Модели создания гнойно-септического воспаления большеберцовой кости у крысы для оценки действия биорезорбируемых материалов с антимикробными препаратами
Автор: Смоленцев Дмитрий Владимирович, Лукина Юлия Сергеевна, Бионышев-Абрамов Леонид Львович, Сережникова Наталья Борисовна, Васильев Максим Геннадьевич, Сенягин Александр Николаевич, Пхакадзе Тамара Яковлевна
Журнал: Гений ортопедии @geniy-ortopedii
Рубрика: Оригинальные статьи
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.29, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Введение. Приведен краткий обзор моделей создания гнойно-септического воспаления у крыс, в том числе с помощью активного бактериального агента и методы диагностики воспаления. Цель. Демонстрация результатов разработки эффективной экспериментальной модели создания гнойно-септического воспаления большеберцовой кости крысы с использованием малоинвазивных методов диагностики заражения in vivo. Материалы и методы. На четырех группах мелких лабораторных животных исследованы различные модели создания гнойно-септического воспаления при применении инокуляции золотистого стафилококка. Отработаны не разрушаемые объект методы оценки гнойно-септического воспаления: микробиологическая, томографическая, морфологическая. Результаты. Результаты исследования свидетельствуют о возможности создания экспериментального гнойно-септического воспаления у крыс к 14-60 суткам с помощью инокуляции S. aureus, которое представляет собой тяжелую, быстро прогрессирующую гнойную инфекцию, приводящую к обширному разрушению кости с образованием секвестров. Обсуждение. Для гарантированного формирования гнойно-воспалительного процесса костной ткани в более короткие сроки наблюдения необходима контролируемая в количественном отношении инвазия активного бактериального агента. Склерозирующий агент и формирование свищевого хода не являются обязательными при создании воспаления. Заключение. Продемонстрированы результаты разработки экспериментальных моделей создания гнойно-септического воспаления с применением малоинвазивных методов диагностики in vivo, что позволит получить адекватную оценку степени инфицирования перед лечением.
Остеомиелит, гнойно-септическое воспаление, бактериальная инвазия, золотистый стафилококк, склерозирующий агент, инокуляция, кое
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142238190
IDR: 142238190 | УДК: 616.718.5-018.46-002-092.9 | DOI: 10.18019/1028-4427-2023-29-2-190-203
Текст научной статьи Модели создания гнойно-септического воспаления большеберцовой кости у крысы для оценки действия биорезорбируемых материалов с антимикробными препаратами
Проблема гнойно-септических осложнений является одной из актуальнейших в современной хирургии, по данным различных авторов, частота их возникновения варьирует от 2 до 63,9 %, и в 12-61 % случаев они приводят к развитию остеомиелита и, как следствие, некрозу кости и ампутации с серьезным риском смертельной септицемии [1-3]. Остеомиелитом ежегодно страдают около 4 миллионов человек во всем мире.
В последние годы был достигнут огромный прогресс в лечении инфекции опорно-двигательного аппарата, однако исследования показали, что уровень инфицирования при плановых операциях не может быть ниже 1-2 %, а неудачи при ревизионных операциях остаются на уровне 33 % [4-6]. Стоимость лечения костной инфекции существенна и будет увеличиваться по мере того, как абсолютное число пациентов, страдающих от нее, продолжает расти [7].
Инфекция кости может развиться в результате прямого заражения (например, открытые переломы) или путем распространения либо через кровоток (гемато-генно), либо из прилегающего участка или имплантата [8]. Традиционно хронический остеомиелит был состоянием, в котором преобладало заболевание, вызванное гематогенным распространением узкого круга микроорганизмов, наиболее важным из которых был золотистый стафилококк [1]. В последнее время эта категория значительно пополнилась посттравматическим хроническим остеомиелитом, связанным с использованием устройств, и контагиозным остеомиелитом после инфекций диабетической стопы [9]. 65 % военных травм носят ортопедический характер, а уровень инфицирования достигает 50 % [10].
Изучение гнойно-септических процессов и остеомиелита, а именно патогенеза заболевания, диагностических инструментов, эффективности профилактических методов или различных вариантов лечения требует экспериментов на животных. Экспериментальные исследования на животных моделях часто используются в клинической практике, несмотря на сложность воспроизводимости характеристик процесса развития инфекции у человека. Детали экспериментальных моделей на животных имеют решающее значение при оценке эффективности противомикробных препаратов и биоматериалов, особенно при сравнении результатов различных исследований.
W. Reizner и соавт. провели большой систематический обзор животных моделей остеомиелита, вызванного золотистым стафилококком [11] по базам данных PubMed и Ovid MEDLINE с 1902 по 2012 год. Из 93 экспериментальных исследований, принятых для анализа, тридцать шесть (38,7 %) ссылок использовали кролика в качестве животного для создания экспериментальной модели, чаще новозеландского белого кролика. В двадцати девяти (31,1 %) ссылках использовалась крысиная модель, в большинстве из которых использовались крысы Wistar или Sprague Dawley. В семи ссылках (7,5 %) использовались мыши: штаммы BALB/c или C57BL/6, в семи (7,5 %) – овцы, в шести (6,5 %) – собаки, в четырех (4,3 %) – козы, в двух (2,2 %) – свиньи, в одном (1,1 %) – морские свинки и в одном (1,1 %) – хомяки [11]. Модели на крысах незначительно уступают моделям на кроликах по количеству использований в экспериментальных исследованиях, но являются альтернативой более крупным животным в связи с невысокой стоимостью, простотой содержания. При этом крысы имеют достаточный размер, чтобы воспроизвести перелом, выполнить сверление и фиксацию винтами и пластинами, а также интрамедуллярное введение инородных тел – винтов, штифтов [12].
Кроме того, при выборе животных для моделирования остеомиелита необходимо учитывать, что признаки хронического остеомиелита, такие как некроз и тяжелый остеолиз, развиваются у мелких животных в течение более короткого периода времени по сравнению с более крупными животными вследствие различий в размере ткани (например, толщина надкостницы) [2].
Известно, что крысы обладают сильной иммунной системой, что иногда может усложнить формирование модели заражения [11]. Для создания острого и хронического остеомиелита используют модели открытого перелома [13-15], перипротезного остеомиелита [16], остеомиелита, связанного с внешней фиксацией [17], гематогенную модель [18].
Целью создания гнойно-септического воспаления является разработка различных протоколов терапевтического и хирургического лечения. Чтобы исследовать эффективность новых адъювантов для лечения остеомиелита, необходимо обеспечить адекватное решение представляющих интерес клинических вопросов. Inzana J.A. с соавторами провели обзор моделей бактериального создания остеомиелита на животных для последующего использования их в исследованиях полимерных, керамических и композиционных материалов, содержащих антибактериальные субстанции [2].
В таблице 1 показаны результаты анализа крысиных моделей для изучения резорбируемых материалов.
Таблица 1
Краткое описание моделей животных, используемых для изучения резорбируемых материалов [2]
|
№ ист. |
Порода |
Зона |
Штамм |
КОЕ |
Склерозант / имплантат |
Время инфицирования |
|
[19] |
Wistar |
Проксимальный отдел б/б кости |
Im2-42 |
Не указан |
нет / имплантат |
4 недели |
|
[20] |
Wistar |
Проксимальный отдел б/б кости |
MSSA (ATCC 29213) |
2·105 |
арахидоновая кислота / нет |
3 недели |
|
[21, 22] |
Wistar |
Проксимальный отдел б/б кости |
MRSA |
2·106 |
нет / спица Киршнера |
6 недель |
|
[23, 24] |
Wistar |
Проксимальный отдел б/б кости |
Клинический изолят MRSA |
2·106 |
нет / спица Киршнера |
3 месяца |
|
[25] |
SD |
Проксимальный отдел б/б кости |
MSSA (ATCC 49230) |
106 |
нет / спица Киршнера (0,2 см) |
7 недель |
|
[26] |
SD |
Проксимальный отдел б/б кости |
Неуточненный MSSA |
106 |
нет / нет |
3 недели |
В большинстве исследований при создании остеомиелита с помощью бактериальной субстанции использовали модель Norden и коллег для кроликов [27], в которой в костномозговую полость проксимального метафиза большеберцовой кости инокулировали золотистый стафилококк ( S. aureus ) через иглу, кортикальное отверстие закрывали костным воском, давали инфекции установиться в течение определенного периода времени. Аналогичная модель была использована другими научными группами на крысах [28, 29]. Модификация модели в части дополнительного размещения в костномозговом канале большеберцовой кости спицы Киршнера в виде короткого отрезка или равного длине канала была использована в некоторых исследованиях [25, 30-33], причем Bisland и коллеги изначально получали на спице биопленку.
