Кинезин: механика молекулярного мотора
Автор: Шестаков Д.А.
Журнал: Российский журнал биомеханики @journal-biomech
Статья в выпуске: 4 (66) т.18, 2014 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Молекулярные наномоторы обеспечивают самые разные механизмы биологической подвижности. Одним из наиболее распространенных и перспективных для изучения является кинезин - белок, служащий, в частности, для внутриклеточной транспортировки «грузов» вдоль особых молекулярных нитей - микротрубочек, образованных белком тубулином. Взаимодействуя с тубулином, он принимает участие в делении клетки, разборке микротрубочек, движении жгутиков и ресничек. Кинезин по структуре моторного домена и биохимическому циклу во многом схож с другим моторным белком - миозином, играющим важнейшую роль в мышечном сокращении. Энергию для работы обоих моторов доставляет реакция гидролиза АТФ. С другой стороны, кинезин имеет также существенные отличия от миозина в общем строении и фазах биомеханического взаимодействия. В наши дни установлено, как именно кинезин связывается с тубулином, как обеспечивается его последовательное и длительное (процессивное) движение по микротрубочкам, какую силу и скорость он развивает на расстояниях, измеряемых тысячами его одиночных шагов. В то же время многие вопросы, относящиеся к механике кинезинового мотора, еще находятся в процессе обсуждения - детали передачи информации от одной глобулярной головы к другой, существование промежуточных состояний биомеханического цикла, природа обратных шагов кинезина. Для выяснения этих и других деталей и дальнейшего анализа проводят биомеханические исследования, строят математические модели, в которых применяют методы механики сплошной среды, теоретической механики, математической статистики. Настоящий обзор имеет целью собрать в одной статье актуальные сведения о кинезине и его взаимодействии с тубулином и представить их в контексте современной биомеханики.
Кинезин, тубулин, молекулярный мотор, наномеханика
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/146216151
IDR: 146216151 | УДК: 532.51:577.35:591.112.3
Текст научной статьи Кинезин: механика молекулярного мотора
Строение тубулина и кинезина и краткая история их исследования
Предметом рассмотрения в этой работе послужит один из наиболее интересных и привлекательных для исследования моторных белков – кинезин, необходимый для решения различных задач молекулярной подвижности, прежде всего – перевозки органелл по внутриклеточным магистралям – микротрубочкам, состоящим из белка тубулина.
Сами микротрубочки исследователи впервые обнаружили очень давно [113]. Правда, в то время у них еще не было названия, выглядели они в доступном тогда масштабе примерно так же, как могла бы выглядеть странная, пучками расходящаяся в стороны сеть дорог ночного города с борта самолета. Лишь через много лет был идентифицирован и назван тубулином строительный материал, из которого сделаны микротрубочки [11, 37]. Еще позже были получены с атомным разрешением структуры
Шестаков Дмитрий Алексеевич, к.ф.-м.н., с.н.с. лаборатории биомеханики, Москва гетеродимеров тубулина [81], кирпичиков, которыми эти дороги вымощены. Гетеродимер представляет собой очень стабильную, нековалентно связанную конструкцию, состоящую из α- и β-тубулина – чрезвычайно близких по строению мономеров (примерно 450 аминокислотных остатков, 55 кДа), каждый из которых содержит молекулу гуанозинтрифосфата (ГТФ) [71]. В процессе сборки димеров в длинные нити – протофиламенты – ГТФ, содержащийся в β-тубулине, гидролизуется, так что в микрофиламентах β-тубулин содержит ГДФ (гуанозиндифосфат) [27]. Небольшие различия в строении α- и β-тубулина влияют на его взаимодействие с кинезином. Известно, что большинство кинезинов движутся по мономерам β-тубулина [75] от центра клетки к периферии, в то время как немногие представители кинезинного семейства, движущиеся в обратном направлении, бывают менее разборчивы в связях и формируют также комплексы с α-тубулином [110]. Конец микротрубочки, который окаймляет β-тубулин, называется плюс-концом, другой конец содержит α-тубулин и называется минус-концом. Микротрубочки преимущественно собираются на плюс-конце и разбираются на минус-конце [14].
Микротрубочки – это цилиндры, которые образованы соединившимися протофиламентами. Поскольку соединение происходит с осевым сдвигом, тубулин микротрубочек образует трехзаходную спираль со смещением 0,92 нм [4] (см. рис. 1). Хотя микротрубочки in vitro образуются из 10–16 протофиламентов [19, 76], а в некоторых случаях способны даже формировать кластеры [109], все же стандартная микротрубочка состоит из 13 нитей тубулина [102]. Сборка микротрубочек начинается в центросоме, от которой они отходят в сторону периферических областей клетки. Их плюс-конец направлен к мембране [3]. Микротрубочки вместе с нитями актина, служащими для более медленной и точной доставки грузов внутри клетки, а также белками промежуточных филаментов формируют клеточный цитоскелет.
Микротрубочки выполняют транспортную функцию, кроме того, они играют важную роль в процессе деления клетки. Именно они образуют волокна веретена деления, которое крепится к кинетохору, особой структуре, связанной с хромосомой. При делении два веретена отодвигаются друг от друга, образуя два новых центра будущих клеток [44]. В этом движении тоже непосредственно участвует кинезин.
Кинезин, наряду с миозином и другими моторными белками, обеспечивает самые разные виды биологической подвижности. В начале 80-х гг. прошлого века были получены микрофотографии цитоскелета, на которых были ясно видны «поперечные мостики» ( cross-bridges ) между микротрубочками тубулина и органеллами
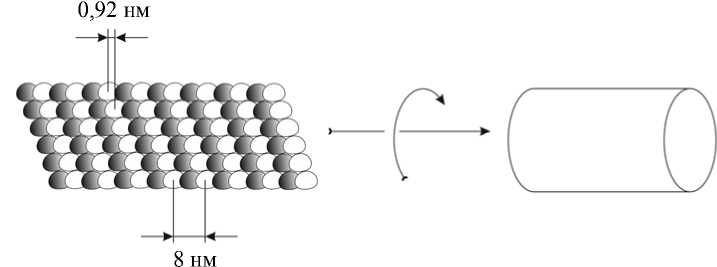
Рис. 1. Схема сборки микротрубочек. Слева показаны протофиламенты, составленные из димеров α-тубулина (незакрашенные мономеры) и β-тубулина (закрашенные мономеры). Указаны направление сборки (сворачивания) листа протофиламентов в микротрубочку, а также размер одного димера (слева внизу) и шаг спирали (слева вверху), возникающей вследствие сдвига протофиламентов при их латеральном соединении друг с другом клетки [47]. Тогда же были высказаны предположения, что некоторые из этих мостиков являются белками внутриклеточного транспорта [47, 48]. Лишь в 1985 г. первый из них был идентифицирован Брэйди [12] и Вэйлом [106] как белок, служащий для быстрого аксонного транспорта. Он получил название кинезин. Год спустя Кузнецов и Гельфанд показали, что он является АТФазой, причем скорость гидролиза АТФ многократно увеличивается в присутствии тубулина, как было показано ранее для миозиновой АТФазы, ускоряемой актином [67].
