Эффекты психологических интервенций на ассоциированные с математической тревожностью функциональные связи головного мозга
Автор: Яковлев Никита Иванович, Есипенко Елена Александровна, Архипова Ольга Викторовна, Марейчева Екатерина Максимовна, Маташова Тахмина Дуйшоналыевна, Мацепуро Дарья Михайловна
Журнал: Психология. Психофизиология @jpps-susu
Рубрика: Психофизиология
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.16, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Обоснование. Математическая тревожность связана с негативными эмоциональными переживаниями, возникающими при необходимости решать математические задачи. Высокий уровень математической тревожности снижает вероятность выбора образовательного и карьерного трека в STEM (наука, технология, инженерное дело и математика) дисциплинах. Для России за последние годы проблема снижения числа студентов STEM-направлений приняла особую остроту. Поэтому изучение методов снижения/регуляции математической тревожности приобретает высокую актуальность. Цель: провести анализ воздействия трёх типов однократных психологических интервенций - экспрессивного письма, переоценки установки отношения к математике и релаксации, с точки зрения способности регулировать объективные нейрофизиологические корреляты математической тревожности. Материалы и методы. Выборка обследованных (78 студентов вузов) была разделена наодну контрольную и три экспериментальные группы. Работа основана на использовании опросника для измерения уровня математической тревожности и объективных электроэнцефалографических данных. Анализ данных был выполнен на основе двухэтапной методологии выделения функциональных связей и функциональных сетей головного мозга. Результаты. Обнаружены отрицательные корреляции (на уровне тенденции) (pho=-0,2) между уровнем математической тревожности и показателями обменной эффективности функциональных сетей альфа-1 (8-10 Гц) и бета-1 (13-20 Гц) диапазонов. Значимых эффектов психологических интервенций выявлено не было. Заключение. Более эффективная организация функциональных сетей головного мозга ассоциирована с меньшим уровнем математической тревожности. Отсутствие эффектов однократных интервенций свидетельствует о необходимости изучения различных по продолжительности реализации программ регуляции уровня математической тревожности.
Математическая тревожность, психологические интервенции, ээг, функциональные связи, функциональные сети
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147240949
IDR: 147240949 | УДК: 612.821 | DOI: 10.14529/jpps230209
Текст научной статьи Эффекты психологических интервенций на ассоциированные с математической тревожностью функциональные связи головного мозга
Математическая тревожность (МТ) является объектом исследований на протяжении уже более 60 лет [1]. Феномен математической тревожности состоит в возникновении негативных эмоциональных переживаний во время ожидания или решения математических задач. Отрицательная связь между уровнем МТ и успеваемостью в точных науках хорошо изучена и является надёжным эмпирическим фактом [1, 2]. Согласно исследованиям, высокий уровень МТ у студентов ассоциирован с нежеланием выбирать учебные и карьерные направления в области STEM (science, technology, engineering and mathematics) [1, 3]. Для России тенденция снижения числа сту- дентов, выбирающих технические и математические специальности обучения в высших учебных заведениях, за последние годы принимает особую остроту [4]. В связи с этим регуляция уровня математической тревожности в настоящее время является актуальной исследовательской проблемой [5]. С этой целью изучаются эффекты влияния психологических интервенций как на математическую тревожность, так и на успешность решения математических задач [6, 7]. Среди многообразия интервенций можно выделить такие, как релаксация и медитация [8], экспрессивное письмо [9] и смена психологической установки [10], которые и были выбраны для изучения в рамках настоящего исследования.
При этом имеется сравнительно мало работ, которые бы опирались на изучение сетевых нейрофизиологических коррелятов математической тревожности в разрезе оценки эффекта той или иной интервенции [11].
Изучение функциональных связей головного мозга является популярной методологией изучения мозговой активности [12]. Данный подход рассматривает головной мозг как большую сеть, между элементами которой происходят те или иные взаимодействия [13]. Такие взаимодействия называются функциональными связями головного мозга (brain functional connectivity). Основная идея подхода состоит в статистической оценке степени схожести колебательной активности между парами участков коры головного мозга. В настоящее время существует не менее 40 различных метрик оценки функциональной связанности [14]. Выделяют три основные группы таких метрик, основанные на оценке амплитудной [15], фазовой [16] или смешанной амплитудно-фазовой синхронизации [17]. Известно, что разные типы метрик способны улавливать различные типы кортикокортикальных взаимодействий [18]. Показано, что функциональные связи характеризуют процессы обмена информацией между участками головного мозга и ассоциированы в том числе и с когнитивными и эмоциональными процессами [19, 20].