В соответствии с литературными данными, S. aureus – наиболее распространенный возбудитель инфекций костей, который является высоко оппортунистическим видом, чрезвычайно трудно поддающимся лечению [34].
Кроме модели создания остеомиелита, на результат исследования оказывает значительное влияние диагностика, которая должна быть качественной и однообразной в рамках одного исследования. Помимо выявления местных (эритема, отек или образование абсцесса) или системных (лихорадка или летаргия) клинических признаков инфекции, в исследованиях часто проводится расширенная визуализация (например, рентгенография, компьютерная томография (КТ) или магнитно-резонансная томография (МРТ)), а также микробиологические и гистологические исследования [11].
В некоторых исследованиях используются методы, при которых производится выемка кости, окружающих мягких тканей [2]. Однако биопсия и мазки имеют преимущество использования одного образца для гистологического анализа, тем самым сводя к минимуму количество необходимых животных. Гистопатологические анализы чаще всего оценивались в соответствии с системой, описанной Smeltzer и коллегами [35]. В этой системе баллы от 0 до 4 присваиваются каждому признаку на основе внутрикостного острого воспаления, внутрикостного хронического воспаления, периостального воспаления и некроза кости. Более высокие баллы указывают на более тяжелый исход. Другие системы оценки учитывают дополнительные факторы, включая наличие нейтрофилов и мононуклеарных клеток, гигантских клеток, фиброз, сосудистость, активность остеокластов и образование абсцесса [2].
Рентгенологическая оценка проводится в соответствии с системой, описанной Norden и коллегами [36] и Smeltzer и коллегами [35]. Критерии Norden включали образование новой надкостничной кости, секвестры, разрушение кости и степень поражения вдоль большеберцовой кости, где более высокие баллы указывают на худший исход. Система Smeltzer оценивает надкостничное возвышение, архитектурную деформацию и образование новой кости в диапазоне от 0 до 4, причем более высокие баллы указывают на большую тяжесть заболевания.
Inzana и коллеги утверждают, что при продолжающемся остеолизе рентгенологическая визуализация улучшения при успешном лечении может отставать на 4-6 недель [2]. Другими методами визуализации развития остеомиелита или его лечения является микрокомпьютерная томография (микро-КТ) [37] и позитронноэмиссионная томография (ПЭТ) [38].
В последние годы несколько исследовательских групп начали использовать биолюминесцентную визуализацию [39, 40]. С помощью этого метода бактерии генетически модифицируются, чтобы испускать фотоны, когда они метаболически активны, после изменения оперона lux.
Цель – демонстрация результатов разработки экспериментальных моделей создания гнойно-септического воспаления большеберцовой кости крысы с использованием малоинвазивных методов диагностики заражения in vivo .
МАТЕРИАЛЫ И МЕТОДЫ
Работа одобрена Локальным этическим комитетом ФГБУ «НМИЦ ТО им. Приорова» Минздрава России (Протокол заседания № 4 от 05 мая 2021 года).
Во всех экспериментальных моделях использовались половозрелые самцы линии Wistar весом 250-300 г. возрастом от 4 до 6 месяцев, специально разведенные в сертифицированном питомнике и ранее не участвовавшие в исследованиях. Все исследовательские процедуры и условия содержания грызунов отвечают этическим правилам работы с лабораторными животными, в том числе Европейской директиве FELASA-2010. Животные были распределены по группам, используя в качестве критерия массу тела. Начальная средняя масса тела была одинаковой в каждой группе, а индивидуальная масса животных не отличалась более чем на 20 % от средней массы животных. Животные были разделены на четыре группы: одну контрольную и три экспериментальные. Оперативное вмешательство осуществлялось согласно существующим международным правилам гуманного обращения с животными, под общей внутримышечной анестезией препаратами Золетил в расчёте 7 мг/кг и Ксилазин – 13 мг/кг. Область моделирования: большеберцовая кость левой и правой задней конечности.
В качестве активного бактериального агента использовали чистую культуру золотистого стафилококка ( S. aureus ) ATCC 6538 в 0,8 % растворе агара на основе физиологического раствора NaCl с целью повышения вязкости инокулята. Инокуляция подготовленной культуры S. aureus проводилась катетеризацией через перфорацию, сначала в проксимальный, потом в дистальный отделы костномозгового канала, заполняя таким образом весь канал. Системная антибактериальная терапия не проводилась.
Количество животных, используемых для каждой модели создания гнойно-септического воспаления, представлено в таблице 2 и отличается за счет двух или более повторений отдельных моделей за период исследования в 1 год.
Используемые модели для формирования гнойносептического воспаления большеберцовой (б/б) кости крысы представлены в таблице 3.
Таблица 2 Количество животных, используемых для моделей создания гнойно-септического воспаления
|
Модель |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
Количество животных |
6 |
30 |
6 |
3 |
Таблица 3
Модели формирования гнойно-септического воспаления
|
№ модели |
Характеристика и позиционирование костной перфорации |
Активный бактериальный агент |
Склерозирующий агент |
Формирование свища |
Импланты |
Длительность наблюдения |
|
1 |
проксимальная 1/3 диафиза, перфорация критического размера (2/3 диаметра кости) |
S. aureus 1,5·103 КОЕ в 250 мкл питательной среды |
нет |
марлевая турунда, соединяющая костную перфорацию и наружную поверхность кожных покровов |
нет |
30 суток |
|
2 |
диафиз, перфорация диаметром 1 мм |
нет |
нет |
нет |
30 суток |
|
|
3 |
бугристость проксимального отдела, перфорация диаметром 1,2 мм с выходом в костный канал |
нет |
нет |
штифт |
60 суток |
|
|
4 |
диафиз, перфорация диаметром 1 мм |
края костной перфорации прижжены |
нет |
нет |
60 суток |
Микробиологическое исследование материала от экспериментальных животных осуществляли в соответствии с общепринятыми методами. В условиях микробиологической лаборатории проводили посев материала от животных, тотчас после его доставки, на плотные питательные среды. Для культивации использовали агар Мюллера–Хинтона (HIMEDIA® M211, Индия) с добавлением 5 % крови, а также дифференциально – диагностические хромогенные среды хромагар, уриселект, на котором микроорганизмы разной видовой принадлежности образуют колонии разных цветов. Параллельно материал помещали в ти-огликолевую среду для накопления микроорганизмов, присутствующих в ограниченном количестве, не позволяющем выявить их при прямом посеве. Посевы культивировали в термостате при 35 ± 2 °С в течение 24-48 часов. Проводя бактериоскопию подготовленных мазков изолированных колоний, оценивали тин-кториальные (окраска по Граму) и морфологические свойства выросших культур.
Определение видовой принадлежности выделенных бактерий осуществляли на бактериологическом анализаторе «Вайтек 2 компакт» (БиоМерье, Франция). В случае выявления представителей рода
Staphylococcus использовали экспресс – диагностикум «Стафи-латекс»-тест для дифференциации стафилококков» (ЗАО ЭКОлаб, РФ). Исследование проводили на 14 и 30 сутки эксперимента.
Для проведения сравнения результатов экспериментов в разных группах была применена балльная шкала оценки чистоты проведения:
0 баллов – микроорганизмы в материале не определяются;
-
1 балл – выявляется только сторонняя флора;
-
2 балла – выявляется S. aureus и сторонняя флора;
-
3 балла – выявляется только S. aureus .
Гистологическая оценка: аутопсийный материал фиксировали в нейтральном формалине, декальцинировали, заливали в парафин, получали срезы толщиной 4 микрона, окрашивали гематоксилин-эозином и пикросириусом красным. Изучали при стандартной световой микроскопии, фазово-контрастной и поляризационной микроскопии в микроскопе Leica DM 4000 B LED с камерой Leica DFC 7000 T.
Для проведения сравнения результатов экспериментов в разных группах была применена балльная шкала оценки результатов, аналогично шкале Smeltzer (табл. 4).
