Морфофункциональная и иммуногистохимическая характеристики клеток лейкоцитарных инфильтратов печени онкологических больных
Автор: Лебединская О.В., Кабановская И.Н., Якушева Т.А., Годовалов А.П., К ахматоваН., Шубина И.Ж., Лебединская Е.А., Киселевский М.В., Хохрякова В.Н.
Журнал: Морфологические ведомости @morpholetter
Рубрика: Оригинальные исследования
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.19, 2011 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Исследование поражённой метастатическим про- цессом печени онкологических больных показало, что клеточный состав разнообразных по распро- странённости и расположению инфильтратов пред- ставлен всеми видами лейкоцитов и макрофагами. Лейкоцитарные инфильтраты паратуморальных участков в отличие от интактных областей печени более обширны и содержат большее количество размножающихся, активированных и зрелых клеток лимфоидного ряда. Установлено, что мононуклеар- ные лейкоциты, инфильтрирующие паратумораль- ные участки поражённой опухолевым процессом печени, могут дифференцироваться в НКТ-клетки. Полученные данные могут быть использованы для разработки методов локорегионарной адъювантной иммунотерапии метастазов в печень.
Лейкоцитарный инфильтрат, печень-ассоциированные лимфоциты, нкт-клетки
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143176980
IDR: 143176980
Текст научной статьи Морфофункциональная и иммуногистохимическая характеристики клеток лейкоцитарных инфильтратов печени онкологических больных
Введение. Значительное влияние на рост и развитие опухоли оказывает система адаптивного иммунитета [1]. Система иммунного надзора не во всех случаях ликвидирует опухолевые клетки [2, 3]. Известно, что при росте опухолей различной локализации печень является одним из основных мест метастазирования. После хирургического лечения по поводу колоректального рака примерно у 20% пациентов обнаруживаются метастазы в печени, которые приводят к печёночной недостаточности и часто являются причиной летального исхода [4, 5]. Анализ клеточного состава опухолевых инфильтратов может быть полезен при прогнозировании течения заболевания [1, 6, 7]. Показано, что опухолевые инфильтраты неоднородны по клеточному составу. Они содержат различные по количеству и виду субпопуляции лимфоцитов, которые называют тумор-инфильтрирующими лимфоцитами (TILs) [8]. Проникновение иммунных клеток в ткань опухоли можно расценивать как противоопухолевый ответ хозяина. Однако было установлено, что плотность инфильтратов не является критическим параметром. Интраопухолевые клетки часто функционально дефектны [9], не полностью активированы и состоят в основном из регуляторных лимфоцитов [10-12]. В последние годы появились экспериментальные исследования, позволившие выделить особую субпопуляцию лимфоцитов — так называемые печень-ассоциированные НК. По своему иммунофенотипу они были отнесены к НКТ-клеткам, так как на их мембране экспрессируются маркёры Т-клеток и натуральных киллеров (НК) [13-18]. По мнению авторов,
НКТ обладают антиметастатической активностью, а их активация может существенно усиливать цитотоксический потенциал данной разновидности НК. В частности было выявлено, что при системном введении мышам производных липополисахаридов (ЛПС) происходит регрессия метастазов в печени [19]. Рассматриваемый антиметастатический эффект связывался с активацией НКТ печени посредством увеличения секреции ИЛ-12 стимулированными ЛПС дендритными клетками печени [20].
Цель исследования – изучение морфологических, иммуногистохимических и функциональных особенностей, а также иммунофенотипа клеток лейкоцитарных инфильтратов печени, пораженной метастатическим опухолевым процессом.
Материалы и методы. Исследовано 30 проб периферической крови и 20 проб биопсийного материала печени больных колоректальным раком с метастатическим процессом в печени. Из фрагментов печени, полученных после резекции, была выделена клеточная суспензия. Гепатоциты отделяли от моно-нуклеарных лейкоцитов (МЛ) путём четырёхкратного центрифугирования при
50 g в течение 5 минут. МЛ выделяли с помощью центрифугирования в градиенте фиколла (Pharmacia, Швеция, плотностью 1,077 г/см3). Лимфоидные клетки, образовавшие интерфазное кольцо, собирали пипеткой и трёхкратно отмывали в среде 199. После каждой отмывки в
10-кратном объёме среды клетки осаждали центрифугированием при 200 g в течение 10 мин, затем переводили в полную культуральную среду (ПКС), включающую RPMI-1640 (Sigma, США) с добавлением 10% эмбриональной телячьей сыворотки, 2 мМ глютамина, стрептомицина с пенициллином по 5000 МЕ/мл. Исследование цитотоксической активности МЛ периферической крови и НК, выделенных из печени онкологических больных, проводили с использованием теста восстановления (3-(4,5-диметилтиазол-2-ил) 2,5-дифенилтетразо-лия бромида) — МТТ-теста, который является одним из основных нерадиометрических методов оценки жизнеспособности и пролиферативной активности клеток. Цитотоксическую активность лимфоцитов человека определяли на НК-чувствительной линии эритробластного лейкоза человека К-562 и клетках аутологичной опухолевой линии. МЛ инкубировали с опухолевыми клетками (3x104 в 1 мл) в полной культуральной среде в соотношениях клетки-мишени/ эффекторы — 1:5, 1:2, 1:1 и 1:0,5 в плоскодонных 96-луночных микропланшетах (Costar, Франция) в течение 48 часов. По истечении срока инкубации в лунки добавляли тетразолиевую соль МТТ (Sigma, США), которая метаболизировалась жизнеспособными клетками и, превращаясь в нерастворимый в воде формазан, изменяла оптическую плотность раствора пропорционально количеству выживших клеток. Для последующей количественной оценки кристаллы формазана растворяли ДМСО (ПанЭко, Россия). Результат оценивали спектрофотометрически по оптической плотности при длине волны 540 нм на мультискане МS (Labsystems, Финляндия). Долю лизированных опухолевых клеток (процент цитоксичности) рассчитывали по формуле: (1 – D и —DмDэ )х100%, где Dи - оптическая плотность клеток эффекторов, инкубируемых с клетками-мишенями; Dэ - оптическая плотность клеток эффекторов; Dм -оптическая плотность клеток-мишеней.
