Моделирование модификаций Девайна и Зудина уравнения Рэлея-Плессе динамики пузырька в трубке
Автор: Клотц Александр, Хайненен Куливерто
Журнал: Техническая акустика @ejta
Статья в выпуске: т.10, 2010 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Микроскопические пузырьки используются в качестве контрастного вещества в ультразвуковых медицинских исследованиях. При моделировании поведения свободных пузырьков (находящихся в свободном пространстве) с использованием уравнения Рэлея-Плессе их динамика внутри сосуда остаётся недостаточно ясной. В статье динамика микропузырьков в цилиндрической трубке моделируется двумя модифицированными уравнениями Рэлея-Плессе. Одно из уравнений получено Ю. Б. Зудиным в 1991 г., другое - Ч. Девайном в 1961. Результаты моделирования сопоставлены друг с другом, с аналитическими решениями и с экспериментальными данными Установлено, что обе модели показывают снижение резонансной частоты и амплитуды колебаний пузырьков при уменьшении радиуса трубки
Ультразвук, контрастное вещество, пузырёк, трубка, сосуд, уравнение рэлея-плессе
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14316265
IDR: 14316265
Текст научной статьи Моделирование модификаций Девайна и Зудина уравнения Рэлея-Плессе динамики пузырька в трубке
Electronic Journal «Technical Acoustics»
Within the human body the bubbles travel in arteries, veins, and capillaries, which are close to cylindrical in form. It is known that non-infinite environments affect bubble dynamics. For instance, a bubble oscillating near a wall will be threaded by a jet that pushes the bubble boundary farthest from the wall into the opposite boundary, firing the jet at the wall and collapsing the bubble into a toroid [12]. Thus, infinite-field models may not be appropriate for bubbles within tubes. A model of radius versus time is important in the study of contrast agent dynamics, as it predicts the ideal frequency for bubble excitation and allows calculation of the pressure and shear forces experienced by the vessel wall, which is a quantity necessary for ultrasound therapy [26]. The results of this paper will allow quick calculations of the necessary parameters for diagnostic and focused contrast-enhanced ultrasound without the need for complex models or extended computation times, leading to improved treatment planning for focused ultrasound therapy.
Numerical models from Sassaroli and Hynynen [21] as well as Oguz and Prosperetti, using the boundary integral method, [18] can determine the resonance frequency of a bubble within a tube. The resonance frequency is expected to decrease as the radius of the tube becomes smaller. A numerical model from Qin and Ferrara [19], using the finite element method, gives similar predictions via different techniques and also predicts the radius of the bubble as a function of time. Miao and Gracewski [16] use a coupled finite element and boundary element method to model the bubble shape with time. More recently, this model has been tested experimentally. A thesis by Jianying Cui Atkisson [1] predicts the frequency response of a bubble in a polygonal channel. The model of Bull and Ye [27] predicts the bubble shape and surrounding velocity field for one cycle of bubble expansion but the focus is primarily embolotherapy and not ultrasound. Experiments from Sassaroli and Hynynen [23] as well as Caskey et al [3][4] show that the amplitude of radial oscillation is suppressed in the presence of a tube, and that greater ultrasonic pressure is required to destroy the bubble: there is less response of the bubble to the sound wave.
Several models have attempted to modify the Rayleigh-Plesset equation to simulate the dynamics of bubbles in tubes. The model of JB Freund [7] was derived for research into shockwave lithotripsy, but describes a different system than that discussed in this paper. Stride et al [25] created a model of a bubble within a shell within a blood vessel within an infinite fluid, although this does not correspond well to a bubble within a tube.
Charles Devin, Jr.'s 1961 technical report “Resonant Frequencies of Pulsating Air Bubbles Generated in Short, Open Ended Pipes” [6] gives a derivation of the resonant frequency of a bubble based on the velocity potential around a bubble in a tube. The velocity potential discussed is based on a sum over Bessel functions of the tube's geometry with boundary conditions causing the potential to vanish at the tube walls. Assumptions are made based on the velocity potential's behavior compared to the free bubble, and an expression for resonance frequency was derived. In addition, experiments were performed using millimeter-scale bubbles that confirm his theory. The frequency equation and experimental results are summarized by Oguz and Prosperetti [18].
