Математическая модель микроциркуляции для прогнозирования реперфузионного синдрома у пациентов с сахарным диабетом
Автор: Шабрыкина Н.С., Лукин П.С.
Журнал: Российский журнал биомеханики @journal-biomech
Статья в выпуске: 4 (98) т.26, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Сахарный диабет - это группа хронических метаболических нарушений, характеризующихся повышенным уровнем сахара в крови. В связи с быстрым ростом числа пациентов с сахарным диабетом резко возрастает и частота осложнений. В настоящее время для оценки микроциркуляторной перфузии и выявления ранней дисфункции диабетической микроангиопатии применяются неинвазивные экспериментальные методы. Поскольку функция микроциркуляции предполагает несколько взаимосвязанных процессов, зависящих от большого количества параметров, схожие клинические проявления нарушения микроциркуляции могут быть вызваны различными изменениями, которые зачастую невозможно определить, используя только экспериментальные данные. Математическое моделирование является перспективным инструментом для преодоления вышеупомянутых проблем и улучшения экспериментальных методов. Данная работа посвящена разработке математической модели, позволяющей прогнозировать реперфузионный синдром у пациентов с сахарным диабетом. Модель микроциркуляции может позволить оценить другие параметры (гидравлическую проводимость капиллярной стенки и онкотическое давление) путем сравнения с измерениями скорости фильтрации с помощью капилляроскопии. Используя представленную математическую модель, можно предложить возможный способ объяснения того, почему реваскуляризация может вызвать обострение синдрома диабетической стопы.
Реперфузионный синдром, микроциркуляция, математическое моделирование
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/146282613
IDR: 146282613 | УДК: 531/534: | DOI: 10.15593/RZhBiomeh/2022.4.07
Текст научной статьи Математическая модель микроциркуляции для прогнозирования реперфузионного синдрома у пациентов с сахарным диабетом
Сахарный диабет – это группа хронических метаболических нарушений, характеризующихся повышенным уровнем сахара в крови [24; 58]. Известно, что в основе диабета 2-го типа лежит нарушение гомеостаза инсулина [29; 54]. Инсулинорезистентность в периферических тканях [53] и дисфункция бета-клеток поджелудочной желе- зы [32] впоследствии приводят к глюкозотоксичности, липотоксичности и развитию опасных для жизни сосудистых заболеваний и осложнений [22; 51; 59].
В связи с быстрым ростом числа пациентов с сахарным диабетом резко возрастает и частота осложнений.
Одним из наиболее серьезных осложнений является синдром диабетической стопы, который объединяет патологические изменения периферической нервной си-


Эта статья доступна в соответствии с условиями лицензии Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International
License (CC BY-NC 4.0)
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0)
стемы, артериального и микрососудистого русла и костно-суставного аппарата стопы [11; 15; 31]. Диабетическая стопа часто приводит к развитию изъязвлений и гангрены стопы [48; 50; 65]. Диабетическая стопа встречается в 25 % случаев сахарного диабета [64]. Другие исследования показывают, что распространенность синдрома диабетической стопы колеблется от 4 % до 15 % [10; 19; 69]. Пятилетняя смертность после ампутации оценивается в 39–68 % [61].
В связи с ростом числа пациентов с сахарным диабетом растет и число его осложнений. Одним из наиболее серьезных осложнений является синдром диабетической стопы (СДС), который объединяет патологические изменения в периферической нервной системе, артериальном и микрососудистом русле, костно-суставном аппарате стопы. СДС приводит к развитию язвы примерно у 25 % пациентов с диабетом, и по крайней мере четверть этих язв не заживает, что подвергает таких пациентов риску ампутации [12; 48]. Согласно статистическим данным, от 40 % до 60 % нетравматических ампутаций нижних конечностей во всем мире вызваны диабетическими осложнениями, и 80 % этих ампутаций следуют за диабетическими язвами стопы [48]. Точное количество случаев СДС в мире неизвестно [50].
Как уже упоминалось ранее, сахарный диабет приводит к неблагоприятным микрососудистым и макрососу-дистым осложнениям [34]. Макроваскулярные изменения включают в себя различные степени ретинопатии, нефропатии, нейропатии и т.д. Частота и тяжесть макро-сосудистых осложнений определяются микрососудисты-ми осложнениями. Дисфункция микроциркуляции является основным ключом в развитии патологии диабетической стопы [12].
Выполняя реваскуляризацию нижних конечностей у пациентов с сахарным диабетом, хирурги все чаще сталкиваются с реперфузионным повреждением. Реперфузионный синдром в основном зависит от функциональных свойств региональной микроциркуляции [66], в то время как причины и механизмы реперфузионного синдрома до сих пор не ясны [16; 20; 68]. Следовательно, не существует «золотого стандарта» тактики лечения.
