Моделирование актин-миозинового мотора скелетных мышц: влияние температуры и биохимических параметров на механику стационарных сокращений
Автор: Шворина Е.Н.
Журнал: Российский журнал биомеханики @journal-biomech
Статья в выпуске: 1 (63) т.18, 2014 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Кинетическая схема взаимодействия миозиновых поперечных мостиков с актином, АТФ и продуктами ее гидролиза, АДФ и неорганическим фосфатом состоит из нескольких присоединенных к актину и отсоединенных от него состояний миозиновой головки и функций перехода из одного состояния в другое. Соответствующая математическая модель представляет собой систему дифференциальных уравнений первого порядка в частных производных для плотностей распределения концентраций мостиков в каждом из состояний. Цель работы состояла в создании программного продукта для расчета различных кинетических моделей мышечного сокращения, а также в разработке конкретной кинетической модели, воспроизводящей результаты экспериментальных исследований стационарных сокращений мышцы при различных значениях температуры и концентраций АТФ, АДФ и неорганического фосфата. Реализован программный модуль, позволяющий рассчитать микро- и макроскопические характеристики мышечного волокна при изометрическом сокращении в условиях полной активации и в ходе стационарного укорочения с постоянной скоростью. Разработана модель, включающая в себя семь присоединенных и три отсоединенных состояния миозинового мостика, которая представляет собой обобщение модели Ferenczi et al. (2005), предложенной ранее для описания структурных изменений в сокращающихся мышечных клетках. Расчеты воспроизводят экспериментальные зависимости динамической жесткости волокна, развиваемой им силы и скорости потребления АТФ от скорости деформации (укорочения) волокна, температуры и концентраций субстрата и продуктов гидролиза АТФ.
Актин, миозин, мышечное сокращение, модель
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/146216127
IDR: 146216127 | УДК: 531/534:
Текст научной статьи Моделирование актин-миозинового мотора скелетных мышц: влияние температуры и биохимических параметров на механику стационарных сокращений
Скелетная мышца состоит из пучков мышечных волокон. Каждое волокно – гигантская многоядерная клетка, вдоль оси которой расположены тысячи миофибрилл, состоящих из белковых нитей двух видов – тонких (актиновых) и толстых (миозиновых). Сокращение происходит в результате взаимного перемещения нитей с минимальными изменениями их длин (деформации меньше 0,003).
Сила, развиваемая сокращающейся мышцей, возникает в результате циклического взаимодействия миозиновых поперечных мостиков с актиновой нитью. Кинетическая схема такого взаимодействия состоит из нескольких присоединенных и нескольких отсоединенных состояний миозиновой головки и переходов из одного состояния в другое, скорости которых зависят от микроскопических перемещений мостика и от биохимических и термодинамических параметров: концентраций
Шворина Елена Николаевна, м.н.с. Института механики, Москва субстрата и продуктов реакции гидролиза АТФ, а также температуры. Соответствующая математическая модель представляет собой систему дифференциальных уравнений первого порядка в частных производных для плотностей распределения концентраций мостиков в каждом из состояний.
За последние 50 лет, начиная с классической работы Хаксли [18], было разработано множество кинетических моделей мышечного сокращения [1, 11, 27, 29], увязывающих в единую схему механические и биохимические процессы в цикле поперечных мостиков. Такие модели различаются количеством присоединенных и отсоединенных состояний миозиновой головки и функциями перехода из одного состояния в другое. Для выяснения молекулярных механизмов работы актинмиозинового мотора полезно иметь програмные средства количественного анализа таких моделей, позволяющие сравнить результаты расчетов с опытными данными, в том числе такими, которые не нашли объяснения в рамках имеющихся моделей.
Целью данной работы было создание программного продукта для расчета кинетических моделей мышечного сокращения с разным количеством присоединенных и отсоединенных состояний поперечных мостиков и возможностью конструирования различных функций перехода между состояниями, который позволяет включать в рассмотрение те или иные параметры, влияющие на макроскопическое поведение мышечного волокна, а также разработка конкретной кинетической модели, воспроизводящей результаты современных экспериментальных исследований, включая зависимости характеристик стационарного мышечного сокращения от термодинамических и биохимических параметров.
Описание модели
В цикле работы миозинового мостика можно выделить несколько биохимических и механических переходов. Эксперименты [14, 18] показывают наличие в миозиновых головках эффективного «упругого элемента», поэтому присоединенные к актину головки будем полагать линейно упругими, не конкретизируя локализацию упругого элемента в молекуле. Соответственно, механическими переходами будем называть такие изменения формы миозиновой головки или характера ее присоединения к актину, при которых происходит смещение положения равновесия их упругого элемента вдоль оси нитей. Таким образом, при механических переходах изменение деформации упругого элемента головки происходит и без относительного проскальзывания нитей за счет изменения формы.
В рассматриваемой модели имеются три биохимических (гидролиз АТФ, сброс фосфата, сброс АДФ) и три механических перехода (обратный поворот «рычага», т.е. шейного участка миозиновой головки относительно ее глобулярного домена, стереоспецифическое застегивание на актине и «рабочий» поворот рычага [13]) между 16 возможными биохимически и механически различными состояниями (рис. 1).
За полный цикл от присоединения головки к актину до ее отсоединения после связывания «новой» молекулы АТФ должны произойти все шесть переходов, а соответствующие семь «активных», т.е. реализуемых состояний мостика определяются последовательностью этих переходов. В модели автора выбран следующий порядок переходов присоединенного мостика (см. рис. 1): обратный поворот рычага с закрытием АТФазного «кармана», гидролиз АТФ, «застегивание» [13], сброс фосфата, силогенерирующий шаг, сброс АДФ [15]. Кроме того, будем предполагать, что сброс АДФ происходит со сдвигом положения равновесия на 0,5 нм [8]. Связывание АТФ с миозиновой головкой сопровождается конформационными изменениями на ее актин-связывающей поверхности [15]. В модели автора оба эти процесса происходят не последовательно, а в один этап.
