Математическое моделирование и исследование оптимальной конфигурации оптической стереосистемы, состоящей из двух плоских зеркал
Автор: Степанов Д.Н., Тищенко И.П.
Журнал: Программные системы: теория и приложения @programmnye-sistemy
Рубрика: Математическое моделирование
Статья в выпуске: 3 (62) т.15, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Статья посвящена математическому моделированию и оптимизации конфигурации оптической стереосистемы, состоящей из видеокамеры и двух плоских зеркал. Отличие данного исследования от ранее проведенных - учет большого количества ограничений на конфигурацию оптической системы: величина стереобазы, размеры зеркал, общие габариты оптической системы, отсутствие двойного отражения световых лучей, недопущение ситуации, когда видеокамера отражается в зеркалах. Выполнена постановка задачи условной оптимизации для поиска оптимальной конфигурации рассматриваемой оптической системы. В качестве целевой функции выбран периметр прямоугольника, ограничивающего габариты оптической системы. Численное решение задачи было найдено с использованием пакета SciPy. Полученные результаты расширяют теорию компьютерного зрения и могут быть использованы в создании и исследовании систем компьютерного зрения для робототехнических комплексов.
Машинное зрение, оптические приборы, математическое моделирование, стереозрение, оптимизация, катоптрическая система
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143183466
IDR: 143183466 | УДК: 004.942:535.318 | DOI: 10.25209/2079-3316-2024-15-3-23-52
Текст научной статьи Математическое моделирование и исследование оптимальной конфигурации оптической стереосистемы, состоящей из двух плоских зеркал
Системы технического зрения широко применяются для решения задач, связанных с неразрушающим контролем качества деталей и материалов, создания трехмерных моделей реальных объектов, в биометрических системах распознавания, в автономных роботах и др. Основными инструментами для восстановления 3D-структуры наблюдаемой сцены в настоящее время являются:
-
• лидары — источники лазерного излучения; принцип действия основан на измерении времени движения отраженных лазерных лучей. Схожий принцип действия имеют времяпролетные (ToF-) камеры.
-
• источники структурированной подсветки: специальный излучатель (проектор) проецирует на сцену некоторый паттерн известной конфигурации, а видеокамера выполняет съемку сцены, подсвеченной проектором. Детектирование элементов паттерна на снимке с видеокамеры позволяет восстановить 3D-координаты точек, на которые попадает паттерн.
-
• съемка сцены несколькими фото- или видеокамерами с разных ракурсов. Для неподвижных объектов также используется вариант, когда снимки с разных ракурсов выполняются одной камерой.
Первые лидары и времяпролетные камеры были достаточно дорогими, громоздкими и ресурсоемкими устройствами, но сейчас в свободной продаже есть много доступных и компактных устройств подобных классов, а их технические характеристики позволяют использовать их для решения многих практических задач. Их важнейшее преимущество перед решениями на основе видеокамер состоит в том, что лидары и ToF-камеры позволяют получить данные о 3D-структуре окружающей обстановки без дополнительных нетривиальных алгоритмов калибровки сенсоров, а также алгоритмов обработки и анализа сенсорных данных. Работа систем на основе нескольких видеокамер основана на решении задачи стереосопоставления (stereo correspondence problem), в которой необходимо находить соответствия между пикселями изображений, выполненных с разных ракурсов и/или в разные моменты времени. Данная задача является одной из самых сложных в компьютерном зрении и не имеет универсального алгоритма ее решения. Если же используется структурированная подсветка, то необходимость в решении задачи стереосопоставления отпадает, но появляется задача поиска элементов подсветки на снимках с видеокамеры. А она тоже может быть нетривиальной, особенно в условиях неконтролируемого освещения.
Для восстановления трехмерной структуры сцены также используются катадиоптрические системы, в состав которых входят видеокамера и комбинация преломляющих и отражающих элементов. На одной светочувствительной матрице создается сразу несколько изображений. Это приводит к тому, что каждая виртуальная видеокамера будет иметь меньшие углы обзора, чем исходная видеокамера, а проблема стереосопоставления остается актуальной, но для получения стереоснимков достаточно одной видеокамеры. Следовательно, в задаче калибровки оптической системы уменьшается количество неизвестных, поскольку внутренние параметры виртуальных камер идентичны. Далее будут описаны примеры практического применения подобных систем, в которых они имеют преимущества перед решениями на основе лидаров и ToF-камер.
Из катадиоптрических систем можно выделить диоптрические (используются только преломляющие элементы) и катоптрические (только отражающие элементы). В качестве примеров работ по исследованию систем из первой группы можно указать статью [1] : исследуются вопросы калибровки системы, в которой эффект стерео достигается за счет использования призмы перед камерой. В статье [2] описана система, в которой похожая призма располагается внутри камеры, между системой линз и светочувствительной матрицей, что позволяет на одном изображении получать два снимка с разных ракурсов.
Катоптрические системы можно условно разделить по типу используемых зеркал, плоских или криволинейных. По сравнению с использованием плоских зеркал, криволинейные зеркала позволяют добиться более широких углов обзора, но видимые размеры объектов становятся меньше, а геометрические искажения на изображениях — более заметными, особенно по краям зеркал. Схожие особенности имеют системы, использующие камеры с широкоугольными объективами типа «рыбий глаз» (англ. fish-eye).
Катоптрические системы с плоскими зеркалами можно классифицировать по количеству используемых зеркал. Однозеркальные системы (пример — статья [3] ) наиболее простые, но имеют узкую область применения ввиду слишком малого угла обзора. Один из способов решения данной проблемы — вращение зеркала: например, в работе [4] зеркало вращается в одной плоскости, а ось вращения зеркала совпадает с направлением оптической оси камеры. В работе [5] представлена система панорамного видения, основанная на использовании камеры и плоского зеркала, вращающегося вокруг двух осей. В статье [6] описана похожая система всенаправленного панорамного видения, в которую входит зеркало, вращающееся со скоростью несколько десятков оборотов в секунду, а также специальный алгоритм управления затвором камеры.
В качестве примеров работ по трехзеркальным системам можно привести статьи [3, 7–9]: например, в статье [3] исследуется оптимальное расположение трех зеркал для получения ректифицированной стереопары с помощью одной камеры. В статьях [7, 8] описана система из одной видеокамеры, трех обычных зеркал и светоделителя (англ. beamsplitter), который половину света пропускает, а вторую половину — отражает. Изображения двух виртуальных камер получаются наложенными друг на друга (т.е. нуждаются в постобработке). Приведены уравнения для расчета размера зеркал, уравнения для восстановления 3D-координат точки, наблюдаемой на снимке со стереоустановки, а также алгоритм построения карты диспаритетов на основе преобразования Фурье. В статье [9] для трехзеркальной системы выведены уравнения эпиполярных ограничений (уравнения, которые связывают координаты пикселей, соответствующих одному и тому же объекту на изображениях одной сцены с разных ракурсов).
Принцип работы трехзеркальных систем, как правило, сводится к тому, что на одну часть светочувствительной матрицы проецируются лучи, претерпевшие отражение от одного зеркала, а на другую часть матрицы — отражение от двух других зеркал. На таком принципе основана и оптическая система, описанная в статье [10] : система из 9 зеркал организована в виде двух пирамид, расположенных друг напротив друга. Поле обзора камеры делится на несколько непересекающихся регионов, и в каждом из них световой поток делится на две вышеуказанные части. Выполнен расчет оптимальной конструкции такой системы, представлен способ ее калибровки. Выполнен расчет погрешностей в оценивании 3D-координат наблюдаемой точки при известных погрешностях при измерении проекций этой точки на паре снимков с двух виртуальных камер. Аналогичная оптическая система исследована и в статье [11] .