В настоящее время для оценки микроциркуляторной перфузии и выявления ранних нарушений диабетической микроангиопатии применяются неинвазивные экспериментальные методы (капилляроскопия ногтевой пластинки [13], лазерная допплеровская флоуметрия [23], лазерная спекл-визуализация [25], интравитальная микроскопия [21], ортогональная поляризационная спектральная визуализация [46], визуализация в темном поле бокового потока [55]). Эти методы позволяют выявить нарушения микроциркуляции на ранней стадии. Поскольку микроциркуляция включает в себя несколько взаимосвязанных процессов, зависящих от большого количества параметров, сходные клинические проявления нарушения микроциркуляции могут быть вызваны различными изменениями, которые зачастую невозмож- но определить, используя только экспериментальные данные.
Математическое моделирование микроциркуляции позволяет лучше понять сложные процессы, обеспечивающие метаболизм в организме, а также выявить причины микроциркуляторных нарушений и предложить способы их лечения.
Экспериментальное и теоретическое изучение процессов микромасштабного обмена было начато в конце XIX в. Э. Старлингом [61], который выдвинул гипотезу о транскапиллярном потоке жидкости, вызванном разницей в гидростатическом и осмотическом давлениях между циркулирующей плазмой и тканями. Были предложены расширенные модели, основанные на принципе Старлинга, описывающие некоторые аспекты микроциркуляции в здоровом состоянии и при патологии [14; 27; 28; 30; 47; 52; 60; 67], но в них не рассматривались случаи микроциркуляции у больных сахарным диабетом.
Causin et al. [41] представили многомасштабную модель, описывающую эффект связи между кровотоком и транспортом кислорода в сетчатке. Кровоток в сети сосудистых деревьев моделируется как одномерный двухфазный поток, включающий плазму и эритроциты.
Лу и соавт. [49] использовали трехмерный вычислительный метод для анализа капиллярной скорости, напряжения сдвига стенок и капиллярного перфузионного давления в реальных структурных парафовеальных капиллярных сетях, что обеспечивает еще один неинвазивный метод для характеристики микроциркуляции у здоровых и больных диабетом.
В настоящее время популярным подходом является многомасштабное моделирование, где кровоток моделируется как поток Пуазейля через проницаемую стенку, а интерстициальный и лимфатический потоки моделируются как транспорт в пористой среде [57; 63]. Cattaneo et al. [17] разработали расчетную модель для обмена жидкостями между микроциркуляцией и интерстицией ткани, где капилляры и интерстициальный объем были описаны как две независимые структуры. Чтобы связать одномерный поток через сеть и трехмерный поток через интерстициальный объем, они использовали метод погруженной границы. Tang et al. [63] предложили модель течения жидкости и переноса кислорода, учитывая взаимодействие между кровью в капиллярной сети и интерстициальном объеме. Метод погруженной границы был использован для сопряжения микроциркуляции и тканевых областей. Используя модель, авторы рассчитали поле потока и распределение кислорода в капиллярной сети и окружающей ткани. Некоторые патологические состояния, которые могут привести к таким клиническим проявлениям, как отек нижних конечностей, ишемия тканей и гипоксия у пациентов с диабетом, были описаны с помощью модели.
Данная работа посвящена математическому моделированию транспорта обмена в капиллярах для прогнози- рования развития реперфузионного синдрома. Наш подход основан на рассмотрении одного капилляра, что делает модель более простой, но позволяет отразить те же эффекты, что и модели, использующие подход моделирования капиллярного русла. Модель позволяет получить результаты, соответствующие клинической практике, и описать принципиальные биомеханические эффекты, возникающие в капиллярах на микроуровне.
Материалы и методы
В работе [12] построена комплексная математическая модель микроциркуляторных процессов. Она включает описание следующих взаимосвязанных процессов: движение жидкости в кровеносном капилляре параллельно с транскапиллярным массопереносом; движение жидкости в ткани; абсорбция в лимфатический капилляр. При этом давление и скорость течения жидкости в капилляре и ткани, а также зависящие от них величины рассматриваются как функции времени и двух пространственных координат.
В моделях микроциркуляции обычно предполагается, что все капилляры в органе одинаковы по размеру, характеристикам течения жидкости и т.д. Поэтому можно рассматривать один представительный капилляр. В работе [12] рассматривается прямой цилиндрический кровеносный капилляр и окружающая его тканевая мантия (рис. 1).
Для описания течения крови в капилляре используется модель неньютоновской жидкости, предложенная Валбурном и Шнеком [11]:
ст = f (y)y- p I,(1)
5V z x 1
— + (V-V)V = -V-ст ,(2)
dtp
V-V = 0,(3)
Y = - (VV + VV T),(4)
f (y) = C-e2H+C4H2 (у)"C3H ,(5)
Y = V2 412 - 21^ = 42^ ,(6)
где ст - тензор напряжений, P = P(t, r, x) - давление в капилляре, I - единичный тензор, у - тензор скоростей деформации, V = V(t, r, x) - вектор скорости течения жидкости, p - плотность жидкости, H - показатель гематокрита крови (в норме 35-50 %), х - содержание протеинов за исключением альбумина в крови (в норме 1,5-4,0 г на 100 мл), C, i = 1...4 - эмпирически найденные коэффициенты. Рассматриваемая в работе биологическая ткань моделируется как пористый, упру- гий, изотропный матрикс, насыщенный интерстициальной жидкостью, содержащейся в порах матрикса.
