Маркеры GSTNL, RARSS2 и RASSF1A в диагностике рака предстательной железы: результаты исследования
Автор: Сивков А.В., Кешишев Н.Г., Меринова О.В., Северин С.Е., Савватеева М.В., Кузнецова Е.М., Раевская А.А., Каприн А.Д.
Журнал: Экспериментальная и клиническая урология @ecuro
Рубрика: Онкоурология
Статья в выпуске: 4, 2016 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Введение. Около 30 лет назад тест PSA перевернул диагностику рака предстательной железы (РПЖ), однако, в настоящее время существуют убедительные данные о недостаточной диагностической значимости данного маркера. Актуальным становится поиск новых маркеров рака предстательной железы и разработка на их основе тест-систем. Материалы и методы: Клинический материал работы представлен результатами исследований 135 пациентов с уровнем ПСА крови от 4 до 10 нг/мл, и 22 здоровых добровольцев. Были выбраны следующие типы биологического материала: кровь, моча после проведения процедуры пальцево-ректального исследования (ПРИ) и биоптаты предстательной железы (ПЖ). Для детекции изменений в статусе метилирования промоторных областей GSTπl, RARβ2 и RASSF1A использовалась ПЦР. Результаты и обсуждения. Средний возраст больных в группе с доброкачественными заболеваниями ПЖ составил 66,62 ± 7,98 лет [M ± m] (41-82). Чувствительность, специфичность, прогностическая ценность положительного и отрицательного результатов определения статуса метилирования промоторных областей генов GSTπl, RARβ2, RASSF1A (суммарно), при определении в ткани ПЖ, составляет 88,9%, 84,3%, 49,5% и 95,6%; при определении в крови - 77,8%, 58,3%, 26,2% и 86%; при определении в образцах мочи после массажа ПЖ - 74,1%, 52,8%, 25,1% и 86,5%, соответственно. При сравнении диагностических характеристик маркеров GSTπ1, RARβ2 и RASSF1A, определяемых в крови, с PSA, специфичность диагностической системы превосходит специфичность теста PSA (58,3% против 13,9%, р
Рак предстательной железы, скрининг, диагностика, онкомаркеры, молекулярные маркеры, днк-маркеры, маркеры gstπ1, rarβ2 и rassf1a
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142188152
IDR: 142188152
Текст научной статьи Маркеры GSTNL, RARSS2 и RASSF1A в диагностике рака предстательной железы: результаты исследования
Около 30 лет назад тест PSA перевернул диагностику РПЖ, вызвав, при этом, значительный подъем частоты обнаружения заболевания на более ранних, курабельных стадиях [1,2,3]. Однако убедительные данные исследований свидетельствуют о недостаточной диагностической значимости данного маркера [4]. Кроме того, опубликованные наблюдения предоставили неоднозначные результаты о роли изучения PSA в снижении смертности от РПЖ [5,6]. Также, в связи с низкой специфичностью теста PSA, особую сложность представляет вопрос проведения биопсий, в особенности повторных, при уровне PSA в «серой зоне» (4-10 нг/мл) [7]. Актуальным является поиск новых маркеров РПЖ и разработка на их основе тест-систем.
На сегодняшний день выявлено более 90 различных генов и их продуктов, потенциально вовлеченных в развитие РПЖ и способных, в той или иной степени, считаться маркерами данного заболевания [8-13]. Изменения ткани предстательной железы (ПЖ) в процессе малигнизации затрагивают все основные клеточные функции и находят отражение на различных уровнях клеточных структур и процессов, таких как цитоморфоло-гические изменения, изменения в уровне экспрессии генов и их продуктов, эпигенетические изменения.