Yuri B. Zudin's 1992 paper “Analog of the Rayleigh Equation for the Problem of Bubble Dynamics in a Tube” [28] shows the formulation of a modified RP equation. The proclamation before presenting the final result was “we obtain the ‘cylindrical’ analog of the Rayleigh equation,” but no actual simulations are presented, so the usefulness of the equation was not tested. Two modified RP equations are presented in that paper; the latter assumes that the standard RP terms are negligible and includes only modified terms. This model, when simulated, shows that as the radius of the tube approaches infinity, the resonance frequency continuously increases towards infinity. Intuition suggests that it merely increases asymptotically towards the free-field value, the Minnaert frequency. The first equation presented, however, passes this basic test. The extra terms go to zero as the tube's length and radius go to infinity, reducing to the standard RP equation. That equation will be discussed in this paper with the final goal of developing a simpler method of calculating insonation parameters for biomedical ultrasound. The model has been used to model heat transfer from bubbles during medical ultrasound [11].
In addition to Devin and Zudin, Sherwood [24] in an appendix derived an equation for the resonance frequency of a bubble in a finite tube with arbitrary cross section. His derivation is based on a modified Green's function for wave propagation in a tube. It will be shown that Sherwood's model is equivalent to Zudin's. In addition, it will be shown that, to within certain approximations, the theories of Zudin and Devin are equivalent and provide similar results to the aforementioned numerical models.
2. THEORY
The radial oscillation of a gas bubble in a liquid can be described with the basic Rayleigh-Plesset equation. There are several assumptions made: the pressure within the gas is uniform, the bubble remains spherical at all times and oscillates only in the radial direction, the liquid is incompressible. The equation can take many forms; a simple and common one is:
- 3 RR + - R 2
A P
,
P
where R refers to radius as a function of time, a dot represents a time-derivative, p is the density of the fluid, and A P is the difference in pressure between the bubble wall and infinity. A P can take many forms depending on the conditions, damping, shell parameters, etc. A common expression is:
AP = P
o
V
P v
2 a ^ + —
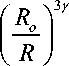
2a
---4 n R + P - P - P sin O tt
R Rvoa
where R o is the equilibrium radius of the bubble, Po is ambient pressure, P v is vapor pressure, a is surface tension, ц is viscosity, P a is applied acoustic pressure, o is driving frequency, t is time, and у is the polytropic exponent, also known as the ratio of specific heats.
The resonance frequency of bubble oscillations is known as the Minnaert frequency. In its simplest form it can be calculated by:
& Minnaert
3 / P o
V P RO ’
The Rayleigh-Plesset equation and the Minnaert frequency can be derived using conservation of energy by assuming small-amplitude linear oscillations. The former is shown in Leighton [13] and the latter in Devaud et al [5]. The derivation is based on definitions of kinetic and potential energy. The kinetic energy ( KE ) of a gas bubble in an infinite liquid is equal to the kinetic energy of the surrounding fluid:
KE = 1 p IwRRdL = - np R! l i 2 . 2 R r 2
Using the classical definition of kinetic energy, ½ mv2 , and assuming that R is very close to its equilibrium value, R o , the effective mass can be expressed as
M ef = 4 np R o h Mo .
The potential energy PE can be taken as the pressure-volume integral of the gas inside the bubble:
PE =
4 R
R o
4 n R 2 P ( R ) dR
This integral is evaluated in the linear regime by Devaud et al. Assuming a harmonic potential, the effective spring constant can be taken as
Keff = Пяу РЛ . (7)
The square of the Minnaert frequency can be found by dividing (7) by (5) and the standard Rayleigh-Plesset equation can be derived by equating (4) and (6), differentiating by R , and eliminating common factors.
Changing the geometry of the fluid will not change the effective spring constant according to this derivation, although the effective mass may change. If the effective mass changes by a function of radius, M eff =M o f ( R ), then both the governing differential equation and the analytical frequency change. The frequency is shifted by the reciprocal square root of f ( R o ):
K eff
V M,f If ( R o ) (8)
The kinetic energy is linear with M and will be scaled by f ( r ) . Balancing the kinetic and potential energies and differentiating, as per Leighton, will yield the following differential equation:
RRf (R) + - R21 f (R) +
Rdf \_P J dR j P'
If f ( r ) is unitary, then this simplifies to the standard RP equation. A corollary of equations 8 and 9 is that if a differential equation or frequency equation is presented, f ( r ) can be gleaned from the square of the relative frequency or the coefficient of RR , respectively.
