Математическое моделирование перистальтического течения литогенной желчи через проток при рубцовом стенозе, рассматриваемый в виде трубки с сужающимися стенками конечной длины
Автор: Кучумов А.Г.
Журнал: Российский журнал биомеханики @journal-biomech
Статья в выпуске: 2 (42) т.20, 2016 года.
Бесплатный доступ
С точки зрения гидродинамики течение желчи зависит от градиента давления и сокращения стенок. Холедохопанкреатический рефлюкс (т.е. течение пузырной желчи из общего желчного протока в панкреатический проток вместо двенадцатиперстной кишки) считается одной из основных причин возникновения панкреатита (воспаления поджелудочной железы). Понимание причин возникновения рефлюкса с точки зрения физиологии, гидродинамики, биомеханики по-прежнему считается сложной задачей. Целью данной работы является разработка модели перистальтического транспорта течения желчи через проток при рубцовом стенозе как трубку с сужающимися стенками конечной длины. С помощью модели были найдены скорости и распределения давления вдоль трубки и определены условия возникновения холедохопанкреатического рефлюкса. Применяя метод возмущений, были найдены аналитические решения для скоростей и давлений. Зависимости распределения давления в трубке по длине в различные моменты времени построены при различных значениях числа Вайсенберга и безразмерной амплитуды. Было показано, что безразмерная амплитуда имеет большее влияние на характер распределения давления вдоль трубки, чем число Вайсенберга. Найдены значения градиента давления, соответствующие возникновению рефлюкса. Более того, отмечено, что величина перепада давления, соответствующая нулевому среднему расходу, может считаться критерием возникновения рефлюкса.
Трубка с сужающимися стенками, трубка конечной длины, перистальтика, жидкость каро, желчь, рубцовый стеноз, фатеров сосок
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/146216204
IDR: 146216204 | УДК: 531/534:[57+61]
Текст научной статьи Математическое моделирование перистальтического течения литогенной желчи через проток при рубцовом стенозе, рассматриваемый в виде трубки с сужающимися стенками конечной длины
Желчь – это биожидкость, которая секретируется гепатоцитами (клетками печени), принимающая участие в эмульгировании жиров [21].
С точки зрения гидродинамики течение желчи зависит от градиента давления и сокращения стенок. Перистальтика играет важную роль в нормальном и патологическом течении. Холедохопанкреатический рефлюкс (т.е. патологическое течение пузырной желчи из общего желчного протока в проток поджелудочной железы, а не в двенадцатиперстную кишку), как известно, является одной из причин возникновению панкреатита (воспаления поджелудочной железы) [54].
Ампула фатерова сосочка образована объединением протока поджелудочной железы и общего желчного протока. Ампула особым образом расположена в области большого дуоденального сосочка [9].
Считается, что гипомоторика сфинктера Одди (мышечного клапана, который регулирует поток желчи и панкреатического сока через ампулу фатерова сосочка в двенадцатиперстную кишку) оказывает влияние на поток желчи и возникновение рефлюкса [11].
Почти у половины больных с желчнокаменной болезнью выявляется рубцовый стеноз, приводящий к серьезным осложнениям. В последнее время обсуждается, что изменения в структуре и геометрии фатерова сосочка вследствие наличия камня или рубцового стеноза играют существенную роль в развитии рефлюкса [25]. Несмотря на то что холедохопанкреатический рефлюкс изучается в медицинской литературе, очень мало информации о рефлюксе как таковом [14, 51].
Понимание причин возникновения рефлюкса с точки зрения физиологии, гидродинамики, биомеханики и т.д. по-прежнему является сложной задачей.
Целью данной работы является разработка математической модели перистальтического течения литогенной желчи (несбалансированной по составу, с пониженным содержанием желчных кислот и имеющей тенденцию к образованию камней) в стенозированном общем желчном протоке для биомеханической оценки причины возникновения холедохопанкреатического рефлюкса. Литогенная желчь рассматривается как жидкость Каро, а фатеров сосок моделируется как коническая трубка конечной длины. Модель позволяет оценить распределения скоростей и давления вдоль трубы и получить количественные характеристики давлений, соответствующие условиям возникновения холедохопанкреатического рефлюкса.
Перистальтика
Физиологическое движение биологических жидкостей (кровь, желчь, моча и т.д.) характеризуется волнообразным сокращением полых органов – перистальтикой (сосудов, желчных протоков, мочеточников, желудка, кишечника) [34, 38, 59].
Первые работы с аналитическими моделями, описывающими перистальтическое течение, были опубликованы в 1960-х годах [13, 19, 22, 28, 53], и интерес к данной теме все еще высок.
Большое количество работ, посвященных перистальтическому течению ньютоновских и неньютоновских сред в трубках и каналах с различной геометрией, доступно в современной литературе [4, 10, 18, 20, 36, 40–43, 45, 50, 56].
Различные аспекты особенностей течения были также исследованы, в том числе оптимизация формы канала [60], учет взаимодействия «жидкость–твердое тело» [35, 39], рефлюкс [34] и перистальтический насос [23, 58].
Моделирование перистальтического течения в трубках конечной длины
Было установлено, что в некоторых случаях (особенно для биологических объектов) перистальтические модели течения жидкостей в бесконечных каналах и трубках не применимы, следовательно, граничные условия по давлению и форме канала должны быть учтены. Следует упомянуть о классической статье Ли и Брассьё [29], где была представлена модель для нестационарного течения ньютоновской жидкости в трубе конечной длины. Численные результаты были сопоставлены с экспериментальными данными, и получено хорошее соответствие. Впоследствии J.C. Misra и S.K. Pandey [37], D. Tripathi et al. [46–48, 56, 57] решили некоторые задачи, основываясь на подходе из работы [29].
-
Y. V.K. Ravi Kumar et al. [49] разработали математическую модель течения ньютоновской жидкости в неоднородной трубе с проницаемой стенкой, используя граничные условия Саффмана [52]. Было проанализировано распределение давления по длине трубы. Было показано, что в течение одного периода волны возникают две волны в трубе. Внутри каждой перистальтической волны существуют два пика при распределении давления с постепенным уменьшением давления между ними. Также было установлено, что с увеличением проницаемости максимальные значения давления снижаются. Результаты сравнивались с данными статьи Ли и Брассьё [29].
Биомеханическое моделирование течения желчи
Существует большое количество работ [5–8, 24, 26, 27, 30, 31, 33, 44], посвященных различным биомеханическим моделям течения желчи в разных элементах билиарной системы с использованием методов вычислительной гидродинамики и аналитических методов без учета перистальтики.
-
R. Bhuvana и M. Anburajan [12] и Кучумов и соавт. [27] сделали первый шаг на пути к созданию реальной модели геометрии внепеченочных желчных протоков конкретного пациента для последующего компьютерного анализа. Тем не менее компьютерной модели течения желчи с использованием геометрии конкретного пациента все еще нет.
-
S. Maiti и J.C. Misra были первыми, кто непосредственно создали математическую модель перистальтики желчи в общем желчном протоке и рассмотрели проблему рефлюкса [34]. Известно, что литогенная желчь является неньютоновской средой [16, 24], однако авторы рассматривали течение ньютоновской жидкости в пористом канале. Результаты сравнивались с данными работы Y.C. Fung и C.S. Yih [19]. Было теоретически показано, что рефлюкс происходит, когда критическое давление довольно мало, а количество камней велико. Было также установлено, что наличие камней в канале приводит к уменьшению скорости течения желчи.
Недавнее исследование R.-C. Lo et al. [31] было также посвящено изучению рефлюкса желчи с использованием подходов механики жидкости и обработки изображений, полученных с помощью холесцинтиграфии. Рассматривались три сегмента билиарного древа. Для моделирования течения в каждом сегменте были использованы различные модели. Тем не менее следует отметить, что желчь рассматривалась как ньютоновская жидкость и перистальтика не учитывалась. Несколько клинических случаев было проанализировано с помощью применения метода гастроскопии, диагностики на основе субъективного опыта врача и метода оптической визуализации течения. Предложенный метод был показан как инструмент для диагностики рефлюкса желчи.