Определение иммунофенотипа (экспрессии поверхностных маркеров) МЛ периферической крови здоровых доноров и МЛ печени онкологических больных проводили при помощи моноклональных антител (Caltag Laboratories, США) против соответствующих антигенов в различное время после активации (от 1 до 10 суток). Клетки отмывали холодным фосфатно-солевым буфером (ФСБ) и окрашивали FITC (флуоресциинизотиоционат)- и РЕ (фикоэритрин)-меченными антителами согласно инструкции производителя. Затем вновь отмывали 2 раза холодным ФСБ в течение 10 мин при 100 g. Результаты учитывали методом проточной цитофлюорометрии на проточном цитометре FACS Calibur (Becton Dickinson, США). На поверхности клеток, полученных из мононуклеаров периферической крови(МНПК) здоровых доноров, МНПК и печени онкологических больных, исследовали уровни экспрессии (с соответствующими изотипическими контролями): дифференцировочных молекул CD3, CD4, CD8, CD16, CD56; активационных антигенов CD25, CD38, HLA-DR; молекул адгезии CD57, CD58, макрофагального маркера CD14, маркёров гемопоэтических клеток-предшественников CD34 и CD45 как в виде отдельных, так и двойных меток. Гейт (окно) популяции клеток устанавливали на основе комбинации прямого бокового светорассеяния и размера клеток. При учёте результатов подсчитывали 10000 событий в гейте. Статистическая обработка данных проточной цитометрии проведена при помощи программного пакета WinMDI 2.8.
Морфологические исследования проводили после окрашивания парафиновых срезов печени и мазков культуральной взвеси МЛ, выделенных из различных участков органа, гематоксином bэозином, по Ван Гизону, азуром II-эозином по Романовскому-Гимза, метиловым зеленым–пирони-ном по Браше с контролем РНК-азой, Шифф-йодной кислотой по Шабадашу с контрольной обработкой амилазой и альциановым синим. Иммуногистохимический анализ выполняли с помощью авидин-биотинового метода на докрашенных гематоксилином парафиновых срезах печени онкологических
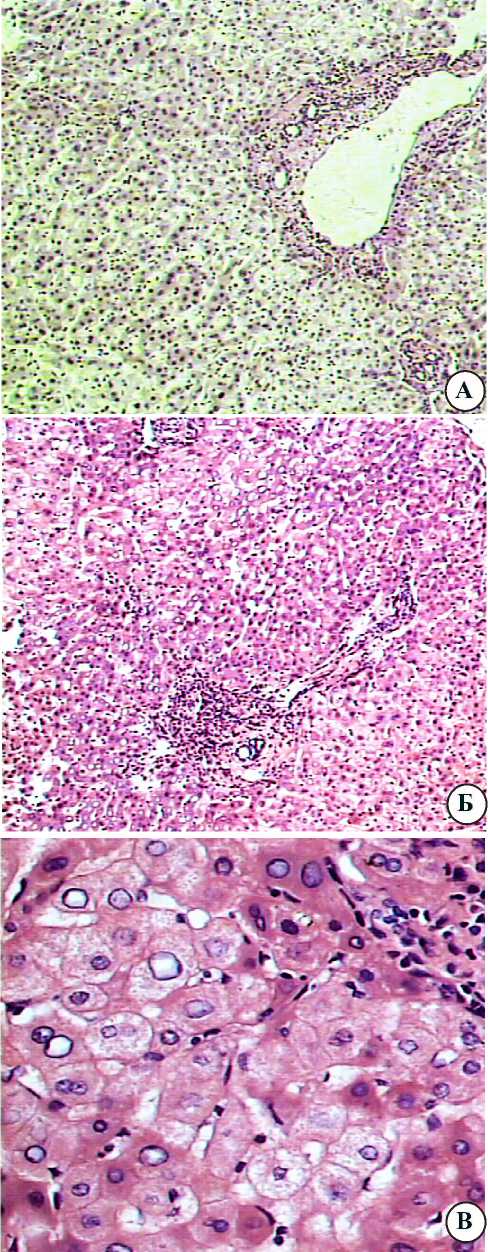
Рис. 1. Интактные участки поражённой метастатическим процессом печени онкологических больных: а — окраска по Ван Гизону; Ув. 100; б — окраска гематоксилином и эозином; Ув.200; в — окраска гематоксилином и эозином; Ув.400.
больных. Использовали моноклональные антитела (Novocastra, Швейцария) к CD3 — общему антигену лимфоцитов, OLA-LCA-DACO (клоны 2В11 и PD7126) — общему лейкоцитарному антигену, CD10 — стволово-клеточному антигену, TdT — антигену предшественников Т и В лимфоцитов, WIM (вимен-тин) — маркёру клеток мезенхимального происхождения, CD15 — нормальных гранулоцитов, CD20 — общему В-клеточному антигену, CD68 — антигену макрофагов и гистиоцитов, Ki-67 — маркёру пролиферации, BCL-2 — белка-негативного регулятора апоптоза. Фиксацию, заливку и получение гистологических срезов осуществляли обычным способом. Подготовленные срезы помещали в термостат (при 56°С) на 30 мин. После распарафирования и промывки проиводили блокирование эндогенной пероксидазы, помещая в 3%-ный водный раствор перекиси на 10 мин с последующей промывкой в трис-буфере. Затем последовательно проводили инкубацию во влажной камере: с нормальной (неиммунной) сывороткой (50–100 мкл) 30 мин при комнатной температуре, с первыми (специфичными) антителами (50–100 мкл) 1 час в термостате при 37°С, со вторыми (биотинилированными) антителами (50–100 мкл) 30 мин при комнатной температуре, с авидин (стрептавидин)-биотин-пероксидазным комплексом (50–100 мкл) 30 мин при комнатной температуре с двукратной промывкой в трис-буфере после каждого этапа. Далее производили выявление пероксидазы хрена диаминобензидином (раствор готовили ех tempore по инструкции, прилагающейся к набору), контролируя реакцию под микроскопом. Окрашенные таким образом срезы просветляли и заключали в бальзам. Статистическую обработку данных проводили с использованием t-критерия Стьюдента, применяя стандартный пакет статистических программ Windows 98 (StatSoft 5.5). Морфологический и гистохимический анализы, а также фотографирование производили с помощью системы AxioVision 4 (Carl Zeiss, Германия).
