Корреляция между источниками звука и качеством акустики в городских районах
Автор: Корниенко С.В., Зенин А.М.
Журнал: Строительство уникальных зданий и сооружений @unistroy
Статья в выпуске: 4 (109), 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Объектом исследования является городская акустическая среда. Были использованы следующие методы исследования: звуковая прогулка, полевые измерения уровней шума, нарративные интервью и корреляционно-регрессионный анализ. Исследованы звуковые ландшафты в различных функциональных зонах города за три периода наблюдения (утром, днем и вечером). Всего получено 9450 ответов от 10 респондентов. Уровень шума в городской зоне измерялся по стандартной методике. Определены воспринимаемые источники звука и их пространственно-временные вариации. Определены пространственно-временные вариации семантических характеристик эмоционально воспринимаемого качества акустической среды. Анализ результатов показывает, что шумы транспорта имеют выраженную обратную корреляцию с эмоциональным критерием «приятность» утром и вечером (r = -0,59 и r = -0,55 соответственно) и высокую обратную корреляцию (r = -0,76) в дневное время. Шумы транспорта имеют заметную обратную корреляцию с этим критерием (r = -0,64). С критерием «событийность» звуки транспорта имеют высокую прямую корреляцию утром и днем (r = 0,75 и r = 0,72 соответственно) и умеренную прямую корреляцию вечером (r = 0,41). Звуки транспорта напрямую коррелируют с этим критерием (r = 0,61). Звуки человека (по общей оценке) не коррелируют с критерием «приятность» (r = 0,04), однако знакопеременный характер коэффициентов корреляции (r = -0,50 утром и r = 0,34 вечером) свидетельствует о различном эмоциональном восприятии разговорной речи в разное время суток. «Событийность» звуков человека характеризуется и различным эмоциональным восприятием во времени: для утренних часов характерна высокая прямая корреляция (r = 0,74); для дневных часов — слабая (r = 0,28); для вечерних часов — умеренная (r = 0,34). Между приятностью и звуками воды существует слабая положительная корреляция, случайность, по общей оценке, также слабо выражена. В целом звуки птиц положительно влияют на человека с точки зрения приятности (r = 0,38), но воспринимаются как несобытийный эффект (r = -0,63). Этот результат хорошо согласуется с временной тенденцией пения птиц, в частности, с доминированием звука в утренние и дневные часы.
Город, городское планирование, акустическая среда, звуковой ландшафт, звуковая дорожка, звуковая дорожка, защита от шума
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143182695
IDR: 143182695 | УДК: 69 | DOI: 10.4123/CUBS.109.2
Текст научной статьи Корреляция между источниками звука и качеством акустики в городских районах
-
1 Introduction / Введение
По мере роста городов шумовое загрязнение становится главной угрозой для окружающей среды [1]. Высокий уровень шума ухудшает здоровье и самочувствие человека, нарушает сон, заглушает полезные акустические сигналы многих видов животных, обитающих в этих районах [2]. Но решения этой проблемы уже есть: от электрификации транспорта до зеленых зон, которые следует включать в планировку городской застройки с целью снижения шумового загрязнения [3]–[5].
В процессах взаимодействия человека с изменяющейся окружающей средой можно выделить два взаимосвязанных тренда [6]. Первый касается изменений среды, определяемых человеческой деятельностью. Второй показывает, что большая часть изменений в среде приводит к изменениям самого человека, его внутренних качеств. Указанные тренды наиболее полно проявляются применительно к акустической среде, представляющей собой сложный и еще малоизученный мир звуков и шумов, окружающих человека [7]. Акустическая среда все больше зависит от деятельности человека, в результате которой появляются новые звуки, а привычные звучания пропадают или меняются [8]. Эти изменения, в свою очередь, влияют на содержание слуховых эталонов и на другие качества восприятия [9]. Изменения звуковой среды в наибольшей степени проявляются на урбанизированных территориях [10], [11].
Среди исследований взаимодействия человека и акустической среды можно выделить два основных, экологически направленных, подхода (рис. 1).
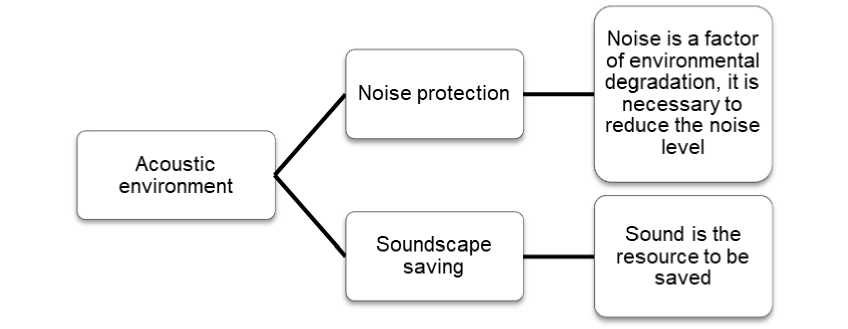
Fig. 1 – Two approaches to research the acoustic environment Рис. 1 – Два подхода к изучению акустической среды
В основе одного из них лежит проблема рассмотрения шумового воздействия на человека [12]. Шум является фактором деградации среды, поэтому необходимо снижать уровень шума. Этот подход часто называют защитой от шума (рис. 1).
Другой подход базируется на положении о том, что звук (подобно воздуху, воде, почве) является ресурсом, поэтому задачей исследователя является выявление и сохранение положительных качеств звука [13]. Управление звуком предполагает его рациональное использование, защиту и усиление в случае необходимости. Это означает борьбу не против шума, а за звуковую среду [14]. Такой подход, который получает все большее распространение [15]–[17], называют чаще всего сохранением звукового ландшафта (рис. 1).
Понятие «звуковой ландшафт» введено Р.М. Шейфером (Schafer, 1979) для интерпретации процессов взаимодействия человека и акустической среды.
Главное различие в указанных выше подходах связано с тем, какие результаты воздействия звука на человека изучают в первую очередь. В подходе, рассматривающем шумовое воздействие акустической среды, изучают неблагоприятные воздействия среды на человека. Речь идет о звуках, вызывающих дискомфорт: нарушение сна, раздражение, неблагоприятные физиологические эффекты, прерывание коммуникации или когнитивных процессов [18], [19]. В отличие от этого подход «звукового ландшафта» направлен на анализ звуков, оказывающих благоприятное воздействие на человека. Эти звуки способствуют улучшению здоровья, повышению качества жизни или облегчению условий деятельности людей [20]. Исследования в этой области в значительной степени направлены на выявление предпочитаемых звуков. При этом в разных местах и в различных контекстах человеческие предпочтения относительно звуков акустической среды могут сильно различаться [21].
Урбанизация приводит к росту уровня шума в городах. Источниками шума в мегаполисе являются: транспортный шум, шум производственных зданий и предприятий, громкая музыка, крики людей и т.д. Методы защиты от шума включают снижение шума в источнике, на пути распространения шума, элементами оболочки зданий, что достаточно полно отражено в литературе [22], [23].
