
-
■ Actinobacteria
-
■ Spirochaetes
-
■ Verrucomicrobia
-
■ Bacteroidetes
Рис. 1. Представленность филумов бактерий в образцах содержимого прямой кишки лошадей ( Equus ferus caballus ) разного возраста, пола и породы, получавших неодинаковый рацион: 1 — жеребец тракененской породы (7 лет), 2 — кобыла тракененской породы (6 лет), 3, 4, 5 — жеребцы ганноверской породы (3 года) (пос. Гришкино, Ленинградская обл., Тосненский р-н, 2017 год). Описание рациона для жеребцов и кобылы см. в разделе «Методика».
В целом при сравнении содержания бактерий высокого таксономического ранга обнаружилось, что в прямой кишке у лошадей присутство- вали довольно сходные микробиомы вне зависимости от типа питания, физиологического статуса, возраста, пола и породы. Исключением оказалась кобыла, ожеребившаяся за 5 сут до исследования, у которой выявили самое высокое (40±3,8 %, р < 0,05) содержание бактерий филума Firmicutes по сравнению с другими особями. Интересно, что в работе A. Schoster с соавт. (18) в кишечнике у кобыл после выжеребки также зафиксировано повышение обилия представителей филума Firmicutes, в частности Streptocococcaceae, при уменьшении относительной численности филума Proteobacteria по сравнению с образцами фекалий до выжеребки.
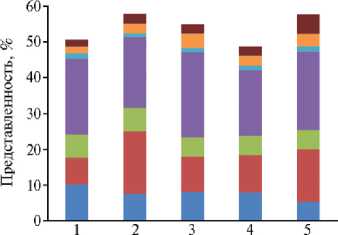
В составе микробиома прямой кишки лошадей необходимо отметить высокое разнообразие таксонов (рис. 2) — семейств Ruminococcaceae, Lachno-spiraceae, Clostridiaceae, Flavobacteriaceae, Prevotellaceae, Eubacteriaceae, порядка Bacteroidales и филума Fibrobacteres, среди которых встречаются бактерии, синтезирующие целлюлазы. Численность представителей некоторых таксонов достигала значительных величин: Bacteroidales — до 23,8±1,30 %, Lachnospiraceae — до 14,7±2,80 %, Ruminococcaceae — до 10,2±3,30 %, Clos-tridiaceae — до 6,6±0,60 %. Это важное наблюдение, поскольку перевари- вание некрахмалистых полисахаридов корма в кишечнике — исключительно микробиологический процесс (19). Представители единственного рода Fibrobacter, относящегося к филуму Fibrobacteres, ранее классифицируемого как род Bacteroides, — F. succinogenes и F. intestinalis (20) известны своей высокой эффективностью в гидролизе растительной целлюлозы (21). S.E. Salem с соавт. (22) наблюдали значительное увеличение относительной численности представителей филума Fibrobacters при введении сенажа в рацион лошадей.
■ Fibrobacteres
■ Eubacteriaceae
Prevotellaceae
■ Flavobacteriaceae
Bacteroidates
Clostridiaceae
■ Lachnospiraceae
■ Ruminococcaceae
Рис. 2. Представленность таксонов бактерий, среди которых встречаются формы, синтезирующие целлюлазы, в содержимом прямой кишки лошадей ( Equus ferus caballus ) разного возраста, пола и породы, получавших неодинаковый рацион: 1 — жеребец тракененской породы (7 лет), 2 — кобыла тра-кененской породы (6 лет), 3, 4, 5 — жеребцы ганноверской породы (3 года) (пос. Гришкино, Ленинградская обл., Тосненский р-н, 2017 год). Описание рациона для жеребцов и кобылы см. в разделе «Методика».
Интересно обнаружение в кишечнике лошадей представителей филума Euryarchaeota , включая метаногены (23, 24), продуцирующие метан, гало-фильные бактерии, сохраняющие жизнеспособность при экстремальных концентрациях соли, а также термоанаэрофилы, выживающие при температуре 41-122 °C (25). Достоверно более высокое обилие филума Euryarchaeota было обнаружено у лошадей 6-7-летнего возраста (от 0,31±0,020 до 0,44±0,020 %)
по сравнению с показателями у лошадей 3-летнего возраста (от 0,03±0,001 до 0,05±0,002 %) (при р < 0,05).