В работе [12] описана система из четырех плоских зеркал, угол между двумя внутренними зеркалами равен 90°. Выведено уравнение для расчета стереобазы между двумя виртуальными камерами. Рассчитана конфигурация системы для обеспечения нужного угла обзора. В статье [13] рассмотрена почти такая же система, но два внешних зеркала могут менять свою ориентацию. Выполнен расчет стереобазы, расчет размеров и расположения зеркал, расчет конфигурации области пересечения полей зрения двух виртуальных камер. Как и в работе [10], произведен расчет погрешностей в оценивании 3D-координат наблюдаемой точки. Статья [14] также посвящена расчету оптимальной конфигурации четырехзеркальной системы, с учетом желаемого угла обзора, рабочей дистанции, точности измерений и общих физических размеров оптической системы. В работе [15] выполнено сравнение возможностей четырехзеркальной системы и стереосистемы из двух видеокамер. Примером статей, в которых описано практическое применение четырехзеркальных систем, является работа [16], посвященная построению 3D-моделей лопастей авиационных двигателей, а также статья [17], в которой описано оригинальная стереонасадка из четырех зеркал, которая позволяет получать стереоснимки с помощью обычного смартфона.
В работе [18] описан оригинальный подход для получения панорамных стереоизображения с широким углом обзора с помощью одной камеры и стереонасадки, состоящей из множества плоских зеркал. Панорамным стереоснимкам посвящена и статья [19] : несколько видеокамер наблюдают конструкцию из набора зеркал, составляющих грани пирамиды.
Данная работа посвящена двухзеркальным системам. На одном фотоприемнике формируется сразу два изображения, чаще всего одно из них занимает левую половину снимка, а второе — правую. Подобным системам посвящено достаточно много работ, но нужно заметить, что в некоторых исследованиях рассматриваются частные случаи конфигурации оптической системы. Например, в статье [20] выведены уравнения эпиполярных ограничений для двухзеркальной системы, но принято допущение, что одно из зеркал располагается параллельно плоскости изображения камеры. Одним из авторов предыдущей статьи, Shree K. Nayar, в работе [21] предложена математическая модель формирования изображений в системах из одной камеры и одного зеркала (плоского, конического, сферического, параболического, эллиптического или гиперболического). Выполнена аналитическая оценка пространственного разрешения подобной оптической системы, а также оценка уровня размытия, вызванного расфокусировкой. В системе, описанной в статье [22] , зеркала располагаются симметрично относительно оптической оси камеры и соприкасаются друг с другом, камера при этом наблюдает отражения объектов, располагающиеся за камерой. Выполнен расчет стереобазы с использованием угла между зеркалами и расстояния до зеркал, а также оценка оптимального взаимного расположения зеркал, чтобы в них не было видно друг друга, и чтобы обе виртуальные камеры могли наблюдать точку, располагающуюся на бесконечности. Показано, что при уменьшении угла между зеркалами увеличивается угол обзора и одновременно увеличивается стереобаза.
Но более общие случаи конфигураций также рассматриваются: например, авторы статей [23, 24] построили математическую модель двухзеркальной системы, вывели уравнения эпиполярных ограничений, предложили алгоритм вычисления фокальной длины камеры по изображениям со стереосистемы, а также рассчитали угол обзора стереосистемы. В работе [25] описана система, состоящая из двух плоских зеркал и RGB-D камеры, которая совмещает в себе обычную видеокамеру и средство для построения карт глубин. Два зеркала позволяют следить за обстановкой в двух направлениях: перед мобильным роботом и за ним. Оптическая ось камеры при этом направлена в точку соединения зеркал. В работе [26] также предложена математическая модель двухзеркальной системы, предложен алгоритм вычисления угла между зеркалами, а также алгоритм вычисления положения и ориентации камеры относительно зеркал по двум наблюдаемым точкам (положение вычисляется с точностью до некоторого положительного коэффициента). В статье [27] двухзеркальная оптическая система используется для измерения уровня вибрации на поверхности устройства для воспроизведения звука (колонка), причем правая часть изображения формируется из световых лучей, которые претерпели отражение от обоих зеркал, а левая часть — лучами, которые не отражались от зеркал. Работа [28] посвящена расчету конфигурации калейдоскопической стереосистемы, состоящей из одной камеры и двух или трех плоских зеркал. В статье [29] предложен способ калибровки подобной калейдоскопической системы. В работе [30] два плоских зеркала используются совместно с дихроичным фильтром, одна из сторон которых пропускает световые волны, соответствующие красному цвету, а другая сторона отражает волны, соответствующие синему.
Что касается практического применения катоптрических систем (в частности, двухзеркальных), то можно выделить следующее:
-
• мобильные наземные роботы, решающие задачи SLAM и/или детектирования и распознавания целевых объектов окружающей обстановки [25] . В работе [31] исследовалась стереонасадка, которая разрабатывалась для применения на мобильных роботах. Конечно, здесь следует заметить, что использование системы зеркал в данной задаче возможно только в тех случаях, когда требуемый размер стереобазы относительно невелик, иначе зеркальная система окажется слишком громоздкой. В частности, это несколько ограничивает использование подобных систем на беспилотных летательных аппаратах.
-
• промышленная робототехника: например, в статье [26] описывается робот-манипулятор, в рабочем пространстве которого располагаются два или более плоских зеркала. Робот оснащен видеокамерой, зеркала позволяют повысить точность работы манипулятора за счет наблюдения рабочего пространства с разных ракурсов. Отдельно взятый лидар или ToF-камера могут обеспечить построение 3D-модели объекта только с одного ракурса.
-
• изменение уровня вибрации на рабочих поверхностях приборов для воспроизведения звука [27] . Одним из способов решения данной задачи является стереозрение, которое имеет ряд преимуществ перед
другими методами: возможность проводить измерения по всему рабочему полю и низкая чувствительность к окружающему акустическому шуму. Высокоскоростные камеры, которые используются для решения при решении данной задачи, являются дорогим специализированным оборудованием, и поэтому использование зеркал для получения эффекта стерео может радикально уменьшить стоимость всей оптической системы. Лидары и ToF-камеры имеют значительно меньшее быстродействие (FPS, Frames per Second — количество кадров в секунду), чем высокоскоростные видеокамеры.
-
• получение трехмерных моделей различных объектов (получение их цифровых копий): в работе [29] использование видеокамеры и двух плоских зеркал позволило получать пять изображений одного объекта с разных ракурсов.
Наконец, можно выделить еще одно преимущество решений на основе видеокамер по сравнению с лидарами и ToF-камерами. Видеокамеры имеют более высокое разрешение и позволяют получить информацию о внешнем виде объекта (например, его текстуру, цвет, надписи на нем), лидары и ToF-камеры позволяют получить только пространственную информацию. Если стоит задача детектирования и распознавания целевых объектов на сенсорных данных в видимом диапазоне, то лидара или ToF-камеры будет недостаточно.
