Моделирование виллизиевого круга человека в норме и при патологии
Автор: Иванов Д.В., Доль А.В., Павлова О.Е., Аристамбекова А.В.
Журнал: Российский журнал биомеханики @journal-biomech
Статья в выпуске: 3 (61) т.17, 2013 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Целью работы является разработка рекомендаций по выбору типа лечения аневризм артерий головного мозга. Сформулирована краевая задача, описывающая течение крови в артериях головного мозга с упругими стенками. С помощью специализированных программных пакетов Mimics и Solid Works построены реалистичные геометрические модели артерий виллизиевого круга в норме и при наличии аневризм. При этом дано описание методики и основных этапов построения таких моделей, а также проведена оценка их пригодности для конечно-элементных расчетов. Далее проведен анализ ультразвуковых исследований артерий виллизиевого круга, сонных и позвоночных артерий, необходимый для получения параметров кровотока и постановки граничных условий. Кроме того, исследованы механические свойства образцов артерий виллизиевого круга, получены константы функции энергии деформации Муни–Ривлина.
Виллизиев круг, аневризма, математическое моделирование, гиперупругий материал, механические испытания, трехмерное проектирование
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/146216107
IDR: 146216107 | УДК: 531/534:[57+61]
Текст научной статьи Моделирование виллизиевого круга человека в норме и при патологии
Аневризмы сосудов головного мозга относятся к заболеваниям, не имеющим яркой клинической картины при стабильном течении, но быстро приводящим к драматическим последствиям при развитии осложнений. Несмотря на социальноэкономическую значимость и длительную историю изучения вопроса с точки зрения медицины, механизм образования аневризм и факторы, влияющие на их образование, еще не до конца изучены [15, 19, 22, 30, 31, 37, 43].
В соответствии с клиническими данными в России до 80–90% нетравматических субарахноидальных (под паутинной оболочкой мозга) кровоизлияний происходят вследствие разрыва внутричерепных (интракраниальных) аневризм. Разрыв аневризм приводит либо к неврологическим расстройствам различной степени тяжести, связанным с повреждением тканей головного мозга, либо к смерти. Особенно важным является тот факт, что субарахноидальные кровоизлияния выводят из строя население работоспособного возраста (40–60 лет).
Иванов Дмитрий Валерьевич, к.ф.-м.н., заместитель начальника отдела математического моделирования образовательно-научного института наноструктур и биосистем, Саратов
Доль Александр Викторович, программист отдела математического моделирования образовательнонаучного института наноструктур и биосистем, Саратов
Аневризмы могут быть приобретенными или врожденными. Последние исследования показывают, что аневризмы в большинстве своем развиваются вследствие гемодинамических и дегенеративных повреждений сосудистой стенки.
Очевидно, что такие повреждения стенки могут быть изучены с помощью методов механики сплошной среды и численного моделирования. Биомеханическое моделирование позволит изучить параметры гемодинамики и напряженно-деформированного состояния данных артерий в норме и при патологии, а также сформулировать практические рекомендации по необходимости и обоснованному выбору того или иного типа лечения аневризм артерий головного мозга.
Существует достаточно исследований, посвященных вопросам возникновения и развития аневризм сосудов головного мозга.
Многие исследователи считают, что аневризмы образуются вследствие гемодинамических повреждений стенки, и обращают внимание на значения касательных напряжений на стенке артерий и аневризм. Авторами [14, 24, 27, 33, 40] отмечается наличие высоких значений касательных напряжений (больше 20 Нм2) в районе бифуркации артерий. Высокие касательные напряжения приводят к повреждению сосудистой стенки и, как следствие, к образованию аневризм.
В работе [36] экспериментально исследуется влияние касательных напряжений в аневризме на ослабление и разрыв ее стенки.
Опубликована целая серия работ [39, 41, 42], выполненных под руководством Holzapfel , посвященных исследованию процессов роста аневризм артерий виллизиевого круга с точки зрения механики сплошной среды. Авторы полагают, что развитие аневризмы сопровождается потерей медии, и вся нагрузка приходится только на коллагеновые волокна.
Большое внимание в современном научном сообществе уделяется восстановлению геометрии сосудов головного мозга посредством обработки изображений компьютерной томографии и магнитно-резонансной томографии [11, 16, 18, 32, 34, 38]. При этом авторы стараются работать с томограммами конкретных пациентов, что позволяет уйти от обобщений и сравнивать результаты расчетов с параметрами кровотока определенного человека. Часто полученные модели хорошо повторяют геометрию исследуемых артерий, но это иногда приводит к определенным сложностям при создании вычислительной сетки, постановке задачи и выполнении расчетов. Приходится принимать дополнительные меры по исправлению и оптимизации геометрии [20]. Для первоначальной обработки томограмм обычно используется специализированное программное обеспечение Mimics [11, 35, 44]. Дальнейшая работа с геометрическими изображениями происходит в сторонних программах и сеточных генераторах, это требует выполнения дополнительных действий часто в ручном режиме, что существенно усложняет этот процесс [1, 28].
Определенное внимание в современной литературе уделяется и численным методам, позволяющим проводить восстановление геометрии. К примеру, для моделирования мозга человека на основе магнитно-резонансной томографии возможно применять метод Монте-Карло, откалиброванный определенным образом [13]. Однако такой подход является довольно сложным и трудозатратным.