Построение оценок попарных функциональных связей в настоящем исследовании осуществлено на основе использования двух метрик – Phase-Lag Index (индекс задержки фазы, PLI) [16] и leekage corrected average envelope correlation (скорректированная на утечку средняя корреляция огибающих, lcAEC) [21]. Данный выбор обусловлен тремя факторами: а) метрики хорошо защищены от эффекта объёмной проводимости [14]; б) обладают высокой реплицируемостью [22, 23]; в) имеют различный статистический характер: PLI отслеживает частотную, а lcAEC – амплитудную синхронизации. После построения на основе той или иной метрики всех попарных оценок функциональных связей исследователь получает возможность использовать использовать данные для дальнейшего анализа [13]. В самом деле, если проинтерпретировать участки коры головного мозга как вершины сети, а статистические оценки между парами участков как силу связи между её вершинами, то получится взвешенная сеть, которая назы- вается функциональной сетью головного мозга. Существует множество подходов к изучению таких сетей, учитывающих как локальные, так и глобальные сетевые характеристики [24]. В рамках текущей работы мы фокусируемся на двух величинах – средняя сила связи и индекс тесного мира (Small World Index, SWI) [24, 26], которые хорошо изучены и хорошо реплицируются [22]. Данные величины характеризуют, в первую очередь, способность сети эффективно передавать информацию внутри себя [27].
Обычно исследователи фокусируются на изучении функциональных сетей в состоянии покоя в силу того, что они описывают характеристики так называемых default mode networks (сети спокойного бодрствования, DMN) [28]. В обзорной работе [29] приводятся результаты, указывающие на то, что компенсация высокого уровня математической тревожности ассоциирована с более высокими показателями активации мозговых сетей эмоционального и когнитивного контроля. В работе [30] была обнаружена отрицательная связь между интеграционными и сегрегационными характеристиками кортикальных сетей в бета- и гамма-диапазонах и уровнем математической тревожности. Другое аналогичное исследование подтвердило эти результаты, кроме того, было обнаружено, что индивиды с высоким уровнем математической тревожности демонстрировали более низкие характеристики интеграции функциональных сетей, связанных с рабочей памятью [31].
В настоящее время на российских выборках проведено сравнительно мало исследований, которые бы изучали связи между характеристиками функциональных сетей покоя и уровнем математической тревожности. Кроме того, по нашим сведениям, не было проведено отечественных исследований, которые бы рассматривали объективные нейрофизиологические показатели, а именно характеристики функциональных сетей покоя, при изучении эффекта психологических интервенций для регуляции математической тревожности. Текущее исследование, направленное на то, чтобы заполнить данный пробел, ставит целью проверку двух гипотез: (i) уровень математической тревожности отрицательно связан с передаточными характеристиками функциональных сетей головного мозга; (ii) все изучаемые нами психологические интервенции – экспрессивное письмо, смена установки и ре-лаксация/медитация – способны регулировать ассоциированные с математической тревожностью характеристики функциональных сетей покоя, а именно, повышать показатели их передаточной эффективности.
Материалы и методы
Выборка и парадигма исследования
В исследовании приняли участие 78 студентов томских университетов (из них 19 мужчин), средний возраст участников составил 19,79 (SD = 1,84) года. Подробное описание сбора данных приведено в нашей предыдущей работе [32], с техническими характеристиками электроэнцефалографического прибора можно ознакомиться в [33].
Парадигма исследования представлена на рисунке. Замер уровня математической тревожности был осуществлён с помощью методики AMAS [34] перед началом сбора ЭЭГ данных.
