Motivation types: a key factor in self-regulated ESP learning
Автор: Afranj J., Bulatovi V., Gak D.
Журнал: International Journal of Cognitive Research in Science, Engineering and Education @ijcrsee
Рубрика: Original research
Статья в выпуске: 2 vol.12, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The objective of this paper is to examine the impact of motivational orientations, or various forms of motivation, on the success of foreign language (L2) learning as a measure of self-regulation for ESP (English for Specific Purposes) students. It has been postulated that the nature of motivation has a substantial impact on second language (L2) learning, as evidenced by success as a measure of self-regulated learning. This association remains consistent even when moderator variables such as gender, age at which L2 learning begins, and years of L2 learning are integrated. This empirical research covered 460 respondents, of whom 245 (53%) were male. The students attended the Faculty of Technical Sciences (FTS) at the University of Novi Sad. The Foreign Language Learning Motivation Questionnaire (LLOS-IEA) was used as an instrument. Scale reliabilities were measured using Cronbach’s alpha indicating satisfactory reliability. An achievement test with 50 tasks and a general data questionnaire were applied. PROCESS macro for SPSS was used for statistical analyses. The initial results indicate that students are highly motivated, with Intrinsic regulation (Knowledge, Achievement, and Stimulation) and Identified regulation achieving the highest scores with good motivational orientation that are significant predictors of self-regulation, which was also seen as an indicator on the L2 achievement test. Additionally, their levels of amotivation are low, while their levels of various categories of motivation are moderate. A notable positive predictor is identified regulation, suggesting that motivation facilitated by identified regulation is linked to an improved grade in L2 and overall achievement. Furthermore, it was determined that ESP students exhibit distinct types of motivation compared to other students, which serves as an indicator of self-regulation in ESP learning. It was established that ESP accomplishments are determined by the types of motivation present in L2 learning. The age of starting L2 learning, years of L2 learning, and gender are insignificant factors in the relationship between the observed variables. Also, it is recommended that future studies should be based on a larger corpus and include not only students of the technical sciences but also students of the social sciences in order to overcome its limitations.
Types of motivation, self-regulation, esp students, l2 learning
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/170206404
IDR: 170206404 | УДК: 159.947.2-057.875 | DOI: 10.23947/2334-8496-2024-12-2-317-334
Текст научной статьи Motivation types: a key factor in self-regulated ESP learning
Self-regulation in learning refers to the capacity to cultivate knowledge, abilities, and attitudes that facilitate and enhance the learning process, as well as transfer it to different learning contexts ( Baumert et al., 1998 ; Sorić, 2014 ; Oga-Baldwin et al., 2022 ). Numerous studies examine it in relation to theoretical approaches and models, in addition to their practical validation. Ziegler et al. (2021) note that effective learning is more important than a high IQ. The same author emphasises that effective learning rooted in self-regulated learning is essential for high achievement. As Zimmerman (2002) remarks, self-regulation in learning is unlikely a mental ability or skill of performing a specific task but a guiding process by which students transform their mental abilities into learning skills. Therefore, it is not about the characteristics that someone possesses, which accordingly can be more or less effective, but about changing a learning style, which is reflected in success in self-regulation and recognised in the fields of meta-cognition and learning motivation. This is important for L2 learning, as it directs the search for ways to develop the above-mentioned mechanisms of self-regulation.
For several decades, motivation has been at the top of the list of research topics in many areas of learning and teaching activity, along with teaching pedagogy, whose role in the speed and success of L2

© 2024 by the authors. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license .
learning is also important. Researchers noticed its importance as an incentive to begin L2 learning, and its subsequent role as an impetus for the continuation of a lengthy and frequently tedious educational process ( Dörnyei, 1998 ). Consequently, despite its complexity and multifaceted nature ( Gardner et al., 1985 ), which is composed of several factors such as the value of the task, the level of success that learners expect, self-confidence, and understanding the reasons for their success or failure on the task ( Dörnyei and Ushioda, 2011 ), motivation has been the focus of researchers for decades due to its complexity. Attention is specifically focused on the types of motivation and motivational strategies that help students adopt positive attitudes towards language learning and develop motivation. This requires knowledge of the motivational levels of the group and individuals in order to define and adjust didactic instructions to the needs of those who are learning, since different levels or types of motivation presuppose different approaches to encourage students, facilitate learning, and make it more efficient ( Reinders et al., 2023 ; Wolters et al., 2023 ). Regarding the ESP students, there is a belief that they learn easily and quickly, as well as that they have a high level of internal motivation. This research aims to investigate these assumptions as well as check the relationship between the type of motivation and achievement.
Pedagogical psychology links research on motivation to the acquisition of L2 skills. Gardner and her associates (1985) investigated the basic elements of motivation for L2 learning: motivational intensity or effort, desire to master L2, and attitude towards L2 learning . According to Dörnyei and Ushioda (2011) , Gardner´s research is important for this field as he noticed the difference between motivation and orientation, i.e., goal. According to Gardner, the goal is an incentive that creates motivation and directs it towards achieving the desired effects. Thus, orientation is considered a significant precursor, or driver of motivation: integrative orientation, or interest in interacting with the L2 group, and instrumental orientation , interest in the more materialistic and practical advantages of L2 learning, i.e., seeking a better career ( Dörnyei and Ushioda, 2011 ; Mystkowska-Wiertelak and Bielak, 2023 ).
Dörnyei and Ushioda (2011) introduced a novel L2 learning method known as «L2 motivational self-respect,» which establishes a connection between L2 learning and personal identity. This method has implications for the acquisition of L2 skills, as it fosters the development of self-motivation and selfmaturity among students.
In opposition to Gardner’s emphasis on integrity, Dörnyei’s perspective is that instrumental orientation has a more significant influence on L2 acquisition in the context of English as a Foreign Language (EFL). In addition, he emphasises the necessity of a more pragmatic education, a focused approach, the study of reality in the classroom, and the identification and examination of motives for L2 learning in the classroom ( Dörnyei and Ushioda, 2011 ). These are all factors that teachers should consider when motivating students for L2 learning.
Also, it is important to point out more details about motivational orientations because their characteristics could be employed to quantify the impact of didactic instructions on the academic efficiency of L2 students in accordance with the characteristics of their motivation. The initial occurrence of amotivation is the failure of students to recognise the connection between their actions and the repercussions of these actions. Amotivated L2 learners are under the impression that they are squandering their time while learning L2. In addition, the difference between demotivation and amotivation should be noted as well. Dornyei (2001a) made a significant finding that holds relevance for educators: when students perceive outcomes as unreasonable and unattainable, it results in amotivation as they recognise that the objective is beyond their capabilities and unattainable. Consequently, amotivation is defined as an absence of motivation.
Instruments such as the Academic Motivation Scale (AMS 28 or 32) and the Foreign Language Learning Motivation Questionnaire (LLOS-IEA; Noels, Pelletier, Clement and Vallerand, 2000, etc. ) are accepted and used in the majority of research. These analyses are grounded in Self-Determination Theory (SDT), as they have received confirmations of their metric properties, including factor analysis, dimensionality, reliability, and construct validity, in statistical analyses conducted in multiple countries. The hypothetical 7-factor model was also mainly confirmed: Internal motivation - knowledge; Internal motivation - achievement; Internal motivation - stimulation; External motivation - identified; external motivation - introjected; External motivation - external regulation; Amotivation . They will be briefly explained in the following part of this paper.
Thus, aspects of motivation line up along the continuum, depending on the internalization of behaviour ( Deci, 1975 ; Deci and Ryan, 1985 ). It is common to distinguish three types of motivation: internal and external motivation, with amotivation located at the far left end of the continuum.