Лишь десятилетие спустя структура моторного домена человеческого и крысиного кинезина была определена посредством рентгеновской кристаллографии [64, 89]. Этот вид кинезина, впоследствии получивший название обычного (англ. conventional ) кинезина, или кинезина-1, был наиболее легко извлекаем и доступен для эксперимента [16]. Позднее стало ясно, что кинезин гидролизует ровно одну молекулу АТФ [23, 95] на один рабочий шаг и что шаг этот равен расстоянию между димерами тубулина – 8 нм [98], что одна молекула кинезина способна осуществлять процессивное (длительное и непрерывное) движение вдоль микротрубочки, перенося грузы со скоростью порядка 900 нм/с [96] на расстояния, измеряемые микрометрами [104], т.е. сотнями шагов.
С помощью дальнейших исследований было открыто множество белков, взаимодействующих с микротрубочками, которые необходимо было систематизировать и классифицировать. Так возникло «суперсемейство» кинезинов, состоящее из 14 классов – от кинезина-1 до кинезина-14. Новая классификация была принята и утверждена в 2004 г. [26, 69].
Все кинезины содержат глобулярные «головы» – моторные домены ( ≅ 40 кДа, 350 аминокислотных остатков), в которых сосредоточены активные центры взаимодействия с тубулином и субстратом или продуктами гидролиза АТФ, жесткие суперспиральные ( coiled coil ) тяжелые цепи, а также легкие цепи, как правило, формирующие «хвост», к которому крепятся грузы (каргосвязывающий участок) [51]. Подвижный шарнирный участок, соединяющий головы с тяжелыми цепями, называется нек-линкером (дословно «шейной застежкой»). Большая часть кинезинов ориентирована на движение от центра клетки к периферии – их называют N -кинезинами, поскольку моторный домен, взаимодействующий с тубулином, находится у них со стороны N -конца молекулы. В то же время С -кинезины, члены класса кинезина-14 (также известного как Ncd -белок), перевозят грузы в обратном направлении, и у них моторный домен находится в C -конце молекулы [88, 91]. Выделяют также особый вид кинезинов – M -кинезины (семейство кинезина-13), у которых моторный домен расположен в центре. Этот мотор участвует в разборке микротрубочек [78]. Особый интерес представляет кинезин-5, образующий гетеродимеры, у которых по два моторных домена расположены с обеих сторон димера. Крепясь к двум различным микротрубочкам, он раздвигает их друг относительно друга – это необходимо во время деления клетки, когда требуется «растащить» в разные стороны два будущих ядра новых клеток [32, 59]. Хвосты кинезинов могут отличаться в зависимости от того, какие грузы они перевозят [94]. Различают также быструю транспортировку органелл по аксону и более медленную перевозку других органелл и белков цитоскелета [49]. Интересно, что кинезин-1, как показывают исследования, принимает участие как в быстрой, так и в медленной транспортировке. Обсуждаются механизмы, управляющие его скоростью [101].
Кинезин также участвует в движении ресничек [82] и жгутиков [8], переносит флюоресцентные белки внутри светящихся клеток – меланофоров [85], присутствует также в растениях и грибах. Сегодня известно около 70 атомных структур моторных доменов различных видов кинезина из почти всех его семейств.
Сходство и отличия кинезина и миозина. Биохимический И МЕХАНИЧЕСКИЙ ЦИКЛЫ
Подобно тому, как кинезин взаимодействует с тубулином, другой важнейший моторный белок миозин взаимодействует с актином, играя ключевую роль в мышечном сокращении и других типах актиновой подвижности [92]. Оба мотора чрезвычайно эффективны – и миозин, и кинезин обеспечивают КПД 50% и выше [9, 97]. И мышечный миозин-2, и немышечный миозин-5, и миозины некоторых других семейств имеют две глобулярные головы, как и являющийся основным предметом этого обзора «обычный» кинезин-1. И так же, как кинезин-1, «шагает», переставляя свои головы по мономерам тубулина, миозин-5 движется вдоль нитей актина, перевозя груз [93]. Оба белка при этом гидролизуют АТФ. Более того, уместна аналогия, по которой внутриклеточная «посылка», доставленная «поездом» (кинезином) по скоростным магистралям (тубулину) до «узловой станции», там может помещаться на скромный «грузовичок» (миозин-5), который по «пыльной проселочной дорожке» (актину) довозит груз до конечного адресата [13]. При этом миозин-5 имеет вдвое большие, чем у кинезина, моторные домены, вчетверо больший шаг, но вдевятеро меньшую скорость [18]. Однако возникает вопрос, насколько же в самом деле схожи и различны миозин и кинезин.
В первую очередь в глаза бросается структурное сходство моторных доменов этих белков, в особенности их активных центров, в которых происходит цикл гидролиза АТФ, т.е. присоединение АТФ, собственно гидролиз и сброс его продуктов – АДФ и неорганического фосфата [64]. Понятно, что в моторных белках, «топливом» для которых служат молекулы АТФ, этапы биохимического цикла непосредственно связаны с изменениями в пространственной конформации. В глобулярных головах таких белков имеются участки, чувствительные к присутствию нуклеотидов и связанных с ними ионов магния. Они должны различать α-, β- и γ -фосфаты и передавать «информацию» об их присутствии посредством особых «переключателей» в другие части моторного домена, вызывая геометрические, а в конечном счете и механические изменения. Именно в структуре этих участков обнаружены четыре консервативных мотива, образующих гибкую фосфатную петлю ( P-loop ), участвующую в связывании фосфата, а также упомянутые выше «переключатели» ( switch I и switch II) [88, 107]. Эти мотивы в кинезине и миозине не только состоят из тех же аминокислотных остатков, но и сходно взаиморасполагаются в пространстве и крепятся к одинаковым семизаходным β -листам, служащим каркасом всего мотора. Перечисленное объясняет сходство в механизме силогенерации [63]. Авторы работы [65] полагают, что сходство в строении кинезина и миозина, по всей видимости, указывает на наличие у них предков – G-белков, участвующих в передаче стимулов внутрь клетки и использующих энергию гидролиза ГТФ. Малые изменения, происходящие в нуклеотидном кармане, впоследствии транслируются в масштабные преобразования. В кинезине это перестройка нек-линкера (в русскоязычной литературе используют неспецифический термин «шарнирный участок»), звена между глобулярной головой молекулы и ее спиральной «шеей» [84]. В миозине это перемещение «конвертера» и вызванный им поворот «рычага» ( lever arm ) [53, 83].