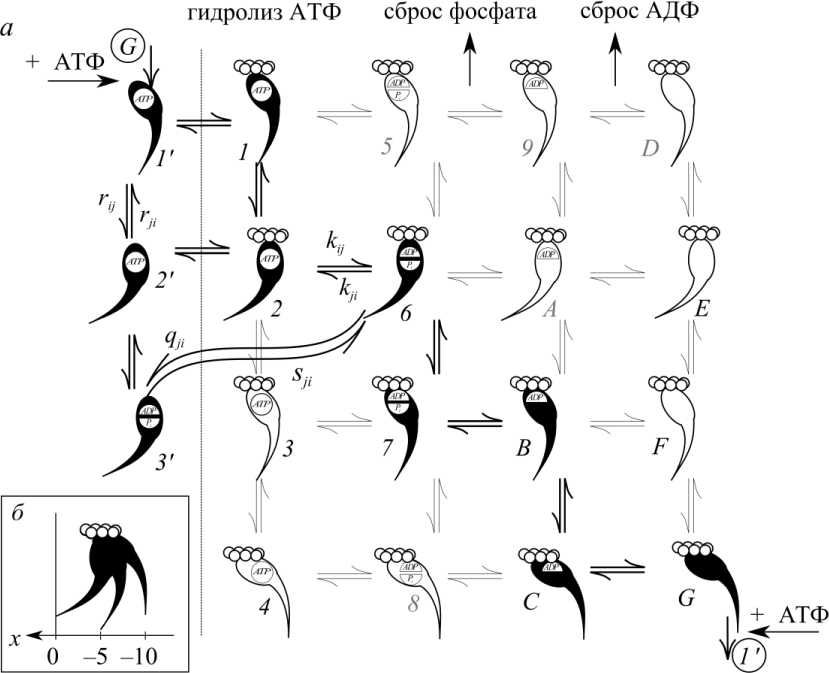
Рис. 1. Схема цикла работы миозинового мостика. Показаны все возможные состояния миозинового мостика. Механические переходы соответствуют (сверху вниз): обратному повороту «рычага», стереоспецифическому застегиванию на актине, «рабочему» повороту рычага. Биохимические переходы соответствуют гидролизу АТФ, сбросу фосфата и сбросу АДФ. Реализуемые в модели состояния выделены черным, фрагмент актиновой нити показан кружками, Z-диск расположен справа
Переходы между тремя отсоединенными состояниями соответствуют гидролизу АТФ и предшествующему ему обратному повороту рычага с закрытием АТФазного кармана [23]. В каждом из этих состояний миозиновая головка может обратимо присоединиться к актину с образованием слабосвязанного, нестереоспецифического комплекса. Поскольку такое слабое связывание с актином почти не влияет на скорости переходов между состояниями миозиновой головки [16], будем считать скорости переходов между тремя отсоединенными и тремя слабосвязанными с актином состояниями одинаковыми. Отметим, что программный комплекс позволяет выбирать любой порядок чередования механических и биохимических переходов, но описанная здесь конкретная модель позволила добиться наилучшего согласования результатов с известными экспериментальными данными.
Введем осевую координату миозиновой головки х , которую будем отсчитывать от положения равновесия ее упругого элемента в слабосвязанном состоянии 2 с закрытым АТФазным «карманом» и «взведенным» рычагом (см. рис. 1).
Броуновское движение отсоединенных головок ограничено упругим элементом, поэтому они могут присоединяться к актину лишь в ограниченном интервале значений х. Зададим свободную энергию для каждого присоединенного к актину состояния головки в виде G1 = G0 +k(x-hi )2 /2, где G0 - свободная энергия Гиббса в отсутствии энергии упругой деформации или в точке равновесия; k – жесткость мостика; hi – положение равновесия состояния; прямые и обратные скорости переходов между состояниями с номерами i и j связаны между собой термодинамическим соотношением kjj = exp(Gi-Gj)
kji kBT где kB и Т – постоянная Больцмана и абсолютная температура. Считается, что жесткость упругих элементов мостика одинакова во всех присоединенных состояниях, а положение равновесия hi – разное для разных состояний. При механических переходах происходит изменение hi. Графики зависимостей Gi(x) показаны на рис. 2.
Все скорости для предотвращения численной неустойчивости из-за высокой жесткости системы уравнений были ограничены сверху значением 30 000 с–1 с сохранением термодинамического соотношения (1).
Состояние системы описывается функциями n i ( x , t ) – плотностями распределений по координате х головок, находящихся в i -м присоединенном состоянии, и вероятностями пребывания в j -м отсоединенном состоянии N j ( t ) в данный момент времени t .
Система дифференциальных уравнений модели имеет следующий вид:
nn
^T + v ( t ) -L = -n i (x, t ) tx
t k j ( x ) + D q8Vx )
. i*j=1 j=1
+ f n,(x, t) kji(x) + "DNj(I) Sji(x), i*j=1j=1
Dd Dd
-=- = -ijt(t) 2 rz+ S Jsj-(x)dx +У, ryNj+5 Jqji(x) nj(x, t)dx, dt Li*V=* j=1 J i*j=1j=1
dD
EInidx+ENi=1-i=1
Здесь k ij – скорости переходов между присоединенными состояниями; r ij – скорости переходов между отсоединенными состояниями; s ij – скорости присоединения и q ij – скорости отсоединения.
Зависимости скоростей переходов от х показаны на рис. 3.