Amotivation represents a state of lack of motivation, and the locus of control is indeterminate. In amo-tivated students, there is a lack of congruence between opinions and activities, and in the academic context, this means that they failed to define reasons for schooling or see any point in it ( Niemiec et al., 2009 ). External motivation is divided into four narrower aspects and defined as regulation. External regulation reflects a behaviour that is determined by external reinforcements with less effective consequences and short-term effects ( Hagger and Chatzisarantis, 2007 ; Ryan et al., 2008 ; Henry and Liu, 2023 ; Al-Hoorie, 2024 ).
|
Amotivation |
Extrinsic motivation |
Intrinsic motivation |
|
|
Non Regulation |
External Introjected |
Identified Integrated |
Intrinsic Regulation |
|
Regulation Regulation |
Regulation Regulation |
||
|
Least selfdeterminated |
<-------- |
--------> |
Most selfdeterminated |
|
Amotivation = |
Controlled motivation = |
Autonomous motivation = |
|
|
lack of motivation |
low-quality motivation |
high-quality motivation |
|
Figure 1. Continuum of self-determination (Ryan and Deci, 2000:72)
Extrinsic or external motivation refers to the pressure or reward of the social environment for L2 learning. Extrinsically motivated students aim to acquire knowledge for better career opportunities and the like. As a result, because external influences stimulate motivation, removing them could potentially lead to the student ceasing to acquire the second language ( Noels et al., 2001 ). Therefore, it pertains to external motivation, encompassing a diverse array of actions employed to attain a specific objective rather than solely for personal fulfilment ( Deci, 1975 ). The first conceptions of external motivation describe behaviour that is not self-determined, and the term implies behaviour that is encouraged by external factors (punishment, reward, control). More recently, researchers ( Ryan et al., 1990 ; Deci and Ryan, 1985 ; Alastair and Meng, 2024 ) determined that external motivation varies along the self-determination continuum. External regulation, introjection, and identification are used to describe self-determination from low to high levels. In recent literature, external regulation is often presented as a type of motivation that refers to behaviour controlled by external factors. (rewards, restrictions, imposition of demands, expectation, etc.).
Introduced regulation occurs when people start to internalize the reasons behind their actions, when they believe their environment has influenced their behavior but have not fully integrated it into their personal value system, and especially when they value and consider their behavior to be significant. Such situations arise as a consequence of avoiding a sense of guilt. Understanding their importance and contribution to self-realization leads to identified regulation. Consequently, identified regulation has come to be defined as conduct that an individual adopts on the basis of its intrinsic value, rather than for future benefits and contributions. Research findings indicate that identified regulation does not stem from internal motivations, and rather, it results in diminished levels of self-determination. ( Jang et al., 2010 ; Baard et al., 2004 ; Alastair and Meng, 2024 ).
The next step on the ladder of motivational hierarchy of self-determination is the so-called adopted or introjected regulation , which is of a higher level and is essentially about the acceptance of behaviours from the environment that are not yet fully internalized in the personal value system. Findings indicate that this type of self-regulation occurs to avoid a sense of guilt.
Integrated regulation is the closest to intrinsic motivation on the continuum of self-regulation and is associated with positive outcomes such as pro-social development and psychological well-being ( Ryan and Deci, 2000 ; Ryan et al., 2008 ). Integrated regulation refers to the behaviours that are consistent with the values of the individual for L2 learning and teaching and are considered the most existing in the system of students’ self-regulation ( Gojkov-Rajic et al., 2021a ; Gojkov-Rajić et al. 2023 ; Wolters et al., 2023 ).
Intrinsic motivation, which contains the internal locus of control and promotes mastery, spontaneous interest, and research, is at the far right end of the self-regulation continuum and is essential for cognitive development (Deci, 1975; Deci and Ryan; Al-Hoorie, 2024). Valerand et al. (2003) hypothesized that intrinsic motivation consists of three dimensions that describe the natural inclination towards cognition, stimulation, and achievement, which is encouraging for further research to provide a clearer picture of the possibilities for personalization of didactic instruction in L2 teaching.
The essential motivation is to know something new. This inner motivation includes inquiry, curiosity, and learning goals. Epistemic knowledge and understanding are essential for intrinsic learning motivation. This involves engaging in activities you enjoy while learning, investigating, or attempting to understand something.
Internal achievement motivation is another intrinsic motivation, and it is recognized in pedagogical psychology and didactics as motivation for mastering, motivation for efficacy, and task orientation. Research indicates that individuals communicate with their environment to feel competent and attain distinct goals ( Deci, 1975 ; Deci and Ryan, 1985 , 1991; Mystkowska-Wiertelak and Bielak, 2023 ). Consequently, we define it as an orientation towards accomplishments, where individuals engage in activities driven by the joy and satisfaction they derive from striving to accomplish or create something novel. This, in turn, leads to a sense of personal satisfaction after mastery of complex training techniques (e.g., participating in scientific meetings, communicating in L2).
The third form of internal motivation, internal motivation for experiencing stimulation , is characterised by participation in an activity with the goal of experiencing stimulating sensations such as fun, aesthetic experiences, and excitement.
|
Amotivation |
Extrinsic motivation |
Intrinsic motivation |
|
|
Non Regulation |
External Introjected |
Identified Integrated |
Intrinsic Regulation |
|
Regulation Regulation |
Regulation Regulation |
||
|
Least selfdeterminated |
<-------- |
--------> |
Most selfdeterminated |
|
Amotivation = |
Controlled motivation = |
Autonomous motivation = |
|
|
lack of motivation |
low-quality motivation |
high-quality motivation |
|
Figure 2. An overview of the above outline of motivational orientations and types
Intrinsic motivation is characterized by a sense of satisfaction and originates from a sense of competence, autonomy, and connectedness ( Ryan and Deci, 2000 ; Oga-Baldwin et al., 2022 ; Henry and Liu, 2023 ). Also, internal motivation is considered more self-determined than external motivation and refers to internal factors such as the sense of pleasure and satisfaction. Internally motivated activities are related to the emotions associated with the exploration of new ideas and the acquisition of abilities and fundamentals related to an attempt to overcome a task or achieve a goal.
The presented types of motivation are also important for research in L2 learning and teaching in order to perceive them more clearly and distinguish the ways in which the teacher can facilitate students in self-regulating their learning, i.e., stimulating their motivational potentials ( Jandrić et al., 2018 ; Vallerand et al., 2021 ; Ramos and Habig, 2019 ; Crnjak, 2019 ; Mystkowska-Wiertelak and Bielak, 2023 ).
The advancement of technology has significantly altered the motivation of contemporary generations. A substantial proportion of the youth population exhibits a lack of motivation and fails to differentiate between their own actions and unanticipated outcomes. These individuals’ motivations are neither intrinsic nor extrinsic. They attend classes with a lack of appreciation for the value of education and consider it a futile investment of time and energy. In their study, Gillet (2012) examined the motivation of young individuals, identified effective strategies, and explored potential avenues for addressing the intricacies of education systems, learning, and assessing positive outcomes of educational endeavours. He suggested modifying existing pedagogical methods and offering a variety of learning environments to accommodate the requirements of the students. Neglect may prevent students from being academically motivated, according to one of his notes. Other authors have also arrived at similar conclusions, which they define as the necessity for increased autonomy in teaching and learning activities (Gojkov-Rajić et al., 2020).
Teachers’ influence on student motivation and methods for fostering and sustaining motivation in the classroom were investigated in Mastoor Al Kaboodi’s (2013) study. He encourages teachers to motivate students and keep them motivated throughout their learning. It is based on a meta-analysis of motivation studies he did to uncover classroom strategies and solutions for teachers.
A number of studies ( Dörnyei, 2003 ; Dörnyei and Ushioda, 2011 ; Wolters et al., 2023 ). found that the integrative component has a significant part in the variance when it comes to motivational spirit and persistence in L2 learning, which in some sense led to upheaval on the scene of acceptance of the motivational model, i.e., transition from the socio-educational to the psychological model. The integrative nature of the multifactorial complexity of L2 learning is the focus of Gardner’s model. However, practical L2 learning research show that instrumental orientation affects language learning more. Research suggests a need for a pragmatic approach to education, focused methodology, classroom investigation, and examining learning motivations ( Dörnyei, 1990, 1994, 1997, 2001a, 2001b ; Dörnyei and Ushioda, 2011 ; Williams, 1994 ; Gojkov-Rajić et al., 2021b ; Wolters et al., 2023 ). A novel L2 learning method called “L2 motivational self-respect” has been promoted. Foreign language learning and personal identity impact self-maturity and motivation to master L2 ( Šafranj et al., 2021 ; Oga-Baldwin et al., 2022 ; Henry and Liu, 2023 ).