При всем сходстве миозина и кинезина мы обнаружим разительные отличия в динамике их взаимодействия с актином и тубулином. Биохимический цикл одинаков: присоединение АТФ к пустому нуклеотидному карману, затем гидролиз, затем сброс фосфата и наконец сброс АДФ. Однако для миозина конформационная перестройка, ведущая к генерации силы, связана со сбросом фосфата [7, 72], в то время как для кинезина – с присоединением АТФ [30, 42, 46]. Пока у миозина открыт нуклеотидный карман, остается закрытым центр связывания с актином [52]. Поэтому миозин
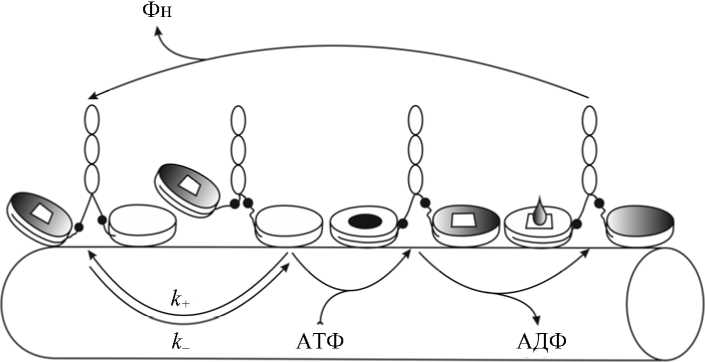
Рис. 2. Схема биомеханического цикла взаимодействия кинезина и тубулина (микротрубочки). Направление движения кинезина – слева направо. Стрелками показаны направления переходов, а также присоединение АТФ и сброс продуктов ее гидролиза. Обозначены константы скоростей перехода между состояниями, находящимися в динамическом равновесии. Одна из голов димера кинезина (в тексте – «передняя») на всех стадиях цикла не закрашена, а другая (в тексте – «задняя») имеет градиентную окраску. Также непосредственно на моторных доменах показаны: АТФ – черный эллипс, АДФ – белый четырехугольник, неорганический фосфат (Фн) – градиентно окрашенная капля. Маленькие черные круги приблизительно показывают характерную позицию шарнирной связи – она либо «пристегнута» к моторному домену (черная линия вдоль профиля глобулярной головы), либо более свободно «болтается» (зигзагообразная линия вне головы)
связывает АТФ и отсоединяется от актина, закрывает карман и гидролизует молекулу АТФ в отсоединенном состоянии. В этом состоянии сброс продуктов гидролиза затруднен, и миозин способен связываться с актином лишь слабо и непрочно. Прочное связывание с актином возможно лишь после открытия нуклеотидного кармана и перестройки актин-связывающей поверхности миозина. Формирование более прочной связи с актином приоткрывает нуклеотидный карман и позволяет сбросить фосфат, что сопровождается силогенерацией и открывает путь для сброса АДФ [36]. Совершенно иначе ведет себя кинезин [3] (рис. 2). В его случае сброс фосфата ведет к ослаблению и в дальнейшем к разрыву связи с тубулином [25]. Напротив, следующий за этим сброс АДФ открывает центр связывания с тубулином и способствует прочному присоединению свободной головы кинезина к микротрубочке [61]. Присоединение АТФ влечет гидролиз и (через нек-линкер) силогенерацию [87]. При этом открывается карман и становится возможен сброс фосфата. Наиболее сильная связь миозина с актином достигается в состоянии ригора, т.е. при отсутствии нуклеотидов в кармане. Cамая же прочная связь тубулина с микротрубочкой имеет место не только в отсутствие нуклеотидов, но и в присутствии АТФ [24]. Стоит заметить, что Тейлор, открывший вместе с Лимном основные фазы актин-миозиновой АТФазы, двадцать с небольшим лет спустя стал одним из главных исследователей кинетики взаимодействия кинезина с тубулином и нуклеотидами.
Механика ходьбы кинезина по тубулину
Прежде чем продолжить, хочу извиниться перед читателем за использование довольно странной терминологии, которую автор не придумал и которая с непривычки может вводить в заблуждение. Традиционно те части кинезина, которые соединяются с тубулином, называют головами, а часть, к которой крепится груз, – хвостом. В то же время очевидной аналогией движения кинезина по тубулину является ходьба, при которой моторные домены служат ногами, а легкие цепи, удерживающие груз, – головой. В результате возникает некоторая путаница, и перед нашим мысленным взором предстает нелепое существо, прогуливающееся на двух головах, задрав кверху хвост. Тем не менее именно такой образ нужно иметь перед глазами, читая этот раздел. В англоязычной литературе для обозначения видов походки кинезина используют еще и термин «hand-over-hand», т.е. «рука-через-руку» – в такой ситуации моторные домены могут в пределах одной статьи предстать и головами, и ногами, и руками [57]. Введение этого термина могло бы, как кажется автору, окончательно запутать читателя, а потому этот термин не используется в данном обзоре. В данном исследовании принято, что области кинезиновых моторов будут относиться к головкам.
Как именно происходит движение двухголового кинезина по микротрубочке? Как было упомянуто выше, каждый полный цикл кинезина происходит благодаря гидролизу одной молекулы АТФ и продвигает его на расстояние 8 нм. В течение нескольких лет различными авторами выдвигались аргументы в пользу существования неких промежуточных «полушагов» [22, 80], но впоследствии доказательства, подтверждающие эти гипотезы, были объяснены неточностями в интерпретации данных [15, 111], так что сегодня мы можем не уделять серьезного внимания этим гипотезам.
Немало споров в свое время вызвал и вопрос о том, какая «походка» присуща шагающему кинезину. Вполне возможными представляли три варианта: 1) симметричная ходьба – одна голова переступает через другую, ведущая и ведомая головы меняются местами при каждом следующем шаге, шаги при этом симметричны и одинаковы; 2) асимметричная ходьба – то же, что и в первом случае, но шаги разных голов механически отличаются; 3) «приволакивание» – одна голова все время является ведущей, а ведомая приставляется к ней после каждого шага.
Противоречивые, на первый взгляд, экспериментальные данные подтверждали возможность существования каждого из этих вариантов. Было установлено, что кинезин-1 не поворачивает свою жесткую суперспираль при ходьбе [54]. Это свидетельствовало о правильности третьего варианта. С другой стороны, эксперименты с флюоресцентными метками показали, что шаг каждой из голов при ходьбе составляет 16 нм, а значит головы по очереди перешагивают через один димер тубулина [115]. Это было серьезным аргументом в пользу первого варианта. Наконец, второй вариант мог бы объяснить оба феномена. К тому же были получены данные, указывающие на то, что кинезин якобы «прихрамывает» на одну голову при ходьбе [5, 60].
С появлением более точной информации картина начала проясняться, и в 2007 г. Блок предложил так называемую «консенсусную» модель, призванную согласовать разные позиции [10]. Спустя 7 лет можно сказать, что споры сегодня вызывают более мелкие детали (см. ниже), но большинство исследователей в общих чертах склоняются к следующему.
Рассмотрим вначале два состояния кинезиновой молекулы, в которых передняя голова свободна от нуклеотида и жестко связана с тубулином, в то время как задняя содержит АДФ и либо отсоединена от тубулина, либо слабо связана с ним. Лишь недавние опыты показали, что эти два состояния находятся в динамическом равновесии с константой k + / k – = 1,4 (здесь k + – скорость присоединения головы, содержащей АДФ, рис. 2) [103]. Но присоединенная вторая голова создает напряжение в области нек-линкера (см. пункт 2), а если она отсоединена, шарнирные участки двух голов оказываются близко друг к другу [103]. Раньше многие полагали, что напряжение нек-линкера на задней голове препятствует связыванию передней с АТФ [43, 86].
Однако результаты недавних экспериментов с флуоресцентными метками позволяют предположить, что именно близость нек-линкеров двух голов открывает возможность для присоединения АТФ к жестко прицепленной голове. Эта близость невозможна, пока задняя голова связана с микротрубочкой [103]. Поэтому лишь при ее отсоединении становится возможным следующий шаг цикла. Мы видим на этом примере, как «информация» о состоянии одного моторного домена передается другому внутри димера кинезина.