Таблица 4
Балльная шкала оценки результатов, аналогично шкале Smeltzer
|
Параметр |
Критерий оценки |
Баллы |
|
Внутрикостное острое воспаление |
отсутствует |
0 |
|
от минимального до слабого без формирования абсцесса |
1 |
|
|
от среднего до сильного без формирования абсцесса |
2 |
|
|
от минимального до слабого с формированием абсцесса |
3 |
|
|
от среднего до сильного с формированием абсцесса |
4 |
|
|
Внутрикостное хроническое воспаление |
отсутствует |
0 |
|
от минимального до слабого без выраженного фиброза |
1 |
|
|
от среднего до сильного без выраженного фиброза |
2 |
|
|
от минимального до слабого с выраженным фиброзом |
3 |
|
|
от среднего до сильного с выраженным фиброзом |
4 |
|
|
Некроз костной ткани |
отсутствует |
0 |
|
одиночный фокус некроза без формирования секвестров |
1 |
|
|
множественные фокусы некроза без формирования секвестров |
2 |
|
|
одиночный секвестр |
3 |
|
|
многочисленные секвестры |
4 |
Микрокомпьютерную томографию (микро-КТ) производили на сканере SkySkan 1178, при напряжении 65 Кв и токе 615 мкА, с фильтром А1 0.5 мм. Пространственное разрешение 84 мкм / пиксел. Реконструкция срезов произведена на программном обеспечении NRecon v1.6.10.4, 3D реконструкции выполнены в программе СTVol.
Для проведения сравнения результатов экспериментов в разных группах была применена балльная шкала оценки результатов, аналогично шкале Norden (табл. 5).
Статистический анализ микробиологического и томографического исследования проводились с использованием программного обеспечения OriginPro 2021. Данные были записаны как среднее значение ± стандартное отклонение. Статистическая разница между группами была определена с помощью критерия Тьюки. Для определения значимости различий между группами использовались тесты ANOVA (Р < 0,05). Значимые различия р < 0,05 между различными группами были помечены знаком *, р < 0,01
между различными группами – знаком **, р < 0,001 между различными группами – знаком ***.
Статистический анализ экспериментальных данных гистологического исследования проводился с использованием программного обеспечения GraphPad Prism 8.00 для Windows (GraphPad Software, США). Различия оценивали с помощью теста Краскела-Уоллиса с тестом множественного сравнения Данна. P-значения ≤ 0,05 считались статистически значимыми (*). Результаты статистического анализа представлены в виде медианных значений и интерквартильного размаха (интервал между 25 и 75 процентилями).
Таблица 5
Балльная шкала оценки результатов, аналогично шкале Norden
|
Параметр |
Критерий оценки |
Вес критерия, баллы |
|
Образование секвестров |
+ присутствует |
1 |
|
- отсутствует |
0 |
|
|
Реактивное периостальное формирование кости |
+ присутствует |
1 |
|
± неопределенно |
0,5 |
|
|
- отсутствует |
0 |
|
|
Деструкция костной ткани |
++ обширная, во всех отделах кости |
2 |
|
+ средняя, только в одном отделе кости |
1 |
|
|
± малая, только в одном отделе кости |
0,5 |
|
|
- отсутствует |
0 |
|
|
Изменения во всех отделах кости (дистальном, диафизе и проксимальном) |
+ присутствует |
1 |
|
± неопределенно |
0,5 |
|
|
- отсутствует |
0 |
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ
Модель 1
У животных в период наблюдений после бактериальной инокуляции не наблюдалось изменений в двигательной активности, шерстяном и кожном покровах. В первую неделю после операции животные щадили оперированные конечности, наблюдалась отечность, гиперемия краев послеоперационной раны. Через 30 суток у всех животных наблюдалось полное зарастание послеоперационной раны, формирования свищей, гнойного отделяемого не наблюдалось, полное восстановление целостности кожного покрова, кроме зоны свищевого хода, сформированного марлевой турундой со спиртом. Края свищевого хода эпителизировались. Гнойное отделяемое по свищу наблюдалось в небольших количествах, спонтанных свищевых ходов не образовалось.
По данным бактериологического исследования у всех животных после 14 суток бактериальной инокуляции был выявлен рост S. aureus (табл. 6). В двух образцах отмечалась дополнительная контаминация кишечной флорой. После 30 суток бактериальной инокуляции S. aureus был обнаружен в 4 образцах из 6 (66,7 % от общего количества). При этом только в двух образцах определялась монокультура S. aureus .
По результатам микро-КТ наблюдаются отсутствие регенерации (закрытия) сформированной костной перфорации, выраженный гиперостоз ткани по периферии костной перфорации (рис. 1). Отмечены рентгенологические признаки снижения плотности костной ткани по периферии от дефекта, секвестрация участков кости. Ось конечности в целом сохранена, но наблюда- ется некоторая деформация, скорее связанная с перестройкой костной ткани и снижением прочности в зоне формирования дефекта.
Таблица 6
Наличие роста микроорганизмов на 14 и 30 сутки. Модель 1
|
14 суток |
30 суток |
Количество животных |
|
S. aureus, E. faecalis |
S. aureus, E. faecalis |
2 |
|
S. aureus |
E. coli, P. mirabilis |
1 |
|
S. aureus |
E. coli |
1 |
|
S. aureus |
S. aureus |
2 |
По результатам гистологического исследования в большинстве образцов обнаруживаются фрагменты некротизированной кости, лишенные клеточных элементов. При окраске гематоксилином и эозином эти участки дают более выраженную эозинофилию, чем нормальная кость (рис. 2). При фазово-контрастной микроскопии тонкая волокнистая структура костной ткани не четко выражена, при поляризационной микроскопии в этой ткани резко снижена или отсутствует анизотропия. Дегенерирующие костные фрагменты окружены выраженной нейтрофильной инфильтрацией. Мозаично расположенные участки фиброзной ткани с фокусами кровоизлияний и воспалительной инфильтрации наблюдаются в части образцов. В одном из образцов отмечаются участки кости с признаками регенерации: больше клеточных элементов и анизотропия при поляризационной микроскопии носит другой характер (рис. 3).
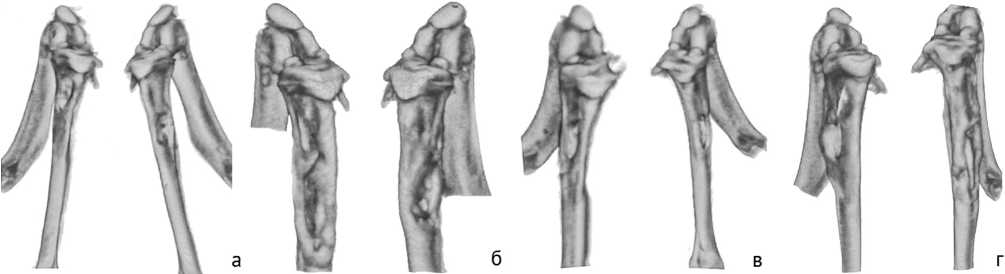
Рис. 1. Примеры трехмерных моделей большеберцовой кости животных по модели 1 в разные сроки после бактериальной инокуляции: а, в – 0 суток; б, г – 30 суток
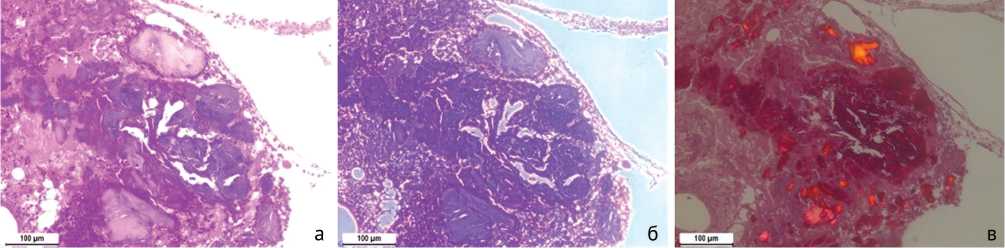
Рис. 2. Некротические изменения костной ткани и выраженное воспаление: а – стандартная световая микроскопия. Окраска гематоксилином и эозином; б – фазово-контрастная микроскопия; в – поляризационная микроскопия. Окраска пикросириусом красным. Увеличение 100×
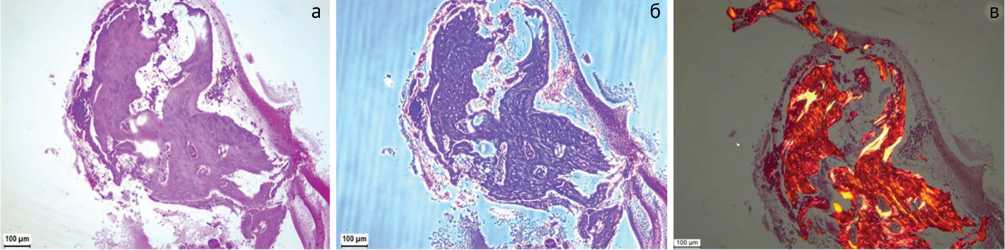
Рис. 3. Участок кости с признаками регенерации: а – стандартная световая микроскопия. Окраска гематоксилином и эозином; б – фазово-контрастная микроскопия; в – поляризационная микроскопия. Окраска пикросириусом красным. Увеличение 100×
Модель 2
У животных в период наблюдений после бактериальной инокуляции не наблюдалось изменений в двигательной активности, шерстяном и кожном покровах. В первую неделю после операции животные щадили оперированные конечности, наблюдалась отечность, гиперемия краев послеоперационной раны. Через 30 суток у всех животных наблюдалось полное зарастание послеоперационной раны, формирования свищей, гнойного отделяемого не наблюдалось.