Очевидно, что трехмерные реалистичные модели сосудов дают возможность более точно описать их поведение и сделать более адекватные выводы относительно вопросов возникновения, роста и разрыва аневризм. Тем не менее некоторые авторы и по сей день применяют одномерные модели [17, 21, 26].
На взгляд авторов, необходимо найти золотую середину среди всех предложенных методик построения геометрических моделей на основе томографических данных. Важно не просто уметь создавать реалистичные модели сосудов. Для выполнения численных расчетов модель должна быть гладкой, не иметь изъянов и покрываться ограниченным числом поверхностей. Более того, методика построения таких моделей не должна быть чрезмерно трудоемкой.
Граничным условиям, которые задаются на входе в сосуд при конечноэлементном расчете, ученые уделяют особое внимание. В основном авторы предпочитают задавать во входном сечении скорость крови [18, 23], однако в некоторых работах представлены данные по объемному кровотоку [12].
Если рассматривать модель виллизиевого круга конкретного пациента, то необходимо учитывать не только геометрию его сосудов, но и скорости кровотока подводящих артерий, а также механические параметры стенки. Если с первыми двумя параметрами можно разобраться, сделав магнитно-резонансную томографию и ультразвуковое исследование сосудов одному и тому же конкретному пациенту, то с механическими характеристиками все намного сложнее.
На сегодняшний день не представляется возможным определить механические характеристики сосудов живого человека, поэтому авторами принято следующее решение: на основе проведенной в 2008–2009 годах серии механических испытаний более 100 образцов артерий виллизиевого круга человека [3] усреднить механические характеристики по половой и возрастной принадлежности, а усредненные данные использовать в численных расчетах, выбрав нужную половую и возрастную группу исследуемого пациента.
Несмотря на обилие работ, посвященных исследованию аневризм артерий виллизиевого круга, не обнаружены работы, содержащие в себе комплексное исследование, не только включающее постановку задачи о поведении артерий для конкретного пациента, но и позволяющее одновременно оценить механические факторы, приводящие к образованию и дальнейшему развитию аневризм и имеющее выход на практическое применение в клинике.
В данной статье записана математическая постановка задачи о течении крови в артериях виллизиевого круга с упругими стенками. Представлена методика построения компьютерных трехмерных реалистичных гладких геометрических моделей артерий виллизиевого круга в норме и при наличии аневризм.
Для постановки граничных условий для линейной скорости потока крови на входе в виллизиев круг обработаны данные ультразвуковых исследований внутренних сонных и позвоночных артерий.
В заключительной части статьи описана процедура получения параметров материала стенок артерий виллизиевого круга на основе данных механических экспериментов образцов исследуемых сосудов.
М атериалы и методы
Моделирование поведения артерий головного мозга требует знания уравнений, граничных и начальных условий, свойств материалов, а также геометрии исследуемых объектов.
Постановка краевой задачи
Рассмотрим трехмерную систему уравнений в частных производных, описывающую движение крови в артериях с упругими стенками.
Кровь будем считать однородной, вязкой несжимаемой ньютоновской жидкостью с постоянными плотностью и динамической вязкостью.
Движение крови в данном случае описывается нестационарным уравнением Навье–Стокса [6]:
— + (v -v)v = F -—grad p + pV2 v,(1)
5tp где V = —i +--j +--k , i, j, k - единичные векторы по осям x, y, z; v - вектор 5x 5y5
скорости частиц жидкости, v = ( u , v , w ) ; t - время; p - плотность крови; р - давление.
К уравнению Навье–Стокса присоединим уравнение неразрывности:
--1+ — = 0, или div v = 0. (2) d x 6 y d z
Основное уравнение движения стенок артерии, называемое уравнением изменения импульса, выглядит следующим образом [35]: .. .
Mu + Cu + Ku = F ( t ), (3)
где М – матрица масс (слагаемое M u является инерционной составляющей в уравнении) объединяет в себе массу движущегося объема; С – матрица
.
демпфирования (слагаемое C u представляет собой демпфирующую составляющую) –
.. .
слагаемое, обусловленное трением; K – матрица жесткости; u – вектор ускорения; u – вектор скорости; u – вектор перемещения узлов; F ( t ) – вектор внешних сил.
Связь между напряжениями и деформациями выглядит следующим образом [35]:
dW
Su = 2 ^W- , (4)
ij acg где Sij – компоненты тензора напряжений Пиолы–Кирхгоффа; W – плотность функции энергии деформации; Cij – компоненты правого тензора деформаций Коши– Грина.
Тензор деформаций Cij выражается через компоненты тензора градиента деформаций Fij [35]:
C ij = F ik F kj . (5)
Вычислительная сетка, на которую разбита стенка артерии, движется вместе со стенкой, и перемещения узлов сетки совпадают с перемещениями стенки артерии. Используются лагранжевы координаты. Для жидкости используют эйлеровы координаты, и вычислительная сетка в данном случае фиксирована. Совместные координаты Лагранжа–Эйлера (совместный подход Лагранжа–Эйлера) применяются в том случае, когда задача является связанной, т.е. граница области, в которой происходит движение жидкости, является подвижной. В этом случае перемещения сетки в области стенки совпадают с перемещениями стенки. В области крови при движении сетки ее перемещения определяются решениями уравнения Лапласа, граничными условиями для которого являются перемещения стенки артерии.