На следующем шаге цикла лишь тогда, когда задняя голова отцеплена, к передней присоединяется АТФ, в результате чего высвобождается энергия, необходимая для практически необратимой перестройки ее нек-линкера, – он «упаковывается» или, как говорят, «застегивается», прочно связываясь с головой [6, 84]. Эта перестройка ведет к геометрическим изменениям – сдвигу свободной головы на 1–2 нм в сторону плюс-конца микротрубочки – силогенерирующему шагу кинезина. Теперь эта голова оказывается в ситуации поиска возможного места присоединения. Существует ненулевая вероятность ее присоединения обратно к прежнему месту, но эта вероятность ничтожна, поскольку «застегнутый» нек-линкер другой головы создает механическое напряжение, делающее присоединение свободной головы к новому «впереди стоящему» мономеру тубулина энергетически на порядки более выгодным [99]. Получается, что, хотя свободная голова под действием броуновских частиц может отклоняться в любую сторону, имеется физическое препятствие, своего рода храповик, запрещающее ей движение назад. Этот феномен, наблюдаемый здесь на практике, давно описан в научной литературе как мысленный эксперимент под названием «броуновский храповик» [33], частный случай «демона Максвелла» («броуновский храповик» как термин для описания миозин-актинового взаимодействия впервые предложил Хаксли [56]). Заметим, что весь процесс, начиная с захвата АТФ передней головой и заканчивая присоединением бывшей задней головы к новому мономеру тубулина, происходит в разы быстрее, чем другие этапы механохимического цикла кинезина [15], что, очевидно, способствует его высокой процессивности, поскольку вероятность того, что обе головы окажутся отсоединенными от тубулина, пренебрежимо мала.
На следующем шаге обе головы связаны с тубулином. Хотя бывшая «задняя» голова по-прежнему содержит АДФ, бывшая «передняя» голова теперь связана с АТФ. Это создает механическое напряжение, которое препятствует присоединению АТФ к сбросившей АДФ голове до тех пор, пока АТФ в другой голове не будет гидролизован [43]. Сброс фосфата с бывшей передней головы довершает картину и завершает цикл ходьбы.
В предложенной схеме обе головы равноправны и последовательно меняются ролями. Эта схема помогает объяснить, почему кинезин способен, не отрываясь от микротрубочки, преодолевать столь большие расстояния, сохраняя при этом направление движения вдоль одного и того же протофиламента микротрубочки.
К ИНЕЗИН ПОД НАГРУЗКОЙ : СИЛА И СКОРОСТЬ
Механические свойства кинезина изучали по-разному. С помощью оптической ловушки исследовали поведение одиночных молекул. Нагружая нити тубулина, смотрели на поведение кинезина, наблюдали за его способностью делать обратные шаги. Проанализируем эти эксперименты подробнее.
Прежде всего у исследователей возникло естественное желание определить силу, которую способна развивать одна молекула кинезина-1. Для этого, например, прикрепляли микротрубочку к измерителю нагрузки посредством материала с известной жесткостью, а после давали молекулам кинезина, приклеенным к подложке, эту трубочку тянуть [77]. В других экспериментах использовали полистироловые микронные шарики, к поверхности которых прикрепляли молекулы кинезина. Шарики помещали в оптическую ловушку, т.е. удерживали на месте при помощи светового давления лазерных лучей. Далее, в непосредственной близости от шариков располагали микротрубочку, присоединяясь к которой одиночные молекулы кинезина развивали усилие, фиксируемое оптической ловушкой по отклонению шарика [108]. Со временем были разработаны компьютеризованные оптические ловушки с двумерной обратной связью [68]. Когда молекула кинезина находится в процессе движения по микротрубочке, оптическая ловушка может создавать силу, действующую в противоположном направлении, уменьшая скорость движения вплоть до полной остановки. С помощью разных методов разными исследователями был получен один результат: сила, которую нужно приложить, чтобы остановить одну молекулу кинезина, или, другими словами, максимальное усилие, которое способен развить кинезин, составляет 5–7 пН [22, 62, 108].
При этом зависимость силы от скорости в самом общем виде можно записать при помощи трехпараметрического отношения в котором v0 - скорость при нулевой силе (= 650-800 нм/с), а Fs - сила, нужная для полной остановки [66]. Параметр w задает степень кривой и может отличаться для разных серий данных. К примеру, данные, полученные с использованием кинезина-1 из бычьего мозга, дают почти линейную зависимость (w « 1, [55]), в то время как данные для кинезина-1 кальмара могут быть хорошо приближены кривой с параметром w = 2,5 [108].
Позже для измерения силы и скорости кинезина применили в некотором смысле обратную методику. Вместо того чтобы крепить к искусственно сделанным шарикам кинезин, шарик с магнитными свойствами закрепляли на плюс-конце микротрубочки. Далее кинезин, приклеенный к стеклу, начинал взаимодействовать с тубулином, толкая микротрубочку в сторону от плюс-конца к противоположному минус-концу. При помощи магнитного поля воздействовали на шарик, создавая силу противоположного направления. Таким способом измеряли силу и скорость кинезина. Чтобы оценить среднюю дистанцию между участвующими в движении микротрубочки молекулами кинезина, направление магнитного поля меняли на противоположное. При этом микротрубочка сгибалась под углом почти 90º в том месте, где она крепилась к первой молекуле кинезина. Остальная часть трубочки продолжала движение пока не проезжала мимо следующей активной молекулы, после чего место сгиба микротрубочки перемещалось. Так оценивали кривую сила–скорость в расчете на одну молекулу. Данные соответствовали кривой (1) с параметром w = 1,8 ± 0,4, что свидетельствует о независимой работе отдельных моторов [31].
Особый интерес вызывают эксперименты с обратными шагами кинезина. Давно было известно, что изредка кинезин может совершить обратный шаг [97]. Однако эксперименты с приложением нагрузки показали, что чем выше нагрузка, тем больше вероятность обратного шага [15, 80]. Когда же нагрузка превышает силу остановки (более 10 пН), кинезин обретает способность к медленному процессивному, т.е. последовательному и достаточно долгому движению в обратном направлении [15]. Этот факт позволил предположить, что обратное движение кинезина сопровождается полным разворотом и в биохимическом цикле, т.е. сопряжено с реакцией синтеза АТФ в моторном домене, как это в самом деле происходит в другом молекулярном моторе F 1 [58].
Были проведены эксперименты, позволившие оценить, например, влияние концентрации АТФ на скорость, силу и процессивность обратных шагов [15, 20, 34]. Многие поставили под сомнение гипотезу обратного цикла [10, 41]. Все это породило длительную дискуссию, в ходе которой гипотеза не подтвердилась. Выяснилось, в частности, что и в отсутствие каких-либо нуклеотидов кинезин совершает последовательное движение назад, если приложить к нему достаточную возвращающую силу. Также и последовательное движение вперед возможно при приложении большой тянущей силы без нуклеотидов [114]. Эти и другие данные заставляют сегодня предлагать иные модели, чтобы объяснить обратные шаги кинезина [17, 20, 57]. Наиболее простая идея состоит в том, что большая внешняя сила компенсирует напряжение, создаваемое застегнутым нек-линкером головы, присоединившей АТФ (см. предыдущий раздел). Тем самым результат броуновского поиска сдвигается в сторону обратного перехода, после чего за достаточное время становится вероятен сброс АДФ. Это вызывает сильное связывание задней головы с тубулином и ведет к следующей фазе обратного шага.