Среди представителей Firmicutes бактерии порядка Lactobacillales присутствовали в достаточно низких количествах во всех образцах, суммарно не превышая 1,35±0,070 % от общего обилия микроорганизмов. При этом типичные кишечные микроорганизмы семейства Bifidobacteriaceae (26)
практически полностью отсутствовали в содержимом прямой кишки.
С одной стороны, наличие лакто- и бифидобактерий в кишечнике служит важным маркером здоровья животных. Широко известно, что лакто- бактерии выполняют ряд значимых функций: защищают макроорганизм от размножения патогенов, проявляют иммуномодулирующую активность, участвуют в синтезе витаминов, незаменимых аминокислот. Лактобактерии и бифидобактерии также используются в качестве пробиотиков (18, 27, 28). В нашем исследовании, несмотря на низкое процентное содержание представителей рода Lactobacillus (от 0,2±0,01 до 0,5±0,03 %), их видовое разнообразие было достаточно широким и насчитывало 25 видов (рис. 3).
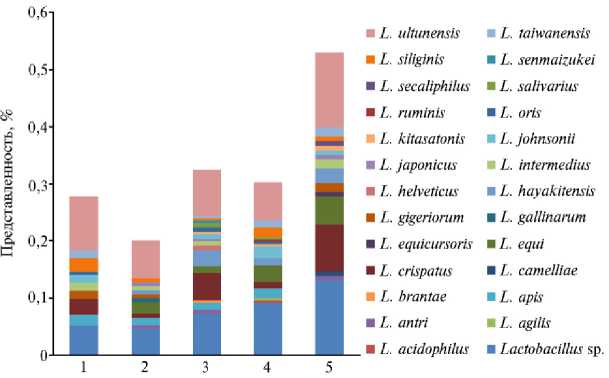
Рис. 3. Представленность бактерий рода Lactobacillus в содержимом прямой кишки лошадей ( Equus ferus caballus ) разного возраста, пола и породы, получавших неодинаковый рацион: 1 — жеребец тракененской породы (7 лет), 2 — кобыла тракененской породы (6 лет), 3, 4, 5 — жеребцы ганноверской породы (3 года) (пос. Гришкино, Ленинградская обл., Тосненский р-н, 2017 год). Описание рациона для жеребцов и кобылы см. в разделе «Методика».
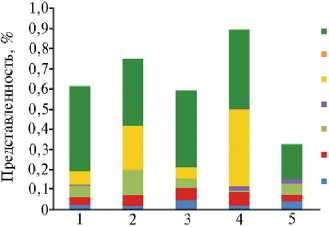
С другой стороны, во всех образцах содержимого прямой кишки также были обнаружены нежелательные представители отряда Lacto-bacillales , такие как Streptococcus equinus и Str. bovis (рис. 4) . Присутствие Str. bovis в пищеварительной системе лошадей связывают с возникновением ламинитов (29). У лошадей (30), как и у крупного рогатого скота (8), численность бактерий, продуцирующих молочную кислоту, увеличивается при введении в рацион значительной доли крахмала, что нередко приводит к возникновению лактатного ацидоза. При этом наблюдается снижение рН толстого отдела кишечника, нарушение процессов переваривания клетчатки и количественного соотношения летучих жирных кислот. Во многих случаях как следствие ацидоза у животных может возникать поражение копыт — ламинит. Как отмечал C. Bergsten (31), в экспериментальных моделях на лошадях и быках ламинит легко провоцировался посредством введения в рацион избыточного количества углеводов. Предполагается, что высокие количества эндотоксинов и гистамина, выделяемые патогенными формами, прежде всего F. necrophorum , которые увеличивают численность в условиях кислого рН, приводят к повреждению слизистой пищеварительной системы (31). Эндотоксины — чрезвычайно мощный фактор запуска каскада простагландинов. Это приводит к образованию тромбов, которые закупоривают мелкие кровеносные сосуды (капилляры) ламинарного кориума, из-за чего возникает нарушение кровообращения. Снижение количества кислорода и питательных веществ повреждает клетки, формирующие роговую оболочку кориума.