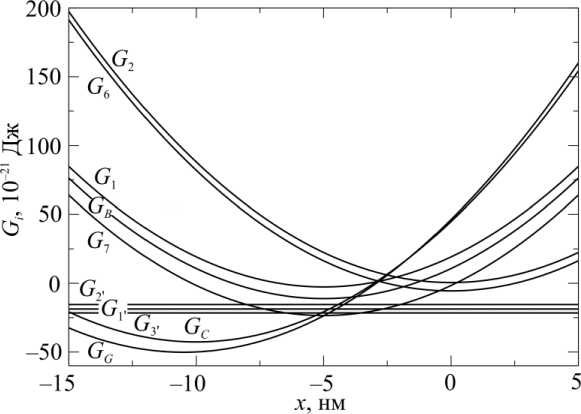
Рис. 2. Зависимости свободных энергий состояний (30 С, стандартные условия: [P] = 0,5 ммоль, [ADP] = 0,05 ммоль, [ATP] = 4 ммоль) от смещения миозиновой головки x
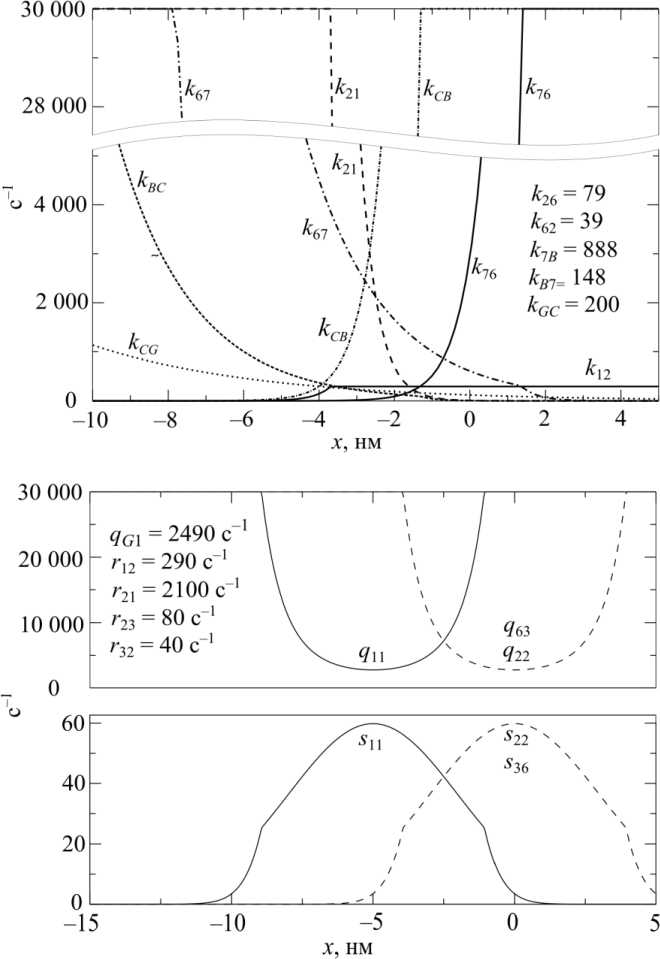
Рис. 3. Скорости переходов между состояниями как функции x : k ij – скорости переходов между присоединенными состояниями; r ij – скорости переходов между отсоединенными состояниями; s ij – скорости присоединения; q ij – скорости отсоединения (30 С, стандартные условия)
Для стационарных сокращений (—L = 0; = 0; v = const) получаем систему tt линейных обыкновенных дифференциальных и алгебраических уравнений:
n vi
x
d
D
d
D
=-n ( x) Z k y ( x )+Z qy ( x ) + Z n j ( x ) k ji ( x )+Z N j s ji ( x ),
D
N i r ij
_ i^j =1
_ i^j =1
d
j =1
D
i*j =1
d
j =1
+ZJ s y ( x > dx +yr ij N j +
j =1
d
i*j =1
D
Z J q ji ( x ) n j ( x ) dx = o, j =1
Z J n i dx+yN t =1.
В качестве граничного условия выступало условие интегрируемости n i при х → ±∞.
Эта система решается следующим образом. На первом этапе методом Адамса находили «базисные» решения n il ( x ) уравнений (3) с граничными условиями n il ( x 0 ) = 0 для случая, когда все N j = 0, за исключением N l = 1.
Тогда
ni Nlnil
будет «полным» решением системы. Подставляя такие разложения n в систему (4) и уравнение (5) и заменяя интегрирование на суммирование значений в точках расчетной сетки методом трапеций, получаем систему линейных алгебраических уравнений для N j . Решение этой системы подставляем в (6) для нахождения n i . При численной реализации решаем задачу Коши с граничными условиями n i = 0 при x = x 0 , x 0 x , x 0 2 x , x 0 3 x , а x 0 выбирается настолько большим, чтобы его дальнейшее увеличение не приводило к изменению n i ( x ) на всем расчетном интервале с машинной точностью. Расчет прекращали при x = x min , которое выбирается так, чтобы его дальнейшее уменьшение также не приводило к изменению численного решения.
Для изометрического сокращения ( v = 0) система принимает вид
-
- ni ( x )
N i
t k ij (x ) + Djo, ( x )
. i*j =1 j =1
+ f пДx ) k j, (x ) + D N jj x ) = 0, i^j =1 j =1
Dd D d
E r ij +E J 4 ( x ) dx + E r jj N j +E R ji ( x ) n j ( x ) dx =0, . j*j =1 j =1 J i*j =1 j =1
dD
E Jni-dx+EN=1- i=1 i=1
Значения функций в узлах расчетной сетки х р получаем, решая систему
линейных алгебраических уравнений для значений n ,. ( xp ) и N i :
—и х„ ip
dD d D
Е kij(xp)+Е чу(xp) + Еп j(xp) ku(xp)+Е Njsij(xp)=0, i^j=1 j=1 J i^j=1 j=1
Dd
D
-
■ N i E r j +Ё p ij -( x ) dx + E
_ j*i= 1 j =1
i*j =1
d rijNj+E J^ji(x) nj(x)dx=0, j=1
dD
E J ndx +E N i =1, i =1 i =1
где p = 0, … , p N , интегралы вычисляются методом трапеций.
