Metrics for Evaluating Pervasive Middleware
Автор: J.Madhusudanan, V. Prasanna Venkatesan
Журнал: International Journal of Intelligent Systems and Applications(IJISA) @ijisa
Статья в выпуске: 1 vol.6, 2013 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Pervasive computing aims at developing smart environments which enable user to interact with other devices. Pervasive computing includes a middleware to support interoperability, heterogeneity and self-management among different platforms. It provides efficient communications and context awareness among devices. Middleware for pervasive computing provides much more attention to coordinate the devices in the smart environment. The evaluation of the pervasive middleware is a challenging endeavor. The scope of evaluating smart environment is mainly increasing due to various devices involved in that environment. In this paper evaluation metrics are proposed based on the contexts available in the environment, how the devices are used, security and autonomy of smart applications. These metrics are used for evaluating different kind of smart applications.
Pervasive Computing, Middleware, Evaluation, Smart Environment
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15010515
IDR: 15010515
Текст научной статьи Metrics for Evaluating Pervasive Middleware
Published Online December 2013 in MECS
Several tools for prototyping pervasive applications exist, such as Activity Designer[1] , DiaSuite[2], City Compiler, to satisfy the diverse requirements evolved into the entire design process: from drafting the concept early with a low-fidelity prototype to deploying a high fidelity prototype and testing it in a realistic environment. Compared to those more mature application domains in pervasive computing, e.g. the middleware for overcoming the heterogeneity via standardized interfaces, design tools are still at an early stage.
For evaluation purposes, any pervasive computing framework can be divided roughly into three layers: system support, application programming support and end-user interface. Evaluation scopes of pervasive computing systems have become increasingly important as various ubiquitous devices and application software start to be emerged. In addition, the evaluation scopes of the pervasive systems would provide the designers with essential system specifications and for the evaluators.
The contribution of this work is defining the metrics for evaluating the pervasive computing applications. Many models are proposed to define the metrics for evaluating smart applications. According to Boehm model, McCall model the metrics for context aware computing is defined based on the technological aspects and social aspects. The ISO/IEC 9126 model[3] is also proposed to add additional metrics for evaluation. In this work the pervasive computing applications is evaluated using some criteria. These criteria are based on the context available in the environment, how the devices are handled, security and autonomy. In section II the evaluation process for pervasive middleware is described. In Section III the evaluation architecture for pervasive application is explained. Section IV describes about the metrics used for evaluation in this work. A summary of the evaluation metrics is presented at the end of the paper.
-
II. Evaluation Process for Pervasive Middleware
The aim of proposing evaluation metrics for pervasive middleware is to determine how it works, what functionalities to add and the appropriate metrics to use. Evaluating the pervasive middleware application is mainly based on the user experience and the computer technology used for that environment. Metrics used for evaluating the context aware computing can also be inherited for evaluating the pervasive middleware. In the related work Gaia middleware [4] is evaluated based on metrics such as context sensitivity, security, discovery, programmability and usability. For evaluation purposes many tools are proposed to evaluate the pervasive middleware based on context awareness. Context aware experience sampling tool[5] is one of simulation tool used for evaluating the context aware middleware. This tool evaluates the middleware from the user perspective by collecting their feedback. Memento[6] is an experience sampling tool it gathers the user log, user experience and other qualitative data. It provides a desktop platform that connects the user and the developer in the same field. Activity designer is based on the test driven design process of pervasive applications. It evaluates field observations, activity analysis and interaction prototyping.
Di Zheng[7] identified qualitative data to evaluate the middleware for context aware based applications. In this work, the context is evaluated based on some quality data such as character of sensors, measurement of sensors and user defined context. The character of sensor is a kind of context used to evaluate the character of sensors such as CPU, energy. The measurement of sensor involves security, authority, completeness, precision, usability, locality, freshness, certainty and reliability.