В 1963 г. Winslow [44] было предложено использовать в качестве уравнений движения узлов вычислительной сетки уравнения Лапласа, что успешно применяется на практике до настоящего времени. В стационарном случае уравнения для перемещения сетки в области течения крови имеют следующий вид:
а 2 x + 6 2 x аX 2 + 6 Y 2
6 2 у а у=о, 6 Y 2
---7 +
аx 2
а в нестационарном случае:
а 2 (а x А а 2 (а x А л ----УI - | + d 1 = 0' а x 2 к а t ) а y 2 <а t )
а 2 (а у А а 2 (а у А м
—т I ~ 1+—d — I = о а x 2 к а t ) а y 2 к а t )
где x , y – текущие координаты узлов сетки, а X , Y – начальные координаты недеформированной сетки.
Торцы стенок артерии жестко закрепляются, внешние стенки артерий считаются свободными от нагрузки и закреплений.
Для корректной постановки связанной упруго-гидродинамической задачи требуется поставить граничные условия, объединяющие гидродинамическую и упругую части. Такие условия ставятся для крови, стенки и вычислительной сетки. На границе крови и стенки ставятся условия прилипания, которые выражаются следующими соотношениями:
а и, а V. 6w,
и = —1 , V = —1 , w = —1 , а t а t а t
• > > где и - скорость крови, и = (и, v, w); и 1 - перемещение стенки, и 1 = (и1, V1, w1).
На стенку со стороны крови действует сила, представляющая собой силы вязкости и давление F = F0, р-0 =- n (-pl + Ц (v и + (v ui ) T)),
где % - вектор внешней нормали к границе; р - коэффициент динамической вязкости крови; р – давление крови; I – единичная матрица; Т – символ транспонирования.
Для узлов вычислительной сетки на границе кровь – стенка ставятся условия равенства перемещений сетки и перемещений стенки артерии:
dx = и 1 , dy = V 1 , dz = w 1 ,
где dx , dy , dz – компоненты перемещения узлов вычислительной сетки.
К записанным уравнениям движения (1)–(3) и (6), (7) и граничным условиям (8) и (9) необходимо добавить граничные условия для скорости крови на торцевых и боковых границах.
Головной мозг питается двумя парами артерий – внутренними сонными и позвоночными. Для получения граничных условий на торцевых поверхностях были использованы данные ультразвуковых исследований сонных и позвоночных артерий. На выходах из передних, средних и задних мозговых артерий задавалось нулевое давление.
Подробнее остановимся на вопросе анализа данных ультразвуковых исследований.
Обработка ультразвуковых исследований
Ультразвуковое исследование (УЗИ) является обязательной процедурой, проводимой больному перед хирургическим вмешательством.
Популярность УЗИ объясняется его низкой стоимостью, высокой информативностью, неинвазивностью, безопасностью и возможностью многократных повторных исследований в случае необходимости [7, 8, 10].
В медицинских ультразвуковых приборах датчик заставляет колебаться частицы упругой среды, в результате чего формируются звуковые волны. В процессе распространения они затухают, рассеиваются и отражаются. При отражении звуковой волны от различных поверхностей образуются эхосигналы. Прием эхосигналов после их отражения или рассеивания дает возможность создавать ультразвуковые изображения [9].
Допплеровский режим УЗИ позволяет оценить кровоток не только качественно (ламинарный или турбулентный), но и количественно (определение скорости, уровня периферического сопротивления, показателей кинематики, состояния допплеровского спектра, реактивности сосудов).
Физиологической основой ультразвуковой допплерографии является эффект Допплера, который заключается в изменении частоты ультразвукового сигнала при отражении от движущихся тел по сравнению с первоначальной частотой посланного сигнала.
Допплеровский сдвиг частот описывается следующим уравнением [9]:
2 vf 0 cos θ
∆f = , c где ∆f – сдвиг частот; v – скорость движения элементов крови (эритроцитов); f 0 – первичная частота излучения; cosθ – косинус угла между осью сосуда и направлением ультразвукового луча; c – скорость распространения ультразвука в среде (принимается постоянной, равной 1540 мс).
Прибор регистрирует допплеровский сдвиг частот в килогерцах, скорость крови вычисляется из допплеровского уравнения.
Разница частот, отражающая линейную скорость движения частиц, может быть отображена графически в виде кривой изменения скорости в зависимости от сердечного цикла.
Граничные условия для скорости на входах в виллизиев круг
Данные представляют собой спектр с огибающей его кривой (контур пиковой скорости). Как правило, измерение скоростей происходит в середине потока, где наблюдается их максимальное значение. По горизонтальной оси откладывается время, а по вертикали – скорость кровотока (см/с , см. рис. 1). Кроме того, отдельно выводятся максимальное значение скорости крови в систолу и диастолу.
Существует несколько способов получения входных данных для скорости. Можно построить аналитическую функцию, описывающую кривую скорости, и менять ее параметры, получая разную высоту и ширину пиков, исходя из значений скорости крови в систолу и диастолу [27].