По данным бактериологического исследования у всех животных после 14 суток бактериальной инокуляции был выявлен рост S. aureus (табл. 7). В двух из шести образцов отмечалась дополнительная контаминация кишечной флорой. После 30 суток бактериальной инокуляции S. aureus был обнаружен в 4 образцах из 6 (66,7 % от общего количества). При этом только в двух образцах определялась монокультура S. aureus .
Таблица 7
Наличие роста микроорганизмов на 14 и 30 сутки. Модель 2
|
14 суток |
30 суток |
Количество животных |
|
S. aureus |
S. aureus |
2 |
|
S. aureus, E. faecalis, E. coli |
E. faecalis, E. coli |
1 |
|
S. aureus |
E. coli |
1 |
|
S. aureus, P. mirabilis |
S. aureus, P. mirabilis |
1 |
|
S. aureus |
S. aureus, Klebsiella |
1 |
По результатам микро-КТ наблюдается отсутствие регенерации (закрытия) сформированной костной перфорации, выраженный гиперостоз ткани по периферии костной перфорации (рис. 4). Отмечены рентгенологические признаки снижения плотности костной ткани по периферии от дефекта, секвестрация участков кости, площадь дефекта в некоторых случаях даже увеличилась по сравнению с первоначальной. Ось конечности деформирована, что скорее связанно с перестройкой костной ткани и снижением прочности в зоне формирования дефекта.
По результатам гистологического исследования биоптатов этой модели в большинстве костных фрагментов отмечаются дистрофические изменения кости с сокращением числа остеоцитов, с разрыхлением и расслаиванием костного матрикса (рис. 5, а). Также происходит деструкция кости с формированием многочисленных мелких костных фрагментов, подвергающихся некрозу: при фазово-контрастной микроскопии в них выявляется более плотная зернисто-волокнистая структура (рис. 5, б), при поляризационной микроскопии отсутствует анизотропия (рис. 5, в). В окружающих тканях обнаруживается выраженная лимфо-макрофагальная инфильтрация с примесью нейтрофилов.
Модель 3
У животных в период наблюдений после бактериальной инокуляции не наблюдалось изменений в двигательной активности, шерстяном и кожном покровах. В первую неделю после операции животные щадили оперированные конечности, наблюдалась отечность, гиперемия краев послеоперационной раны в зоне выхода штифта. Через 30 суток у всех животных наблюдалось полное зарастание послеоперационной раны, спонтанных свищевых ходов не образовалось, но при удалении штифта отмечено гнойное отделяемое. В период наблюдения гнойных выделений по штифту не наблюдалось.
По данным бактериологического исследования у всех животных после 14 суток бактериальной инокуляции был выявлен рост S. aureus (табл. 8). После 30 суток бактериальной инокуляции S. aureus был обнаружен также во всех образцах (100 % от общего количества). При этом в трех образцах определялась монокультура S. aureus, а в остальных микст-культура.
Таблица 8
Наличие роста микроорганизмов на 14 и 30 сутки.
Модель 3
|
14 суток |
30 суток |
Количество животных |
|
S. aureus |
S. aureus |
3 |
|
S. aureus, E. faecium |
S. aureus, E. faecium |
1 |
|
S. aureus |
S. aureus, E. coli |
1 |
|
S. aureus, P. mirabilis |
S. aureus, P. mirabilis |
1 |
Для модели 3 характерна массивная инфекция: при удалении штифта через 60 суток после установки наблюдалась гнойное отделяемое из очага инфекции, выходящее вместе со штифтом.
По результатам микро-КТ наблюдалось снижение костной плотности в проксимальном отделе большеберцовой кости и зазор между штифтом и костной тканью (рис. 6).
Миграции металлоконструкций не отмечалось, однако деформации оси конечности и, возможно, срощен-ные переломы на штифте привели к изгибу штифтов у некоторых животных. Оценить изменение сформированного дефекта оказалось невозможным вследствие наводок металлоконструкции.
По результатам гистологического исследования биоптатов этой модели обнаруживаются многочисленные некротизированные костные фрагменты, окруженные лимфоцитами, макрофагами и нейтрофилами, отмечается образование секвестров (рис. 7). В биоптатах также встречаются некротизированные участки в мышечной и соединительной тканях с очагами выраженной воспалительной инфильтрации (рис. 8).
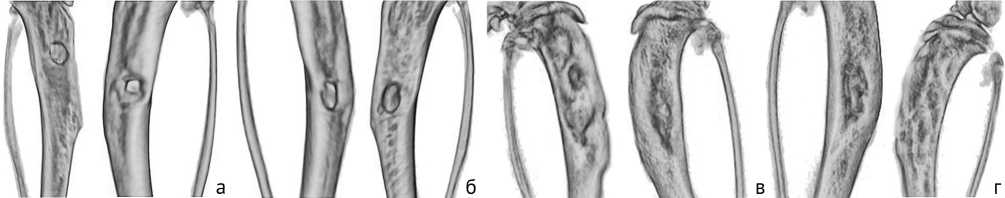
Рис. 4. Примеры трехмерных моделей б/б кости животного по модели 2 в разные сроки после бактериальной инокуляции: а, в – 0 суток; б, г – 30 суток
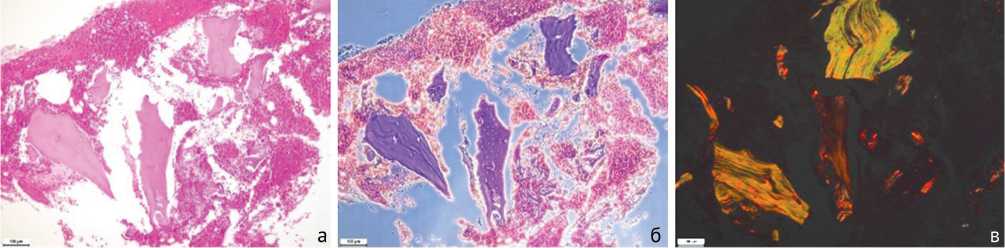
Рис. 5. Дистрофия, деструкция и некроз костной ткани и выраженное воспаление: а – стандартная световая микроскопия. Окраска гематоксилином и эозином; б – фазово-контрастная микроскопия. Окраска гематоксилином-эозином; в – поляризационная микроскопия. Окраска пикросириусом красным. Увеличение 100×
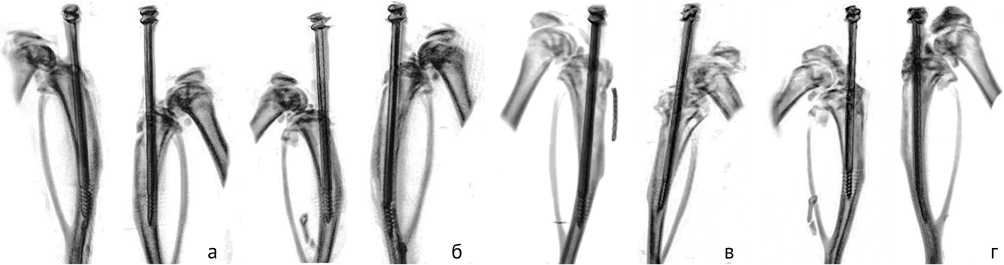
Рис. 6. Примеры трехмерных моделей б/б кости животного по модели 3 в разные сроки после бактериальной инокуляции: а, в – 0 суток; б, г – 30 суток
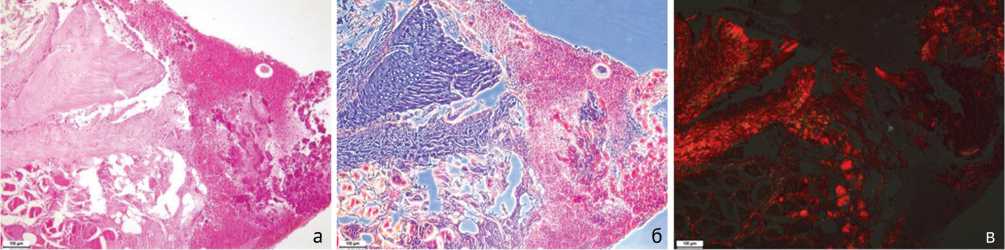
Рис. 7. Некроз костной ткани, формирование секвестров и выраженное воспаление: а – стандартная световая микроскопия. Окраска гематоксилином и эозином; б – фазово-контрастная микроскопия. Окраска гематоксилином-эозином; в – поляризационная микроскопия. Окраска пикросириусом красным. Увеличение 100×
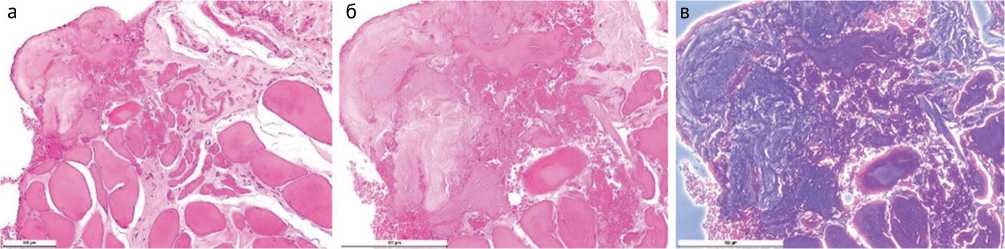
Рис. 8. Некротизированные участки в мышечной и соединительной тканях: а – стандартная световая микроскопия. Увеличение 200×; б – стандартная световая микроскопия. Увеличение 400×; в – фазово-контрастная микроскопия. Увеличение 400×. Окраска гематоксилином и эозином
Модель 4
У животных в период наблюдений после бактериальной инокуляции не наблюдалось изменений в двигательной активности, шерстяном и кожном покровах. В первую неделю после операции животные щадили оперированные конечности, наблюдалась отечность, гиперемия краев послеоперационной раны. Через 30 суток у всех животных наблюдалось полное зарастание послеоперационной раны, формирования свищей, гнойного отделяемого не наблюдалось.