Simulation tools such as Ubiwise[8], TATUS[9], UbiReal[10], C-Promise[11] are also used to design and evaluate the smart applications. Ubiwise aims to test the hardware and software used for the devices embedded in the smart applications. It evaluates the user interaction with the devices in the environment. The i*CATch[12] test kit was designed and developed to address the problem of quality control. The purpose of the kit is to quickly determine whether the connection between each socket is functional. C-Promise, the middleware has been quantitatively evaluated by discrete event simulation. The simulation models have been derived from black box assessments of prototyped systems components. Other than these simulation tools questionnaires, prototyping [13], field trail approaches are also implemented.
-
III. Evaluation Architecture
-
3.1. Context Evaluator
-
3.2. Device Evaluator
-
3.3. Security Evaluator
The architecture for the evaluation of pervasive middleware is composed of Context evaluator, Device evaluator, Security evaluator and Autonomy Evaluator. The architecture diagram is depicted in Fig.1:
The context evaluator is responsible for evaluating the generic context middleware. The scenario collected from the user is managed and evaluated. The contexts can be defined as any information that is bounded in the smart environment. The context can be location, time, environment and user activities.
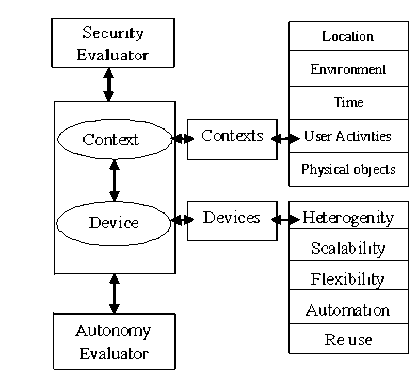
Fig. 1: Pervasive Middleware Evaluation Architecture
In the context middleware, contexts are identified from the user scenario and stored in the database using ontology web language. The context information is represented as XML based language.
The middleware should allow integrating a wide range of different devices into the system. Enabling devices to cooperate with each other requires interoperability between these devices. The device evaluator evaluates the interoperability of the middleware to ensure scalability and heterogeneity. It evaluated how the devices are used and its flexible in the smart environment.
The goal of the security evaluator is to identify a specification of suitable security mechanisms for the scenarios, and to use this to measure the security of the evaluated platform, security being vital in user acceptance for a large number of pervasive computing technologies. The security evaluator applies to both the device part and context part of a middleware. In order to evaluate, the middleware is analyzed to identify weaknesses with respect to authentication, control over private information, conflict resolution and uncertainty handling. Middleware should have minimal support for the application developer that allows them to incorporate privacy and security into their applications. At least middleware should have the responsibility for protecting the device end security.
-
3.4. Autonomy Evaluator
The autonomy evaluator is used to evaluate the autonomous nature of the devices in the pervasive applications. This evaluates both the context middleware and device middleware. Every ubiquitous middleware should have self-healing mechanism to adopt with the error conditions and should provide the flexibility to recover from failures without hampering the application running on top of it.
-
IV. Metrics for Evaluation
To show the effectiveness of the smart application, it should be evaluated using the metrics. According to Elliot stern different meanings for evaluation is proposed they are as follows: judgment, explanation, development, empowerment. The evaluation technique can also be classified into two approaches in the computing area. The two approaches are formative evaluation and summative evaluation. Formative evaluation is done during the design process to improve the design development. Summative evaluation is performed at the user side to evaluate the usability of the application. From these approaches some of the quantitative measurements are termed as metrics for evaluating the pervasive application.
In this paper the evaluation metrics are classified into four categories. They are context evaluation, device evaluation, security evaluation and autonomy evaluation. The context evaluation metrics are identified by the contexts available in the environment. The context can be location, time, user activities, object movements etc. these contexts can then be evaluated by the end user of the application. The user can check the application by generating different kind of scenarios for evaluating the context aware. The interoperability and device management are also one of the evaluation metrics. These metrics evaluate the heterogeneity, scalability of the devices present in the environment. The security evaluation evaluates the security perspective of the pervasive middleware. This evaluation improves the privacy of the application. The autonomy evaluation metrics are self-configuration, resource management, failure toleration and decision making. The metrics used for evaluation and its scale definition is shown from Table 1 to Table 5.