Материалы и методы
Анатомические сведения
Фатеров сосочек является сложной анатомической структурой, которая находится в соединении общего желчного протока и протока поджелудочной железы, объединяет билиарную систему с двенадцатиперстной кишкой (рис. 1) [1]. Правильное функционирование фатерова сосочка регулирует холединамику и поступление панкреатического сока в двенадцатиперстную кишку. Несмотря на ряд исследований, физиологические механизмы функции фатерова сосочка до сих пор полностью не понятны [17].
Рубцовый стеноз – это сужение сосочка и дисфункция моторики сфинктера Одди, вызванные воспалительными и дегенеративными изменениями в элементах сосочка и их замещением соединительной тканью. Соединительная ткань образуется в результате повреждения стенки сосочка желчными камнями или вследствие операционных вмешательств в этой области [15]. В результате рубцового стеноза просвет ампулы фатерова сосочка уменьшается. Таким образом, с математической точки зрения проток с рубцовым стенозом можно рассматривать как трубку конической формы. Существуют медицинские наблюдения [61], что рубцовый стеноз связан с холедохопанкреатическим рефлюксом (т.е. патологическим течением пузырной желчи, поступающей из общего желчного протока в проток поджелудочной железы вместо двенадцатиперстной кишки).
Несмотря на ряд медицинских работ, посвященных холедохопанкреатическому рефлюксу, его биомеханические причины до сих пор не ясны. В данной работе представлена модель холедохопанкреатического рефлюкса желчи при рубцовом стенозе.
Было показано, что литогенная желчь может считаться жидкостью Каро [24], таким образом, эта модель применяется к решению проблемы. Ее описание дано в следующем разделе.
Жидкость Каро
Определяющее соотношение для неньютоновской жидкости описывается уравнением Каро [4]:
S j =- p 5 j + j (1)
m - 1
"j = n , + ( П о — П , )(1 + ( гу ) 2 ) 2
Y j ,
где p - давление; 5y - дельта Кронекера; ту - тензор напряжений; По — вязкость при нулевом сдвиге; η∞ – вязкость при бесконечном сдвиге; Г – константа; m – показатель Каро. Скорость сдвига у определяется следующим образом:
Y = 1 ^^^ = ^п, (3)
где П - второй инвариант тензора скоростей деформаций. В случае, когда пх = 0, и при разложении (2) в ряд Тейлора уравнение (2) примет вид m - L^-^x -
-
1 + —— ( ГУ ) ) Y ij .
-
2 _
т у =П о
Общий желчный проток Панкреатический проток
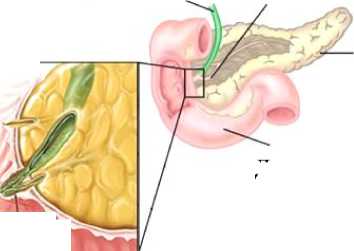
Поджелудочная железа
Стеноз
Рис. 1. Анатомия сфинктера Одди (как части билиарной системы) с рубцовым стенозом
Двенадцатиперстная кишка
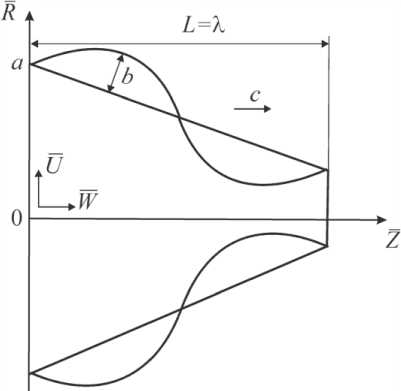
Рис. 2. Перистальтическое течение в трубке конечной длины с сужающимися стенками: геометрия задачи
Постановка задачи
Рассматривается перистальтическое течение неньютоновской жидкости (жидкости Каро) в конической трубке конечной длины (рис. 2). Синусоидальная волна с постоянной скоростью распространяется вдоль стенки канала. Длина волны сопоставима с длиной трубки ( L ≈ λ), волновое число и число Рейнольдса малы.
Перемещение стенки описывается соотношением
H (Z, t) = a - IZ + b sin — (Z - ct), λ где a – начальный радиус; l – коэффициент наклона; Z – продольная координата; b – амплитуда перистальтической волны; c – скорость волны.
Уравнения движения:
£ d(RU)
R dR dZ ~’
Введем безразмерные переменные:
|
R r = — , a |
Z z = T, |
W w = —, u = c |
λ U , ac |
ct a t =-- , О = —, λλ |
a 2 p p = 1« , c λη0 |
c Г We = —, a |
|
λ S 11 S 11 , c η0 |
S 13 = |
aS 13 a γ , Y , c η0 c |
Re = ca P, η0 |
λ lz
= 1--- + ф sin 2n(z - 1) ,
a
h h = —
a где φ – безразмерная амплитуда,
b ф = —; We - число Вайсенберга, We = —;
ca ρ
Re - число Рейнольдса, Re = —-.
η0
Тогда уравнения (6)–(8) примут вид
Re - 5
Re - 5 3
1 d(ru) dw r dr dz
dwd u+
5 r
^ p + - — ( rSx 3) + 5 — ( S 3) , a z r d r 137 d zv 33’
du du w--+ u — dz dr
-З р + 52- £( rS ) + 52 — ( S ,). d r r d г 117 d z 31
Для упрощения задачи воспользуемся допущениями гидродинамической теории смазки о бесконечно малой кривизне стенки (δ→0) и малом числе Рейнольдса (Re→0). Допущения предполагают, что инерционные эффекты незначительны, а течение в продольной оси оказывает большее влияние, чем течение в поперечном направлении [3].
Следовательно,
sp=-2 dz r dr
1 d( ru) dw r dr dz
1 +
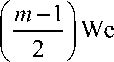
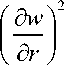
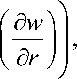
d p _ d r
где S 31 = S 13
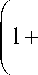
m — 1
We2
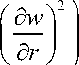

Граничные условия:
– для осевой скорости:
— = 0 при r = 0, d r
w = 1 при r = h ;
– для радиальной скорости:
u = 0 при r = 0, dH _ u =--- при r = h.
d t
В случае рассмотрения перистальтического течения в трубке конечной длины также задаются давления на входе и выходе:
p = p I при z = 0,
p = pL при z = L .