Интервенция «смена установки» основана на предложении участникам ознакомиться с идеей о том, что определенный уровень тревожности-возбуждения может улучшить продуктивность при выполнении когнитивных заданий [35]. Интервенция «экспрессивное письмо является методом регуляции психологического состояния, который заключается в изложении своих чувств и мыслей в письменной форме, что, в свою очередь, может изменить отношение к тому, что волнует или беспокоит [9]. В ходе интервенции «релаксация» участникам предлагалось расслабиться и сфокусироваться на их дыхании [36].
Предобработка ЭЭГ-данных
Предобработка ЭЭГ-данных была проведена по следующей схеме. Для каждого из участников из полной записи было выделено три трёхминутных сегмента фоновой записи: первый – обычное состояние покоя, второй – фоновая запись после инструкции, согласно которой участнику будет предложен для решения ряд математических задач, третий – фоновая запись после проведения интервенции (см. рисунок). Каждый из этих трёх сегментов был отфильтрован полосовым фильтром Баттерворда четвёртого порядка (0,5–40 Гц). Далее путём визуальной инспекции были удалены глазодвигательные артефакты и сегменты с ошибками, после чего для дальнейшей очистки записи был использован анализ независимых компонент (Independent Component Analysis, ICA). Компоненты, содержащие шумы, были удалены. Путём повторной визуальной инспекции были удалены оставшиеся сегменты с ошибками записи. Для дальнейшего анализа были выделены три временных сегмента по одной минуте для каждого из описанных выше состояний покоя. Далее в работе эти временные сегменты мы будем называть фон-0 (состояния покоя), фон-1 (первое ожидание перед предъявлением математических задач) и фон-2 (второе ожидание перед предъявлением математических задач). В силу наличия ошибок записи трое участников были исключены из анализа. Итоговый объём выборки был равен 75.
Дальнейший анализ был выполнен отдельно для каждого из следующих частотных диапазонов: тета (4–8 Гц), альфа-1 (8–10 Гц),
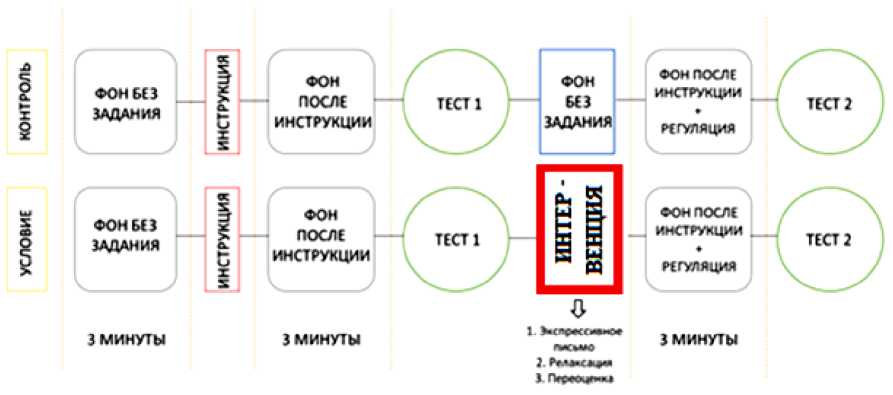
Рис. Парадигма исследования Fig. Study design
альфа-2 (10–13 Гц), бета-1 (13–20 Гц) и бета-2 (20–30 Гц), для чего был использован полосовой фильтр. Предобработка данных была выполнена в среде MATLAB с использованием свободно распространяемой утилиты
EEGLAB.
