Макроэкономическое влияние «умной экономики» на процесс глобализации: перспективы и последствия
Автор: Ван М.
Статья в выпуске: 1, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В статье рассматриваются вопросы, связанные с процессами цифровизации, использования новых технологий и инноваций в макроэкономике. Целью проведенного исследования является изучение влияния «умной экономики» на процесс глобализации, а также определение перспектив развития и последствий. Основными методами являются анализ, сравнение, логическое рассуждение. Научная новизна проведенного исследования заключается в расширении и дополнении основных понятий по исследуемой проблеме, а также в разработке ряда рекомендаций для совершенствования развития «умной экономики» на перспективу. Рассмотрены факторы, являющиеся барьером на пути развития «умной экономики» на современном этапе. Выполнен анализ совокупных внутренних расходов на развитие цифровой экономики в России. Установлен индекс цифровизации для различных секторов экономики и социальной сферы. Изучены показатели использования информационных технологий России в различных областях. Разработаны рекомендации по совершенствованию развития «умной экономики» на перспективу.
Макровоздействие, общество, умная экономика, процесс, глобализация, перспективы, последствия, барьеры, факторы, эффективность
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148330980
IDR: 148330980 | УДК: 338.2 | DOI: 10.18101/2304-4446-2025-1-33-39
Текст научной статьи Макроэкономическое влияние «умной экономики» на процесс глобализации: перспективы и последствия
Wang Mengyao. The Macro Impact of “Smart Economy” on the Globalization Process: Perspectives and Implications. Bulletin of Buryat State University. Economy and Management. 2025; 1: 33‒39.
In a globalized economy, there are continuous processes of production development, new products and innovations appear on the market, perfect ways of providing services are created, and so on. In these conditions, the phrase "smart economy" has increasingly entered mainstream discourse, referring to an innovative and advanced economic model that seeks to transform traditional methods of organizing and managing production and economic activities across various sectors. This transformation aims to enhance public welfare, elevate living standards, and establish favorable conditions for a comfortable lifestyle. In contemporary society, the "smart economy" is often equated with the digital economy [6, p. 200].
Significant changes in the volume of production using a particular set of technologies, as well as in the structure of equipment costs, market prices for equipment and components and industrial logistics services, and changes in leading technologies in products, services and information systems constitute structural changes [8, p. 176]. Moreover, the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and big data analytics plays a crucial role in streamlining operations and fostering data-driven decision-making. As industries embrace these innovative tools, they not only improve efficiency but also create new market opportunities that can drive economic growth. Additionally, public-private partnerships are becoming increasingly vital in developing smart infrastructure, which underpins the effectiveness of a "smart economy." Ultimately, this evolution offers a holistic approach that prioritizes sustainability alongside economic success.
The issues of macroeconomic impact of "smart economy" on globalization have been considered by many scientists, among which we can mention the works of I. V. Gurleyev, V. A. Gerba, O. L. Kazantseva, O. S. Kozello, M. A. Kovalev, Ya. V. Mochalova, E. N. Smirnov, L. N. Ustinova, A. V., Ukhina E. V. Shkarupet and many others.
It is important to note that the "smart economy" has a direct macroeconomic impact on all processes of globalization. Consequently, it directly influences the expansion of gross domestic product (GDP), enhances public welfare, and contributes to national wealth. Additionally, it helps lower production costs, improves environmental quality and safety, reduces unemployment levels in society, and generates new employment opportunities [3, p. 22]. The integration of advanced technologies and data analytics within a "smart economy" framework further amplifies productivity and fosters innovation across various sectors. Moreover, these developments can lead to a more resilient economy that is better equipped to adapt to global challenges and shifts. Consequently, the development of the "smart economy" has its macroeconomic prospects and implications for the state and the country as a whole. This confirms the relevance of the chosen research topic and its theoretical and practical significance in terms of addressing the most important issues of globalization.
The emergence of digitalization in society has forced a new look at all the processes taking place in modern society. There has been a transformation of many economic systems, a change of mechanisms and tools for managing various links and chains of this system, a reorientation of ideological values from traditional views to modern concepts and approaches has taken place [10, p. 30].