Решение
Для решения уравнений (12)–(14) и учета граничных условий (15)–(20) воспользуемся методом возмущений, согласно которому решение может быть представлено в виде разложения по малому параметру (в данном случае числу Вайсенберга (We)):
w = w + (We)2 w + O (We4),(21)
u = uQ + (We)2 u + O (We4),(22)
p = p0 + (We)2 px + O (We4 ).(23)
Подставляя (21)–(23) в (12)–(14) с учетом граничных условий (15)–(20), получим две системы уравнений для w , u , p и w , u , p . Система нулевого порядка:
|
1 £k u j + ^0 : 0 r 5 r 5 z |
(24) |
|
5Po _ 1 5 f 5 w ^ 5 z r 5 r v 5 r ) |
(25) |
|
, p = 0, 5 r |
(26) |
|
5 w 0 = 0 при r = 0, 5 r |
(27) |
|
w 0 = 0 при r = h, |
(28) |
|
u0 = 0 при r = 0, |
(29) |
|
5 h _ u 0 = — при r = h, 0 5 1 |
(30) |
|
p 0 = p I при z = 0 , |
(31) |
|
P 0 = P L при z = L . |
(32) |
Система первого порядка:
|
5 P i |
1 5 |
1 5 ( r u i ) + 5 w i =0 |
(33) ^ |
||
|
r < |
5 r 5 z 5 w (m -1\„r 7 |
3 5 w |
|||
|
5 z |
= r 5 r |
r v 5i "1 |
[5. 2 ) We2 5 p i = 0, 5 r — = 0 при r = 0, r |
— v 5 r ) _ |
, (34) ) (35) (36) |
|
w = 0 при r = h, |
(37) |
||||
|
ux = 0 при r = 0, |
(38) |
||||
|
ux = 0 при r = h , |
(39) |
||||
|
p 1 = 0 при z = 0, |
(40) |
||||
|
px = 0 при z = L . |
(41) |
||||
Решение системы нулевого порядка
Из решения системы (24)–(26) с граничными условиями осевая и радиальная скорости получены в следующей форме:
( X 1 2 7 2 A dpO w0(r, z) = т(r -h ), 4 х ' оz
r u o( r, z) = -
d h d p , d z d z
- - ( r 2 - 2 h 2 j ^ p 4 х ' dz 2
Используя граничное условие (30), получим
8 h _ h 2 5 h d p0 h 3 d 2 p0
d t 4 d z 8 z 16 d z2
Решая (44) как линейное обыкновенное дифференциальное уравнение с переменными коэффициентами, получим выражение для p 0 :
8z dPo dz
G „ < t ) + 16 j h <| t ) ^ h^d d t
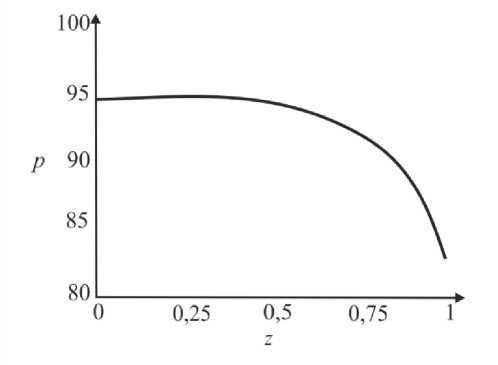
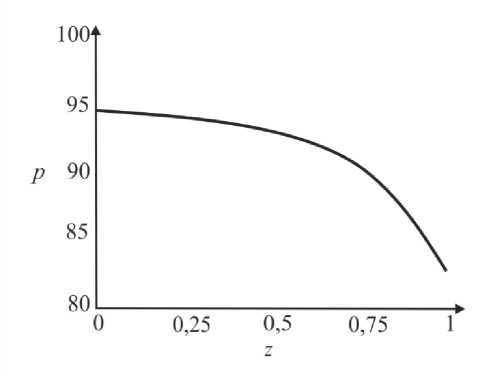
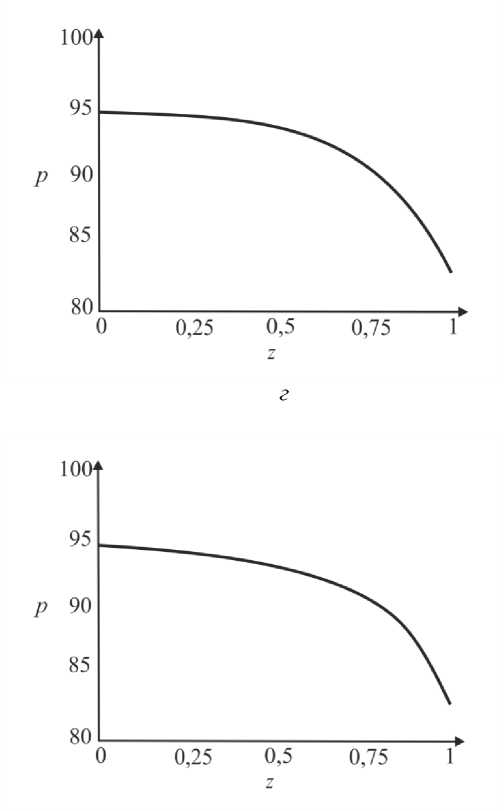
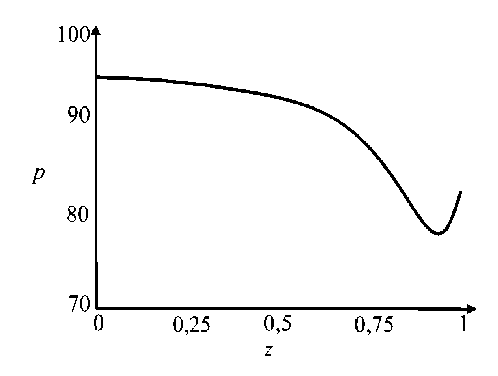
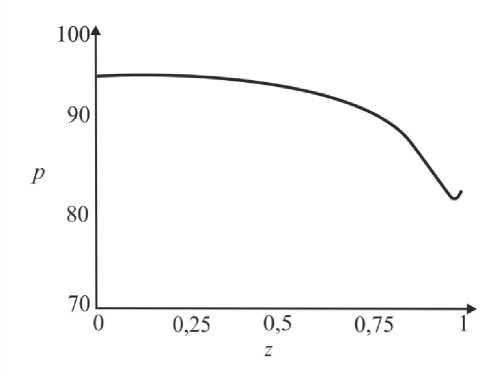
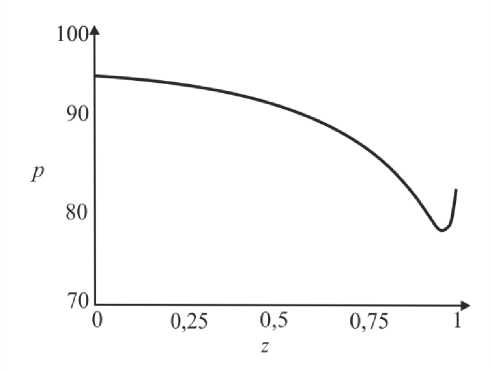
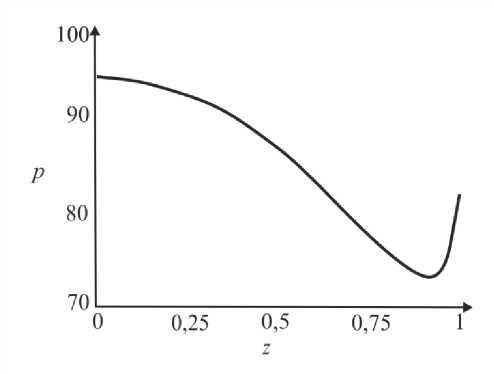
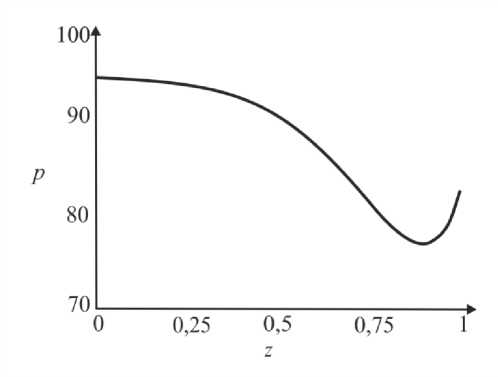
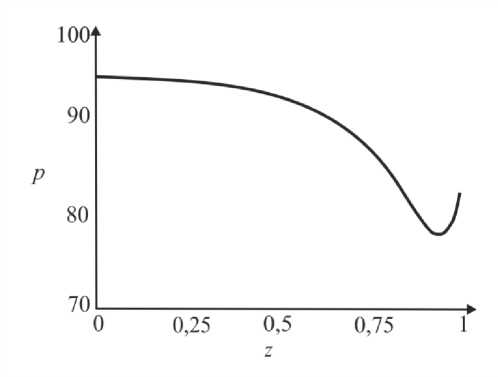
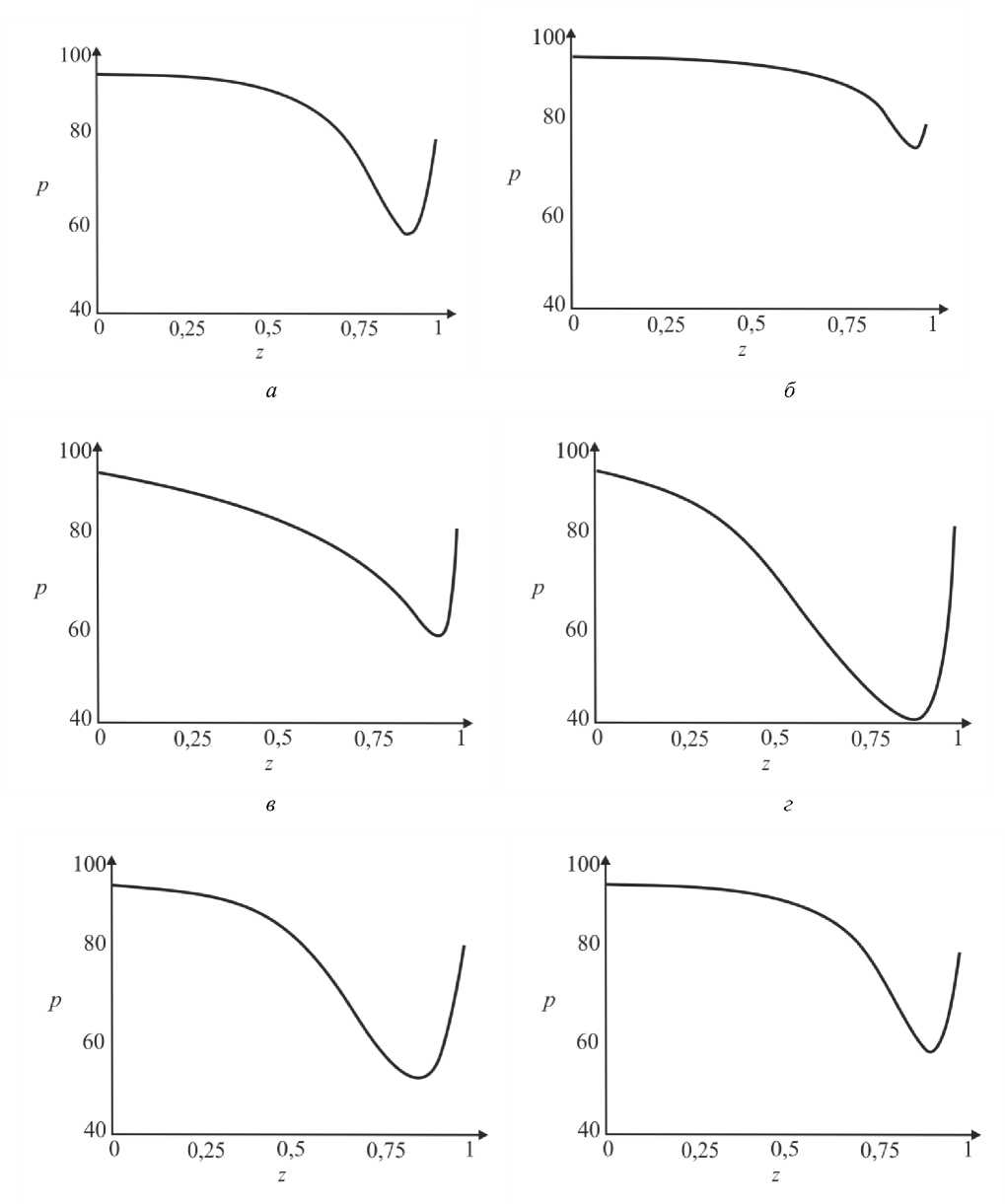
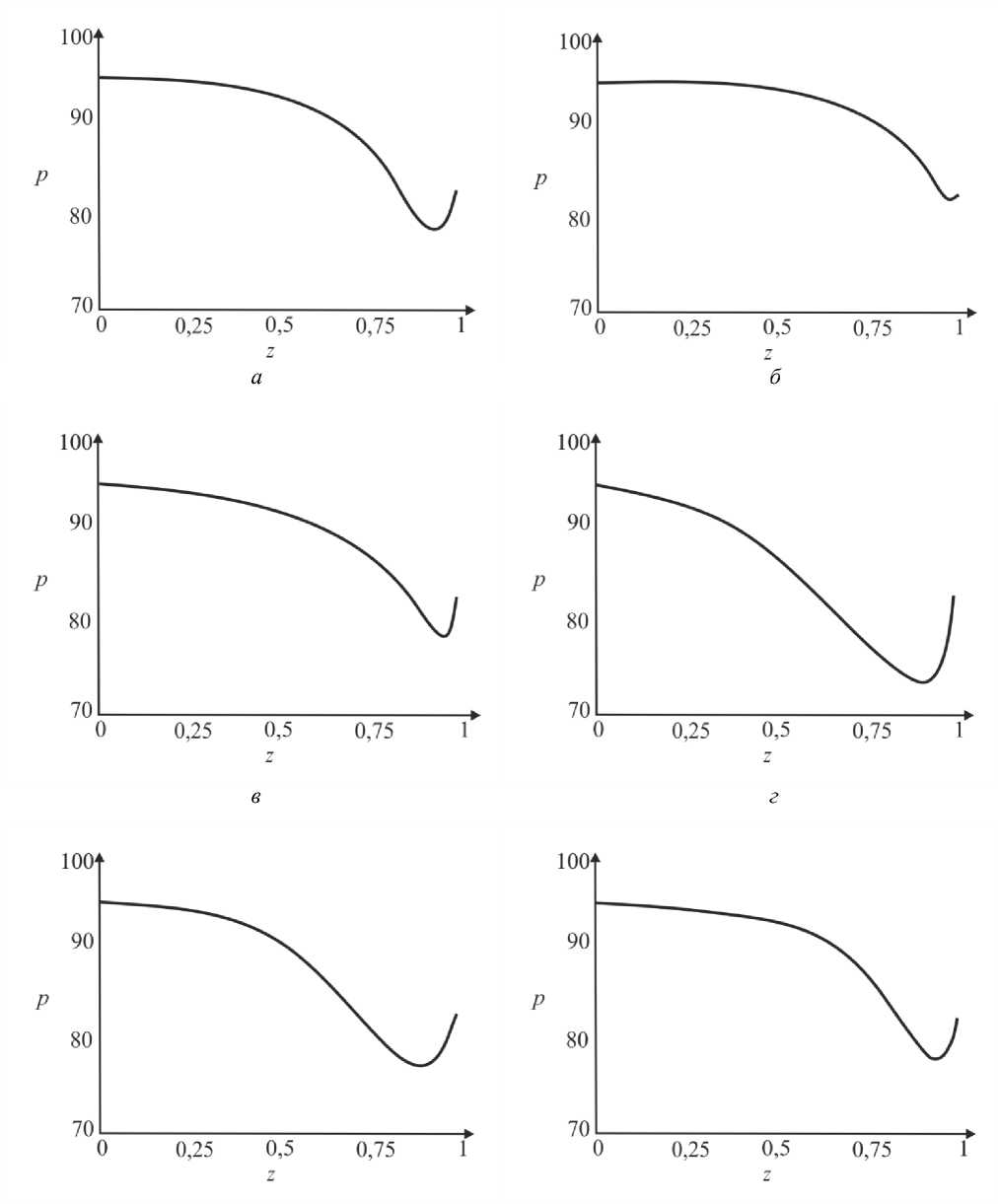
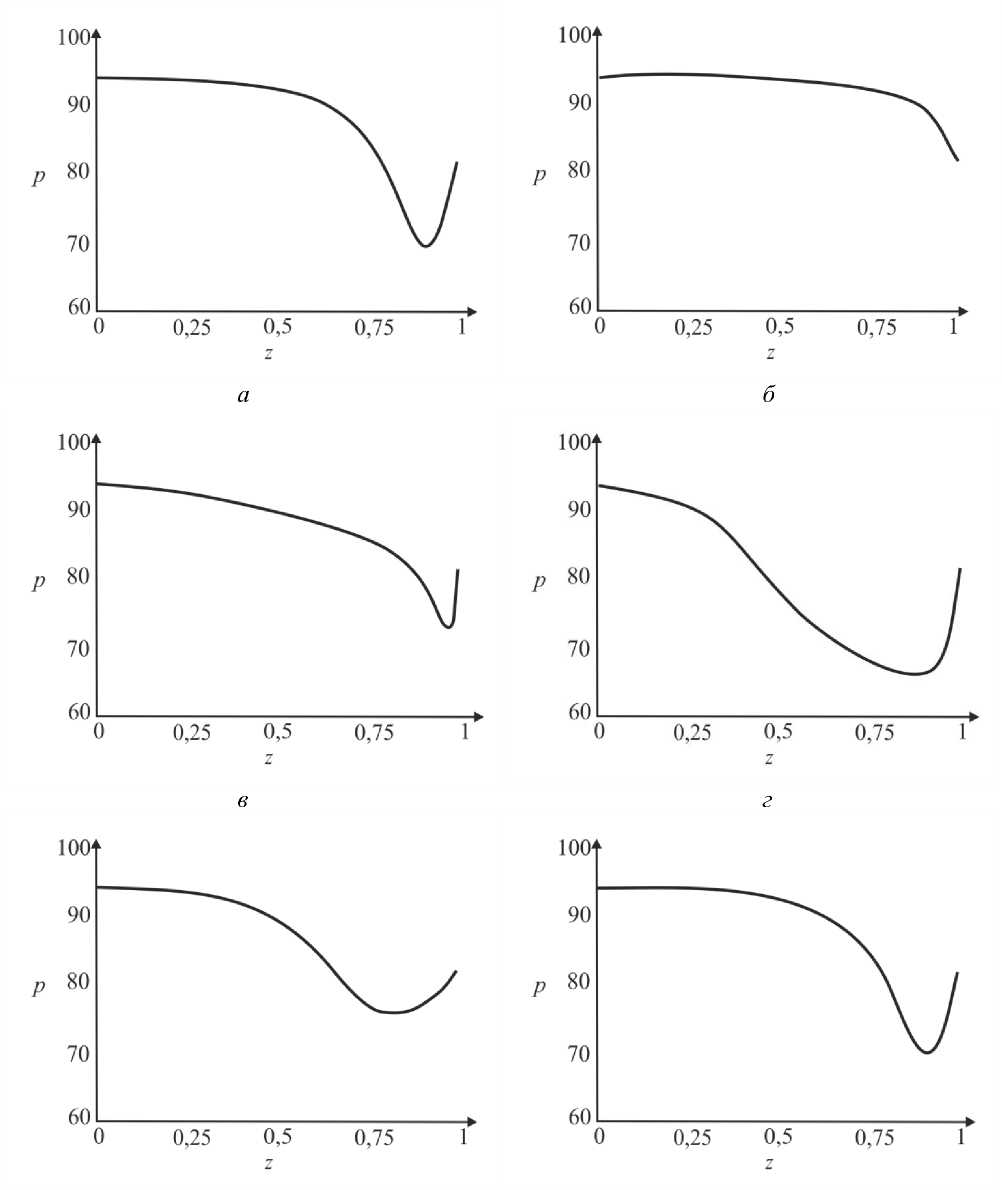
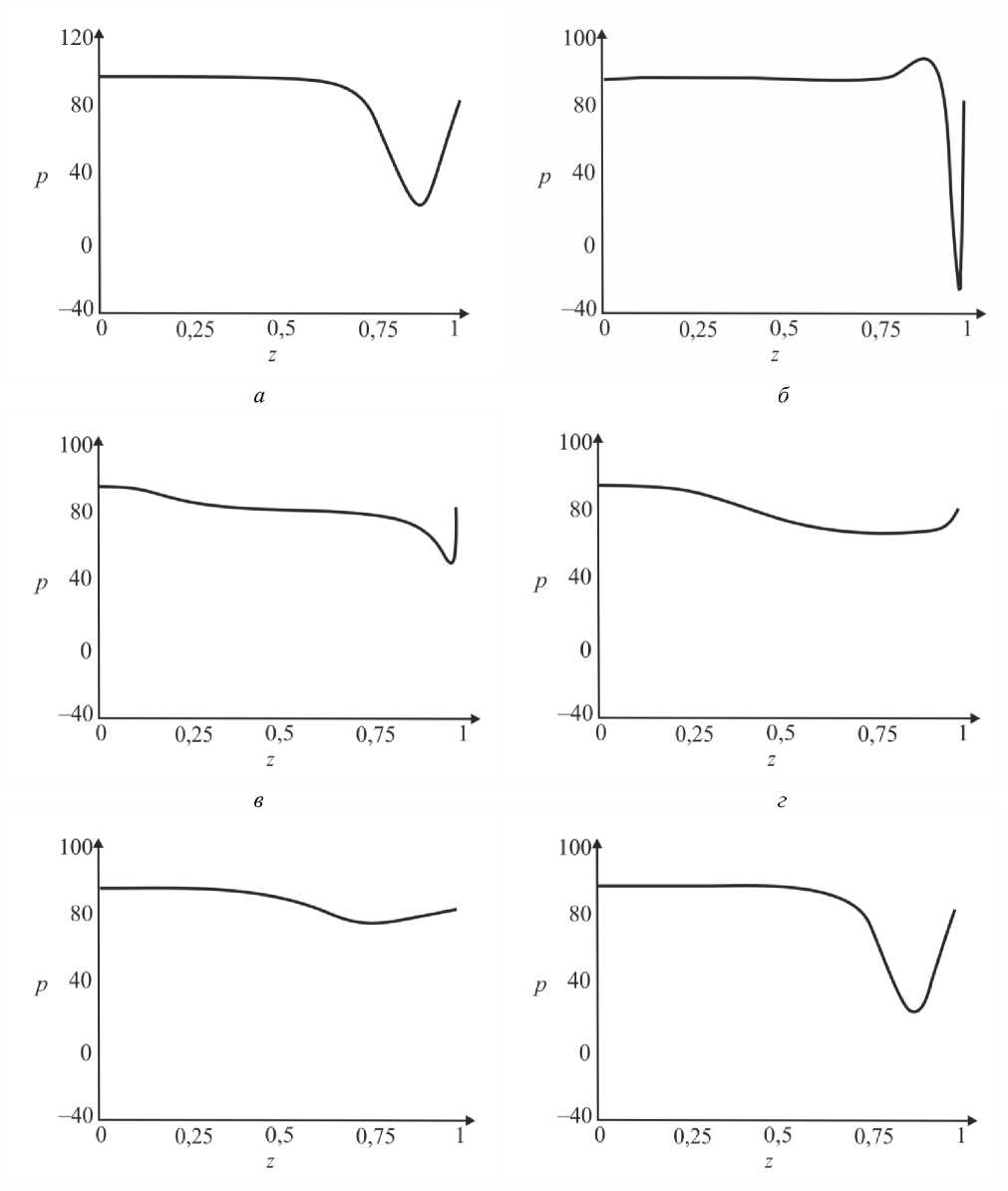
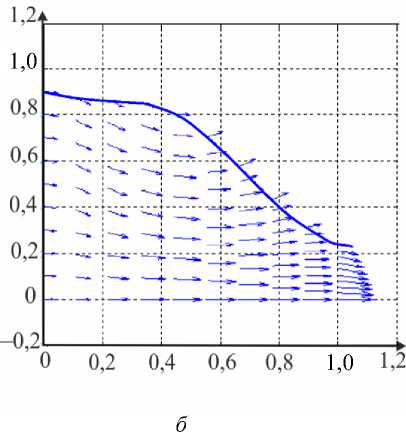
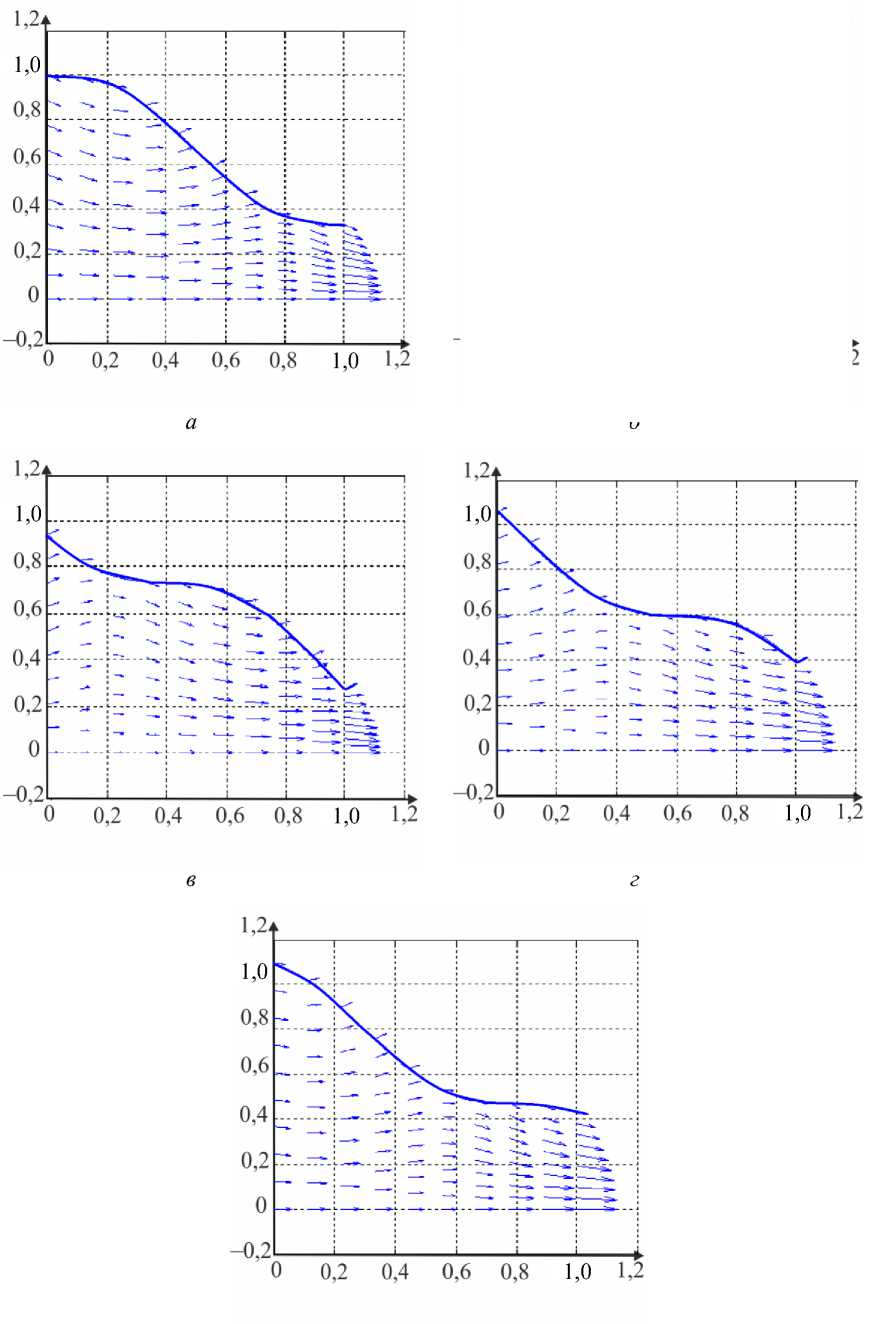
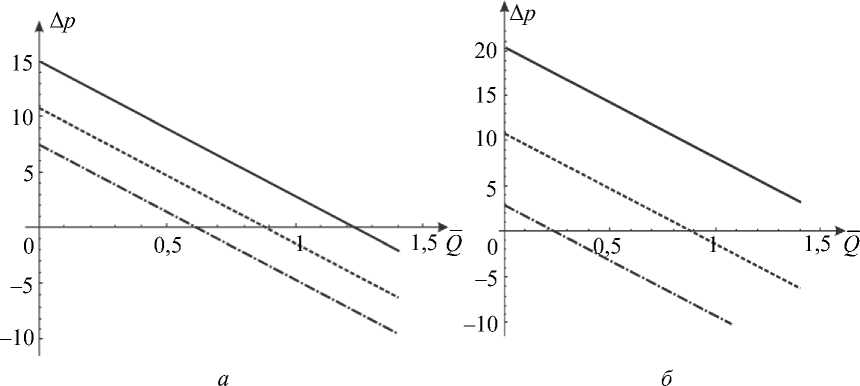