Построение оценок функциональных связей
Функциональные связи оценивались двумя метриками - PLI и IcAEC. Рассмотрим процедуру построения этих метрик. Для данной пары сигналов x(t) и y(t), которые были предварительно отфильтрованы полосовым фильтром в каждом из пяти диапазонов, были построены аналитические сигналы x(t) = x(t) + iHx(t) и x(t) = y(t) + iHy(t), где I - комплексная единица, а Hx(t) - преобразование Гильберта временного ряда x(t) Далее аналитические сигналы
x(t) = Ax(t)e l ^x (t) y(t) = A y (t)ei Vy (t), где Ax(t),Ay(t) и фx(t),фy(t) - огибающие и фазы сигналов x(t) и y(t) соответственно. На основе данного представления индекс задержки фазы определяется как [16]
PLI(x(t), y(t)) = \ Далее скорректированная на утечку средняя корреляция огибающих вычисляется по формуле lcAEC^x(t),y(t)~) = Icorr (Ax(t),Ay(t))|, где Ax(t),Ay(t) — огибающие предварительно ортогонализированных друг на друга сигналов xr(t),yr(t). Ортогонализация x(t) относительно y(t) вычисляется как xr (t) = x(t) — ay(t), где а является коэффициентом линейной регрессии y(t) на x(t). Данная процедура проводится с целью снижения эффекта объемной проводимости за счёт удаления линейно зависимых компонент в данной паре сигналов [18]. Итоговые оценки силы функциональных связей были посчитаны как усреднённые по 30 эпохам значения описанных выше метрик на каждом из двухсекундных интервалов. Построение и анализ функциональных сетей Процедура построения функциональных сетей устроена следующим образом. Для каж- дого из пяти частотных диапазонов, для каждой пары электродов, для трёх интервалов времени записи фона, для обеих метрик PLI и IcAEC были построены оценки силы попарных взаимодействий между участками головного мозга. Тем самым для каждого участника всего было построено 30 матриц, элементами которых являлись значения силы функциональных связей. Рассмотрим пока одну такую матрицу A. Каждый a^j элемент этой симметричной матрицы равен силе взаимодействия между i-м и j-м сигналами соответствующих электро- дов, которые в свою очередь описывают динамику электрической активности участков коры головного мозга. В терминах сетевой науки такие участки интерпретируются как вершины сети, а а^ обозначает силу связей между всеми парами вершин этой сети. В дальнейший анализ шли две глобальные характеристики сетей: средняя сила связи и индекс тесного мира (Small World Index, SWI). Рассмотрим процедуру их построения. Средняя сила связи строится как среднее значение всех элементов матрицы A: W = (A). Данный показатель характеризует среднюю силу связей функциональной сети головного мозга. Большее значение соответствует большей способности сети осуществлять обмен информацией между её вершинами [25]. Построение индекса тесного мира основано на вычислении двух дополнительных характеристик – нормированного взвешенного среднего коэффициента кластеризации Cw и нормированной средней длины кратчайшего пути Lw. Коэффициент кластеризации i-й вершины характеризует важность этой вершины в смысле устойчивости способности сети обмениваться информацией при удалении данной вершины: Р _ Sj^t Sfc^t,fc^j' AiJAikAkJ . _ . „ ‘ = SjtiStoMM». ,i = ...... N ^w=N^ct ■ i=1 Для построения средней кратчайшей длины пути сначала строится вспомогательная мат- рица D с элементами йц = , a,-,- ^ 0 au lJ , +^, atj = 0 которые характеризуют «расстояния» между вершинами. Затем строится матрица кратчайших попарных расстояний L. Интересующая нас величина Lw считается как среднее по элементам матрицы L. Для того чтобы устранить влияние весов рёбер в сети при построении SWI и тем самым позволить лучше сравнивать эти индексы между различными сетями, обычно применяют процедуру случайной перестановки рёбер (reshuffling) [22]. Для матрицы A производится случайная перестановка рёбер (очевидно, с сохранением свойства симметрии матрицы), для полученной матрицы затем считаются величины Cw^ и Lw^. Данная процедура проводится т = 50 раз, после чего нормированный взвешенный коэффициент кластеризации вычисляется как датта = Cw/^qw у а нормированная взвешенная кратчайшая длина пути как lambda = Lw/^wу где Cw и Lw - соответствующие величины для исходной матрицы A. Затем, наконец, индекс тесного мира считается как SW1 = датта/lambda. Большие значение этой величины соответствуют, с одной стороны, большей эффективности сети в процессах передачи информации, с другой – более высокой устойчивости сети к потере её вершин [27]. Пары глобальных сетевых характеристик - средняя сила связи W и индекс тесного мира SW1 - были построены по всем частотным диапазонам для всех трёх состояний покоя для обеих метрик функциональных связей (lcAEC и PLI). Тем самым каждая ЭЭГ-запись характеризовалась 