Представленность в содержимом прямой кишки лошадей бактерий рода Bacillus — микроорганизмов с широкими антагонистическими свой-676
ствами также была достаточно низкой и не превышала 0,32±0,020 %, несмотря на то, что эти микроорганизмы, благодаря образованию спор в цикле развития, более устойчивы к агрессивным условиям ЖКТ, чем многие другие формы (32). Их функциональную роль связывают со способностью к колонизации пищеварительного тракта, что обеспечивает взаимодействие с эпителием кишечника организма-хозяина (33). По меньшей мере 4-5 % генома каждого из штаммов Bacillus sp. отводится на долю генов, связанных с синтезом антимикробных соединений (34). Антимикробные бактериальные метаболиты Bacillus sp. включают в среднем 87 % органических кислот, спиртов, кетонов, алканов, альдегидов, алкенов от суммарной доли общего пула антимикробных компонентов и 13 % других веществ — рибосомных пептидов (бактериоцинов и ферментов), поликетидов, нерибосомных пептидов (35). Кроме того, большинство штаммов бацилл обладает широкой ферментативной активностью и принимает участие в метаболизме различных питательных субстратов (32).
Интересно присутствие в содержимом прямой кишки обследованных животных бактерий рода Treponema (от 2,2±0,22 до 6,5±0,40 %), среди которых было выявлено 11 видов, преимущественно Treponema bryantii . Бактерий рода Treponema ассоциированы с возникновением периодонтита у лошадей (36). Тем не менее в недавних исследованиях отмечалось присутствие 2-3 % бактерий рода Treponema у здоровых лошадей (14).
Synergistetes Enterobacter
Escherichia
Serratia
Streptococcus equinus
Clostridium histolyticum
Streptococcus bovis
Рис. 4. Представленность различных таксонов бактерий, связанных с патологическими состояниями, в содержимом прямой кишки лошадей ( Equus ferus caballus ) разного возраста, пола и породы, получавших неодинаковый рацион: 1 — жеребец тракененской породы (7 лет), 2 — кобыла тракенен-ской породы (6 лет), 3, 4, 5 — жеребцы ганноверской породы (3 года) (пос. Гришкино, Ленинградская обл., Тосненский р-н, 2017 год). Описание рациона для жеребцов и кобылы см. в разделе «Методика».
Важно также обнаружение в составе кишечной микрофлоры лошадей представителей относительно нового филума Syner-gistetes (рис. 3). Бактерий этого таксона нередко выявляют в местах кист и абсцессов у человека (37, 38), в связи с чем их относят к оппортунистическим патогенам (38, 39). Считается, что некоторые представители филума Synergistetes также вовлечены в процесс возникновения желудочно-кишечных инфекций (37) и, соответственно, могут иметь связь с возникновением симптомокомплекса колик. Представляет интерес выявление в составе микрофлоры ЖКТ изученных животных энтеробактерий родов Enterobacter, Serratia, Escherichia, среди которых нередко встречаются возбудители гастроэнтеритов. Кроме того, детектировано присутствие у лошадей бактерий рода Clostridium. Достоверно более высокое содержание представителей рода Clostridium было выявлено у лошадей 6-7-летнего возраста (от 4,1±0,25 до 4,3±0,29 %) по сравнению с животными 3-летнего возраста (от 3,1±0,18 до 3,3±0,13 %) (при р ≤ 0,05). В частности, обнаружен Clostridium histolyticum — возбудитель некротических инфекций (40).
Отдельно следует отметить, что в микробиоме кишечника лошадей мы обнаружили ряд микроорганизмов, которые могут сопутствовать возникновению симптомокомплекса колик (3, 4) — основной причины смертности лошадей. У лошадей, особенно тех, которые специализированы для верховой езды и ипподромных соревнований, вследствие значительной нагрузки на копыта очень высок риск возникновения ламинита (15, 16). Эффективной профилактикой ламинита служит поддержание здорового микробиома кишечника и предотвращение дисбиоза и ацидоза как основных причин ламинита. При разработке профилактических мероприятий по регуляции микробиома кишечника важно учитывать, что в основе современной концепции борьбы с патогенами лежит оптимизация микроэколо-гических ниш, которая должна учитывать принцип саморегуляции и экологизации (41). Натуральные кормовые добавки, такие как штаммы бактерий с пробиотическими свойствами (42-44) и растительные эфирные масла (4547), могут оказаться эффективными для поддержания баланса нормобиоты пищеварительной системы лошадей.