Результаты исследования. На серийных гистологических срезах печени онкологических больных обнаруживается следующая картина. В участках, удалённых от метастаза, на фоне сохранения структуры долек с синусоидами неравномерного кровенаполнения в области триад наблюдается избыток волокнистой соединительной ткани, содержащей умеренные лимфо-макрофагальные инфильтраты (рис. 1а,б). Внутри долек, образованных гепатоцитами в состоянии белковой и очаговой жировой дистрофии, лейкоцитарные клетки немногочисленны (рис. 1в).
В параметастатических участках при стёртой дольковой структуре, неравномерном кровенаполнении синусоидов с признаками частичной капил-ляризации, белковой и мелкокапельной жировой дистрофии гепатоцитов вокруг сосудов портального тракта и синусоидов выявляются обширные лейкоцитарные инфильтраты. Они состоят в основном из лимфоидных клеток, но включают макрофагальные элементы и одиночные зернистые лейкоциты (рис. 2а,б). Такие же клетки инфильтрируют вокругсину-соидальные пространства (рис. 2в).
При иммуноцитохимическом исследовании с помощью моноклональных антител в лейкоцитарных инфильтратах интактных участков печени выявляется (на два-три креста) маркёр CD15, который метит созревающие моноциты, нейтрофилы и эозинофилы (рис. 3а,б). Внутри синусоидов можно обнаружить отдельные слабо положительные CD10+ (CALLA-“common”) и хорошо окрашенные TdT+ клетки, являющиеся бластными предшественниками В- и Т-лимфоцитов (рис. 3в,г). В мелких лейкоцитарных инфильтратах параметастатических участков определяются лимфоциты (CD3+ клетки), дающие средний уровень окрашивания в области цитоплазмы и ядерной оболочки клеток (рис. 3д). В крупных портальных лейкоцитарных инфильтратах пара-туморальных участков печени выявляются многочисленные клетки, экспресcирующие антиген всех клеток мезенхимного происхождения — виментин (WIM) (рис. 3е). Такая же яркая реакция отмечается на ядерной оболочке и в цитоплазме лейкоцитов крупных паратуморальных инфильтратов при использовании маркёров ОЛА-LCA-DAKO (клоны 2B11 и PD7126) к общему лейкоцитарному антигену (рис. 3ж). Антиген CD68 экспрессируется в цитоплазме моноцитов и макрофагов, расположенных в стенке синусоидных капилляров (рис. 3з). Отдельные клетки параметастатических участков метятся маркёром пролиферации (Ki-67) (рис. 3и). В лимфоидных инфильтратах печени почти отсутствует реакция при метке CD20 — pan-В-маркёром (В-лимфоцитов и В-лимфом).
Для того, чтобы выяснить, какие популяции мононуклеарных лейкоцитов формируют инфильтраты в паратуморальных и интактных участках печени онкологических больных, были проведены исследования морфологических, иммунофеноти-пических и функциональных особенностей клеточных популяций, выделенных из различных участков поражённой метастатическим процессом печени онкологических больных. У первичных больных, которым в предоперационном периоде не проводилась лучевая и химио- терапия, удалось выделить 5-6 x 10 6 мононуклеарных клеток из 1 см 3 печени. При этом в количество клеток в паратуморальной области в 1,5–2 раза превышало их число в интактных участках печени. У пациентов, получивших в предоперационном периоде курс лучевой и химиотерапии, количество МЛ печени составляло не более 1 x 10 6 в 1 см 3 . У больной раком молочной железы с метастазами в печень, предварительно получившей 4 курса химиотерапии, не удалось выделить МЛ из
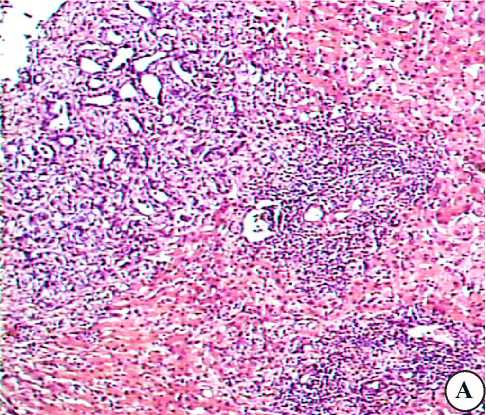
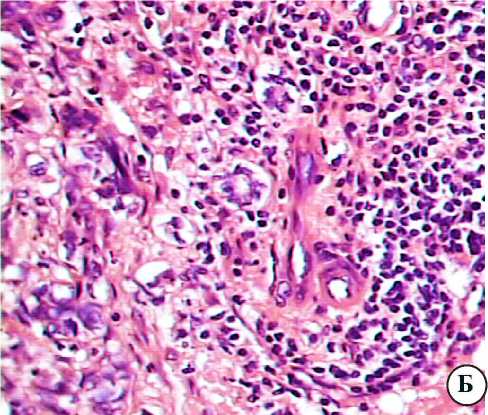
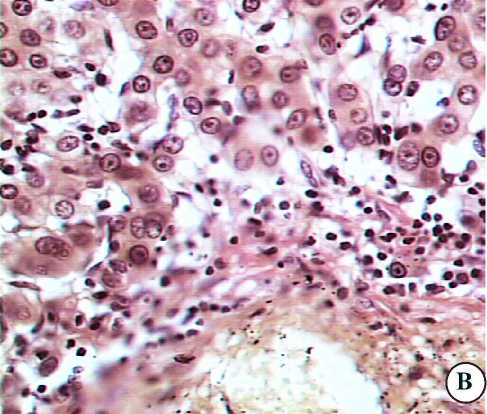
Рис. 2. Паратуморальные участки поражённой метастатическим процессом печени онкологических больных: а — окраска гематоксилином и эозином; Ув. 200; б,в — окраска гематоксилином и эозином. Ув. 400.