Снижение уровня шума в источнике относят к технологическим задачам, поэтому в градостроительном проектировании этот метод не рассматривают. Методы снижения шума на пути его распространения от источника достаточно разнообразны. Известно, что при каждом удвоении расстояния от точечного источника уровень звука падает на 6 дБА, от линейного Korniyenko, S.; Zenin, A.
Correlation between sound sources and acoustic quality in urbanized areas;
источника падает на 3 дБА, поэтому защищаемые от шума объекты следует располагать как можно дальше от источника шума. Применение шумовых карт облегчает поиск комфортных городских территорий [24]. Эффективными способами защиты от шума являются: акустическое зонирование территории города, использование естественных и искусственных элементов рельефа, применение шумозащитных зданий и экранов, озеленение и благоустройство городских территорий [23], [25], [26], [27]. Высокий уровень звукоизоляции помещений могут обеспечить светопропускающие фасадные конструкции с применением многокамерных стеклопакетов [28]–[30], [31], [32].
Таким образом, процессы распространения городского шума изучены достаточно глубоко, и получен ряд решений, включенных в нормативные документы. Однако методы сохранения звукового ландшафта на урбанизированных территориях разработаны недостаточно полно. Отсутствие четких представлений о городских звуковых ландшафтах, «размытость» характеристик пространственно-временных изменений среды, недостаточная изученность корреляционной зависимости между источниками звука и эмоционально воспринимаемым качеством среды затрудняет решение актуальной задачи сохранения и реконструкции акустической среды для будущих поколений.
Целью данной работы является установление корреляционной зависимости между источниками звука и воспринимаемым эмоционально качеством акустической среды на урбанизированных территориях.
В соответствии с поставленной целью необходимо решить следующие задачи:
-
- выполнить идентификацию воспринимаемых источников звука и оценить их вариации в различных функциональных зонах;
-
- выполнить анализ воспринимаемого эмоционально качества акустической среды в различных функциональных зонах;
-
- оценить фактический уровень звука в различных функциональных зонах;
-
- установить корреляцию между источниками звука и воспринимаемым эмоционально качеством акустической среды.
2 Materials and Methods / Материалы и методы
2.1 Case Study Area / Область тематического исследования
Исследование звукового ландшафта проводилось на территории г. Волгограда (координаты: 48.707067, 44.516975). В 1990-х годах произошло срастание городских районов за счет ликвидации зеленых зон. Жилая застройка возле промышленных предприятий, оказавшихся при расширении города в центрах районов города, усугубляет экологические проблемы города. Основным шумовым загрязнителем является автомобильный транспорт, а также промышленные предприятия.
Для анализа звукового ландшафта города были выбраны различные функциональные зоны, характеризующиеся значительными изменениями морфологических характеристик:
-
- жилая зона с размещением домов разных типов (многоквартирные многоэтажные, средней и малой этажности), объектов социального и культурно-бытового обслуживания, культовых зданий;
-
- общественно-деловая зона с выделением исторического центра города,
специализированной и недифференцированной подзон;
- производственная зона, зоны транспортной и инженерной инфраструктуры;
- зона рекреационного назначения (скверы, парки, городские сады).
2.2 Data Collection / Сбор данных
В процессе исследования данные по звуковому ландшафту были собраны с 21 участков, расположенных в различных территориальных зонах.
Сбор данных звукового ландшафта объекта исследования производился в период с 27.06.2022 по 30.06.2022 при дневном освещении в ясную погоду.
Методы и соответствующие инструменты, использованные для сбора данных звукового ландшафта, приведены на рис. 2.
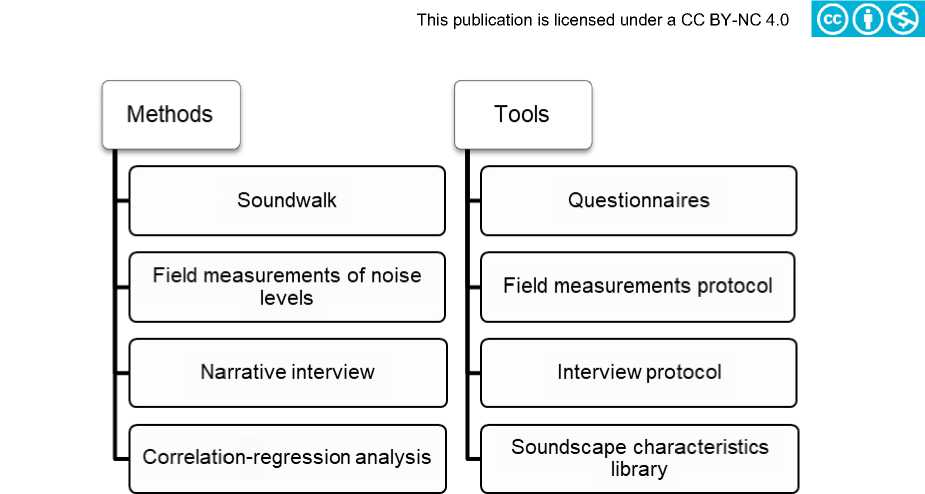
Fig. 2 – Methods and corresponding tools to collect soundscape data
Рис. 2 – Методы и соответствующие инструменты для сбора данных звукового ландшафта
Все натурные наблюдения выполнялись экологически безопасным методом звуковой прогулки. Метод является прогрессивным и ориентирован на здоровый образ жизни в связи с перемещением респондентов пешком по заранее установленным маршрутам (рис. 3).

Fig. 3 – Example of a soundwalk (Volgograd, “Zero kilometer” point)
Рис. 3 – Пример звуковой прогулки (г. Волгоград, «Нулевой километр»)
Данные по звуковому ландшафту города были собраны с использованием опросника, как показано ниже.
Опросник был разделен на два взаимосвязанных модуля. Первый модуль предназначен для идентификации воспринимаемых источников звука и оценки степени их доминирования. Второй модуль использовался для оценки воспринимаемого качества акустической среды.
Для выявления воспринимаемых источников звука был поставлен вопрос: «В какой степени вы слышите следующие звуки?» . Все источники звука были классифицированы на семь категорий: транспортный шум; разговор людей, крики, игра детей; звук воды; пение птиц; шум ветра; музыка; другие звуки. Оценка производилась по пятибалльной шкале от 1 до 5: не слышно вообще; немного слышно; умеренно слышно; хорошо слышно; источник является доминирующим. Необходимо было выбрать один вариант ответа для каждого источника звука.
Эмоциональное воздействие звуковой среды оценивалось с помощью вопроса: «В какой степени вы согласны с эмоциональным воздействием звука?» . Использовались следующие семантические характеристики воспринимаемого качества звуковой среды [33]: приятная; не приятная; спокойная; беспорядочная; насыщена событиями; не насыщена событиями; волнующая; монотонная. Оценка также производилась по пятибалльной шкале от 1 до 5: категорически не согласен; не согласен; нейтрально (ни да, ни нет); согласен; полностью согласен. Необходимо было выбрать один вариант ответа для каждого типа звуковой среды.