Table 1: Metrics For Evaluating Pervasive Middleware
|
CONTEXT AWARE |
Location |
How many locations used in application. Identify which location is most used. |
|
Environment |
Identify the environments in the available space. Sensing the environment and identify what type of sensors used and whether they are effective. |
|
|
User activities |
Specify various user activities involved in an application. Check whether the application responding correct to the activities. |
|
|
Time |
Specify AM or PM, working hours. |
|
|
Physical objects |
Movement of devices in environment |
|
|
INTER OPERABILITY AND DEVICE MANAGEMENT |
Heterogeneity |
How the different devices communicate with each other. What are all the devices involved. How they are interoperate. |
|
Scalability |
Extend the application by adding new devices. |
|
|
Flexibility |
Adding the new devices in the environment and check those devices are adaptable. |
|
|
Respond to contexts |
How many devices are used and how they react to the user |
|
|
Dynamic |
Identify which devices are active in the application |
|
|
Automation |
Make the device to take part in the environment and work itself |
|
|
Reuse |
Use a device for various purposes ex: mobile can be used for communication and sensing activities. |
|
|
SECURITY |
Authentication |
Authenticate the user using log in process |
|
Control Over Private Information |
Privacy is ensured using security policies. |
|
|
Conflict Resolution |
How the devices are handled in the conflict situation. |
|
|
Uncertainty Handling |
How to act under incomplete context information. Policies are set to work with incomplete information. |
|
|
AUTONOMY |
Self -Configuration |
How the devices are configure itself to new environment. |
|
Resource Management |
Make the devices available to the user and work properly in an environment ex: sensor sleep/ wake, power management. |
|
|
Failure Toleration |
How the Smart environment is managed in case of failures |
|
|
Decision Making |
How the device handles the critical situation and makes the decision according to that. |
Table 2: Context-Aware Metric and Its Scale Definition
|
Attribute |
Scale definition |
||
|
High |
Middle |
Low |
|
|
Location |
Supports for more number of locations |
Supports limited locations |
Supports only one location |
|
Environment |
Supports all environment in the application |
Supports few environment |
Supports one environment |
|
User activities |
Support for different kind of user activities |
Support for specified user activities |
Supports pre- defined use activities |
|
Time |
Fully supported |
Support with limitations |
Not supported |
|
Physical objects |
Movement of devices are fully supported |
Few device movements are supported |
Not supported |
Table 3: Inter Operability and Device Management Metric and Its Scale Definition
|
Attribute |
Scale definition |
||
|
High |
Middle |
Low |
|
|
Heterogeneity |
Supports hetero geneity of devices |
Supports heterogeneity for small number of devices |
Not supported |
|
Scalability |
Supports for extensibility |
Supported with limitations |
Not supported |
|
Flexibility |
Fully supported |
Supported with limitations |
Not supported |
|
Respond to contexts |
Responds to the user |
Few responses are available to the user |
The number of response will be less than 1 |
|
Dynamic |
Fully supported |
Supported with limitations |
Not supported |
|
Automation |
Fully supported |
Supported with limitations |
Not supported |
Table 4: Security Metric and Its Scale Definition
|
Attribute |
Scale definition |
||
|
High |
Middle |
Low |
|
|
Authentication |
Fully supported |
Supported with limitations |
Not supported |
|
Control Over Private Information |
Security policies are ensured for all applications |
Supported for limited applications |
Not supported |
|
Conflict Resolution |
Devices are handled with conflict resolution |
Limited number of devices are handled |
No devices conflict with each other |
|
Uncertainty Handling |
Application provides a better result for incomplete context information |
Provides a medium result |
Provides no result for incomplete context information |
Table 5: Autonomy Metric and Its Scale Definition
|
Attribute |
Scale definition |
||
|
High |
Middle |
Low |
|
|
Self - Configuration |
Supports configuration |
Support with limitations |
Not supported |
|
Resource Management |
The devices available to the user and works properly |
The devices are partially available to the user |
The number of devices available to the use is less |
|
Failure Toleration |
All type of failures are handled |
Work with tolerable failures |
Does not handle failures |
|
Decision Making |
Fully supported |
Supported with limitations |
Not supported |
-
V. Case Study
The case study used in this paper is about a generic pervasive middleware for context aware applications. This middleware is used to develop different kind of smart environment applications such as smart home, bank, hospital etc. the generic middleware is divided into two layers, they are context aware layer and device layer. The context aware layer is responsible for collecting the scenarios from the user request whereas these scenarios identify the context. It provides best service to the user based on the varying context. The device layer is responsible for integration of devices, communication of devices and manages devices.