Culture and identity also motivate L2 students, according to Cortazzi and Jin (1999) .
The abovementioned studies rely on a theoretical orientation that also includes the dynamic dimension of motivation, and is relevant as a theoretical approach due to its possibility of being applied in didactic practice.
-
• In their research, Utvær and Gørill (2016) also started from the principles of Self-Determination Theory, distinguishing types of motivation according to the types of self-regulation along the continuum of internalization, which are also used as types of motivation related to quality and outcome. In the research, the following variables were identified as predictors of educational outcomes: learning, performance, engagement, and persistence. This leaves room for further research into the relationship between types of motivation and academic success, which is the basis of our research. Specifically, the previously mentioned findings raise the following question or issue:
-
• The problem or research question is whether there are differences in motivational orientations, or types of motivation, between the ESP and other students, which are indicators of self-regulation in L2 learning. What is the extent to which the types of motivation determine the achievements in L2 learning?
-
• Objective : The paper aims to reach the relationship between types of motivation for L2 learning and their effect on success in L2 learning as a measure of success in self-regulation for ESP students. The intention is to understand their influence on the success of L2 learning.
-
• Hypothesis : It is assumed that the types of motivation significantly affect L2 learning, that this will affect success as an indicator of self-regulated learning, and that this relation will be maintained even in the case of the introduction of moderator variables.
-
• Working hypotheses :The types of motivation are correlated with success in L2 and explain a significant part of the variance in learning self-regulation, resulting in learning outcomes, i.e., L2 achievement test L2 for ESP students in relation to others (grades on the L2 achievement test correspond to the types of motivation, which allows to make conclusions about self-regulation as a factor of academic achievement of ESP students; or grades on the L2 achievement test depend on the type of motivation).Age of starting L2 learning, years of L2 learning, and gender are insignificant factors in the relationship between the observed variables.
-
• Variables :
predictors: types of motivation (intrinsic motivations, extrinsic motivations, and amotivation; subclasses: amotivation, external incentives, integrated incentives, identified regulation, internal motivation-knowledge, internal motivation-fulfilment, internal motivation-stimulation);
criteria: success in the L2 achievement test moderators: age of starting L2 learning; years of L2 learning; gender
Method
Sample
The convenience sampling was applied to 460 respondents who participated in the research, of whom 245 (53%) were male. The students were from the Faculty of Technical Sciences in Novi Sad. There were 205 ESP students and 255 other students. The research was organised based on a quantitative design and performed through systematic, non-experimental observation.
Tools
Foreign Language Learning Motivation Questionnaire (LLOS-IEA; Noels, Pelletier, Clement and Vallerand, 2000) The questionnaire consists of 21 items on a five-point Likert scale and measures seven types of motivation for L2 learning: Amotivation, External regulation, Introjected regulation, Identified regulation, Knowledge, Achievement and Stimulation. The reliability of the scales measured by Cronbach’s alpha was as follows: Amotivation α = 0.87, External regulation α = 0.69, Introjected regulation α = 0.76, Identified regulation α = 0.88, Knowledge α = 0.89, Achievement α = 0.79, Stimulation α = 0.89, indicating satisfactory scale reliability.
The authors of this paper created the L2 Achievement Test, which has 40 questions, 10 for each language skill. The general questionnaire refers to general data, such as the average grade at the study, gender, years of L2 learning, and age of starting L2 learning.
Data analysis
To make it easier to understand and compare the results, we found Pearson’s correlation coefficient and average summation scores for the Foreign Language Learning Motivation Questionnaire scales. We also looked for links between different aspects of motivation and success on the L2 Achievement Test. We performed a multiple regression analysis to systematically examine the influence of motivation on success on the L2 Achievement Test. The criterion was success on the L2 Achievement Test, and the predictors included different types of motivation, the age at which the student started learning L2, how long they had been learning it, and gender.
By using the PROCESS macro for SPSS, moderator analyses were performed on gender, age of starting L2 learning, years of L2 learning, and gender to determine how they affected motivation and L2 Achievement Test success. The PROCESS macro analyses moderation using one predictor, one moderator, and one dependent variable per analysis.
We used logistic regression to examine the influence of different aspects of motivation on the prediction of ESP students. Various aspects of motivation were predicted, and whether someone was an ESP student or not was a criterion variable.
Results
Descriptive statistics
Table 1 displays the basic descriptive indicators for the study’s variables. The skewness and kurtosis values for all variables are within the acceptable range of ± 2 (George and Mallery, 2010), indicating no substantial deviation from the univariate normal distribution. On average, students show relatively low levels of amotivation, moderate levels of various aspects of motivation, and the highest scores for indenti-fied regulation. The average grade in L2 language is 8.69, indicating fine achievement in this teaching subject. On average, students started L2 learning at the age of 7, with the earliest beginning at the age of 2 and the latest at the age of 15. The average number of years of L2 learning is 12.08.
Table 1. Research variable descriptive indicators
|
Minimum |
Maximum |
Arithmetic mean |
Standard deviation |
Skewness |
Kurtosis |
|
|
Amotivation |
1.00 |
3.61 |
1.35 |
0.75 |
1.54 |
1.32 |
|
External regulation |
1.00 |
5.00 |
3.08 |
1.09 |
-0.23 |
-0.35 |
|
Introjected regulation |
1.00 |
5.00 |
2.47 |
1.09 |
0.35 |
-0.51 |
|
Identified regulation |
1.00 |
5.00 |
3.72 |
1.24 |
-0.59 |
-0.62 |
|
Knowledge |
1.00 |
5.00 |
3.26 |
1.17 |
-0.21 |
-1.00 |
|
Achievement |
1.00 |
5.00 |
3.36 |
1.09 |
-0.09 |
-1.14 |
|
Stimulation |
1.00 |
5.00 |
3.29 |
1.27 |
-0.19 |
-1.08 |
|
Age of beginning L2 learning |
2 |
15 |
7.18 |
1.89 |
0.99 |
0.83 |
|
Years of L2 learning |
3 |
20 |
12.08 |
3.79 |
-0.44 |
0.83 |
|
Grade in L2 |
6 |
10 |
8.69 |
1.31 |
-0.41 |
-0.89 |
Correlation of variables
Table 2 displays Pearson’s correlation coefficient between research variables. A high correlation exists between the variables of motivation for knowledge, achievement, and stimulation, while the intensity of the correlation is around 0.70. The grade in L2 language is significantly related to all types of motivation except external regulation . It has a mild negative correlation with amotivation , while with other types of motivation it shows a mild to moderate positive correlation. Starting a foreign language later lowers grades, while more years of learning improves them.