При злокачественных заболеваниях ПЖ одними из наиболее значимых событий на молекулярном уровне являются эпигенетические изменения, в частности, статуса метили- рования ДНК [10-20]. Установлено, что опухоль-специфическое гиперметилирование 5'-регуляторных областей ряда генов, приводящее к их инактивации, можно использовать для диагностики разных патологических состояний ткани предстательной железы [21]. Одной из наиболее широко описанных эпигенетических аномалий в опухолевых клетках (в том числе ПЖ) является изменение профиля метилирования промотор-ной области гена GSTπ1 (Glutathione-S-Transferase π1), вовлеченного в регуляцию апоптоза и утилизацию ксенобиотиков [13]. Также при ма-лигнизации ткани ПЖ значительные эпигенетические изменения наблюдают среди генов-супрессоров опухолевого роста [21,22]. Метилирование CрG-островков в промотор-ных областях таких генов приводит к их инактивации и повышению риска возникновения злокачественных заболеваний.
Из большого числа инактивируемых при РПЖ супрессоров опухолевого роста нами были выбраны следующие гены: RARβ2 (Retinoic Acid Receptor β2), гормоно-чувствительный, вовлеченный в рецептор-опосре-дованную супрессию опухолевого роста и RASSF1A (RAS association domain family protein 1A), участвующий в регуляции апоптоза и поддержании генетической стабильности клетки [23]. Так как получение биоптата ткани ПЖ является достаточно инвазивным методом, одной из задач данного исследования было сравнение диагностических параметров исследуемых маркеров при использовании биоматериала различных типов для разработки неинвазивного способа диагностики РПЖ.
Нами определены границы про-моторных областей выбранных генов и выявлены GC-богатые участки, а также предложены пары праймеров для амплификации метилированной и неметилированной последовательностей данных генов, которые могут быть использованы для детекции данных маркеров методом метил-специфической ПЦР.
Таким образом, целью настоящей работы явилось повышение эффективности диагностики РПЖ путем определения наиболее специфичной и чувствительной комбинации указанных выше молекулярных маркеров.
МАТЕРИАЛЫ И МЕТОДЫ
Материал работы представлен результатами клинических, лабораторных и морфологических исследований 135 пациентов европеоидной расы с подозрением на РПЖ, находившихся на обследовании в НИИ уроло-гии1 в 2009-2012 годах и 22 здоровых добровольцев. Критерием включения в основную группу пациентов было значение PSA крови от 4 до 10 нг/мл. Контрольная группа была сформирована из практически здоровых мужчин без выявленных патологических изменений в ПЖ. В данной группе не было образцов ткани ПЖ в силу отсутствия показаний к биопсии.
На основе гистологически верифицированных диагнозов были сформированы следующие экспериментальные группы:
I – группа больных хроническим простатитом вне обострения (n=46);
II – группа больных доброкачественной гиперплазией предстательной железы (ДГПЖ) с простатической интраэпителиальной неоплазией (ПИН) разной степени (n=62);
-
III – группа больных РПЖ (аденокарцинома ПЖ) разной степени дифференцировки (n=27);
-
IV – группа условно-здоровых лиц без выявленных патологических изменений в предстательной железе (n=22).
Для сравнения параметров получаемого генетического материала, эффективности проведения амплификации и с учетом экономической целесообразности исследования, были выбраны следующие типы биологического материала: цельная кровь; моча, собираемая после проведения процедуры пальцевого ректального исследования (ПРИ) предстательной железы; образцы ткани ПЖ, полученные при биопсии, как наиболее полноценный тип материала для исследования. Из данных видов биоматериала выделены образцы ДНК и сформирован банк материалов для дальнейшего изучения указанной панели молекулярных маркеров.
Для детекции изменений в статусе метилирования промоторных областей указанных выше генов использовали одну из модификаций ПЦР – метилспецифическую ПЦР (МС-ПЦР или MSP). Выделение геномной ДНК (гДНК) проводили при помощи набора реагентов Genomic
Таблица 1. Общая характеристика больных РПЖ (n=27)
|
Показатель |
Среднее значение |
|
Возраст |
67,3±8,3 (47-79) |
|
PSA |
7,3±1,7 (4,7– 9,7) |
|
Показатель Gleason |
6,3±0,7 (5-8) |
|
Среднее число «положительных» биоптатов |
3,6±2,5 (1-12) |
|
Средний % поражения биоптата |
49,3±28,0 (10-100) |
DNA Purification kit (Promega), согласно инструкции производителя. Концентрацию гДНК определяли спектрофотометрически. Затем гДНК подвергали метабисульфитной конверсии при помощи набора реагентов EpiTect® Bisulfite kit (Qiagen) согласно инструкции производителя.