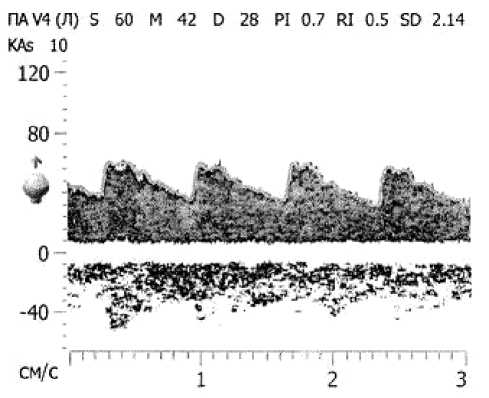
Рис. 1. Данные ультразвуковой допплерографии для позвоночной артерии [4]
ПАУ4(Л) S 60 М 42 D 28 PI 0.7 RI 0.5 SD 2.14
KAs 10
120 -
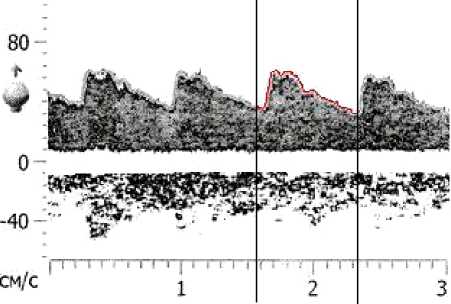
Рис. 2. Обведение графика изменения скорости в MS Paint
В данной работе использовался другой подход, который позволяет получить более точную кривую скорости. Для этого были выполнены следующие действия:
-
1. График изменения скорости за сердечный цикл, полученный по допплерограмме, оцифровывается в растровом графическом редакторе (например, Microsoft Paint ) путем его обведения (рис. 2).
-
2. Затем проводится масштабирование полученных значений к значениям скорости в систолу и диастолу, определенным по ультразвуковой допплерограмме.
-
3. Длина сердечного цикла масштабируется к единичному отрезку.
В результате был получен набор значений скоростей для внутренних сонных и позвоночных артерий. Графики скоростей представлены на рис. 3.
Полученные графики могут быть использованы при постановке граничных условий на входах в виллизиев круг – позвоночные и внутренние сонные артерии.
Далее опишем процедуру построения реалистичных моделей артерий виллизиевого круга человека в норме и при наличии аневризм.
Построение геометрической модели виллизиевого круга
В настоящее время существует три метода диагностирования аневризм сосудов головного мозга у пациентов: компьютерная томография с использованием контрастного вещества, магнитно-резонансная томография и церебральная пункционная ангиография.
Пункционная ангиография считается на сегодняшний день наиболее точным методом диагностирования и исследования свойств внутричерепных аневризм. Но ввиду ее сложности и определенного вреда рентгеновского излучения для организма человека ее использование прописывают только больным, перенесшим субарахноидальное кровоизлияние. В данном случае исследовались здоровые сосуды головного мозга, а также аневризмы на стадиях до разрыва.
Компьютерная томография, по данным Федерального центра нейрохирургии [9], также дает высокие результаты при диагностировании аневризм, однако этот метод в большинстве случаев требует введения человеку контрастного вещества. В случае визуализации здорового виллизиевого круга введение контраста ничем не обосновано, поэтому данная методика также не была использована.
Магнитно-резонансная томография – это наименее травматичный способ диагностики. Во время процедуры пациент не подвергается рентгеновскому излучению, введение контрастного вещества не требуется. При этом большая часть аневризм на снимках довольно четко просматриваются в виде ограниченных образований. Таким образом, магнитно-резонансная томография является идеальным методом для изучения сосудов виллизиевого круга как без патологий, так и с аневризмами до субарахноидального кровоизлияния.
Построение модели виллизиевого круга человека проводилось на основе магнитно-резонансной томографии. Данные для исследования были предоставлены лечебно-диагностическим центром Международного института биологических систем им. С.М. Березина, г. Саратов [4].
Для восстановления геометрии сосудов было использовано программное обеспечение Mimics , которое применяется для обработки данных магнитнорезонансной томографии и последующего их преобразования в 3 D- модели. Также с помощью инструментов Mimics возможно определение плотностей тканей, которые могут быть использованы в численных расчетах.
В программный пакет Mimics были загружены снимки головы. После этого был выбран диапазон оттенков серого, соответствующий плотности крови, и на основе этих данных автоматически воспроизведена геометрическая модель (рис. 4).
В полученном изображении с помощью программных средств Mimics [25] были удалены все элементы сосудистого русла, которые не планируется использовать в дальнейших расчетах, а также незначащие элементы, плотность которых близка к плотности крови, что и позволило им попасть в интересующий нас диапазон.
Полученная таким образом модель была сохранена в формате STL (рис. 5), что позволило в дальнейшем импортировать ее в CAD -систему для сглаживания геометрии, т.е. построения модели без неровностей и искажений.
Дальнейшее построение трехмерной модели виллизиевого круга проводилось в программном пакете Solid Works . Обработка данной модели была необходима, так как множественные дефекты, вызванные методикой восстановления 3 D -объектов по снимкам в программе Mimics , не позволили бы впоследствии выполнять конечноэлементные расчеты.