Table 2. Research variables’ correlation
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
|
Amotivation (1) |
1 |
0.00 |
.26** |
-.37** |
-.26** |
-.20** |
-.26** |
.15** |
-.28** |
-.14** |
|
External regulation (2) |
1 |
.21** |
.25** |
-.22** |
-.11* |
-.18** |
-.13** |
.13** |
0.06 |
|
|
Introjected regulation (3) |
1 |
0.05 |
.20** |
.18** |
.21** |
-0.06 |
-0.06 |
.13** |
||
|
Identified regulation (4) |
1 |
.32** |
.38** |
.35** |
-.12** |
.20** |
.29** |
|||
|
Knowledge (5) |
1 |
.72** |
.71** |
-.14** |
.18** |
.31** |
||||
|
Achievement (6) |
1 |
.69** |
-.13** |
.23** |
.33** |
|||||
|
Stimulation (7) |
1 |
-.22** |
.25** |
.34** |
||||||
|
Age of starting L2 learning (8) |
1 |
-.78** |
-.29** |
|||||||
|
Years of L2 learning(9) |
1 |
.35** |
||||||||
|
Grade in L2 and overall success (10) |
1 |
Note: * - p < 0.05; ** - p < 0.01
Multiple regression
Table 3 shows how motivation, gender, age of starting L2 learning, and years of L2 study affect foreign language grades and success. The overall model was significant, F (11, 447) = 13.01, p < 0.001, where the predictors explained about 24% of the criterion variance (R2 = 0.24, R2 adjusted = 0.22). Since the VIF indicator did not exceed the value of 4 for any of the predictors, distinct multicollinearity was not present among the predictors. Years of L2 learning and identified regulation are strong indicators, showing that more years of learning and motivation through identified regulation lead to better L2 language grades and success.
Table 3. Partial predictor contribution in the regression model
|
Predictor |
Beta |
t |
p |
VIF |
|
Gender |
0.05 |
1.18 |
0.240 |
1.24 |
|
Age of starting L2 learning |
-0.06 |
-0.80 |
0.425 |
3.27 |
|
Years of L2 learning |
0.25 |
3.30 |
0.001 |
3.29 |
|
Amotivation |
0.01 |
0.18 |
0.861 |
1.63 |
|
External regulation |
0.04 |
0.73 |
0.469 |
1.51 |
|
Introjected regulation |
0.07 |
1.40 |
0.163 |
1.40 |
|
Identified regulation |
0.16 |
3.12 |
0.002 |
1.59 |
|
Knowledge |
0.09 |
1.35 |
0.178 |
2.77 |
|
Achievement |
0.04 |
0.63 |
0.531 |
2.71 |
|
Stimulation |
0.09 |
1.27 |
0.205 |
2.70 |
Gender-based moderation analysis
The moderation role of gender in relation to different types of motivation and grade in a second language was examined by conducting a moderation analysis. In Table 4, interactions in models that investigated predictors and moderators (gender) on second language grade are shown. Gender moderated the association between identified regulation, knowledge, achievement, and stimulation and second language grade. To enhance the interpretation of the moderation effect, we present significant interaction effects as charts. Figure 3 shows moderation between identified regulations and gender. It is noticeable that female respondents have significantly higher grades at higher levels of identified regulation, while at lower levels of identified regulation, grades are similar for both male and female respondents. In a similar way, gender moderates the relationship between knowledge and grades in L2 language (Figure 4). Women receive higher L2 language grades at higher motivation for knowledge, but there are no differences at lesser motivation. At lesser motivation for achievement (Figure 5), female students get lower grades than male students, but at increased motivation for achievement, they get the best grades. A similar pattern of moderation but a milder level of interaction, is also present between stimulation and gender (Figure 6).
Table 4. Contribution of introducing interaction of the types of motivation and gender in the model
|
Interaction |
F |
df1, df2 |
p |
|
Amotivation x gender |
1.22 |
1. 456 |
0.270 |
|
External motivation x gender |
0.30 |
1. 456 |
0.581 |
|
Introjected regulation x gender |
1.02 |
1. 456 |
0.313 |
|
Identified regulation x gender |
5.52 |
1. 456 |
0.011 |
|
Knowledge x gender |
4.54 |
1. 456 |
0.033 |
|
Achievement x gender |
15.31 |
1. 456 |
0.000 |
|
Stimulation x gender |
4.35 |
1. 456 |
0.037 |
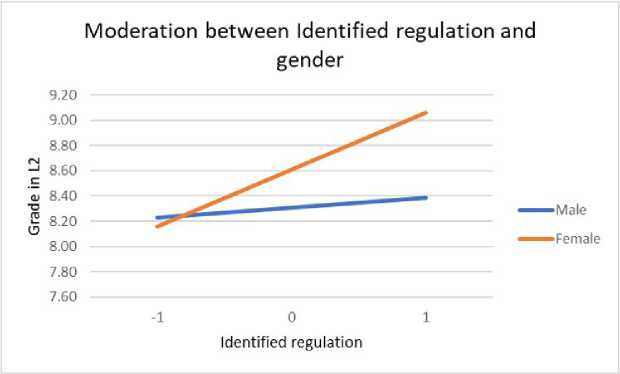
Figure 3. Moderation of gender and identified regulation by L2 grade
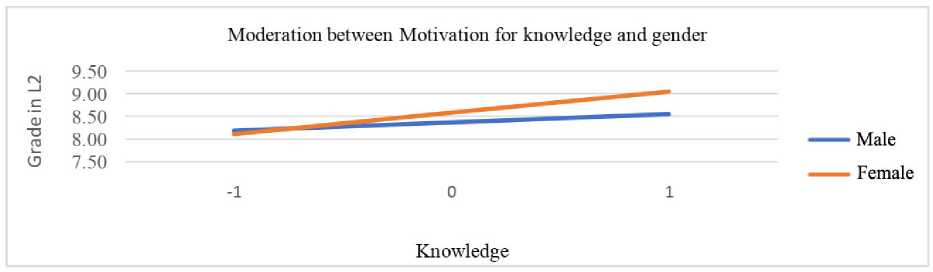
Figure 4. Moderation of knowledge motivation and gender by grade in L2
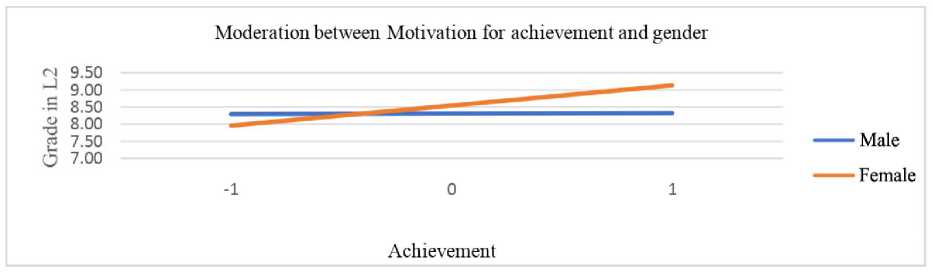
Figure 5. Moderation of achievement motivation and gender by grade in L2
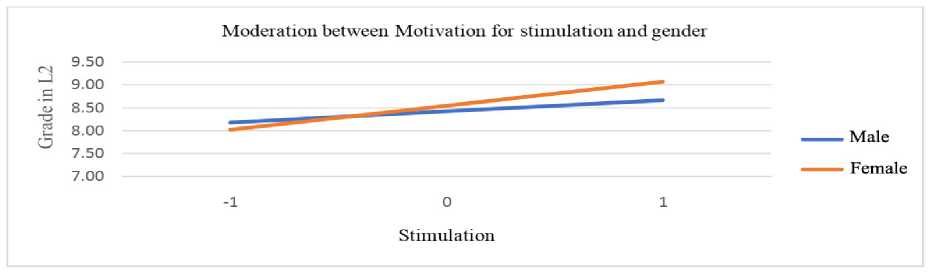
Figure 6. Moderation of stimulation motivation and gender by grade in L2
Moderation analysis – age of starting L2 learning as a moderator
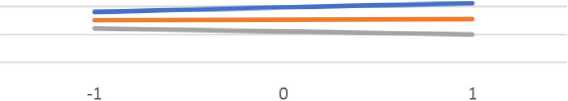
The moderation role of the age when the respondent started L2 learning in relation to different types of motivation and grade in L2 language was examined by conducting moderation analysis. Table 5 shows the contribution of introducing interactions in the model that tested the influence of predictors and moderators (age of starting L2 learning) on the grade in L2 language. The age of starting L2 learning moderated effectively external regulation and grade and knowledge and grade. Figure 7 shows moderation between external regulation and the age of starting L2 learning. In general, those who started earlier have higher grades, but the achievement is most remarkable at higher levels of external regulation, while for those who started learning later, the relationship is reversed. Higher motivation for knowledge is important for L2 achievement, and those with higher motivation achieve high grades regardless of the age of starting L2 learning. At lower motivation, the age of starting L2 learning is more important (Figure 8).