Two models to describe a bubble inside a rigid tube of radius R T and of length L will be examined. Zudin presents a modified Rayleigh-Plesset equation as follows:
и»Ci J^V 3д
RR 1 ++ R
R 2 2
G+4-L1
2 к 3 r t 7
A P
P
Comparing this to the form of equation 9, f ( R ) can be easily isolated and it can be seen that the effective mass is:
C
Meff = Mo 1 +
к RT 7
Thus the resonance frequency relative to the Minnaert frequency is:
^
Zudin
^ Minnaert
RT 2
RL
1 +
R 2
\ - T + R o L
This is equivalent to Sherwood's equation (A32 of [24]) for resonance frequency in an open ended tube if circular cross section is assumed and the bubble is equidistant from each end.
Similarly, Oguz and Prosperetti present Devin's expression for relative resonance frequency:
Zudin
^ Minnaert
RT 2
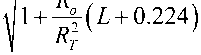
\ - T + RoL + 0.224 R o R T ’
This is similar to Zudin's frequency, and using equation 8 the effective mass can be found:
Meff
= M o
R L
1 + — + 0.224
к - T к - T
The value 0.224 is based on two correction factors given by Devin. Typically L/R T >>0.224, thus the factor can be ignored in many cases, making the Zudin and Devin effective masses equal and rendering the two physical models identical.
Finally, following equation 9, the differential equation for Devin's model can be found:
• ■
RR
1 +--+ 0.224
R t к R t
+ 3 R2
C
к
4 R
+
3 RT
C
— + 0.224 к R t
A P
.
P
The important term in these equations is the ratio R o L/R T 2, which will be referred to as the
cylindricity. As this term increases, the dynamics depart further from the free bubble. This corresponds to decreased radius and increased length: tubular as opposed to drum-shaped.
Neither Devin (including Oguz and Prosperetti in their summary of his work) nor Zudin give an explanation for the behavior of the bubble if it is located at various positions along the tube. However, both papers describe the situation for similar physical models: Zudin for the extremely-long-tube model, and Oguz and Prosperetti for a ‘large bubble,’ taking up the entire cross section of the tube. Sherwood [24] also provides the same expression taking into account the behavior of the bubble at various positions in the tube. The explanation is as follows: given that two lengths exist, one between the bubble and each of the ends of the tube ( L 1 and L 2, where L=L 1 +L 2) the equivalent length L' is given as if the two lengths were resistors added in parallel. Alternately, the bubble can be said to be situated at fraction x along the tube. L' must be multiplied by 4 in order to reconcile with L for x= 1/2 (L 1 =L 2 =L/ 2 ).
L ' = 4 LL-
L 1 + L 2
= 4 L (x - x2) .
This can be substituted into the frequency equations or the modified Rayleigh-Plesset equations. The cylindricity term can be modified by substituting L with L' . It is useful to compare the expected frequency for the Zudin model to the value at the midpoint:
a
(x) = a- I
1 2 Ц
R T + RL
R T + 4 R o L ( x - x 2 ) ‘
Expanding the above radical as a Taylor series about x= 1/2 will yield a sum over even powers of x , similar to a hyperbolic cosine, indicating it is bowl-shaped and evenly symmetric about that point.
An exact solution to equation 10 is given by Zudin assuming a constant pressure difference. The equation presented is incorrect: various coefficients must be changed in order to satisfy the differential equation. The correct result is:
R (t )=^
L
1+
f. 3^P Л< Lt ^
1 ■ ,.2
L 2p J L RT J
- 1
The difference between the Zudin and Devin models becomes more pronounced as the cylindricity decreases. This is seen in Figure 2, comparing the oscillations of a 1 µ bubble in a tube with a 10 µ diameter and 100 µ length to a tube with a 40 µ diameter and the same length. The difference between the two models becomes more significant when the tube is wider.