При восстановлении геометрии предполагалось, что все сосуды имеют круговое поперечное сечение. На рис. 6 показаны окружности, на основе которых был построен участок внутренней сонной артерии (см. рис. 7) с помощью инструмента «вытягивание по сечениям».
Аналогично были восстановлены модели остальных сосудов виллизиевого круга (рис. 8).
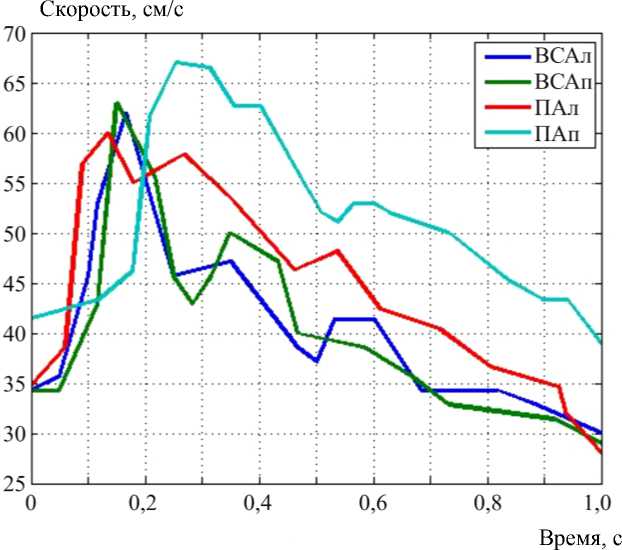
Рис. 3. График изменения скоростей в левой (ВСАл) и правой (ВСАп) внутренних сонных артериях, в левой (ПАл) и правой (ПАп) позвоночных артериях
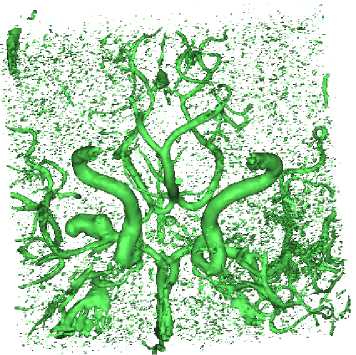
Рис. 4. Трехмерное изображение сосудов в Mimics

Рис. 5. Геометрическая модель, импортированная из Mimics

Рис. 6. Окружности, использовавшиеся для создания модели внутренней сонной артерии
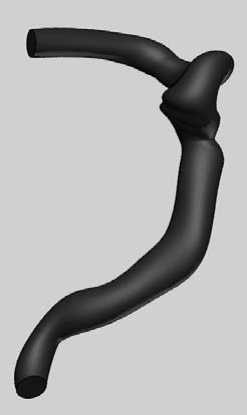
Рис. 7. Модель внутренней сонной артерии
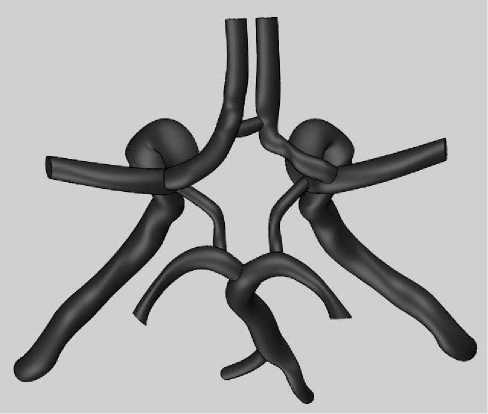
Рис. 8. Восстановленная модель виллизиевого круга
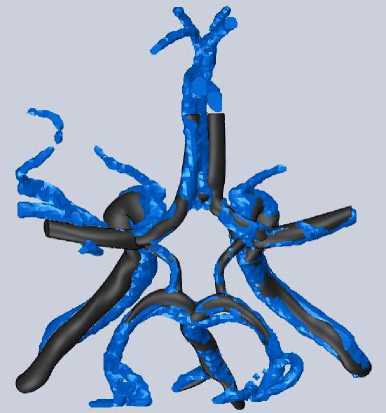
Рис. 9. Совпадение моделей из Mimics и Solid Works
Совпадение построенной модели с изображением, полученным с помощью программы Mimics , представлено на рис. 9. Из рисунка видно, что на большинстве участков достигнуто максимальное сходство.
Следует отметить, что стенки сосудов в импортированной из Mimics геометрии отсутствовали, так как их плотность выше плотности крови, а значит на томограмме им соответствует другой диапазон серого цвета.
В связи с этим стенки сосудов были достроены в пакете Solid Works . Толщину стенок на каждом участке сосудистого русла определяли на основе морфологических данных, предоставленных кафедрой анатомии Саратовского государственного медицинского университета им. В.И. Разумовского.
Аналогичным образом была построена модель незамкнутого виллизиевого круга с аневризмой средней мозговой артерии (рис. 10).