Обзор показал, что для расчета оптимальной конфигурации подобных зеркальных систем используется небольшое количество параметров: в частности, для двухзеркальных — только угол обзора и размер стереобазы. Кроме того, в существующих моделях игнорируется наличие практических ограничений на размер и конфигурацию отдельных элементов подобных оптических систем (это замечание относится и к моделям с большим количеством зеркал). Например, слишком большие зеркала может быть или невозможно изготовить, или невозможно установить из-за специфики того технического средства, на котором функционирует катоптрическая система (например, летающий или ездящий автономный робот могут иметь ограничения на максимальный размер полезной нагрузки). Кроме того, в существующих моделях не затрагивается проблема многократного отражения: если в одном из зеркал отражается другое зеркало, то результирующее изображение будет содержать неинформативные области. Наконец, сама видеокамера может наблюдать зеркала — этой ситуации также следует избегать, но в разработанных ранее моделях подобная проблема игнорируется. Таким образом, актуальной видится разработка такой математической модели двухзеркальной катоптрической системы, в которой бы учитывались перечисленные практические аспекты проектирования подобных систем.
В конечном итоге, предлагается выполнить формальную постановку задачи условной оптимизации, которая бы учитывала все эти ограничения, для поиска оптимальной конструкции оптической системы. В данной работе будут использованы некоторые выкладки из статьи [32] , которая посвящена разработке математической модели двухзеркальной системы, предложенная модель отличается учетом дисторсии на изображениях с реальных видеокамер.
Существуют различные программы для расчета и оптимизации оптических систем, одной из наиболее популярных является Zemax. Рассматриваемый класс задач имеет важную особенность: требуется, чтобы световой поток от каждого из пары зеркал в итоге проецировался только на одну из половин площади фотоприемника (плоскости изображения), а два зеркала в совокупности должны полностью захватывать поле зрения камеры, т.е. камера не должна наблюдать ничего, помимо зеркал. Это достигается не только определенным положением и ориентацией каждого из зеркал, но и их определенными размерами. Zemax подобный режим не поддерживает: в оптической схеме перед фотоприемником может быть только один оптический элемент, световые лучи от которого поступают на фотоприемник. Кроме того, в Zemax напрямую нельзя задать размеры оптического элемента «Плоское зеркало» (только его положение и угол наклона). Более того, в изученных статьях из списка литературы не было найдено упоминаний о том, что для исследования оптической системы был использован Zemax или какой-то аналог, причем это справедливо и для самых свежих публикаций.
1. Математическая модель оптической стереосистемы из двух плоских зеркал
На рисунке 1 приведена иллюстрация модели оптической стереосистемы из двух плоских зеркал, подробное ее описание доступно в работе [32] . Используется вид сверху, начало координат (точка O) расположено в оптическом центре камеры, ось OX направлена вправо от камеры, ось OY — вниз (на рисунке 1 она направлена от наблюдателя, используется вид сверху), ось OZ — вперед (оптическая ось). Центр объектива камеры совпадает с началом координат, на рисунке 1 объектив изображен в виде тонкой линзы. Фокальная длина камеры равна f , плоскости обоих зеркал перпендикулярны плоскости OXZ. Отрезки AB 1 и B 2 C соответствуют плоскостям зеркал, вместе они перекрывают все поле зрения камеры. Точки B 1 и B 2 располагаются на оси OZ . Два световых луча, проходящих через точку P пространства, отражаются от зеркал и проецируются на матричный фотоприемник F 1 F 2 (плоскость изображения камеры)
в точки q 1 и q 2 соответственно (углы падения равны углам отражения). Точки P 1 и P 2 — наблюдаемые образы точки P . Отрезки AB 1 и B 2 C лежат на прямых с уравнениями z = tan (ф 1 ) x + b 1 и z = tan (ф 2 ) x + b 2 , здесь ϕ 1 и ϕ 2 — углы между прямыми и положительным направлением оси OX , ф 1 , 2 G [0, п].
P 1
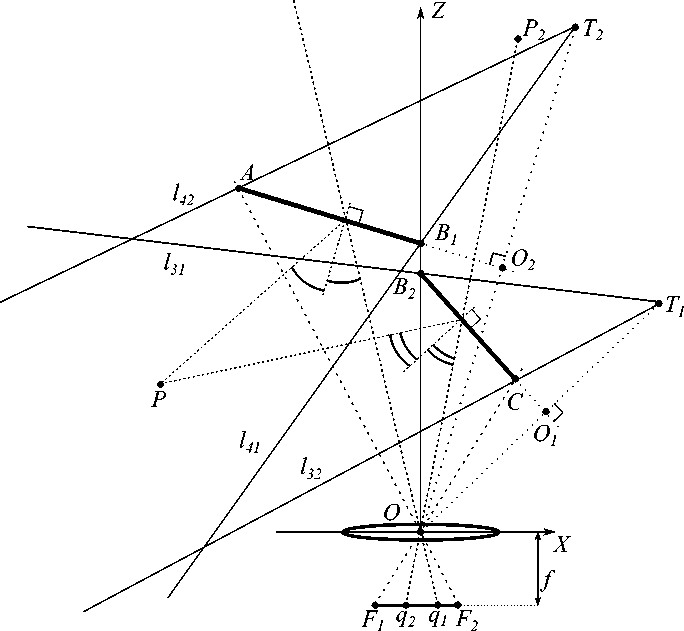
Рисунок 1. Модель оптической стереосистемы из видеокамеры и двух плоских зеркал
Введем и обоснуем использование двух допущений в используемой модели. Первое допущение: параметры используемой видеокамеры (размер матрицы, фокусное расстояние, разрешение матрицы, количество линз, их взаимное положение и конфигурация) являются неизменными и не входят в состав параметров, которые требуется оптимизировать. Единственный параметр, который характеризует непосредственно камеру в рассматриваемой задаче — это ее фиксированный угол обзора (Field of View — FOV). В рассмотренных статьях не было обнаружено моделей, в которых бы оптические характеристики фото- или видеокамер являлись оптимизируемыми и изменяемыми параметрами, т.е. камера жестко задана. Авторам статей достаточно только угла обзора, что позволяет смоделировать камеру с помощью модели «камера-обскура» и перспективной проекции. Также угол обзора может быть вычислен при известном разрешении камеры и фокальной длине, последняя может быть вычислена в ходе калибровки либо с использованием известного фокусного расстояния и размера одного элемента светочувствительной матрицы. Чувствительность, отношение сигнал/шум, размер матрицы, параметры линз, апертура и др. — все эти параметры камер в статьях не рассматриваются. Создание собственной фото/видеокамеры — намного более трудная задача, по сравнению с созданием системы из зеркальных элементов и/или разделителей лучей (beam splitter) и готовой цифровой камеры. Таким образом, допущение о фиксированных характеристиках фото/видеокамер вполне отвечает действительности, с которой сталкиваются другие исследователи.
Второе допущение — дисторсия на снимках либо незначительна, либо устранена программными методами (камера при этом должна быть заранее откалибрована). Если же учитывать в математической модели коэффициенты дисторсии, то вывод аналитических зависимостей будет невозможен из-за невозможности получить аналитическое решение системы нелинейных уравнений, которую порождает математическая модель. Современные цифровые камеры, как правило, обладают незначительной дисторсией. Исключение — камеры с большим или сверхбольшим углом обзора, но для таких камер используются другие математические модели (отличные от модели «камера-обскура» и перспективной проекции), в настоящем исследовании подобные камеры не рассматриваются. В рассмотренных статьях других исследователей не было обнаружено, чтобы дисторсия линз принималась во внимание.
Cделаем еще несколько допущений:
-
• зеркала примыкают друг к другу, т.е., B 1 = B 2 = B и b 1 = b 2 = b. Такое допущение присутствует в части рассмотренных статей, также оно имеет место в той оптической системе, которая далее будет исследована с помощью предложенной математической модели.
