Эволюция эндопротезирования первого плюснефалангового сустава
Автор: Котельников Г. П., Николаенко А. Н., Гранкин И. О., Иванов В. В., Исайкин П. Ю., Дороганов С. О., Згирский Д. О.
Журнал: Гений ортопедии @geniy-ortopedii
Рубрика: Обзор литературы
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.30, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Введение. Среди заболеваний первого плюснефалангового сустава (1 ПФС), требующих оперативного лечения, выделяют остеоартроз (до 69 %), ревматоидный артрит (до 26 %), а также опухоли, опухолеподобные заболевания и гнойные артриты (до 5 %). Актуальность лечения артроза 1 ПФС определяется высокой заболеваемостью и функциональной значимостью этой анатомической структуры. Хирургия суставов на сегодняшний день сосредоточена на восстановительном эндопротезировании, при котором используют импланты, выдерживающие вес тела человека, восстанавливающие движения в суставе, поддерживающие функцию плюсне-сесамовидных суставов, а также сохраняющие длину плюсневой кости.Цель работы - проанализировать данные зарубежной и отечественной литературы, посвященной эндопротезированию 1 ПФС, и кратко представить аналитические данные по результатам использования различных имплантов.Материалы и методы. В данной статье представлены обобщенные сведения отечественных и зарубежных публикаций на тему эндопротезирования 1 ПФС. В информационных системах PubMed, eLIBRARY, MedLine, Scopus проводился анализ литературы с использованием следующей терминологии: «эндопротезирование первого плюснефалангового сустава», «оперативное лечение hallux rigidus», «остеоартроз первого плюснефалангового сустава», «results of endoprosthetics of the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint», «modernization of implants of the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint». Проанализированы материалы с 1968 по 2022 год включительно.Результаты и обсуждение. Идеальный имплант должен восстанавливать движения, улучшать функцию, поддерживать суставную стабильность, распределять нагрузку на суставные поверхности и быть износостойким. На протяжении многих лет использовались различные материалы для достижения простоты и надежности конструкций. Эндопротезы совершенствовались и изменялись. Их стали подразделять на группы по материалу и конструкции, а также по признакам ограничения степеней свободы, состава трибологической пары, количества замещения суставных поверхностей.Заключение. Импланты нового поколения имеют более прочную конструкцию, анатомичную форму и улучшенную остеоинтеграцию. Эти достижения обусловили повышение удовлетворенности пациентов и увеличение срока службы эндопротезов. Тем не менее, остается высокий процент осложнений после эндопротезирования 1 ПФС. Это свидетельствует о необходимости продолжения исследований и дальнейшей работы по усовершенствованию имплантов, чтобы сделать их более эффективными и удобными в использовании.
Эндопротезирование первого плюснефалангового сустава, остеоартроз первого плюснефалангового сустава, эволюция эндопротезирования суставов стопы
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142240829
IDR: 142240829 | УДК: 616.727.8-002-77-089.843 | DOI: 10.18019/1028-4427-2024-30-2-309-319
Текст обзорной статьи Эволюция эндопротезирования первого плюснефалангового сустава
Одной из главных особенностей строения стопы является наличие продольного и поперечного сводов, которые обеспечивают равномерное распределение нагрузки между пяточным бугром и 5 плюсневыми костями, а также выполняют амортизирующую функцию во время ходьбы и бега. В среднем 50 % опорной нагрузки приходится на головку первой плюсневой кости, входящей в состав первого плюс-нефалангового сустава (1 ПФС). Также 1 ПФС имеет большое значение в биомеханике ходьбы человека, обеспечивая телу ускорение по горизонтали в фазе толчка [1, 2]. Даже незначительное повреждение данного сустава приводит к нарушению нормального функционирования стопы, ограничивая трудовую и бытовую деятельность человека.
Среди заболеваний 1 ПФС, требующих оперативного лечения, выделяют остеоартроз (до 69 %), ревматоидный артрит (до 26 %), а также опухоли, опухолеподобные заболевания и гнойные артриты (до 5 %). Актуальность лечения артроза 1 ПФС определяется высокой заболеваемостью населения болезнями этой анатомической структуры. Остеоартроз 1 ПФС (hallux rigidus) — это дегенеративно-дистрофическое заболевание, связанное с повреждением суставного хряща. Этиология данной патологии многогранна и связана с нарушениями сустава различными факторами: травматическими, биомеханическими, метаболическими, нервно-мышечными, послеоперационными и другими [3, 4]. Перед врачом стоит непростая задача выбора способа лечения в зависимости от степени артроза, возраста пациента, его ожиданий и уровня активности. Консервативное лечение может обеспечить удовлетворительные показатели у отдельных пациентов с 0-й и 1-й степенью артроза первого плюснефалангового сустава с низкими функциональными запросами. На средних стадиях артроза выполняются органосохранные операции, такие как изолированная хейлэктомия или остеотомии проксимальной фаланги и плюсневой кости. Для лечения тяжелых артрозов 3-й степени, при которых суставные поверхности полностью разрушены, применяют артродезирование, эндопротезирование и артропластику по Келлеру [5].
Несмотря на то, что артродез первого плюснефалангового сустава остается «золотым стандартом» лечения hallux rigidus, данный способ лечения не приводит к значительному улучшению функциональных результатов. В то же время, артродезирование не обходится без осложнений, таких как не-сращение, искривление оси первого луча и разрушение металлофиксаторов [6, 7]. В хирургии суставов на сегодняшний день преобладает восстановительное эндопротезирование, при котором используют импланты, выдерживающие вес тела человека. Также современные эндопротезы обеспечивают восстановление движений в 1 ПФС и поддерживают функцию плюсне-сесамовидных суставов [8]. Показаниями для применения эндопротезирования 1 ПФС являются артрозы (идиопатический, посттравматический и дегенеративный), проведение ревизионных операций (по методам Brandes – Keller и Morbus Köhler), а также ревматоидный артрит.
В настоящий момент существует множество видов эндопротезов 1 ПФС, отличающихся по строению, материалам, трибологической паре трения. Несмотря на то, что каждый вид импланта прошел длительный путь эволюции в несколько десятков лет, эндопротезирование 1 ПФС приводит к противоречивым результатам и большому числу послеоперационных осложнений [9].