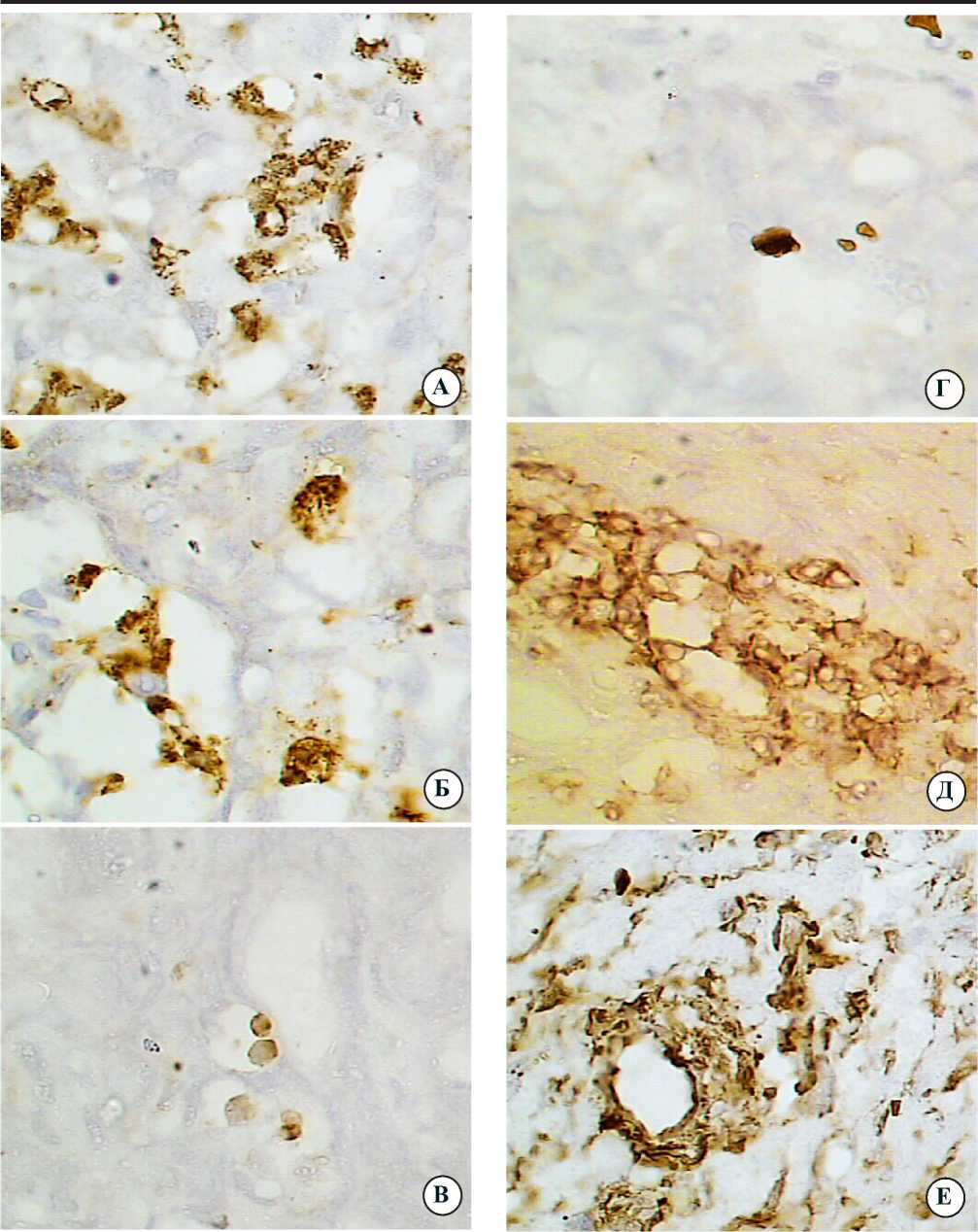
Рис. 3. Интактные и паратуморальные участки печени онкологических больных с клетками, меченными моноклональными антителами: а,б — CD15; в — CD10; г — Tdt; д — CD3; е - WIM; ж — Ola;
з — CD68; и — Ki67; докраска ядер гематоксилином; Ув.900..