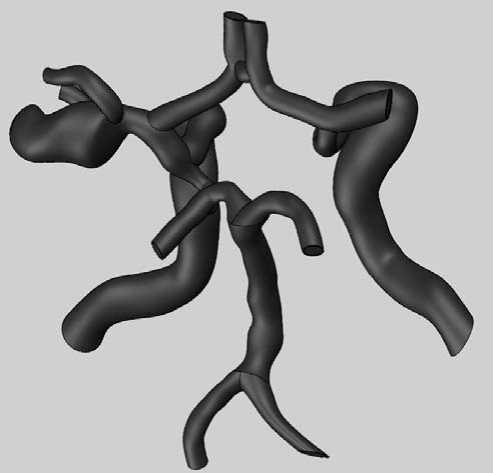
Рис. 10. Незамкнутый виллизиев круг с аневризмой средней мозговой артерии
Описанная выше методика позволяет создавать трехмерные геометрические модели сосудов конкретного пациента на основе данных компьютерной томографии. Кроме того, такие модели очень удобны для использования в конечно-элементных расчетах. Во-первых, они имеют гладкие стенки, что позволяет создавать вычислительные сетки высокого качества. Во-вторых, создаваемые таким образом модели покрыты ограниченным числом поверхностей, что важно при постановке граничных условий. В-третьих, геометрия может быть изменена в случае, если, например, необходимо изменить форму сечений иди добавить какие-либо патологии.
Далее опишем процедуру получения граничных условий для линейной скорости кровотока на входах внутренних сонных и позвоночных артерий. Эти две пары артерий питают головной мозг и ответственны за наполнение виллизиевого круга.
Получение параметров материала стенок артерий
Опишем процедуру получения констант функции энергии деформации Муни– Ривлина на основе числовых результатов механических экспериментов исследуемых артерий.
В качестве модели материала стенки используем модель Муни–Ривлина
W = С ( 1 1 - 3 ) + C 2 ( 1 2 - 3 ) + C 3 ( 1 1 - 3 )( 1 2 - 3 ) , (11)
где W – функция энергии деформации материала; C 1 , C 2 , C 3 – неизвестные параметры материала, подлежащие определению; I 1 , I 2 – инварианты тензора деформаций Коши–Грина.
Этот вид функции энергии деформации W (11) был получен Rivlin и Saunders из экспериментов по деформации тонкого листа [29].
Для получения параметров модели сверхупругого резиноподобного материала Муни-Ривлина необходимо вывести зависимость о от X (напряжение - степень удлинения) для одноосного растяжения с использованием функции энергии деформации данного материала. В настоящей работе подробно останавливаться на вопросе вывода этой зависимости не будем, так как это уже было сделано ранее [2, 3].
С учетом выбранной функции энергии деформации Муни–Ривлина зависимость σ от λ выглядит следующим образом:
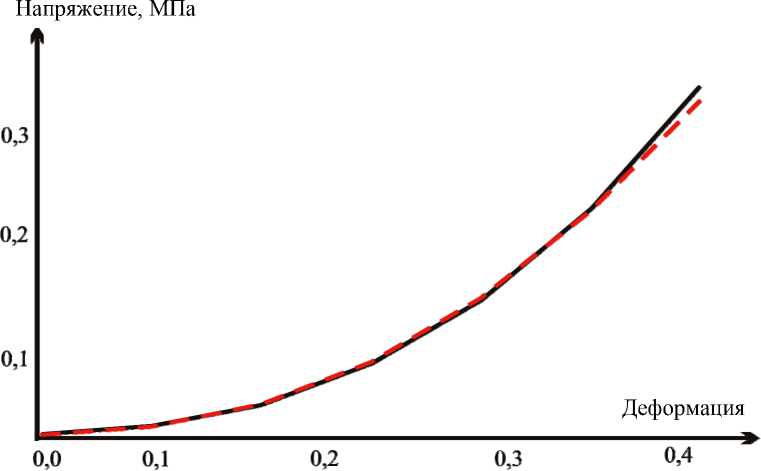
Рис. 11. Зависимость σ от λ , построенная по интерполированным точкам экспериментальных данных (сплошная линия), и зависимость σ от λ , полученная по формуле (12) (пунктирная линия)
G = 2 |X 2
^^^^^^^в
I
V
C i + 1 C 2 + 2 C3
1 I 2 3
( 1 1 AA
I-^ + CT -1
V 1 I ))
Подбор неизвестных констант C 1, C 2 , C 3 осуществлялся с помощью метода наименьших квадратов [5].
Приведем экспериментальную и теоретическую диаграммы зависимости σ от λ для базилярной артерии. На рис. 11 пунктирная линия – зависимость σ от λ , построенная по интерполированным точкам экспериментальных данных, сплошная линия – зависимость σ от λ , полученная по формуле (12) с найденными неизвестными константами C 1 , C 2 , C 3 .
Из графика (см. рис. 11) видно, что теоретическая и экспериментальная кривые практически полностью совпадают на всем диапазоне изменения деформаций. Выбранная функция энергии деформации Муни–Ривлина с найденными константами достаточно хорошо описывает материал стенок артерий виллизиевого круга в предположении их изотропности.
В ыводы
В статье представлена методика построения реалистичных трехмерных геометрических моделей сосудов виллизиевого круга, пригодных для выполнения численных расчетов. Данный метод позволяет достаточно легко изменить конфигурацию геометрии, если это необходимо при выполнении численных экспериментов.
На основе данных ультразвукового исследования получены граничные условия для линейной скорости кровотока на входе в виллизиев круг. Константы функции энергии деформации Муни–Ривлина, применяющейся для описания поведения стенок артерий, были рассчитаны с использованием метода наименьших квадратов на основе данных механических экспериментов.
