Наноиндентация и характеристика поверхности клинических мультисиловых ортодонтических дуг из сплава NiTi
Автор: Чернева С., Стоянова-иванова А., Георгиева М., Андреева Л., Петков А., Петров В., Петрова В., Микли В.
Журнал: Российский журнал биомеханики @journal-biomech
Статья в выпуске: 3 (89) т.24, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Никель-титановые (NiTi) сплавы из-за их свойств сверхэластичности и эффекта памяти формы широко используются в ортодонтическом лечении. Их сверхэластичность позволяет ортодонту прикладывать почти непрерывную малую силу с большей активацией, что снижает травмирование тканей и дискомфорт пациента и, таким образом, способствует перемещению зубов. Производители обычно не предоставляют информацию о механических свойствах производимых дуг на упаковке или на веб-страницах, что затрудняет для стоматологов выбор наиболее подходящего материала с большей рентабельностью использования. В настоящей работе исследовались и сравнивались механические и физико-химические свойства неиспользованных и использованных в течение 6 и 9 недель силовых никель-титановых дуг, производимых American Orthodontics под торговой маркой TriTaniumTM , чтобы оценить, есть ли изменения в их свойствах при клиническом использовании. Механические свойства были исследованы с помощью наноиндентирования. Морфология поверхности и элементарный состав дуги были изучены с помощью сканирующей электронной микроскопии и энергодисперсионного анализа соответственно. Сравнение механических свойств неиспользованных и использованных в течение 6 и 9 недель дуг TriTaniumTM показало, что их твердость при вдавливании и модуль упругости уменьшаются с увеличением времени использования. Существенных изменений элементного состава дуги после их клинического использования не наблюдалось.
Силовые ортодонтические дуги, никель-титановый сплав, механические свойства, морфология, химический состав
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/146282173
IDR: 146282173 | УДК: 531/534: | DOI: 10.15593/RZhBiomeh/2020.3.02
Текст научной статьи Наноиндентация и характеристика поверхности клинических мультисиловых ортодонтических дуг из сплава NiTi
Согласно мнению Всемирной организации здравоохранения, здоровье полости рта имеет важное значение как для общего здоровья, так и для качества жизни [19]. В недавнем систематическом обзоре было обнаружено, что неправильный прикус отрицательно влияет на качество жизни детей и подростков, особенно на эстетику лица [6].
Коррекция аномалий прикуса включает механотерапию с применением фиксированных приспособлений посредством приложения слабых и непрерывных сил, которые могут обеспечить оптимальное движение зубов за счет перестройки окружающей кости и тканей пародонта [20]. Устанавливаемые в брекеты ортодонтические дуги создают силу, которая вызывает ортодонтическое движение зубов [24].
Ортодонтические дуги изготавливаются из различных сплавов. В ортодонтической механотерапии широко используются никель-титановые сплавы (NiTi) благодаря их свойствам сверхэластичности и эффекта памяти формы [9]. Сверхэластичность NiTi-дуг позволяет ортодонту прикладывать непрерывные слабые силы с большей активацией, что снижает травмирование тканей и дискомфорт пациента и, таким образом, способствует перемещению зубов [3]. Это позволяет использовать NiTi-дуги на первом этапе ортодонтического лечения.
Основным недостатком обычных сверхэластичных NiTi-дуг является то, что длительные ортодонтические силы действуют на все зубы [25]. Данную величину нагрузки следует рассматривать по отношению к зубам, на которые она действует. В работе [4] описана взаимосвязь между прилагаемой силой и площадью корня. Что касается поверхности корней, то очевидно, что силы, действующие на резцы, особенно нижние, должны быть значительно меньше, чем на моляры.
Сплав NiTi представляет собой интерметаллическое соединение, близкое к эквиатомному, на которое может влиять способ производства. Сплав имеет по крайней мере две различные кристаллические структуры в зависимости от температуры: при высоких температурах сплав NiTi находится в аустенитной фазе, которая представляет собой объемно-центрированную кубическую решетку, а при низких температурах он находится в мартенситной фазе, которая является плотноупакованной гексагональной решеткой. Управляя диапазоном низких и высоких температур, можно изменять кристаллическую структуру, что называется мартенситным превращением. Температура, при которой происходит это явление, называется температурой перехода сплава и влияет на величину силы, развиваемой дугой при работе на сверхупругом плато. Чем меньше разница между температурой перехода и рабочей температурой, тем меньше будут прилагаемые силы [8]. Применение термообработки сверхупругого NiTi-сплава [15], влияние различной температуры и продолжительности термообработки на переходный температурный диапазон привело к разработке дуги с переменной силой на разных участках одной дуги [16]. Путем специальной термической обработки в определенных областях дуг достигается изменение модуля упругости. Его значение отражает жесткость материала. Дуги с низкой жесткостью обладают высокой эластичностью, а наклон плато наблюдается практически горизонтальным. Их можно легко согнуть и после этого вернуть первоначальную форму. Снижение жесткости уменьшает силы, создаваемые дугами.
Преимущества переменного модуля упругости по длине дуги заключаются в возможности начальной установки дуги прямоугольной формы, что позволяет контролировать крутящий момент в фазе выпрямления, точно распределить нагрузку, а также в целом сократить количество используемых дуг в течение периода лечения.