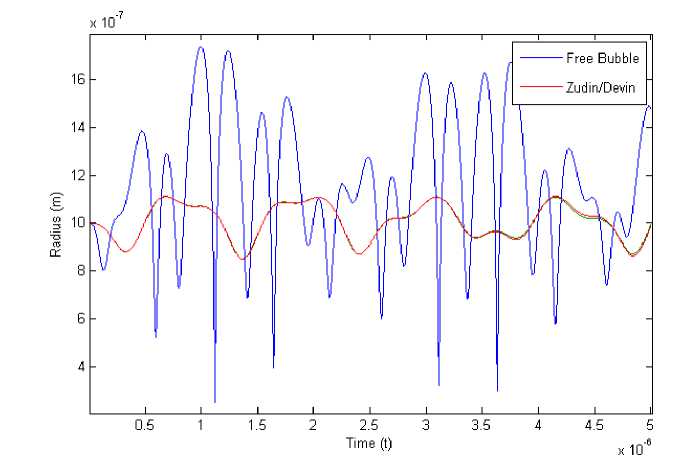
Figure 1: Comparison between free bubble and in-tube model for a 5 µ radius, 500 µ long tube: radius of a 1 µ bubble versus time during a 2 MHz, 100 kPa insonation. The Zudin and Devin models are both displayed but essentially overlap
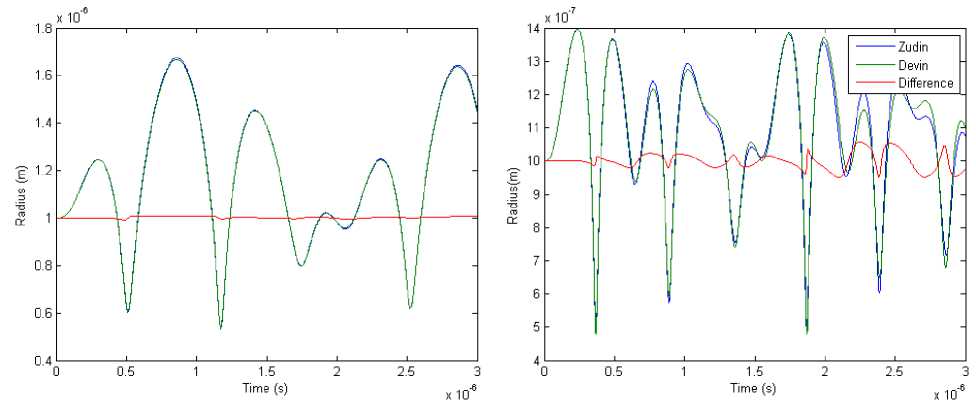
Figure 2: Radius versus time of both models with a 1 µ bubble in a 5 µ (left) and 20 µ (right) radius, 100 µ long tube during a 2 MHz, 100 kPa insonation with surface tension. The smallamplitude red curve represents the difference between the Zudin and Devin Models, relative to the equilibrium value
The resonance frequency of the bubble can be ascertained by simulating low-amplitude oscillations in the linear regime, and extracting the frequency from a Fourier transform or by taking the reciprocal of the observed period. These results can then be compared to equation 12 and 13. No difference is expected between the simulation and analytic predictions. In this regime, no difference is expected between the two models. In actuality, simulations differed by less than one part in one thousand between the two models.
The simulated values of relative resonance frequency as a function of tube radius can be seen in Figure 3. These are overlaid with function plots of equation 12, which overlap the simulated values. Values calculated from equation 12 and compared to the simulations get closer to each other as R T increases, but the differences are on the order of a few parts per thousand.
These values are in nearly perfect agreement with Qin and Ferrara [20], as well as Sassaroli and Hynynen [21]. For instance, a plot of equations 12 or 13 is almost identical with figure 3B from Qin and Ferrara [20], with differences between data points of 2–3%. The results from Qin and Ferrara are compared with results from Zudin's model in Figure 3. The same is true when comparing the data to figure 5 from Sassaroli and Hynynen [21].
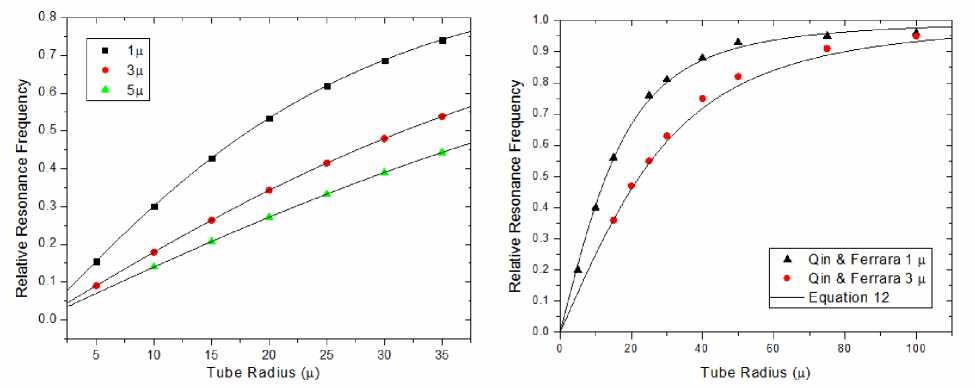
Figure 3: Left: Relative resonance frequency vs. tube radius in a 1 mm long tube for bubbles of 1, 3 and 5 µ in radius. Right: Data from Qin and Ferrara [20] figure 3B compared to Zudin's predictions (equation 12)
Simulating the resonance frequency in the case in which the bubble is located a certain fraction along the tube shows the frequency increasing as the bubble gets closer to either end. This is in accordance with equation 17. A plot of simulation points compared to the analytical prediction can be seen in Figure 4. These predictions are confirmed experimentally by Jang et al [10], with divergence at the ends of the tube.