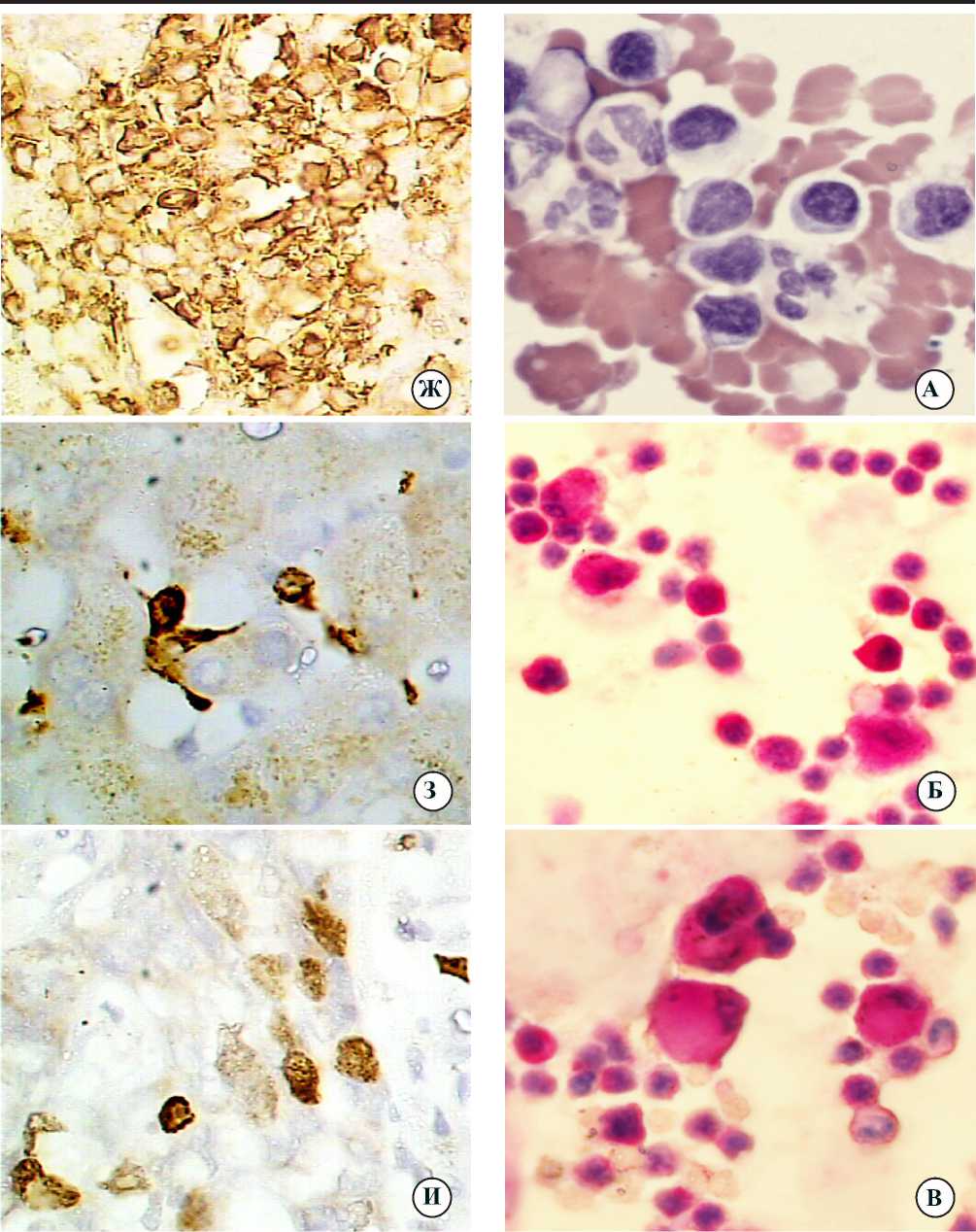
Рис. 4. Мононуклеарные лейкоциты (МЛ) в мазках культуральной взвеси клеток, выделеннвых из интактного, параметастатического и метастатического участков печени онкологических больных: а —МЛ из интактного участка; окраска азуром II-эозином по Романовскому-Гимза; Ув.900; б — пиронинофильные лимфоциты, бластные формы и дендритные клетки из параметастатического участка; в —пиронинофильные лимфоциты, бластные формы и дендритные клетки из метастаста-тического участка; б,в — окраска метиловым зеленым-пиронином по Браше; Ув.400
печени. В то же время у пациента больного раком почки, получавшим перед операцией один курс иммунотерапии (Интрон А), количество выделенных из печени МЛ составляло 10 x 10 6 в 1 см 3 . Следовательно, количество мононуклеарных клеток в печени зависит от типа предоперационного лечения: при лучевой и химио-терапии количество МЛ минимальное, при иммунотерапии число мононуклеарных лейкоцитов печени, по сравнению с нелечеными больными, значительно увеличивается. Морфогистохимические исследования МЛ, полученных из различных участков печени, показали, что данные клетки имеют характерные морфологические особенности. Пораженная опухолевым процессом печень инфильтрирована лимфоидными клетками типа пролимфоцитов и иммунобластов (наиболее многочисленных в параметастатических областях), которые взаимодействуют с макрофагами, нейтрофилами и дендритными клетками (рис. 4а). Среди мононуклеаров выявляется значительное количество лимфоцитов, имеющих яркую пиронинофиль-ную окраску цитоплазмы и ядрышек, исчезающую после обработки РНКазой, что свидетельствует о повышенном содержании РНК в клетках, и следовательно, об их высокой синтетической активности (рис. 4б). Пиронинофильные лимфоциты обнаруживаются как в параметастической области, так и в ткани метастатического узла (рис. 4в).
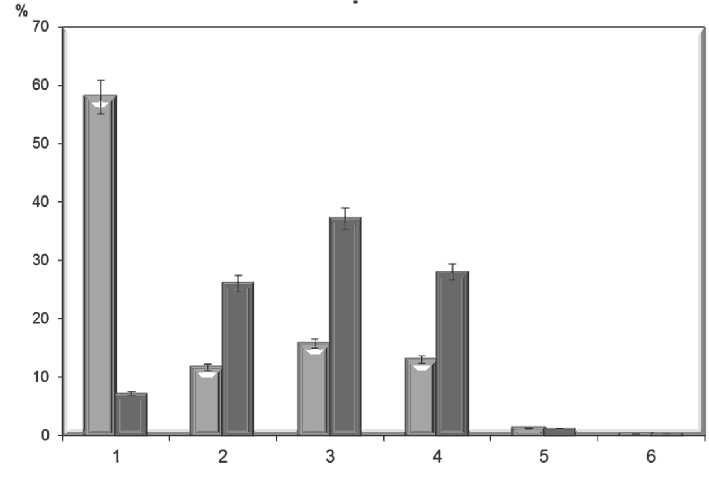
Пролимфоциты и иммунобласты, согласно данным цитологического анализа, составляют 24,7%
МЛ интактных участков печени, при этом количество пиронифильных лимфоцитов достигает 15,7% (рис. 5). В параметастатической области абсолютное большинство мононуклеарных клеток (91,3%) представлено активированными клетками лимфоидного ряда: пролимфоцитами, иммунобластами и пирони-нофильными лимфоцитами (рис. 5).