Для анализа пространственного изменения характеристик звукового ландшафта были разработаны три звуковых маршрута, расположенных в различных частях Волгограда.
Первый маршрут (T-1) располагался в Центральном районе, в границах набережной 62-й Армии, ул. Коммунистическая, ул. Ленина, ул. Комсомольская. Средняя продолжительность движения по маршруту – 64 мин.
Второй маршрут (T-2) находился в Ворошиловском районе, в границах ул. им. Степана Разина, ул. им. Милиционера Буханцева, ул. Североморцев, ул. Баррикадная. Средняя продолжительность движения по маршруту составляет 43 мин.
Третий маршрут (T-3) был расположен в Советском районе, в границах ул. Даугавская, ул. им. Ухтомского, пр-т Университетский, ул. Электролесовская. Средняя продолжительность движения по маршруту – 34 мин.
Каждый маршрут состоял из семи узлов (P1–P7), расположенных в различных функциональных зонах города: жилой, общественно-деловой (исторический центр, недифференцированная, специализированная), производственной, рекреационного назначения.
Координаты узлов звуковых маршрутов, расположенных в различных функциональных зонах города, приведены в табл. 1.
Table 1. Coordinates of soundtrack nodes
Таблица 1. Координаты узлов звуковых маршрутов
|
Маршрут |
Узлы маршрута |
Координаты маршрута |
Функциональная зона города |
|
P1 |
48.704597, 44.520478 |
Рекреационного назначения |
|
|
P2 |
48.705652, 44.518790 |
То же |
|
|
P3 |
48.706208, 44.517064 |
Общественно-деловая (исторический центр) |
|
|
T-1 |
P4 |
48.707366, 44.516496 |
Рекреационного назначения |
|
P5 |
48.708572, 44.514833 |
Общественно-деловая (исторический центр) |
|
|
P6 |
48.708364, 44.511978 |
Рекреационного назначения |
|
|
P7 |
48.707043, 44.513040 |
Общественно-деловая (исторический центр) |
|
|
P1 |
48.689424, 44.494077 |
Общественно-деловая (недифференцированная) |
|
|
P2 |
48.690756, 44.490690 |
То же |
|
|
T-2 |
P3 |
48.688942, 44.488813 |
Жилая (среднеэтажной и многоэтажной застройки) |
|
P4 |
48.688104, 44.486603 |
То же |
|
|
P5 |
48.688193, 44.485687 |
Производственная |
|
|
P6 |
48.690120, 44.484124 |
То же |
|
|
P7 |
48.690816, 44.488391 |
Общественно-деловая (недифференцированная) |
|
|
P1 |
48.657577, 44.447275 |
Производственная |
|
|
P2 |
48.657932, 44.445778 |
Рекреационного назначения |
|
|
P3 |
48.658654, 44.445209 |
Общественно-деловая (специализированная) |
|
|
T-3 |
P4 |
48.658564, 44.443556 |
Жилая |
|
P5 |
48.657291, 44.441310 |
Общественно-деловая (специализированная) |
|
|
P6 |
48.659332, 44.441220 |
Жилая |
|
|
P7 |
48.660439, 44.440699 |
Общественно-деловая (недифференцированная) |
Общее число узлов – 21.
Для анализа изменений звукового ландшафта во времени наблюдения проводились в течение суток для каждого маршрута: утром с 07:00 до 09:00 (SP-1); днем с 13:00 до 15:00 (SP-2); вечером с 19:00 до 21:00 (SP-3).
Для повышения точности результатов исследования в выходные дни сбор данных не производился, поскольку звуковой ландшафт в это время может существенно отличаться от рабочих дней.
Данные звукового ландшафта были собраны группой из десяти респондентов (5 мужчин и 5 женщин). Респондентами являлись студенты четвертого курса по специальности 07.03.01 «Архитектура» (уровень бакалавриата), проходившие научно-производственную практику на кафедре «Архитектура зданий и сооружений» Волгоградского государственного технического университета. Минимальный возраст респондентов на момент проведения исследования составлял 21 год, максимальный возраст составлял 30 лет, средний возраст составлял 23.7 года, среднеквадратичное отклонение SD = 2.65.
Отличительная особенность данного исследования – ярко выраженный международный характер. Респондентами являлись граждане четырех различных государств: 6 человек (2 мужчин, 4 женщины) из Российской Федерации; 2 человека (мужчины) из Республики Гамбия;1 человек (женщина) из Республики Мозамбик; 1 человек (мужчина) из Республики Ирак.
Расчетом установлено высокое значение а -Кронбаха (около 0.9), что указывает на внутреннюю согласованность опроса и надежность полученных результатов.
Всего было получено 9450 ответов респондентов (15 ответов в каждой анкете х 10 респондентов х 7 узлов х 3 временных интервала х 3 маршрута).
Для получения репрезентативных значений в каждом узле маршрута ответы десяти респондентов были усреднены, объем выборки составил 945.
Фактические характеристики звуковой среды определялись параллельно с опросом респондентов путем натурных измерений уровней шума по стандартной методике.
Для измерения шума использовался шумомер «Октава–110А» (ПО «Октава-ЭлектронДизайн», Москва, Россия). Класс точности прибора составляет 1. Погрешность измерений шумомера в нормальных условиях применения для плоской волны частотой 1000 Гц и уровнем 94 дБ, распространяющейся в опорном направлении в условиях свободного акустического поля, на характеристике S не превышает ± 0.7 дБА.
Измерения корректированных уровней звука (с частотной коррекцией «А» и временной характеристикой L eq ) выполнены в соответствии с руководством по эксплуатации прибора.
Измерения производились по три раза в каждом узле звукового маршрута в вышеуказанные временные интервалы. Всего было проведено 189 измерений (3 измерения в каждом узле х 21 узел х 3 временных интервала). После усреднения количество измеренных значений уровня звука равно 63.
Все измерения были зафиксированы в протоколе натурных измерений уровней шума.
Для контроля было проведено выборочное интервьюирование респондентов с использованием следующих вопросов:
-
1. Что такое звуковой ландшафт?
-
2. Каким образом звуковой ландшафт связан с социокультурными особенностями и контекстом городской среды?
-
3. Как звуковой ландшафт влияет на здоровье и качество жизни людей?
-
4. Как измерить звуковой ландшафт?
-
5. Каким образом можно улучшить звуковой ландшафт городской среды?
На все поставленные вопросы респонденты дали корректные ответы.
Ответы респондентов были занесены в протокол собеседования.
Обработка полученных экспериментальных данных осуществлялась с помощью стандартных методов корреляционно-регрессионного анализа.
Результаты обработки данных были включены в библиотеку характеристик звукового ландшафта и использованы для выявления пространственно-временных вариаций акустической среды города.