■ Simulation Analytic



0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8
Fraction Along Tube
Figure 4: Relative resonance frequency of a 1 µ bubble in a 15 µ radius, 1000 µ long tube, at various positions along the tube
Again, the ratios predicted here match well with pre-existing literature: Sassaroli and Hynynen predict that the frequency at the midpoint is approximately 70% of the frequency at x=0.1 along the tube, matching these predictions. The agreement between analytical expressions and numerical simulations validates the method of manipulating the expressions while assuming non-linear oscillations. The effective mass can be gleaned from frequency equations presented in other papers and used with equation 9 to develop new versions of the Rayleigh-Plesset equation.
The resonance frequency decreases as the length increases, based on both equations 12 and 13 and confirmed by numerical simulations. As cylindricity increases, the system becomes more one-dimensional, departing further from the infinite three dimensional model. As the length of tube increases the liquid inertia increases and the bubble requires more energy to expand and push the fluid outward [18]. Correspondence to the infinite fluid is still preserved as both the radius and length increase to infinity. Little investigation has been undertaken in other studies regarding vessel length, although figure 8 in Sassaroli and Hynynen also suggests that a longer tube will have more deviation from the free model than a shorter one while Miao et al [17] predict that oscillation amplitude decreases in a longer tube, consistent with the predictions of this paper.
The expansion of the bubble as a function of the tube radius corresponds to Figure 6 of Miao and Gracewski [16]. A radius-time graph of the Zudin model compared to Miao and Gracewki's predictions can be seen in Figure 5. A table is given comparing the peak radii in both models; they are similar in both appearance and peak radius. Predictions of expansion ratio also match those of Qin and Ferrara [20] in their rigid tube case, with the values corresponding in three of three examples.
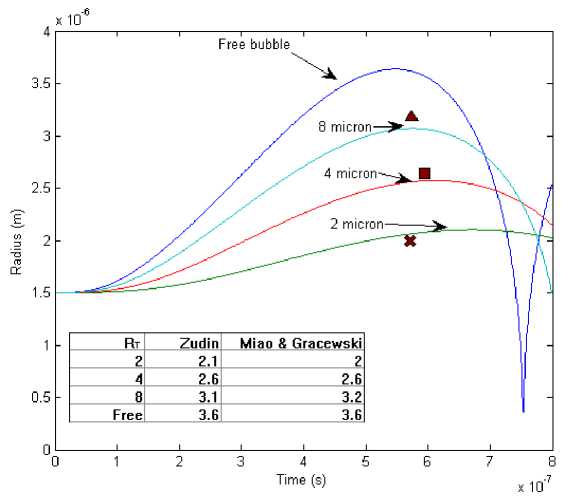
Figure 5: Radius versus time of a 1.5 µ bubble in a 30 µ long tube at different tube radii under a 200 kPa, 1 MHz signal. The block symbols represent the approximate location of the peaks as presented by Miao and Gracewski [16]
Table 1: Comparison of simulation predictions and experiments from Caskey et al [3],[4] of peak expansion ratio as at different pressures and tube diameters
|
Pressure (MPa) |
Tube Diameter (µ) |
Experimental |
Simulated |
|
1.4 |
12 |
2.8±1 |
3.6 |
|
0.8 |
14 |
1.5±0.3 |
1.5 |
|
1.4 |
25 |
6±2 |
3.2 |
Few experiments have been published measuring the dynamics of microscale bubbles in tubes, mainly by Caskey et al. in 2006 [3] and 2007 [4]. The measured data of peak relative expansion for bubbles in various tube sizes is compared with the simulated values (the tubes used in the experiments were long enough such that the Zudin and Devin models predict the same value) with similar insonation and tube parameters, in Table 1. Due to the high error and uncertain conditions it is difficult to tell whether theory and experiment match, although it appears that preliminary data suggests that the models are appropriate: the simulations are within error range of two out of three data points. Until more data is available it is impossible to determine exactly how accurate the models are.