Оценивали чувствительность, специфичность, предсказательную ценность положительного теста и предсказательную ценность отрицательного результата. При расчете диагностических параметров разрабатываемой системы маркеров использовали условные обозначения, определения и формулы стандартной четырехпольной таблицы (Р. Флетчер «Клиническая эпидемиология»). Также были рассчитаны показатели площади под ROC-кривой (AUC). Качество исследуемых диагностических маркеров оценивали по экспертной шкале для значений AUC.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ И ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Средний возраст пациентов с доброкачественными заболеваниями ПЖ I-II групп составил 66,6 ± 8,0 лет [M ± m] (41-82). Средний уровень PSA у этих пациентов был равен 7,0±1,8 нг/мл (4,09,9), а у больных РПЖ (III группа) – 7,3±1,7 (4,7-9,7). Средний объем ПЖ в I и II группах составил 51,6±24,2 см 3 (46,9-56,2), а у больных РПЖ (III) – 41,4±24,3 см 3 (31,8-51). Среднее значение показателя Gleason в группе с диагностированным РПЖ составило 6,6± 0,7 балла (5-8). Индекс Gleason ≤ 6 баллов выявлен у 20 (74%) больных, ≥7 баллов – у 7 (26%). Среднее число «позитивных» биоптатов – 3,6±2,5 (1-12), средний процент поражения биоптата 49,3±28,0% (10-100) (табл. 1).
В группе больных РПЖ отмечено следующее распределение по стадиям заболевания:
-
- T1сNoMo – 37% (n=10);
-
- T2аN0M0 – 22% (n=6);
-
- T2bN0M0 – 14,8% (n=4);
-
- T2сN0M0 -14,8% (n=4);
-
- T3аN0M0 – 3,7% (n=1);
-
- T3bN0M0 – 7,4% (n=2).
При спектрофотометрическом определении концентрации полученной гДНК было обнаружено, что наиболее эффективное ее выделение возможно из образцов ткани ПЖ, цельной крови больных и лимфоцитов (образцы 1-4), в то время как выделение гДНК из клеток, обнаруживаемых в образцах мочи, оказалось гораздо менее эффективным (образцы 5 и 6). Таким образом, была определена наиболее перспективная среда и способ хранения биологического материала (рис. 1).
М 1 2 3 4 5 6
гДНК
3000п.н.
500 п.н.
Условные обозначения:
М – маркеры молекулярной массы.
-
1 – гДНК, выделенная образца ткани предстательной железы, полученного при биопсии и замороженного при -70°С, 2 – гДНК, выделенная из цельной крови, замороженной при -20°С, 3,4 – гДНК, выделенная из лимфоцитов периферической крови, лизированных и замороженных при -70°С, 5 – гДНК, выделенная из клеток, обнаруженных в моче после проведения ПРИ, лизированных и замороженных при -70°С.
-
6 – гДНК, выделенная из клеток, обнаруженных в моче после проведения ПРИ и замороженных в PBS при -20°С.
Рис. 1. Электрофоретический анализ качества геномной ДНК, выделенной из различных типов биологического материала, хранившегося в различных условиях (0,7% агарозный гель)
Чувствительность, специфичность, предсказательная ценность положительного и отрицательного тестов были вычислены для каждого маркера в отдельности и для системы маркеров в целом. В таблице 2 отражены значения чувствительности, специфичности, положительной и отрицательной прогностической ценности исследуемых ДНК-маркеров, с учетом типа биологического мате- риала, из которого была выделена ДНК для проведения анализа.