По данным бактериологического исследования у всех животных после 14 суток бактериальной инокуляции был выявлен рост S. aureus (табл. 9). После 30 суток бактериальной инокуляции S. aureus был обнаружен в 5 из 6 образцов (83,3 % от общего количества). При этом только в одном образце определялась монокультура S. aureus , а в остальных микст-культура. Кроме того, в одном из образцов данной модели ни один микроорганизм не был определен.
Результаты микробиологического исследования представлены в таблице 9.
Таблица 9
Наличие роста микроорганизмов на 14 и 30 сутки.
Модель 4
|
14 суток |
30 суток |
Количество животных |
|
S. aureus |
– |
1 |
|
S. aureus |
S. aureus, S. epidermidis |
1 |
|
S. aureus |
S. aureus |
1 |
|
S. aureus, E. coli |
S. aureus, E. coli |
1 |
|
S. aureus, E. faecium |
S. aureus E. faecium |
1 |
|
S. aureus, P. mirabilis |
S. aureus, P. mirabilis |
1 |
По результатам микро-КТ наблюдалось увеличение плотности содержимого костномозгового канала, сохранение перфорации или ее увеличение, что является косвенным признаком развития остеомиелита Деформация оси конечностей меньше, чем в других группах, признаки секвестрации кости (рис. 9). У одного животного наблюдалось закрытие костной перфорации. Одно животное погибло на 58 сутки.
По результатам гистологического исследования биоптатов этой модели отмечается накопление фибринозно-гнойного экссудата, выраженная воспалительная инфильтрация тканей, очаговые некрозы и деструкция костной ткани с потерей ее тонкой структуры (рис. 10). В одном случае (умершее животное) на месте дефекта наблюдался крупный абсцесс с некротическим детритом в центре, вокруг которого располагается лейкоцитарный вал, состоящий преимущественно из ней- трофилов, а во внешнем слое находилась фиброзногрануляционная соединительная ткань с выраженной воспалительной инфильтрацией (рис. 11).
Сравнительные результаты томографического исследования по моделям создания гнойно-септического воспаления представлены в таблице 10 и рисунке 12.
Сравнительные результаты микробиологического исследования по моделям создания гнойно-септического воспаления представлены на рисунке 13.
Сравнительные результаты гистологического исследования по моделям создания гнойно-септического воспаления представлены в таблице 11.
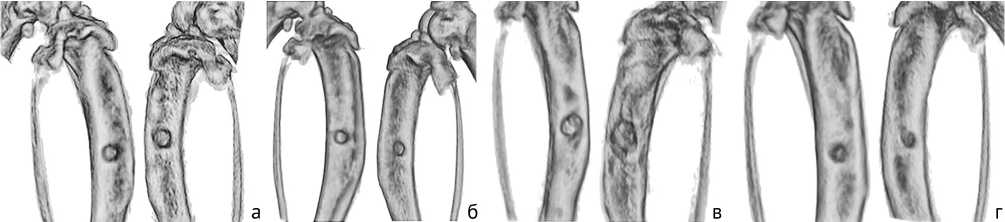
Рис. 9. Примеры трехмерных моделей большеберцовой кости животного по модели 4 в разные сроки после бактериальной инокуляции: а, в – 0 суток; б, г – 30 суток
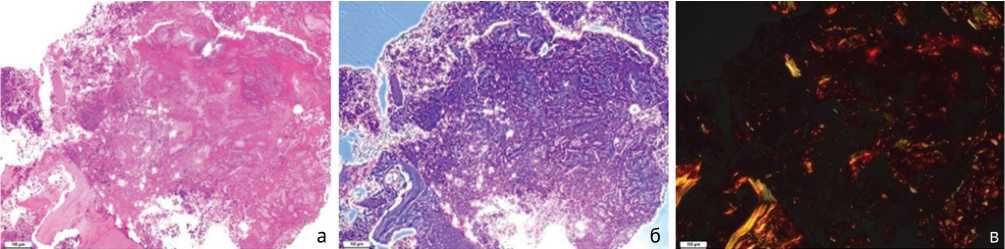
Рис. 10. Некротизированные фрагменты кости в окружении воспалительного инфильтрата: а – стандартная световая микроскопия. Окраска гематоксилином-эозином; б – фазово-контрастная микроскопия. Окраска гематоксилином и эозином; в – поляризационная микроскопия. Окраска пикросириусом красным. Увеличение 100×
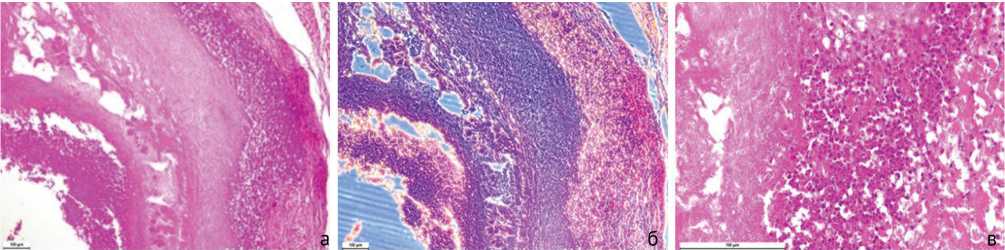
Рис. 11. Абсцесс на месте дефекта: а – стандартная световая микроскопия. Увеличение 100×; б – фазово-контрастная микроскопия. Увеличение 100×; в – стандартная световая микроскопия. Увеличение 400×. Окраска гематоксилином и эозином
Таблица 10
Сравнительные результаты томографического исследования
|
№ модели |
Образование секвестров |
Реактивное периостальное формирование кости |
Деструкция костной ткани |
Изменения в отделах кости |
|
1 |
0,5 ± 0,55 |
1 ± 0,0 |
0,75 ± 0,27 |
0,67 ± 0,0 |
|
2 |
0 ± 0,0 |
1 ± 0,0 |
2 ± 0,0 |
0,67 ± 0,0 |
|
3 |
1 ± 0,0 |
0,5 ± 0,0 |
2 ± 0,0 |
0,67 ± 0,0 |
|
4 |
1 ± 0,0 |
0,5 ± 0,0 |
0,33 ± 0,26 |
0,67 ± 0,0 |
Таблица 11
Сравнительные результаты гистологического исследования
|
№ модели |
Острое внутрикостное воспаление |
Хроническое внутрикостное воспаление |
Некроз костной ткани |
Всего |
|
1 |
1 (0; 2) |
3 (2; 3) |
2 (2; 4) |
6 (4; 9) |
|
2 |
1 (1; 2) |
4 (2; 4) |
2 (2; 3) |
7 (5; 9) |
|
3 |
3 (2; 4) |
2 (1; 2) |
4 (3; 4) |
9 (6; 10) |
|
4 |
2 (2; 4) |
1 (1; 1) |
3 (2; 4) |
6 (5; 9) |
|
1 и 2 |
p > 0,9999 |
p > 0,9999 |
p > 0,9999 |
p > 0,9999 |
|
1 и 3 |
p = 0,0970 |
p > 0,9999 |
p > 0,9999 |
p > 0,9999 |
|
1 и 4 |
p = 0,2997 |
p = 0,1131 |
p > 0,9999 |
p > 0,9999 |
|
2 и 3 |
p = 0,4963 |
p = 0,4452 |
p = 0,4907 |
p > 0,9999 |
|
2 и 4 |
p > 0,9999 |
p = 0,0471* |
p > 0,9999 |
p > 0,9999 |
|
3 и 4 |
p > 0,9999 |
p > 0,9999 |
p > 0,9999 |
p > 0,9999 |
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
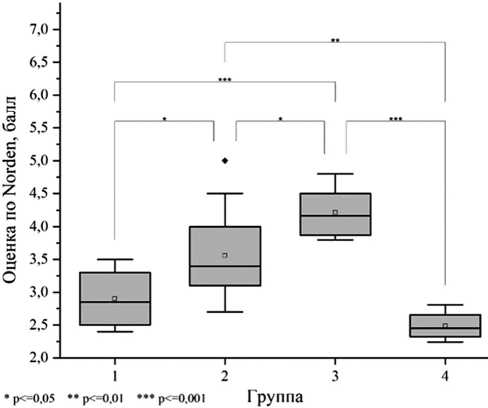
Рис. 12. Средние значения результатов томографического исследования по группам
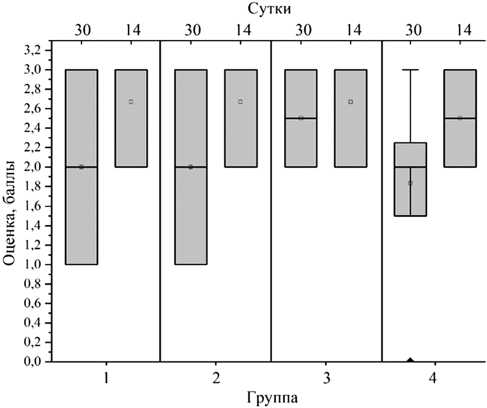
Рис. 13. Средние значения результатов микробиологического исследования по группам
В соответствии с литературными данными по обзору моделей бактериального создания остеомиелита на животных для последующего использования их в исследованиях остеопластических материалов, содержащих антибактериальные субстанции, в нашей работе мы провели сравнительный анализ четырех моделей, которые могут быть применены для последующего лечения животных с помощью имплантации резорбируемых остеопластических материалов – носителей антибактериальных субстанций. Основная задача разрабатываемых моделей и выбор методов диагностики – сохранение целостности кости.
