Механика жидкости в периваскулярном пространстве
Автор: Ванг П., Олбрихт У.Л.
Журнал: Российский журнал биомеханики @journal-biomech
Статья в выпуске: 3 (49) т.14, 2010 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Периваскулярное пространство в мозге является важным транспортным путем для доставки интерстициальной жидкости и растворов. Течения жидкостей в периваскулярном пространстве, которые играют важную роль в физиологии, могут влиять на эти транспортные процессы. В данной работе был проведен теоретический анализ для исследований биомеханики жидкости в периваскулярном пространстве. При некоторых допущениях и аппроксимациях было получено аналитическое решение проблемы. Был выявлен физический смысл решения и, в частности, изучены последствия индуцированного потока жидкости в рамках метода конвекционно-усиленной доставки лекарств (convection enhanced delivery). Было обнаружено, что перистальтическое движение стенок кровеносных сосудов может обеспечивать транспортировку жидкостей и растворов в периваскулярном пространстве.
Преобразование координат, перистальтическая волна, гидравлическая проницаемость, закон дарси, конвекционно-усиленная доставка лекарств, теория смазывания
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/146216000
IDR: 146216000 | УДК: 531/534:
Текст научной статьи Механика жидкости в периваскулярном пространстве
Эксперименты Гадашека и соавт. ( Hadaczek et al. ) [9] выявили, что артериальные пульсации играют важную роль в транспортировке молекул лекарственных веществ в мозг при конвекционно-усиленной доставке лекарств ( convection enhanced delivery ). Конвекционно-усиленная доставка – это метод локальной доставки лекарств для лечения неврологических заболеваний [3]. Согласно этому методу лекарства впрыскиваются непосредственно в ткань через иглу или катетер. Гадашек и соавт. ( Hadaczek et al. ) [9] обнаружили, что у крыс без сердечных сокращений наблюдается значительно меньший объем распределения полученных лекарств, чем у живых крыс. Нивс и соавт. ( Neeves et al. ) [16], а также Фоли и соавт. ( Foley et al. ) [7] показали, что наночастицы, добавленные в мозг, двигаются преимущественно через периваскулярное пространство, а не внешнеклеточный матрикс. Главная цель данной работы – исследовать с помощью методов математического моделирования механику жидкости в периваскулярном пространстве, индуцированной перистальтическим движением стенок кровеносных сосудов, и показать его влияние на транспортировку жидкостей и растворов в периваскулярном пространстве.
Течение жидкости, вызванное перистальтикой, активно изучается в литературе. Классический обзор может быть найден в работе [12]. Для математической
Ванг Пенг, аспирант факультета химической и биомолекулярной инженерии, Университет Корнелл, Итака Олбрихт Уильям Л., профессор, кафедра биомедицинской инженерии, Университет Корнелл, Итака формулировки и упрощений большинство исследователей рассматривают перистальтические волны как бесконечный набор синусоид. Если отношение амплитуды волны к полуширине пути прохождения предположить малым, то можно использовать пертурбационные подходы, основанные на разложениях в ряд Тейлора, и можно получить получисленные решения. Если отношение длины волны к полуширине пути прохождения большое, тогда могут применяться теории смазки и при некоторых условиях могут быть получены аналитические решения. Численные методы в исследованиях динамики жидкостей позволили напрямую решать уравнения Навье–Стокса со сложной геометрией границ и граничными условиями (например, сложные формы перистальтических волн [1]). Более того, эти методы позволили лучше понять влияние перистальтики на течение жидкостей. Большое число предыдущих работ было посвящено описанию различных биологических и физиологических процессов. Например, полученная в работе Шапиро и соавт. (Shapiro et al.) [21] математическая модель применялась для описания системы мочеточника и обсуждались физиологические влияния на феномены рефлюкса и запирания жидкости. Мишра (Mishra) и Рао (Rao) [14] предложили подход для моделирования течения жидкости в желудочно-кишечном тракте с учетом изучения перистальтического движения в канале с пористым периферическим слоем. В работе Билстона и соавт. (Bilston et al.) [1] был проведен детализированный численный анализ движения спинномозговой жидкости вдоль периваскулярного пространства в спинном мозге с использованием численных методов. В работе Склея и соавт. (Schley et al.) [20] была построена математическая модель для проверки гипотезы о том, что периваскулярный дренаж интерстициальной жидкости и растворов из тканей мозга был вызван пульсациями стенок кровеносных сосудов. В данной работе предложена новая модель для описания течения жидкости, индуцированного перистальтическим движением стенок кровеносных сосудов в периваскулярном пространстве мозга, и изучены физиологические и терапевтические воздействия на эти движения в рамках метода конвекционно-усиленной доставки лекарств.