Таким образом, поставлена краевая задача о поведении сосудов виллизиевого круга человека. В дальнейшем эта задача будет решена численно с использованием метода конечных элементов. Численные результаты будут проанализированы с точки зрения влияния механических факторов на процессы возникновения, роста и разрыва аневризм артерий виллизиевого круга человека.
Б лагодарности
Работа выполнена при финансовой поддержке РФФИ (проект № 12–01–31310).
Список литературы Моделирование виллизиевого круга человека в норме и при патологии
- Голядкина А.А., Иванов Д.В., Каменский А.В., Кириллова И.В., Сальковский Ю.Е., Сафонов Р.А., Щучкина О.А. Практическое применение системы автоматизированного проектирования Solid Works в моделировании кровеносных сосудов: учеб. пособие для студ. естеств. дисциплин. -Саратов: Наука, 2011. -148 с.
- Иванов Д.В. Исследование артерий виллизиевого круга человека в норме и при патологии//Известия Саратовского университета. Новая серия. Сер. Математика. Механика. Информатика. -Саратов, 2010. -Т. 10, вып. 1. -С. 35-44.
- Иванов Д.В., Фомкина О.А. Определение механических свойств артерий виллизиевого многоугольника//Российский журнал биомеханики. -2008. -Т. 12, № 4. -С. 75-83.
- Лечебно-диагностический центр Международного института биологических систем [Электронный ресурс]. -http://www.ldc.ru (дата обращения: 10.02.2012).
- Линник Ю.В. Метод наименьших квадратов и основы математико-статистической теории обработки наблюдений. -М.: Физматгиз, 1958. -336 с.
- Лойцянский Л.Г. Механика жидкости и газа. -М.: Наука, 1970. -904 с.
- Никитин Ю.М. Ультразвуковая допплерография в диагностике поражений магистральных артерий головы и основания мозга: учеб. пособие/Ин-т неврологии РАМН, АО «Спектромед». -СПб., 1995. -45 с.
- Ультразвуковая допплеровская диагностика в клинике/под ред. Ю.М. Никитина, А.И. Труханова. -М.; Иваново: МИК, 2004. -496 с.
- Федеральный центр нейрохирургии [Электронный ресурс]. -http://www.brainport.su (дата обращения: 20.02.2012).
- Цвибель В.Дж., Пеллерито Дж.С. Ультразвуковое исследование сосудов. -М.: Видар, 2008. -644 с.
- Auricchio F., Conti M., de Beule M., de Santis G., Verhegghe B. Carotid artery stenting simulation from patient-specific images to finite element analysis//Medical Engeneering Physics. -2011. -Vol. 33, Iss. 3. -P. 281-289.
- Balossino R., Pennati G., Migliavacca F., Formaggia L., Veneziani A., Tuveri M., Dubini G. Computational models to predict stenosis growth in carotid arteries: which is the role of boundary conditions?//Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering. -2009. -Vol. 12, Iss. 1. -P. 113-123.
- Chuang Ch.-Ch., Lee Yu.-T., Chen Ch.-M., Hsieh Y.-Sh., Liu T.-Ch., Sun Ch.-W. Patient-oriented simulation based on Monte-Carlo algorithm by using MRI data//Biomedical Engineering online. -2012. -Vol. 11. -P. 1-15.
- Dempere-Marco L. CFD analysis incorporating the influence of wall motion: application to intracranial aneurysms//Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. -2006. -P. 438-445.
- Eppinger H. Pathogenesis (Histogenesis und Aetiologie) der Aneurysmen einschliesslich des Aneurysma Equiverminosum. Pathologisch-anatomische Studien//Arch. Klin. Chir. -1887. -Vol. 35, Sup. 1. -P. 1-563.
- Fu W., Qiao A. Fluid structure interaction of patient specific internal carotid aneurysms: a comparison with solid stress models//WCB 2010, IFMBE Proceedings. -2010. -Vol. 31. -P. 422-425.
- Grinberg L., Cheever E., Anor T., Madsen J.R., Karniadakis G.E. Modeling blood flow circulation in intracranial arterial networks: a comparative 3D/1D simulation study//Annals of Biomedical Engineering. -2011. -Vol. 39, Iss. 1. -P. 297-309.
- Ho H., Cooling M.T., Hunter P.P. Towards a multiscale integrative model of WSS-induced signaling pathways in cerebral aneurysms//WCB 2010, IFMBE Proceedings. -2010. -Vol. 31. -P. 1159-1162.
- Jou L.-D., Mawad M.E. Timing and size of flow impingement in a giant intracranial aneurysm at the internal carotid artery//Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing. -2011. -Vol. 49, Iss. 8. -P. 891-899.
- Kim C.S., Kiris C., Kwak D., David T. Numerical simulation of local blood flow in the carotid and cerebral arteries under altered gravity//Journal of Biomechanical Engeneering. -2006. -Vol. 128, Iss. 2. -P. 194-203.
- Liang F., Fukasaku K., Liu H., Takagi S. A computational model study of the influence of the anatomy of the circle of Willis on cerebral hyperperfusion following carotid artery surgery//Biomedical Engineering online. -2011. -Vol. 10. -P. 1-22.