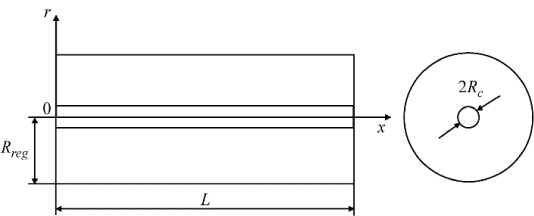
Рис. 1. Модель представительного капилляра в цилиндрической системе координат: R – радиус капилляра, L – длина капилляра, r – радиальная координата, x – аксиальная координата
Далее приведены уравнения, описывающие деформацию упругого матрикса и течение жидкости в его порах:
Важной особенностью микроциркуляторных процессов является наличие обмена жидкости и растворенных в ней веществ между кровеносным капилляром и окружающей его тканью. Транскапиллярный обмен описывается законом Старлинга, согласно которому скорость течения жидкости через капиллярную стенку пропорциональна разнице гидростатического и онкотического давления в кровеносном капилляре и в ткани. Используя закон Старлинга, можно записать граничное условие на радиальную компоненту скорости на границе между кровеносным капилляром и тканевой областью:
V r = L p ( ( P - P ) - P o ) , (13)
где L – гидравлическая проницаемость капиллярной стенки, P – результирующее онкотическое или коллоидно-осмотическое давление, связанное с разностью концентраций белков в капилляре и ткани. Поскольку стенка кровеносного капилляра хорошо проницаема для воды и низкомолекулярных веществ, но не для белков, именно онкотическое давление оказывает влияние на течение жидкости через стенку кровеносного капилляра.
Следует отметить, что в работе [12] онкотическое давление в капилляре и ткани считается постоянным, т.е. не учитывается изменение концентрации веществ, содержащихся в различных частях системы. Такое предположение является упрощением реально происходящих процессов, поскольку диффузия играет значительную роль при обмене веществ. Тем не менее хорошее соответствие результатов моделирования и экспериментальных данных для параметров, зависящих в основном от фильтрации, а не от диффузии (таких, как объемный поток жидкости через стенку кровеносного капилляра), дает право говорить о применимости модели в данной постановке.
Представленные выше соотношения для течения крови в кровеносном капилляре (2)–(6), течения жидкости в ткани (11), (12) и деформации тканевого матрикса (7)–(10) совместно с условием транскапиллярного об мена (13) и другими начальными и граничными условиями позволяют описать течения в капилляре и ткани.
Существуют две модификации модели представительного капилляра. В первой тканевая мантия, окружающая капилляр, имеет конечный радиус R и при этом предполагается, что на границах между соседними тканевыми областями, принадлежащими различным капиллярам, обмена не происходит. Во второй тканевая мантия считается бесконечной.
Результаты
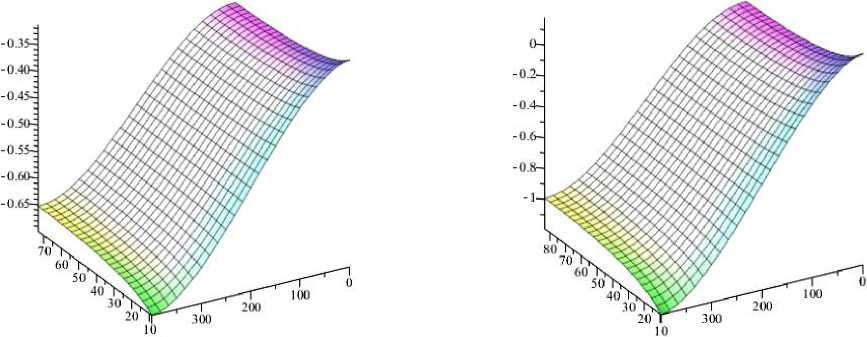
Результаты по интерстициальному давлению и полю скоростей потока для физиологических условий и с сахарным диабетом представлены на рис. 2, 3. Распределение давления для физиологических значений параметров показывает (рис. 2, а ), что давление на границе между капилляром и тканью уменьшается от артериального к венозному концу. Изолинии давления и поле потока (см. рис. 3) иллюстрируют, что из капилляра жидкость в основном идет в радиальном направлении, а движение в осевом направлении происходит в центральной области. Фильтрацию жидкости из капилляра в ткань можно наблюдать на артериальном конце капилляра. А реабсорбция жидкости из ткани в капилляр преобладает на венозной части, что согласуется с классической гипотезой Старлинга о транскапиллярном обмене.