При анализе характеристик диагностической системы, вычисленных на выборке образцов гДНК, выделенных из цельной крови, чувствительность составила 77,8%, а специфичность – 58,3%. Чувствительность и специфичность системы маркеров, определенная в выборке образцов гДНК, выделенных из мочи, оказалась несколько ниже: 74,1% и 52,8%, тогда как для ткани ПЖ эти показатели достигли 88,9% и 84,3%, соответственно.
Произведена оценка качества диагностической модели определения исследуемых маркеров в различных диагностических средах посредством ROC-анализа для каждого маркера в отдельности и их совокупности. При определении исследуемой панели маркеров в совокупности AUC составил: для мочи после ПРИ – 0,672 (95% ДИ 0,586 – 0,751); для крови – 0,736 (95% ДИ 0,653-0,808) и для биоптатов ПЖ – 0,891 (95% ДИ 0,826 – 0,938) (рис. 2). Согласно экспертной шкале значений AUC, эти показатели соответствуют диагностической модели среднего, хорошего и очень хорошего качества, соответственно.
Таким образом, наиболее эффективное выделение изучаемой гДНК возможно из образцов ткани
Таблица 2. Клинические характеристики диагностической системы маркеров РПЖ, выделенных из цельной крови, образцов ткани предстательной железы и мочи после пальцевого ректального исследования
|
Показатель |
Среда |
Метилирование промоторной области гена |
|||
|
GSTπ1 |
RARβ2 |
RASSF1A |
Суммарно |
||
|
Чувствительность |
Кровь |
63,0 |
70,4 |
77,8 |
77,8 |
|
Биоптат |
85,2 |
88,9 |
88,9 |
88,9 |
|
|
Моча |
85,2 |
66,7 |
74,1 |
74,1 |
|
|
Специфичность |
Кровь |
59,3 |
33,3 |
57,4 |
58,3 |
|
Биоптат |
68,5 |
75,0 |
84,3 |
84,3 |
|
|
Моча |
38,0 |
38,0 |
57,4 |
52,8 |
|
|
+ PV |
Кровь |
28,0 |
20,7 |
29,9 |
26,2 |
|
Биоптат |
41,3 |
46,2 |
59,8 |
49,1 |
|
|
Моча |
24,4 |
21,0 |
29,9 |
25,1 |
|
|
- PV |
Кровь |
86,2 |
82,5 |
89,3 |
86,0 |
|
Биоптат |
94,9 |
95,5 |
96,5 |
95,6 |
|
|
Моча |
89,0 |
81,7 |
88,9 |
86,5 |
|
|
Диагностическая точность |
Кровь |
60,9 |
44,0 |
60,6 |
33,2 |
|
Биоптат |
72,8 |
77,1 |
85,7 |
60,3 |
|
|
Моча |
45,7 |
44,8 |
60,0 |
26,9 |
|
ПЖ и цельной крови, в то время, как выделение ДНК из клеток, обнаруживаемых в образцах мочи, является значительно менее эффективным.
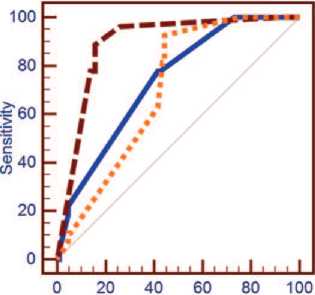
10O-Specificity
^— Панель маркеров в крови ■ ■ Панель маркеров в ПЖ • • • Панель маркеров в моче
Рис. 2. ROC- кривая панели маркеров, определенных в крови, моче и биопсийном материале
Проведен корреляционный анализ зависимости экспрессии исследуемых маркеров в различных средах организма при РПЖ от других клинико-морфологических параметров. Определяли коэффициент корреляции Спирмена (r) и коэффициент значимости (р). Статистически значимая корреляционная связь была выявлена между уровнем PSA и маркером RARβ2 в крови (r=0,3950, p=0,0414). Также установлена достоверная обратная корреляция числа позитивных биоптатов с экспрессией маркера RASSF1A в моче (r=-0,4065, p=0,0354) и статистически значимая обратная корреляция объема ПЖ с экспрессией данного маркера в ткани ПЖ (r= -0,4505, p=0,0184). Такие параметры, как процент пораженного опухолью столбика, стадия заболевания, сумма баллов по шкале Gleason не выявили статистически значимой корреляции с экспрессией маркеров в различных биологических средах.