-
3 Results and Discussion / Результаты и обсуждение
3.1 Identification of Perceived Sound Sources and their Spatiotemporal Variations / Идентификация воспринимаемых источников звука и их пространственновременные вариации
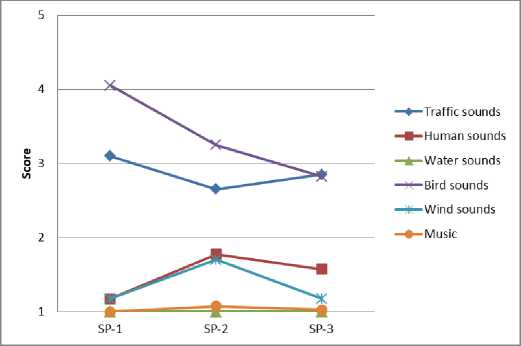
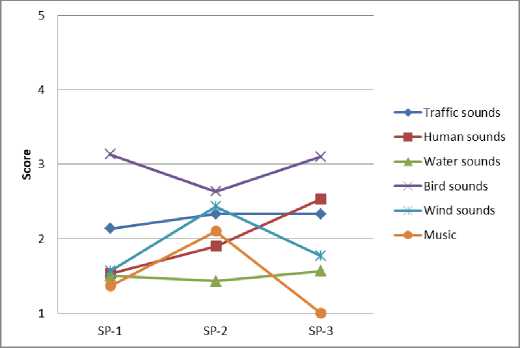
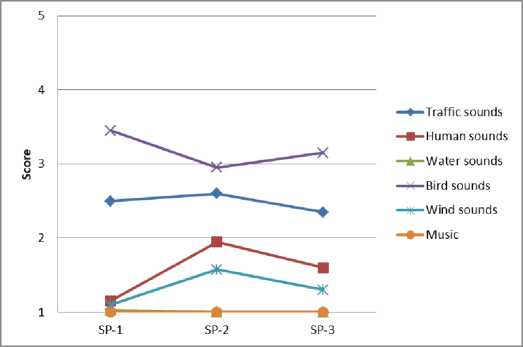
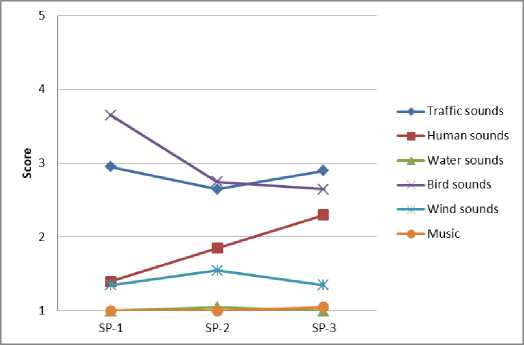
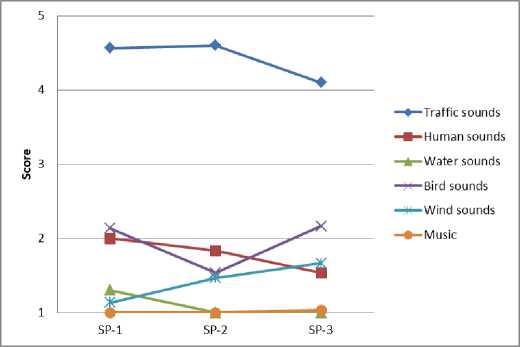
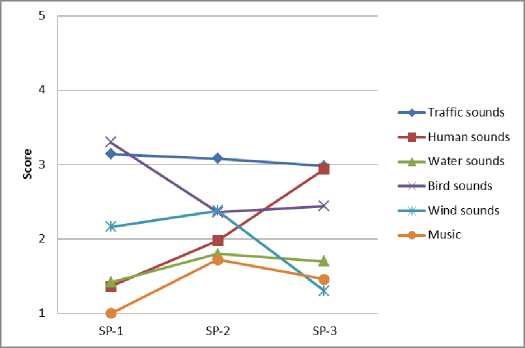
Результаты опроса респондентов позволяют идентифицировать воспринимаемые источники звука и оценить их пространственно-временные вариации в различных функциональных зонах города (рис. 4).
Korniyenko, S.; Zenin, A.
Correlation between sound sources and acoustic quality in urbanized areas;
a
b
c
d
e
f
Fig. 4 – Spatio-temporal variations of sound sources: a – residential area; b – historic city center; c – public and business undifferentiated area; d – specialized social and business zone; e – production area; f – recreational area
Рис. 4 – Пространственно-временные вариации источников звука: a – жилая зона; b – исторический центр города; c – общественно-деловая недифференцированная зона; d – специализированная общественно-деловая зона; e – производственная зона; f – зона рекреационного назначения
Анализ результатов показывает, что транспортный шум преобладает вблизи дорог с высокой интенсивностью движения и промышленных предприятий, наименее заметен в историческом центре города. Разговор людей и музыкальные звуки преобладают в городских парках, а также вблизи торговых зданий. Звуки птиц часто наблюдаются на территории жилой застройки, на озелененных участках, в общественно-деловых зонах. Звуки воды хорошо слышны около фонтанов и городских водоемов.
Выявленные источники звука меняются в наблюдаемые периоды. Небольшие изменения воспринимаемого звука во времени характерны для транспортного шума и воды, поскольку обычно такие источники расположены в фиксированных местах. Вместе с тем, вариации звука, продуцируемого разговором людей и пением птиц, более значительны, поскольку модели поведения людей и птиц имеют сложные биоритмы и зависят от времени суток [34], [35].
Звуки, возникающие при разговоре людей, зависят в основном от их активности. Так, например, в жилой и общественно-деловой зонах некоторые всплески активности отмечаются в дневные часы, в это время отмечается более высокая частота посещений. В историческом центре города, специализированной общественно-деловой зоне и зоне рекреационного назначения активность людей усиливается к вечеру, что связано, главным образом, с проведением досуговых мероприятий.
Шум ветра обусловлен вариациями климатических факторов и морфологическими особенностями застройки.
3.2 Perceived Affective Quality of Acoustic Environment / Воспринимаемое эмоционально качество акустической среды
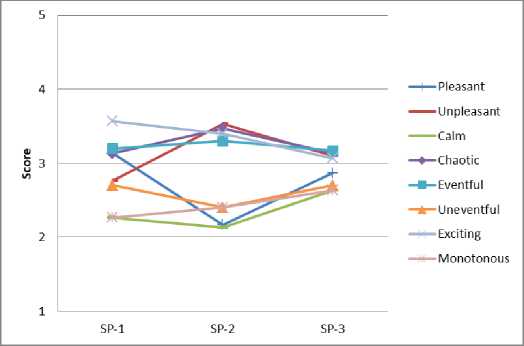
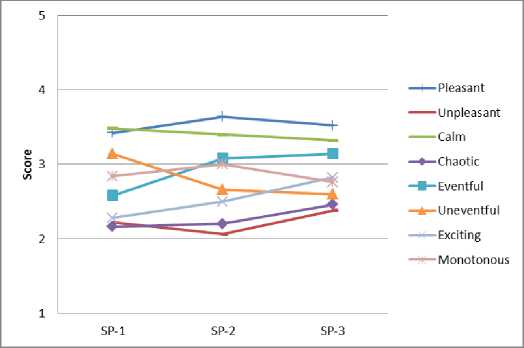
Анализ результатов опроса респондентов позволяет оценить пространственно-временные вариации семантических характеристик эмоционально воспринимаемого качества акустической среды в различных функциональных зонах города (рис. 5).