“Smart economy” has significantly increased the efficiency of production, various technologies, led to the acceleration of trade turnover between countries, increased the level of competition and identified priority areas for the development of sectors of the national economy.
The macro-impact of the smart economy on globalization is as follows:
-
1) An escalation in international trade;
-
2) A growth in the scale of product manufacturing;
-
3) The establishment of a unified network model for market relations;
-
4) A decrease in economic costs alongside an increase in profits;
-
5) An enhancement in the social development levels of countries;
-
6) A decrease in poverty and socioeconomic disparities within societies;
-
7) Improved efficiency in agricultural practices;
-
8) An expansion of political influence;
-
9) An increase in the speed of international information exchange among all global stakeholders;
-
10) Progress in addressing political matters on the international stage, among others [7, p. 393].
In order to fully transition to the “smart economy” in the context of globalization, it is necessary to radically change traditional approaches in the political, economic and social spheres of life activities [5, p. 28]. To accomplish long-term goals and objectives, it is essential to modernize the economy using advanced technologies and mechanisms. First of all, it is necessary to pay attention to the main tools and the possibility of their expansion, as well as the resources needed to implement the digitalization process at the global level [11, p. 232].
On the way to its development, the smart economy faces a number of factors that act as a barrier to its existence. Such factors include the following:
-
1) insufficient level of investment for the development of innovative enterprises and organizations, as well as the development of innovative projects;
-
2) lack of qualified specialists in the field of digital economy development;
-
3) the presence of internal and external security threats that may lead to the loss of digital data, their theft, leakage;
-
4) unpreparedness of the population for the emergence and introduction of innovations in the sphere of public life;
-
5) Expensive development of certain digital technologies, which may automatically lead to their rejection by the manufacturer;
-
6) the insufficient level of profitability of many enterprises and organizations that create opportunities for the introduction of new digital technologies and mechanisms, and many others [2, p. 11].
Nonetheless, despite various limitations, the "smart economy" is still progressing actively in the current global context, with an increasing demand for its primary production outputs. Russia is investing significantly in the development of the digital economy, investing more than 500 billion rubles in 2022. In recent years, the country has been leading among states in terms of the pace of digital technology development [1, p. 15]. (Fig. 1).
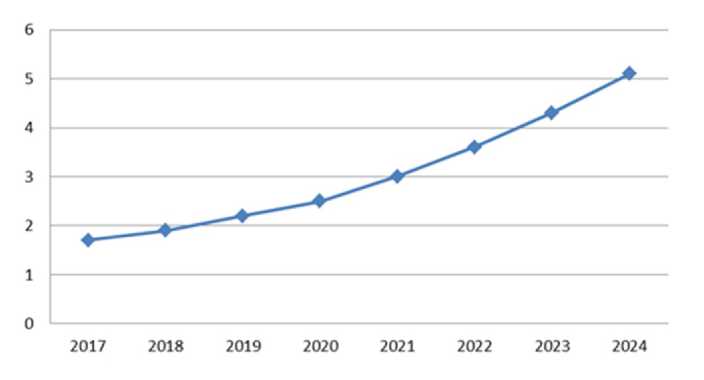
Fig.1. Gross domestic expenditures on the development of the digital economy in Russia, bln rub.
Therefore, we can observe the trends in the rise of gross domestic expenditures allocated for the advancement of the digital economy. In 2021, these costs in absolute terms amounted to 4,848 billion rubles, an increase of 785 billion rubles compared to the previous year. This indicates that these costs were spent on the development of new startups, the creation of innovative platforms, the creation of new technologies and digital governance mechanisms [9, p. 1481]. (Fig. 1).
Thus, the digitalization index for a number of industries showed the highest value in the IT sector. Here this index reached the value of — 34. The second place is occupied by information and communication. The index reached a value of — 27. In third place is the system of higher education. The value of the index amounted to — 24.
It is important to note that Russia ranked 10th in the global ranking of leaders of countries for the development of the “smart economy” in the main priority areas of development, which reflect the level of use of digital mechanisms and tools in such areas as the economy, budget, tax, financial sphere, as well as healthcare, education, etc. (Table 1).