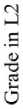
10.00
9.00
8.00
7.00
Moderation between External regulation and the age of starting to learn L2
— starting to learn (-1)
-----starting to learn (0) ------- starting to learn (1)
External regulation
Figure 7. Moderation of External regulation and the age of starting to learn L2 by grade in L2
Table 5. Contribution of introducing motivation types and the age of starting L2 learning in the model
|
Interaction |
F |
df1, df2 |
p |
|
Amotivation x age of starting to learn L2 |
2.95 |
1. 456 |
0.086 |
|
External regulation x age of starting to learn L2 |
3.93 |
1. 456 |
0.048 |
|
Introjected regulation x age of starting to learn L2 |
1.21 |
1. 456 |
0.270 |
|
Identified regulation x age of starting to learn L2 |
3.61 |
1. 456 |
0.057 |
|
Knowledge x age of starting to learn L2 |
8.16 |
1. 456 |
0.004 |
|
Achievement x age of starting to learn L2 |
3.60 |
1. 456 |
0.058 |
|
Stimulation x age of starting to learn L2 |
1.36 |
1. 456 |
0.244 |
Moderation between Motivation for knowledge and the age of starting to learn L2
10.00
9.00
3-00 । 1 ' starting to learn (-1)
' ------starting to learn (0)
o.UU
-10 1
Knowledge
Figure 8. Moderation of knowledge motivation and the age of starting L2 learning by grade in L2
Moderation analysis - years of L2 learning as a moderator
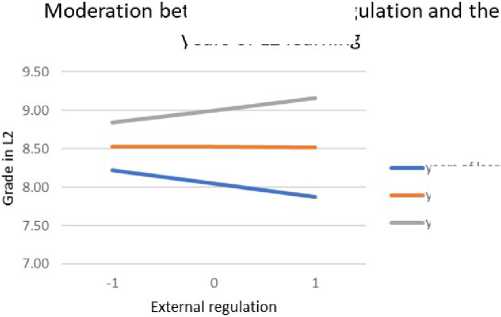
The moderation role of years of L2 learning in relation to different types of motivation and grade in L2 language was examined by conducting moderation analysis. Table 6 shows the contribution of in- troducing interactions in the model, which tested the influence of predictors and the moderator (years of L2 learning) on the grade in L2 language. The years of L2 learning prove to be a significant moderator of the influence of all types of motivation on the grade, except amotivation and identified regulation. In the case of moderation between the years of L2 learning and external regulation, it is noticeable that at higher levels of external regulation, students with more years of learning achieve better results (Figure 9). At high levels of introjected regulation, the grades achieved in L2 language are high regardless of the years of learning, while at lower levels of this motivation, the years of learning are more significant for achievement in L2 language (Figure 10). The pattern of relationship is similar in moderation between knowledge and years of L2 learning (Figure 11), achievement and years of L2 learning (Figure 12), and stimulation and years of L2 learning (Figure 13).
Table 6. Contribution of introducing motivation types and the years of L2 learning in the model
years of learning (-1)
years of learning (0)
years of learning (1)
Figure 9. Moderation of External regulation and the years of L2 learning by grade in L2
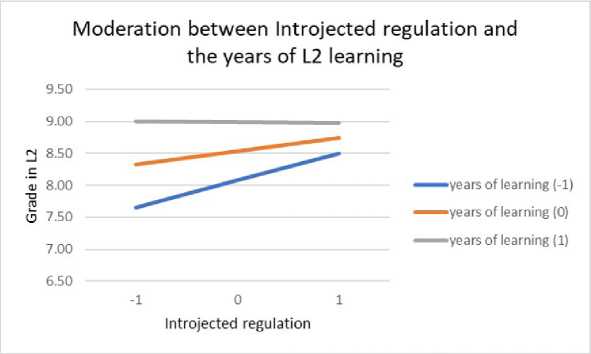
Figure 10. Moderation of Introjected regulation and the years of L2 learning by grade in L2
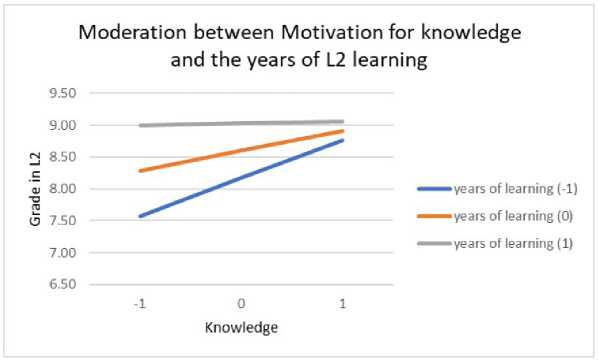
Figure 11. Moderation of knowledge motivation and the years of L2 learning by grade in L2
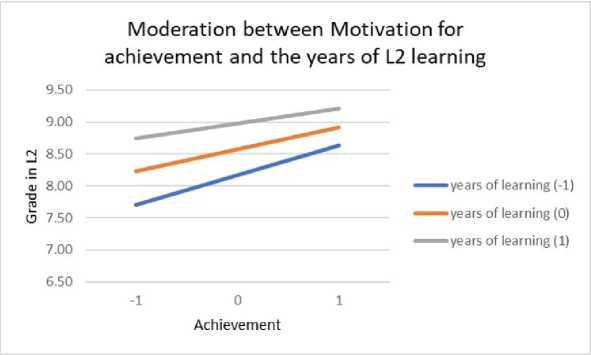
Figure 12. Moderation of achievement motivation and the years of L2 learning by grade in L2
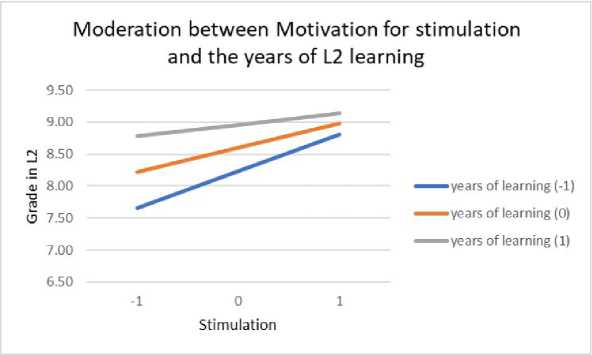
Figure 13. Moderation of stimulation motivation and the years of L2 learning by grade in L2
Logistic regression - influence of the types of motivation on learning ESP
The influence of different aspects of motivation on learning ESP was examined using binary logistic regression. After the introduction of predictors, the overall model was significant, χ2 (7) = 111.49, p <0.001, with the types of motivation explaining about 29% of the criterion variance (Nagelkerke R2 = 0.29). The influence of predictors is shown in Table 7. Motivation for achievement and stimulation stand out as significant positive predictors. A unit increase on the scale of achievement increases the chance that a student will be in the group of learning ESP compared to other students by 66%, while this percentage is higher in the case of stimulation by 41%.External regulation stands out as a significant negative predictor, whereby a unit increase on this scale reduces the chances that someone will be in the group of ESP students by 31%.