Цель работы — проанализировать зарубежные и отечественные научные публикации, посвященные эндопротезированию 1 ПФС, и кратко представить аналитические данные по результатам использования различных имплантов.
МАТЕРИАЛЫ И МЕТОДЫ
В данной статье представлены обобщенные сведения отечественных и зарубежных публикаций на тему эндопротезирования 1 ПФС, описана эволюция развития и проектирования эндопротезов 1 ПФС, представлена классификация наиболее распространенных имплантов 1 ПФС. Отбор научных источников проведен в информационных системах PubMed, eLIBRARY, MedLine, Scopus с использованием следующих поисковых слов и словосочетаний: эндопротезирование первого плюснефалангового сустава, оперативное лечение hallux rigidus, остеоартроз первого плюснефалангового сустава, results of endoprosthetics of the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint, modernization of implants of the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint. В анализ включены материалы, опубликованные с 1968 по 2022 г. Кроме того, в данный обзор вошли сведения статей, посвященных функциональной анатомии и биомеханике 1 ПФС.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ И ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Важную роль для успешного проведения эндопротезирования 1 ПФС и исключения интра- и послеоперационных осложнений играет знание анатомии и биомеханики этой структуры.
1 ПФС состоит из 4 костей и включает в себя головку первой плюсневой кости, основание проксимальной фаланги первого пальца, а также две элипсовидные сесамовидные кости. По форме этот сустав относят к шаровидным. Он имеет 3 степени свободы: сгибание/разгибание, отведение/приведение, наружная/ внутренняя ротация. На подошвенной поверхности головки первой плюсневой кости имеются две борозды, разделенные гребнем, образующие суставные фасетки для сесамовидных костей, включенные в толщу капсулы сустава, которая представляет собой площадку и образует сесамовидный гамак [10].
Капсула 1 ПФС проксимально крепится к нижней части головки первой плюсневой кости, а дистально — к основанию проксимальной фаланги первого пальца. По бокам капсула укреплена коллатеральными связками, которые придают суставу дополнительную стабильность. С медиальной стороны к связке сесамовидного гамака фиксируется сухожилие мышцы, приводящей большой палец стопы, и медиальная головка сухожилия короткого сгибателя первого пальца. К латеральной части капсулы прикрепляется сухожилие мышцы, отводящей первый палец, и латеральная головка сухожилия короткого сгибателя первого пальца. Сесамовидные кости участвует в равномерном распределении нагрузки, защите плюсневой и фаланговой суставных поверхностей и служат опорой в фазе толчка. Также сесамовидный гамак входит в состав фиброзно-хрящевой подошвенной пластины и создает прочную связь между звеньями сустава. С тыльной стороны 1 ПФС укреплен сухожилием мышцы короткого разгибателя первого пальца, который прикрепляется к верхней части основной фаланги, и сухожилием длинного разгибателя первого пальца, фиксирующегося к дистальной фаланге. Оба сухожилия закреплены фиброзным капюшоном, который вплетается в капсулу и дополнительно укрепляет сустав [11, 12].
Около 40 % цикла шага нагрузка приходится на передний отдел стопы. При этом она постепенно перераспределяется с латерального отдела на медиальный, из чего можно сделать вывод, что 1 ПФС имеет важную функцию в биомеханике ходьбы. Амплитуда движений в 1 ПФС в норме достигает 45° подошвенного сгибания и 90° тыльного сгибания при пассивных движениях, а под нагрузкой — 44°. В результате оценки нагрузки, воздействующей на 1 ПФС во время ходьбы, измеренной во время конечной фазы опоры стопы, предложено среднее значение силы, действующей на сустав, равное 0,86 × масса тела. Для 70-килограммового человека это значение равняется 61 Н [13, 14].
Исследования последних лет доказали, что звенья анатомических структур в виде связок, мышц, костей и капсулы 1 ПФС являются единым целым, в котором патология любой составляющей приводит к каскаду биомеханических нарушений и необратимым последствиям [15].
Исторически первоначальной целью создания эндропротеза 1 ПФС была разработка конструкции такой же простой и надежной, как современные импланты коленного или тазобедренного суставов. Однако при проектировании возникали трудности со структурными и функциональными особенностями 1 ПФС. Основная классификация наиболее распространённых эндопротезов 1 ПФС представлена в таблице 1.
Таблица 1
Классификация наиболее распространённых эндопротезов 1 ПФС [18, 19]
|
I. Гемиэндопротезы |
|
|
Силиконовые эндопротезы Swanson, 1968 г.; эндопротезы дизайна Swanson с модификацией по Weil, 1977 г. |
|
|
Металлические эндопротезы Swanson, 1986 г.; Townley, 1986 г.; HemiCap первого поколения, производство Arthrosurface, 1998 г.; HemiCap второго поколения, производство Arthrosurface, 2012 г. |
|
|
II. Тотальные эндопротезы |
|
|
Связанные |
Двуствольный шарнирный силиконовый эндопротез 1 ПФС, дизайн Swanson, 1974 г. |
|
Двуствольный шарнирный силиконовый эндопротез 1 ПФС с полиэстерными рукавами и дополнительным шовным материалом дизайна Kampner, производства Sutter Biomedical, 1971 г. |
|
|
Двуствольный шарнирный силиконовый эндопротез 1 ПФС, дизайн Лоуренс и дизайн LaPorta, производства Sutter Biomedical, 1982 г. |
|
|
Двуствольный силиконовый эндопротез 1 ПФС с дакроновым покрытием дизайна Helal, 1977 г. Двуствольный шарнирный силиконовый эндопротез 1 ПФС, дизайн Swanson с титановыми втулками, производство Wright Medical, 1985г. |
|
|
Несвязанные с парой трения металл-полимер |
Тотальный эндопротез производства Richards Manufacturing с фаланговым компонентом из полиэтилена сверхвысокой молекулярной массы и плюсневым компонентом из нержавеющей стали, 1975 г. |
|
Тотальный эндопротез системы Total Toe System производства Biomet c плюсневым компонентом, изготовленным из титана, и фаланговым — из полиэтилена (Варшава, США), 1989 г. |
|
|
Тотальный эндопротез Bio action great toe implant производства Osteomed c плюсневым компонентом, изготовленным из кобальт-хрома, и фаланговым — из полипропилена (Техас, США), 1991 г. |
|
|
Несвязанные с парой трения керамика-керамика |
Эндопротез производства Moje Ceramic (Германия), 2004 г. |
|
Несвязанные с парой трения металл-металл |
Тотальный эндопротез системы Movement Great Toe System производства Integra (Нью-Джерси, США), 2019 г. |
|
III. Интерпозиционные эндопротезы |
|
|
Эндопротез дизайна Regno из нержавеющей стали, 1975 г. |
|
|
Эндрпротез дизайна Barouk из нержавеющей стали, 1987 г. |
|
|
Гидрогелевый эндопротез из поливинилового спирта производства CARTIVA (Джорджия, США), 2016 г. |
|
На сегодняшний день эндопротезы 1 ПФС делятся на следующие категории:
-
1) по ограничению степеней свободы: связанные или несвязанные;
-
2) по трибологической паре: металл-металл, металл-полиэтилен, керамика-керамика, пирокарбон, силикон; 3) по количеству замещения суставных поверхностей: униполярные или биполярные [16].