где G(t) – постоянная. Интегрируя (45), определим p0 О h (|1, t) 0 h (|1, t) I 0 dtJ где G(t) может быть найдено с учетом граничных условий (31) и (32): (pL pI) -6J h<5,, t) [i h(|2 ’ t) Pt2 ’) d12d11 Go( t) =------------0---- ;------------------'—.(47) Г j h4 (I-, t) Решение системы первого порядка Решая (33)–(34) с учетом граничных условий, получим осевую и радиальную скорости в виде wx (r, z) = - (r2 - h^p- - ^-^We2 Xp- | Г r4 - h41, (48) 1 4V ’6z 64 Idz J L J, ^“ ( a 1 eh 8px u. (r, z) = — hr--1 1 4 dz dz r Г + - h 22 r d px ч Jiz2" 3(m-1)We2 f 5p0Y 128 ( dz J 4 r4 r--h d 2 p 0 8z2 ^“ <m- 1)h3 rwe2 8h f dpG 32 8z v 8z Используя граничное условие (39), найдем h2dhdpi+h3a2^ (m-1)We2^52pоfdpо 4 dz dz 16 dz2 64 dz2Idz J 3 V 7 (50) - m^ h * ^ (®Pl ] = 0. 32 dz v dz J Решая (50) как линейное обыкновенное дифференциальное уравнение с переменными коэффициентами, определим выражение для ^p-: az з р = 1 dz h 4 ) дz J где Gv (t) - постоянная. Интегрируя (51), получим Z3Z Pi(Z, t)-Pi(0,t) = (m—)We2 fhX t)7p) d^ + G(t)f-d— 12 1 Uz J S 1V 7J h X t) где G(t) может быть найдено с учетом граничных условий (40) и (41). G1 We2Zh:.,t) dp ) d^ G( t) = — 12 о v dz J Z d1 1h X t) Результаты и обсуждение Данный раздел посвящен анализу влияния числа Вайсенберга (We) и безразмерной амплитуды (ф) на распределение давления [pG, t) - p(0, t)] вдоль трубки, а также зависимости осредненного расхода желчи (Q) от давления для анализа условий возникновения рефлюкса. Графики построены с помощью программного обеспечения MatLab. Для вычислений использовались следующие параметры: a = 0,006, X = 0,5, l = 1, m = 0,56. Давления на входе и выходе соответствуют давлению в общем желчном протоке (1,12 кПа) и двенадцатиперстной кишке (0,98 кПа) [2]. Влияние числа Вайсенберга на распределение давления На рис. 3-5 показаны распределения давлений при различных числах Вайсенберга (We = 0,1; 0,5; 0,9). Распространение давления вдоль трубки с сужающимися стенками при числе Вайсенберга, равном 0,5, представлено на рис. 4, a - е. На рис. 4, a (t = 0) показано, что сначала давление медленно убывает и затем быстро возрастает. Это соответствует фазе окончания распространения содержимого. После половины периода цикла (рис. 4, г) величина давления достигает минимума. Далее при t = 1 (рис. 4, е), соответствующему окончанию периода, значения распределения давления равны значениям при t = 0; это означает старт нового цикла (рис. 4, а). Похожее поведение кривой давления можно заметить на рис. 5, графики которого построены для We = 0,9. Рис. 3. Распределение давления вдоль осевой координаты z при We = 0,1 в различные моменты времени: a – t = 0; б – t = 0,2; в – t = 0,4; г – t = 0,6; д – t = 0,8; е – t = 1 е a б в г д е Рис. 4. Распределение давления вдоль осевой координаты z при We = 0,5 в различные моменты времени: a – t = 0; б – t = 0,2; в – t = 0,4; г – t = 0,6; д – t = 0,8; е – t = 1 Рис. осевой координаты давления вдоль е z при We = 0,9 д 5. Распределение в различные моменты времени: a – t = 0; б – t = 0,2; в – t = 0,4; г – t = 0,6; д – t = 0,8; е – t = 1 Из рисунка видно, что разность давления на разных участках трубки