-
• ось OZ делит угол обзора пополам: ∠ AOB = ∠ COB = α. Это соответствует ситуации, когда положение оптического центра камеры незначительно отличается от центра фоточувствительной матрицы. Для большинства современных камер это условие выполняется.
-
• выполняется следующий набор условий:
α ∈
00, 2 ) ’^ 1 > 2 + a,^ 1 > ф 2 ,Ф - , 2 e
(П4
Условие a > 2 может выполняться только для сверхширокоуголь- ных камер, которые в данном исследовании не рассматриваются. Если ф1 < 2 + а, то прямая AB не будет пересекаться с лучом OA, то есть, точка A не будет лежать на левой границе поля зрения камеры. Если ϕ1 ≤ ϕ2 , то поля зрения виртуальных камер не будут пересекаться (данная закономерность была выведена эмпирическим путем, с помощью геометрического построения различных конфигураций рассматриваемой оптической системы). Если ф1,2 < 2, то камера будет наблюдать заднюю поверхность зеркала.
Поскольку использование зеркал делает изображения зеркально повернутыми относительно вертикальной оси, то необходимо развернуть изображения еще раз. Пусть P 1 и P 2 — трехмерные координаты наблюдаемых образов точки P на изображении с оптической стереосистемы, которое было подвергнуто зеркальному повороту. В статье [32] были выведены следующие формулы для вычисления координат P 1 ,2 :
^
P - , 2 =
R l , 2 =
I
^
X 1 , 2
^
Y l , 2
^
_ Z1 , 2.
cos 2ф 2-
sin 2 ф 2 , 1
P 2 =
R- , 2 P + T -2 = R^ (P - T - , 2 ) ,
sin 2^ 2 , 1
R t PP P - - t)
cos 2 ф 2,1
] ,T l , 2 = b [
sin 2ф 2 , 1
1 + cos 2ф 2 , 1
,R = R - R 2 ,T = R - (T 2
t - ) .
I
,
Матрицы R1 и R2 задают ориентации систем координат, привязанных к правой и левой виртуальным камерам соответственно (обозначим эти системы как СК1 и СК2), относительно системы координат, привязанной к реальной монокулярной камере. Верхний индекс t — операция транспо- нирования. T1 и T2 — координаты оптических центров виртуальных камер,
начала СК1 и СК2. Пара RR,T^ относительно СК1.
задает ориентацию и положение СК2
Пусть (xi, yi) — двумерные координаты проекции точки P на изображении с i-той виртуальной камеры, Mi — матрица внутренних параметров i-той камеры (camera intrinsic matrix), строение матриц Mi в контексте данной задачи изложено в статье [32]. 3D-координаты точки P неизвестны, как и координаты P1 и P2. Матрицы Mi связывают координаты P1 и P2 с 2D-координатами проекций точки P :
x i x i
W i У г = M i P i ^ P i = W i M -- У г .
Здесь w 1 и w 2 — неизвестные масштабирующие множители. Выражение
-1
P 2
= R t (P 1 - T^
можно переписать следующим образом:
w 2 M 2 - 1
x 2 y 2
= RR t ^w 1 M f 1
x 1 y 1
')
Нетрудно убедиться, что это выражение является переопределенной системой из трех линейных алгебраических уравнений относительно двух неизвестных w 1 и w 2 , которые могут быть найдены, к примеру, с помощью метода наименьших квадратов. Необходимо только заметить, что дисторсия на снимке с видеокамеры должна быть предварительно устранена.
Используя координаты точек T 1 , 2 , нетрудно доказать, что они являются отражением точки O относительно двух зеркал (см. рисунок 1, O 1 € B 2 C,OT 1 ±B 2 C,O 1 O = O 1 T 1 , O 2 € B 1 A,OT 2 ±B 1 A,O 2 O = O 2 T 2 ). Угол обзора правой виртуальной камеры задается лучами l 41 (лежит на отрезке T 2 B 1 ) и l 42 (лежит на отрезке T 2 A ). Аналогично задается угол обзора левой виртуальной камеры: лучи l 31 и l 32 . Также нетрудно доказать, что углы обзора обеих виртуальных камер равны α : поскольку выполняются равенства △ OB 2 O 1 = △ T 1 B 2 O 1 и АОСО 1 = △ T 1 CO 1 (по первому признаку равенства треугольников), то Z B 2 T 1 C = AB 2 OC = а. Доказательство по аналогичной схеме используется для случая, когда точка O 1 располагается внутри отрезка B 2 C , а также для левого зеркала (отрезок AB 1 ).
2. Ограничения, связанные со величиной стереобазы
Расстояние между камерами (в данном случае виртуальными) — один из основных параметров, характеризующих оптическую стереосистему:
T 1 T 2 = 2b |sin (Ф 1 - ^ 2 )|, Ф 1 >ф 2 ^ T 1 T 2 = 2bsin (ф 1 - Ф 2 ) .
Если система из двух камер откалибрована (известны их внутренние
R ˆ︁ , T ˆ︁ )
параметры и пара
то к полученной стереопаре можно применить процедуру геометрического выравнивания — ректификации [33]. Изобра- жения в итоге получаются такими, как если бы они были выполнены двумя камерами с одинаковыми внутренними параметрами и с одинаковой ориентацией (Rˆ︁ становится равной единичной матрице), а смещение между их оптическими центрами имеет место только вдоль оси OX , т.е 'T = [T 0 0]t. При таких условиях, коэффициенты увеличения обеих камер станут одинаковыми, а проекция любой точки пространства, которая наблюдаема на обеих снимках, будет располагаться в пикселях, имеющих одинаковый номер строки, что значительно облегчает решение задачи стереосопоставления. Пусть проекция этой точки располагается на левом и правом снимках в пикселах с номерами столбцов xl и xr соответственно, величина d = xi — xr именуется диспаритетом. Тогда расстояние до точки рассчитывается по формуле Z = Z (d) = fT [33]. Оценим погрешность AZ в вычислении функции Z (d), если известна некоторая априорная оценка Ad погрешности в вычислении диспаритета (она зависит от особенностей используемого алгоритма поиска стереосоответствия):
AZ = ^ Ad =
∂d
(fdT 2 ) fT Ad = ZT Ad.
Рассмотрим следующую задачу: известно Z 0 — расстояние до наблюдаемого объекта, необходимо найти параметры оптической системы, при которых погрешность в вычислении расстояния составляет не более AZ o :
ZAd
Это выражение имеет следующий смысл: какой должна быть минимальная величина стереобазы, чтобы при известной фокальной длине f обеих камер, известной погрешности Ad в вычислении диспаритета, погрешность в вычислении расстояния до объектов с помощью триангуляции не превосходила величину AZ0 (если про объект известно, что он находится на расстоянии не более чем Z0). Например, если автономный подвижный робот решает задачу навигации внутри помещений, то величина Z0 может быть равна, скажем, 3-4 метра. Априорная оценка этой величины зависит от скорости движения робота, быстродействия алгоритмов навигации и технических характеристик камеры (к примеру, достаточно удаленные объекты будут, скорее всего, плохо различимы на снимках, но в то же время, в силу удаленности в данный момент они не представляют опасности для робота).
В итоге ограничение на минимальную величину стереобазы задается следующим образом:
base (ф 1 , Ф 2 , b) := 2b sin (ф 1 - Ф 2 ) > T min .
