Marine plastic debris pollution in the western sector of the Russian Arctic
Автор: Konstantin S. Zaikov, Nikita A. Sobolev
Журнал: Arctic and North @arctic-and-north
Рубрика: Reviews and reports
Статья в выпуске: 43, 2021 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article discusses the pollution of marine environment with plastic waste, in particular, the accumulation of microplastics in the oceans, which is one of the most serious environmental problems both in the world and in the Russian Arctic. Alongside with other world oceans, the Arctic Ocean and the Barents Sea have become places of plastic accumulation, causing great harm to the fragile ecosystem of the Arctic region. Researchers have found microplastics not only in Arctic waters, but also in the ice of the Arctic seas. Plastic debris is carried by ocean currents from more densely populated areas of the planet. Local sources, such as fishing and other commercial activities, as well as waste water, are one more reason. Microplastics adversely affect living organisms in the ocean. In particular, plastic can cause physical harm and disrupt body formation of marine animals, as well as cause death by suffocation or ingestion of plastic. At the same time, plastics can accumulate persistent organic pollutants on their surface, which can poison marine animals, damaging the entire food chain.
Marine ecosystem, debris, biodegradation, plastic pollution, microplastics, the Arctic
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148318438
IDR: 148318438 | УДК: [504.5:556](985)(045) | DOI: 10.37482/issn2221-2698.2021.43.246
Текст научной статьи Marine plastic debris pollution in the western sector of the Russian Arctic
The annual global demand for plastics is constantly increasing and in 2011 it amounted to 245 million tons [4]. In this regard, according to scientists, in 2010, from 4.8 to 12.7 million tons of plastic were thrown into the world's oceans, and these figures are getting higher every year.
The ever-increasing volumes of plastic production, together with a fairly long lifetime (about 1000 years), make the problem of plastic pollution of the marine environment and the ecosystem one of the most significant nowadays.
Currently, another problem related to plastic has arisen — the problem of marine ecosystems pollution with microplastics. Despite the fact that microplastics in the marine environment were discovered several decades later than plastic, the problem of microplastics pollution has already become a global environmental problem.
Microplastic is a term used to describe the vast volume of microscopic plastic debris currently found throughout the world's oceans. Microplastics are plastic particles ranging in size from about a few microns to 5 mm. Microplastics can be found almost everywhere, from beaches and coastlines to subtropical oceanic whirlpools, polar ice caps and even the deepest parts of the ocean.
Microplastics are divided into 2 types by their origin: primary and secondary.
Primary microplastics are microgranules of plastic specially produced and added to various products. This plastic is commonly used in facial cleansers and cosmetics, or as fillers for soft furniture, toys, and as a primary raw material for the production of macroplastics.
Secondary microplastics are plastic fragments less than 5 mm in size, which are formed by the destruction of larger plastic debris both at sea and on land. Over time, physical, biological and chemical processes reduce the structural integrity of plastic debris, resulting in its fragmentation into smaller particles and degradation. Large amounts of secondary microplastics are generated by washing synthetic things in washing machines.
Microplastic contained in cosmetics and formed during washing gets in wastewater. The main problem is that microplastics are so small in size (Fig. 1) that they are not captured by wastewater filtration systems, and, as a result, these particles enter water bodies and become an environmental hazard [1].
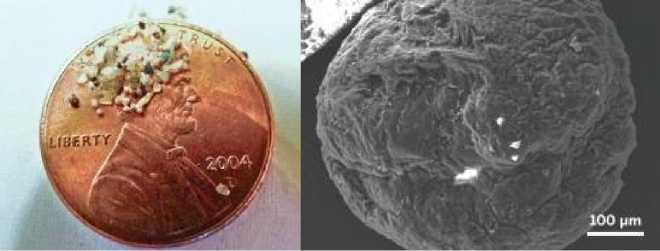
Fig. 1. Microplastic from cosmetics.
Plastic debris on beaches has a high oxygen availability and direct exposure to sunlight, so it degrades quickly, becoming brittle over time, cracking and “yellowing” (Figure 2). With the loss of structural integrity, these plastics degrade more rapidly in the environment as a result of abrasion, wave influence and turbulence [1].