The metrics such as context aware, device management, interoperability, security and autonomy are evaluated on this generic middleware. The context aware is evaluated based on the user scenarios. These scenarios are collected and stored in the database using the xml language. These contexts can be location, time, environment, user activities. The middleware can be evaluated by testing how many locations are supported and graph is also generated based on these metrics. The metrics can be rated as high, middle and low based on the values used for location, devices and activities. These values are calculated based on the total number of location, devices, activities used for that environment.
The location context is evaluated by using the formula shown in (1)
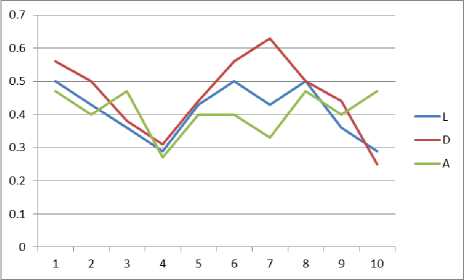
Fig. 3: Graph for context aware evaluation Environment 2
Eval ( l ) =
No of location present in the scenario n
(l)
Total no of location in the environment
Z n (l)
Similarly the metric device is calculated as shown in
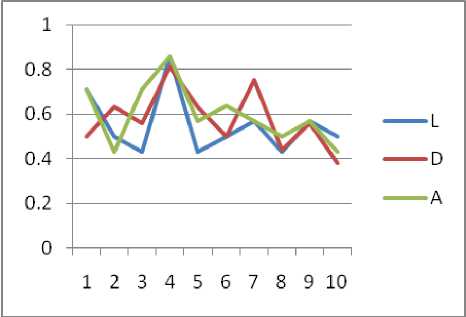
Fig. 4: Graph for context aware evaluation Environment 3
Eval ( d ) =
No of devices in scenario
n (d )
Total no of devices in
the environment Z n ( d )
The activity metric is calculated as shown in (3)
Eval ( a ) =
No of activities in Scenario n ( a )
Total no of activities in the environment
Z n ( a )
For every scenario the metrics can be calculated and then they are represented in the matrix form. Using this matrix the graph can be generated with one curve as location, device and activities. Graphs are displayed below for different scenarios of three environments in Fig.2, Fig.3 and Fig.4.
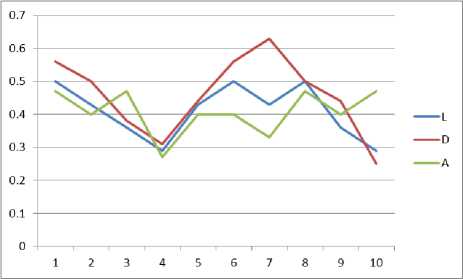
Fig.2: Graph For Context Aware Evaluation Environment 1
-
VI. Conclusion
Pervasive computing includes a middleware to support interoperability, heterogeneity and selfmanagement among different platforms. In this work the pervasive middleware is proposed to evaluate based on context awareness. Here we have evaluated context awareness based on location, device and activity involved in the given environment. The metrics used for the evaluation is summarized in the table. Architecture for middleware evaluation is described which evaluates the metrics used in the paper. These metrics can be generally used for all type of middleware used for designing smart applications. The result of the evaluation is an analysis containing: choice of technology, a description of scenarios, evaluations of the middleware based on each view, a prototype and finally an overall assessment of the middleware. The future work is based on developing the formula models for remaining metrics.