Сравнительное исследование цитотоксической активности МЛ, выделенных из интактного и паратуморального участков печени, выявило, что при тестировании на НК-чувствительной линии К-562 они не имеют достоверных отличий. В то же время по отношению к аутологичным опухолевым клеткам киллерная активность МЛ из паратумораль-ной области почти в 3 раза выше цитотоксической активности МЛ интактного участка печени (табл. 1).
Мононуклеарные клетки периферической крови больных по сравнению с мононуклеарами (МНК) печени характеризуются достоверно меньшим уровнем НК-активности и соответствуют степени активности мононуклеаров периферической крови здоровых доноров (табл. 1). МНПК больных практически не обладают киллерной способностью по отношению а аутологичным опухолевым клеткам (их активность составляет в среднем 11%). В то же время МНК интактной и особенно паратуморальной областей печени способны эффективно лизировать аутологичные опухолевые клетки. Следовательно, наибольшую цитотоксическую активность по отношению к аллогенным и аутологичным опухолевым клеткам демонстрируют мо-
Иинтактный участок нпараметастатический участок
Рис. 5. Содержание мононуклеарных лейкоцитов, выделенных из интактных и параметастатических участков печени онкологических больных: 1 – лимфоциты, 2 – пролимфоциты, 3 – пиронинофильные лимфоциты, 4 – бластные формы, 5 – макрофаги, 6 – гранулоциты.
нонуклеары, выделенные из паратуморальных участков печени больных.
Сравнительный анализ иммунофенотипа монону-клеарных лейкоцитов, выделенных из двух различных областей печени онкологических больных, показал, что процентное содержание клеток, экспрессирующих на своей поверхности диф-ференцировочные антигены СD4, СD8, СD3, CD16, в интактном и паратуморальном участках примерно одинаково (табл. 2).
Однако следует отметить, что интенсивность флюоресценции этих молекул на поверхности МНК, выделенных из параме-тастатических участков, в 1,2–1,3 раза выше, чем у МНК интактных участков. Различия иммунофенотипа
МНК двух исследованных областей печени по уровню экспрессии активационных антигенов СD25, СD38 и НК-маркёра CD57 также незначительны. В то же время число мононуклеаров паратуморальной области, экспрессирующих на поверхности молекулы адгезии (СD58), почти в 3 раза превышает их количество в интактном участке печени (табл. 2). При сравнении особенностей иммунофенотипа мононуклеарных лейкоцитов периферической крови больных и мононукле-аров поражённой опухолью печени выявлено, что наиболее выраженные различия наблюдаются между МНПК и МНК, выделенными из па-ратуморального участка. Как следует из таблицы 2, у МНК поражённой метастазами печени по сравнению с мононуклеарными лейкоцитами периферической крови онкологических больных значительно повышены уровни экспрессии дифференцировочного маркёра СD8 (в 1,5 раза), активационных антигенов СD38 (в 2,6 раза), НК-маркёра СD57 (в 1,7 раза) и молекул адгезии СD58 (в 4,6 раза). В то же время процентное содержание CD4+ клеток среди МНПК почти в 4 раза выше, чем среди МНК печени.
Таким образом, мононуклеарные лейкоциты печени онкологических больных по иммунологическому фенотипу и уровню НК-активности су-
Таблица 1 Цитотоксическая и НК-активность мононуклеарных лейкоцитов поражённой метастатическим процессом печени и периферической крови онкологических больных по отношению к опухолевым линиям
|
№ |
Источник МНК* |
К-562, % |
Достоверность различий между группами |
Аутологичные опухолевые клетки, % |
Достоверность различий между группами |
|
1 |
Интактный участок |
83,0±18,0 |
Р2 > 0,05 Р3,4 < 0,05 |
25,0±9,8 |
Р2<0,05 Р3,4>0,05 |
|
2 |
Паратуморальная участок |
90,0±6,0 |
Р1>0,05 Р3,4< 0,05 |
62,0±16,0 |
Р1<0,05 Р3,4<0,01 |
|
3 |
Кровь больных |
43,0±9,0 |
Р1,2<0,05; Р4 >0,05 |
11,0±3,3 |
Р1<0,05 Р2<0,01 Р4>0,05 |
|
4 |
Кровь здоровых доноров |
37,0±2,0 |
Р1,2<0,05 Р3>0,05 |
19,0±4,2 |
Р1,3 >0,05 Р2<0,01 |
Примечание: соотношение клеток-эффекторов и клеток-мишеней 1:5.
щественно отличаются от МНПК тех же больных. Из полученных данных следует, что они являются преимущественно СD3+
Т-лимфоцитами, но в отличие от мононуклеа-ров периферической крови активно экспрессируют на своей поверхности антигены натуральных киллеров (СD57).