Математическая модель
Периваскулярное пространство моделируется как пористая среда, окружающая кровеносный сосуд (рис. 1). Естественно, мы выбираем цилиндрическую систему координат, чтобы ось z совпадала с центральной линией. Поперечное сечение периваскулярного русла является кольцом. Для упрощения математической формулировки задачи сделаем несколько допущений. Внешняя и внутренняя стенки цилиндра считаются непроницаемыми. Внешняя стенка кольца закреплена при r = R 2 , а внутренняя стенка осциллирует по закону
h ( t , z ) = R 1 + b sin
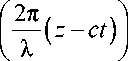
где h ( t , z ) – радиальная координата точки с осевой координатой z на внутренней стенке во время t . Форма колебаний на внутренней стенке представляет собой синусоидальную перистальтическую волну с половиной амплитуды b , длиной волны λ и скоростью волны c , которая двигается по внутренней стенке (чей средний радиус равен R 1 ) в положительном направлении оси z . Частота этой волны равна f = c / λ. Периваскулярное пространство задается как пористая среда с постоянной пористостью ε и проницаемостью κ. Жидкость считается ньютоновской и несжимаемой с постоянной вязкостью µ и плотностью ρ. В табл. 1 приведены основные обозначения, используемые в данной работе. В табл. 2 представлены значения параметров, используемых в данной работе.
В инерциальной системе отсчета, в которой пористая среда движется со скоростью v med , определяющим соотношением является обобщённое уравнение Бринкмана (дополненное уравнение Дарси) [4, 16, 17]
fd v ^ 8Ц
Р I + v - V v I = - V p - ( v - v med ) .
V d t ) к
Учитывая, что уравнение (1) справедливо в любой инерциальной системе отсчета (в отличие от оригинального уравнения Бринкмана–Дарси, которое справедливо только в том случае, когда пористая среда неподвижна в выбранной системе отсчета).
Уравнение неразрывности записывается в виде
V - v = 0.
В решении задач, связанных с перистальтикой, удобно применять преобразование координат [21]. Вместо рассмотрения отсчетной конфигурации Σ, в которой пористая среда (периваскулярное пространство) неподвижна, а перистальтическая волна перемещается, перейдём к волновой системе отсчета,
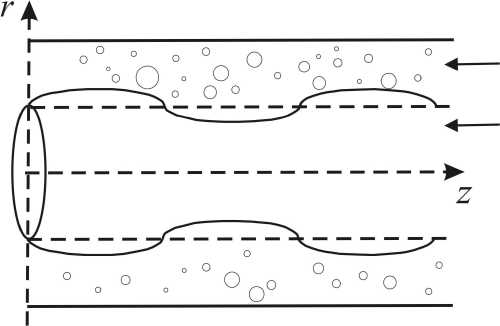
Периваскулярное пространство
Кровеносный сосуд
Рис. 1. Геометрическая область задачи
Таблица 1
Обозначение параметров и переменных
|
Символ |
Физический смысл |
Символ |
Физический смысл |
|
R 2 |
Внешний радиус |
f |
Частота волны |
|
R 1 |
Средний внутренний радиус |
T |
Период волны |
|
b |
Половина амплитуды |
ρ |
Плотность жидкости |
|
λ |
Длина волны |
v |
Истинная скорость жидкости (в отличие от скорости поверхности) |
|
c |
Скорость волны |
p |
Давление жидкости |
|
κ |
Проницаемость Дарси |
ε |
Пористость среды |
|
K |
Гидравлическая проницаемость (= κ/µ) |
h |
Радиальная координата внутренней стенки |
Таблица 2
Значения параметров, входящих в модель
|
Параметр |
Значение |