Table7. Partial relationship of predictors in the binary logistic regression model
|
Predictor |
Wald |
p |
Exp (B) |
|
Amotivation |
0.00 |
0.969 |
1.01 |
|
External regulation |
4.85 |
0.028 |
0.76 |
|
Introjected regulation |
1.88 |
0.170 |
1.17 |
|
Identified regulation |
1.98 |
0.159 |
1.18 |
|
Knowledge |
0.10 |
0.748 |
1.05 |
|
Achievement |
13.66 |
0.000 |
1.66 |
|
Stimulation |
6.35 |
0.012 |
1.41 |
Discussion
Findings in descriptive statistics are the first step in achieving the research goal, as they indicate the levels of motivational orientations in L2 learning and their influence on L2 learning achievement as a measure of the success of ESP students, which helps explain L2 learning motivation among the surveyed students. The results suggest that, on average, students show relatively low levels of amotivation and moderate levels of various aspects of motivation, with the highest scores received by intrinsic motivation (knowledge, achievement, and stimulation) and identified regulation . These findings conclude that students are highly motivated, i.e., with a good motivational orientation and types of motivation that are significant predictors of self-regulation. This is reflected as an indicator of success on the L2 achievement test and also in overall success, which was taken as an indicator of ESP students. Multiple regression also singled out identified regulation as a positive predictor, indicating that motivation through identified regulation is linked to better L2 grades and higher overall success. Thus, it is concluded that motivation, as a source of self-regulation, corresponded to the academic achievements of ESP students, and significant correlations between academic and linguistic achievements were obvious with motivation types, and the outcomes were apparent in self-regulation as a factor of academic achievement. The above conclusion could be the answer to the research question, given that the results suggest that there are differences in motivational orientations, or types of motivation, between ESP and other students. They are indicators of self-regulation in L2 learning, and the types of motivation determine achievements in L2 learning.
It is noted that identified regulation , as one of the external types of motivation, although the closest to intrinsic motivation, is closely related to the types of intrinsic motivation and to the high overall success and achievements in L2.
In addition, variables of motivation, especially between motivation for knowledge, achievement, and stimulation are highly correlated, where the intensity of the correlation is around 0.70, and the grade in L2 language is significantly associated with all types of motivation except external regulation . It has a slight negative correlation with amotivation , while with other types of motivation, it has a slight to moderate positive correlation. This confirms a part of the general hypothesis, given that types of motivation significantly affect L2 learning, which is reflected in success as an indicator of self-regulated learning. Consequently, it can be noted that success as an indicator of self-regulation is in line with motivational orientations and types of motivation, i.e., that types of motivation significantly affect L2 learning, and that this reflects on success as an indicator of self-regulated learning. This confirms the first working hypothesis regarding the correlation between the type of motivation and success in L2 learning.
The data obtained by binary logistic regression, used to determine the influence of motivation types on learning ESP, also contributes to the achievement of the research objective. They suggest that the whole seven-factor model, with all known aspects of motivation, was significant and explains about 29% of the criterion variance, which can be accepted as an important positive predictor for L2 learning and teaching. It can be seen from the data that motivation for achievement and stimulation, i.e., types of in- trinsic motivation, stand out as significant positive predictors. A unit increase on the scale of achievement increases the chance that the student will be in the group of ESP students compared to other students by 66%, while this percentage is higher in the case of stimulation by 41%. External regulation stands out as a significant negative predictor. A unit increase on this scale reduces the chances that the student will be in the group of ESP students by close to 31%. Thus, the above findings confirm the assumption that the types of motivation are correlated with success in L2 learning, and explain a significant part of the variance in self-regulation in learning outcomes, i.e., the L2 achievement test, among ESP students compared to others. The results on the L2 achievement test correspond to the types of motivation, which points out self-regulation as a factor in the academic achievement of ESP students.
The previous findings are consistent with the conclusions of other research ( Ramos and Habig, 2019 ; Utvær and Gørill (2016) ; Henry and Liu, 2023 ) that the construct of motivation is multidimensional. As a phenomenon, it cannot be considered appropriately by simplified divisions into basic motivational orientations, and it is necessary to delve deeper into the multidimensionality, complexity of the motivational construct and several motivational orientations, or types of motivation, which further confirm the concepts of Self-Determination Theory ( Deci and Ryan, 1985 ; Baard et al., 2004 ). This important conclusion has practical pedagogical implications for teachers, administrators, and creators of educational policy. Students need accurate and precise information to direct themselves in self-regulation, and the contents of the curriculum should be more closely associated with their future careers. Consequently, it is more efficient in practice, because identified regulation appears as an important predictor, which is understood as behaviour that an individual accepts because of its importance and expected benefits in the future. This finding confirms the opinion stated in the introductory part of the paper, which emphasize that technological progress has changed the way today’s generations are motivated. Many youth are amotivated and fail to see unexpected effects of their behaviour. As Gillet and his associates (2012) recommend, it is necessary to change didactic approaches and provide different learning environments to meet students’ needs in order to avoid a sense of negligence. At the same time, the results indicate that strategies significantly facilitate the need for higher autonomy in learning and teaching ( Gojkov-Rajić et al., 2021a ; Reinders et al., 2023 ).
Moderation analyzes examine the moderation roles of the age of starting L2 learning, years of L2 learning, and gender as factors in the relationship between the observed variables of ESP students and self-regulation in the field of L2 learning and teaching. The previously presented contributions of introducing interactions in the model that tested the influence of predictors and a moderator (gender) on grade in L2 language refer to gender as a significant moderator in the case of the relationship between identified regulation, knowledge, achievement, and stimulation and grade in L2 language . Moderation between identified regulation and gender indicates that female students have significantly higher grades at higher levels of identified regulation , while grades are similar for both male and female students at lower levels of identified regulation . Similar to this, gender moderates the relationship between knowledge and grade in L2 language; we found no differences at lower levels of motivation for knowledge, but at lower levels, female students achieve higher grades on the L2 achievement test. In the case of motivation for achievement, at lower levels, female students achieve lower grades than male students, while at higher levels, female students achieve the highest grades. A similar pattern of moderation, but a milder level of interaction, is present between stimulation and gender. The abovementioned moderation role of gender seems to be stronger self-regulation for female students in types of motivation that directly affect achievements, and ultimately they are an indicator of higher motivation for female students, which indicates the importance of gender as a moderator in L2 learning.
Identified regulation and gender are closely related to success in L2 learning, since identified motivation has been understood as a behaviour that someone accepts due to its importance and the expected benefit in the future. Thus, female students have a more pronounced practical side in self-regulation because, as studies conclude, behaviour caused by identified regulation is not induced by internal need, so the outcome of this type of regulation is a lower level of self-determination (Baard et al., 2004; Jang et al., 2010; Alastair and Meng, 2024). Essential motivation is intrinsic motivation that involves research, curiosity, learning objectives, and performing activities for pleasure and satisfaction while learning, researching, or trying to understand something. It raises the question of the relationship between these types of motivation, and ultimately the seven-factor model of self-regulation, which is also confirmed in this research. The question arises as to whether Allport’s (1950) understanding of autonomy of motives is essentially identified here, which can logically explain these findings. Allport believes that the human dynamic system is unlimited, which explains the diversity and the large number of motives. He considers functional autonomy as the possibility that certain forms of behaviour, which served to satisfy some primary motive, may become a goal and acquire motivational properties over time. Thus, an activity that is originally related to satisfying some motive can eventually become autonomous and become the objective itself. If so, and there is a basis for such a claim, it is very important in L2 teaching because it confirms the path that can be followed from external to internal motivation, which is not only educationally more effective but has multiple psychological effects (sense of self-efficacy, self-esteem, emotional stability, absence of stress, etc.). This certainly requires a new research pattern with a focus on the above question.
Moderation analysis shows that the age of starting L2 learning moderates the relationship between external regulation and grade, and knowledge and evaluation, so the types of extinct and intrinsic motivation are closely related . It is also interesting that, in general, those who started earlier have higher grades in L2. However, achievement is the highest at higher levels of external regulation as motivation to learn, to be efficient, and to be task-oriented, which is characterized by learning due to the need to communicate with the environment in order to feel competent ( Deci and Ryan, 1991 ), engage in activities out of pleasure, and find satisfaction in attempts at self-realisation after mastering complex training techniques and the like. A sense of personal satisfaction is created while communicating in L2 or participating in scientific meetings inEnglish for Specific Purposes, etc., which is essentially close to the intrinsic level of motivation. It can be understood because practical motives that fall into the domain of extrinsic motivation lead to self-realisation, and its consequence is a sense of satisfaction gained through achievement. Thus, it is the same pattern as in gender moderation.