Для выбора имплантата важно оценить степень разрушения суставных поверхностей головки плюсневой кости и основания проксимальной фаланги. В литературе нет точных рекомендаций для выбора того или иного импланта, в большинстве случаев тактику определяет именно хирург, основываясь на собственном опыте, знакомстве с эндопротезом и оборудованием, используемым для операции [17].
Силиконовые эндопротезы
A.B. Swanson в 1968 г. впервые разработал два типа силиконовых полуинтерпозиционных имплантатов. Первым использовали эндопротез головки плюсневой кости, который впоследствии был заменен имплантом для основания проксимальной фаланги первого пальца стопы. Он представлял собой одноствольную конструкцию с силиконовой головкой и ножкой, предназначенной для замены суставной поверхности основания проксимальной фаланги (рис. 1, а). A.B. Swanson полагал, что имплант, размещенный именно на этой стороне сустава, станет наиболее стабильным, поскольку он не будет подвергаться чрезмерной нагрузке. Эндопротез использовался по принципу артропластики Келлера и действовал как распорка в межсуставной щели; объем движений при этом увеличился незначительно [20, 21]. H.B. Ris et al. в своих исследованиях сообщили о состоянии 53 пациентов через 48 месяцев после операции, у которых были установлены 68 силиконовых гемиимплантатов конструкции Swanson. Физикальное обследование пациентов выявило уменьшение объема движений в 1 ПФС по сравнению с первоначальными показателями, зафиксированными у 62 % пациентов. Разрушение импланта отмечено в 57 % случаев при рентгенологическом исследовании [22].
В 1971 г. S.L. Kampner разработал первый двуствольный силиконовый имплант, который изготавливался из силикона и полиэфирного материала. Первая конструкция содержала рукава из полиэстера, прикрепленные к ножкам, а также шовный материал для фиксации к надкостнице и улучшения стабильности эндопротеза. Дизайн с полиэстерными рукавами был позже снят с производства в связи с развитием тугоподвижности сустава и повышением нагрузки на шарнирную часть [23, 24].
В 1974 г. A.B. Swanson представил двуствольную конструкцию с двумя конусными ножками и гибким u-образным шарниром, который обеспечивал тыльное сгибание (рис. 1, б). Шарнир этого эндопротеза подвергался критике за то, что он не достигает физиологического объема движений. Изгиб ножек во фронтальной и боковой плоскостях отсутствовал. При установке оригинальной конструкции хирургу часто приходилось укорачивать ножку фалангового имплантата. Спустя год A.B. Swanson et al. представили силиконовый имплант с укороченными ножками [25].
В 1985 г. компания Wright Medical изготовила двуствольный эндопротез дизайна Swanson с титановыми втулками. Эти втулки разработаны для защиты ножек эндопротеза в наиболее уязвимом месте между краем резецированной кости и шарниром импланта. Втулки запрессовывались в костномозговые каналы перед установкой импланта [26]. В 1991 г. J. Gerbert провел ретроспективный анализ результатов эндопротезирования пациентов имплантами Swanson с титановыми втулками. Были исследованы 22 пациента за период 33 месяца, средний возраст составил 61 год. Анкетирование проводили по шкале PASCOM (Podiatric Audit in Surgery and Clinical Outcome Measure), в 72 % случаев получены удовлетворительные результаты. Угол тыльного сгибания 1 пальца составил в среднем 21° [27, 28].
В 1982 г. компания Sutter Biomedical представила несколько конструкций силиконовых шарнирных имплантатов 1 ПФС стопы дизайна LaPorta и дизайна Lawrence (рис. 1, в, г). Эти эндопротезы в настоящее время производит компания Futura Biomedical. Обе конструкции включают в себя прямоугольноконические ножки. Проксимальная ножка немного крупнее и длиннее дистальной, наклонена на 15° в тыльную сторону. Эта особенность включена в конструкцию, чтобы обеспечить физиологическое наклонение первой плюсневой кости без дополнительного напряжения шарнирной части. Имплант LaPorta подразделяется на правые, левые и нейтральные варианты компонентов, которые отличаются друг от друга углом наклона ножек в горизонтальной плоскости. У нейтрального дизайна угол наклона ножек в горизонтальной плоскости равен 0°, у правого и левого варианта угол наклона равен 10°. Имплантат Lawrence имеет нейтральную форму. Шарнир обоих имплантатов имеет форму песочных часов, при этом сгибание происходит в центральной части соединения. Конструкция LaPorta симметрична от тыльной до подошвенной части и рассчитана на 60° тыльного сгибания. Обе стороны головок имеют плоскую поверхность для того, чтобы обеспечить полное прилегание к костным краям. Дизайн Lawrence отличается тем, что шарнирная часть основной фаланги удлинена тыльно и наклонена вниз. Его основным преимуществом является обеспечение 85° тыльного сгибания. Подошвенный угол на фаланговой стороне шарнира позволяет уменьшить объем резекции основной фаланги и, таким образом, увеличивает стабильность сустава за счет сохранения места прикрепления ножек сухожилия сгибателя [29, 30, 31].