Матрица этой системы имеет блочный вид.
|
( A 0 |
0 • A i ' |
•• 0 •• 0 |
B 0) B i |
(n ^ n 0 n i |
0^ 0 |
|
|
0 |
0 • |
Ap |
B p |
n p |
• 9 0 |
|
|
v C 0 |
C i • |
C p |
P 7 |
N |
H |
N = ( N 1,..., N d ) , H j = ( n i( x j ),..., n d ( x j )) .
Решение этой системы
p
N = H ( P-TC i A i' B i )' , n j = "A7' Bi N .
i =1
В результате расчетов получаем распределения по x мостиков в каждом из присоединенных состояний и их количество в каждом из отсоединенных состояний. На рис. 4 можно увидеть результаты расчетов n i ( x ) для изометрического сокращения ( а ) и стационарного сокращения с максимальной скоростью v = v max = 1550 нм/c ( б ) при 10 С. Видно, что укорочение с максимальной скоростью приводит к сдвигу распределений миозиновых головок в каждом из присоединенных к актину состояний в направлении меньших значений x , и, кроме того, происходит их перераспределение между состояниями. Из полученных таким образом распределений вывели следующие
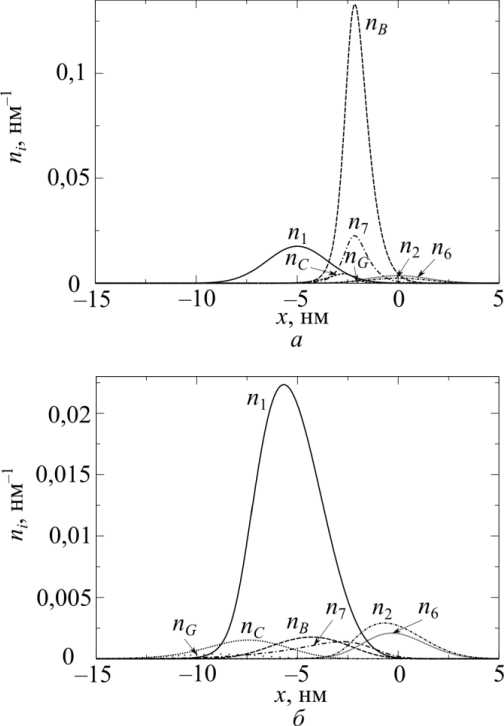
Рис. 4. Распределения миозиновых головок по состояниям n i ( x ) при 10 С и стандартных условиях: а – при изометрическом сокращении; б – при стационарном сокращении с максимальной скоростью ( v = v max = 1550 нм/с)
d макроскопические величины: силу F = kV р; (x-ht) dx, динамическую жесткость i-1
(учитывая, что часть податливости саркомера приходится на актиновые и миозиновые нити, а часть - на миозиновые мостики [21, 22]), скорость гидролиза АТФ (при стационарных сокращениях она равна скорости связывания АТФ с миозиновыми головками) QATP = Пвдв1<Хх , а также кажущиеся константы скорости перехода из одного состояния в другое, которые можно сравнить с известными экспериментальными данными.
Выбор параметров модели
Значения параметров модели оценивались по имеющимся экспериментальным данным. Осевые перемещения при «застегивании» миозиновой головки на актине и при повороте рычага, а также закрытия АТФазного кармана полагались равными 5 нм. За отсчетную конфигурацию актин-миозинового комплекса принимались состояния 2 и 6 , в которых миозиновая головка слабо присоединена к актину непосредственно перед или сразу после гидролиза АТФ, когда «рычаг» уже произвел обратный поворот. Соответственно h 1 = -5 нм, h 2 = 0 нм, h3 = -5 нм, h 4 = -10 нм, h4' = -10,5 нм. Последний сдвиг равновесия обусловлен небольшим изменением конфигурации актинмиозинового комплекса при сбросе АДФ [8, 10]. Константы скоростей переходов между тремя отсоединенными от актина состояниями ( r ij , i , j = 1, 2, 3) и их температурная зависимость определяли по данным работы [36].
Поскольку слабое связывание миозиновых головок с актином почти не влияет на скорости переходов между первыми тремя состояниями миозиновой головки (открытое и закрытое состояния АТФазного кармана для комплекса миозин - АТФ и постгидролизное состояние с закрытым карманом [37]), скорости переходов между первыми тремя слабо присоединенными к актину состояниями головки полагались такими же, как и для соответствующих отсоединенных состояний. Жесткость миозиновой головки, присоединенной к актину как сильно, так и слабо, полагалась одинаковой и равной 1,75 пН/нм [20, 22]. Скорости слабого присоединения миозиновых головок к актину s ij задавали в виде однотипных функций осевой координаты: они были симметричны относительно положения равновесия данного состояния h j и быстро снижались до нуля при отклонении от положения равновесия на 5 нм (см. рис. 3). Скорости обратных переходов q j задавались по соотношению (1).
Скорость отсоединения миозиновой головки, прочно связанной с актином, при связывании ею АТФ и зависимость этой скорости от температуры оценивались по результатам экспериментов с быстро фотолизуемым негидролизуемым аналогом АТФ в отсутствии АДФ [35]. Скорости прямых и обратных быстрых силогенерирующих переходов: «застегивания на актине» k 67, к 76 и поворота «рычага» kBC , kCB - выбирали так, чтобы суммарные эффективные скорости этих переходов к 67 + к 76, kBC + kCB не возрастали слишком сильно при умеренных укорочениях, точнее в области 0 < x < 5 нм. Также было предположено, что сброс фосфата происходит уже после застегивания миозиновой головки на актине, но до поворота рычага (см. рис. 1) и скорость этого процесса не зависит от механической координаты, а АДФ сбрасывается уже после поворота рычага из полностью открытого АТФазного кармана [15].
Кроме того, было положено, что скорость сброса АДФ увеличивается при укорочении волокна, т.е. при перемещении актина к М-линии, а сам этот процесс, как уже упоминалось выше, сопровождается смещением положения равновесия на 0,5 нм ( h 4 = -10 нм, h 4 * = -10,5 нм).