Ссылка |
|
R 1 |
1∙10 –5 м |
[13] |
|
R 2 |
1,1∙10 –5 м |
[11] |
|
b |
5∙10 –7 м 2,5 ∙ 10 –7 м 1,25 ∙ 10 –7 м |
[1] |
|
c |
1 м∙с –1 |
[8, 10, 13] |
|
f |
5 Гц |
[9] |
|
µ |
9 ∙ 10 –4 Па∙с |
[2] |
|
K |
2 ∙ 10 –12 м 4 ∙Н –1 ∙с –1 2 ∙ 10 –11 м 4 ∙Н –1 ∙с –1 2 ∙ 10 –10 м 4 ∙Н –1 ∙с –1 |
[15, 22] |
|
ε |
0,26 |
[18, 19] |
θ'
в которой перистальтическая волна оказывается неподвижной, а пористая среда осуществляет движение. Замена координат – r′ = r, θ′ = θ, z′ = z-ct, t′ = t , а соответствующие замены скоростей – vr = vr, vθ = vθ, v z = vz -c . При переходе к волновой системе отсчета Σ′ появляется преимущество в том, что форма волны
Г 2п ,) внутренней стенке описывается выражением h(t , z ) = R1 + b sin I —z I, которое v ^ / зависит от времени (нет зависимости от t ). Другим преимуществом перехода к является то, что периодическое движение в Σ становится стационарным течением в [21]. Эти два преимущества значительно упрощают задачу.
на
не
Σ′
Σ′
Определяющие соотношения в Σ′ для осесимметричной задачи, для которой ∂ справедливы vθ' = 0 и ∂θ′ = 0, записываются в виде для компоненты r :
ρ
∂v ∂v vr r +vz r
∂ r ∂ z
∂p εµ v -;
r ;
∂ r κ
для компоненты z :
ρ
∂v ∂v vr z +vz z
∂ r ∂ z
∂ p εµ εµ c - v -∂ z κ z κ
Далее используется теория смазки. Эта теория была впервые предложена для тонкопленочного течения в пустом пространстве (в отличие от пористой среды). ρ c κ R
Однако можно показать, что при Re = ≪ 1 и β = 2 ≪ 1 , согласно значениям,
µλ λ взятым из табл. 2, определяющие соотношения могут быть упрощены
^ _ 0, д r'
др! _ - гЦ v- д z’ к z '
Уравнение (5) приводится к виду
εµ c κ
.
p ' = p ‘ ( z ') .
Уравнение (6) приводится к виду и к dp' v z ' ( z' )_-TV- c . εµ dz
В волновой системе отсчета S' объемная скорость течения жидкости является R 2
постоянной, равной Q' _ J h ( vz , ■ 2п r'dr' и не зависящей от z [21]. Подставляя (8) в вышеуказанное уравнение и проводя интегрирование, получим
Q _ n [ R 2 - h 2 ( z' ) ]
\- А dp; V гц dz'
)
c
.
dp'
Выразим : dz'
dp'_ гц ----_-- < dz' κ
Q'
. n [ R 2 - h 2 ( z' ) ]
+ c
.
Так как h ( z´ ) является периодической функцией от z´ с периодом λ, то из (10) dp'
следует, что тоже является периодической функцией от z´ с периодом λ. Интеграл dz'
dp'
от --- по z на любом интервале с длиной к должен быть равен Арх вне зависимости dz' λ от начальной точки интервала. После некоторых прямых преобразований получим
, 8 С цк А p к _ — < κ
Q ' 4π cR 2 2
1 - R 1
Г b
+
R 2 )
V R 2 7
1 + R 1
v R 2 7
В начальной системе отсчета Σ изменение давления А p к _ А p{ , а объемная скорость течения за время t через координатой z равна
R 2 R 2 1
Q ( t , z ) _ 2п г vrdr _ 2пг v ,,( z' ) + c\rdr =—
h ( t , z ) z h ( t , z ) z ' 2
где h _ h ( t , z ) _ R 1 + b sin
выражение для Q ( t , z )
r b
- 1
V R 2 7
на длине волны равно поперечное сечение с
г Q' + пг c ( R 2 2 - h 2 ) ,
. Подставляя эти соотношения в (11), получим
2πε cR
, 2 Г K\p.