Результаты исследования свидетельствуют о возможности создания экспериментального гнойно-септического воспаления у крыс к 14-60 суткам с помощью инокуляции чистой культуры S. aureus , которое представляет собой тяжелую, быстро прогрессирующую гнойную инфекцию – остеомиелит, приводящий к обширному разрушению кости с образованием секвестров.
Основным различием в степени тяжести воспаления при использовании различных моделей был различный объем деструкции костной ткани и некроза. Положительный результат создания модели воспале- ния обусловлен инокуляцией бактериального агента с полным заполнением костномозгового канала, что облегчает распространение бактериального агента. Авторы [41] использовали в качестве носителя инфицирующего агента аллокость для локализации S. aureus в зоне имплантации. В своей работе мы использовали 0,8 % раствор агара для уменьшения ретроградной миграции внесенной культуры S. aureus из костномозгового канала обратно через перфорацию после извлечения катетера без дополнительной пломбировки. Образование абсцесса у одного животного в четвертой группе, который мы связываем с выходом бактериального агента из костномозгового канала б/б кости, является осложнением при используемом инъекционном способе введения S. aureus, однако количество осложнений составляет лишь 2 %. Таким образом, указанный способ показал себя эффективным и не требующим внесения каких-либо материалов в образованные дефекты кости, что выгодно с точки зрения дальнейшего использования модели для последующего изучения новых хирургических и терапевтических протоколов лечения гнойно-септических воспалений с использованием биорезорбируемых материалов с антимикробными препаратами.
Формирование свищевого хода используется для локализации остеомиелитического очага с целью исключения развития осложнений и гибели животного [41], как правило, кроликов. Создание моделей гнойно-септического воспаления на крысах и кроликах значительно отличается друг от друга. Если при создании модели на кроликах формирование свищевого хода обеспечивает выживаемость, то при создании модели на крысах выживаемость животных составляет 98 % во всех представленных моделях, что связано с сильной иммунной системой. В связи с этим можно сделать вывод, что формирование свищевого хода не является обязательным при создании гнойно-септического воспаления у крыс.
При инокуляции S. aureus через костную перфорацию независимо от ее размера во всех моделях наблюдалось изменение анатомической формы большеберцовой кости. Низкие дозы активного бактериального агента (1,5·103 КОЕ) являются менее эффективными при создании гнойно-септического воспаления, хотя, по литературным данным, оптимальные инокуляцион-ные дозы культуры для крыс варьировали в диапазоне 103-106 КОЕ, причем в некоторых моделях открытых переломов используют всего 102 КОЕ [11]. Возможно, столь низкие дозы могут быть эффективны при использовании внутрикостных систем совместно с инокуляцией. При концентрации S. aureus 1,5·103 КОЕ физиологическая форма кости меняется менее чем в половине случаев, гиперостоз наблюдается только по краям костной перфорации, степень проявления характерных для остеомиелита признаков варьирует. Увеличение концентрации S. aureus в 1000 раз приводит к развитию стойких инфекций в большинстве случаев.
Изменения, наблюдаемые при томографическом исследовании, коррелировали с практически идентичными результатами гистологии. Характерные признаки остеомиелита – дистрофия, деструкция, некроз костной ткани, воспалительная инфильтрация окружающих тканей наблюдаются в большей степени при инокуляции S. aureus 1,5·106 КОЕ. Гнойный деструктивный некроз характерен инфекции, вызванной стафилококками [36]. Наиболее высокие показатели некроза костной ткани, согласно гистологическому исследованию, наблюдаются при использовании моделей 3 и 4, что связано, по нашему мнению, с более длительным сроком после инокуляции стафилококка. Показатель хронического внутрикостного воспаления наиболее высок у второй группы, причем различия по этому параметру между четвертой и второй группами статистически достоверны.
Культуры мазков, полученные с мест инокуляции, подтверждают присутствие S. aureus через 14 суток во всех образцах. Через 30 суток S. aureus не обнаружен в мазках 21 % образцов. Вместо S. aureus обнаружены грамположительные энтерококки E. faecium и грамотрицательные бактерии E. coli и P. mirabilis , относящиеся к кишечной флоре, что может свидетельствовать о контаминации раневого канала в постоперационном периоде.
Склерозирующий агент может быть использован, однако он, по нашим наблюдениям, незначительно влияет на формирование гнойно-септического воспаления. При высокой эффективности заражения животных по модели 4 наблюдалось одно выздоровление на шесть случаев. По литературным данным, 5 % морриат натрия, арахидоновая кислота использовались в качестве склерозирующих агентов при моделировании остеомиелита у животных. Buxton и коллеги при моделировании открытого перелома прерывали эндостальное кровоснабжение прижиганием, после чего проводили бактериальное заражение [15]. С одной стороны, локальное нарушение микроциркуляции и очаговый некроз делают кость более восприимчивой к инфекции, с другой стороны, могут искусственно искажать результаты исследований лечения, особенно тех, которые основаны на распределении системных антибиотиков по сосудам [2].