Для моделирования диабетических условий мы ис-
а б
Рис. 2. Распределение давлений интерстициальной жидкости в норме ( а ) и при сахарном диабете ( б )
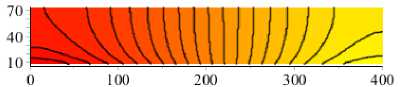
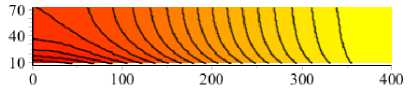
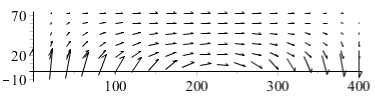
Рис. 3. Изолинии и линии тока для скоростей течения интерстициальной жидкости в норме ( а ) и при сахарном диабете ( б )
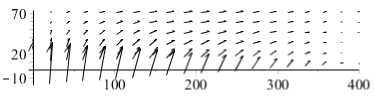
пользовали больший радиус капилляра, увеличенное внутрикапиллярное расстояние и повышенную гидравлическую проводимость стенки капилляра. Распределение давления интерстициальной жидкости и поле скоростей в целом такие же (см. рис. 2, 3), но скорость потока и, следовательно, скорость фильтрации намного выше.
В результате среднее интерстициальное давление для физиологических параметров составляет -0,5 мм рт. ст., максимальная скорость интерстициальной жидкости составляет 2,9 м/с. Для диабетического состояния среднее давление такое же, но Δ P повышается до 1,4 мм рт. ст. и максимальная скорость интерстициальной жидкости 10,4 м/с.
Когда лимфатический дренаж усиливается, фильтрация жидкости преобладает над реабсорбцией в кровеносный капилляр (рис. 4). В этом случае лимфатический дренаж становится основным механизмом удаления жидкости из ткани. Также лимфатический дренаж любой интенсивности приводит к снижению тканевого давления и, таким образом, увеличивает скорость фильтрации.
Как для физиологических, так и для диабетических параметров распределение давления внутри кровеносного капилляра отличается от линейного закона незначительно. Только очень большие изменения гидравлической проводимости стенки капилляра L p или вязкости жидкости одновременно приводят к существенным изменениям в распределении капиллярного давления, которое становится нелинейным.
Обсуждение
Математическое моделирование и методы биомеханики позволяют оценить прогностические данные, которые не могут обеспечить современные методы визуализации [1–9; 35–45; 56; 62].
Чтобы сравнить результаты нашей модели с имеющимися данными, мы использовали давление интерстициальной жидкости. Ebah et al. [26] сообщили, что для здоровых добровольцев интерстициальное давление составляет -0,9 ± 1,3 мм рт. ст. А среднее значение давления интерстициальной жидкости, рассчитанное с помощью нелинейной модели лимфатического дренажа Possenti et al. [57], составляет -1,17 мм рт. ст. Таким образом, для физиологических условий значения давления интерстициальной жидкости согласуются как с экспериментальными данными, так и с другой моделью.
Предложенная модель зависит от многих параметров микроциркуляции: радиуса и длины капилляра, гидростатического давления на артериальном и венозном концах капилляра, результирующего онкотического давления, вязкости крови, гидравлической проводимости стенки капилляра, гидравлической проводимости и пористости ткани. Чтобы оценить влияние изменения параметров, мы провели серию расчетов, в которых все остальные параметры были установлены в физиологических условиях. Результаты анализировались в терминах среднего давления интерстициальной жидкости и скорости фильтрации. Повышение среднего давления интерстициальной жидкости вызвано повышением капиллярного давления на артериальном или венозном конце или снижением онкотического давления. Другие параметры (т.е. пористость, гидравлическая проводимость ткани и стенки капилляра) не оказывают существенного влияния на среднее давление. Увеличение скорости фильтрации вызвано возрастанием капиллярного давления в артериальной части, снижением давления в венозной части, увеличением проводимости капиллярной стенки. Последние два параметра оказывают большее влияние, чем все остальные. Изменение онкотического давления, пористости и проводимости тканей не оказывает существенного влияния на скорость фильтрации.
Некоторые параметры микроциркуляции (геометрические параметры капилляров, давление и вязкость крови) могут быть измерены индивидуально для каждого пациента. А модель микроциркуляции может позволить оценить другие параметры (гидравлическую проводимость капиллярной стенки и онкотическое давление) путем сравнения результатов расчета с капилляроскопическими измерениями скорости фильтрации.
С помощью представленной математической модели можно предложить возможный способ объяснения того, почему реваскуляризация может вызывать обострение синдрома диабетической стопы. Сахарный диабет вызывает изменения морфологии капилляров, повышение гидравлической проводимости капиллярной стенки и вязкости крови, а также часто недостаточный лимфатический дренаж. Эти изменения могут усугубляться связанным с ишемией падением давления в артериальном конце капилляра. Когда кровоток восстанавливается, расширенный капилляр и повышенная проницаемость стенки приводят к резкому увеличению скорости фильтрации при недостаточном дренаже из-за нарушения работы лимфатических сосудов, что может вызвать отек и дальнейшие микро-циркуляторные нарушения.