Рис. 1. Внешний вид силиконовых эндопротезов 1 ПФС: а — одноствольный эндопротез 1 ПФС, дизайн Swanson, 1965 г.; б — двуствольный шарнирный эндопротез 1 ПФС, дизайн Swanson, 1974 г.; в — двуствольный шарнирный эндопротез 1 ПФС дизайн LaPorta, производство Sutter Biomedical, 1982 г.; г — двуствольный шарнирный эндопротез 1 ПФС, дизайн Lawrence, производство Sutter Biomedical, 1982 г. [26]
Проведено несколько исследований для оценки эффективности гибких шарнирных имплантатов. В 1989 г. W. Granberry et al. провели ретроспективное исследование 90 пациентов после эндопротезирования силиконовыми гибкими шарнирными эндопротезами в течение трех лет. Большинство пациентов указало на удовлетворительные результаты в отношении интенсивности боли. W. Granberry обнаружил три основных недостатка в использовании гибких шарнирных имплантатов. При осмотре у 30 % пациентов тыльное сгибание в 1 ПФС достигало менее 15° (тыльное сгибание первого пальца стопы является ключевым компонентом биомеханики ходьбы человека). Вторым осложнением являлось появление поражений кожи. У 69 % пациентов отмечались болезненные кератозы по подошвенной поверхности стопы в проекции головки первой плюсневой кости в результате укорочения первого луча. Третьим осложнением, отмеченным W. Granberry et al., было образование остеофитов в области 1 ПФС или вокруг него. Рентгенологическое исследование выявило образование остеофитов вокруг имплантата у 53 % пациентов [32].
Металлические эндопротезы
Металлические гемиэндопротезы разработаны, в основном, с целью устранения избыточной резекции суставной поверхности и укорочения первого луча при установке силиконовых имплантов [33]. В 1986 г. A.B. Swanson разработал гемиимплант из титана, который применялся для замены суставной поверхности основной фаланги (рис. 2, а). В 1987 г. C.O. Townley модифицировал эндопротез и начал его производить из сплава кобальта и хрома (рис. 2, б). Он отличался тонким мечевидным стержнем, при установке которого не требовалось дополнительной обработки костномозгового канала. В том числе, этот имплант включал в себя тонкую головку, что позволяло ограничить резекцию проксимальной фаланги и сохранить прикрепленные мягкие ткани. Эндопротезы производит компания Wright Medical в пяти размерах (от 0 до 4). Фаланговые полуимпланты не в полной мере уменьшали болевой синдром и улучшали подвижность сустава, так как первоначально не выполняли обработку дегенеративно измененной головки первой плюсневой кости. Впоследствии процедура шлифовки головки первой плюсневой кости стала обязательной при имплантации эндопротезов данной модели [34].
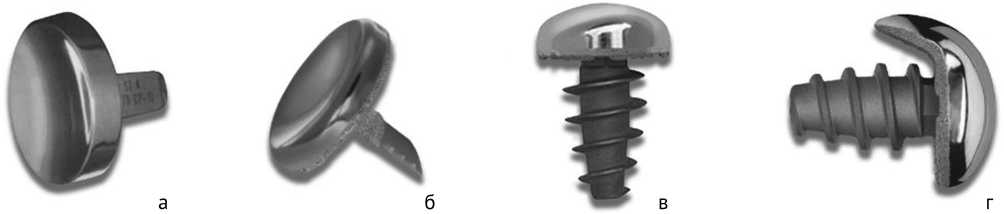
Рис. 2. Внешний вид металлических гемиэндопротезов 1 ПФС: а — гемиэндопротез 1 ПФС, дизайн Swanson, производство Wright Medical, Теннеси, США, 1986 г.; б — гемиэндопротез 1 ПФС, дизайн Townley, производство Wright Medical, Теннеси, США, 1986 г.; в — гемиэндопротез головки первой плюсневой кости HemiCap первого поколения, компания Arthrosurface, Массачусетс, США, 1998 г.; г — гемиэндопротез головки первой плюсневой кости HemiCap второго поколения, компания Arthrosurface, Массачусетс, США, 2012 г. [37]
K.F. Konkel et al. в 2009 г. провели ретроспективный анализ результатов лечения 33 пациентов с артрозом 1 ПФС, которым были установлены гемиэндопротезы. Средний период наблюдения составил 6 лет. У пациентов с ранними признаками артроза третьей степени был выявлен рецидив роста тыльного остеофита. По принятой в США шкале AOFAS (Шкала клинической оценки заболеваний стопы и голеностопного сустава Американской Ассоциации Ортопедов Стопы и Голеностопного Сустава) результаты лечения составили 67 баллов [18].
В 1998 г. также была разработана конструкция первого поколения для эндопротезирования головки плюсневой кости компанией Arthrosurface (Массачусетс, США) и названа HemiCap (рис. 2, в). Это двухкомпонентный имплант, суставная часть которого имела форму головки с кобальт-хромовой суставной поверхностью, а фиксирующий компонент представлял собой конический титановый винт для фиксации в плюсневой кости [35].
В 2012 г. компания Arthrosurface разработала имплантат второго поколения для головки первой плюсневой кости. Предыдущий имплантат HemiCap, используемый для гемиартропластики, был модернизирован и получил название HemiCap DF (Dorsal Flange) (рис. 2, г). В новой конструкции HemiCap DF используется тыльный козырек, предназначенный для улучшения тыльного сгибания первого пальца во время ходьбы. Тыльный козырек, который изгибается на поверхности головки первой плюсневой кости, также предотвращает частое послеоперационное осложнение — повторный рост остеофитов [36].
В 2021 г. P.H. Jørsboe et al. провели анализ 116 пациентов, которым ранее был установлен эндопротез HemiCap первого и второго поколения. Через 2 года, 4 года и 6 лет после операции приживаемость протеза составила 87 %, 83 % и 74 % соответственно. При среднем пятилетнем наблюдении у 47 пациентов тыльное сгибание — 45°. Функциональные результаты, оцененные по шкале AOFAS, были 77,2 ± 2,8 балла и по Визуальной Аналоговой Шкале (ВАШ) — 2,0 ± 1,6 балла [38].