Sassaroli and Hynynen [22] measured the acoustic pressure required to induce inertial cavitation as a function of tube radius. Their data showed a decreasing pressure as the tube increased, towards the free-field required-pressure for large enough tubes. A linearized forced harmonic oscillator model is juxtaposed with their data: the pressure required to excite the bubble to twice its equilibrium radius is taken to be that required for inertial cavitation. The experimental data and numerical simulations of the Zudin model can be compared (Figure 6). The model corresponds well to the data with the exception of the smallest-tube datum.
Zudin Model
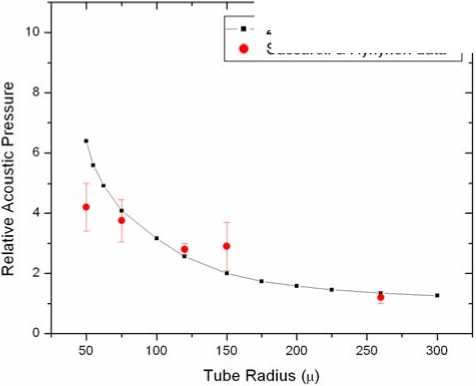
Figure 6: Pressure required to excite bubble to twice its equilibrium radius normalized with the free-field value, compared to experimental data from Sassaroli and Hynynen [22]
In addition to the scarcity of experimental data with regards to expansion ratios, there have not been many experiments performed on the frequency of a bubble within a tube. Devin performed frequency measurements on bubbles in a 15 mm radius tube in water, the results of which are presented in Oguz and Prosperetti [18]. As an example, in a 15 mm radius, 12 cm long tube, a 1.52 mm bubble was measured to have a relative resonance frequency of 0.74. According to Devin's theory, 0.74 is expected. No error analysis is given. The correspondence between Devin's predictions and experiments further supports his and Zudin's theories, as well as the other models discussed predicting similar frequencies. Devin also performed the experiment with a non-rigid PMMA tube. The relative frequency for a 1.5 millimeter bubble 5 feet under water in a 12 cm long, 3 cm diameter tube is approximately 1.2.
More recently, the frequency of a bubble contained in a balloon suspended in a vertical tube was measured by Jang et al [10]. The results of that experiment were compared to the model outlined in [16]. The frequency measurements from Jang et al when the bubble is in the centre of the tube correspond with the models discussed in this paper. The results for a bubble positioned at various locations within a tube correspond to equation 17 towards the centre of the tube, although there is disagreement at the ends.
The obvious question that arises when comparing two physical models of the same situation is as to which model is more correct. Since the two models are so similar it is difficult to ascertain which more accurately describes a bubble oscillating in a tube. The derivations of both models are based on the velocity potential in an infinite tube, although the potentials used are different in each case.
The differentiating term, 0.224, comes from two statements by Devin: that the velocity potential in a tube on the axis at 1.108 radii from the bubble is equal to the free field potential at infinity, and that the kinetic energy contributed by fluid motion outside the tube is equivalent to increasing the length of the tube by an additional 1.22 radii. Comparing both to Devin's experiments as presented by Oguz and Prosperetti, Zudin's predictions are slightly closer to the measurements than Devin's, but the difference is negligible.
In addition, Zudin's model was independently derived by Sherwood using different mathematical methods. The goal of Zudin was to model bubbles in long tubes, while Devin aimed to model bubbles in short tubes. Because at long tube lengths the models are the same, while the difference is apparent at shorter tubes, the Devin model may be more appropriate. Given the coarse nature of experimental results in this field, it is unlikely that any experiment will be able to determine which of the two models is correct. For typical scales of human blood vessels, the two models are identical and Zudin's is simpler to use.
There are several models that describe the oscillations of a bubble in a tube. Three established models are discussed for comparison: the Oguz-Prosperetti model [18], the Qin-Ferrara model [20], and the Miao-Gracewski model [16].
The Oguz-Prosperetti model uses the boundary element method as well as an approximation based on a sum of Bessel functions and Legendre polynomials and predicts the resonant frequency of the bubble under various conditions. This model is confirmed experimentally by Geng et al [8] for bubbles that occupy the entire cross section of the tube. Its predictions for small bubbles match those of the Zudin or Devin models: Oguz and Prosperetti compare their predictions to Devin's in figures 2 through 5 of their paper, and good agreement is found although Devin's model approaches the free bubble in large tubes faster than the Oguz-Prosperetti model. Devin's equation for frequency is simpler to implement than either of the Oguz and Prosperetti methods.