Для представленной модели существуют некоторые ограничения. Во-первых, модель описывает только устойчивое состояние и не учитывает переходные явления. Кроме того, для описания потока жидкости через стенку капилляра мы использовали принцип фильтрации Старлинга. Однако существует множество доказательств того, что гликокаликс влияет на фильтрацию и снижает поглощение капиллярной сетью, делая лимфатический дренаж основным механизмом удаления жидкости из интерстиция [47]. Учет этого эффекта является важным будущим усовершенствованием. Наконец, мы использовали модель Крога для одиночного капилляра и распределенного лимфатического дренажа. Учет реалистичной геометрии капил- лярной сети может помочь в моделировании диабетических микрососудистых особенностей, таких как аваскулярные зоны и извилистость. Однако создание подобных моделей для больших органов чрезвычайно сложно.
Заключение
Данная работа посвящена разработке математической модели, позволяющей прогнозировать реперфузи онный синдром у пациентов с сахарным диабетом.
Модель микроциркуляции может позволить оценить такие параметры пациента, как гидравлическая проводимость капиллярной стенки и онкотическое давление, путем сравнения с измерениями скорости фильтрации с помощью капилляроскопии.
Используя представленную математическую модель, можно предложить возможный способ объяснения того, почему реваскуляризация может вызвать обострение синдрома диабетической стопы.
Оценка эффективности установки модифицированного шунта Блэлок – Тауссиг у детей с врожденным пороком сердца // Российский журнал биомеханики. – 2020. – Т. 24, № 1. – С. 76–96.
Финансирование. Работа выполнена при финансовой поддержке Пермского научно-образовательного центра «Рациональное недропользование», 2022 г.
Список литературы Математическая модель микроциркуляции для прогнозирования реперфузионного синдрома у пациентов с сахарным диабетом
- Камалтдинов М.Р., Кучумов А.Г. Применение математической модели системного кровообращения для определения параметров кровотока после операции шунтирования у новорожденных // Российский журнал биомеханики. - 2021. - Т. 25, № 3. - С. 313-330.
- Кучумов А.Г. Математическое моделирование накопления частиц на поверхности пластикового билиарного стента для прогнозирования его окклюзии // Известия Саратовского университета. Новая серия. Серия: Математика. Механика. Информатика. - 2020. - Т. 20, № 2. - С. 220-231.
- Кучумов А.Г. Математическое моделирование перистальтического течения литогенной желчи через проток при рубцовом стенозе, рассматриваемый в виде трубки с сужающимися стенками конечной длины // Российский журнал биомеханики. - 2016. - Т. 20, № 2. -С. 96-115.
- Кучумов А.Г., Гилёв В.Г., Попов В.А., Самарцев В.А., Гаврилов В.А. Экспериментальное исследование реологии патологической желчи // Российский журнал биомеханики. - 2011. - Т. 15, № 3 (53). - С. 52-60.
- Кучумов А.Г., Камалутдинов А.М., Лукин П.С. Математическое моделирование течения химуса в персонализированной модели толстого кишечника // Колопроктология. - 2019. - Т. 18, № S3 (69). -С. 100-101.
- Кучумов А.Г., Няшин Ю.И., Самарцев В.А., Гаврилов В.А., Ивонина Е.В. Перистальтическое течение патологической желчи при рубцовом стенозе большого дуоденального сосочка // Российский журнал биомеханики. - 2014. - Т. 18, № 4. - С. 441-451.
- Кучумов А.Г., Няшин Ю.И., Самарцев В.А., Гаврилов В.А., Менар М. Биомеханический подход к моделированию билиарной системы как шаг в направлении к построению виртуальной модели физиологии человека // Российский журнал биомеханики. - 2011. - Т. 15, № 2. - С. 32-48.
- Кучумов А.Г., Самарцев В.А., Няшин Ю.И., Породиков А.А. Применение методов вычислительной гидродинамики в решении актуальных задач хирургии // Современный мир, актуальные вопросы биоэтики, молекулярной и персонализированной медицины: материалы междунар. евро-азиатского конгресса по вопросам биоэтики, молекулярной и персонализированной медицины Biomed-inn2019 / под ред. И.П. Корюкиной, Ю.В. Каракуловой, В.Ю. Мишланова, Е.Г. Фурмана. - Пермь, 2019. - С. 9296.
- Кучумов А.Г., Хайрулин А.Р., Биянов А.Н., Породиков А.А., Арутюнян В.Б., Синельников Ю.С. Оценка эффективности установки модифицированного шунта Блэлок - Тауссиг у детей с врожденным пороком сердца // Российский журнал биомеханики. - 2020. - Т. 24, № 1. - С. 76-96.
- Abdissa D., Adugna T., Gerema U., Dereje D. Prevalence of diabetic foot ulcer and associated factors among adult diabetic patients on follow-up clinic at jimma medical center southwest ethiopia 2019: an institutional-based cross-sectional study // J. Diabetes Res. - 2020. - Vol. 2020. - Art. 4106383. DOI: 10.1155/2020/4106383.
- Amin N., Doupis J. Diabetic foot disease: From the evaluation of the "foot at risk" to the novel diabetic ulcer treatment modalities // World J. Diabetes. - 2016. - Vol. 7. -P. 153-164. DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i7.153.