Во времена роста популярности двухстержневых силиконовых имплантов также свершилась «революция» в создании двухкомпонентных несвязанных эндопротезов. Силиконовые эндопротезы выходили из строя, главным образом, вследствие чрезмерного износа и стесненной конструкции. С более глубоким пониманием биомеханических характеристик 1 ПФС возникла потребность в конструкции, которая учитывала бы весовые нагрузки, скольжение и разнонаправленную подвижность сустава. Поскольку 1 ПФС является шарнирным суставом, при сгибании проксимальной фаланги под углом более 30° его ось в горизонтальной плоскости смещается в тыльную сторону. Поскольку силиконовые имплантаты с двумя ножками не были адаптированы к нормальному физиологическому объему движений, аномальные нагрузки, приложенные к имплантату, в конечном итоге приводили к его разрушению [39]. В 1985 г. A.M. Zeichner попытался сконструировать шаровидный эндопротез из существующих в то время материалов, чтобы избежать эффекта поршневой кинематики, характерного для шарнирных имплантатов, и создать протез с переменной осью [40]. P.F. Merkle и T.P. Sculco в 1989 г. разработали имплант из титанового сплава и полиэтилена высокой плотности и использовали полиметилметакрилатный костный цемент для его фиксации. Их конструкция не включала интрамедуллярную ножку на плюсневом компоненте. Из-за высокой частоты расшатывания (54,5 %) два имплантата были удалены. Авторы пришли к выводу, что эндопротезирование 1 ПФС с цементной фиксацией не дало удовлетворительных результатов, и рекомендовали дальнейшие исследования для улучшения методов фиксации [41].
Лишь в 1989 г. R.D. Koenig разработал двухкомпонентную систему для замены 1 ПФС, аналогичную той, которая используется для замены коленного сустава. Компонент головки плюсневой кости имел интрамедуллярный стержень и был изготовлен из титанового сплава. Для сочленения с сесамовидными костями, несущими нагрузку, в его состав входила подошвенная поверхность, воспроизводящая мыщелки головки плюсневой кости. Фаланговый компонент изготовлен из полиэтилена сверхвысокой молекулярной массы с интрамедуллярным стержнем, и оба компонента устанавливали методом press-fit [42]. В настоящее время аналогичную систему Total Toe System выпускает компания Biomet (США, г. Варшава). Для нее характерны полностью полиэтиленовые или титановые фаланговые компоненты. Для улучшения интеграции в костномозговой канал производят плазменное напыление обеих ножек (рис. 3, а) [43].
В 1991 г. R.D. Koenig наблюдал 18 пациентов спустя 18 мес. после оперативного лечения, исследовал рентгенограммы для измерения межплюсневого угла, угла отведения большого пальца, длины первой плюсневой кости и определения положения импланта. Только в 7 случаях получено правильное положение эндопротеза и полная остеоинтеграция. В 12 случаях достигнут полный объем движения в 1 ПФС, а в одном случае при выявлении металлоза потребовалась ревизия. Впоследствии R.D. Koenig и L.R. Horwitz в 1996 г. опубликовали исследования 61 пациента за 5-летний послеоперационный период. У 80,5 % пациентов получены отличные результаты, и в 10 % случаев отмечены разной степени неудовлетворительные исходы [44].
В 1991 г. компания Orthopedic Bio-systems разработала имплант системы Bioaction Great Toe System. Данный эндопротез имеет плюсневый компонент, изготовленный из кобальт-хрома, и фаланговый компонент, изготовленный из титана и полиэтиленовой вставки. В настоящее время эта конструкция производится компанией Osteomed. R.S. Pulavarti et al. сообщили о 77 % удовлетворенных пациентов, в то время как у 23 % были выявлены рентгенологические признаки расшатывания и проседания импланта [45].
В 2019 г. на рынке появилась система Movement Great Toe System, произведенная в США (Integra, Нью-Джерси), — новый тотальный имплант (рис. 3, б). Компоненты анатомической формы имеют кобальтхромовую суставную поверхность. Для улучшения остеоинтеграции по задней поверхности эндопроте- за произведено титановое плазменное напыление. Конструкция ножки данного импланта отличается от других моделей, представленных на рынке. Цилиндрическая ножка с четырьмя ребрами обеспечивает улучшенную фиксацию и антиротационную стабильность. Для предотвращения повторного образования остеофитов плюсневый компонент имеет тыльный козырек. Компонент проксимальной фаланги содержит отверстия для швов на подошвенной части имплантата, что позволяет повторно прикрепить сгибательный аппарат в случае его повреждения. Эндопротез впервые имплантирован в январе 2018 г., и выпускается в четырех размерах [46].
M.D. Johnson в 2016 г. проанализировал 35 пациентов с артрозом 1-го ПФС спустя 2 года после эндопротезирования, проведенного с использованием системы Movement Great Toe System. Он выяснил, что 82 % пациентов были удовлетворены результатами по шкале PASCOM, а 62,9 % избавились от боли при ходьбе в обуви. Средний диапазон движений составил 57,6° при тыльном сгибании и 10,5° при подошвенном сгибании. Рентгенологических признаков расшатывания компонентов имплантата не было [47].
Керамические эндопротезы
В 1994 г. компания Moje Ceramic Implants (Petersperg, Германия) представила циркониевые керамические имплантаты для 1 ПФС. Плюсневой компонент имеет полусферическую форму, а фаланговый компонент — вогнутую. Их первоначальная конструкция включала два позиционирующих титановых винта для плюсневых и фаланговых компонентов, в то время как в современной конструкции используется метод press fit (рис. 3, в). Имплантат подвергают плазменному напылению с кристаллами апатита и фостерита для улучшения остеоинтеграции, он обладает очень хорошей биосовместимостью и превосходной устойчивостью к износу [48, 49].