Зависимости скоростей переходов из одного состояния в другое от температуры t, С, задавались в виде k4 (t ) = kij (5o)exp(- Hj-aT ), где H - постоянные; aT = 1/(273,15 + t) - 1/278,15. Соответственно, независимые от микродеформации компоненты свободной энергии Gi0 зависели от температуры так, чтобы соотношение (1) выполнялось тождественно.
Уточнение значений параметров модели, главным образом тех, которые характеризуют температурную зависимость скоростей переходов, проводилось путем сравнения базовых характеристик, полученных в результате расчетов, с их экспериментальными значениями. В числе этих базовых характеристик были использованы среднее число миозиновых головок, присоединенных к актину, и скорость гидролиза АТФ в ходе изометрического сокращения при низкой (10 С) и высокой (30 С) температурах.
Результаты и обсуждение
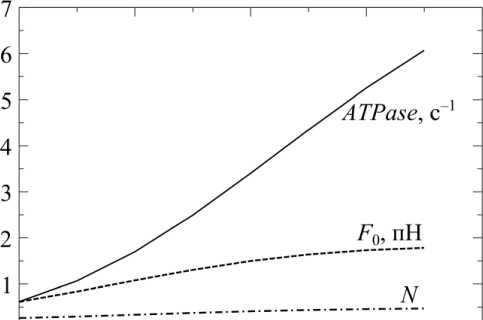
На рис. 5 изображены температурные зависимости доли присоединенных мостиков, силы, развиваемой волокном, и скорости гидролиза АТФ при изометрическом сокращении. Количество присоединенных мостиков остается практически неизменным при изменении температуры, в то время как изометрическая сила и скорость гидролиза АТФ растут с температурой, причем скорость гидролиза растет в несколько раз быстрее, чем изометрическая сила. Увеличение силы с температурой обусловлено опережающим ростом доли прочно присоединенных генерирующих силу миозиновых мостиков, в то время как полное число миозиновых головок, присоединенных к актину слабо или сильно, остается практически неизменным. Все эти закономерности соответствуют экспериментальным наблюдениям [2, 17, 25, 26].
На рис. 6 изображена зависимость развиваемой силы от скорости укорочения при разных температурах ( а ) и зависимость максимальной скорости укорочения от температуры ( б ). Графики сила – скорость имеют гиперболический вид, соответствующий уравнению Хилла. Максимальная скорость возрастает с изменением температуры на 10 С в 2,3 раза, что согласуется с результатами экспериментов, проведенных на мышцах лягушки [28].
_i_________________।_________________i_________________i_________________i_________________।_________________
10 20 30 40
t,°C
Рис. 5. Температурные зависимости доли присоединенных мостиков N , силы, развиваемой волокном F , пН, и скорости гидролиза АТФ ATPase , с –1 , при изометрическом сокращении и в стандартных условиях
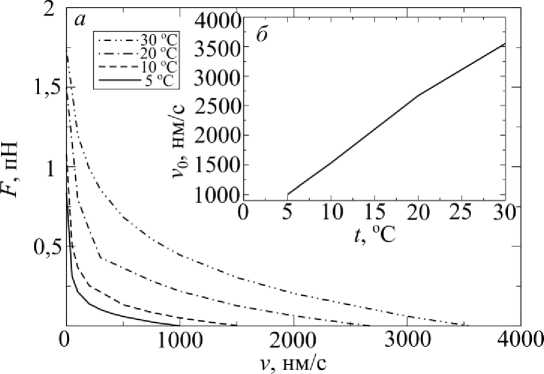
Рис. 6. Зависимости: а – развиваемой силы от скорости укорочения при разных температурах; б – максимальной скорости укорочения от температуры
На рис. 7 изображены зависимость количества присоединенных мостиков от скорости укорочения при разных температурах и зависимость динамической жесткости волокна от развиваемой силы. При расчетах считалось, что при изометрическом сокращении податливость (величина обратная жесткости) актиновых и миозиновых нитей составляет 40% податливости саркомера [21]. Графики жесткость – сила при всех температурах хорошо аппроксимируются прямыми и при высоких температурах находятся в хорошем соответствии с экспериментальными данными, полученными на мышцах лягушки [14].
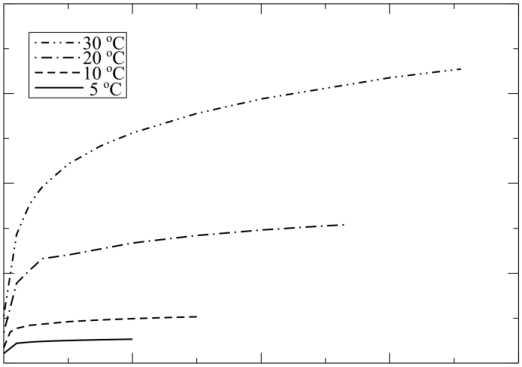
Зависимость скорости гидролиза АТФ от скорости укорочения при разных температурах приведена на рис. 8, а зависимости изометрической силы и максимальной скорости от концентрации АТФ при разных температурах показаны на рис. 9, а и б соответственно. Результаты расчетов коррелируют с данными экспериментов [4, 5, 12, 33].