Следует признать, впрочем, что сегодня вопрос о механике обратного шага еще не закрыт.
Математические модели
Следует сказать несколько слов о математических моделях, используемых для изучения кинезинового мотора. В экспериментах in vitro , описанных выше, легко определять хорошо видимую в микроскоп скорость движения микротрубочек или прикрепленных к кинезину микроскопических шариков. Однако для отыскания силы кинезиновой молекулы в соотношении (1) приходится порой решать нетривиальные механические задачи. Например, в экспериментах [38] микротрубочку одним концом (отрицательно заряженным) крепили к приборному стеклу. С плюс-концом взаимодействовала молекула кинезина, развивая тем самым сжимающее усилие. Поскольку эта сила превышала критическую силу Эйлера, прямолинейная конфигурация микротрубочки теряла устойчивость, и она изгибалась (рис. 3). Чтобы рассчитать силу, вызывающую наблюдаемый в микроскоп изгиб микротрубочки, решали задачу об изгибе упругого стержня, сжатого по оси. Использовали уравнение [1]
0"( 5 ) = e2sin (0( 5 )-фf), (2)
где в = 4/ \р |2 / ( EI ) 2 ; 5 - натуральный параметр кривой, совпадающей с осью микротрубочки; 0 - угол между первоначальной осью прямой трубочки и касательной в данной точке изогнутой микротрубочки (рис. 3), а ф f - угол между той же осью и направлением вектора силы F ; EI - изгибная жесткость микротрубочки, которую определяли по изменению формы микротрубочек вследствие броуновских колебаний [39].
Уравнение (2), как известно, имеет точное решение, выраженное через неполные эллиптические интегралы первого рода [1]. Оно позволяет после дополнительных преобразований, учета известных параметров, а также граничных условий получить выражение для эйлеровой критической силы и оценить величину реальной действующей силы F .
Другой способ определить силу кинезина in vitro – постепенно увеличивать вязкость окружающего раствора до тех пор, пока скорость не упадет до практически неизмеримой величины. Для оценки силы необходимо решить задачу о движении
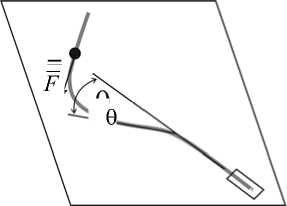
Рис. 3. Эксперимент по изменению силы одиночного димера кинезина. Серой кривой показана микротрубочка, с одной стороны присоединенная к приборному стеклу на минус-конце. С другой стороны к трубочке прикрепился димер кинезина, развивающий сжимающее усилие. Место его крепления показано черным кругом, а направление силы - стрелкой. Также обозначен угол 0 между изначальным направлением прямой микротрубочки и касательной к ней после изгиба (см. уравнение (2))
цилиндра (микротрубочки) в вязкой среде (см., например, [2]). При этом приходится дополнительно учитывать, что в условиях эксперимента вещество, меняющее вязкость, делает жидкость неньютоновской, точнее, удовлетворяющей в плоскости оси цилиндра уравнениям «обобщенной ньютоновской жидкости»
о = П 5,
5 = V и, п = п(| 51).
Эти уравнения записаны в плоскости, перпендикулярной оси цилиндра. Тут вектор касательного напряжения 6 связан с градиентом скорости V и через коэффициент обобщенной вязкости п , который, в свою очередь, является функцией скорости сдвига. Возникающая сложная система уравнений не решается в квадратурах, но численное решение хорошо аппроксимируется формулой, выражающей зависимость силы от скорости [55]:
(
F ( v ) = С 0 v 1 + k
0,75 v 0
v
Описывая биомеханический цикл кинезина, чаще всего используют модели двух типов. Первый – марковские модели, в которых множество всех возможных биохимически и (или) механически различных состояний (как правило, более сложных и подробных, чем показано на рис. 2) представлено вероятностями нахождения кинезина в них, а переходы из одного состояния в другое – «константами скоростей». При этом появлялись системы вида
/ -£ [ W W].
которые мы часто встречаем и в работах, описывающих миозин-актиновый цикл. Здесь p i - вероятность нахождения кинезина в состоянии i, а r ij - скорость его перехода из состояния i в состояние j . При этом состояниям можно присваивать некую характерную линейную координату вдоль микротрубочки, а скорости перехода будут зависеть не только от неё, но и от концентраций АТФ, АДФ и неорганического фосфата. Соотношения Аррениуса для прямых и обратных скоростей перехода и законы сохранения дополняют систему. Далее, например, можно искать (как авторы [73]) стационарное решение и подсчитывать макроскопические характеристики, выводя зависимость силы от таких переменных, как концентрации АТФ и продуктов ее гидролиза.
Главной трудностью, встающей перед всяким, кто конструирует модели марковского типа, является большое количество параметров – скоростей перехода, которые можно оценивать лишь приблизительно.
Другой подход представляет модель, в которой различные равновесные положения кинезина внутри цикла разделены энергетическими барьерами. В такой модели механическое напряжение между двумя головами кинезина передается посредством упругой пружины [29]. При этом возникают уравнения Ланжевена
ГXn =-д XV ( Xn )-F + K [ Xm - xn - 1 ( t )] + £ n ( t ) , (6)
в которых m, n = 1, 2 - номера голов кинезина (если n = 1, то m = 2, и наоборот); Г -коэффициент трения; V – периодический потенциал; x – осевая координата; K – коэффициент жесткости пружины; l – центр положения равновесия для головы (0 или 8 нм в зависимости от того, совершен ли шаг); ^ - гауссов белый шум, т.е. величина случайной броуновской силы. Систему (6) решали методом Монте-Карло [29].
Выводы
В последние годы были достигнуты большие успехи в изучении кинезин-тубулинового взаимодействия, однако многое еще предстоит выяснить. Не полностью ясна механика обратных шагов кинезина. Еще впереди получение новых комплексов кинезин–тубулин в различных биохимических состояниях. Как устроено коллективное взаимодействие одинаковых и разных видов кинезина? Как организовано непрерывное движение грузов вдоль микротрубочек попеременно в разные стороны? Как именно кинезин строго сохраняет постоянным направление движения вдоль одного протофиламента тубулина? Как сочетается броуновский храповик и механика силогенерирующего шага? Хватает ли одного только застегивания нек-линкера для совершения этого шага? Вот лишь немногие из вопросов, окончательные ответы на которые еще не получены.
Дальнейшее изучение кинезина крайне важно. К нему как к одному из главных нейронных белков проявляют большой интерес исследователи болезни Альцгеймера [40, 45]. Влияние на кинезин как на белок, участвующий в делении клеток, рассматривается как один из путей лечения раковых заболеваний [70, 90]. Искусственные или полуискусственные молекулярные моторы, служащие для доставки лекарств, конструируются сейчас по образцу кинезина [28].
Хочется пожелать удачи всякому, кто выберет кинезин предметом своего исследования в будущем. Для более подробного знакомства с проблемами, кратко изложенными в этой работе, можно порекомендовать обзоры [10, 25, 50, 74, 100, 105, 112].
Благодарности
Автор благодарен А.К. Цатуряну за неоценимую помощь в написании и правке этой статьи. Работа поддержана грантом РФФИ КОМФИ № 14-04-40100-Н.