к +1
Q ( t , z ) = в
V s c цХ 7
+ ns c ( R2 - h 2 ) .
1 в R 1
V R 2 7
Г b
+
V R 2 7
1 + R 1
V R 2 7
Г ь
V R 2 7
Обозначим среднюю по времени
скорость
течения
1T как Q (z )=-j Q (t, z) dt.
T 0
После небольших вычислений получим
Q = ns cR 22 <
1 в R 1
2( в K^ P x
εcµλ
Г ь
+
+ 1
в
( р А
R-
V R 2 7
в
Г ь
2 V R 2 7
V R 2 7
1 + R L
Г ь
V R 2 7
Учтем, что Q является константой, не зависящей от z .
Результаты и обсуждение
На первый взгляд, теория смазки линеаризует определяющие соотношения и стремится решить проблему с помощью принципа суперпозиции, т.е. полная объемная скорость течения является сумной вкладов от градиента давления и перистальтического движения границы. В волновой системе координат Σ’ полученное определяющее соотношение является неоднородным (6), в то время как в начальной системе отсчета граница является подвижной. Эти факты делают принцип суперпозиции неприменимым в любой системе отсчета. Как результат, градиент давления и перистальтическая волна объединены в решении. Чтобы прояснить ситуацию, был рассмотрен особый случай, в котором очень мало. В данном случае были
R 2
использованы разложение в ряд Тейлора относительно правой части уравнения (13) R 2
и аппроксимация результата с сохранением слагаемых до второго порядка: R 2
Q - ns cR 22 <
1 в
IT
V R 2 7
1 + 3 R L
2 1
в
V
. V R 2 7 .
( R A
R 1
V R 2 7
Г ь)
V R 2 7
( в K^PX в 1) + 1 в ε c µλ
с р л
V R 2 7
Г b
2 V R 2 7
^ . (14)
Уравнение (14) может быть записано в следующем виде:
Q - ns cR 2 <
-
R 1
-
κΔ p λ
2 R 1
V
V R 2 7
V s c цХ 7
+
V R 2 7
b
1 + 3 R 1
-
R 1
V R 2 7
+
V R 2 7
b
κ ∆ p λ
V R 2 7
2 1
-
R 1
\
V R 2 ) s c цХ
^ . (15)
V
V R 2 7
Первое слагаемое в правой части уравнения (15) зависит от градиента давления (положим b = 0 в (15)). Второе слагаемое зависит от перистальтической волны с очень маленькой амплитудой (положим ∆pλ = 0 в уравнении (13) и разложим выражение в ряд Тейлора относительно ). Третье слагаемое учитывает совместный вклад R2
градиента давления и перистальтической волны. Этот член необязательно является малым по сравнению со вторым слагаемым, так как на величину ∆pλ не накладывались какие-либо ограничения. Однако при условии, что мало, третий член всегда
R 2
меньше по сравнению с первым слагаемым вне зависимости от величины ∆ p λ .
Интересно сравнить наши результаты с данными, полученными в работе
Билстона и соавт. (Bilston et al.) [1]. В статье было проведено численное моделирование динамики течения жидкости в периваскулярном пространстве спинного мозга. В работе считалось, что периваскулярное пространство в спинном мозге – пустое пространство (в отличие от пористой среды). Из (13) видно, что в нашей модели скорость течения линейно зависит от градиента давления, что также отмечалось в работе [1]. В отсутствие градиента давления и при маленькой амплитуде волны скорость течения
( R 1
равна
V R 2 7
Г ь Y
-
( R i
V R 2 7
⋅ π cR 22 ,
которая пропорциональна скорости распространения
V R 2 7
волны, как было показано в [1]. Однако тот факт, что скорость течения пропорциональна квадрату амплитуды волны, отличается от линейной зависимости, предложенной в работе Билстона и соавт. (Bilston et al.) [1]. В нашей модели учитывается скачок градиента давления, при котором скорость течения падает до нуля. Вычисление критического скачка градиента давления проводилось при b = 1, 25⋅10-7м и K = 2 ⋅10-10 м4 ⋅ Н-1 ⋅ с-1 , взятых из табл. 2. Приравнивая к нулю Q в уравнении (13), можно получить величину градиента давления, равную 9, 4⋅106Па ⋅ м-1 . Большее значение b и/или меньшее значение K дает гораздо большую величину критического градиента давления. В работе Билстона и соавт. (Bilston et al.) [1] эта величина равна 1,4⋅107Па⋅м-1.