The Miao-Gracewski model uses a coupled boundary element and finite element method to simulate the bubble shape as a function of time, as well as the pulsation of the vessel walls. Radius-time plots can be generated from this model. As seen in Figure 5, the predictions of this model in the regime of higher Young's modulus are nearly the same as those of the models discussed in this paper. However, Miao and Gracewski state that they cannot simulate bubbles in tubes longer than 30 microns due to computational restrictions, a constraint that does not apply to the Runge-Kutta method.
The Qin-Ferrara model uses the finite element method and the COMSOL software package to model the feedback between bubble shape and vessel wall shape. It predicts both resonant frequency and radius-time curves. The resonant frequencies predicted by the Devin and Zudin models match the computationally-intensive predictions of the Qin-Ferrara model assuming a rigid or very stiff tube. Figure 12 of Qin and Ferrara gives expansion ratios of the bubble under Alexander R. KlotzP, Kullervo Hynynen
Simulations of the Devin and Zudin modified Rayleigh-Plesset equations to model bubble dynamics in a tube various conditions, and the rigid tube predictions match the Zudin and Devin models in three of three cases if the expansion ratio is measured on the first peak. Figure 10 of Qin and Ferrara gives a radius-time curve for a stiff tube which does not match predictions from the Zudin or Devin model (Figure 7): the two models are similar at low times but deviate, and the Qin-Ferrara prediction is more damped. The discrepancy between the two models may be due to extra effects taken into account in the Qin-Ferrara model such as non-spherical oscillation of the bubble. A detailed comparison between the Qin-Ferrara and Miao-Gracewski models is necessary to determine which should serve as the basis of validation.
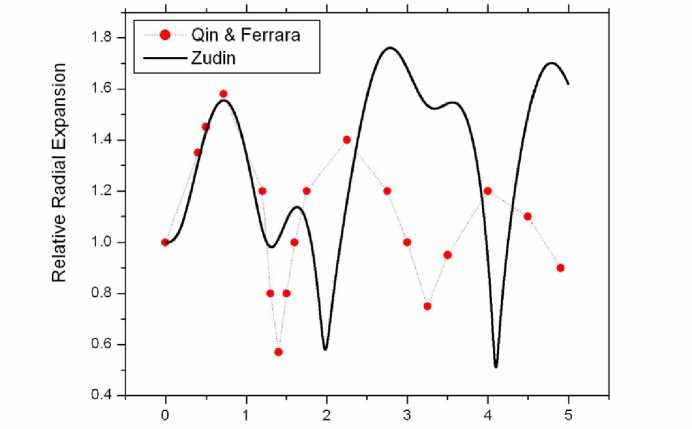
Time (ps)
Figure 7: Relative radius versus time of a 1.5 µ bubble in a 200 µ long, 4 µ radius tube at different tube radii under a 500 kPa, 1 MHz signal with the same parameters used by Qin and
Ferrara. Data points were estimated from figure 10a from Qin and Ferrara [20]
One of the purposes of a modified Rayleigh-Plesset model for a bubble in a tube is to predict the frequency to use during diagnostic or therapeutic ultrasound. It has been shown that the models discussed in this paper can calculate frequencies analytically that match computational predictions from more complex models.
CONCLUSION
The equations presented by Zudin and Devin were analyzed and shown to be nearly identical. The analytic predictions of a bubble's relative resonance frequency in a tube were shown to correspond with numerical simulations. With decreasing tube radius, both resonant frequency and oscillation amplitude decreased. The predictions of these models regarding resonance frequency and expansion ratio are in agreement with many published computational models: Qin-Ferrara, Oguz-Prosperetti and Miao-Gracewski. Although superficial agreement was found with published results, more experimental data is necessary to verify these theories.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors with to thank David Goertz and Nazanin Hossein Khah for their insight as well as the Terry Fox Foundation for their generous funding.
Список литературы Моделирование модификаций Девайна и Зудина уравнения Рэлея-Плессе динамики пузырька в трубке
- J. C. Atkisson. Models for acoustically driven bubbles in channels. Ph.D. Dissertation, 2008.
- J. L. Bull. The application of microbubbles for targeted drug delivery. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery, 4(5):475-493, 2007. PMID: 17880272.