The relationship is reversed in the case of those who started learning later. It considers moderation between knowledge and the age of starting L2 learning and indicates that levels of motivation for knowledge are important for achievement and that those with higher levels of motivation achieve high grades regardless of the age of starting L2 learning, while at lower levels of motivation, the age is more important. These types of motivation in this case are interrelated in a way that students who started learning later have clearer learning objectives, curiosity in discovering new elements and language structure, as well as other characteristics of motivation for knowledge that regulate intrinsic motivation for achievement, efficacy, and task orientation, which are realised in success in L2 learning. It could be concluded that these cases contributed to differences in motivational orientations or types of motivation between ESP and other students and the level of indicators of self-regulation in L2 learning, which answered the research question on the types and extent of differences between ESP and other students. This also indicates the importance of applying didactic instructions in practise based on the type of student motivation. The obtained data also confirm a part of the first hypothesis, which refers to expectations that grades on the L2 achievement test correspond to types of motivation. It confirms our hypothesis regarding the influence of self-regulation on the academic performance of ESP students, namely that the grades obtained on L2 achievement examinations are contingent upon the nature of the motivation.
Moderation analysis also evaluated the significance of the variable relating to the respondents’ type of faculty, in addition to gender and years of L2 learning. Namely, part of the students studied engineering sciences, while the other part studied social sciences, which could be significant for motivation and relations between the observed variables. Pragmatism and self-regulation in studying engineering sciences are encouraged by learning strategies, task solving, while broadness, flexibility, freedom of choice, and greater autonomy are more pronounced in social sciences.
This failed to confirm the second hypothesis, which considered that the age of starting L2 learning, years of L2 learning, and gender were insignificant factors in the relationship between the observed variables. It shows that more variables should be included in the research in order to better understand the phenomenon.
Conclusion
After interpreting the statistical analyzes, several basic conclusions could be drawn. First, the findings confirm that, on average, students show relatively low levels of amotivation and moderate levels of various aspects of motivation, with the highest scores received by intrinsic (knowledge, achievement, and stimulation) and identified regulation, indicating that students are well motivationally oriented, i.e., with good motivational orientation and types of motivation that are significant predictors of self-regulation. It is an indicator of success in the L2 achievement test, i.e., high achievements in L2 learning, as well as overall success.
It is concluded that identified regulation stands out as a positive predictor, which indicates that motivation through identified regulation is associated with higher grades in L2 language and higher overall success. Thus, motivation as a source of self-regulation corresponds to the academic achievements of ESP students, and significant correlations are observed between academic and linguistic achievements and the types of motivation. This is evident in outcomes and, thus, in self-regulation as a factor of academic achievement. There are differences in motivational orientations, or types of motivation, between ESP and other students, which are indicators of self-regulation in L2 learning, as well as that types of motivation in learning are crucial for achievements in L2 learning.
One of the conclusions considers identifiedregulation as one of the external types of motivation and the closest to the intrinsic, thus related to the types of intrinsic motivation and to high achievements in overall success and L2 achievements. This finding is in accordance with Allport’s theory of functional motives. In addition, this is important for the didactic implications of the findings, as it directs L2 teachers where to look for sources of motivation and build strategies appropriately. This is a powerful tool in their hands. It is a particularly important finding, as respondents are students learning English for specific purposes, and it is expected that the identified regulation and the other ones similar to the types of extrinsic motivation will appear rather than the intrinsic type, which is more present in philological studies. Therefore, these findings provide L2 teachers with a clear path, and they can direct self-regulation of L2 learning to the right course.
The age of starting L2 learning, years of L2 learning, and gender were insignificant factors in the relations between the observed variables. The research should incorporate more variables to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the phenomenon’s complexity.Thus, we should further look for other factors of motivation and self-determination, which are below the perceptual surface of personality, in the structure of understanding the sense, purpose, and philosophy of life, based on which an individual accustoms themselves in life and from which stems self-regulation and contributing motivation.
Acknowledgement
The research has been conducted within the project “Improving the teaching process in the English language in fundamental disciplines” developed at the Department for Fundamental Disciplines in Engineering, Faculty of Technical Sciences, University of Novi Sad, Serbia.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author contributions
Conceptualization J.Š. and V.B.; Methodology D.G. and J.Š.; Writing - original draft preparation D.G., V.B. and J.Š.; Writing - review and editing V.B., J.Š. and D.G.; Analysis, discussion and conclusion J.Š., D.G. and V.B.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Список литературы Motivation types: a key factor in self-regulated ESP learning
- Al-Hoorie, A. H. (2024). Metamotivation: Self-regulating task-motivation fit. Porta Linguarum: revista internacional de didáctica
- de las lenguas extranjeras, 2. https://doi.org/10.30827/portalin.viIX.29880 Alastair, H. & Meng L. (2024). L2 motivation and self regulated learning: An integrated model, System, Vol. 123, 103301.
- https://doi.org/10.1016/j.system.2024.103301 Allport, G.W. (1950): Theindlvidualandhisreliglon, New York: Macmillan.
- Baard, P. P., Deci, E. L., & Ryan, R. M. (2004). Intrinsic need satisfaction: a motivational basis of performance and weil-being in two work settings 1. Journal of applied social psychology, 34(10), 2045-2068. https://doi.org/10.1111Zj.1559-1816.2004. tb02690.x
- Baumert, J.,Lehmann, R., Lehrke, M., Clausen, M., Hosenfeld, I., &Neubrand, J. (Eds.) (1998). Testaufgaben Naturwissenschaften TIMSS 7./8. Klasse (Population 2) [TIMSS science items for 7th/8th grade (population 2)], Max-Planck-Institut für Bildungsforschung, Berlin
- Crnjak, K. (2019). Povezanost motivacije studenata s razlicitim aspektima prilagodbe na studij (Doctoral dissertation, University of Zagreb. Department of Croatian Studies. Division of Psychology). https://repozitorij.hrstud.unizg.hr/islandora/object/ hrstud:1902/datastream/PDF
- Cortazzi, M., & Jin, L. X. (1999). Cultural mirrors: Materials and methods in the EFL classroom. In E. Hinkel (Ed.), Culture in second language teaching and learning (pp. 196-219). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Deci, E. L. (1975). Intrinsic motivation Plenum Press. New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-4446-9
- Deci, E. L., & Ryan, R. M. (1985). Intrinsic Motivation and Self-Determination in Human Behavior. New York, NY: Plenum.
- https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-2271-7 Deci, E. L., & Ryan, R. M. (1991). A motivational approach to self: Integration in personality. In R. A. Dienstbier (Ed.), Nebraska Symposium on Motivation, 1990: Perspectives on motivation (pp. 237-288). University ofNebraska Press.
- Dörnyei, Z. (1990). Conceptualizing motivation in foreign-language learning. Language learning, 40(1), 45-78. https://doi. org/10.1111/j.1467-1770.1990.tb00954.x
- Dörnyei, Z. (1994). Motivation and motivating in the foreign language classroom. The modern language journal, 78(3), 273284. https://doi.org/10.2307/330107 Dörnyei, Z. (1997). Psychological processes in cooperative language learning: Group dynamics and motivation. The modern
- languagejournal, 81(4), 482-493. http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/328891 Dörnyei, Z. (1998). Motivation in second and foreign language learning. Language teaching, 31(3), 117-135. http://dx.doi.
- org/10.1017/S026144480001315X Dörnyei, Z. (2001a). Motivational Strategies in the Language Classroom. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, http://
- dx.doi.org/10.1017/CB09780511667343 Dörnyei, Z. (2001b). New themes and approaches in second language motivation research. Annual Review of Applied Linguistics, 21, 43-59. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0267190501000034
- Dörnyei, Z. (2003). Attitudes, orientations, and motivations in language learning: Advances in theory, research, and applications. Language learning, 53.
- Dörnyei, Z. & Ushioda, E. (2011). Teaching and Researching Motivation. 2nd Edition, Pearson, Harlow.