возрастает с увеличением числа Вайсенберга. Физически это можно интерпретировать следующим образом: чем меньше вязкость жидкости Каро, тем меньше давления требуется для ее продвижения вдоль трубки с сужающимися стенками. Влияние безразмерной амплитуды на распределение давления Влияние безразмерной амплитуды на распределение давления вдоль трубки показано на рис. 6–8. д е Рис. 6. Распределение давления вдоль осевой координаты z при φ = 0,1 в различные моменты времени: a – t = 0; б – t = 0,2; в – t = 0,4; г – t = 0,6; д – t = 0,8; е – t = 1 Расчеты сделаны для трех амплитуд: φ = 0,1; 0,2; 0,3. Значение числа Вайсенберга принималось равным 0,5. Увеличение амплитуды приводит к уменьшению поперечного сечения трубки при распространении желчи и вслед за этим приводит к увеличению перепада давления. Можно увидеть, что безразмерная амплитуда оказывает большее влияние на распространение давления, чем число Вайсенберга. д е Рис. 7. Распределение давления вдоль осевой координаты z при φ = 0,2 в различные моменты времени: a – t = 0; б – t = 0,2; в – t = 0,4; г – t = 0,6; д – t = 0,8; е – t = 1 Векторы скоростей в различные моменты времени Векторы скоростей в различные моменты времени построены с использованием формул (21), (22), (42), (43), (48), (49) и представлены на рис. 9 при We = 0,5 и φ = 0,1. Поскольку рассматривается осесимметричная задача, скорости построены для верхней части трубы. д е Рис. 8. Распределение давления вдоль осевой координаты z при φ = 0,3 в различные моменты времени: a – t = 0; б – t = 0,2; в – t = 0,4; г – t = 0,6; д – t = 0,8; е – t = 1 д Рис. 9. Векторы скоростей вдоль трубки при We = 0,5 и φ = 0,1 в различные моменты времени: a – t = 0; б – t = 0,2; в – t = 0,4; г – t = 0,6; д – t = 0,8; е – t = 1 Зависимость давления от расхода желчи Зависимость перепада давления от среднего расхода желчи при различных числах Вайсенберга и безразмерной амплитуды представлена на рис. 10, a, б. Было обнаружено, что величина среднего расхода возрастает с увеличением числа Вайсенберга и безразмерной амплитуды. Число Вайсенберга оказывает значительное влияние на сдвиг давлений по сравнению с безразмерной амплитудой. Следует отметить, что при Q = 0 величина ∆p максимальна, и далее градиент давления снижается с увеличением расхода желчи. Более того, можно заметить, что при больших значениях давления объемный расход желчи может принимать отрицательные значения, что соответствует движению жидкости в обратном направлении (рефлюкс) (условие Q< 0 обычно рассматривается как состояние рефлюкса). Таким образом, в нашем случае величины давления, соответствующие Q = 0, могут быть названы критериями возникновения холедохопанкреатического рефлюкса, т.