- Balasubramanian G.V., Chockalingam N., Naemi R. The role of cutaneous microcirculatory responses in tissue injury inflammation and repair at the foot in diabetes // Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. - 2021. - Vol. 9. - Art. 732753.
- Bernardino V., Rodrigues A., Llado A., Fernandes M., Panarra A. The impact of nailfold capillaroscopy in the approach of microcirculation. Vascular biology - selection of mechanisms and clinical applications [Электронный ресурс]. - URL: https://cdn.intechopen.com/pdfs /70549.pdf (дата обращения 01. 12.2022).
- Blake T.R., Gross J.F. A mathematical model of fluid exchange from an array of capillaries // Microvasc. Res. -1980. - Vol. 19. - P. 80-98. DOI: 10.1016/0026-2862(80)90085-0.
- Boulton A.J.M. The diabetic foot // Med. (United Kingdom). - 2015. - Vol. 43. - P. 33-37. DOI: 10.1016/j.mpmed.2014.10.006.
- Carden D.L., Granger D.N. Pathophysiology of ischaemia-reperfusion injury // J. Pathol. - 2000. - Vol. 190. - P. 255266.
- Cattaneo L., Zunino P. Computational models for fluid exchange between microcirculation and tissue interstitium // Networks Heterog. Media. - 2014. - Vol. 9. - P. 135-159. DOI: 10.3934/nhm.2014.9.135.
- Causin P., Guidoboni G., Malgaroli F., Sacco R., Harris A. Blood flow mechanics and oxygen transport and delivery in the retinal microcirculation: multiscale mathematical modeling and numerical simulation // Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. - 2016. - Vol. 15. - P. 525-542. DOI: 10.1007/s10237-015-0708-7.
- Chiwanga F.S., Njelekela M.A. Diabetic foot: Prevalence knowledge and foot self-care practices among diabetic patients in Dar es Salaam Tanzania - a cross-sectional study // J. Foot Ankle Res. - 2015. - Vol. 8. - Art. 20. DOI: 10.1186/s13047-015-0080-y.
- Cowled P., Fitridge R. Pathophysiology of reperfusion injury. Mechanisms of Vascular Disease. - Adelaide: University of Adelaide Press, 2020. - 18 p.
- de Oliveira T.H.C., Marques P.E., Poosti F., Ruytinx P., Amaral F.A., Brandolini L., Allegretti M., Proost P., Teixeira M.M. Intravital microscopic evaluation of the effects of a CXCR2 antagonist in a model of liver ischemia reperfusion injury in mice // Front. Immunol. - 2018. - Vol. 8. - Art. 1917. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01917.
- DeFronzo R.A. Insulin resistance lipotoxicity type 2 diabetes and atherosclerosis: The missing links. The Claude Bernard Lecture 2009 // Diabetologia. - 2010. - Vol. 53. - P. 12701287.
- den Uil C.A., Klijn E., Lagrand W.K., Brugts J.J., Ince C., Spronk P.E., Simoons M.L. The microcirculation in health and critical disease // Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. - 2008. - Vol. 51. - P. 161-70.
- Dilworth L., Facey A., Omoruyi F. Diabetes mellitus and its metabolic complications: The role of adipose tissues // Int. J. Mol. Sci. - 2021. - Vol. 22. - Art. 7644.
- Dyachenko Timoshina P.A., Bashkatov A.N., Alexandrov D.A., Kochubey V.I., Tuchin V.V. Laser speckle contrast imaging for monitoring of acute pancreatitis at ischemia-reperfusion injury of the pancreas in rats // J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. - 2022. - Vol. 15. - Art. 2242002. DOI: 10.1142/S1793 545822420020.
- Ebah L.M., Wiig H., Dawidowska I., O'Toole Ch., Summers A., Nikam M., Jayanti A., Coupes B., Brenchley P., Mitra S. Subcutaneous interstitial pressure and volume characteristics in renal impairment associated with edema // Kidney Int. -2013. - Vol. 84. - P. 980-988. DOI: 10.1038/ki.2013.208.
- Facchini L., Bellin A., Toro E.F. A time-dependent multi-layered mathematical model of filtration and solute exchange the revised Starling principle and the Landis experiments // Veins Lymphat. - 2017. - Vol. 6. - P. 8-12. DOI: 10.4081/vl.2017.6849.
- Farina A., Fasano A., Rosso F. Mathematical models for some aspects of blood microcirculation // Symmetry (Basel). - 2021. - Vol. 13. - Art. 1020. DOI: 10.3390/sym13061020.
- Galicia-Garcia U., Benito-Vicente A., Jebari S., Larrea-Sebal A., Siddiqi H., Uribe K.B., Ostolaza H., Martín C. Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus // Int. J. Mol. Sci. - 2020. - Vol. 21. - Art. 6275.
- Groome L.J., Kinasewitz G.T. Spatial heterogeneity and microvascular fluid exchange: A simple macroscopic equation // Microvasc. Res. - 1987. - Vol. 33. - P. 155-166. DOI: 10.1016/0026-2862(87)90014-8.