3. Расчет уравнений лучей, определяющих углы обзора виртуальных камер
Выведем уравнения лучей l ij . Поскольку AAOB = AC OB = а, то уравнения лучей OA и OC имеют вид z = x • cot (уа). Точка A является пересечением луча OA и прямой, на которой располагается левое зеркало. Координаты точки C вычисляются по аналогии:
A, C =
b cot (ya) — tan ф1,2
cot (ya)
Уравнения лучей l ij имеют следующий вид:
l i1 : z =
— cot (2ф 5-^ • x + b = tan
(2 5 + 2)
• x + b,
(10) П cos ф5 -i sin(ф5 -i + ja)
' li 2 : z = tan I 2 ф5-i + ja + у )• x + 2b---- ;—77-7-----—-y----,
2 sin (2ф 5-i + ja)
j =7 — 2i.
Для дальнейших выкладок нам потребуется информация об углах наклона прямых l ij , их можно получить из уравнений прямых, но следует учесть периодичность функции тангенс и набор условий (1) . В итоге получаем:
^ 2 ф 5 -i + ja (k — 1) + П — n, ф 5 -i G ( 2 , 34 n — j 2 ( k — 1)] 1 2ф 5 -i + ja (k — 1) + П — 2 n, ф 5 -i G ( 3 n — j a ( k — 1) ,n]
Путем геометрических построений нетрудно убедиться, что первый вариант соответствует случаю, когда луч l ij направлен вверх от оси OX и не пересекает ее, а второй вариант — когда направлен вниз и пересекает.
4. Ограничения на размер зеркал
Вычислим расстояния AB и CB (ширина левого и правого зеркал):
AB,CB =
b sin a
|cos (^ 1 , 2 T a)|.
С учетом набора условий (1) нетрудно убедиться, что оба выражения под модулями всегда меньше нуля. Пусть максимальная ширина левого и правого зеркал ограничена некоторыми значениями L 10 и L 20 (например, в силу технологических причин или ограничений на габариты технического средства, на котором установлена оптическая система). В итоге ограничения на размер зеркал задаются следующими неравенствами:
b sin a
L 1 (Ф 1 , b) • = -------77------V - L 10 ,
-
— cos (Ф 1 — a)
b sin a
L 2 (ф 2 , b) •= -------77---.---7 — L 20 .
— cos (Ф2 + a)
5. Условия, при которых не наблюдается взаимное отражение зеркал
6. Условия, при которых зеркала умещаются внутри короба фиксированного размера
Исследуем, при каких условиях в поля зрения виртуальных камер не попадают зеркала. С учетом выражений (1) и (2) получаем, что точка T 2 всегда лежит правее оси OZ , следовательно, поле обзора правой виртуальной камеры не может пересекать первую координатную четверть, в которой находится правое зеркало.
Перейдем к левой виртуальной камере. Исходя из геометрических соображений, факт наблюдения камерой левого зеркала определяется взаимным положением зеркала и луча l 31 . Угол ∠ l 31 может выражаться двумя разными способами (выражение (11) ). Если ф 2 е [3 П , п] , то луч 1 з1 будет направлен вниз, а левое зеркало будет располагаться над полем зрения левой виртуальной камеры (в плоскости OXZ ) и заведомо не будет попадать в это поле. Если же ф 2 е (П , 3 т] , то камера не будет наблюдать левое зеркало при ф 1 < Л1з1 = 2ф 2 — 2 .
Если же ф 2 е [ 3 П , п], то (2ф 2 — 2 ) е [ п, 3^] , т.е. при таких значениях ф 2 условие (ф 1 < 2ф 2 — п) тоже выполняется. В итоге, условия, при которых не наблюдается взаимное отражение зеркал, записывается следующим образом:
ф 1 < 2ф 2 — 2.
В наших предыдущих статьях [31 , 32] исследовался образец двухзеркальной оптической системы — стереонасадка для цифровой камеры Raspberry Pi Camera, данная камера достаточно широко в различных проектах, связанных с компьютерным зрением. Камера предназначена для подключения к микрокомпьютеру Raspberry Pi с помощью шлейфа (рисунок 2) . Согласно информации с официального сайта , данная камера (ее первая версия) имеет горизонтальный угол обзора 53,5 ° = 0, 934 рад., т.е. а = 26, 75 ° = 0, 467 рад.
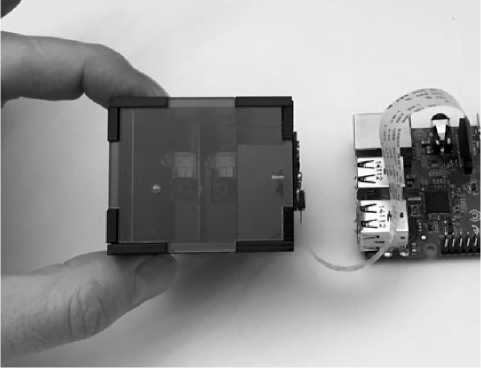
Рисунок 2. Стереонасадка с инсталлированной цифровой камерой Raspberry Pi Camera, подключенной к микрокомпьютеру
Вся конструкция заключена внутри пластикового короба в виде прямоугольного параллелепипеда, одна из граней короба сделана из прозрачного пластика, остальные грани — из черного пластика. Размещение зеркал внутри короба позволяет жестко зафиксировать зеркала относительно камеры и защищает зеркала от внешних воздействий. На рисунке 3 показана схема стереонасадки (вид сверху). Стороны короба — это прямоугольник DEW A, сторона AD является прозрачной, а камера крепится на стороне DE . Короб определяется своей шириной wbox = ∥ DE ∥ и высотой xbox = ∥ AD ∥ . Центр объектива камеры принимается за начало координат, которое располагается на стороне DE .
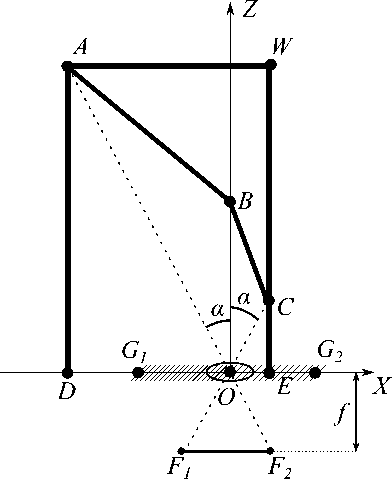
Рисунок 3. Схема двухзеркальной системы внутри прямоугольного короба
Максимальные размеры подобного короба могут быть ограничены: например, если требуется разместить его на беспилотном летательном аппарате или наземном подвижном роботе. Следующие два неравенства обеспечивают то, что конструкция из зеркал будет помещаться внутри короба заданного размера:
( X c — X a ) < wbox, Z A ≤ hbox.
7. Условия, при которых в зеркалах не отражаются запрещенные области
Любая реальная видеокамера имеет определенные габариты, в том числе лицевая часть видеокамеры. При использовании камеры в подобной катоптрической системе возможна ситуация, когда камера будет отражаться в зеркалах, чего желательно избегать, поскольку на изображениях окажутся неинформативные области. Например, камера Raspberry Pi Camera размещена на микросхеме в форме квадрата со стороной 2,5 см., а объектив располагается приблизительно в центре микросхемы. Таким образом, в поле зрения виртуальных камер не должна попадать не только видеокамера, но и области слева и справа от видеокамеры шириной по 1,25 см. на стороне DE. Назовем подобные области запрещенными. На рисунке 3 отрезок G1 G2 соответствует области, которая занимает конструкция видеокамеры.