Рис. 3. Внешний вид тотальных эндопротезов 1 ПФС: а — эндопротез системы Total Toe System, производство Biomet, Варшава, США,1989 г.; б — эндопротез системы Movement Great Toe System, производство Integra, Нью-Джерси, США, 2019 г.; в — керамический эндопротез фирмы Moje Ceramic Implants, Петерсбург, Германия, 2004 г. [51]
В 2020 г. M.T. Nagy et al. исследовали 30 пациентов после установки керамического тотального эндопротеза первого плюснефалангового сустава. Средний период наблюдения составил 81 ± 27 мес. после операции, средний диапазон пассивных движений сустава — 32° тыльного сгибания, средний балл по шкале AOFAS — 84 баллов. Довольны результатом 24 пациента (84 %). На последующих рентгенограммах выявлено изменение угла наклона эндопротеза, а также обнаружена миграция проксимального или дистального компонентов. В осложнения включен один случай раневой инфекции. Ревизия выполнена в 5 случаях (16 %) из-за расшатывания, миграции, подвывиха или разрушения ножки импланта. Приживаемость эндопротезов составила 92 % через 5 лет, 85 % — через 7 лет и 78 % — через 9 лет [50].
Гидрогелевые эндопротезы
Новый гидрогелевый имплант из поливинилового спирта (CARTIVA, Джорджия, США) получил одобрение Управления по санитарному надзору за качеством пищевых продуктов и медикаментов в июле 2016 г. (рис. 4) и был апробирован в Великобритании и Канаде. Оба исследования показали многообещающие результаты до выхода на рынок США. Имплант, изготовленный из гидрогеля поливинилового спирта, при установке действует как прокладка между первой плюсневой костью и основанием проксимальной фаланги. Поскольку поливиниловый спирт нетоксичен и не канцерогенен, его используют при производстве контактных линз и упаковочных материалов для пищевых продуктов. По своей способности сопротивляться нагрузкам он при давлении в 17 МПа имеет предельную прочность на растяжение, сравнимую с хрящом человека, а также аналогичное содержание воды [52, 53].

Рис. 4. Гидрогелевый эндопротез 1 ПФС из поливинилового спирта (CARTIVA, Джорджия, США, 2016 г.) [54]
В проспективном исследовании, выполненном в 2018 г., J. Baumhauer et al. сравнили синтетический гидрогелевый имплант с артродезом по безопасности и эффективности (артродез первого плюсне-фалангового сустава применяют для лечения тяжелых степеней артроза). По завершении 24-мес. исследования в обеих группах пациентов, перенесших как эндопротезирование гидрогелевым имплантом Cartiva, так и артродезирование, отмечено значительное снижение интенсивности боли по шкале ВАШ. Частота повторных операций в группе после эндопротезирования имплантом из синтетического хряща составила 11 %, что эквивалентно частоте повторных операций в группе артродеза первого плюснефалангового сустава (12 %). Имплант из гидрогеля сохранил функцию и тыльное сгибание (в среднем 29,7°). Рентгенологические сравнения не выявили расшатывания или разрушения импланта, хотя у двух пациентов в проксимальной фаланге образовалась периостальная киста [55, 56].
W. Lee et al. в течение 26 мес. исследовали 90 пациентов, перенесших установку гидрогелевого импланта. Средний бал по шкале ВАШ составлял 4,0, по шкале AOFAS — 64 балла. На послеоперационных обзорных рентгенограммах, проведенных через 4 нед. после операции, миграцию имплантата наблюдали в 60 % случаев, а при последующих осмотрах — в 90 %. Резорбция кости, развившаяся вокруг импланта, выявлена при рентгенографии у 50 % пациентов [57, 58].
В целом, концепция гидрогелевых эндопротезов выглядит многообещающей. Для предотвращения миграции протезов этой разновидности, тем не менее, требуется провести значительную модернизацию их конструкции.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Использование силиконовых эндопротезов обеспечило удовлетворительные функциональные результаты в 72 % случаев по шкале PASCOM. Наилучшего результата среди силиконовых имплантов достигло применение двуствольного эндопротеза Swanson с титановыми втулками. Использование металлических гемиэндопротезов в наилучшем варианте показало 74 % приживаемости импланта и 77 балов по шкале AOFAS при применении импланта HemiCup DF. Результаты применения тотальных металлических эндопротезов показали 82 % удовлетворительных результатов по шкале PASCOM после установки эндопротеза системы Movement Great Toe System. После использования керамических тотальных имплантов фирмы Moje Ceramic пациенты были удовлетворены в 85 % случаев. Применение гидрогелевых эндопротезов показало до 50 % неудовлетворительных результатов. Эндопротезирование 1 ПФС претерпело значительные изменения за последние шесть десятилетий, а достижения в области технологий способствовали прогрессивным изменениям в материалах и хирургической технике. Импланты нового поколения имеют более прочную конструкцию, анатомичную форму, улучшенную остеоинтеграцию, их изготавливают из наиболее износостойких материалов. Эти достижения обеспечили повышение удовлетворенности пациентов и увеличение срока службы эндопротезов. Количество ревизионных операций после эндопротезирования 1 ПФС на сегодняшний день уменьшается и сопоставимо с числом повторных операций после артродези-рования. Тем не менее, остается высокий процент осложнений после эндопротезирования 1 ПФС. Это свидетельствует о необходимости продолжения исследований и дальнейшей работы по усовершенствованию имплантов, чтобы сделать их более эффективными и удобными в использовании.
Список литературы Эволюция эндопротезирования первого плюснефалангового сустава
- Карданов А.А. Хирургическая коррекция деформация стопы. М.: Медпрактика-М; 2016:220.
- Хирургия стопы и голеностопного сустава. Многосторонний подход. Под ред. Хайера К.Ф., Берлета Г.Ч., Филбина Т.М. и др.; науч. ред. пер. О. А. Каплунов. Москва: ГЭОТАР-Медиа; 2022:528.