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
В последние годы появляется все больше исследований, посвященных генетическим маркерам РПЖ, в том числе и включенным нами в изучаемую панель. Авторы приводят различные данные об их диагностической значимости, в зависимости от метода детекции, среды определения, клинической группы и пр. (табл.3) [24].
Так, чувствительность и специфичность GSTπ1 (GSTP1) при исследовании биоптатов оценивают в 73-91% и 100%, в сыворотке крови – 72% и 100%, а в постмассажной порции мочи, как 36-73% и 98-100%, соответственно [25]. В нашем исследовании
Таблица 3. Метилированные гены, определяемые при диагностике РПЖ в биоптатах и других биологических жидкостях [24]
|
Gene/Gene cohort |
Specimen |
Sensitivity % |
Specificity % |
Refs. |
|
GSTP1 |
Biopsy |
91 (10/11) |
100 |
52 |
|
GSTP1 |
Biopsy |
73(11/15) |
100 |
141 |
|
GSTP1 |
Biopsy |
75 (46/61) |
100 |
142 |
|
GSTPt RARp2. АРС. TIG1 |
Biopsy |
97 (59/61) |
100 |
144 |
|
GSTP1 |
Biopsy washing |
100(10/10) |
100 |
143 |
|
GSTP1 |
Ejaculate |
44 (4/9) |
NA |
139 |
|
GSTP1 |
Ejaculate |
50 (4/8) |
100 |
140 |
|
GSTP1 |
Serum |
72 (23/32) |
100 |
140 |
|
GSTPt PTGS2. Reprimo. TIG1 |
Serum |
42—47 |
92 |
148 |
|
GSTPt RASSFt RAR02 |
Serum |
28 (24/83) |
100 |
149 |
|
GSTP1 |
Unne |
27 (6/22) |
100 |
145 |
|
GSTP1 |
Urine post massage |
36(4/11) |
100 |
140 |
|
GSTP1 |
Urine post massage |
73 (29/40) |
98 |
152 |
|
GSTP1 |
Urine post biopsy |
39(7/18) |
NA |
151 |
|
GSTPt APC, EDNRB |
Urine post biopsy |
71 (12/17) |
NA |
153 |
|
GSTPt INK4a, ARP, MGMT |
Urine |
87 (45/52) |
100 |
154 |
|
GSTPt INK4a. ARE MGMT. RARp2. ТІМРЗ. CDHt RASSF1A, APC |
Urine |
100 (52/52) (positive for at least one gene) |
<100 |
154 |
|
GSTPt RAR02. APC. RASSF1A |
Urine post massage |
86 |
89 |
86 |
|
GSTPt RASSF1A. ECDHt APC. DAPK. MGMT, pl4. p16. RAR02. TIMP3 |
Urine post massage |
93 (positive for at least one gene) |
NA |
86 |
|
GSTPt RARp2 APC |
Urine |
55 |
80 |
120 |
|
GSTP1, gal3 |
Biopsy |
96 (26/27) |
100 |
127 |
|
GSTPt gal3 |
Serum |
100 (4/4) |
100 |
127 |
|
GSTP1, ga!3 |
Urine |
100 (22/22) |
ND |
Unpublished |
эти показатели оказались несколько ниже, практически во всех средах.