Обсуждение. Сравнительная характеристика лейкоцитарных инфильтратов различных областей поражённой метастазами печени показала, что в зависимости от локализации они имеют разные размеры и клеточный состав. В интактных участках печени онкологических больных лейкоцитами инфильтри-
Таблица 2
Ииммунологический фенотип мононуклеарных лейкоцитов, выделенных из поражённой метастатическим процессом печени и периферической крови онкологических больных
|
CD-маркёр |
Содержание мононуклеарных лейкоцитов (МЛ), % |
Достоверность различий между группами |
||
|
Интактный участок печени (группа №1) |
Паратуморальный участок печени (группа №2) |
Периферическая кровь (группа №3) |
||
|
CD3 |
60,5±14,0 |
79,9±20,0 |
76,9±18,0 |
Р1,2 > 0,05; Р1,3 > 0,05; Р2,3 > 0,05 |
|
CD4 |
9,1±1,7 |
10,4±4,4 |
36,6±13,0 |
Р1,2 > 0,05; Р1,3 < 0,05; Р2,3 < 0,05 |
|
CD8 |
42,2±4,7 |
50,9±12,0 |
35,0±12,0 |
Р1,2 > 0,05 Р1,3 > 0,05; Р2,3 > 0,05 |
|
CD16 |
10,4±4,2 |
12,2±1,1 |
19,1±6,0 |
|
|
CD25 |
5,7±1,7 |
6,6±1,4 |
4,5±1,6 |
|
|
CD38 |
42,2±2,0 |
35,9±4,3 |
13,8±2,7 |
Р1,2 > 0,05; Р1,3 < 0,05; Р2,3 < 0,05 |
|
CD57 |
31,9±5,2 |
37,1±4,9 |
24,3±3,4 |
Р1,2 > 0,05; Р1,3 > 0,05; Р2,3 > 0,05 |
|
CD58 |
24,0±9,0 |
71,5±19,0 |
15,6±3,8 |
Р1,2 < 0,05; Р1,3 > 0,05; Р2,3 < 0,01 |
руется в основном междольковая соединительная ткань, а среди клеток преобладают макрофаги, моноциты и гранулоциты. В параметастатических областях печени более крупные и распространённые лейкоцитарные инфильтраты расположены как в соединительной ткани вокруг портальных сосудов, так и среди гепатоцитов в нарушенных дольках. Клеточный состав инфильтратов здесь представлен всеми видами клеток мезенхимного происхождения (WIM+) и лейкоцитов (OLA+), среди которых обязательно присутствуют лимфоциты (CD3+) и размножающиеся клетки (Ki67+). Макрофаги в стенке синусоидных капилляров, меченные маркёром CD68, выявляются и в интактных, и в околометастатических участках, так же как и незначительное количество слабо окрашивающихся CD10+ и Tdt+ бластных клеток-предшественников — внутри синусоидов тех и других областей. Таким образом паратуморальные участки поражённой метастазами печени онкологических больных содержат большее, чем интактные, количество мононуклеарных лейкоцитов, которые включают размножающиеся, активированные и зрелые лимфоциты. Морфогистохимический анализ показал, что популяция мононуклеарных лейкоцитов в паратуморальных областях пораженной метастазами печени состоит в основном из молодых (бластных форм и пролимфоцитов) и синтетически активных (обладающих ярко пиронинофильной цитоплазмой и многочисленными крупными пиро-нинофильными ядрышками) клеток лимфоидного ряда, что свидетельствует о процессах клеточной дифференцировки, бласттрансформации и активации, приводящих, по-видимому, к формированию субпопуляции НКТ-клеток. Обнаруживаются также отдельные клеточные формы, имеющие морфогистохимические характеристики дендритных клеток. По иммунологическому фенотипу мононуклеарные лейкоциты печени онкологических больных, выделенные из параметастатических участков, существенно отличаются от клеток лейкоцитарных инфильтратов интактных областей, а также от МЛ периферической крови тех же больных и характеризуются повышенным уровнем экспрессии молекул CD38, CD57, CD58. Они являются преимущественно СD3+ Т-лимфоцитами, но в отличие от мононуклеаров периферической крови активно экспрессируют на своей поверхности антигены натуральных киллеров (СD57). Печень-ассоциированные лимфоциты, выделенные из паратуморальных областей, обладают достоверно большей НК-активностью по отношению к линии опухолевых клеток эритробластного лейкоза К 562 и большей цитотоксической способностью по отношению к аутологичным опухолевым клеткам, чем лимфоциты периферической крови больных. Наиболее значимые различия выявляются при соотношениях клетка-мишень/эффектор — 1:2, 1:1, 1:0,5. Основываясь на выявленных морфологиче- ских, функциональных и иммунофенотипических особенностях и учитывая литературные данные, лимфоциты, выявляющиеся в лейкоцитарных инфильтратах паратуморальных областей печени онкологических больных с распространённым метастатическим процессом можно отнести к популяции НКТ-клеток. Эту особую субпопуляцию лимфоцитов — так называемые печень-ассоциированные НК, или натуральные киллеры Т-клетки — в последние годы выделили в процессе экспериментальных исследований. Данные клетки — уникальный подтип Т-лимфоцитов, вовлечённых в процессы регуляции иммунного ответа и связанных с большим количеством заболеваний, включая онкологические, аутоиммунные и инфекционные. НКТ-клетки реагируют с I классом антигенпрезентирующих молекул CD1d и распознают гликолипидные антигены лучше, чем пептидные. Более того, они могут оказывать стимулирующее или угнетающее действие на иммунный ответ посредством стимуляции секреции регуляторных цитокинов Th1 и Th2 клетками и рассматриваются в качестве эффекторов для клеточной терапии [21]. По своим фенотипическим характеристикам данные лимфоциты печени отнесены к НКТ-клеткам, поскольку на их мембране наблюдается экспрессия и маркеров Т-клеток, и натуральных киллеров (СD16, СD57, CD161 или NK1.1 у мышей) [13, 14, 16-18, 22]. Эта субпопуляция лимфоцитов характеризуется высокой НК-активностью, повышенной экспрессией молекул адгезии (что обеспечивает их фиксацию в области поражения и взаимодействие с антигенпрезентирующими дендритными и с опухолевыми клетками), увеличенным количеством активационных антигенов на поверхности. Большое количество экспериментальных исследований, проводимых на мышах, показало, что НКТ-клетки печени играют важную роль в формировании противоопухолевого иммунитета. В частности, обнаружена инфильтрация НКТ-клетками ткани печени мышей, пораженной опухолевым процессом, особенно параметастатиче-ских участков этого органа [5, 17, 19, 22-25]. Известно, что НКТ обладают антиметастатической активностью и их активация может существенно усиливать цитотоксический потенциал данной разновидности НК. Рассматриваемый антиметастатический эффект авторы связывают с активацией натуральных киллеров печени посредством увеличения секреции ИЛ-12, стимулированными ЛПС дендритными клетками органа [20, 23].
Заключение. При исследовании поражённой метастатическим процессом печени онкологических больных выявлено, что лимфоциты, инфильтрирующие паратуморальные области органа, могут дифференцироваться в НКТ-клетки. При стимуляции НКТ-клеток онкологических больных IL-2 возможна дифференцировка их в активные ЛАК-клетки, которые играют важную роль в противоопухолевом иммунитете. Полученные данные могут быть использованы для разработки методов локорегионарной адъювантной иммунотерапии метастазов в печень.