Информация, полученная нами в результате исследований микробиомов лошадей, может применяться для разработки биомаркеров в качестве предикторов ответа на лечение лекарственными веществами, пробиотиками и на изменения состава рациона.
Таким образом, с применением высокопроизводительного секвенирования у пяти особей Equus ferus caballus разного возраста, пола и породы, содержащихся на неодинаковом рационе, были выявлены довольно сходные микробиомы кишечника. Показано высокое биоразнообразие как представителей нормофлоры, так и патогенных микроорганизмов. Важно обнаружение в составе микрофлоры значительного количества микроорганизмов, связанных с процессами переваривания кормов, прежде всего некрахмалистых полисахаридов, что представляет интерес для дальнейшего изучения. Кроме того, можно предположить, что микробиом кишечника лошадей связан с общим состоянием их здоровья.
Список литературы Изучение кишечных микробных профилей Equus ferus caballus методом NGS-секвенирования
- Al Jassim R.A.M., Andrews F.M. The bacterial community of the horse gastrointestinal tract and its relation to fermentative acidosis, laminitis, colic, and stomach ulcers. Veterinary Clinics of North America: Equine Practice, 2009, 25(2): 199-215 ( ). DOI: 10.1016/j.cveq.2009.04.005
- Fink-Gremmels J. The role of mycotoxins in the health and performance of dairy cows. The Veterinary Journal, 2008, 176(1): 84-92 ( ). DOI: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2007.12.034
- Bäverud V., Gustafsson A., Franklin A., Lindholm A., Gunnarsson A. Clostridium difficile associated with acute colitis in mature horses treated with antibiotics. Equine Veterinary Journal, 1997, 29(4): 279-284 ( ). DOI: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1997.tb03124.x
- Chapman A.M. Acute diarrhea in hospitalized horses. Veterinary Clinics of North America: Equine Practice, 2009, 25(2): 363-380 ( ). DOI: 10.1016/j.cveq.2009.05.001
- Kohnke J., Kelleher F., Trevor-Jones P. Feeding horses in Australia, a guide for horse owners and managers. Union Offset, Canberra, ACT, Australia, 1999.
- Santos A.S., Rodrigues M.A.M., Bessa R.J.B., Ferreira L.M., Martin-Rosset W. Understanding the equine cecum-colon ecosystem: current knowledge and future perspectives. Animal, 2011, 5(1): 48-56 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1017/S1751731110001588
- Fliegerova K., Mura E., Mrázek J., Moniello G. A comparison of microbial profiles of different regions of the equine hindgut. Livestock Science, 2016, 190: 16-19 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1016/j.livsci.2016.05.015
- Nocek J.E. Bovine acidosis: implications on laminitis. Journal of Dairy Science, 1997, 80(5): 1005-1028 (
- DOI: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(97)76026-0)
- Sergeant M.J., Constantinidou C., Cogan T.A., Bedford M.R., Penn C.W., Pallen M.J. Extensive microbial and functional diversity within the chicken cecal microbiome. PLoS ONE, 2014, 9(3): e91941 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091941
- Stanley D., Geier M.S., Denman S.E., Haring V.R., Crowley T.M., Hughes R.J., Moore R.J. Identification of chicken intestinal microbiota correlated with the efficiency of energy extraction from feed. Veterinary Microbiology, 2013, 164(1-2): 85-92 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.01.030
- Kim B.R., Shin J., Guevarra R., Lee J.H., Kim D.W., Seol K.-H., Lee J.-H., Kim H.B., Isaacson R. Deciphering diversity indices for a better understanding of microbial communities. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 27(12): 2089-2093 ( ).
- DOI: 10.4014/jmb.1709.09027
- Tian K., Liu J., Sun Y., Wu Y., Chen J., Zhang R., He N., Dong G. Effects of dietary supplementation of inulin on rumen fermentation and bacterial microbiota, inflammatory response and growth performance in finishing beef steers fed high or low-concentrate diet. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2019, 258: 114299 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2019.114299
- Ильина Л.А. Изучение микрофлоры рубца крупного рогатого скота на основе молекулярно-биологического метода T-RFLP с целью разработки способов ее оптимизации. Канд. дис. СПб, 2012.