В работе Склея и соавт. (Schley et al.) [20] была предложена математическая модель, описывающая обратный периваскулярный транспорт амилоида-β из мозга. В нашей модели может быть показано, что перемещение любой частицы, осредненное по времени, всегда положительно вне зависимости от ее начального положения, тем самым обратный транспорт веществ не учитывается. В нашей модели периваскулярное пространство в мозге моделируется как пористая среда (частично заполненная и поддерживаемая клетками) с заданной шириной 1 мкм [11] (зависящей от размера кровеносного сосуда). Уравнение (1) используется для изучения объемного течения жидкости в этой пористой среде. Течение жидкости в пограничном слое не может быть изучено с помощью уравнения (1), так как в нем не учитывается важное слагаемое (т.е. слагаемое, учитывающее вязкость жидкости) для исследования пограничного слоя [5]. Толщина пограничного слоя порядка κ , которая равна 42 нм при K = 2 ■Ю-12 м4 ■ Н-1 ■ с-1 и 420 нм при K = 2 ЛО-10 м4 ■ Н-1 ■ с-1. Так как толщина слоя сопоставима с размерами пор в среде, то можно смоделировать этот слой как непористую среду и использовать уравнение Навье–Стокса для исследования эффектов в этом слое (что и было сделано в работе Склея и соавт. (Schley et al.) [20], где периваскулярное пространство моделировалось как пустое кольцевое пространство с шириной 100–150 нм). Следовательно, в данном случае нет никаких противоречий между нашей моделью и их моделью.
Как было ранее упомянуто во введении, комбинированные эффекты перистальтического движения стенки кровеносного сосуда и влияние лечения по методу конвекционно-усиленной доставки лекарств представляют наибольший интерес. При лечении данным методом лекарства впрыскиваются непосредственно в мозговую ткань (серое вещество) через иглу или катетер. Макроскопическое давление, приложенное к точке от источника впрыскивания [15], имеет следующий вид:
p ( r ) = P-a , (16)
R где P0 – давление в полости, заполненной жидкостью с радиусом a, окружающим источник, а R – расстояние от источника. Типичным значением для P0 является 7 кПа, а для a – 13 мкм [15].
В зоне R градиент микроскопического давления вдоль направления R равен dP _ P0 ■ a
dR " 1R
Взаимодействие между перистальтическим движением стенок кровеносного сосуда и внешним градиентом давления вследствие конвекционно-усиленной доставки зависит от расположения кровеносного сосуда. Например, если кровеносный сосуд в области R расположен перпендикулярно к направлению R , то градиент внешнего давления будет оказывать незначительное влияние на градиент давления в периваскулярном пространстве вдоль направления кровеносного сосуда. Для авторов интересен случай, при котором кровеносный сосуд ориентирован вдоль направления R при рассмотрении этой области, перистальтическая волна распространяется кнаружи. В этом случае изменение давления на длине волны A p л в уравнении (13) может быть
P ■ a .