Список литературы Metrics for Evaluating Pervasive Middleware
- Y. Li and J. A. Landay. “Activity-based prototyping of ubicomp applications for long-lived, everyday human activities” Proc. the twenty-sixth annual SIGCHI conference on Human factors in computing systems, ser. CHI ’08. New York, NY, USA: ACM, 2008, pp. 1303–1312.
- Benjamin Bertrana, JulienBruneaua, Damien Cassoua, Nicolas Loriantb, Emilie Ballanda, Charles Consela. “DiaSuite: a Tool Suite To Develop Sense/Compute/Control Applications”, May 2012.
- TeddyMantoro. “Metrics Evaluation for Context aware Computing”. Proceedings of MoMM2009, December 2009.
- AnandRanganathan, Jalal Al-Muhtadi, Jacob Biehl, Brian Ziebart, Roy Campbell, Brian Bailey. “Evaluating GAIA using a Pervasive Computing Benchmark” 2005.
- S. S. Intille, J. Rondoni, C. Kukla, I. Ancona, and L. Bao. “A context-aware experience sampling tool” CHI ’03 extended abstracts on Human factors in computing systems, ser. CHI EA ’03. New York, NY, USA: ACM, 2003, pp. 972–973.
- S. Carter, J. Mankoff, and J. Heer. Momento: “support for situated ubicomp experimentation” Proc. SIGCHI conference on Human factors in computing systems, ser. CHI ’07. New York, NY, USA: ACM, 2007, pp. 125–134.
- Di Zheng, Jun Wang, Ben Kerong. “Evaluation of Quality Measure factors for the middleware based Context-aware Applications” IEEE TRANSACTIONS, 2012.
- J. Barton and V. Vijayaraghavan. “UBIWISE, a simulator forubiquitous computing systems design” Hewlett-Packard Labs, Palo Alto, Tech. Rep. HPL-2003-93, 2003.
- E. O’Neill, M. Klepal, D. Lewis, T. O’Donnell, D. O’Sullivan, and D. Pesch. “A testbed for evaluating human interaction with ubiquitous computing environments” First International Conference on Testbeds and Research Infrastructures for the Development of Networks and Communities (Tridentcom) 2005., ser. TRIDENTCOM ’05. Washington, DC, USA: IEEE Computer Society, 2005, pp.60–69.
- H. Nishikawa, S. Yamamoto, M. Tamai, K. Nishigaki, T. Kitani,N. Shibata, K. Yasumoto, and M. Ito. Ubireal: “Realistic smartspacesimulator for systematic testing” UbiComp 2006: Ubiquitous Computing, ser. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, P. DourishandA. Friday, Eds. Springer Berlin / Heidelberg, 2006, vol. 4206, pp.459–476.
- E. Reetz, M. Knappmeyer, S. Kiani, A. Anjum, N. Bessis, and R.Tonjes. “Performance simulation of a context provisioning middleware based on empirical measurements” Simulation Modeling Practice and Theory, 2012.
- Grace Ngai, Stephen C.F. Chan, Vincent T.Y. Ng, Joey C.Y. Cheung, Sam S.S. Choy, Winnie W.Y. Lau and Jason T.P. Tse. “i*CATch: A Scalable, Plug-n-Play Wearable Computing Framework for Novices and Children” ACM Transactions, April 2010.
- Jason B. Forsyth, Thomas L. Martin. “Tools for interdisciplinary design of pervasive computing” International Journal of Pervasive Computing and Communications, Vol. 8 Iss: 2 pp. 112 – 132.