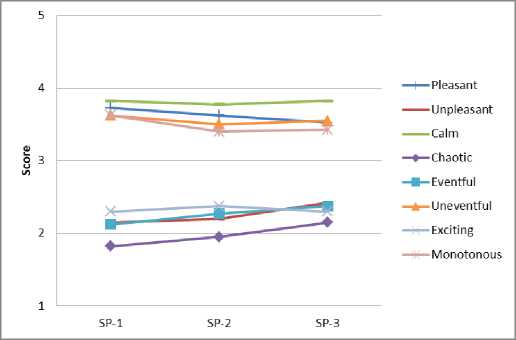
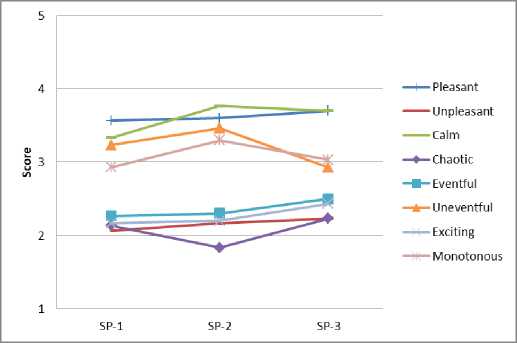
a b
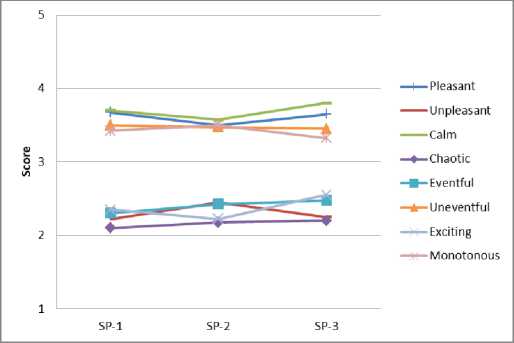
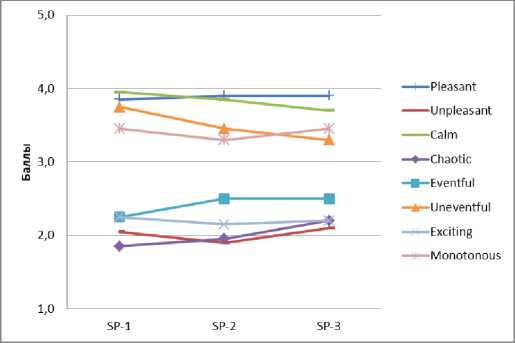
c d
e f
Fig. 5 – Spatio-temporal variations of acoustic quality characteristics: a – residential area; b – historic city center; c – public and business undifferentiated area; d – specialized public and business area; e – production area; f – recreational area
Рис. 5 – Пространственно-временные вариации характеристик качества акустической среды: a – жилая зона; b – исторический центр города; с – общественно-деловая недифференцированная зона; d – специализированная общественно-деловая зона; e – производственная зона; f – зона рекреационного назначения
По оценке большинства респондентов акустическая среда в жилой зоне воспринимается как приятная, спокойная, не насыщенная событиями, монотонная в утренние, дневные и вечерние часы, т.е. почти не меняется во времени.
Акустическая среда в историческом центре города воспринимается преимущественно как приятная, спокойная, не насыщенная событиями, монотонная в утренние и дневные часы, однако при переходе к вечерним часам респонденты отмечают насыщенность среды событиями, беспорядочность, волнующее действие, что объясняется повышением активности в это время.
Воспринимаемое эмоционально качество акустической среды в недифференцированной общественно-деловой зоне, как отмечают респонденты, сходно с жилой зоной, с некоторым снижением монотонного воздействия вечером.
Акустическая среда в специализированной общественно-деловой зоне по оценке большинства респондентов воспринимается в целом как приятная, спокойная, монотонная.
Респонденты отмечают, что производственная зона в целом насыщена событиями, волнующая, беспорядочна, не всегда приятна. Это связано с тем, что в производственной зоне преобладающим является шум, оказывающий на человека неблагоприятное акустическое воздействие.
Для зоны рекреационного назначения характерен широкий спектр эмоционального восприятия звука в различное время, что объясняется воздействием различных источников звука в этой зоне.
3.3 Actual Sound Level / Фактический уровень звука
Анализ результатов натурных акустических измерений показывает, что фактический уровень звука также имеет сложные пространственно-временные вариации в различных функциональных зонах города (рис. 6).
Максимальные фактические уровни звука отмечаются в производственной зоне (70.4—73.3 дБА), что объясняется наличием ярко выраженного производственного шума, особенно в дневные часы. В рекреационной зоне фактический уровень звука снижается до 64.5 дБА. Зеленые насаждения являются своеобразным акустическим фильтром, блокирующим производственный шум. В историческом центре города максимальный уровень звука отмечается в утренние часы (63.1 дБА), минимальный – в вечерние часы (57.8 дБА), что связано со снижением активности в этой зоне вечером. Наоборот, в недифференцированной общественноделовой зоне максимальная активность отмечается в вечерние часы, что приводит к росту уровня звука до 57.4 дБА. Минимальные уровни звука характерны для жилой и специализированной общественно-деловой зон (48.7–51.1 дБА), как показано на рис. 6.
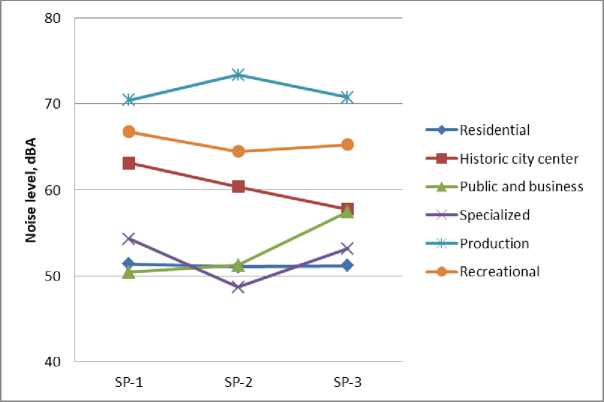
Fig. 6 – Spatio-temporal variations of actual sound level
Рис. 6 – Пространственно-временные вариации фактического уровня звука
Согласно санитарно-гигиеническим нормам допустимый уровень звука для территорий, непосредственно прилегающих к жилым зданиям, равен 55 дБА (с 07:00 до 23:00), следовательно, нормативные требования для рассматриваемых жилых зон обеспечены.
Полученные результаты натурных акустических измерений дополняют данные опросов респондентов и уточняют параметры акустической среды с точки зрения шумового загрязнения.