вычислено как — ■ л , тогда
R 2
Q ( 1 ) _ ns cR 2 2 <
R 1
г
R 2 )
2( κ P 0 a ε c µ R 2
b
+
- 1)
+ 1
г
-
R 1
V 1 2 )
^ ( b 1 2 V 1 2 )
^ . (18)
V R 2 )
1 + it
V R 2 )
г
b
V 1 2 )
Отметим, что Q зависит от рассмотрения расположения зоны R относительно кровеносного сосуда. Для сравнения эффектов терапии при конвекционно-усиленной доставке лекарств в присутствии и отсутствии перистальтического движения стенок кровеносного сосуда введем следующее безразмерное число:
log R, мкм
a
б
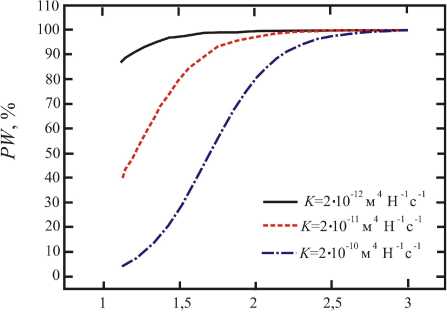
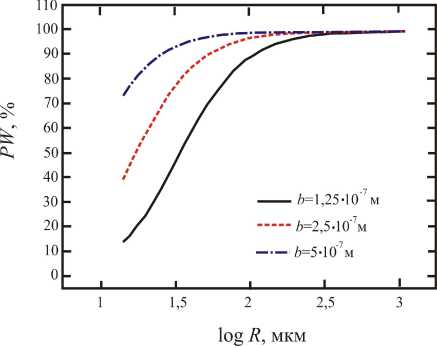
Рис. 2. Зависимости PW oт log R : a – при трех различных значениях K с асимптотой, равной b ; б – при трех различных значениях b с асимптотой, равной значению K
PW ( R ) = Q ( R ^Q^b = 0 100%, (19)
где PW – сокращение от “ peristaltic wave ” («перистальтическая волна»). Это число характеризует вклад доставки жидкости от перистальтической волны. Можно показать, что величина PW всегда неотрицательная.
На данном этапе авторы испытывают необходимость в экспериментальных данных для непосредственного сравнения с теоретическими результатами. Следовательно, необходимо провести анализ чувствительности к параметрам, принятым в модели. Выберем b и K как варьируемые параметры и зафиксируем остальные параметры, поскольку в литературе наблюдается их разброс согласно приведенным данным. Зависимости PW от log R показаны на рис. 2, где R меняется от a до 1000 мкм. На рис. 2, a была построена зависимость PW (%) от log R (мкм) для трех различных значений K с асимптотой b, а на рис. 2, б зависимости PW (%) от log R (мкм) строились для трех различных значений b c асимптотой K. Как можно увидеть из рис. 2, транспортировка жидкости в периваскулярное пространство в большей степени обеспечивается конвекционно-усиленной добавкой, так и перистальтическая волна чувствительна к расположению R и, в частности, к значению b и K. Во всех случаях, изображенных на рис. 2, в зоне, которая находится далеко от источника впрыскивания лекарства (~1000 мкм) транспортирование жидкости главным образом осуществляется за счет перистальтической волны. Рядом с источником впрыскивания перистальтическая волна играет важную роль или не зависит от выбора значений параметров. В некоторых случаях даже рядом с источником впрыскивания перистальтическая волна может всё ещё вносить большой вклад (например, её показатель равен 80% рядом с R = a при b = 2,5· 10–7 м и K = 2· 10–12 м4/(Н·с)). Поскольку K – гидравлическая проницаемость периваскулярного пространства, её снижение должно привести к увеличению процентного вклада перистальтической волны, что согласуется с рис. 2, а. Так как b – половина амплитуды волны, то при увеличении значения b, вклад перистальтической волны должен увеличиваться, что согласуется с рис. 2, б. Отметим, что при анализе чувствительности параметры b увеличивались в 2 раза, в то время как параметры K – в 10 раз. Авторам кажется, что система уравнений больше чувствительна к изменению b, чем к изменению K. Как обсуждалось выше, при некоторых условиях система является аддитивной (см. (15)). Чувствительность PW к значениям b и K можно интерпретировать, учитывая, что скорость течения жидкости вследствие конвекционно-усиленной доставки пропорциональна К (первое слагаемое в правой части (15)), в то время как скорость течения вследствие перистальтической волны (второе слагаемое в правой части (15)) пропорциональна b2.
Список литературы Механика жидкости в периваскулярном пространстве
- Bilston L.E., Fletcher D.F., Brodbelt A.R., Stoodley M.A. Arterial pulsation-driven cerebrospinal fluid flow in the perivascular space: a computational model//Comput. Meth. Biomech. Biomed. Eng. -2003. -Vol. 6, No. 4. -P. 235-241.
- Bloomfield I.G. Effects of proteins, blood cells and glucose on the viscosity of cerebrospinal fluid//Pediatric Neurosurg. -1998. -Vol. 28, No. 5. -P. 246-251.