- Márquez JA, Oliva XM. Hallux rigidus: aetiology, diagnosis, classification and treatment. Rev esp cir ortop traumatol. 2010;54(5):321-328. doi: 10.1016/S1988-8856(10)70254-6
- Нурмухаметов М.Р. Принципы хирургического лечения больных с остеоартритом I плюснефалангового сустава. Научно-практическая ревматология. 2018;56(3):122-125. doi: 10.14412/1995-4484-2018-363-372
- Hamid KS, Parekh SG. Clinical Presentation and Management of Hallux Rigidus. Foot Ankle Clin. 2015;20(3):391-9. doi: 10.1016/j.fcl.2015.04.002
- Бобров Д.С., Слиняков Л.Ю., Ченский А.Д. и др. Деформирующий остеоартроз первого плюснефалангового сустава, или ригидный I палец стопы: клиника, диагностика и лечение (аналитический обзор литературы). Кафедра травматологии и ортопедии. 2014;(3):4-12.
- Brage ME, Ball ST. Surgical options for salvage of end-stage hallux rigidus. Foot Ankle Clin. 2002;7(1):49-73. doi: 10.1016/ s1083-7515(01)00004-3
- Turner WA, Merriman LM. Clinical Skills in Treating the Foot. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone Publ.; 2005:496.
- Sullivan MR. Hallux rigidus: MTP implant arthroplasty. Foot Ankle Clin. 2009;14(1):33-42. doi: 10.1016/j.fcl.2008.11.009
- Joyce TJ. Implants for the first metatarsophalangeal joint and prospective considerations. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2005;2(4):453-464. doi: 10.1586/17434440.2.4.453
- Stone OD, Ray R, Thomson CE, Gibson JN. Long-Term Follow-up of Arthrodesis vs Total Joint Arthroplasty for Hallux Rigidus. Foot Ankle Int. 2017;38(4):375-380. doi: 10.1177/1071100716682994
- Linklater JM. Imaging of sports injuries in the foot. AJR Am JRoentgenol. 2012;199(3):500-508. doi: 10.2214/AJR.12.8547
- Stokes IA, Hutton WC, Stott JR. Forces acting on the metatarsals during normal walking. J Anat. 1979;129(Pt 3):579-590.
- Santos Silva M, Rodrigues-Pinto R, Barros LH, Sousa A, Muras J. Arthrodesis versus Arthroplasty of the First Metatarsophalangeal Joint in the Treatment of Hallux Rigidus - A Comparative Study of Appropriately Selected Patients. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2020;55(1):40-47. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1700815
- Hallinan JTPD, Statum SM, Huang BK, et al. High-Resolution MRI of the First Metatarsophalangeal Joint: Gross Anatomy and Injury Characterization. Radiographics. 2020;40(4):1107-1124. doi: 10.1148/rg.2020190145
- Vulcano E, Chang Al, Solomon D, Myerson M. Long-Term Follow-up of Capsular Interposition Arthroplasty for Hallux Rigidus. Foot Ankle Int. 2018;39(1):1-5. doi: 10.1177/1071100717732124
- Perler AD, Nwosu V, Christie D, Higgins K. End-stage osteoarthritis of the great toe/hallux rigidus: a review of the alternatives to arthrodesis: implant versus osteotomies and arthroplasty techniques. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2013;30(3):351-395. doi: 10.1016/j.cpm.2013.04.011
- Konkel KF, Menger AG, Retzlaff SA. Results of metallic Hemi-Great Toe Implant for Grade III and early Grade IV hallux rigidus. Foot Ankle Int. 2009;30(7):653-660. doi: 10.3113/FAI.2009.0653
- Dos Santos AL, Duarte FA, Seito CA, et al. Hallux Rigidus: prospective study of joint replacement with hemiarthroplasty. Acta Ortop Bras. 2013;21(2):71-75. doi: 10.1590/S1413-78522013000200001
- Vanore J, O'Keefe R, Pikscher I. Complications of silicone implants in foot surgery. Clin Podiatry. 1984;1(1):175-198.
- Poutoglidou F, Drummond I, Ha J, et al. Thou Shalt Not Fuse: Implant Survival Outcomes And Complications Following Arthroplasty In Hallux Rigidus. J Foot Ankle Surg (Asia-Pacific). 2023;10(4):175-181. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10040-1316
- Ris HB, Mettler M, Engeloch F. Langzeitergebnisse mit der Silastik-Endoprothese nach Swanson am Grosszehengrundgelenk. Diskrepanz zwischen Klinik und radiologischem Befund. Zeitschr Orthop. 1988;126:526-529. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1044478
- Kampner SL. Total joint replacement in bunion surgery. Orthopedics. 1978;1(4):275-84. doi: 10.3928/0147-7447-19780701-03
- Kampner SL. Total joint prosthetic arthroplasty of the great toe--a 12-year experience. Foot Ankle. 1984;4(5):249-261. doi: 10.1177/107110078400400506
- Swanson AB, Lumsden RM, Swanson GD. Silicone implant arthroplasty of the great toe. A review of single stem and flexible hinge implants. Clin Orthop RelatRes. 1979;(142):30-43.
- Hetherington VJ, Cwikla PS, Malone M. Review of First Metatarsophalangeal Joint Implants. In: Hetherington VJ. (eds.) Textbook of Hallux Valgus and Forefoot Surgery. 2000:347-358.
- Gerbert J. Textbook of Bunion Surgery. 4th ed. London; Eurospan Publ.; 2012:388.
- Clough TM, Ring J. Silastic first metatarsophalangeal joint arthroplasty for the treatment of end-stage hallux rigidus. Bone Joint J. 2020;102-B(2):220-226. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.102B2.BJJ-2019-0518.R2
- Jarvis BD, Moats DB, Burns A, Gerbert J. Lawrence design first metatarsophalangeal joint prosthesis. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 1986;76(11):617-624. doi: 10.7547/87507315-76-11-617
- Hetherington VJ, Cuesta AL. Implant arthroplasty of the first metatarsophalangeal joint and alternatives. In Levy LA, Hetherington VJ (eds.) Principles and Practice of Podiatric Medicine. New York: Churchill Livingstone Publ.; 1990:1005.
- Dobbs B. LaPorta great toe implant. Long-term study of its efficacy. Student Research Group. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 1990;80(7):370-373. doi: 10.7547/87507315-80-7-370
- Granberry W, Schafer KA, McCormick JJ, Marks RM. Forefoot Success. Instr Course Lect. 2021;70:587-610.