3.4 Correlation between sound sources and emotionally perceived acoustic quality / Корреляция между источниками звука и эмоционально воспринимаемым качеством акустической среды
Как показано в работах [36], [37], [38], эмоционально воспринимаемое качество акустической среды может быть достаточно точно описано с помощью двух критериев – приятности и событийности. Первый критерий характеризует меру общей удовлетворенности акустической средой, второй определяет степень насыщенности среды событиями.
На основе проведенного многофакторного корреляционного анализа городской акустической среды получены коэффициенты корреляции, приведенные в табл. 2.
Table 2. Correlation coefficients between sound sources and perceived emotional quality of acoustic environment (p < 0.05) Таблица 2. Коэффициенты корреляции между источниками звука и воспринимаемым эмоционально качеством акустической среды ( p < 0.05)
|
Критерии |
Период |
Транспортный шум |
Разговор людей |
Звук воды |
Пение птиц |
Шум ветра |
Музыкальный шум |
|
SP-1 |
–0.59 |
–0.50 |
0.19 |
0.46 |
0.06 |
–0.09 |
|
|
Приятность |
SP-2 |
–0.76 |
0.01 |
0.24 |
0.49 |
0.37 |
0.08 |
|
SP-3 |
–0.55 |
0.34 |
0.30 |
0.18 |
0.08 |
–0.04 |
|
|
Общий |
–0.64 |
0.04 |
0.25 |
0.38 |
0.15 |
0.00 |
|
|
SP-1 |
0.75 |
0.74 |
0.26 |
–0.77 |
–0.03 |
0.01 |
|
|
Событийность |
SP-2 |
0.72 |
0.28 |
0.08 |
–0.64 |
0.25 |
0.25 |
|
SP-3 |
0.41 |
0.34 |
0.39 |
–0.39 |
–0.08 |
0.25 |
|
|
Общий |
0.61 |
0.44 |
0.23 |
–0.63 |
0.09 |
0.22 |
Для оценки силы корреляционной связи воспользуемся шкалой Чэддока: слабая от 0.1 до 0.3; умеренная от 0.3 до 0.5; заметная от 0.5 до 0.7; высокая от 0.7 до 0.9; весьма высокая (сильная) от 0.9 до 1.0. Для обратной корреляционной связи коэффициенты корреляции шкала используется со знаком минус.
Анализ результатов показывает, что, как и ожидалось, транспортный шум имеет заметную обратную корреляционную связь с эмоциональным критерием «приятность» в утренние и вечерние часы (соответственно, r = –0.59 и r = –0.55) и высокую обратную корреляционную связь ( r = –0.76) дневные часы. В целом, для всех периодов выборки, транспортный шум имеет заметную обратную корреляционную связь с данным критерием ( r = –0.64).
С критерием «событийность» транспортный шум имеет высокую прямую корреляционную связь в утренние и дневные часы (соответственно, r = 0.75 и r = 0.72) и умеренную прямую корреляционную связь в вечерние часы ( r = 0.41). В целом, транспортный шум имеет заметную прямую корреляционную связь с данным критерием ( r = 0.61). Достаточно высокая оценка событийности транспортного шума обусловлена, по-видимому, возникновением «всплесков» звуковых волн от различных типов транспорта (троллейбусов, автобусов, различных автомобилей) на достаточно стабильном звуковом фоне.
Разговор людей (при общей оценке) не коррелирует с критерием «приятность» ( r = 0.04), однако знакопеременный характер коэффициентов корреляции ( r = –0.50 утром и r = 0.34 вечером) свидетельствует о различном эмоциональном восприятии разговорной речи в разное время суток.
«Событийность» разговора людей также характеризуется различным эмоциональным восприятием по времени: для утренних часов характерна высокая прямая корреляционная связь ( r = 0.74), для дневных часов – слабая ( r = 0.28), для вечерних часов – умеренная ( r = 0.34).
Существует слабая положительная корреляционная связь между приятностью и звуком воды, событийность, по общей оценке, также выражена слабо.
В целом, пение птиц оказывает положительное воздействие на человека с точки зрения приятности ( r = 0.38), однако воспринимается как не событийное воздействие ( r = –0.63). Этот результат хорошо согласован с временной тенденцией пения птицы, в частности, со звуковым доминированием в утренние и дневные часы.
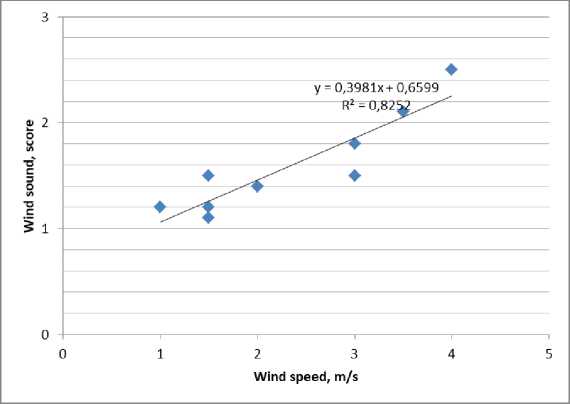
Fig. 7 – Graph of the relationship between wind speed and wind noise
Рис. 7 – График зависимости между скоростью и шумом ветра
Шум ветра связан с природными климатическими факторами и особенностями городской застройки. На основе архивных данных погоды в г. Волгограде в период проведения исследований установлена сильная корреляционная связь ( r = 0.908) между скоростью и шумом ветра (рис. 7).
По графику (рис. 7) видно, что при скорости ветра 1 м/с, шум ветра оценивается одним баллом (не слышно вообще), а при скорости ветра 3.5 м/с шум ветра оценивается двумя баллами (немного слышно). Следовательно, при малых скоростях ветра шум ветра на территории застройки почти не слышен. Вместе с тем шум ветра носит эпизодический локальный характер, поэтому в целом не коррелирует с воспринимаемыми эмоционально критериями качества акустической среды.
Корреляция музыкального шума с критериями «приятность» и «событийность» не выявлены.
-
4 Conclusions / Заключение
Научной новизной данного исследования являются впервые установленные пространственно-временные закономерности между различными источниками звука и акустическим качеством среды на урбанизированных территориях. Практическая значимость исследования заключается в разработке корреляционной модели, позволяющей прогнозировать изменение критериев эмоционально воспринимаемого качества городской среды в зависимости от источника звука.
На основании полученных результатов сформулированы следующие выводы:
-
1. Идентифицированы воспринимаемые источники звука и определены их пространственно-временные вариации. Показано, что транспортный шум преобладает вблизи дорог с высокой интенсивностью движения и промышленных предприятий, наименее заметен в историческом центре города. Разговор людей и музыкальные звуки преобладают в городских парках, а также вблизи торговых зданий. Звуки птиц часто наблюдаются на территории жилой застройки, на озелененных участках, в общественно-деловых зонах. Звуки воды хорошо слышны около фонтанов и городских водоемов. Небольшие изменения воспринимаемого звука во времени характерны для транспортного шума и воды, поскольку обычно такие источники расположены в фиксированных местах. Вариации звука, продуцируемого разговором людей и пением птиц, более значительны, поскольку модели поведения людей и птиц имеют сложные биоритмы и зависят от времени суток. Звуки, возникающие при разговоре людей, зависят в основном от их активности. Шум ветра обусловлен вариациями климатических факторов и морфологическими особенностями застройки и при малых скоростях ветра (до 3 м/с) почти не слышен.