- Bobo R.H., Laske D.W., Akbasak A., Morrison P.F., Dedrick R.L., Oldfield E.H. Convection-enhanced delivery of macromolecules in the brain//PNAS. -1994. -Vol. 91. -P. 2076-2080.
- Brinkman H.C. A calculation of the viscous force exerted by a flowing fluid on a dense swarm of particles//Appl. Sci. Res. -1947. -A1. -P. 27-34.
- Deen W.M. Analysis of transport phenomena. -New York: Oxford University Press, 1998. -597 р.
- Edelman I. Wave dynamics of saturated porous media and evolutionary equations//Transport Porous Med. -1999. -Vol. 34. -P. 117-128.
- Foley C.P. Neural drug delivery: novel microfluidic delivery devices and studies of transport phenomena: Ph.D. Dissertation. -Cornell University, 2009.
- Gladdish S., Dulka M., Winston B., James C., Christopher J., Chakravarthi R. Repeatability of non-invasive measurement of intracerebral pulse wave velocity using transcranial Doppler//Clinical Science. -Vol. 108. -P. 433-439.
- Hadaczek P., Yamashita Y., Mirek H., Tamas L., Bohn M.C., Noble, C., Park J.W., Bankiewicz K. The 'perivascular pump' driven by arterial pulsation is a powerful mechanism for the distribution of therapeutic molecules within the brain//Molecular Therapy. -2006. -Vol. 14, No. 1. -P. 69-78.
- Hoeks A.P.G., Brands P.J., Willigers, J.M., Reneman, R.S. Non-invasive measurement of mechanical properties of arteries in health and disease. P. I.//Mech. Eng. -1999. -Vol. 213 (Part H). -P. 195-202.
- Ichimura T., Fraser P.A., Cserr H.F. Distribution of extracellular tracers in perivascular spaces of the rat brain//Brain Res. -1991. -Vol. 545. -P. 103-113.
- Jaffrin M.Y., Shapiro A.H. Peristaltic pumping//Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. -1971. -Vol. 3. -P. 13-37.
- Lightfoot E.N. Transport phenomena and living systems. -New York: Wiley, 1973.
- Mishra M., Rao A.R. Peristaltic transport in a channel with a porous peripheral layer: model of a flow in gastrointestinal tract//J. Biomech. -2004. -Vol. 38. -P. 779-789.
- Neeves K.B., Lo C.T., Foley C.P., Saltzman W.M., Olbricht W.L. Fabrication and characterization of microfluidic probes for convection enhanced drug delivery//J. Control Release. -2006. -Vol. 111. -P 252-262.
- Neeves K.B., Sawyer A.J., Foley C.P., Saltzman W.M., Olbricht W.L. Dilation and degradation of the brain extracellular matrix enhances penetration of infused polymer nanoparticles//Brain Res. -2007. -Vol. 11, No. 80. -P. 121-132.
- Nield D., Bejan A. Convection in porous media. -New York: Springer-Verlag, 1998.
- Sarntinoranont M., Banerjee R.K., Lonser R.R., Morrison P.F. A computational model of direct interstitial infusion of macromolecules into the spinal cord//Ann. Biomed. Eng. -2003. -Vol. 31. -P. 448-461.
- Sarntinoranont M., Chen X., Zhao J., Mareci T.H. Computational model of interstitial transport in the spinal cord using diffusion tensor imaging//Ann. Biomed. Eng. -2006. -Vol. 34, No. 8. -P. 1304-1321.
- Schley D., Carare-Nnadi R., Please C.P., Perry V.H., Weller R.O. Mechanisms to explain the reverse perivascular transport of solutes out of the brain//J. Theor Biol. -2006. -Vol. 238. -P. 962-974.
- Shapiro A.H., Jaffrin M.Y., Weinberg S.L. Peristaltic pumping with long wavelengths at low Reynolds number//J. Fluid Mech. -1969. -Vol. 37, No. 4. -P. 799-825.
- Smith J.H., Humphrey J.A.C. Interstitial transport and transvascular fluid exchange during infusion into brain and tumor tissue//Microvasc. Res. -2007. -Vol. 73. -P. 58-73.