(I-II) various types of expandable polystyrene, (III) non-woven geotextile material, (IV) facing fiberglass profiles, (V) gabion mesh with plastic coating (PVC / HDPE), (VI) fragments from a textive big bag (PP).
Fig. 2. Plastic with fragmentation on the seashore.
Microplastics can have a negative impact on organisms living in the ocean. In particular, plastic can cause physical harm and disrupt the body formation of marine animals, as well as cause death by suffocation or ingestion of plastic. The scientific literature has noted the physical effects of microplastics on small organisms, such as internal abrasions and blockages. It was also found that microplastics blocks the gastrointestinal tract, disrupts the body growth and the reproductive system functioning. Microplastics have been found in the blood, lymph and liver of some animals. At the same time, plastic is able to accumulate persistent organic pollutants on its surface, which can cause poisoning and store in the marine animals bodies, causing harm to the entire food chain [5]. In addition, plastic has a negative aesthetic impact on the environment.
Due to the fact that about half of all plastic is lighter than water, it can move on its surface with world currents and spread throughout the planet. At the same time, due to the peculiarities of ocean currents, the Arctic, the Arctic Ocean and the Barents Sea can become a place for plastic accumulation, causing great harm to the fragile ecosystem of the Arctic region. In addition, the Barents Sea is an active fishing area. In this regard, plastic and paint particles from fishing boats can get into the sea water, as well as both pieces of fishing nets, often made of plastic, and their whole fragments. The Barents Sea and the Arctic Ocean serve as drainage points for large Arctic rivers, such as the Pechora, the Northern Dvina, and others. They also carry plastic particles that enter their waters with industrial and domestic wastewater.
At present, the western part of the Russian Arctic is rather poorly studied for pollution by marine debris. However, current studies allow us to describe the situation in this sector of the Arctic.
A group of scientists from the Marine and Freshwater Research Center and the Istituto Na-zionale di Oceanografia e di Geofisica Sperimentale (OGS) [6] explored a part of the Barents Sea in the area of the Svalbard archipelago, located on the western border with the territorial waters of the Russian Federation. The authors note that the content of plastic particles ranges from 0 to
-
1.31 particles per m3, with plastic particles being detected in 95% of the analyzed samples. According to the researchers, the source of this debris can be both the transportation of pollution by ocean currents from more populated areas of the planet, and local sources, such as fishing and other commercial activities, as well as sewage.
There is also an acute problem of the ingestion and absorption of microplastics by marine dwellers (including crustaceans, molluscs, fish and marine mammals). This issue is extremely poorly investigated on the territory of the Russian Federation in general and in the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation in particular. Currently, there is no information on the concentration, type and form of plastic absorbed by marine animals in the western part of the Russian Arctic. At the same time, there are a number of works reflecting this situation in the regions bordering on the Russian Arctic. According to studies in the Greenland Sea [7], the concentration of microplastics in water was 2.4 ± 0.8 particles / m3, and microplastics in fish were found in 34% and 18% (in triglops and cod, respectively) of the fish sampled for analysis. Microplastics have also been found in crustaceans sampled off the coast of the Svalbard archipelago. Particles of plastic were found in each of 20 samples of Gammarida crustaceans. Most of the particles consisted of polymethacrylamide, a thermoplastic widely used in the marine industry as a coating to prevent fouling of ships, as well as anti-corrosion and waterproof coatings [8]. The results show that microplastic penetrates even the most remote parts of the planet, causing harm to organisms living there. The content of plastic particles is at comparable levels that have been found in more industrialized regions of the planet, indicating the transfer of particles by ocean currents.
It is also worth noting the discovery of microplastics in the Arctic sea ice. According to the results presented in the work of a group of researchers from the Thayer School of Engineering at Dartmouth College and Marine Biology and Ecology Research Center [9], the content of plastic particles in ice cores of central part of the Arctic Ocean is in the range of 38 to 234 particles per m3, which is significantly higher than the heavily polluted ocean currents. According to the authors, this is due to the effects of concentration in the process of ice formation.