60 (три отрезка фоновой записи, пять частотных диапазонов, две метрики и сетевые характеристики) скалярными величинами, описывающими интегральные характеристики обменной эффективности функциональных сетей головного мозга. Статистический анализ данных Для проверки гипотезы (i) о взаимосвязях между показателями связности и уровнем математической тревожности был использован тест Манна – Уитни: были проверены различия между группами с высоким и низким уровнем (деление осуществлялось по медианному значению) МТ в фоне-0 по характеристикам функциональных сетей покоя (фрагмент записи фон-0). Кроме того, был проведён непараметрический корреляционный анализ (был использован коэффициент корреля- ции Спирмена) для изучения связей между результатами теста AMAS и характеристиками W и SW1 функциональных сетей. Для оценки эффекта интервенций в рамках проверки гипотезы (ii) был использован t тест для парных выборок: для каждой из групп интервенций была проверена гипотеза о наличии разницы между показателями функциональных сетей в фоне-1 и фоне-2. Эффект интервенций был оценён показателем Cohen`s d [37]. Оценка силы функциональных связей, анализ функциональных сетей и статистический анализ были выполнены на языке программирования Python в среде Visual Studio Code с использованием ряда дополнительных библиотек. Результаты Для функциональных сетей, построенных на основе метрики связанности PL1, значимых различий между группами участников с высоким и низким уровнем математической тревожности выявлено не было (все р > 0,127). Аналогично не было выявлено различий по показателям функциональных сетей, построенных на основе метрики IcAEC (все р > 0,132). Была обнаружена значимая на уровне статистической тенденции корреляция между значением индекса тесного мира функциональной сети на основе метрики PL1 в бета-1 диапазоне (pho = -0,203, р = 0,08). Индекс тесного мира функциональной сети альфа-1 диапазона, построенной на основе IcAEC, на уровне статистической тенденции отрицательно коррелировал с баллами AMAS (pho = -0,2, р = 0,087). Для сетей, построенных с помощью метрики PL1, значения средней силы функциональных связей W альфа-1 диапазона на уровне статистической тенденции различались между фоном-1 и фоном-2 для контрольной группы (t = -1,994, р = 0,06), при этом размер эффекта был средний (d = -0,473). Для построенных на основе метрики IcAEC сетей в контрольной группы на уровне статистической тенденции были обнаружены различия в индексе тесного мира SW1 в альфа-2 диапазоне (t = 2,01, р = 0,059) со средним размером эффекта d = 0,303. Кроме того, в бета-1 диапазоне для этой же метрики оценки функциональных связей диапазоне на уровне статистической тенденции (для контрольной группы) были выявлены различия в средней силе связи t = -2,03, р = 0,057 со слабой силой эффекта (d = -0,187). Стати- стически значимых эффектов интервенций выявлено не было. Обсуждение результатов Текущее исследование ставило целью проверить две гипотезы: (i) уровень математической тревожности негативно ассоциирован с показателями обменной эффективности функциональных сетей головного мозга; (ii) психологические интервенции - экспрессивное письмо, релаксация/медитация и смена установки - способны регулировать нейрофизиологические корреляты математической тревожности. В ходе проверки гипотезы (i) значимых различий в характеристиках функциональных сетей обнаружено не было. Это может быть связано как с относительно небольшими объёмами групп (с высоким и низким уровнем МТ), так и с небольшими различиями. Корреляционный анализ, однако, на уровне статистической тенденции выявил наличие отрицательных ассоциаций между показателями функциональных сетей покоя в альфа-1 и бета-1 диапазонах и уровнем МТ. Поэтому данную гипотезу с осторожностью можно принять. Обнаруженные отрицательные корреляции хорошо согласуются с известными результатами, согласно которым передаточные характеристики функциональных сетей покоя, в том числе в бета-диапазоне, негативно связаны с уровнем математической тревожности [30, 31]. Небезынтересно, что сети, построенные на основе различных по природе метрик функциональных связей, показали примерно одинаковые по силе корреляции (pho--0,2) с уровнем математической тревожности для индекса тесного мира, различаясь, однако, по диапазонам. Интерпретация полученных результатов может быть следующей. Показано, что лучше организованные в смысле эффективности обменных процессов функциональные сети покоя, с одной стороны, положительно связаны с успешностью решения математических задач [38], с другой - отрицательно ассоциируются с уровнем математической тревожности [31]. Можно заключить, что эффективно (в упомянутом выше