Список литературы Морфофункциональная и иммуногистохимическая характеристики клеток лейкоцитарных инфильтратов печени онкологических больных
- Halama N, Michel S, Kloor M, Zoernig I, Pommerencke T, von Knebel Doeberitz M, Schirmacher P, Weitz J, Grabe N, Jager D. The localization and density of immune cells in primary tumors of human metastatic colorectal cancer shows an association with response to chemotherapy // Cancer Immun. -2009. - №19. - Р910.
- Zitvogel L, Tesniere A, Kroemer G. Cancer despite immunosurveillance: immunoselection and immunosubversion // Nat Rev Immunol. - 2006. - №6. - Р.715727.
- Dunn GP, Bruce AT, Ikeda H, Old LJ, Schreiber RD. Cancer immunoediting: from immunosurveillance to tumor escape // Nat Immunol. - 2002. - №3. - Р.991 998.
- Abo T., Kawamura T., Watanabe H. Phisiological responses of extrathimic T cells in the liver // Immunology Review. - 2000. - V.174(2). - P.135-149.
- Fuji N., Ueda Y., Fujiwara H. et al. Antitumor effect of agalactosylceramide (KRN7000) on spontaneous hepatic metastases requires endogenous interleukin 12 in the liver // Clinical Cancer Research. - 2000. - V. 6. - № 8. - P.3380-3387.
- Bui JD, Schreiber RD. Cancer immunosurveillance, immunoediting and inflammation: independent or interdependent processes? // Curr Opin Immunol. - 2007. - №19. - Р.203208.
- Swann JB, Vesely MD, Silva A, Sharkey J, Akira S, Schreiber RD, Smyth MJ. Demonstration of inflammationinduced cancer and cancer immunoediting during primary tumorigenesis // Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. - 2008. - V.105. - P.652656.
- Oble DA, Loewe R, Yu P, Mihm MC Jr. Focus on TILs: prognostic significance of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in human melanoma // Cancer Immun. - 2009. - №2. - Р.913.
- Bai A, Higham E, Eisen HN, Wittrup KD, Chen J. Rapid tolerization of virusactivated tumorspecific CD8 T cells in prostate tumors of TRAMP mice // Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. - 2008. - V.105. - P.1300313008.
- Parmiani G. Tumorinfiltrating T cellsfriend or foe of neoplastic cells? // N Engl J Med. - 2005. -V.353. - P.26402641.
- Yu P, Fu Y. Tumorinfiltrating T lymphocytes: friends or foes? // Lab Invest. - 2006. - V.86. - P.231245.
- Chiou S, Sheu B, Chang W, Huang S, HongNerng H. Current concepts of tumorinfiltrating lymphocytes in human malignancies // J Reprod Immunol. - 2005. - V.67. - P.3550.
- Emoto M., Kaufmann S.H. Liver NKT cells: an account of heterogeneity // Trends Immunology. -2003. - V.24. - № 7. - P.368-369.
- Godfrey D.I., Hammond K.J., Poulton L.D. et al. NKT cells: facts, functions and fallacies // Immunology Today. - 2000. - № 21. - P.573-583.
- Kakimi K., Guidotti L.G., Koezuka Y. and Chisari F.V. Natural killer T cell activation inhibits hepatitis B virus replication in vivo // The Journal of Experimental Medicine. - 2000. - V.192 (7). - P.921930.
- Kasper H.U., Drebber U., Zur Hausen A. et al. Dominance of CD4 alpha/beta Tcells and inferior role of innate immune reaction in the liver metastases // Anticancer Research. - 2003. - V.23. - №4. - P.3175-3181.
- Kenna T., Mason L.G., Porcelli S.A. et al. NKT cells from normal and tumorbearing human liver are phenotypically and functionally distinct from murine NKT cells // Journal of Immunology. - 2003. - V.166. - № 11. - P. 6578-6584.
- Lucas M., Gadola S., Meier U. et al. Frequency and phenotype of Circulating Va24/Vb11 doublepositive natural killer cells during hepatitis C infection // Journal of Virology. - 2003. - V.77( 3). P. - 2251-2257.
- Nakagawa R., Nagafune I., Tazunoki Y. et al. Mechanisms of the antimetastatic effect in the liver and of the hepatocyte injury induced by agalactosylceramide in mice // The Journal of Immunology. - 2001. - V.166. - № 11. - P. 6578-6584.
- Park S.H., Kyin T., Bendelas A., Carnaud C. The contribution of NKT cells, NK cells, and other gammachain dependent nonT nonB cells to IL12mediated rejection of tumors // The Journal of Immunology. - 2003. - V.170. - № 3. - P.1197-1201.
- Godfrey D.L., Kronenberg M. Going both ways: Immune regulation via CD1dpdependent NKT cells // Clin. Invest. - 2004. - V.114. - P.1379-1388.
- Joyce S., Van Kaer L. CD1restricted antigen presentation: an oily matter // Curr. Opin. Immunol. -2003. - V.15. - P.95-104.
- Stober D., Jomantaite I., Schirmbeck R., Peimann J. NKT cells provide help for dendritic celldependent priming of MHC class Irestricted CD8 T cells in vivo // The Journal of Immunology. - 2003. - V.170. - № 5. - P.2540-2548.
- Trobonjaca Z., Kroger A., Stober D. et al. Activating immunity in the liver. II. IFNb attenuates NK celldependent liver injury triggered by liver NKT cell activation // The Journal of Immunology. - 2002. - V.168. - № 8. - P.3763-3770.
- Varma T.K., Lin C.Y., ToliverKinsky T.E. et al. Endotoxininduced gamma interferon production: contributing cell types and key regulatory factors // Clinical and Diagnostic Laboratory Immunology. -2002. - V.9. - № 3. - P.530-54.