Чувствительность и специфичность RARβ2 в зависимости от метода исследования T. Gao c соавт. оценивают следующим образом: для био-птатов ПЖ в 54-97% и 77-100%; в моче – 35-62% и 91-97%, соответственно [24]. Отдельные авторы публикуют данные о крайне высокой эффективности определения RARβ2 в крови с использованием метода количественной ПЦР (КМС-ПЦР или QMSP): чувствительность – 98%; специфичность – 89%; AUC – 0,936 (95% ДИ 0,895 – 0,977; p < 0,001) [26]. В нашем исследовании чувствительность МС-ПЦР при определении RARβ2 в крови и специфичность во всех средах оказались несколько ниже.
Ряд авторов указывают на существование некоторых различий экспрессии генов GSTπ1 и RARβ2 в ткани РПЖ у мужчин кавказской и негроидной рас: AUC для GSTπ1 -0,969 и 0,811, а для RARβ2 – 0,969 и 0,922, соответственно [27].
По данным метаанализа J. Pan и соавт. обобщенные показатели чувствительности и специфичности RASSF1A в ткани ПЖ достигают
0,79 (95% ДИ 0,64-0,89) и 0,84 (95% ДИ 0,63-0,94), соответственно [28]. Объединенные показатели чувствительности и специфичности RASSF1A в биологических жидкостях (кровь, сыворотка, моча) – существенно ниже: 0,6 (95% ДИ 0,08-0,96) и 0,93 (95% ДИ 0,75-0,98). Эти же тенденции отмечены и в нашем исследовании.
Найдены результаты лишь одного исследования, в котором оценивали метилирование в сыворотке крови комбинации генов, аналогичной нашей ( GSTπ1, RARβ2 и RASSF1A ), методом МС-ПЦР [29]. Чувствительность и специфичность теста по данным авторов составила 20% и 100%, соответственно, тогда как в нашей работе эти показатели были равны 77,8% и 58,3%.
Сравнение диагностических параметров разрабатываемой панели с другими маркерами РПЖ демонстрирует преобладание ее специфичности в крови относительно PSA (58,3% против 13,9%, p <0,05), при сопоставимой чувствительности. С клинической точки зрения определенный интерес представляет возможность совместного применения теста PSA и исследуемых маркеров в крови, для увеличения диагностической эффективности за счет повышения чувствительности и специфичности комбинации. Проведенные расчеты показали некоторое увеличение AUC до 0,746 (95% ДИ(0,664-0,817) при таком подходе, что соответствует диагностической модели хорошего качества (рис. 3).
Панель маркеров в крови с PSA
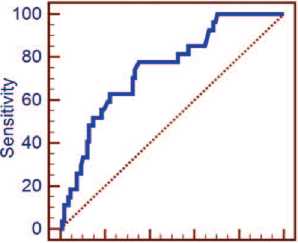
О 20 40 60 80 100
10O-Specificity
Рис. 3. ROC-кривая для совокупной панели маркеров и PSA, определенных в сыворотке крови
Специфичность изучаемой в настоящей работе панели маркеров превосходит таковую для соотношения свободного fPSA к PSA, нового маркера [-2]proPSA и PHI («индекс здоровья ПЖ), для которых при 90% чувствительности она составляет 17%, 33% и 32%, соответственно [30]. В то же время, как свидетельствуют недавно опубликованные нами данные, чувствительность и специфичность комбинации генов PCA3 и TMPRSS2-ERG при определении их в постмассажной порции мочи, превышает параметры изучаемой панели и составляют 83% и 78%, соответственно [31].
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Резюме:
Введение. Около 30 лет назад тест PSA перевернул диагностику рака предстательной железы (РПЖ), однако, в настоящее время существуют убедительные данные о недостаточной диагностической значимости данного маркера. Актуальным становится поиск новых маркеров рака предстательной железы и разработка на их основе тест-систем.
Материалы и методы: Клинический материал работы представлен результатами исследований 135 пациентов с уровнем ПСА крови от 4 до 10 нг/мл, и 22 здоровых добровольцев. Были выбраны следующие типы биологического материала: кровь, моча после проведения процедуры пальцево-ректального исследования (ПРИ) и биоптаты предстательной железы (ПЖ). Для детекции изменений в статусе метилирования промоторных областей GSTπ1, RARβ2 и RASSF1A использовалась ПЦР.