Имплантация инородных тел повышает восприимчивость к инфекциям и является альтернативой склерозирующим агентам. При введении штифта в костномозговой канал наблюдается устойчивая гнойная инфекция, что, вероятно, связано с образованием биопленки на поверхности введенной конструкции и внутри кости [42]. Бактерии внутри биопленки могут уклоняться от иммунологического ответа хозяина и часто переходить в спящее или покоящееся состояние [43], что может снизить эффективность антибиотиков и требовать значительного повышения минимальной эффективной концентрации препарата [44]. Кроме того, требуется дополнительное вмешательство для удаления штифта перед терапевтическим или хирургическим лечением. Данные моменты необходимо учитывать при выборе модели.
Таким образом, способ по модели 2 мы считаем наиболее технически простым и эффективным для создания гнойно-септического воспаления. Применимость разработанных моделей для использования в качестве экспериментальных при медико-биологических исследованиях остеопластических материалов, обладающих антибактериальными свойствами, требует отдельного изучения, однако основное требование к модели – сохранение целостности кости, выполнено.
В научной литературе для подтверждения эффективности создания гнойно-септического воспаления различными методами, как правило, животные выводятся из эксперимента [41, 45]. В работах по исследованию эффективности разработанных материалов для лечения гнойно-септического воспаления используется комплексная диагностика после выведения животных из эксперимента [20-24]. Рентгенологическая оценка и оценка клинических признаков использовалась одними авторами [25], микробиологическая и рентгенологическая оценки – другими [26]. Полное отсутствие или частичная диагностика не дают возможности оценить степень воспаления до начала лечения, интерпретация полученных результатов лечения может быть ложной. В своей работе мы использовали томографическое, микробиологическое и гистологическое исследование для обнаружения инфекции. При множестве существующих способов анализа бактериальной инфекции, наша задача заключалась в оценке наличия и степени гнойно-септического воспаления малоинва- зивными методами диагностики in vivo для получения исходных данных перед терапевтическим или хирургическим лечением. Это необходимо для возможности последующей оценки эффективности лечения и интерпретации его результатов.
По нашим наблюдениям, наиболее достоверно степень заражения может быть определена при применении совокупности томографического, гистологического и микробиологического исследований. Так, бактериальная инфекция внутри кости может быть очень изменчивой и пространственно неоднородной, мазки с некоторой вероятностью могут давать ложноотрицательные результаты. Томографическая оценка позволяет визуализировать инфицирование кости по периостальной реакции, остеолизу, отеку мягких тканей, деформации, образованию секвестра, спонтанному перелому, но улучшения могут отставать от действительных при лечении. При использовании внутрикостных конструкций эффективность томографической оценки значительно снижается из-за артефактов от металлических деталей. Гистологическая оценка биоптатов учитывает наличие характерных для остеомиелита морфологических признаков: некроз костной ткани и воспалительная инфильтрация. Но при обособленном гистологическом исследовании степень проявления этих признаков может значительно варьировать в зависимости от участка взятия, размера и количества биоптатов, поэтому комплексный подход дает более объективную и репрезентативную картину протекания процесса остеомиелита.
Совместное применение указанных малоинвазивных методов диагностики in vivo позволяет получить адекватную оценку степени инфицирования перед лечением.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Продемонстрированы результаты разработки четырех экспериментальных моделей создания гнойно-септического воспаления большеберцовой кости крысы. Во всех моделях проведена инокуляция бактериальной культуры золотистого стафилококка в концентрации 1,5·103 или 1,5·106 КОЕ в растворе агара в костномозговой канал б/б кости крысы. Отличие моделей состоит в концентрации бактериального агента, использовании склерозирующего агента, формировании свищевого хода или использовании интрамедуллярного штифта.
Все описанные модели пригодны для создания гнойно-септического воспаления, однако наиболее технически простым является способ заполнения костномозгового канала бактериальным агентом инокуляцией последнего в растворе агара без использования склерозирующего агента, имплантации инородных тел, формирования свищевого хода. Предложенный способ хорошо воспроизводим, позволяет создать гнойно-септическое воспаление за 30 дней.
В работе показано, что известные способы диагностики (томографическое, микробиологическое и гистологическое исследования) в совокупности являются эффективным методом определения уровня инфекции без разрушения объекта. Это является важным для получения исходных данных перед терапевтическим или хирургическим лечением, что дает возможность последующей оценки эффективности лечения и интерпретации его результатов.
Таким образом, нам удалось достичь поставленной цели, продемонстрировав результаты разработки экспериментальных моделей создания гнойно-септического воспаления с применением малоинвазивных методов диагностики in vivo , что позволит получить адекватную оценку степени инфицирования перед лечением.
Список литературы Модели создания гнойно-септического воспаления большеберцовой кости у крысы для оценки действия биорезорбируемых материалов с антимикробными препаратами
- Lew DP, Waldvogel FA. Osteomyelitis. Lancet. 2004;364(9431):369-79. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16727-5
- Inzana JA, Schwarz EM, Kates SL, Awad HA. Biomaterials approaches to treating implant-associated osteomyelitis. Biomaterials. 2016;81:58-71. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.12.012
- Rao N, Lipsky BA. Optimising antimicrobial therapy in diabetic foot infections. Drugs. 2007;67(2):195-214. doi: 10.2165/00003495-20076702000003
- Cram P, Lu X, Kates SL, Singh JA, Li Y, Wolf BR. Total knee arthroplasty volume, utilization, and outcomes among Medicare beneficiaries, 19912010. JAMA. 2012;308(12):1227-36. doi: 10.1001/2012.jama
- Rosas S, Ong AC, Buller LT, Sabeh KG, Law TY, Roche MW, Hernandez VH. Season of the year influences infection rates following total hip arthroplasty. World J Orthop. 2017;8(12):895-901. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v8.i12.895
- Geurts JAP, van Vugt TAG, Arts JJC. Use of contemporary biomaterials in chronic osteomyelitis treatment: Clinical lessons learned and literature review. J Orthop Res. 2021;39(2):258-264. doi: 10.1002/jor.24896
- Schwarz EM, Parvizi J, Gehrke T, Aiyer A, Battenberg A, Brown SA, Callaghan JJ, Citak M, Egol K, Garrigues GE, Ghert M, Goswami K, Green A, Hammound S, Kates SL, McLaren AC, Mont MA, Namdari S, Obremskey WT, O'Toole R, Raikin S, Restrepo C, Ricciardi B, Saeed K, Sanchez-Sotelo J, Shohat N, Tan T, Thirukumaran CP, Winters B. 2018 International Consensus Meeting on Musculoskeletal Infection: Research Priorities from the General Assembly Questions. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(5):997-1006. doi: 10.1002/jor.24293
- Sheehy SH, Atkins BA, Bejon P, Byren I, Wyllie D, Athanasou NA, Berendt AR, McNally MA. The microbiology of chronic osteomyelitis: prevalence of resistance to common empirical anti-microbial regimens. J Infect. 2010;60(5):338-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2010.03.006
- Trampuz A, Zimmerli W. Diagnosis and treatment of infections associated with fracture-fixation devices. Injury. 2006;37 Suppl 2:S59-66. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2006.04.010
- Murray CK, Hsu JR, Solomkin JS, Keeling JJ, Andersen RC, Ficke JR, Calhoun JH. Prevention and management of infections associated with combat-related extremity injuries. J Trauma. 2008;64(3 Suppl):S239-51. doi: 10.1097/TA.0b013e318163cd14
- Reizner W, Hunter JG, O'Malley NT, Southgate RD, Schwarz EM, Kates SL. A systematic review of animal models for Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis. Eur Cell Mater. 2014 25;27:196-212. doi: 10.22203/ecm.v027a15
- Histing T, Garcia P, Holstein JH, Klein M, Matthys R, Nuetzi R, Steck R, Laschke MW, Wehner T, Bindl R, Recknagel S, Stuermer EK, Vollmar B, Wildemann B, Lienau J, Willie B, Peters A, Ignatius A, Pohlemann T, Claes L, Menger MD. Small animal bone healing models: standards, tips, and pitfalls results of a consensus meeting. Bone. 2011;49(4):591-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2011.07.007
- Lindsey BA, Clovis NB, Smith ES, Salihu S, Hubbard DF. An animal model for open femur fracture and osteomyelitis: Part I. J Orthop Res. 2010;28(1):38-42. doi: 10.1002/jor.20960
- Li B, Jiang B, Dietz MJ, Smith ES, Clovis NB, Rao KM. Evaluation of local MCP-1 and IL-12 nanocoatings for infection prevention in open fractures. J Orthop Res. 2010;28(1):48-54. doi: 10.1002/jor.20939
- Buxton TB, Travis MT, O'Shea KJ, McPherson JC 3rd, Harvey SB, Plowman KM, Walsh DS. Low-dose infectivity of Staphylococcus aureus (SMH strain) in traumatized rat tibiae provides a model for studying early events in contaminated bone injuries. Comp Med. 2005;55(2):123-128.