смысле) устроенные функциональные сети в силу более быстрых обменов информацией между участками головного мозга успешно справляются с когнитивными задачами. Поэтому уровень МТ не повышается. Другое объяснение заключается в том, что более эффективно устроенные сети лучше справляются и с задачей подавления уровня тревожности. В пользу данного объяснения может служить результат, согласно которому подавление высокой тревожности требует более высокой активности головного мозга [33]. Отрицательные же корреляции с уровнем МТ показателей сетей, построенных на основе различных метрик и в различных диапазонах, говорит в пользу того, что математическая тревожность ассоциирована с целым комплексом различных процессов, происходящих в сетях покоя. В рамках исследования не были обнаружены статистически значимые эффекты ни одной из взятых в изучение интервенций. При этом выявлены изменения показателей функциональных сетей фона-1 и фона-2. Интерпретация отсутствия различий может строиться на основе следующих факторов. Во-первых, объем групп (менее двадцати участников в каждой из подгрупп) мог быть недостаточным, чтобы обнаружить значимые эффекты. Во-вторых, следуя обзорной работе [39], интервенции показывают свою эффективность при регулярном их осуществлении на протяжении некоторого времени, когда как в текущем исследовании изучался однократный эффект их применения. В-третьих, разнонаправленные изменения показателей функциональных сетей в контрольной группе могут свидетельствовать в пользу того, что под контроль могли быть не взяты иные факторы (например, эффект ожидания когнитивной, точнее, математической нагрузки), связанные с изменением режима работы сетей покоя [40]. Исследование имеет ряд ограничений. Во-первых, объём выборки относительно мал (N = 75), как следствие, и размеры групп интервенций, что может быть причиной того, что, с одной стороны, обнаруженные связи между передаточными характеристиками функциональных сетей и уровнем математической тревожности значимы лишь на уровне тенденции, с другой - значимых эффектов интервенций не выявлено вовсе. Во-вторых, несмотря на то, что выбранные нами метрики оценки силы функциональных связей хотя и защищены от эффекта объёмной проводимости, но устроены так, что могут отбрасывать существующие взаимодействия между участками мозга [15, 16]. В-третьих, анализ выполнен в пространстве сигналов, а не источ- ников, что может негативно влиять на точность выявления функциональных сетей [41]. В-четвёртых, так как мы фокусировались только на глобальных характеристиках функциональных сетей, ничего нельзя сказать о пространственной локализации кортикальных связей, ассоциированных с высоким уровнем математической тревожности [14, 41]. Наконец, в-пятых, изучались эффекты лишь однократного использования интервенций, которых может быть недостаточно для появления нейрофизиологических изменений. Выводы В настоящем исследовании впервые на российской выборке были изучены эффекты влияния трёх психологических интервенций – релаксации, экспрессивного письма и смены установки – на ассоциированные с математической тревожностью функциональные сети головного мозга. Обнаруженные отрицательные корреляции (на уровне тенденции) уровня МТ и эффективности организации функциональных сетей головного мозга, в том числе в альфа-1 диапазоне, находятся в соответствии с литературными данными. Отсутствие обнаруженных эффектов интервенций может быть объяснено как недостаточным объёмом выборки, так и неэффективностью однократных методов регуляции МТ. Дальнейшее развитие исследования может идти по следующим путям: использование долгосрочных программ интервенций, набор большего объема выборки и взятие в анализ локальных характеристик функциональных сетей в пространстве источников. Финансирование и этика Исследование одобрено этическим комитетом междисциплинарных исследований Томского государственного университета в апреле 2020 года, номер формы 03042020-32. Все участники после ознакомления с условиями физиологических экспериментов подписывали информированное согласие на участие в исследовании. По окончанию исследования участники получали денежное вознаграждение. Авторы заявляют об отсутствии конфликта интересов в рамках данной работы.
Список литературы Эффекты психологических интервенций на ассоциированные с математической тревожностью функциональные связи головного мозга
- Dowker A., Sarkar A., Looi C. Y. Mathematics anxiety: What have we learned in 60 years? Frontiers in psychology. 2016;7:508. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00508
- Whyte J., Anthony G. Maths anxiety: The fear factor in the mathematics classroom. New Zealand Journal of Teachers' Work. 2012;9(1):6-15.