е. рефлюкс появляется, когда перепад давления больше некоторого критического значения (∆p > ∆pкр). Выводы Рубцовый стеноз – это заболевание, проявляющееся в сужении ампулы фатерова сосочка как конической трубки. Перистальтика играет огромную роль в этой зоне. Ранее было показано, что литогенная желчь может рассматриваться как неньютоновская жидкость. В данной работе рассматривается течение литогенной желчи как жидкости Каро в фатеровом сосочке, моделируемом как трубка с сужающимися стенками конечной длины. Представлены аналитические решения для осевой и радиальной скоростей, а также для перепада давления. Распределения давления вдоль трубки в различные моменты времени построены для различных значений чисел Вайсенберга и безразмерной амплитуды. Было показано, что величина безразмерной амплитуды оказывает большее влияние на распределение давления, чем число Вайсенберга. Получены величины градиента давления, соответствующие возникновению рефлюкса. Более того, установлено, что перепад давления, соответствующий среднему расходу Q = 0, может быть назван критерием возникновения рефлюкса. Рис. 10. Зависимость давления от осредненного расхода желчи: a – при варьировании φ: φ = 0,1 – ; φ = 0,2 – ; φ = 0 – ; б – при варьировании We: We = 0,1 – ; We = 0,5 – ; We = 0,9 – Благодарности Работа выполнена при поддержке Российского фонда фундаментальных исследований в рамках проекта № 16-08-00718 А.
Список литературы Математическое моделирование перистальтического течения литогенной желчи через проток при рубцовом стенозе, рассматриваемый в виде трубки с сужающимися стенками конечной длины
- Виноградов В.В. Заболевания фатерова сосочка. -М.: Наука, 1962.
- Кучумов А.Г., Няшин Ю.И., Самарцев В.А., Гаврилов В.А., Менар М. Биомеханический подход к моделированию билиарной системы как шаг в направлении к построению виртуальной модели физиологии человека//Российский журнал биомеханики. -2011. -Т. 15, № 2. -C. 32-48.
- Abd El Maboud Y., Mekheimer Kh.S., Abd El Salam S.I. A study of nonlinear variable viscosity in finite-length tube with peristalsis//Applied Bionics and Biomechanics. -2014. -Vol. 11. -P. 197-206.
- Akbar N.S., Nadeem S., Khan Z.H. Numerical simulation of peristaltic flow of a Carreau nanofluid in an asymmetric channel//Alexandria Engineering Journal. -2014. -Vol. 53. -P. 191-197.
- Al-Atabi M., Chin S.B., Luo X.Y. Experimental investigation of the flow of bile in patient-specific cystic duct models//ASME J. of Biomechanical Engineering. -2010. -Vol. 132. -P. 1-10.
- Al-Atabi M., Chin S.B., Luo X.Y., Beck S. Investigation of flow in a compliant idealised human cystic duct//ASME J. of Biomedical Science and Engineering. -2008. -Vol. 3. -P. 411-418.
- Al-Atabi M., Ooi R.C., Luo X.Y., Chin S.B., Bird N.C. Computational analysis of the flow of bile in human cystic duct//Medical Engineering & Physics. -2012. -Vol. 34. -P. 1177-1183.