Table 1
Metrics for the application of information technologies across different sectors in Russia (within the framework of international rankings)
|
Place |
Economy |
GTMI |
CGSI |
PSDI |
DCEI |
GTEI |
|
10. |
Russia |
0,897 |
0,881 |
0,960 |
0,828 |
0,919 |
GTMI — a general indicator of information technology utilization.
CGSI — this indicator reflects the level of use of digital technologies in government systems of data analysis, accounting and control;
PSDI — an indicator that characterizes the provision of public services;
DCEI — this indicator reflects the level of public engagement;
GTEI — indicator of institutional support [4, p.109].
In order to continue to develop the “smart economy” in modern conditions, it is necessary to focus on the following key aspects: first, the state should participate in all spheres of activity related to making major decisions on digital technologies and innovations, as well as to invest in the creation of new “smart projects”; second, it is necessary to use the available foreign experience in the field of formation of the “smart economy”; third, an important component is to ensure information security; and third, it is necessary to use the existing foreign experience in the field of the “smart economy”.
In the conditions of globalization development, information support, data exchange between participants, and the speed of obtaining information play an important role in the economy. Consequently, in order to improve the efficiency of the “smart economy” in this paper we have developed promising recommendations presented in Figure 2.
The developed recommendations, in our opinion, can help to create favorable opportunities for further growth and development of the “smart economy,” as well as reduce the negative impact of factors that hinder its development. “Smart economy in the context of macroeconomic globalization creates great development prospects. It creates favorable conditions for economic growth and international exchanges, stimulates pro- duction and improves the efficiency of activities, increases the main macroeconomic indicators, as well as enhances the competitiveness of economic entities in the world market as a whole [12, p. 921]. Despite a number of constraints, it continues to actively develop at present, solving complex goals and tasks of long-term development. The main consequence of such development in the future may be the creation of a highly developed international “smart economy” with all the advantages and new opportunities in the context of globalization.
Uti li z a t i on o f f or e ig n experience in the field of “smart economy” dev el opm e nt
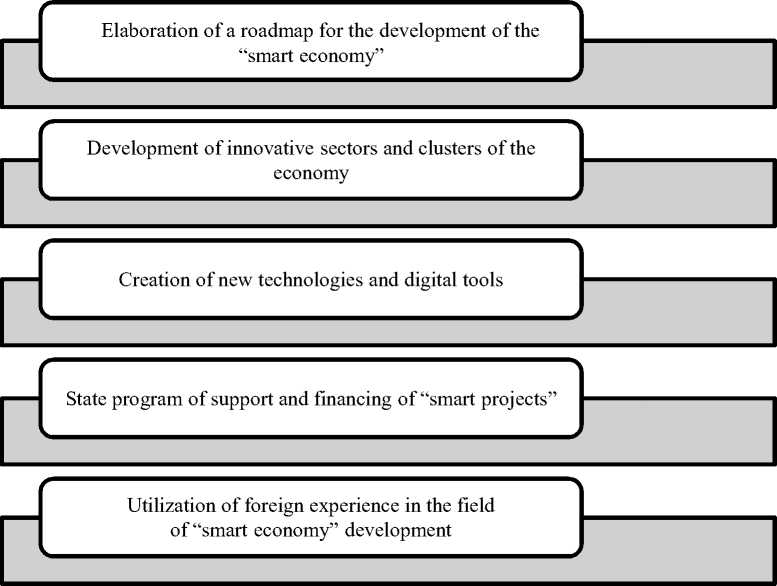
Fig. 2. Reco mmen dati o n s f or improving the development of the “smart economy” in t he f utur e
Th i s e v ol uti on is li k ely to lead to enhanced collaboration between na t i o ns, f os t e r i ng i nnova ti o n a nd tec hnological advancements. As countries invest more i n t he i r dig i t a l infr a struc ture s , t h e y w ill become better equipped to meet the challenges of a ra p i dly c ha ng i ng g l oba l l an dsc ape. Moreover, the integration of smart technol ogi es h a s t he pot e nt ia l t o c re a te more s ustainable economic practices, addressing environm ent al con c e rn s w hil e pr om oti ng g rowth. Ultimately, a robust “smart economy” co ul d serv e as a c at a l y st for soc i e t a l pr og r ess, improving the quality of life for individuals g lo bal l y .