Список литературы Кинезин: механика молекулярного мотора
- Ландау Л.Д., Лифшиц Е.М. Теория упругости. Теоретическая физика: в 10 т. Т. VII. -Изд. 5. -М.: Физматлит, 2003. -264 с.
- Слёзкин Н.А. Динамика вязкой несжимаемой жидкости. -М.: Гос. изд-во техн.-теорет. лит-ры, 1955. -521 с.
- Allen C., Borisy G.G. Structural polarity and directional growth of microtubules of Chlamydomonas flagella//J. Mol. Biol. -1974. -Vol. 90. -P. 381-402.
- Amos L., Klug A. Arrangement of subunits in flagellar microtubules//J. Cell Sci. -1974. -Vol. 14. -P. 523-549.
- Asbury C.L., Fehr A.N., Block S.M. Kinesin moves by an asymmetric hand-over-hand mechanism//Science. -2003. -Vol. 302. -P. 2130-2134.
- Asenjo A.B., Weinberg Y., Sosa H. Nucleotide binding and hydrolysis induces a disorder-order transition in the kinesin neck-linker region//Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. -2006. -Vol. 13. -P. 648-54.
- Bagshaw C.R., Trentham D.R. The characterization of myosin-product complexes and of product-release steps during the magnesium ion-dependent adenosine triphosphatase reaction//Biochem. J. -1974. -Vol. 141. -P. 331-349.
- Bernstein M. Flagellar kinesins: new moves with an old beat//Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton. -1995. -Vol. 32. -P. 125-128.
- Block S.M. Nanometres and piconewtons: the macromolecular mechanics of kinesin//Trends Cell Biol. -1995. -Vol. 5. -P. 169-175.
- Block S.M. Kinesin motor mechanics: binding, stepping, tracking, gating, and limping//Biophys. J. -2007. -Vol. 92. -P. 2986-2995.
- Borisy G.G., Taylor E.W. The mechanism of action of colchicine. Binding of colchincine-3H to cellular protein//J. Cell Biol. -1967. -Vol. 34. -P. 525-533, 535-548.
- Brady S.T. A novel brain ATPase with properties expected for the fast axonal transport motor//Nature. -1985. -Vol. 317. -P. 73-75.
- Brown S.S. Cooperation between microtubule-and actin-based motor proteins//Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. -1999. -Vol. 15. -P. 63-80.
- Caplow M. Microtubule dynamics//Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. -1992. -Vol. 4. -P. 58-65.
- Carter N.J., Cross R.A. Mechanics of the kinesin step//Nature. -2005. -Vol. 435. -P. 308-312.
- Carter N.J., Cross R.A. Kinesin’s moonwalk//Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. -2006. -Vol. 18. -P. 61-67.
- Carter N.J., Cross R.A. Kinesin backsteps//Biochem. Soc. Trans. -2012. -Vol. 40. -P. 400-403.
- Cheney R.E., O'Shea M.K., Heuser J.E., Coelho M.V., Wolenski J.S., Espreafico E.M., Forscher P., Larson R.E., Mooseker M.S. Brain myosin-V is a two-headed unconventional myosin with motor activity//Cell. -1993. -Vol. 75. -P. 13-23.
- Chretien D., Wade R.H. New data on the microtubule surface lattice//Biol. Cell. -1991. -Vol. 71. -P. 161-174.
- Clancy B.E., Behnke-Parks W.M., Andreasson J.O.L., Rosenfeld S.S., Block S.M. A universal pathway for kinesin stepping//Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. -2011. -Vol. 18. -P. 1020-1027.
- Coppin C.M., Finer J.T., Spudich J.A., Vale R.D. Detection of sub-8-nm movements of kinesin by high-resolution optical-trap microscopy//Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. -1996. -Vol. 93. -P. 1913-1917.
- Coppin C.M., Pierce D.W., Hsu L., Vale R.D. The load dependence of kinesin's mechanical cycle//Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. -1997. -Vol. 94. -P. 8539-8544.
- Coy D.L., Wagenbach M., Howard J. Kinesin takes one 8-nm step for each ATP that it hydrolyzes//J. Biol. Chem. -1999. -Vol. 274. -P. 3667-3671.
- Crevel I.M., Lockhart A., Cross R.A. Weak and strong states of kinesin and ncd//J. Mol. Biol. -1996. -Vol. 257. -P. 66-76.
- Cross R.A. The kinetic mechanism of kinesin//Trends Biochem. Sci. -2004. -Vol. 29. -P. 301-309.
- Dagenbach E.M., Endow S.A. A new kinesin tree//J. Cell Sci. -2004. -Vol. 117. -P. 3-7.
- David-Pfeuty T., Erickson H.P., Pantaloni D. Guanosinetriphosphatase activity of tubulin associated with microtubule assembly//Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. -1977. -Vol. 74. -P. 5372-5376.
- Delius M., Leigh D.A. Walking molecules//Chem. Soc. Rev. -2011. -Vol. 40. -P. 3656-3676.
- Derenyi I., Vicsek T. The kinesin walk: a dynamic model with elastically coupled heads//Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. -1996. -Vol. 93. -P. 6775-6779.
- Endres N.F., Yoshioka C., Milligan R.A., Vale R.D. A lever-arm rotation drives motility of the minus-end-directed kinesin Ncd//Nature. -2006. -Vol. 439. -P. 875-878.
- Fallesen T.L., Macosko J.C., Holzwarth G. Force-velocity relationship for multiple kinesin motors pulling a magnetic bead//Eur. Biophys. J. -2011. -Vol. 40. -P. 1071-1079.
- Ferenz N.P., Gable A., Wadsworth P. Mitotic functions of kinesin-5//Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. -2010. -Vol. 21. -P. 255-259.
- Feynman R.P. Ratchet and pawl//The Feynman lectures on physics. -Massachusetts: Addison-Wesley, 1963. -Vol. 1. -P. 443-451.
- Fisher M.E., Kim Y.C. Kinesin crouches to sprint but resists pushing//Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. -2005. -Vol. 102. -P. 16209-16214.
- Friel C.T., Bagshaw C.R., Howard J. Analysing the ATP turnover cycle of microtubule motors//Methods Mol. Biol. -2011. -Vol. 777. -P. 177-192.
- Geeves M.A., Holmes K.C. The molecular mechanism of muscle contraction//Adv. Protein Chem. -2005. -Vol. 71. -P. 161-193.
- Gibbons I.R. Studies on the protein components of cilia from tetrahymena pyriformis//Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. -1963. -Vol. 50. -P. 1002-1010.
- Gittes F., Meyhofer E., Baek S., Howard J. Directional loading of the kinesin motor molecule as it buckles a microtubule//Biophys. J. -1996. -Vol. 70. -P. 418-429.
- Gittes F., Mickey B., Nettleton J., Howard J. Flexural rigidity of microtubules and actin filaments measured from thermal fluctuations in shape//J. Cell Biol. -1993. -Vol. 120. -P. 923-934.
- Goldstein L.S. Kinesin molecular motors: transport pathways, receptors, and human disease//Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. -2001. -Vol. 98. -P. 6999-7003.
- Hackney D.D. The tethered motor domain of a kinesin-microtubule complex catalyzes reversible synthesis of bound ATP//Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. -2005. -Vol. 102. -P. 18338-18343.