В общем случае, точки G 1 и G 2 могут располагаться или внутри отрезка DE, или вне его, или совпадать с точками D и E. Если G 1 располагается внутри отрезка DO , то отрезок DG 1 может быть прозрачным и может попадать в поле зрения виртуальных камер, что продемонстрировано на рисунке 4. Здесь изображена 3D-модель, включающая в себя два зеркала и короб. На грани, включающей в себя отрезок G 1 E , закрепляется видеокамера. Точки E и G 2 совпадают. То есть, запрещенной областью является не вся сторона DE , а только ее часть, отрезок G 1 E .
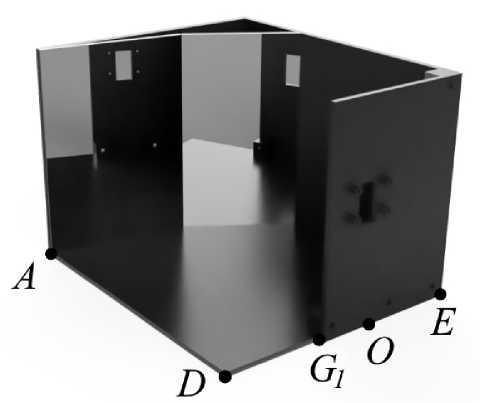
Рисунок 4. 3D-модель катоптрической системы внутри короба с частично прозрачной стороной DE
С учетом вышесказанного, введем новые обозначения: пусть запрещенная область задается в виде отрезка S 1 O длиной s 1 и отрезка OS 2 , оба они лежат на оси OX . В поле зрения правой виртуальной камеры отрезок S 1 S 2 не попадает, если выполняется одно из условий:
-
• луч l 41 не пересекает прямую, на которой лежит этот отрезок.
Тогда луч l 41 направлен вниз (по отношению к положительному направлению оси OZ). Согласно выражению (11) , это выполняется, если угол наклона левого зеркала не превосходит 4 π .
-
• луч l 41 пересекает отрезок S 1 S 2 левее точки S 1 ;
-
• луч l 42 пересекает отрезок правее точки S 2 — невозможно при допустимых конфигурациях зеркал.
По аналогичной схеме исследуются условия, при которых отрезок S 1 S 2 не попадает в поле зрения левой виртуальной камеры. Обозначим через u ij абсциссу точки пересечения луча l ij и оси OX. В итоге условия, при которых в зеркалах не отражаются запрещенные области, описываются следующим набором выражений:
(. , < 3П) OR ф1 > (^ < (Т - а)) OR ( 2 >
3π
AND (u 41 <
s 1 ) ,
(3П - а) )and (U 32 < -s i )).
Сторону EW можно не рассматривать, поскольку ее нижняя часть не попадает в поле зрения видеокамеры, а та часть, которая могла бы попасть, перекрыта зеркалами.
8. Постановка и решение задачи условной оптимизации для поиска оптимальной конфигурации оптической системы
Зафиксируем параметры задачи. Будем использовать видеокамеру Raspberry Pi Camera, угол а = 26,75 ° = 0,467 рад.. Если использовать разрешение 960 х 720 пикс., то фокальная длина f равна 960/ (2 tan α) = 952 пикс. Обозначим условия, в которых будет функционировать проектируемая оптическая система. Она закреплена на беспилотном летательном аппарате, который будет использоваться для инспекции состояния высотных зданий и линий электропередач. Введем минимально допустимую величину стереобазы, используя выражение (7) . Пусть Z 0 = 100 см., примем эту величину в качестве безопасного рабочего расстояния между БПЛА и исследуемыми объектами. Погрешность ∆d положим равной 2 пикс. Это значение, конечно же, сильно зависит от особенностей используемого алгоритма поиска стереосоответствия. Допустимую погрешность ∆Z 0 в вычислении расстояния положим равной 3 см. Тогда T min = 7 см. Максимально возможную ширину обоих зеркал положим равной L 10 = L 20 = 10 см. Зеркала заключены внутри короба, максимально допустимые размеры которого равны wbox = hbox = 15 см. Камера располагается в центре квадратной микросхемы со стороной
-
2,5 см. (как уже упоминалось с предыдущем разделе). Пусть ширина s 1 = |G 1 O| запрещенной области равна 1,5 см., немного больше половины ширины микросхемы, а отрезок DG 1 прозрачен, т.е. может попадать в поле зрения виртуальных камер.
Полный набор ограничений на конфигурацию оптической системы задается выражениями (1) , (8) , (13) , (14) , (15) , (16) . Оптимизируемыми параметрами являются два угла ϕ 1 , ϕ 2 и длина b, в совокупности они однозначно определяют конфигурацию зеркал относительно видеокамеры. При проектировании оптических систем часто необходимо не только достижение заданных оптических характеристик, но и минимизация размеров системы. Одним из возможных параметров, характеризующих размер рассматриваемой системы, является периметр прямоугольника DEWA. Т есть, необходимо найти условный минимум следующей функции:
(17) F (Ф1,Ф2,Ь) = 2 ((Хс (ф1, b) - Xa (^2, b)) + Za (^2, b)) ^ min .
9. Расчет коэффициента увеличения для виртуальных камер
Аналитическое решение задачи получить не удалось, поэтому задача решалась численно, с использованием возможностей программного пакета SciPy . Была задействована функция differential_evolution из модуля optimize, она позволяет вычислять глобальный минимум скалярной функции F (X) при заданном наборе ограничений вида bi < F X^^ < bu, здесь ⃗bl и ⃗bu — векторы из вещественных чисел. Используется алгоритм дифференциальной эволюции, который является эвристическим. При вызове функции значения всех ее настроек были выбраны по умолчанию.
Программа доступна в github-репозитории . В результате был найдено минимальное значение целевой функции, равное 20,6 см., оно достигается при ф 1 = 172 ° = 3 рад., ф 2 = 131 ° = 2, 288 рад., b =5, 3 см. Размеры зеркал — 3 см. и 2,6 см. Полученная оптическая система помещается в короб размером (Х с — X a ) х Z a =4, 6 х 5,8 см.
Осталось найти высоту обоих зеркал и короба. Необходимо добиться, чтобы в поле зрения видеокамеры не попадало ничего, кроме зеркал. Будем использовать следующее соображение: точка A является наиболее удаленной от видеокамеры точкой, принадлежащей зеркалам, поэтому если левый край левого зеркала занимает по высоте весь кадр с видеокамеры, то зеркала будут занимать все поле зрения камеры. Здесь мы также учитываем, что зеркала прямоугольные и параллельны оси OY . Камера Raspberry Pi Camera имеет вертикальный угол обзора 2в = 41, 41 ° = 0, 934 рад. Тогда высота зеркал равна 2Z a tan (в) = 5, 9 см.
Использовать предложенную методику расчета параметров оптической системы можно следующим образом: имеется некоторая видеокамера с известными характеристиками (разрешение и углы обзора). Это соответствует ситуации, когда проектировщик оптической системы не имеет возможности заниматься разработкой и созданием непосредственно видеокамер, но он может выбрать одну из нескольких доступных видеокамер, чтобы в итоге получить оптическую стереосистему с заданными характеристиками. Заданы максимально допустимые размеры короба, внутри которого должна помещаться оптическая система, и максимально допустимые ширины зеркал. Необходимо рассчитать конфигурацию зеркал таким образом, чтобы минимизировать размеры короба, но при этом чтобы полученное значение стереобазы было не меньше нужного значения. Размеры короба и зеркал могут задаваться, исходя из особенностей конкретной задачи: например, для установке на подвижном роботе вся конструкция должна быть достаточно компактной, а для задачи, описанной, к примеру, в статье [26], ограничения на габариты могут быть менее строгими.