- Al-Atabi M.T., Chin S.B., Luo X.Y. Visualization experiment of flow structures inside two-dimensional human biliary system models//Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology. -2006. -Vol. 6. -P. 249-260.
- Allescher H.D. Papilla of Vater: structure and function//Endoscopy. -1989. -Vol. 21. -P. 324-329.
- Aranda V., Cortez R., Fauci L. A model of Stokesian peristalsis and vesicle transport in a three-dimensional closed cavity//Journal of Biomechanics. -2015. -Vol. 9. -P. 1631-1638.
- Ballal M.A., Sanford P.A. Physiology of the sphincter of Oddi -the present and the future? Part 2//The Saudi Journal of Gastroenterology. -2000. -Vol. 7. -P. 16-21.
- Bhuvana R., Anburajan M. Patient specific mimicing CAD models of biliary tract with and without gallstone for CFD analysis of bile dynamics//International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing. -Melmaruvathur, 2013. -P. 658-662.
- Burns J.C., Parkes T. Peristaltic motion//J. Fluid Mech. -1967. -Vol. 29, № 4. -P. 731-743.
- Christopher P., Armstrong F.R.C.S., Taylor T.V. Pancreatic-duct reflux and acute gallstone pancreatitis//Ann. Surgery. -1986. -Vol. 15. -P. 59-64.
- Classen M., Ossenberg F.W. Non-surgical removal of common bile duct stones//Gut. -1977. -Vol. 18. -P. 760-769.
- Coene P.P., Coene L.O., Groen A.K., Davids P.H.P., Hardeman M., Tytgat G.N.T., Huibregtse K. Bile viscosity in patients with biliary drainage//Scand. J. Gastroenterol. -1994. -Vol. 29. -P. 757-763.
- Edemskiy A.I., Edemskiy D.A. Major duodenal papilla’s pathology//Surgery Bulletin. -2002. -Vol. 7. -P. 35-42.
- Elshehawey E.F., Misery A.E.M.E., Abd El Naby A.E.H. Peristaltic motion of generalized Newtonian fluid in a non-uniform channel//J. Phys. Sot. Japan. -1998. -Vol. 67. -P. 434-440.
- Fung Y.C., Yih C.S. Peristaltic transport//J. Appl. Mech. -1968. -Vol. 35. -P. 669-675.
- Hariharan P., Seshadri V., Banerjee R.K. Peristaltic transport of non-Newtonian fluid in a diverging tube with different wave forms//Mathematical and Computer Modelling. -2008. -Vol. 48. -P. 998-1017.
- Hofmann A.F. Bile acids: the good, the bad, and the ugly//Physiology. -1999. -Vol. 14. -P. 24-29.
- Jaffrin M.Y., Shapiro A.H. Peristaltic pumping//Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics. -1971. -Vol. 3. -P. 13-35.
- Klespitz J., Kovács L. Peristaltic pumps -a review on working and control possibilities//12th International Symposium on Applied Machine Intelligence and Informatics. -Herlany, 2014.
- Kuchumov A.G., Gilev V.A., Popov V.A., Samartsev V.A., Gavrilov V.A. Non-Newtonian flow of pathological bile in the biliary system: experimental investigation and CFD simulations//Korea-Australia Rheology Journal. -2014. -Vol. 26. -P. 81-90.