- Husso A., Jalanka J., Alipour M.J., Huhti P., Kareskoski M., Pessa-Morikawa T., Iivanainen A., Niku M. The composition of the perinatal intestinal microbiota in horse. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 441 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-57003-8
- Steelman S.M., Chowdhary B.P., Dowd S., Suchodolski J., Janečka J.E. Pyrosequencing of 16S rRNA genes in fecal samples reveals high diversity of hindgut microflora in horses and potential links to chronic laminitis. BMC Veterinary Research, 2012, 8: 231 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-6148-8-231
- Venable E.B., Bland S.D., McPherson J.L., Francis J. Role of the gut microbiota in equine health and disease, Animal Frontiers, 2016, 6(3): 43-49 ( ).
- DOI: 10.2527/af.2016-0033
- Morrison P.K., Newbold C.J., Jones E., Worgan H.J., Grove-White D.H., Dugdale A.H., Barfoot C., Harris P.A., McG Argo C. The equine gastrointestinal microbiome: impacts of age and obesity. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9: 3017 ( ).
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.03017
- Schoster A., Weese J.S., Guardabassi L. Probiotic use in horses - what is the evidence for their clinical efficacy? Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 2014, 28(6): 1640-1652 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1111/jvim.12451
- Тараканов Б.В. Методы исследования микрофлоры пищеварительного тракта сельскохозяйственных животных и птицы. М., 2006.
- Jewell K.A., Scott J.J., Adams S.M., Suen G. A phylogenetic analysis of the phylum Fibrobacteres. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 2013, 36(6): 376-382 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1016/j.syapm.2013.04.002
- Ransom-Jones E., Jones D.L., McCarthy A.J., McDonald J.E. The Fibrobacteres: an important phylum of cellulose-degrading bacteria. Microbial Ecology, 2012, 63(2): 267-281 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1007/s00248-011-9998-1
- Salem S.E., Maddox T.W., Berg A., Antczak P., Ketley J.M., Williams N.J., Archer D.C. Variation in faecal microbiota in a group of horses managed at pasture over a 12-month period. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 8510 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-26930-3
- Hogan C.M. "Archaea", encyclopedia of Earth /E. Monosson, C. Cleveland (eds.). National Council for Science and the Environment, 2010.
- Bomberg M., Timonen S. Distribution of cren- and euryarchaeota in scots pine mycorrhizospheres and boreal forest humus. Microbial Ecology, 2007, 54(3): 406-416 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1007/s00248-007-9232-3
- Lincoln S.A., Wai B., Eppley J.M., Church M.J., Summons R.E., DeLong E.F. Planktonic Euryarchaeota are a significant source of archaeal tetraether lipids in the ocean. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(27): 9858-9863 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1409439111
- Rychlik I. Composition and function of chicken gut microbiota. Animals, 2020, 10(1): 103 ( ).
- DOI: 10.3390/ani10010103
- Gotić J., Grden D., Babić N.P., Mrljak V. The use of probiotics in horses with gastrointestinal disease. American Journal of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, 2017, 12(3): 159-168 ( ).
- DOI: 10.3844/ajavsp.2017.159.168
- Ishizaka S., Matsuda A., Amagai Y., Oida K., Jang H., Ueda Y., Takai M., Tanaka A., Matsuda H. Oral administration of fermented probiotics improves the condition of feces in adult horses. Journal of Equine Science, 2014, 25(4): 65-72 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1294/jes.25.65
- Bailey S.R., Baillon M.-L., Rycroft A.N., Harris P.A., Elliott J. Identification of equine cecal bacteria producing amines in an in vitro model of carbohydrate overload. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2003, 69(4): 2087-2093 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1128/aem.69.4.2087-2093.2003
- Al Jassim R.A.M. Supplementary feeding of horses with processed sorghum grains and oats. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2006, 125(1): 33-44 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2005.05.019
- Bergsten C. Causes, risk factors, and prevention of laminitis and related claw lesions. Acta Veterinaria Scandinavica, 2003, 44: S157 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1186/1751-0147-44-S1-S157
- Bernardeau M., Lehtinen M.J., Forssten S.D., Nurminen P. Importance of the gastrointestinal life cycle of Bacillus for probiotic functionality. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 2017, 54(8): 2570-2584 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1007/s13197-017-2688-3
- Abriouel H., Franz C.M.A.P., Ben Omar N., Gálvez A. Diversity and applications of Bacillus bacteriocins. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2011, 35(1): 201-232 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00244.x
- Stein T. Bacillus subtilis antibiotics: structures, syntheses and specific functions. Molecular Microbiology, 2005, 56(4): 845-857 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04587.x
- Caulier S., Nannan C., Gillis A., Licciardi F., Bragard C., Mahillon C. Overview of the antimicrobial compounds produced by members of the Bacillus subtilis. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10: 302 ( ).