- Chang H., Beilock S.L. The math anxiety-math performance link and its relation to individual and environmental factors: A review of current behavioral and psychophysiological research. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences. 2016;10;33-38. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cobeha.2016.04.011
- Chemekov V.N., Krylov D.A. STEAM-a new approach to engineering education. Vestnik Ma-riiskogo gosudarstvennogo universiteta = Bulletin of the Mari State University. 2015;5(20):59-64.
- Moustafa A.A., Al-Emadi A.A., Megreya A.M. The Need to Develop an Individualized Intervention for Mathematics Anxiety. Frontiers in Psychology. 2021:12. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/ fpsyg.2021.723289
- Samuel T.S., Warner J. "I can math!": Reducing math anxiety and increasing math self-efficacy using a mindfulness and growth mindset-based intervention in first-year students. Community College Journal of Research and Practice. 2021;45(3):205-222. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/ 10668926.2019.1666063
- Henslee A., Klein B. Using brief guided imagery to reduce math anxiety and improve math performance: A pilot study. Journal of STEM Education. 2017;18(4):32-36.
- Durak Y.H. The effects of using different tools in programming teaching of secondary school students on engagement, computational thinking and reflective thinking skills for problem solving. Technology, Knowledge and Learning. 2020;25(1):179-195. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10758-018-9391-y
- Park D., Ramirez G., Beilock S.L. The Role of Expressive Writing in Math Anxiety. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied. 2014;20(2):103-111. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1037/xap0000013
- Crum A.J., Jamieson J.P., Akinola M. Optimizing stress: An integrated intervention for regulating stress responses. Emotion. 2020;20(1):120-125. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1037/emo0000670
- Chen M. Research on Math Anxiety of Elementary School Teachers. In 2021. International Conference on Education, Language and Art (ICELA 2021). 2022;637:325-330.
- Power J.D., Cohen A.L., Nelson S.M. et al. Functional network organization of the human brain. Neuron. 2011;72(4):665-678. DOI: https://doi.org/10.10167j.neuron.2011.09.006
- Rubinov M., Sporns O. Complex network measures of brain connectivity: uses and interpretations. Neuroimage. 2010;52(3):1059-1069. DOI: https://doi.org/10.10167j.neuroimage.2009.10.003
- Bastos A.M., Schoffelen J.M. A tutorial review of functional connectivity analysis methods and their interpretational pitfalls. Frontiers in systems neuroscience. 2016;9:175. DOI: https://doi.org/ 10.3389/fnsys.2015.00175
- Colclough G.L., Brookes M.J., Smith S.M., Woolrich M.W. A symmetric multivariate leakage correction for MEG connectomes. Neuroimage. 2015;117:439-448. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/ j.neuroimage.2015.03.071
- Stam C.J., Nolte G., Daffertshofer A. Phase lag index: assessment of functional connectivity from multi-channel EEG and MEG with diminished bias from common sources. Human brain mapping. 2007;28(11): 1178-1193. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20346
- Nolte G., Bai O., Wheaton L. et al. Identifying true brain interaction from EEG data using the imaginary part of coherency. Clinical Neurophysiology. 2004;115(10):2292-2307. DOI: https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.clinph.2004.04.029
- Colclough G.L., Woolrich M.W., Tewarie P.K. et al. How reliable are MEG resting-state connectivity metrics? Neuroimage. 2016;138:284-293. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016Zj.neuroimage.2016.05.070
- van den Heuvel M.P., Stam C.J., Kahn R.S., Pol H.E.H. Efficiency of functional brain networks and intellectual performance. Journal of Neuroscience. 2009;29(23):7619-7624. DOI: https://doi.org/ 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1443-09.2009
- Modi S., Kumar M., Kumar P., Khushu S. Aberrant functional connectivity of resting state networks associated with trait anxiety. Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging. 2015;234(1):25-34. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/jj.pscychresns.2015.07.006
- Brookes M.J., Woolrich M.W., Barnes G.R. Measuring functional connectivity in MEG: a multivariate approach insensitive to linear source leakage. Neuroimage. 2012;63(2):910-920. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j .neuroimage.2012.03.048
- Hardmeier M., Hatz F., Bousleiman H. et al. Reproducibility of functional connectivity and graph measures based on the phase lag index (PLI) and weighted phase lag index (wPLI) derived from high resolution EEG. PloSone. 2014;9(10):e108648. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0108648
- Schoonhoven D.N., Briels C.T., Hillebrand A. et al. Sensitive and reproducible MEG resting-state metrics of functional connectivity in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's research and therapy. 2022;14(1):38. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-022-00970-4
- Ismail L.E., Karwowski W. A graph theory-based modeling of functional brain connectivity based on EEG: A systematic review in the context of neuroergonomics. IEEE Access. 2020;8:155103-155135.