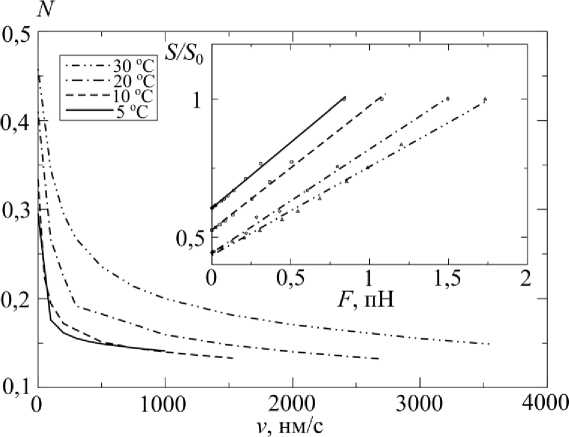
Рис. 7. Зависимость доли присоединенных мостиков N от скорости укорочения и зависимость динамической жесткости волокна S / S 0 от развиваемой силы при укорочении с постоянной скоростью (прямые аппроксимируют расчетные точки) при разных температурах и в стандартных условиях
2000 v, нм/с
Рис. 8. Зависимость скорости гидролиза АТФ от скорости укорочения при разных температурах (в стандартных условиях)
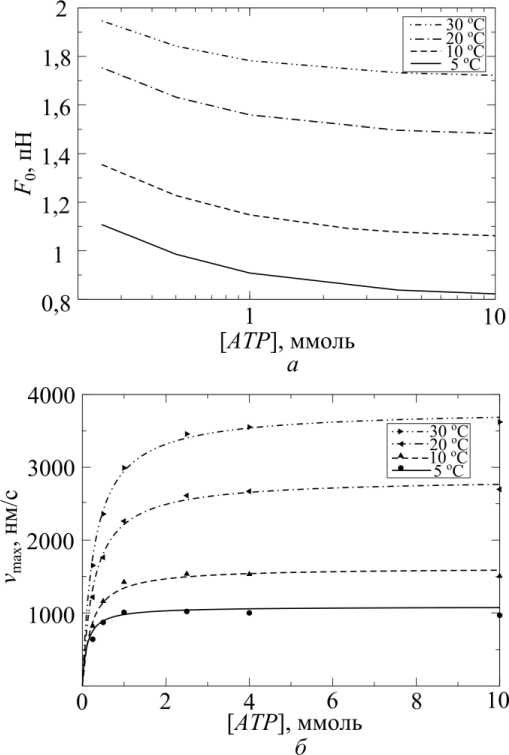
Рис. 9. Зависимости: а – изометрической силы; б – максимальной скорости v max от концентрации АТФ при разных температурах (концентрации АДФ и фосфата – стандартные). Расчетные точки v max аппроксимируются кривыми Михаэлиса– Ментен с константами Михаэлиса K M (5 ) = 0,115, K M (10 ) = 0,320, K M (20 ) = 0,284, K M (30 ) = 0,287 (показаны кривыми вместе с расчетными точками)
На рис. 10 показаны зависимости изометрической силы и максимальной скорости от концентрации АДФ при разных температурах. Вид кривых совпадает с результатами, полученными в экспериментах [5, 7, 31]. С ростом температуры кривая изометрической силы смещается вверх без изменения формы, что согласуется с результатами экспериментов [7]. Кроме того, расчет предсказывает снижение чувствительности максимальной скорости к температуре при больших концентрациях АДФ.
На рис. 11 приведены зависимости изометрической силы ( а ) и максимальной скорости укорочения ( б ) от концентрации неорганического фосфата при разных температурах. Результаты моделирования зависимостей изометрической силы (см. рис. 10, а ) и динамической жесткости (не показаны) мышечных волокон от концентрации неорганического фосфата хорошо описывают данные экспериментов [5, 6, 15, 34]. Чем выше температура, тем слабее эффект добавления фосфата на развиваемую силу. Эти результаты расчетов также хорошо описывают эксперименты [19]. Однако проведенные расчеты предсказывают снижение максимальной скорости укорочения с ростом концентрации неорганического фосфата, особенно при высокой температуре. Это не соответствует результатам экспериментов [5], показывающих независимость v max от концентрации фосфата.
Следует отметить, что до сих пор нет окончательной ясности в вопросе о том, в какой момент цикла работы миозиновой головки происходит сброс неорганического фосфата из активного центра миозиновой головки. В исходной схеме Лимна–Тейлора
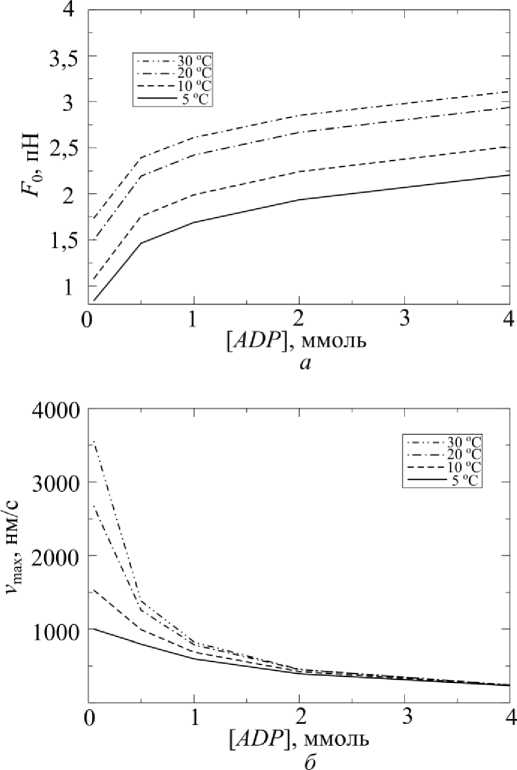
Рис. 10. Зависимости: а – изометрической силы; б – максимальной скорости от концентрации АДФ при разных температурах (концентрации АТФ и фосфата – стандартные)
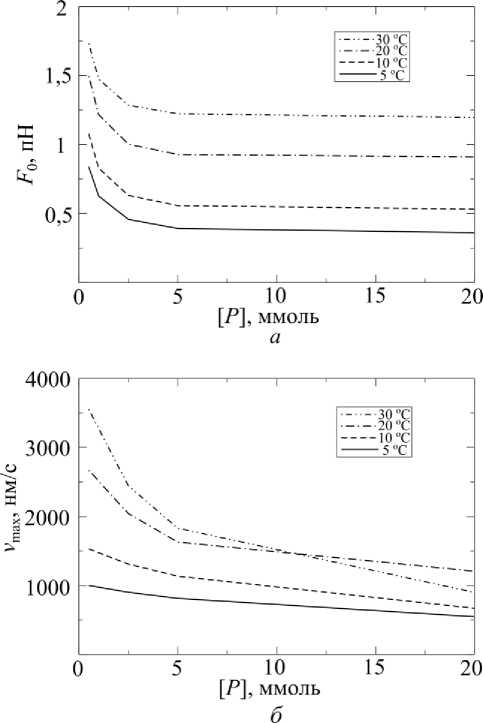
Рис. 11. Зависимости: а – изометрической силы; б – максимальной скорости от концентрации фосфата при разных температурах (концентрации АТФ и АДФ – стандартные)
сброс фосфата и силогенерирующий шаг миозиновой головки происходят одновременно [24]. Со временем появилось некоторое количество данных о том, что сброс фосфата происходит после силогенерирующего шага [9, 30, 32].