-
2. Определены пространственно-временные вариации семантических характеристик эмоционально воспринимаемого качества акустической среды. Акустическая среда в жилой зоне воспринимается как приятная, спокойная, не насыщенная событиями, монотонная в утренние, дневные и вечерние часы. Акустическая среда в историческом центре города воспринимается преимущественно как приятная, спокойная, не насыщенная событиями, монотонная в утренние и дневные часы, однако при переходе к вечерним часам отмечается насыщенность среды событиями, беспорядочность, волнующее действие, что объясняется повышением активности в это время. Качество акустической среды в недифференцированной общественно-деловой зоне сходно с жилой зоной, с некоторым снижением монотонного воздействия вечером. Акустическая среда в специализированной общественно-деловой зоне воспринимается в целом как приятная, спокойная, монотонная. В производственной зоне преобладающим является шум, оказывающий на человека неблагоприятное акустическое воздействие. Для зоны рекреационного назначения характерен широкий спектр эмоционального восприятия звука в различное время.
-
3. Максимальные фактические уровни звука отмечаются в производственной зоне (70.4— 73.3 дБА), минимальные уровни звука характерны для жилой и специализированной общественно-деловой зон (48.7—51.1 дБА). Установлено, что жилые зоны отвечают санитарногигиеническим нормам по допустимому уровню шума.
-
4. На основе проведенного многофакторного анализа городской акустической среды получена корреляционная модель, позволяющая прогнозировать изменение критериев «приятность» и «событийность» в зависимости от выявленных источников звука. Транспортный шум имеет заметную обратную корреляционную связь с эмоциональным критерием «приятность» в утренние и вечерние часы (соответственно, r = –0.59 и r = –0.55) и высокую обратную корреляционную связь ( r = –0.76) дневные часы. В целом, для всех периодов выборки, транспортный шум имеет заметную обратную корреляционную связь с данным критерием ( r = – 0.64). С критерием «событийность» транспортный шум имеет высокую прямую корреляционную связь в утренние и дневные часы (соответственно, r = 0.75 и r = 0.72) и умеренную прямую корреляционную связь в вечерние часы ( r = 0.41). В целом, транспортный шум имеет заметную прямую корреляционную связь с данным критерием ( r = 0.61). Достаточно высокая оценка событийности транспортного шума обусловлена, по-видимому, возникновением «всплесков» звуковых волн от различных типов транспорта (троллейбусов, автобусов, различных автомобилей) на достаточно стабильном звуковом фоне. Разговор людей (при общей оценке) не коррелирует с критерием «приятность» ( r = 0.04), однако знакопеременный характер коэффициентов корреляции ( r = –0.50 утром и r = 0.34 вечером) свидетельствует о различном эмоциональном восприятии разговорной речи в разное время суток. «Событийность» разговора людей также характеризуется различным эмоциональным восприятием по времени: для утренних часов характерна высокая прямая корреляционная связь ( r = 0.74), для дневных часов – слабая ( r = 0.28), для вечерних часов – умеренная ( r = 0.34). Существует слабая положительная корреляционная связь между приятностью и звуком воды, событийность, по общей оценке, также выражена слабо. В целом, пение птиц оказывает положительное Korniyenko, S.; Zenin, A.
-
5. Результаты исследования убедительно доказали необходимость применения метода анализа звуковых ландшафтов в градостроительстве. Наряду с традиционным подходом, основанным на снижении транспортного шума, чрезвычайно большое значение имеет максимальное сохранение природных источников звука. Решение этой задачи повышает качество природного звукового ландшафта на урбанизированных территориях и способствует сохранению экологически безопасной комфортной среды для будущих поколений.
-
6. Дальнейшие исследования будут направлены на создание математической модели, устанавливающей связь между морфологическими характеристиками городской застройки и эмоционально воспринимаемым качеством акустической среды, с целью разработки научно обоснованных решений по улучшению акустической среды мегаполисов.
Correlation between sound sources and acoustic quality in urbanized areas;
воздействие на человека с точки зрения приятности ( r = 0.38), однако воспринимается как не событийное воздействие ( r = –0.63). Этот результат хорошо согласован с временной тенденцией пения птицы, в частности, со звуковым доминированием в утренние и дневные часы.
Список литературы Корреляция между источниками звука и качеством акустики в городских районах
- Frontiers 2022: Noise, Blazes and Mismatches. URL: https://www.unep.org/ru/resources/rubezhi-2022-goda-shum-plamya-i-perekosy.
- Watts, G. (2017) The Effects of "Greening" Urban Areas on the Perceptions of Tranquillity. Urban Forestry and Urban Greening, Elsevier GmbH, 26, 11–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ufug.2017.05.010.
- Kornienko, S.; Dikareva, E (2022) The Sky Visibility at Shading by Trees. Construction of Unique Buildings and Structures, 102, 10203. https://doi.org/10.4123/CUBS.102.3.
- Korniyenko, S. (2021) Progressive Trend in Adaptive Façade System Technology . A Review. AlfaBuild; 19, 1902. https://doi.org/10.57728/ALF.19.2.
- Korniyenko, S.V. (2021) Advantages , Limitations and Current Trends in Green Roofs Development . A Review. AlfaBuild; 20, 2002. https://doi.org/10.57728/ALF.20.2.
- Hornikx, M. (2016) Ten Questions Concerning Computational Urban Acoustics. Building and Environment, Elsevier Ltd, 106, 409–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2016.06.028.
- Kang, J., Aletta, F., Gjestland, T.T., Brown, L.A., Botteldooren, D., Schulte-Fortkamp, B., Lercher, P., van Kamp, I., Genuit, K., Fiebig, A., Bento Coelho, J.L., Maffei, L. and Lavia, L. (2016) Ten Questions on the Soundscapes of the Built Environment. Building and Environment, 108, 284–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2016.08.011.
- Kang, J. and Schulte-Fortkamp, B. (2016) Soundscape and the Built Environment. Soundscape and the Built Environment. https://doi.org/10.1201/b19145.
- Wang, J., Li, C., Lin, Y., Weng, C. and Jiao, Y. (2023) Smart Soundscape Sensing: A Low-Cost and Integrated Sensing System for Urban Soundscape Ecology Research. Environmental Technology and Innovation, Elsevier B.V., 29, 102965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2022.102965.
- Guedes, I.C.M., Bertoli, S.R. and Zannin, P.H.T. (2011) Influence of Urban Shapes on Environmental Noise: A Case Study in Aracaju Brazil. Science of the Total Environment, Elsevier B.V., 412–413, 66–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.10.018.
- Baranova, D., Sovetnikov, D. and Borodinecs, A. (2018) The Extensive Analysis of Building Energy Performance across the Baltic Sea Region. Science and Technology for the Built Environment, Taylor & Francis, 24, 982–993. https://doi.org/10.1080/23744731.2018.1465753.