Результаты и обсуждения. Средний возраст больных в группе с доброкачественными заболеваниями ПЖ составил 66,62 ± 7,98 лет [M ± m] (41-82). Чувствительность, специфичность, прогностическая ценность положительного и отрицательного результатов определения статуса метилирования промоторных областей генов GSTπ1, RARβ2, RASSF1A (суммарно), при определении в ткани ПЖ, составляет 88,9%, 84,3%, 49,5% и 95,6%; при определении в крови – 77,8%, 58,3%, 26,2% и 86%; при определении в образцах мочи после массажа ПЖ – 74,1%, 52,8%, 25,1% и 86,5%, соответственно. При сравнении диагностических характеристик
Список литературы Маркеры GSTNL, RARSS2 и RASSF1A в диагностике рака предстательной железы: результаты исследования
- Stamey TA, Yang N, Hay AR, McNeal JE, Freiha FS, Redwine E et al. Prostate-specific antigen as a serum marker for adenocarcinoma of the prostate. N Engl J Med 1987; 317(5): 909-916.
- Cooner WH, Mosley BR, Rutherford CL Jr, Beard JH, Pond HS, Terry WJ, et al. Prostate cancer detection in a clinical urological practice by ultrasonography, digital rectal examination and prostate specific antigen. J Urol 1990; 143(6): 1146-1154.
- Catalona WJ, Smith DS, Ratliff TL, Dodds KM, Coplen DE, Yuan JJ, et al. Measurement of prostate-specific antigen in serum as a screening test for prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 1991; 325(18): 1156-1161.
- Yao SL, Lu-Yao G. Understanding and appreciating overdiagnosis in the PSA era. J. Natl Cancer Inst 2002; 94(13): 958-960.
- Collin SM, Martin RM, Metcalfe C, Gunnell D, Albertsen PC, Neal D, et al. Prostate-cancer mortality in the USA and UK in 1975-2004: an ecological study. Lancet Oncol 2008; 9(5):445-52 DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70104-9
- Schröder FH, Hugosson J, Roobol MJ, Tammela TL, Zappa M, Nelen V. et al. Screening and prostate cancer mortality: results of the European Randomised Study of Screening for Prostate Cancer (ERSPC) at 13 years of follow-up. Lancet 2014; 384(9959):2027-35 DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60525-0
- Krumholtz JS, Carvalhal GF, Ramos CG, Smith DS, Corson P, Yan Y, et al. Prostate-specific antigen cutoff of 2.6 ng/mL for prostate cancer screening is associated with favorable pathologic tumor features. Urology 2002; 60(3):469-473.
- Schröder FH, Hugosson J, Roobol MJ, Tammela TL, Ciatto S, Nelen V, et al. Screening and prostate-cancer mortality in a randomized European study. N Engl J Med 2009; 360(13):1320-1328 DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa0810084
- O'Shaughnessy M, Konety B, Warlick C. Prostate cancer screening: issues and controver-sies. Minn Med 2010; 93(8):39-44.
- Baylin SB, Herman JG, Graff JR, Vertino PM, Issa JP. Alterations in DNA methylation: a fundamental aspect of neoplasia. Adv Cancer Res 1998; 72: 141-196.
- Bird A. The essentials of DNA methylation. Cell 1992; 70 (1):5-8.
- Merlo A., Herman J.G., Mao L., Lee DJ, Gabrielson E, Burger PC et al. 5' CpG island methylation is associated with transcriptional silencing of the tumor suppressor p16/CDKN2/MTS1 in human cancers. Nat Med 1995; 1(7): 686-692.
- Herman JG, Umar A, Polyak K, Graff JR, Ahuja N, Issa JP, et al. Incidence and functional consequences of hMLH1 promoter hypermethylation in colorectal carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95(12):6870-6875.