Summing up, it should be noted that the scientific results described above indicate an increasingly aggravating situation with microplastics pollution of the world's oceans. Arctic pollution is of particular concern, as its fragile ecosystem is most susceptible to even the smallest changes. Microplastics can harm the ecosystems of the region, which can result in economic, environmental and aesthetic losses for the population of regions and entire countries. In this regard, it is necessary to take measures to identify and reduce the negative consequences of microplastic pollution of the ecosystem.
Recommendations
Based on the above data, it is obvious that there is almost complete lack of information on the content of microplastics in surface waters, sea animals and ice in the Russian part of the Arctic.
As a result, a large-scale international research programme aimed at establishing a microplastics monitoring system in the Arctic seas may provide a solution.
Assessment of environmental damage and risks associated with the Arctic ecosystem pollution by microplastics, based on the results of scientific research, is an important factor for further research to reduce possible ecological losses and search for ways to decrease risks for the population, including the reduction of ichthyofauna in the Russian Arctic.
Reducing the flow of marine debris and plastic into the waters of the Arctic seas is an important task, the goal of which is to alleviate the anthropogenic load on the region as a whole. Emissions reduction is possible in several ways:
-
1. increase the share of biodegradable plastics in the total volume of plastic production;
-
2. proliferation of waste recycling facilities that can dispose and recycle plastic;
-
3. increase fines for waste disposal in the water protection zone;
-
4. information and educational work with the population on the topics of plastic pollution;
-
5. use of alternative plastic household items and items of daily use;
-
6. introduction of separate waste collection.
Acknowledgments and funding
The article was prepared within the framework of a project supported by EC DG NEAR (grant agreement ENI / 2017 / 387-477, Development of a think tank functions of the Northern Dimension Institute project).
Список литературы Marine plastic debris pollution in the western sector of the Russian Arctic
- Cole M., Lindeque P., Halsband C., Galloway T.S. Microplastics as Contaminants in the Marine Envi-ronment: a Review. Marine pollution bulletin, 2011, no. 62 (12), pp. 2588–2597. DOI: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.09.025
- Tokiwa Y., Calabia B.P., Ugwu C.U., Aiba S. Biodegradability of Plastics. International journal of mo-lecular sciences, 2009, no. 10 (9), pp. 3722–3742. DOI: 10.3390/ijms10093722
- Lu L., Luo T., Zhao Y., Cai C., Fu Z., Jin Y. Interaction between Microplastics and Microorganism as well as Gut Microbiota: A Consideration on Environmental Animal and Human Health. Science of the To-tal Environment, 2019, no. 667, pp. 94–100. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.380
- Andrady A.L. Microplastics in the Marine Environment. Marine pollution bulletin, 2011, No. 62 (8), pp. 1596–1605. DOI: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.05.030
- Rodrigues J.P., Duarte A.C., Santos-Echeandía J., Rocha-Santos T. Significance of Interactions be-tween Microplastics and POPs in the Marine Environment: a Critical Overview. TrAC. Trends in Ana-lytical Chemistry, 2019, no. 111, pp. 252–260. DOI: 10.1016/j.trac.2018.11.038
- Lusher A.L., Tirelli V., O’Connor I., Officer R. Microplastics in Arctic Polar Waters: the First Reported Values of Particles in Surface and Sub-Surface Samples. Scientific reports, 2015, no. 5, p. 14947. DOI: 10.1038/srep14947
- Morgana S., Ghigliotti L., Estévez-Calvar N., Stifanese R., Wieckzorek A., Doyle T., Christiansen J.S., Faimali M., Garaventa F. Microplastics in the Arctic: A Case Study with Sub-Surface Water and Fish Samples off Northeast Greenland. Environmental pollution, 2018, vol. 242, pp. 1078–1086. DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.08.001
- Iannilli V., Pasquali V., Setini A., Corami F. First Evidence of Microplastics Ingestion in Benthic Amphi-pods from Svalbard. Environmental research, 2019, no. 179, p. 108811. DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2019.108811
- Obbard R.W., Sadri S., Wong Y.Q., Khitun A.A., Baker I., Thompson R.C. Global Warming Releases Mi-croplastic Legacy Frozen in Arctic Sea Ice. Earth's Future, 2014, no. 2 (6), pp. 315–320. DOI: 10.1002/2014EF000240