- Kuchumov A.G., Nyashin Y.I., Samartsev V.A. Modelling of peristaltic bile flow in the papilla ampoule with stone and in the papillary stenosis case: application to reflux investigation//Proceedings of 7th WACBE World Congress on Bioengineering. -Singapore, 2015. -Vol. 52. -P. 158-161.
- Kuchumov A.G., Nyashin Y.I., Samartsev V.A., Gavrilov V.A. Modelling of the pathological bile flow in the duct with a calculus//Acta of Bioengineering and Biomechanics. -2013. -Vol. 15. -P. 9-17.
- Kuchumov A.G., Nyashin Yu.I., Samartsev V.A. CFD approach to bile flow problems solution//Proceedings of 18th Symposium on Computational Biomechanics in Ulm. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18725/OPARU-3181.
- Latham T.W. Fluid motion in a peristaltic pump. Master Thesis. -Cambridge, MA, USA: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1966.
- Li M., Brasseur J.G. Non-steady peristaltic transport in finite length tubes//Journal of Fluid Mechanics. -1993. -Vol. 248. -P. 129-151.
- Li W.G., Luo X.Y., Chin S.B., Hill N.A., Johnson A.G., Bird N.C. Non-Newtonian bile flow in elastic cystic duct -One and three dimensional modelling//Annals of Biomedical Engineering. -2008. -Vol. 36. -P. 1893-1908.
- Li W.G., Luo X.Y., Johnson A.G., Hill N.A., Bird N., Chin S.B. One-dimensional models of the human biliary system//ASME J. of Biomech. Eng. -2007. -Vol. 129. -P. 164-173.
- Lo R.-C., Huang W.-L., Fan Y.-M. Evaluation of bile reflux in HIDA images based on fluid mechanics//Computers in Biology and Medicine. -2015. -Vol. 60. -P. 51-65.
- Luo X.Y., Li W.G., Bird N., Chin S.B., Hill N.A., Johnson A.G. On the mechanical behaviour of the human biliary system//World Journal of Gastroenterology. -2007. -Vol. 13. -P. 1384-1392.
- Maiti S., Misra J.C. Peristaltic flow of a fluid in a porous channel: a study having relevance to flow of bile within ducts in a pathological state//International Journal of Engineering Science. -2015. -Vol. 49. -P. 950-966.
- Maiti S., Misra J.C. Peristaltic transport of a couple stress fluid: some applications to hemodynamics//Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology. -2012. -Vol. 12. -P. 1-24.
- Mernone A.V., Masumdar J. Mathematical modelling of peristaltic transport of a non-Newtonian fluid//J. Australian Physical and Engineering Sciences in Medicine. -1998. -Vol. 21. -P. 126-140.
- Misra J.C., Pandey S.K. A mathematical model for oesophageal swallowing of a food bolus//Mathematical and Computer Modelling. -2001. -Vol. 33. -P. 997-1009.
- Misra M., Rao A.R. Peristaltic transport in a channel with a porous peripheral layer: model of a flow in gastrointestinal tract//Journal of Biomechanics. -2005. -Vol. 38. -P. 779-789.
- Mittra T.K., Prasad S.N. On the influence of wall properties and Poiseuille flow in peristalsis//Journal of Biomechanics. -1973. -Vol. 6. -P. 681-693.
- Nadeem S., Hayat T., Akbar N.S., Malik M.Y. On the influence of heat transfer in perstalsis with variable viscosity//International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer. -2009. -Vol. 52. -P. 4722-4730.
- Nagarani P., Sarojamma G. Peristaltic transport of a Casson fluid in an asymmetric channel//Australasian Physical & Engineering Sciences in Medicine. -2004. -Vol. 27. -P. 49-59.
- Nagarani P., Lewis A. Peristaltic flow of a Casson fluid in an annulus//Korea-Australia Rheology Journal. -2012. -Vol. 24. -P. 1-9.
- Nagarani P., Sarojamma G. Peristaltic transport of small particles -power law fluid suspension in a channel//Australasian Physics & Engineering Sciences in Medicine. -2007. -Vol. 30. -P. 185-193.
- Ooi R.C., Luo X.Y., Chin S.B., Johnson A.G. The flow of bile in the human cystic duct//Journal of Biomechanics. -2004. -Vol. 37. -P. 1913-1922.
- Pandey S.K., Chaube M.K. Peristaltic transport of a visco-elastic fluid in a tube of non-uniform cross section//Mathematical and Computer Modelling. -2010. -Vol. 52. -P. 501-514.
- Pandey S.K., Tripathi D. A mathematical model for peristaltic transport of micro-polar fluids//Applied Bionics and Biomechanics. -2011. -Vol. 8. -P. 279-293.
- Pandey S.K., Tripathi D. A mathematical model for swallowing of concentrated fluids in oesophagus//Applied Bionics and Biomechanics. -2011. -Vol. 8. -P. 309-321.
- Pandey S.K., Tripathi D. Peristaltic transport of a Casson fluid in a finite channel: application to flows of concentrated fluids in oesophagus//International Journal of Biomathematics. -2010. -Vol. 3. -P. 473-491.
- Ravi Kumar Y.V.K., Krishna S.V.H.N., Kumari P., Ramana Murthy M.V., Sreenadh S. Unsteady peristaltic pumping in a finite length tube with permeable wall//ASME Journal of Fluids Engineering. -2010. -Vol. 132. -P. 10201-10214.
- Riaz A., Nadeem S., Ellahi R., Akbar N.S. Series solution of unsteady peristaltic flow of a Carreau fluid in small intestines//Int. J. Biomath. -2014. -Vol. 7. -P. 1-9.
- Roig M.P., Villar Ú.P., Monzó F.P., Franco A.C., Gil N.O., Matoses Á.B., Aparisi E.S., Gonzalez L.M., Martínez F.C. Biliary pancreatitis. Liver function tests and common biliopancreatic channel kinetics -Biliopancreatic reflux//Cirugía Española (English Edition). -2015. -Vol. 93. -P. 326-333.
- Saffman P.G. On the boundary condition at the surface of a porous media//Stud. Appl. Math. -1971. -Vol. 50. -P. 93-101.
- Shapiro A.H., Jaffrin M.Y., Weinberg S.L. Peristaltic pumping with long wavelength at low Reynolds number//Journal of Fluid Mechanics. -1969. -Vol. 37. -P. 799-825.
- Siqin D., Wang C., Zhou Z., Li Y. The key event of acute pancreatitis: pancreatic duct obstruction and bile reflux, not a single one can be omitted//Med. Hypotheses. -2009. -Vol. 72. -P. 589-591.
- Srinivas S., Muthuraj R. Effects of chemical reaction and space porosity on MHD mixed convective flow in a vertical asymmetric channel with peristalsis//Mathematical and Computer Modelling. -2011. -Vol. 54. -P. 1213-1227.
- Tripathi D., Pandey S.K., Anwar Bég O. Mathematical modelling of heat transfer effects on swallowing dynamics of viscoelastic food bolus through the human oesophagus//International Journal of Thermal Sciences. -2013. -Vol. 70. -P. 41-53.
- Tripathi D., Pandey S.K., Chaube M.K. Peristaltic transport of power law fluid in finite length vessels//International Journal of Mathematical Sciences and Engineering Applications. -2009. -Vol. 3. -P. 279-289.
- Tsui Y.-Y., Guo D.-C., Chen S.-H., Lin S.-W. Pumping flow in a channel with a peristaltic wall//Journal of Fluids Engineering. -2014. -Vol. 136. -P. 1-9.
- Vahidi B., Fatouraee N. A biomechanical simulation of ureteral flow during peristalsis using intraluminal morphometric data//Journal of Theoretical Biology. -2012. -Vol. 298. -P. 42-50.
- Walker S.W., Shelley M.J. Shape optimization of peristaltic pumping//Journal of Computational Physics. -2010. -Vol. 229. -P. 1260-1291.
- Yasuda I., Tomita E., Enya M., Kato T., Moriwaki H. Can endoscopic papillary balloon dilation really preserve sphincter of Oddi function?//Gut. -2001. -Vol. 49. -P. 686-691.