В представленной модели генерация силы происходит в два этапа, а сброс фосфата происходит после первого силогенерирующего шага, «застегивания» миозиновой головки на актине, но до второго и последнего шага – поворота «рычага». Были также рассмотрены другие кинетические схемы, в которых сброс фосфата происходит после поворота рычага или до его «застегивания». В этих случаях не удалось воспроизвести зависимости изометрической силы и динамической жесткости от концентраций фосфата и температуры, даже меняя в широких пределах скорость сброса фосфата и вид ее зависимости от х . Предположение, сделанное автором, позволило воспроизвести зависимости силы и динамической жесткости от концентрации фосфата и от температуры, но, к сожалению, неудовлетворительно описывало действие фосфата на скоростные характеристики мышечных волокон. Результаты данного моделирования не дают окончательного ответа на вопрос о месте сброса фосфата в цикле актинмиозинового взаимодействия, сопряженного с гидролизом АТФ. Для прояснения этого вопроса, с одной стороны, нужны дополнительные эксперименты, а с другой, – проведение модельных расчетов ответов напряжения на ступенчатые изменения длины мышечных волокон при различной концентрации фосфата, моделирующих эксперименты [3].
Описанная выше модель является расширением и обобщением модели [13], в которой были конкретизированы зависимости констант скорости переходов от микроперемещения головки х и дополнительно введены переходы, соответствующие сбросу АДФ и фосфата. В целом результаты моделирования широкого круга экспериментов в рамках предложенной модели показали ее способность адекватно описывать зависимость макроскопических характеристик от температуры, скорости укорочения волокон и концентраций АТФ, АДФ и, отчасти, неорганического фосфата. В то же время данная модель предсказывает некоторые структурные характеристики сокращения, которые могут быть проверены с помощью рентгеновской дифракции и, возможно, других методов.
Благодарности
Автор благодарит академика С.С. Григоряна и А.К. Цатуряна за поддержку и внимание к работе. Исследование поддержано грантами РФФИ 04-11-00908 и 13-04-40100-Н.
Список литературы Моделирование актин-миозинового мотора скелетных мышц: влияние температуры и биохимических параметров на механику стационарных сокращений
- Цатурян А.К., Антипов Д.M. Кинетическая модель мышцы: моделирование стационарных сокращений//Биофизика. -1991. -Т. 36, № 4. -С. 669-675.
- Bershitsky S.Y., Tsaturyan A.K. The elementary force generation process probed by temperature and length perturbations in muscle fibres from the rabbit//The Journal of Physiology. -2002. -Vol. 540, № 3. -P. 971-988.
- Caremani M., Dantzig J., Goldman Y.E., Lombardi V., Linari M. Effect of inorganic phosphate on the force and number of myosin cross-bridges during the isometric contraction of permeabilized muscle fibers from rabbit psoas//Biophysical Journal. -2008. -Vol. 95, № 12. -P. 5798-5808.
- Cooke R., Bialek W. Contraction of glycerinated muscle fibers as a function of the ATP concentration//Biophysical Journal. -1979. -Vol. 28, № 2. -P. 241-258.
- Cooke R., Pate E. The effects of ADP and phosphate on the contraction of muscle fibers//Biophysical Journal. -1985. -Vol. 48, № 5. -P. 789-798.
- Coupland M.E., Puchert E., Ranatunga K.W. Temperature dependence of active tension in mammalian (rabbit psoas) muscle fibres: effect of inorganic phosphate//The Journal of Physiology. -2001. -Vol. 536, № 3. -P. 879-891.
- Coupland M.E., Pinniger G.J., Ranatunga K.W. Endothermic force generation, temperature-jump experiments and effects of increased [MgADP] in rabbit psoas muscle fibres//The Journal of Physiology. -2005. -Vol. 567, № 2. -P. 471-492.
- Dantzig J.A., Hibberd M.G., Trentham D.R., Goldman Y.E. Cross-bridge kinetics in the presence of MgADP investigated by photolysis of caged ATP in rabbit psoas muscle fibres//The Journal of Physiology. -1991. -Vol. 432 -P. 639-680.
- Dantzig J.A., Goldman Y.E., Millar N.C., Lacktis J., Homsher E. Reversal of the cross-bridge force-generating transition by photogeneration of phosphate in rabbit psoas muscle fibres//The Journal of Physiology. -1992. -Vol. 451. -P. 247-278.
- Dantzig J.A., Barsotti R.J., Manz S., Sweeney H.L., Goldman Y.E. The ADP release step of the smooth muscle cross-bridge cycle is not directly associated with force generation//Biophysical Journal. -1999. -Vol. 77, № 1. -P. 386-397.
- Eisenberg E., Hill T.L., Chen Y. Cross-bridge model of muscle contraction. Quantitative analysis//Biophysical Journal. -1980. -Vol. 29, № 2. -P. 195-227.
- Ferenczi M.A., Goldman Y.E., Simmons R.M. The dependence of force and shortening velocity on substrate concentration in skinned muscle fibres from Rana temporaria//The Journal of Physiology. -1984. -Vol. 350. -P. 519-543.
