Methodologies for determining M&A performance
Автор: Tsypkina K.Y.
Журнал: Экономика и социум @ekonomika-socium
Статья в выпуске: 4-1 (23), 2016 года.
Бесплатный доступ
During long time, researchers tried to understand the significance of adopting M&A strategy for organizations. Their motives were to understand whether the benefits from this strategy have occurred or not. They were trying to analyse whether these acquisitions are value creating or value destructive for the acquiring organization. For this purpose, many methods were used. Several research papers were revised to identify the most suitable methodologies and their benefits to measure M&A outcomes.
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140119046
IDR: 140119046
Текст научной статьи Methodologies for determining M&A performance
-
1) The first methodology to consider is Event Study methodology. It is the most popular methodology adopted by researchers. It was found that in 41% of studies the short-term event study method was used, while in 16% of studies the long term event study method was used. [1]
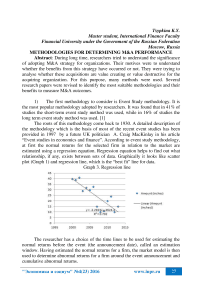
The roots of this methodology come back to 1930. A detailed description of the methodology which is the basis of most of the recent event studies has been provided in 1997 by a future UK politician A. Craig MacKinlay in his article “Event studies in economics and finance”. According to event study methodology, at first the normal returns for the selected firm in relation to the market are estimated using a regression equation. Regression equation helps to find out what relationship, if any, exists between sets of data. Graphically it looks like scatter plot (Graph 1) and regression line, which is the “best fit” line for data.
Graph 3. Regression line
The researcher has a choice of the time lines to be used for estimating the normal returns before the event (the announcement date), called an estimation window. Having estimated the normal returns for a firm, the market model is then used to determine abnormal returns for a firm around the event announcement and cumulative abnormal returns.
-
2) Accounting Returns Methodology or operating performance methodology. Accounting Returns studies involve the analysis of the accounting performance of the combined company measured in terms of Return on Assets (ROA) or Return on Equity (ROE). Intervals for estimation usually include from two to three years after the bid termination. The pre acquisition accounting data of the target and bidding firms prior to merger is calculated to obtain pre-merger performance of the combined firm and compare it to post merger results.[2]
-
3) Economic Value Added methodology. This methodology determines the expected level of annual operating performance expressed in terms of Economic Value Added (EVA) to satisfy the acquisition. EVA provides a useful benchmark to use to measure actual versus expected acquisition performance. All in all, this methodology is designed to show what is the combined organization must reach if it wants shareholders to benefit.There is one more approach similar to the EVA methodology, where the fundamental value of acquirers before acquisition with the fundamental value post acquisition is compared. It is called Residual Income Approach.[3]
-
4) Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA). It is a linear programming technique more prevalent in operations research for comparing the relative efficiency of decision making units. The efficiency of each unit is measured in terms of a ratio of output to input variables.
-
5) Innovative Performance methodology. Measures the impact of M&A on innovation. For example, this methodology may be used to measure innovation performance of technological acquisition, of innovations generated by bidder in the chemicals industry.
-
6) Questionnaire Method, is used to measure perceptions, attitudes which are not possible using objective measures, for example in case of very small companies.[4]
The second most popular technique according to number of studies is the Accounting Performance measure. The limitation of this method is connected with difficulties in comparing accounting returns for companies from different geographical regions where regulations and accounting practices differ. This approach also does not take into account the market value of the firm.
Список литературы Methodologies for determining M&A performance
- Zollo, M and and Singh, H., (2004). Deliberate learning in corporate acquisitions: post-acquisition strategies and integration capability in U.S. bank mergers. Strategic Management Journal, 25(13), 1243-1257
- Healy, Paul, K. Palepu, and Richard Ruback, 1992, Does Corporate Performance Improve After Mergers?, Journal of Financial Economics 31, 145-155
- Kiymaz, H., and Baker, H. (2008). Short-Term Performance, Industry Effects, and Motives: Evidence from Large M&As. Quarterly Journal of Finance and Accounting, 47(2), 17-24
- Schoenberg, R. (2006), Measuring the Performance of Corporate Acquisitions: An Empirical Comparison of Alternative Metrics. British Journal of Management, 17, 363-371
- Guest, P., Bild, M., and Runsten, M. (2010). The effect of takeovers on the fundamental value of acquirers. Accounting and Business Research, 40(4), 353-356
- McKinlay, A. Craig, (1997) “Event Studies in Economics and Finance.” Journal of Economic Literature 35, 13-39