- Joyce TJ. Implants for the first metatarsophalangeal joint and prospective considerations. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2005;2(4):453-464. doi: 10.1586/17434440.2.4.453
- Brage ME, Ball ST. Surgical options for salvage of end-stage hallux rigidus. Foot Ankle Clin. 2002;7(1):49-73. doi: 10.1016/ s1083-7515(01)00004-3
- Hasselman CT, Shields N. Resurfacing of the First Metatarsal Head in the Treatment of Hallux Rigidus. Tech Foot Ankle Surg. 2008;7(1):31-40. doi: 10.1097/BTF.0b013e318165c356
- Arthrosurface HemiCAP Resurfacing. In Wiesel SW. (ed.) Operative Techniques in Orthopaedic Surgery. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: LWW Publ.; 2015;4:135-146.
- Butterworth ML, Ugrinich M. First Metatarsophalangeal Joint Implant Options. ClinPodiatrMedSurg.2019;36(4):577-596. doi: 10.1016/j.cpm.2019.07.003
- J0rsboe PH, Pedersen MS, Benyahia M, et al. Mid-Term Functionality and Survival of 116 HemiCAP® Implants for Hallux Rigidus. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2021;60(2):322-327. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2020.10.010
- Park YH, Jung JH, Kang SH, et al. Implant Arthroplasty versus Arthrodesis for the Treatment of Advanced Hallux Rigidus: A Meta-analysis of Comparative Studies. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2019;58(1):137-143. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2018.08.045
- Zeichner AM. Component first metatarsophalangeal joint replacement. A new approach. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 1985;75(5):254-257. doi: 10.7547/87507315-75-5-254
- Merkle PF, Sculco TP. Prosthetic replacement of the first metatarsophalangeal joint. Foot Ankle. 1989;9(6):267-71. doi: 10.1177/107110078900900603
- Boberg JS: Koenig total toe implant arthroplasty. In: Vickers NS, (ed.) Reconstructive Surgery of the Foot and leg, Update 96. Tucker, Ga: Podiatry Institute Publ.; 1996:136-138.
- Koenig RD. Revision arthroplasty utilizing the Biomet Total Toe System for failed silicone elastomer implants. J Foot Ankle Surg. 1994;33(3):222-227.
- Koenig RD, Horwitz LR. The Biomet Total Toe System utilizing the Koenig score: a five-year review. J Foot Ankle Surg. 1996;35(1):23-26. doi: 10.1016/s1067-2516(96)80008-1
- Pulavarti RS, McVie JL, Tulloch CJ. First metatarsophalangeal joint replacement using the bio-action great toe implant: intermediate results. Foot Ankle Int. 2005;26(12):1033-1037. doi: 10.1177/107110070502601206
- Bartak V, Hert J, Stedry J, et al. Long-term results of total joint arthroplasty and phalangeal hemiarthroplasty of the first metatarsophalangeal joint using the ToeFit Plus™ system. Foot Ankle Surg. 2022;28(1):56-61. doi: 10.1016/j.fas.2021.01.014
- Johnson MD, Brage ME. Total Toe Replacement in the United States: What Is Known and What Is on the Horizon. Foot Ankle Clin. 2016;21(2):249-266. doi: 10.1016/j.fcl.2016.01.004
- Arbuthnot JE, Cheung G, Balain B, et al. Replacement arthroplasty of the first metatarsophalangeal joint using a ceramic-coated endoprosthesis for the treatment of hallux rigidus. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2008;47(6):500-504. doi: 10.1053/j. jfas.2008.08.007
- Dawson-Bowling S, Adimonye A, Cohen A, et al. MOJE ceramic metatarsophalangeal arthroplasty: disappointing clinical results at two to eight years. Foot Ankle Int. 2012;33(7):560-564. doi: 10.3113/FAI.2012.0560
- Nagy MT, Walker CR, Sirikonda SP. Second-Generation Ceramic First Metatarsophalangeal Joint Replacement for Hallux Rigidus. Foot Ankle Int. 2014;35(7):690-8. doi: 10.1177/1071100714536539
- Johnson MD, Brage ME. Total Toe Replacement in the United States: What Is Known and What Is on the Horizon. Foot Ankle Clin. 2016;21(2):249-66. doi: 10.1016/j.fcl.2016.01.004
- Richter M. Total joint replacement of the first metatarsophalangeal joint with Roto-Glide as alternative to arthrodesis. Fuß Sprunggelenk. 2019;17(1):42-50. doi: 10.1016/j.fuspru.2019.01.003
- Daniels TR, Younger AS, Penner MJ, et al. Midterm Outcomes of Polyvinyl Alcohol Hydrogel Hemiarthroplasty of the First Metatarsophalangeal Joint in Advanced Hallux Rigidus. Foot Ankle Int. 2017;38(3):243-247. doi: 10.1177/1071100716679979
- Glazebrook M, Morash J, Alhadhoud M, Daniels TR. Preliminary Experience With Polyvinyl Alcohol Hydrogel Implant for Pathology of the Second Metatarsal Head. Foot Ankle Int. 2019;40(11):1304-1308. doi: 10.1177/1071100719866700
- Baumhauer JF, Singh D, Glazebrook M, et al. Prospective, Randomized, Multi-centered Clinical Trial Assessing Safety and Efficacy of a Synthetic Cartilage Implant Versus First Metatarsophalangeal Arthrodesis in Advanced Hallux Rigidus. Foot Ankle Int. 2016;37(5):457-469. doi: 10.1177/1071100716635560
- Eble SK, Hansen OB, Chrea B, et al. Clinical Outcomes of the Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) Hydrogel Implant for Hallux Rigidus. Foot Ankle Int. 2020;41(9):1056-1064. doi: 10.1177/1071100720932526
- Shimozono Y, Hurley ET, Kennedy JG. Early Failures of Polyvinyl Alcohol Hydrogel Implant for the Treatment of Hallux Rigidus. Foot Ankle Int. 2021;42(3):340-346. doi: 10.1177/1071100720962482
- Lee W, Wang C, Prat D, et al. Patient Satisfaction Following Hallux Rigidus Treatment With a Synthetic Cartilage Implant. Foot Ankle Spec. 2023;16(6):527-536. doi: 10.1177/19386400211001993