Если в зеркалах отражается некоторый точечный объект с координатами [X Y Z ] t , то оптический путь до него будет различаться для левой и правой виртуальных камер, т.е., два изображения будут получены с разным коэффициентом увеличения. Оценим, насколько могут различаться эти коэффициенты при различных положениях объекта. Для этого вычислим координаты объекта относительно левой и правой виртуальных камер (выражение (2) ) и рассмотрим отношение расстояний от объекта до плоскостей изображений обеих камер:
Z 1 , 2 = X Sin 2^ 2 , 1 + (b - Z ) cos 2^ 2 , 1 + b,
2 X b - Z
S := у X2 + (b — Z ) , sin в := —, cos в := —=— SS
S
S’ : = b, -Z 1 , 2 = b yS cos (2Ф 2 , 1 — в)+ lj ,
-1
Z 2
Z 1
= k(S,^ =
K 1 S ˆ︁ , θ
K 2 (︂ S ˆ︁ , θ )︂
S cos (2^ 1 — в) + 1
→ extr,
S cos (2^ 2 — в) + 1
в G [0, 2n) ,S > 0.
Таким образом, положение объекта задается в полярной системе координат, привязанной к точке соприкосновения зеркал, угол θ задается относительно отрицательного направления оси OZ . В то же время, объект должен находиться в области, образованной пересечением полей зрения обеих виртуальных камер (обозначим эту область как V ), т.е. есть ограничения на возможные значения величин S и 0. В программной среде Maple было выполнено исследование возможных конфигураций области V при различных значениях углов ϕ1 и ϕ2 . Моделирование показало, что область V может иметь одну из трех конфигураций, в зависимости от значения ϕ1 - ϕ2 :
-
a) ( ф 1 - ф 2 ) < 2,
-
b ) (ф 1 - ф 2 ) ^ [^ ,aj, c ) ( ф 1 - ф 2 ) с (а, 2}.
Результаты расчета оптической системы из предыдущего раздела подпадают под случай c). В случае а) область V имеет наиболее простую конфигурацию и лежит между лучами l31 и l41 , в двух остальных случаях конфигурация более сложная и будет подробно рассмотрена в следующей публикации. Оба луча выходят из точки соприкосновения зеркал.
Координаты множества точек, лежащих между этими лучами, можно параметризовать следующим образом: S > 0,0 с [64,63]. Геометрические построения показали, что
точки функции K
( V):
6 i = 2ф i-2 — 2п. Нужно найти экстремальные
( ф 1 — ф 2 ) < ^ с ( 0 , 4) ^ cos 2 ( ф 1 — ф 2 ) с (0 ,1), (20) 6 с [2ф 2 - 2п, 2ф 1 - 2п], 2ф 1 - 6 с [2п, 2 (ф 1 - ф 2 ) + 2п] ^
cos (2ф 1 - 6) > 0 ^ K 1 (S?, 6) > 0.
Аналогично доказывается, что K 2 (s, 6^ > 0. Таким образом, функция K (s, 6^ непрерывна и ограничена внутри области V. Также функция не имеет стационарных точек внутри этой области, следовательно, достигает максимального значения на границах области:
max K ^S>, 6^ = K (+м, 6 4 ) =
cos2 (ф 1 - ф 2 ).
Рассчитаем коэффициент увеличения для конкретной двухзеркальной системы. Пусть а = 40° = 0, 698 рад., ф1 = 154° = 2, 688 рад., ф2 = 135° = 2, 356 рад., b = 5 см, Smax = 200 см. Согласно выражению (8), величина стереобазы будет равна 5,2 см, K (smax,^) = 1,256, а maxK ^,^ = 1,269.
Заключение
Разработана математическая модель катоптрической системы, состоящей из двух плоских зеркал и обеспечивающей получение стереопар изображений с помощью единственной видеокамеры. Модель имеет качественные преимущества перед аналогами за счет учета практических аспектов, которые возникают при проектировании подобных систем: ограничения на размер отражающих элементов, возможность взаимного отражения зеркал, возможность отражения в зеркалах запрещенных областей, общие габариты оптической системы.
Выполнена постановка задачи условной оптимизации для поиска оптимальной конфигурации рассматриваемой оптической системы, в качестве целевой функции выбран периметр короба в форме прямоугольного параллелепипеда, в этот короб заключена катоптрическая система, и его периметр необходимо минимизировать. С использованием возможностей программного пакета SciPy была написана программа для численного решения этой задачи. Выполнен теоретический расчет коэффициента увеличения для виртуальных камер.
В дальнейшем будут рассмотрены ограничения, связанные с конфигурацией области, которая является пересечением полей зрения двух виртуальных камер. Полученные ограничения будут добавлены в уже рассмотренную задачу условной оптимизации. Также планируется использовать предложенный подход к исследованию трехзеркальных и четырехзеркальных катоптрических стереосистем.
Список литературы Математическое моделирование и исследование оптимальной конфигурации оптической стереосистемы, состоящей из двух плоских зеркал
- Gorevoy A. V., Machikhin A. S. Optimal calibration of a prism-based videoendoscopic system for precise 3D measurements // Computer Optics.– 2017.– Vol. 41.– No. 4.– Pp. 535–544. https://doi.org/10.18287/2412-6179-2017-41-4-535-544 ↑25
- Zhou F., Chen Y., Zhou M., Li X. Effect of catadioptric component postposition on lens focal length and imaging surface in a mirror binocular system // Sensors.– 2019.– Vol. 23.– No. 19.– id. 5309.– 20 pp. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19235309 ↑25
- Gluckman J., Nayar S. K. Rectified catadioptric stereo sensors // IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence.– 2002.– Vol. 24.– No. 2.– Pp. 224–236. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.982902 ↑25
- Clark A. F., Chan S. W. Single-camera computational stereo using a rotating mirror // Proc. 1994 British Machine Vision Conference, ed. Hancock E. R..– BMVA Press.– 1994.– ISBN 952-1898-1-X.– Pp. 761–770. https://doi.org/10.5244hU/tCRt.pL8s.:7/5/bmva-archive.org.uk/bmvc/1994/bmvc-94-075.pdf ↑25
- Nakao T., Kashitani A. Panoramic camera using a mirror rotation mechanism and a fast image mosaicing // Proc 2001 International Conference on Image Processing (07–10 October 2001, Thessaloniki, Greece).– 2001.– ISBN 0-7803-6725-1.– Pp. 1045–1048. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2001.958676 ↑25
- Hu S., Dong H., Shimasaki K., Jiang M., Senoo T., Ishii I. Omnidirectional panoramic video system with frame-by-frame ultrafast viewpoint control // IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters.– 2022.– Vol. 7.– No. 2.– Pp. 4086–4093. https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2022.3150484 ↑25
- Pachidis T., Lygouras J. A pseudo stereo vision system as a sensor for real time path control of a robot // Proceedings of the 19th IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference.– V. 2, IMTC/2002 (21–23 May 2002, Anchorage, AK, USA).– 2002.– ISBN 0-7803-7218-2.– Pp. 1589–1594. https://doi.org/10.1109/IMTC.2002.1007197 ↑25 26
- Vernon D. An optical device for computation of binocular stereo disparity with a single static camera, Opto-Ireland 2002: Optical Metrology, Imaging, and Machine Vision, Proc. SPIE.– vol. 4877.– 2003.– Pp. 38–46. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.463762 ↑25 26
- Chai X., Zhou F., Chen X. Epipolar constraint of single camera mirror binocular stereo vision systems // Optical Engineering.– 2017.– Vol. 56.– No. 8.– id. 084103.– 8 pp. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.OE.56.8.084103 ↑25 26