- Watts D.J., Strogatz S.H. Collective dynamics of 'small-world'networks. Nature. 1998;393(6684):440-442.
- Bassett D.S., Sporns O. Network neuroscience. Nature neuroscience. 2017;20(3):353-364. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4502
- Latora V., Marchiori M. Efficient behavior of small-world networks. Physical review letters. 2001;87(19): 198701. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.87.198701
- Greicius M.D., Krasnow B., Reiss A.L., Menon V. Functional connectivity in the resting brain: a network analysis of the default mode hypothesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2003;100(1):253-258. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0135058100
- Artemenko C., Daroczy G., Nuerk H.C. Neural correlates of math anxiety - an overview and implications. Frontiers in Psychology. 2015;6:1333. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01333
- Klados M.A., Pandria N., Micheloyannis S. et al. Math anxiety: Brain cortical network changes in anticipation of doing mathematics. International Journal of Psychophysiology. 2017;122:24-31. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/jijpsycho.2017.05.003
- Klados M.A., Paraskevopoulos E., Pandria N., Bamidis P.D. The impact of math anxiety on working memory: A cortical activations and cortical functional connectivity EEG study. IEEE Access. 2019;7:15027-15039.
- Esipenko E.A., Matsepuro D.M., Arhipova O.V. et al. Physiological correlates of mathematical anxiety in resting state and during anticipation of math. Psikhologiya. Psikhofiziologiya = Psychology. Psychophysiology. 2022;15(1):131-141. DOI: https://doi.org/10.14529/jpps220112.
- Savostyanov A. N. et al. EEG Correlates of Trait and Mathematical Anxiety during Lexical and Numerical Error-Recognition Tasks. International Journal of Social, Behavioral, Educational, Economic and Management Engineering. 2015;9(7):2162-2166.
- Hopko D R., Mahadevan R., Bare R.L., Hunt M.K. The Abbreviated Math Anxiety Scale (AMAS): Construction, Validity, and Reliability. Assessment. 2003;10(2):178-182. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1073191103010002008
- Jamieson J.P., Mendes W.B., Blackstock E., Schmader T. Turning the knots in your stomach into bows: Reappraising arousal improves performance on the GRE. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology. 2010;46(1):208-212. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/jjesp.2009.08.015
- Brunyé T.T., Mahoney C.R., Giles G.E. et. al. Learning to relax: Evaluating four brief interventions for overcoming the negative emotions accompanying math anxiety. Learning and Individual Differences. 2013;27(7):1-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2013.06.008
- Peng C.Y.J., Chen L.T. Beyond Cohen's d: Alternative effect size measures for between-subject designs. The Journal of Experimental Education. 2014;82(1):22-50. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/ 00220973.2012.745471
- Chaddock-Heyman L. Weng T.B., Kienzler C. et al. Scholastic performance and functional connectivity of brain networks in children. PloS one. 2018;13(1):e0190073. DOI: https://doi.org/ 10.1371/j ournal .pone.0190073
- Ramirez G., Shaw S.T., Maloney E.A. Math anxiety: Past research, promising interventions, and a new interpretation framework. Educational Psychologist. 2018;53(3): 145-164. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00461520.2018.1447384
- Lyons I.M., Beilock S.L. When math hurts: math anxiety predicts pain network activation in anticipation of doing math. PloS one. 2012;7(10):e48076. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0048076
- Xie W., Toll R.T., Nelson C.A. EEG Functional Connectivity Analysis in the Source Space. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience. 2022:101119. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcn.2022.101119