- Jeffcoate W.J., Harding K.G. Diabetic foot ulcers // Lancet. -2003. - Vol. 361. - P. 1545-1551. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13169-8.
- Kahn S.E. The relative contributions of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction to the pathophysiology of Type 2 diabetes // Diabetologia. - 2003. - Vol. 46. - P. 3-19.
- Kamaltdinov M.R., Kuchumov A.G., Sadeghy K. Chyme flow numerical modelling in the colon in normal conditions and in disorders // Series on Biomechanics. - 2022. - Vol. 36(1). - P. 105-112.
- Kosiborod M., Gomes M.B., Nicolucci A., Pocock S., Rathmann W., Shestakova M.V., Watada H., Shimomura I., Chen H., Cid-Ruzafa J. et al. Vascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes: Prevalence and associated factors in 38 countries (the DISCOVER study program) // Cardiovsc. Diabetol. - 2018. - Vol. 17. - Art. 150. DOI: 10.1186/12933-018-0787-8.
- Kuchumov A. Biomechanical modelling of bile flow in the biliary system // MATEC Web of Conferences. - 2018. - Vol. 13. - Art. 04004.
- Kuchumov A. Patient-specific bile flow simulation to evaluate cholecystectomy outcome // IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. - 2019. - Art. 012022.
- Kuchumov A., Tuktamyshev V., Kamaltdinov M. Peristaltic flow of lithogenic bile in the Vateri's papilla as non-Newtonian fluid in the finite-length tube: analytical and numerical results for reflux study and optimization // Lekar a Technika. - 2017. - Vol. 47, no. 2. - P. 35-42.
- Kuchumov A.G., Gilev V., Popov V., Samartsev V., Gavrilov V. Non-Newtonian flow of pathological bile in the biliary system: experimental investigation and CFD simulations // Korea-Australia Rheology Journal. - 2014. - Vol. 26. - P. 81-90.
- Kuchumov A.G., Khairulin A., Shmurak M., Porodikov A., Merzlyakov A. The effects of the mechanical properties of vascular grafts and an anisotropic hyperelastic aortic model on local hemodynamics during modified Blalock-Taussig shunt operation, assessed using FSI simulation // Materials. -2022. - Vol. 15(8). - Art. 2719.
- Kuchumov A.G., Khairulin A.R., Kamaltdinov M.R., Ivashova Y.A., Samartsev V.A., Taiar R. Patient-specific simulation of a gallbladder refilling based on mri and ultrasound in vivo measurements // AIP Conference Proceedings. 28th Russian Conference on Mathematical Modelling in Natural Sciences, RuMoNaS. - 2019. - Art. 060004.
- Kuchumov A.G., Nyashin Y.I., Samartsev V.A. Modelling of peristaltic bile flow in the papilla ampoule with stone and in the papillary stenosis case: application to reflux investigation // IFMBE Proceedings 7th WACBE World Congress on Bioengineering. - 2015. - P. 158-161.
- Kuchumov A.G., Nyashin Y.I., Samarcev V.A., Gavrilov V.A. Modelling of the pathological bile flow in the duct with a calculus // Acta of Bioengineering and Biomechanics. -2013. - Vol. 15, no. 4. - P. 9-17.
- Kuchumov A.G., Selyaninov A. Application of computational fluid dynamics in biofluids simulation to solve actual surgery tasks // Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing. -2020. - Vol. 1018. - P. 576-580.
- Kuchumov A.G., Selyaninov A., Kamaltdinov M., Samartsev V. Numerical simulation of biliary stent clogging // Series on Biomechanics. - 2019. - Vol. 33, no. 1. - P. 3-15.
- Kuchumov A.G., Vedeneev V., Samartsev V., Khairulin A., Ivanov O. Patient-specific fluid-structure interaction model of bile flow: comparison between 1-way and 2-way algorithms // Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering. - 2021. - Vol. 24(15). - P. 16931717.
- Langer S., Harris A.G., Biberthaler P., Von Dobschuetz E., Messmer K. Orthogonal polarization spectral imaging as a tool for the assessment of hepatic microcirculation // Transplantation. - 2001. - Vol. 71. - P. 1249-1256. DOI: 10.1097/00007890-200105150-00012.
- Levick J.R., Michel C.C. Microvascular fluid exchange and the revised Starling principle // Cardiovasc. Res. - 2010. -Vol. 87. - P. 198-210.
- Lin C., Liu J., Sun H. Risk factors for lower extremity amputation in patients with diabetic foot ulcers: A meta-analysis // PLoS One. - 2020. - Vol. 15. - P. 1-15. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239236.
- Lu Y., Bernabeu M.O., Lammer J., Cai C.C., Jones M.L., Franco C.A., Aiello L.P., Sun J.K. Computational fluid dynamics assisted characterization of parafoveal hemodynamics in normal and diabetic eyes using adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscopy // Biomed. Opt. Express - 2016. - Vol. 7. - P. 4958-4973. DOI: 10.1364/boe.7.004958.