- Ferenczi M.A., Bershitsky S.Y., Koubassova N., Siththanandan V., Helsby W.I., Panine P., Roessle M., Narayanan T., Tsaturyan A.K. The "roll and lock" mechanism of force generation in muscle//Structure. -2005. -Vol. 1, № 13. -P. 131-141.
- Ford L.E., Huxley A.F., Simmons R.M. Tension transients during steady shortening of frog muscle fibres//The Journal of Physiology. -1985. -Vol. 361. -P. 131-150.
- Geeves M.A., Holmes K.C. The molecular mechanism of muscle contraction//Advances in Protein Chemistry. -2005. -Vol. 71. -P. 161-193.
- Gyimesi M., Kintses B., Bodor A., Perczel A., Fischer S., Bagshaw C.R., Málnási-Csizmadia A. The mechanism of the reverse recovery step, phosphate release, and actin activation of Dictyostelium myosin II//The Journal of Biological Chemistry. -2008. -Vol. 283, № 13. -P. 8153-8163.
- He Z.H., Bottinelli R., Pellegrino M.A., Ferenczi M.A., Reggiani C. ATP consumption and efficiency of human single muscle fibers with different myosin isoform composition//Biophysical Journal. -2000. -Vol. 79, № 2. -P. 945-961.
- Huxley A.F. Muscle structure and theories of contraction//Progress in Biophysics and Biophysical Chemistry. -1957. -Vol. 7. -P. 255-318.
- Karatzaferi C., Chinn M.K., Cooke R. The force exerted by a muscle cross-bridge depends directly on the strength of the actomyosin bond//Biophysical Journal. -2004. -Vol. 87, № 4. -P. 2532-2544.
- Lewalle A., Steffen W., Stevenson O., Ouyang Z., Sleep J. Single-molecule measurement of the stiffness of the rigor myosin head//Biophysical Journal. -2008. -Vol. 94, № 6. -P. 2160-2169.
- Linari M., Caremani M., Piperio C., Brandt P., Lombardi V. Stiffness and fraction of myosin motors responsible for active force in permeabilized muscle fibers from rabbit psoas//Biophysical Journal. -2007. -Vol. 92, № 7. -P. 2476-2490.
- Linari M., Dobbie I., Reconditi M., Koubassova N., Irving M., Piazzesi G., Lombardi V. The stiffness of skeletal muscle in isometric contraction and rigor: the fraction of myosin heads bound to actin//Biophysical Journal. -1998. -Vol. 74, № 5. -P. 2459-2473.
- Málnási-Csizmadia A., Woolley R.J., Bagshaw C.R. Resolution of conformational states of Dictyostelium myosin II motor domain using tryptophan (W501) mutants: implications for the open-closed transition identified by crystallography//Biochemistry. -2000. -Vol. 39, № 51. -P. 16135-16146.
- Pate E., Cooke R. A model of cross-bridge action: the effects of ATP, ADP and Pi//Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility. -1989. -Vol. 10. -P. 181-196.
- Pate E., Wilson G.J., Bhimani M., Cooke R. Temperature dependence of the inhibitory effects of orthovanadate on shortening velocity in fast skeletal muscle//Biophysical Journal. -1994. -Vol. 66, № 5. -P. 1554-1562.
- Piazzesi G., Reconditi M., Koubassova N., Decostre V., Linari M., Lucii L., Lombardi V. Temperature dependence of the force-generating process in single fibres from frog skeletal muscle//The Journal of Physiology. -2003. -Vol. 549, № 1. -P. 93-106.
- Propp M.B. A model of muscle contraction based upon component studies//Lectures on Mathematics in the Life Sciences. -1986. -Vol. 16. -P. 61-74.
- Rall J.A., Woledge R.C. Influence of temperature on mechanics and energetics of muscle contraction//American Journal of Physiology. -1990. -Vol. 259, № 2. -P. R197-R203.
- Smith D.A., Geeves M.A. Strain-dependent cross-bridge cycle for muscle//Biophysical Journal. -1995. -Vol. 69. -P. 524-537.
- Steffen W., Sleep J. Using optical tweezers to relate the chemical and mechanical cross-bridge cycles//Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. -2004. -Vol. 359, № 1452. -P. 1857-1865.
- Stienen G.J., Kiers J.L., Bottinelli R., Reggiani C. Myofibrillar ATPase activity in skinned human skeletal muscle fibres: fibre type and temperature dependence//The Journal of Physiology. -1996. -Vol. 493, № 2. -P. 299-307.
- Takagi Y., Shuman H., Goldman Y.E. Coupling between phosphate release and force generation in muscle actomyosin//Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. -2004. -Vol. 359, № 1452. -P. 1913-1920.
- Tesi C., Colomo F., Nencini S., Piroddi N., Poggesi C. Modulation by substrate concentration of maximal shortening velocity and isometric force in single myofibrils from frog and rabbit fast skeletal muscle//The Journal of Physiology. -1999. -Vol. 516, № 3. -P. 847-853.
- Tesi C., Colomo F., Nencini S., Piroddi N., Poggesi C. The effect of inorganic phosphate on force generation in single myofibrils from rabbit skeletal muscle//Biophysical Journal. -2000 -Vol. 78, № 6. -P. 3081-3092.
- Thirlwell H., Corrie J.E., Reid G.P., Trentham D.R., Ferenczi M.A. Kinetics of relaxation from rigor of permeabilized fast-twitch skeletal fibers from the rabbit using a novel caged ATP and apyrase//Biophysical Journal. -1994. -Vol. 67, № 6. -P. 2436-2447.
- Urbanke C., Wray J. A fluorescence temperature-jump study of conformational transitions in myosin subfragment 1//Biochemical Journal. -2001. -Vol. 358, № 1. -P. 165-173.
- Zeng W., Conibear P.B., Dickens J.L., Cowie R.A., Wakelin S., Málnási-Csizmadia A., Bagshaw C.R. Dynamics of actomyosin interactions in relation to the cross-bridge cycle//Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. -2004. -Vol. 359, № 1452. -P. 1843-1855.