- Hallen M.A., Liang Z.Y., Endow S.A. Two-state displacement by the kinesin-14 Ncd stalk//Biophys. Chem. -2011. -Vol. 154. -P. 56-65.
- Hancock W.O., Howard J. Kinesin’s processivity results from mechanical and chemical coordination between the ATP hydrolysis cycles of the two motor domains//Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. -1999. -Vol. 96. -P. 13147-13152.
- Heneen W.K. Kinetochores and microtubules in multipolar mitosis and chromosome orientation//Exp. Cell Res. -1975. -Vol. 91. -P. 57-62.
- Hidaka M., Koga T., Gotoh A., Sanada M., Hirose K., Uchida T. Alzheimer's disease-related protein hGas7b interferes with kinesin motility//J. Biochem. -2012. -Vol. 151. -P. 593-598.
- Higuchi H., Muto E., Inoue Y., Yanagida T. Kinetics of force generation by single kinesin molecules activated by laser photolysis of caged ATP//Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. -1997. -Vol. 94. -P. 4395-4400.
- Hirokawa N. Cross-linker system between neurofilaments, microtubules, and membranous organelles in frog axons revealed by the quick-freeze, deep-etching method//J. Cell Biol. -1982. -Vol. 94. -P. 129-142.
- Hirokawa N. Quick freeze, deep etch of the cytoskeleton//Methods Enzymol. -1986. -Vol. 134. -P. 598-612.
- Hirokawa N. Axonal transport and the cytoskeleton//Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. -1993. -Vol. 3. -P. 724-731.
- Hirokawa N. From electron microscopy to molecular cell biology, molecular genetics and structural biology: intracellular transport and kinesin superfamily proteins, KIFs: genes, structure, dynamics and functions//J. Electron Microsc. (Tokyo). -2011. -Vol. 60, supp. 1. -P. S63-S92.
- Hirokawa N., Noda Y., Tanaka Y., Niwa S. Kinesin superfamily motor proteins and intracellular transport//Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. -2009. -Vol. 10. -P. 682-696.
- Holmes K.C., Angert I., Kull F.J., Jahn W., Schroder R.R. Electron cryo-microscopy shows how strong binding of myosin to actin releases nucleotide//Nature. -2003. -Vol. 425. -P. 423-427.
- Houdusse A., Cohen C. Structure of the regulatory domain of scallop myosin at 2 A resolution: implications for regulation//Structure. -1996. -Vol. 15. -P. 21-32.
- Hua W., Chung J., Gelles J. Distinguishing inchworm and hand-over-hand processive kinesin movement by neck rotation measurements//Science. -2002. -Vol. 295. -P. 844-848.
- Hunt A.J., Gittes F., Howard J. The force exerted by a single kinesin molecule against a viscous load//Biophys. J. -1994. -Vol. 67. -P. 766-781.
- Huxley A.F., Simmons R.M. Proposed mechanism of force generation in striated muscle//Nature. -1971. -Vol. 233. -P. 533-538.
- Hyeon C., Klumpp S., Onuchic J.N. Kinesin's backsteps under mechanical load//Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. -2009. -Vol. 11. -P. 4899-4910.
- Itoh H., Takahashi A., Adachi K., Noji H., Yasuda R., Yoshida M., Kinosita K. Jr. Mechanically driven ATP synthesis by F1-ATPase//Nature. -2004. -Vol. 427. -P. 465-468.
- Kapitein L.C., Peterman E.J., Kwok B.H., Kim J.H., Kapoor T.M., Schmidt C.F. The bipolar mitotic kinesin Eg5 moves on both microtubules that it crosslinks//Nature. -2005. -Vol. 435. -P. 114-118.
- Kaseda K., Higuchi H., Hirose K. Alternate fast and slow stepping of a heterodimeric kinesin molecule//Nat. Cell Biol. -2003. -Vol. 5. -P. 1079-1082.
- Kikkawa M., Hirokawa N. High-resolution cryo-EM maps show the nucleotide binding pocket of KIF1A in open and closed conformations//EMBO J. -2006. -Vol. 25. -P. 4187-4194.
- Kojima H., Muto E., Higuchi H., Yanagida T. Mechanics of single kinesin molecules measured by optical trapping nanometry//Biophys. J. -1997. -Vol. 73. -P. 2012-2022.
- Kull F.J., Endow S.A. Force generation by kinesin and myosin cytoskeletal motor proteins//J. Cell Sci. -2013. -Vol. 126. -P. 9-19.
- Kull F.J., Sablin E.P., Lau R., Fletterick R.J., Vale R.D. Crystal structure of the kinesin motor domain reveals a structural similarity to myosin//Nature. -1996. -Vol. 380. -P. 550-555.
- Kull F.J., Vale R.D., Fletterick R.J. The case for a common ancestor: kinesin and myosin motor proteins and G proteins//J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. -1998. -Vol. 19. -P. 877-886.
- Kunwar A., Mogilner A. Robust transport by multiple motors with nonlinear force-velocity relations and stochastic load sharing//Phys. Biol. -2010. -Vol. 7. -P. 16012.
- Kuznetsov S.A., Gelfand V.I. Bovine brain kinesin is a microtubule-activated ATPase//Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. -1986. -Vol. 83. -P. 8530-8534.
- Lang M.J., Asbury C.L., Shaevitz J.W., Block S.M. An automated two-dimensional optical force clamp for single molecule studies//Biophys. J. -2002. -Vol. 83. -P. 491-501.
- Lawrence C.J., Dawe R.K., Christie K.R., Cleveland D.W., Dawson S.C., Endow S.A., Goldstein L.S., Goodson H.V., Hirokawa N., Howard J., Malmberg R.L., McIntosh J.R., Miki H., Mitchison T.J., Okada Y., Reddy A.S., Saxton W.M., Schliwa M., Scholey J.M., Vale R.D., Walczak C.E., Wordeman L. A standardized kinesin nomenclature//J. Cell Biol. -2004. -Vol. 167. -P. 19-22.
- Liu X., Gong H., Huang K. Oncogenic role of kinesin proteins and targeting kinesin therapy//Cancer Sci. -2013. -Vol. 104. -P. 651-656.
- Luduena R.F. Multiple forms of tubulin: different gene products and covalent modifications//Int. Rev. Cytol. -1998. -Vol. 178. -P. 207-275.
- Lymn R.W., Taylor E.W. Mechanism of adenosine triphosphate hydrolysis by actomyosin//Biochemistry. -1971. -Vol. 10. -P. 4617-4624.
- Maes C., Wieren M.H. A Markov model for kinesin//Journal of Statistical Physics. -2003. -Vol. 112. -P. 329-355.
- Marx A., Hoenger A., Mandelkow E. Structures of kinesin motor proteins//Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton. -2009. -Vol. 66. -P. 958-966.
- Marx A., Müller J., Mandelkow E.M., Hoenger A., Mandelkow E. Interaction of kinesin motors, microtubules, and MAPs//J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. -2006. -Vol. 27. -P. 125-137.
- Meurer-Grob P., Kasparian J., Wade R.H. Microtubule structure at improved resolution//Biochemistry. -2001. -Vol. 40. -P. 8000-8008.
- Meyhofer E., Howard J. The force generated by a single kinesin molecule against an elastic load//Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. -1995. -Vol. 92. -P. 574-578.
- Moores C.A., Yu M., Guo J., Beraud C., Sakowicz R., Milligan R.A. A mechanism for microtubule depolymerization by KinI kinesins//Mol. Cell. -2002. -Vol. 9. -P. 903-909.