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00302
- Kennedy R., Lappin D.F., Dixon P.M., Buijs M.J., Zaura, E., Crielaard W., O'Donnell L., Bennett D., Brandt B.W., Riggio M.P. The microbiome associated with equine periodontitis and oral health. Veterinary Research, 2016, 47: 49 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1186/s13567-016-0333-1
- Jumas-Bilak E., Carlier J.P., Jean-Pierre H., Citron D., Bernard K., Damay A., Gay B., Teyssier C., Campos J., Marchandin H. Jonquetella anthropi gen. nov., sp. nov., the first member of the candidate phylum ‘Synergistete'' isolated from man. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2007, 57(12): 2743-2748 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1099/ijs.0.65213-0
- Vartoukian S.R., Palmer R.M., Wade W.G. The division "Synergistes". Anaerobe, 2007, 13(3-4): 99-106 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2007.05.004
- Marchandin H., Damay A., Roudière L., Teyssier C., Zorgniotti I., Dechaud, H., Jean-Pierre H., Jumas-Bilak E. Phylogeny, diversity and host specialization in the phylum Synergistetes with emphasis on strains and clones of human origin. Research in Microbiology, 2010, 161(2): 91-100 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resmic.2009.12.008
- Hatheway C.L. Toxigenic clostridia. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 1990, 3(1): 66-98 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1128/cmr.3.1.66
- Bauer M.A., Kainz K., Carmona-Gutierrez D., Madeo F. Microbial wars: competition in ecological niches and within the microbiome. Microbial Сell, 2018, 5(5): 215-219 ( ).
- DOI: 10.15698/mic2018.05.628
- Markowiak P., Śliżewska K. The role of probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics in animal nutrition. Gut Pathogens, 2018, 10: 21 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1186/s13099-018-0250-0
- Лаптев Г.Ю., Новикова Н.И., Йылдырым Е.А., Ильина Л.А., Тарлавин Н.В. Микробиом сельскохозяйственных животных: связь со здоровьем и продуктивностью. СПб, 2020.
- Fernández S., Fraga M., Silveyra E., Trombert A.N., Rabaza A., Pla M., Zunino P. Probiotic properties of native Lactobacillus spp. strains for dairy calves. Beneficial Microbes, 2018, 9(4): 613-624 ( ).
- DOI: 10.3920/BM2017.0131
- Йылдырым Е.А., Ильина Л.А., Лаптев Г.Ю., Зайцев С.Ю. Микробиом рубца и продуктивность дойных коров под влиянием энтеросорбента микотоксинов Заслон®-Фито. Сельскохозяйственная биология, 2019, 54(6): 1144-1153 ( ).
- DOI: 10.15389/agrobiology.2019.6.1144rus
- Нuerta B., Barrero-Domínguez B., Galán-Relaño Á., Tarradas C., Maldonado A., Luque I. Essential oils in the control of infections by Staphylococcus xylosus in Horses. Journal of Equine Veterinary Science, 2016, 38: 19-23 ( ).
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jevs.2015.11.011
- Laptev G.Y., Filippova V.A., Kochish I.I., Yildirim E.A., Ilina L.A., Dubrovin A.V., Brazhnik EA., Novikova N.I., Novikova O.B., Dmitrieva M.E., Smolensky V.I., Surai P.F., Griffin D.K., Romanov M.N. Examination of the expression of immunity genes and bacterial profiles in the caecum of growing chickens infected with Salmonella enteritidis and fed a phytobiotic. Animals, 2019, 9(9): 615 ( ).
- DOI: 10.3390/ani9090615