- C. F. Caskey, D. E. Kruse, P. A. Dayton, T. K. Kitano, and K. W. Ferrara.Microbubble oscillation in tubes with diameters of 12, 25, and 195 microns. Applied Physics Letters, 88(3), 2006.
- C. F. Caskey, S. M. Stieger, S. Qin, P. A. Dayton, and K. W. Ferrara. Direct observations of ultrasound microbubble contrast agent interaction with the microvessel wall. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 122(2):1191-1200, 2007.
- M. Devaud, T. Hocquet, J.-C. Bacri, and V. Leroy. The Minnaert bubble: an acoustic approach. European Journal of Physics, 29(6):1263-1285, 2008.
- C. Devin. Resonant frequencies of pulsating air bubbles generated in short, open-ended pipes. US Navy Technical Report, 1961.
- J. B. Freund. Suppression of shocked-bubble expansion due to tissue con_nement with application to shock-wave lithotripsy. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 123(5):2867-2874, 2008.
- X. Geng, H. Yuan, H. N. Oguz, and A. Prosperetti. The oscillation of gas bubbles in tubes: Experimental results. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 106(2):674-681, 1999.
- K. Hynynen, N. McDannold, N. Vykhodtseva, and F. A. Jolesz. Noninvasive MR Imaging-guided Focal Opening of the Blood-Brain Barrier in Rabbits. Radiology, 220(3):640-646, 2001.
- N. W. Jang, S. M. Gracewski, B. Abrahamsen, T. Buttaccio, R. Halm, and D. Dalecki. Natural frequency of a gas bubble in a tube: Experimental and simulation results. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 126(1):EL34-EL40, 2009.
- A. R. Klotz, L. Lindvere, B. Stefanovic, and K. Hynynen. Temperature change near microbubbles within a capillary network during focused ultrasound. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 55(6):15-49, 2010.
- W. Lauterborn and H. Bolle. Experimental investigations of cavitation-bubble collapse in the neighbourhood of a solid boundary. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 72:391-399, 1975.
- T. Leighton. Derivation of the Rayleigh-Plesset equation in terms of volume. ISVR Technical Reports, 1994.
- T. G. Leighton and R. E. Apfel. The acoustic bubble. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 96(4), 1994.
- P. Marmottant and S. Hilgenfeldt. A bubble-driven microuidic transport element for bioengineering. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101(26):9523-9527, 2004.
- H. Miao and S. Gracewski. Coupled fem and bem code for simulating acoustically excited bubbles near deformable structures. Computational Mechanics, 42:95-106, April 2008.
- H. Miao, S. Gracewski, and D. Dalecki. Ultrasonic excitation of a bubble inside a deformable tube: Implications for ultrasonically induced hemorrhage J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 124:2374-2384, October 2008.
- H. N. Oguz and A. Prosperetti. The natural frequency of oscillation of gas bubbles in tubes. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America,103(6):3301-3308, 1998.
- S. Qin and K. W. Ferrara. Acoustic response of compliable microvessels containing ultrasound contrast agents. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 51:5065-5088, Oct. 2006.
- S. Qin and K. W. Ferrara. The natural frequency of nonlinear oscillation of ultrasound contrast agents in microvessels. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology, 33(7):1140-1148, 2007.
- E. Sassaroli and K. Hynynen. Resonance frequency of microbubbles in small blood vessels: a numerical study. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 50(22):5293-5305, 2005.
- E. Sassaroli and K. Hynynen. On the impact of vessel size on the threshold of bubble collapse. Applied Physics Letters, 89(12), 2006.
- E. Sassaroli and K. Hynynen. Cavitation threshold of microbubbles in gel tunnels by focused ultrasound. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology, 33(10):1651-1660, 2007.
- J. D. Sherwood. Potential flow around a deforming bubble in a venturi. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 26(12):2005-2047, 2000.
- E. Stride and N. Safari. Theoretical and experimental investigation of the behaviour of ultrasound contrast agent particles in whole blood. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology, 30(11):1495-1509, 2004.
- Wu. J. Theoretical study on shear stress generated by microstreaming surrounding contrast agents attached to living cells. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology, 28:125-129(5), January 2002.
- T. Ye and J. L. Bull. Microbubble expansion in a flexible tube. Journal of Biomechanical Engineering, 128(4):554-563, 2006.
- Y. B. Zudin. Analog of the Rayleigh equation for the problem of bubble dynamics in a tube. Journal of Engineering Physics and Thermophysics, 63:672-675, July 1992.