- Nishiyama M., Higuchi H., Yanagida T. Chemomechanical coupling of the forward and backward steps of single kinesin molecules//Nat. Cell Biol. -2002. -Vol. 10. -P. 790-797.
- Nishiyama M., Muto E., Inoue Y., Yanagida T., Higuchi H. Substeps within the 8-nm step of the ATPase cycle of single kinesin molecules//Nat. Cell Biol. -2001. -Vol. 3. -P. 425-428.
- Nogales E., Wolf S.G., Downing K.H. Structure of the alpha beta tubulin dimer by electron crystallography//Nature. -1998. -Vol. 391. -P. 199-203.
- Orozco J.T., Wedaman K.P., Signor D., Brown H., Rose L., Scholey J.M. Movement of motor and cargo along cilia//Nature. -1999. -Vol. 398. -P. 674.
- Rayment I., Holden H.M., Whittaker M., Yohn C.B., Lorenz M., Holmes K.C., Milligan R.A. Structure of the actin-myosin complex and its implications for muscle contraction//Science. -1993. -Vol. 261. -P. 58-65.
- Rice S., Lin A.W., Safer D., Hart C.L., Naber N., Carragher B.O., Cain S.M., Pechatnikova E., Wilson-Kubalek E.M., Whittaker M., Pate E., Cooke R., Taylor E.W., Milligan R.A., Vale R.D. A structural change in the kinesin motor protein that drives motility//Nature. -1999. -Vol. 402. -P. 778-784.
- Rodionov V.I., Gyoeva F.K., Gelfand V.I. Kinesin is responsible for centrifugal movement of pigment granules in melanophores//Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. -1991. -Vol. 88. -P. 4956-4960.
- Rosenfeld S.S., Fordyce P.M., Jefferson G.M., King P.H., Block S.M. Stepping and stretching. How kinesin uses internal strain to walk processively//J. Biol. Chem. -2003. -Vol. 278. -P. 18550-18556.
- Rosenfeld S.S., Jefferson G.M., King P.H. ATP reorients the neck linker of kinesin in two sequential steps//J. Biol. Chem. -2001. -Vol. 276. -P. 40167-40174.
- Sablin E.P., Kull F.J., Cooke R., Vale R.D., Fletterick R.J. Crystal structure of the motor domain of the kinesin-related motor ncd//Nature. -1996. -Vol. 380. -P. 555-559.
- Sack S., Muller J., Marx A., Thormahlen M., Mandelkow E.M., Brady S.T., Mandelkow E. X-ray structure of motor and neck domains from rat brain kinesin//Biochemistry. -1997. -Vol. 36. -P. 16155-16165.
- Sanhaji M., Friel C.T., Wordeman L., Louwen F., Yuan J. Mitotic centromere-associated kinesin (MCAK): a potential cancer drug target//Oncotarget. -2011. -Vol. 12. -P. 935-947.
- Sellers J.R. Kinesin and NCD, two structural cousins of myosin//J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. -1996. -Vol. 17. -P. 173-175.
- Sellers J.R. Myosins: a diverse superfamily//Biochim. Biophys. Acta. -2000. -Vol. 1496. -P. 3-22.
- Sellers J.R., Veigel C. Walking with myosin V//Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. -2006. -Vol. 18. -P. 68-73.
- Sheetz M.P. Motor and cargo interactions//Eur. J. Biochem. -1999. -Vol. 262. -P. 19-25.
- Schnitzer M.J., Block S.M. Kinesin hydrolyses one ATP per 8-nm step//Nature. -1997. -Vol. 388. -P. 386-390.
- Schnitzer M.J., Visscher K., Block S.M. Force production by single kinesin motors//Nat. Cell Biol. -2000. -Vol. 2. -P. 718-723.
- Svoboda K., Block S.M. Force and velocity measured for single kinesin molecules//Cell. -1994. -Vol. 77. -P. 773-784.
- Svoboda K.C., Schmidt F., Schnapp B.J., Block S.M. Direct observation of kinesin stepping by optical trapping interferometry//Nature. -1993. -Vol. 365. -P. 721-727.
- Taniguchi Y., Nishiyama M., Ishii Y., Yanagida T. Entropy rectifies the Brownian steps of kinesin//Nat. Chem. Biol. -2005. -Vol. 1. -P. 342-347.
- Taylor E.W., Borisy G.G. Kinesin processivity//J. Cell Biol. -2000. -Vol. 151. -P. F27-F29.
- Terada S., Kinjo M., Aihara M., Takei Y., Hirokawa N. Kinesin-1/Hsc70-dependent mechanism of slow axonal transport and its relation to fast axonal transport//EMBO J. -2010. -Vol. 29. -P. 843-854.
- Tilney L.G., Bryan J., Bush D.J., Fujiwara K., Mooseker M.S., Murphy D.B., Snyder D.H. Microtubules: evidence for 13 protofilaments//J. Cell Biol. -1973. -Vol. 59. -P. 267-275.
- Toprak E., Yildiz A., Hoffman M.T., Rosenfeld S.S., Selvin P.R. Why kinesin is so processive//Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. -2009. -Vol. 106. -P. 12717-12722.
- Vale R.D., Funatsu T., Pierce D.W., Romberg L., Harada Y., Yanagida T. Direct observation of single kinesin molecules moving along microtubules//Nature. -1996. -Vol. 380. -P. 451-453.
- Vale R.D., Milligan R.A. The way things move: looking under the hood of molecular motor proteins//Science. -2000. -Vol. 288. -P. 88-95.
- Vale R.D., Reese T.S., Sheetz M.P. Identification of a novel force-generating protein, kinesin, involved in microtubule-based motility//Cell. -1985. -Vol. 42. -P. 39-50.
- Vale R.D. Switches, latches, and amplifiers: common themes of G proteins and molecular motors//J. Cell Biol. -1996. -Vol. 135. -P. 291-302.
- Visscher K., Schnitzer M.J., Block S.M. Single kinesin molecules studied with a molecular force clamp//Nature. -1999. -Vol. 400. -P. 184-189.
- Voter W.A., Erickson H.P. Tubulin rings: curved filaments with limited flexibility and two modes of association//J. Supramol. Struct. -1979. -Vol. 10. -P. 419-431.
- Walker R.A. Ncd and kinesin motor domains interact with both alpha-and beta-tubulin//Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. -1995. -Vol. 92. -P. 5960-5964.
- Wang M.D., Schnitzer M.J., Yin H., Landick R., Gelles J., Block. S.M. Force and velocity measured for single molecules of RNA polymerase//Science. -1998. -Vol. 282. -P. 902-907.
- Wade R.H. On and around microtubules: an overview//Mol. Biotechnol. -2009. -Vol. 43. -P. 177-191.
- Wilson E.B. The cell in development and heredity. -New York: MacMillan Publishing Co., 1928. -377 p.
- Yildiz A., Tomishige M., Gennerich A., Vale R.D. Intramolecular strain coordinates kinesin stepping behavior along microtubules//Cell. -2008. -Vol. 134. -P. 1030-1041.
- Yildiz A., Tomishige M., Vale R.D., Selvin P.R. Kinesin walks hand-over-hand//Science. -2004. -Vol. 303. -P. 676-678.