- Liu H., Yamaguchi T. Waveform dependence of pulsatile flow in a stenosed channel//J. Biomech. Eng. -2001. -Vol. 123 (1). -P. 88-96.
- Marzo A., Singh P., Reymond Ph., Stergiopulos N., Patel U., Hose R. Influence of inlet boundary conditions on the local haemodynamics of intracranial aneurysms//Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering. -2009. -Vol. 12, Iss.4. -P. 431-444.
- Masaaki S. Magnitude and role of wall shear stress on cerebral aneurysm//Stroke. -2004. -Vol. 35. -P. 2500-2505.
- Mimics [Электронный ресурс]. -http://biomedical.materialise.com (дата обращения: 10.03.2012).
- Moore S.M., Moorhead K.T., Chase J.G., David T., Fink J. One-dimensional and three-dimensional models of cerebrovascular flow//J. Biomech. Eng. -2005. -Vol. 127, Iss. 3. -P. 440-450.
- Oubel E., De Craene M., Putman C.M., Cebral J.R., Frangi A.F. Analysis of intracranial aneurysm wall motion and its effects on hemodynamic patterns//Medical Imaging 2007: Physiology, Function, and Structure from Medical Images. -Cardiff, 2007. -Vol. 6511. -P. 65112A.
- Release 14.5 documentation for ANSYS [Электронный ресурс]. -http://www.ansys.com (дата обращения: 25.03.2012).
- Rivlin R.S., Saunders D.W. Large elastic deformations of isotropic materials VII. Experiments on the deformation of rubber//Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A. -1951. -Vol. 243. -P. 251-288.
- Sahs A.L., Perret G.E., Locksley H.B. Observations on the pathology of saccular aneurysms//Journal of Neurosurgery. -1966. -Vol. 24, Iss. 4. -P. 792-806.
- Scott R.M., Ballantin H.T. Spontaneous thrombosis in a giant middle cerebral artery aneurysm//Journal of Neurosurgery. -1972. -Vol. 37. -P. 361-363.
- Torii R. Fluid-structure interaction modeling of aneurismal conditions with high and normal blood pressures//Computational Mechanics. -2006. -Vol. 38. -P. 482-490.
- Torii R. Fluid-structure interaction modeling of blood flow and cerebral aneurysm: Significance of artery and aneurysm shapes//Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering. -2008. -Vol. 198. -P. 3613-3621.
- Torii R., Oshima M. An integrated geometric modelling framework for patient-specific computational haemodynamic study on wide-ranged vascular network//Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering. -2011. -Vol. 15, Iss. 6. -P. 615-625.
- Trachet B., Renard M., de Santis G., Staelens S., de Backer J., Antiga L., Loeys B., Segers P. An integrated framework to quantitatively link mouse-specific hemodynamics to aneurysm formation in angiotensin II-infused ApoE -/-mice//Annals of Biomedical Engineering. -2011. -Vol. 39, Iss. 9. -P 2430-2444.
- Tsai W.W., Savas Ö., Maitland D., Ortega J., Small W., Wilson Th.S., Saloner D. Experimental study of the vascular dynamics of a saccular basilar aneurysm//International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, 5-10 November, 2006. -Chicago, 2006. -Paper No. IMECE2006-14662. -P. 317-326.
- Valen-Sendstad K., Mardal K.-A., Steinman D.A. High-resolution computational fluid dynamics detects high-frequency velocity fluctuations in bifurcation, but not sidewall, aneurysms//Journal of Biomechanics. -2012. -Vol. 46 (2). -P. 402-407.
- Wang X.H., Li X.Y., Zhang X.J. A computational study on bomechanical differences between cerebral aneurysm and normal cerebral artery employing fluid-structure interaction analysis//WCB 2010, IFMBE Proceedings. -2010. -Vol. 31. -P. 1503-1506.
- Watton P.N., Selimovic A., Raberger N.B., Huang P., Holzapfel G.A., Ventikos Y. Modelling evolution and the evolving mechanical environment of saccular cerebral aneurysms//Biomechanics and Modeling in Mechanobiology. -2011. -Vol. 10. -P. 109-132.
- Watton P.N., Raberger N.B., Holzapfel G.A., Ventikos Y. Coupling the hemodynamic environment to the evolution of cerebral aneurysms: computational framework and numerical examples//Journal of Biomechanical Engineering. -2009. -Vol. 10. -P. 12-22.
- Watton P.N., Ventikos Y., Holzapfel G.A. Modelling cerebral aneurysm evolution/ed. T. McGloughlin//Biomechanics and Mechanobiology of Aneurysms. -Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2011. -P. 373-399.
- Watton P.N., Ventikos Y., Holzapfel G.A. Modelling the growth and stabilisation of cerebral aneurysms//Mathematical Medicine and Biology. -2009. -Vol. 26. -P. 133-164.
- Winslow A.M. Equipotential zoning of two-dimensional meshes//Report UCRL-7312. -University of California, Lawrence Radiation Laboratory, 1963. -P. 25.
- Xenos M., Rambhia S.H., Alemu Y., Einav S., Labropoulos N., Tassiopoulos A., Ricotta J.J., Bluestein D. Patient-based abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture risk prediction with fluid structure interaction modeling//Annals of Biomedical Engineering. -2010. -Vol. 38, Iss. 11. -P. 3323-3337.