- Gardner, R. C., Lalonde, R. N., & Moorcroft, R. (1985). The role of attitudes and motivation in second language learning: Correlational and experimental considerations. Language learning, 35(2), 207-227. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-1770.1985.tb01025.x
- George, D. & Mallery, M. (2010). SPSS for Windows Step by Step:ASimple Guide and Reference, 7.0 update (10a ed.) Boston; Pearson. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0013164492052004025
- Gillet, N., Vallerand, R. J., & Lafreniere, M. A. K. (2012). Intrinsic and extrinsic school motivation as a function of age: The mediating role of autonomy support. SocialPsychologyofEducation, 15, 77-95.
- Gojkov Rajic, A., Safranj, J., Gojkov.G. & Stojanovic, A., (2020). Motivacione strategije kao faktor uspeha akademski darov-itih studenata, Zbornik radova 26. okruglog stola o darovitima: Licna i socijalna perspektiva, 26. jun 2020. Vrsac. 26 (2021), p.38-81.
- Gojkov-Rajic, A., Stojanovic.A., Safranj,J.&Gojkov,G. (2021a). Didakticki aspekti samoregulacije ucenja darovitih, Monografija, Srpska akademija obrazovanja, Beograd, p.260.
- Gojkov-Rajic, A., Safranj, J.& Gojkov.G. (2021b). Relationship between didactic instructions and metacognition in foreign language learning. In: Herzog, J. (Ed.) Giftedness in a Variaty of Educational Fields (57-79). Verlag Dr. Kovac GmbH, Hamburg. ISBN 978-3-339-12195-0
- Gojkov-Rajic, A., Safranj, J., & Gak, D. (2023). Self-Confidence In Metacognitive Processes In L2 Learning, International Journal of Cognitive Research in Science, Engineering and Education (IJCRSEE), 11(2), 1-13. https://doi. org/10.23947/2334-8496-2023-11-1-1-13
- Hagger, M. S., & Chatzisarantis, N. L. D. (Eds.). (2007). Intrinsic motivation and self-determination in exercise and sport. Human Kinetics.
- Henry, A. & Liu, M. (2023). Can L2 motivation be modelled as a self-system? A critical assessment System, 119, p. 103158. https://doi.org/10.1016Zj.system.2023.103158
- Henry, A., & Liu, M. (2024). L2 motivation and self regulated learning: An integrated model. System, 123, 103301. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.system.2024.103301
- Jandric, D., Boras, K., & Simic, Z. (2018). Rodne i dobne razlike u motivaciji i samoregulaciji ucenja [Gender and age differences in motivation andself-regulated learning], Psihologijske Teme, 27(2), 177-193. https://pt.ffri.hr/pt/article/view/384
- Jang, H., Reeve, J., & Deci, E. L. (2010). Engaging students in learning activities: It is not autonomy support or structure but autonomy support and structure. JournalofEducationalPsychology, 102(3), 588-600. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0019682
- Mastoor, A. K. (2013). Second Language Motivation: The Role of Teachers in Learners' Motivation, Journal of Academic and Applied Studies, 3(4) 45-54.
- Mystkowska-Wiertelak, A., & Bielak, J. (2024). The link between learner engagement and self-regulation. A multiple case study. International Journal of Applied Linguistics, 34(2), 709-727. pp. 1-19, https://doi.org/10.1111/ijal.12530
- Niemiec, C. P., Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2009). The path taken: Consequences of attaining intrinsic and extrinsic aspirations in post-college life. Journal of Research in Personality, 43(3), 291-306. https://doi.org/10.1016/jjrp.2008.09.001
- Noels, K. A., Pelletier, L. G., Clément, R., & Vallerand, R. J. (2000). Why are you learning a second language? Motivational orientations and self-determination theory. Language learning, 50(1), 57-85. https://doi.org/10.1111/0023-8333.00111
- Noels, K., Clément, R., & Pelletier, L. (2001). Intrinsic, extrinsic, and integrative orientations of French Canadian learners of English. Canadian Modern Language Review, 57(3), 424-442. https://doi.org/10.3138/CMLR.57.3.424
- Oga-Baldwin, W. L. Q., Parrish, A., & Noels, K. (2022). Taking root: Self-determination in language education. Journal for the PsychologyofLanguage Learning, 4(1), 1-7. https://doi.org/10.52598/jpll/4/1/9
- Ramos, D. P. R., & Habig, E. G. (2019). Measuring the academic motivation of selected first year nursing students: A preliminary study. International Journal of Education and Research, 7(8), 173-182. https://www.ijern.com/journal/2019/ August-2019/14.pdf
- Reinders, H., Phung, L., Ryan, S. & Thomas, N. (2023). The Key to Self-regulated Learning - a systematic approach to maxl-mislnglts potential, Oxford University Press.
- Ryan, R. M., Connell, J. P., & Plant, R. W. (1990). Emotions in nondirected text learning. Learning and Individual Differences, 2(1), 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1016/1041-6080(90)90014-8
- Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2000). Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. American Psychologist, 55(1), 68-78. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.55.168
- Ryan, R. M., Huta, V., & Deci, E. L. (2008). Living well: A self-determination theory perspective on eudaimonia. Journal of Happiness Studies: An Interdisciplinary Forum on Subjective Weil-Being, 9(1), 139-170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-006-9023-4
- Soric, I. (2014). Samoregulacija ucenja: mozemo li nauciti uciti [Self-regulation of learning: can we learn to learn], Napredak, 155(4) 467- 472.
- Safranj, J., Gojkov-Rajic, A., & Bogdanovic, V. (2021). The ideal L2 self as a Factor of self-motivation in willingness to communicate, International Journal of Cognitive Research in Science, Engineering and Education (IJCRSEE), 9(2), 189-202. https://doi.org/10.23947/2334-8496-2021-9-2-189-202
- Utvœr, B. K. S., & Haugan, G. (2016). The academic motivation scale: dimensionality, reliability, and construct validity among vocational students. Nordic Journal of Vocational Education and Training, 6(2), 17-45. https://doi.org/10.3384/ njvet.2242-458X.166217
- Vallerand, R. J., Pelletier, L. G., Blais, M. R., Briere, N. M., Senecal, C., & Vallieres, E. F. (1992). The Academic Motivation Scale: A measure of intrinsic, extrinsic, and amotivation in education. Educational and psychological measurement, 52(4), 1003-1017. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013164492052004025
- Vallerand, R. J., Blanchard, C., Mageau, G. A., Koestner, R., Ratelle, C., Léonard, M., Gagne, M. &Marsolais, J. (2003). Les passions de l'âme: On obsessive and harmonious passion. Journal ofPersonality and Social Psychology, 85(4), 756767. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.85.4756
- Vallerand, R. J. (2021). Reflections on the legacy of self-determination theory. Motivation Science, 7(2), 115-116. https://doi. org/10.1037/mot0000227
- White, R. W. (1959). Motivation reconsidered: the concept of competence. Psychological review, 66(5), 297. 297-333. https:// doi.org/10.1037/h0040934
- Williams, M. (1994). Motivation in foreign and second language learning: An interactive perspective. Educational and Child Psychology, 11,77-84.
- Wolters, C. A., laconelli, R., Peri, J., Hensley, L. C., & Kim, M. (2023). Improving self-regulated learning and academic engagement: Evaluating a college learning to learn course. Learning and Individual Differences, 103, 102282. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.lindif.2023.102282
- Ziegler, A., Daunicht, T.M., &Quarda, A.K.(2021). Self-Regulation and Development of Potentials of the Gifted,27th Round Table on Giftedness Self-Regulation and Development of Potentials of the Gifted International Scientific Conference, Book of Abstracts, Vrsac. http://www.nauka.uskolavrsac.in.rs/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/Zbornik-rezimea-27-0S.pdf
- Zimmerman, B. J. (2002). Becoming a self-regulated learner: An overview. Theory into practice, 41(2), 64-70. https://doi. org/10.1207/s15430421tip4102_2