- Antoci V Jr, Adams CS, Hickok NJ, Shapiro IM, Parvizi J. Vancomycin bound to Ti rods reduces periprosthetic infection: preliminary study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;461:88-95. doi: 10.1097/BLO.0b013e318073c2b2
- Holt J, Hertzberg B, Weinhold P, Storm W, Schoenfisch M, Dahners L. Decreasing bacterial colonization of external fixation pins through nitric oxide release coatings. J Orthop Trauma. 2011;25(7):432-437. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0b013e3181f9ac8a
- Hienz SA, Sakamoto H, Flock JI, Mörner AC, Reinholt FP, Heimdahl A, Nord CE. Development and characterization of a new model of hematogenous osteomyelitis in the rat. J Infect Dis. 1995;171(5):1230-1236. doi: 10.1093/infdis/171.5.1230
- Itokazu M, Yamamoto K, Yang WY, Aoki T, Kato N, Watanabe K. The sustained release of antibiotic from freeze-dried fibrin-antibiotic compound and efficacies in a rat model of osteomyelitis. Infection. 1997;25(6):359-363. doi: 10.1007/BF01740818
- Mendel V, Simanowski HJ, Scholz HC, Heymann H. Therapy with gentamicin-PMMA beads, gentamicin-collagen sponge, and cefazolin for experimental osteomyelitis due to Staphylococcus aureus in rats. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005;125(6):363-368. doi: 10.1007/s00402-004-0774-2
- Cevher E, Orhan Z, Mülazimoglu L, Sensoy D, Alper M, Yildiz A, Ozsoy Y. Characterization of biodegradable chitosan microspheres containing vancomycin and treatment of experimental osteomyelitis caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with prepared microspheres. Int J Pharm. 2006;317(2):127-135. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.03.014
- Orhan Z, Cevher E, Mülazimoglu L, Gürcan D, Alper M, Araman A, Ozsoy Y. The preparation of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride-loaded chitosan and pectin microspheres: their evaluation in an animal osteomyelitis model. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88(2):270-275. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.88B2.16328
- Cevher E, Orhan Z, Sensoy D, Ahiskali R, Kan PL, Sagirli O, Mülazimoglu L. Sodium fusidate-poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres: preparation, characterisation and in vivo evaluation of their effectiveness in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis. JMicroencapsul. 2007;24(6):577-595. doi: 10.1080/02652040701472584
- Orhan Z, Cevher E, Yildiz A, Ahiskali R, Sensoy D, Mülazimoglu L. Biodegradable microspherical implants containing teicoplanin for the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010;130(1):135-142. doi: 10.1007/s00402-009-0886-9
- Solberg BD, Gutow AP, Baumgaertner MR. Efficacy of gentamycin-impregnated resorbable hydroxyapatite cement in treating osteomyelitis in a rat model. J Orthop Trauma. 1999;13(2):102-106. doi: 10.1097/00005131-199902000-00006
- Zelken J, Wanich T, Gardner M, Griffith M, Bostrom M. PMMA is superior to hydroxyapatite for colony reduction in induced osteomyelitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;462:190-194. doi: 10.1097/BLO.0b013e3180ca9521
- Norden CW. Experimental osteomyelitis. I. A description of the model. J Infect Dis. 1970;122(5):410-418. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.5.410
- Subasi M, Kapukaya A, Kesemenli C, Kaya H, Sari I. Effect of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor on treatment of acute osteomyelitis. An experimental investigation in rats. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2001;121(3):170-173. doi: 10.1007/s004020000209
- Burch S, Bisland SK, Bogaards A, Yee AJ, Whyne CM, Finkelstein JA, Wilson BC. Photodynamic therapy for the treatment of vertebral metastases in a rat model of human breast carcinoma. J Orthop Res. 2005;23(5):995-1003. doi: 10.1016/j.orthres.2004.12.014
- Ersoz G, Oztuna V, Coskun B, Eskandari MM, Bayarslan C, Kaya A. Addition of fusidic acid impregnated bone cement to systemic teicoplanin therapy in the treatment of rat osteomyelitis. J Chemother. 2004;16(1):51-55. doi: 10.1179/joc.2004.16.1.51
- Lucke M, Schmidmaier G, Sadoni S, Wildemann B, Schiller R, Stemberger A, Haas NP, Raschke M. A new model of implant-related osteomyelitis in rats. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2003;67(1):593-602. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.10051
- Bisland SK, Chien C, Wilson BC, Burch S. Pre-clinical in vitro and in vivo studies to examine the potential use of photodynamic therapy in the treatment of osteomyelitis. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2006;5(1):31-38. doi: 10.1039/b507082a
- García-Alvarez F, Navarro-Zorraquino M, Castro A, Grasa JM, Pastor C, Monzón M, Martínez A, García-Alvarez I, Castillo J, Lozano R. Effect of age on cytokine response in an experimental model of osteomyelitis. Biogerontology. 2009;10(5):649-658. doi: 10.1007/s10522-008-9211-1
- Darouiche RO. Treatment of infections associated with surgical implants. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(14):1422-1429. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra035415
- Smeltzer MS, Thomas JR, Hickmon SG, Skinner RA, Nelson CL, Griffith D, Parr TR Jr, Evans RP. Characterization of a rabbit model of staphylococcal osteomyelitis. J Orthop Res. 1997;15(3):414-421. doi: 10.1002/jor.1100150314
- Norden CW, Myerowitz RL, Keleti E. Experimental osteomyelitis due to Staphylococcus aureus or Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a radiographic-pathological correlative analysis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1980;61(4):451-460.
- Inzana JA, Trombetta RP, Schwarz EM, Kates SL, Awad HA. 3D printed bioceramics for dual antibiotic delivery to treat implant-associated bone infection. Eur Cell Mater. 2015;30:232-247. doi: 10.22203/ecm.v030a16
- Koort JK, Mäkinen TJ, Suokas E, Veiranto M, Jalava J, Knuuti J, Törmälä P, Aro HT. Efficacy of ciprofloxacin-releasing bioabsorbable osteoconductive bone defect filler for treatment of experimental osteomyelitis due to Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005;49(4):1502-1508. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.4.1502-1508.2005
- Li D, Gromov K, S0balle K, Puzas JE, O'Keefe RJ, Awad H, Drissi H, Schwarz EM. Quantitative mouse model of implant-associated osteomyelitis and the kinetics of microbial growth, osteolysis, and humoral immunity. J Orthop Res. 2008;26(1):96-105. doi: 10.1002/jor.20452
- Kadurugamuwa JL, Sin L, Albert E, Yu J, Francis K, DeBoer M, Rubin M, Bellinger-Kawahara C, Parr TR Jr, Contag PR. Direct continuous method for monitoring biofilm infection in a mouse model. Infect Immun. 2003;71(2):882-890. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.2.882-890.2003
- Королев С.Б., Митрофанов В.Н., Живцов О.П., Орлинская Н.Ю., Юлина Д.П. Моделирование хронического остеомиелита в эксперименте. Гений ортопедии. 2022;28(2):223-227. doi: 10.18019/1028-4427-2022-28-2-223-227
- Waeiss RA, Negrini TC, Arthur RA, Bottino MC. Antimicrobial effects of drug-containing electrospun matrices on osteomyelitis-associated pathogens. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;72(7):1310-1319. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2014.01.007
- Rani SA, Pitts B, Beyenal H, Veluchamy RA, Lewandowski Z, Davison WM, Buckingham-Meyer K, Stewart PS. Spatial patterns of DNA replication, protein synthesis, and oxygen concentration within bacterial biofilms reveal diverse physiological states. J Bacteriol. 2007;189(11):4223-4233. doi: 10.1128/JB.00107-07
- Mihailescu R, Furustrand Tafin U, Corvec S, Oliva A, Betrisey B, Borens O, Trampuz A. High activity of Fosfomycin and Rifampin against methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus biofilm in vitro and in an experimental foreign-body infection model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(5):2547-2553. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02420-12
- O'Reilly T, Mader JT. Rat model of bacterial osteomyelitis of the tibia. In: Zak O, Sande MA, editors. Handbook of Animal Models of Infection: Experimental Models in Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. San Diego, CA: Academic Press. (1999), p. 561-575. doi: 10.1016/B978-012775390-4/50205-0