- Hoque MO, Topaloglu O, Begum S, Henrique R, Rosenbaum E, Van Criekinge W, et al. Quantitative methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction gene patterns in urine sediment distinguish prostate cancer patients from control subjects. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23(27):6569-6575.
- Cooper CS, Foster CS. Concepts of epigenetics in prostate cancer development. Br J Cancer 2009; 100(2): 240-245 DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604771
- Nelson WG, Yegnasubramanian S, Agoston AT, Bastian PJ, Lee BH, Nakayama M, et al. Abnormal DNA methylation, epigenetics, and prostate cancer. Front Biosci 2007; 12:4254-4266.
- Dobosy JR, Roberts JL, Fu VX. The expanding role of epigenetics in the de velopment, diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 2007; 177(3):822-831.
- Li LC. Epigenetics of prostate cancer. Front Biosci 2007; 12:3377-3397.
- Esteller M. Cancer epigenomics: DNA methylomes and histone-modification maps. Nat Rev Genet 2007; 8(4):286-298.
- Hoque MO, Kim MS, Ostrow KL, Liu J, Wisman GB, Park HL, et al. Genome-wide promoter analysis uncovers portions of the cancer methylome. Cancer Res 2008; 68(8):2661-2670 DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5913
- Henrique R, Jeronimo C, Teixeira MR, Hoque MO, Carvalho AL, Pais I, et al. Epigenetic heterogeneity of high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia: clues for clonal progression in prostate carcinogenesis. Mol Cancer Res 2006; 4 (1):1-8.
- Jeronimo C, Henrique R, Hoque MO, Mambo E, Ribeiro FR, Varzim G, et al. A quantitative promoter methylation profile of prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 10:8472-8478.
- Aitchison A, Warren A, Neal D, Rabbitts P. RASSF1A promoter methylation is frequently detected in both pre-malignant and non-malignant microdissected prostatic epithelial tissues. Prostate 2007; 67(6):638-644.
- Gao T, He B, Pan Y, Li R, Xu Y, Chen L, Nie Z, Gu L, Wang S. The association of retinoic acid receptor beta2 (RARb2) methylation status and prostate cancer risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLOS One 2013; 8(5):62950 DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062950
- Ahmed H. Promoter Methylation in Prostate Cancer and its Application for the Early Detection of Prostate Cancer Using Serum and Urine Samples. Biomarkers in Cancer 2010; 2010(2):17-33.
- Dumache R, Puiu M, Minciu R, Bardan R, David D, Tudor A, Bumbäcilä B. Retinoic acid receptor ß2 (RARß2): nonivasive biomarker for distinguishing malignant versus benign prostate lesions from bodily fluids. Chirurgia (Bucur) 2012; 107(6):780-784.
- Kwabi-Addo B, Wang S, Chung W, Jelinek J, Patierno S, Wang B, et al. Identification of Differentially Methylated Genes in Normal Prostate Tissues from African American and Caucasian Men. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16(14):3539-3547 DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-3342
- Pan J, Chen J, Zhang B, Chen X, Huang B, Zhuang J, Mo C, et al. Association between RASSF1A promoter methylation and prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLOS One 2013; 8(9):75283. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0075283
- Sunami E, Shinozaki M, Higano CS, Wollman R, Dorff TB, Tucker SJ, et al. Multimarker circulating DNA assay for assessing blood of prostate cancer patients. Clin Chem 2009; 55(3):559-567 DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2008.108498
- Filella X, Giménez N. Evaluation of proPSA and Prostate Health Index (phi) for the detection of prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Chem Lab Med 2013; 51(4):729-739 DOI: 10.1515/cclm-2012-0410
- Sivkov A, Efremov G, Mihaylenko D, Apolikhin O. PCA3 and TMPRSS2-ERG for prostate cancer diagnosis. 8th European Multidisciplinary Meeting on Urological Cancers