- Lukin P., Kuchumov A.G., Zarivchatskiy M.F., Kravtsova T. Clinical classification of the diabetic foot syndrome adapted to icd-10 as a solution to the problem of diagnostics statistics and standardisation // Med. - 2021. - Vol. 57. - Art. 817. DOI: 10. 3390/medicina57080817.
- Meex R.C.R., Blaak E.E., van Loon L.J.C. Lipotoxicity plays a key role in the development of both insulin resistance and muscle atrophy in patients with type 2 diabetes // Obes. Rev. - 2019. - Vol. 20. - P. 1205-1217.
- Michel C.C., Woodcock T.E., Curry F.R.E. Understanding and extending the Starling principle // Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. - 2020. - Vol. 64. - P. 1032-1037.
- Mu W., Xuefang C., Liu Y., Qianzhou L., Gaolin L., Jigang Z., Xiaoyu L. Potential nexus of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus: Insulin resistance between hepatic and peripheral tissues // Front. Pharmacol. -2019. - Vol. 9. - Art. 1566.
- Norris J.M., Rich S.S. Genetics of glucose homeostasis: Implications for insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome // Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. - 2012. - Vol. 32. - P. 2091-2096. DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA. 112.255463.
- Pelland A., George R.B., Lehmann C., Coolen J. Sidestream dark field imaging of the microcirculation to assess preeclampsia microvascular dysfunction // J. Clin. Med. Res. - 2018. - Vol. 10. - P. 391-395. DOI: 10.14740/jocmr3368w.
- Permyakova A.V., Porodikov A., Kuchumov A.G., Furman E.G., Sinelnkov Y.S. Discriminant analysis of main prognostic factors associated with hemody-namically significant pda: Apgar score, silverman-anderson score, and nt-pro-bnp level // Journal of Clinical Medicine. - 2021. -Vol. 10(16). - Art. 3729.
- Possenti L., Casagrande G., Di Gregorio S., Zunino P., Costantino M.L. Numerical simulations of the microvascular fluid balance with a non-linear model of the lymphatic system // Microvasc. Res. - 2019. - Vol. 122. - P. 101-110. DOI: 10.1016/j.mvr.2018.11.003.
- Saeedi P., Petersohn I., Salpea P., Malanda B., Karuranga S., Unwin N., Colagiuri S., Guariguata L., Motala A.A., Ogurtsova K. et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas 9th edition // Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. - 2019. - Vol. 157. - Art. 107843. DOI: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843.
- Sivitz W.I. Lipotoxicity and glucotoxicity in type 2 diabetes // Postgrad. Med. - 2001. - Vol. 109. - P. 55-64. DOI: 10.3810/pgm.2001.04.908.
- Speziale S., Tenti G., Sivaloganathan S. A poroelastic model of transcapillary flow in normal tissue // Microvasc. Res. -2008. - Vol. 75. - P. 285-295. DOI: 10.1016 /j.mvr.2007.07.001.
- Starling E.H. On the Absorption of fluids from the connective tissue spaces // J. Physiol. - 1896. - Vol. 19. - P. 312-326. DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.1896.sp000596.
- Taghilou B., Pourjafar-Chelikdani M., Taghavi S.M., Kuchumov A., Sadeghy K. Numerical simulation of viscoelastic effects in peristaltic transport of drops // Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics. - 2022. - Vol. 306. -Art. 104826.
- Tang Y., He Y. Numerical modeling of fluid and oxygen exchanges through microcirculation for the assessment of microcirculation alterations caused by type 2 diabetes // Microvasc. Res. - 2018. - Vol. 117. - P. 61-73. DOI: 10.1016/j.mvr.2018.01.006.
- Volmer-Thole M., Lobmann R. Neuropathy and Diabetic Foot Syndrome // Int. J. Mol. Sci. - 2016. - Vol. 17. - Art. 917. DOI: 10.3390/ijms17060917.
- Weledji E.P., Fokam P. Treatment of the diabetic foot - to amputate or not? // BMC Surg. - 2014. - Vol. 14. - P. 1-6. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2482-14-83.
- Widgerow A.D. Ischemia-reperfusion injury: Influencing the microcirculatory and cellular environment // Ann. Plast. Surg. - 2014. - Vol. 72. - P. 253-260. DOI: 10.1097/SAP.0b013e31825c089c.
- Woodcock T.E., Woodcock T.M. Revised Starling equation and the glycocalyx model of transvascular fluid exchange: An improved paradigm for prescribing intravenous fluid therapy // Br. J. Anaesth. - 2012. - Vol. 108. - P. 384-394.
- Wu M.Y., Yiang G.T., Liao W.T., Tsai A.P.Y., Cheng Y.L., Cheng P.W., Li C.Y., Li C.J. Current mechanistic concepts in ischemia and reperfusion injury // Cell. Physiol. Biochem. -2018. - Vol. 46. - P. 1650-1667.
- Zhang P., Lu J., Jing Y., Tang S., Zhu D., Bi Y. Global epidemiology of diabetic foot ulceration: a systematic review and meta-analysis // Ann. Med. - 2017. - Vol. 49. - P. 106116.