- Meng, Q. and Kang, J. (2016) Effect of Sound-Related Activities on Human Behaviours and Acoustic Comfort in Urban Open Spaces. Science of the Total Environment, Elsevier B.V., 573, 481–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.08.130.
- Meng, Q., Sun, Y. and Kang, J. (2017) Effect of Temporary Open-Air Markets on the Sound Environment and Acoustic Perception Based on the Crowd Density Characteristics. Science of the Total Environment, Elsevier B.V., 601–602, 1488–1495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.017.
- Hong, J.Y. and Jeon, J.Y. (2015) Influence of Urban Contexts on Soundscape Perceptions: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach. Landscape and Urban Planning, Elsevier B.V., 141, 78–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2015.05.004.
- Aletta, F., Kang, J. and Axelsson, Ö. (2016) Soundscape Descriptors and a Conceptual Framework for Developing Predictive Soundscape Models. Landscape and Urban Planning, Elsevier B.V., 149, 65–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2016.02.001.
- Zhao, C., Fu, G., Liu, X. and Fu, F. (2011) Urban Planning Indicators, Morphology and Climate Indicators: A Case Study for a North-South Transect of Beijing, China. Building and Environment, Elsevier Ltd, 46, 1174–1183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2010.12.009.
- Hong, J.Y. and Jeon, J.Y. (2017) Relationship between Spatiotemporal Variability of Soundscape and Urban Morphology in a Multifunctional Urban Area: A Case Study in Seoul, Korea. Building and Environment, Elsevier, 126, 382–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2017.10.021.
- Salomons, E.M. and Berghauser Pont, M. (2012) Urban Traffic Noise and the Relation to Urban Density, Form, and Traffic Elasticity. Landscape and Urban Planning, Elsevier B.V., 108, 2–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2012.06.017.
- Eggenschwiler, K., Heutschi, K., Taghipour, A., Pieren, R., Gisladottir, A. and Schäffer, B. (2022) Urban Design of Inner Courtyards and Road Traffic Noise: Influence of Façade Characteristics and Building Orientation on Perceived Noise Annoyance. Building and Environment, 224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2022.109526.
- Jeon, J.Y. and Hong, J.Y. (2015) Classification of Urban Park Soundscapes through Perceptions of the Acoustical Environments. Landscape and Urban Planning, Elsevier B.V., 141, 100–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2015.05.005.
- Mohammadzadeh, N., Karimi, A. and Brown, R.D. (2023) The Influence of Outdoor Thermal Comfort on Acoustic Comfort of Urban Parks Based on Plant Communities. Building and Environment, Elsevier Ltd, 228, 109884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2022.109884.
- Rey Gozalo, G., Barrigón Morillas, J.M., Trujillo Carmona, J., Montes González, D., Atanasio Moraga, P., Gómez Escobar, V., Vílchez-Gómez, R., Méndez Sierra, J.A. and Prieto-Gajardo, C. (2016) Study on the Relation between Urban Planning and Noise Level. Applied Acoustics, Elsevier Ltd, 111, 143–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2016.04.018.
- Ouis, D. (2001) Annoyance from Road Traffic Noise: A Review. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 21, 101–120. https://doi.org/10.1006/jevp.2000.0187.
- Liu, Q., Liu, Z., Jiang, J. and Qi, J. (2020) A New Soundscape Analysis Tool: Soundscape Analysis and Mapping System (SAMS). Applied Acoustics, Elsevier Ltd, 169, 107454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2020.107454.
- Abo-Qudais, S. and Abu-Qdais, H. (2005) Perceptions and Attitudes of Individuals Exposed to Traffic Noise in Working Places. Building and Environment, 40, 778–787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2004.08.013.
- Yuan, C., Ng, E. and Norford, L.K. (2014) Improving Air Quality in High-Density Cities by Understanding the Relationship between Air Pollutant Dispersion and Urban Morphologies. Building and Environment, Elsevier Ltd, 71, 245–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2013.10.008.
- Li, X. and Zhao, Y. (2023) Evaluation of Sound Environment in Departure Lounges of a Large Hub Airport. Building and Environment, 232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2023.110046.
- Attia, S., Bilir, S., Safy, T., Struck, C., Loonen, R. and Goia, F. (2018) Current Trends and Future Challenges in the Performance Assessment of Adaptive Façade Systems. Energy and Buildings, 179, 165–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2018.09.017.
- Barile, C.J., Slotcavage, D.J., Hou, J., Strand, M.T., Hernandez, T.S. and McGehee, M.D. (2017) Dynamic Windows with Neutral Color, High Contrast, and Excellent Durability Using Reversible Metal Electrodeposition. Joule, 1, 133–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2017.06.001.
- Khaled, K. and Berardi, U. (2021) Current and Future Coating Technologies for Architectural Glazing Applications. Energy and Buildings, 244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2021.111022.
- Valeryevich, S. (2022) Optical Remote Sensing for Urban Heat Islands Identification 1 Introduction / Введение. https://doi.org/10.4123/CUBS.104.4.
- Korniyenko, S. and Glukhoverya, D. (2018) Influence of Placement of the Window Block on Wall Thickness on Heat Losses. Construction of Unique Buildings and Structures, 67, 62–71. https://doi.org/10.18720/CUBS.67.5.
- Ryu, H., Park, I.K., Chun, B.S. and Chang, S. Il. (2017) Spatial Statistical Analysis of the Effects of Urban Form Indicators on Road-Traffic Noise Exposure of a City in South Korea. Applied Acoustics, The Author(s), 115, 93–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2016.08.025.
- Jiang, L., Bristow, A., Kang, J., Aletta, F., Thomas, R., Notley, H., Thomas, A. and Nellthorp, J. (2022) Ten Questions Concerning Soundscape Valuation. Building and Environment, Elsevier Ltd, 219, 109231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2022.109231.
- Ng, E., Yuan, C., Chen, L., Ren, C. and Fung, J.C.H. (2011) Improving the Wind Environment in High-Density Cities by Understanding Urban Morphology and Surface Roughness: A Study in Hong Kong. Landscape and Urban Planning, Elsevier B.V., 101, 59–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2011.01.004.
- Rychtáriková, M. and Vermeir, G. (2013) Soundscape Categorization on the Basis of Objective Acoustical Parameters. Applied Acoustics, 74, 240–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2011.01.004.
- Maristany, A., López, M.R. and Rivera, C.A. (2016) Soundscape Quality Analysis by Fuzzy Logic: A Field Study in Cordoba, Argentina. Applied Acoustics, Elsevier Ltd, 111, 106–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2016.04.013.
- Bo, E., Astolfi, A., Pellegrino, A., Pelegrin-Garcia, D., Puglisi, G.E., Shtrepi, L. and Rychtarikova, M. (2015) The Modern Use of Ancient Theatres Related to Acoustic and Lighting Requirements: Stage Design Guidelines for the Greek Theatre of Syracuse. Energy and Buildings, Elsevier B.V., 95, 106–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2014.12.037.