- Zhou F., Chai X., Chen X., Song Y. Omnidirectional stereo vision sensor based on single camera and catoptric system // Applied Optics.– 2016.– Vol. 55.– No. 25.– Pp. 6813–6820. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.55.006813 ↑26
- Liu Y., Zhou F., Guo Z., Tan H., Zhang W. Design and optimization of a quad-directional stereo vision sensor with wide field of view based on single camera // Measurement.– 2022.– Vol. 203.– No. 7.– id. 111915.– 11 pp. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2022.111915 ↑26
- Wang R., Li X., Zhang Y. Analysis and optimization of the stereo-system with a four-mirror adapter // Journal of the European Optical Society Rapid Publications.– 2008.– Vol. 3.– id. 08033.– 7 pp. https://doi.org/10.2971/jeos.2008.08033 ↑26
- Yu L., Pan B. Structure parameter analysis and uncertainty evaluation for single-camera stereo-digital image correlation with a four-mirror adapter // Applied Optics.– 2016.– Vol. 55.– No. 25.– Pp. 6936–6946. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.55.006936 ↑26
- Luo H., Yu L., Pan B. Design and validation of a demand-oriented single-camera stereo-DIC system with a four-mirror adapter // Measurement.– 2021.– Vol. 186.–No. 5.– id. 110083.– 13 pp. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2021.110083 ↑26
- López-Alba E., Felipe-Sesé L., Schmeer S., Díaz F. A. Optical low-cost and portable arrangement for full field 3D displacement measurement using a single camera // Measurement Science and Technology.– 2016.– Vol. 27.– No. 11.– id. 115901. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-0233/27/11/115901 ↑26
- Yu Z., Ma K., Wang Z., Wu J., Wang T., Zhuge J. Surface modeling method for aircraft engine blades by using speckle patterns based on the virtual stereo vision system // Optics Communications.– 2018.– Vol. 411.– No. 1.– Pp. 33–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2017.10.064 ↑27
- Bartol K., Bojanić D., Petković T., Pribanić T. Catadioptric stereo on a smartphone // Proc. 2021 12th International Symposium on Image and Signal Processing and Analysis, ISPA (13–15 September 2021, Zagreb, Croatia), Piscataway, NJ: IEEE.– 2021.– ISBN 1-66542-639-X.– Pp. 189–194. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISPA52656.2021.9552146 ↑27
- Aggarwal R., Vohra A., Namboodiri A. M. Panoramic stereo videos with a single camera // 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (27–30 June 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA).– IEEE.– 2016.– ISBN 978-1-4673-8850-4.– Pp. 3755–3763. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.408 ↑27
- Zhu L., Wang W., Liu Y., Lai S., Li J. A virtual reality video stitching system based on mirror pyramids // 2017 International Conference on Virtual Reality and Visualization (ICVRV) (21–22 October 2017, Zhengzhou, China).– IEEE.– 2017.– ISBN 978-1-5386-2636-8.– Pp. 288–293. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICVRV.2017.00066 ↑27
- Nene S. A., Nayar S.K. Stereo with mirrors // Sixth International Conference on Computer Vision (07 January 1998, Bombay, India).– IEEE.– 1998.– ISBN 81-7319-221-9.– Pp. 1087–1094. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.1998.710852 ↑27
- Baker S., Nayar S. K. A theory of single-viewpoint catadioptric image formation // International Journal of Computer Vision.– 1999.– Vol. 35.– No. 2.– Pp. 175–196. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1008128724364 ↑27
- Goshtasby A., Gruver W.A. Design of a single-lens stereo camera system // Pattern Recognition.– 1993.– Vol. 26.– No. 6.– Pp. 923–937. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-3203(93)90058-5 ↑27
- Gluckman J., Nayar S. K. Planar catadioptric stereo: geometry and calibration // Proceedings 1999 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.– V. 1 (23–25 June 1999, Fort Collins, CO, USA).– IEEE.– 1999.– ISBN 0-7695-0149-4.– Pp. 22–28. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.1999.786912 ↑27
- Gluckman J., Nayar S. K. Catadioptric stereo using planar mirrors // International Journal of Computer Vision.– 2001.– Vol. 44.– No. 1.– Pp. 65–79. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011172403203 ↑27
- Endres F., Sprunk C., Kümmerle R., Burgard W. A catadioptric extension for RGB-D cameras // 2014 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (14–18 September 2014, Chicago, IL, USA).– IEEE.– 2014.– ISBN 9781479969357.– Pp. 466–471. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2014.6942600 ↑27 28
- Mariottini G. L., Scheggi S., Morbidi F., Prattichizzo D. Catadioptric stereo with planar mirrors: multiple-view geometry and camera localization // Visual Servoing via Advanced Numerical Methods, Lecture Notes in Control and Information Sciences.– vol. 401, eds. Chesi G., Hashimoto K., London: Springer.– 2010.– ISBN 978-1-84996-088-5.– Pp. 3–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-84996-089-2_1 ↑28 43
- Durand-Texte T., Melon M., Simonetto E., Durand S. 3D vision method applied to measure the vibrations of non-flat items with a two-mirror adapter, 13th International Conference on Vibration Measurements by Laser and Noncontact Techniques (20-–22 June 2018, Ancona, Italy) // Journal of Physics Conference Series.– 2018.– Vol. 1149.– No. 1.– id. 012008.– 9 pp. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1149/1/012008 ↑28
- Takahashi K., Nobuhara S. Structure of multiple mirror system from kaleidoscopic projections of single 3D point // IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence.– 2022.– Vol. 44.– No. 9.– Pp. 5602–5617. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3070347 ↑28
- Zhao Y., Chen Y., Yang L. Calibration of double-plane-mirror catadioptric camera based on coaxial parallel circles // Journal of Sensors.– 2022.– Vol. 2022.– id. 145400.– 15 pp. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7145400 ↑28 29
- Zhong F, Quan C. A single color camera stereo vision system // IEEE Sensors Journal.– 2018.– Vol. 18.– No. 4.– Pp. 1474–1482. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2017.2786747 ↑28
- Степанов Д. Н., Смирнов А. В. Исследование процесса калибровки и оптических характеристик стереонасадки 3Dberry // Программные системы: теория и приложения.– 2018.– Т. 9.– №3(38).– С. 11–28. https://doi.org/10.2520hU9t/Rt2pL0:7/9/-p3s3t1a6.p-2si0r1a8s-.r9u-3/-/1r1e-a2d8/psta2018_3_11-28.pdf ↑28 38
- Степанов Д. Н. Математические модели получения стереоизображений с двухзеркальных катадиоптрических систем с учетом дисторсии объективов // Компьютерная оптика.– 2019.– Т. 43.– №1.– С. 105–114. https://doi.org/10.18287/2412-6179-2019-43-1-105-114 ↑30 33 38
- Bradski G., Kaehler A. Learning OpenCV: Computer Vision with the Opencv Library.– Sebastopol, CA: O’Reilly Media Inc.– 2008.– ISBN 978-0-596-51613-0.–575 pp. ↑35