Обычные ортодонтические NiTi-дуги широко используются и относительно хорошо изучены [7, 13, 17, 22, 23]. Однако информации о механических свойствах мультисиловых NiTi-дуг последнего поколения недостаточно [12, 14]. Производители не предоставляют информацию об их механических свойствах на упаковке и на вебстраницах, что затрудняет для стоматологов выбор наиболее подходящего материала с большей рентабельностью использования [1]. В связи с этим настоящая работа направлена на исследование и сравнение механических и физико-химических свойств используемых в течение 6 и 9 недель мультисиловых NiTi-дуг последнего поколения, чтобы оценить, есть ли изменения их свойств при клиническом использовании.
Материалы и методы
Материалы
Были исследованы верхние ортодонтические дуги с размерами 0,016×0,022 дюйма, изготовленные American Orthodontics, TriTaniumTM (новые и использовавшиеся в течение 6 и 9 недель). Механические и химические испытания проводились в трех отдельных сегментах с различным модулем упругости: передний – участок четырех резцов, двустворчатый – участок клыков и премоляров, задний – участок коренных зубов. Передний сегмент был промаркирован на длине в пятнадцать миллиметров от середины дуги по обе стороны. После этого были определены двустворчатый и задний сегменты длиной 30 мм также с обеих сторон. Дуга была разрезана с помощью высокоскоростного сверла с распылителем воды и алмазным бором в отмеченных областях. Все дуги были собраны у пациентов со скученностью верхних передних зубов, проходивших лечение в отделении ортодонтии Медицинского университета в Софии (Болгария). Авторы выполнили все клинические процедуры в соответствии с указаниями по надлежащей клинической практике Министерства здравоохранения Болгарии и Хельсинкской декларацией Всемирной медицинской ассоциации. Пациенты были заранее проинформированы о том, что извлеченные дуги будут протестированы in vitro, и они согласились на это. После удаления извлеченных дуг изо рта пациента их поместили в дезинфицирующую ванну на 30 минут, а затем очистили ватным тампоном, смоченным в 95%-ном спиртовом растворе, для удаления любых отложений и остатков пищи. Затем каждый сегмент дуги был помещен в герметичный пластиковый пакет вместе с таблицей данных, готовой для анализа.
Методы
Сканирующая электронная микроскопия / Энергодисперсионная рентгеновская спектроскопия
Морфология поверхности и элементарный состав изучались с помощью растрового электронного микроскопа ZEISS FE-SEM Ultra 55, ускоряющее напряжение измерений которого при обычном наблюдении составляло 20 кВ. Одинаковые образцы каждой области каждой ортодонтической дуги были установлены на шпильки и помещены в вакуумную камеру аппарата микроскопа. Угол посадки, ускоряющее напряжение и апертура были отрегулированы для оптимизации качества микрофотографии. Поверхность и поперечное сечение сканировались и просматривались на мониторе при разном увеличении. Были получены репрезентативные микрофотографии участков каждого провода.
Для количественной оценки элементного состава дуг был использован метод энергодисперсионного анализа (рентгеновский дисперсионный анализ) с системой Bruker Esprit 1.82. Качественный и количественный элементарный анализ проводился при ускоряющем напряжении 20 кВ.
Чтобы получить четкие изображения и точные результаты с помощью микроскопа и анализа поперечного сечения дуги, потребовался процесс травления. Травление проводили с помощью реактива Кролла, который состоит из 1HF + 2HNO 3 + + 50H 2 O. Реагент Кролла часто используется в качестве металлографического травителя для травления титановых сплавов, поскольку он выявляет структурные детали, а с некоторыми сплавами он может показывать границы зерен [10]. Все образцы были приготовлены в одинаковых условиях.
Наноиндентирование
Эксперименты по наноиндентированию неиспользованных и использованных в течение 6 или 9 недель дуг TriTaniumTM размером 0,016×0,022 дюйма были выполнены при помощи Nanoindenter G 200 ( KLA Corporation , США), снабженного наконечником Berkovich с радиусом 20 нм в соответствии со стандартом ISO 14 577. Был применен метод вдавливания с контролем нагрузки. Сделано 12 вдавливаний каждого образца в трех сегментах (переднем, двустворчатом и заднем). Максимальная нагрузка составляла 30 гс (≈ 300 мН), время удержания пика = 10 с, а время нагрузки = 15 с.
Статистический анализ
Для каждого сегмента дуги (переднего, двустворчатого и заднего) авторы сравнили количественные измерения содержания никеля, модуля вдавливания и твердости при вдавливании для трех отдельных групп (неиспользованных, использованных в течение 6 недель, использованных в течение 9 недель). Для изучения статистических распределений значений, полученных с помощью количественных измерений, был использован непараметрический односторонний тест ANOVA Краскела-Уоллиса. Уровень значимости различий между группами определяли путем выполнения многовариантного сравнения на основе статистики теста ANOVA и множественных сравнительных тестов Манна-Уитни, скорректированных Бонферрони. Результаты считаются статистически значимыми, если они достигли уровня достоверности выше 95% ( p < 0,05).
Обсуждение результатов
Результаты наблюдений и анализа
На рис. 1 показаны микрофотографии поверхности дуг (новых и использованных в течение 6 и 9 недель). Видно, что при длительном использовании поверхность в трех областях становится более шероховатой. Общая поверхность неиспользованной дуги TriTaniumTM относительно гладкая по сравнению с использованными.
Из полученных микрофотографий можно сделать вывод, что неиспользованная дуга TriTaniumTM демонстрирует мелкозернистую структуру, тогда как зернистая структура дуги, использованной в течение 6 недель, начинает рекристаллизоваться в более крупные зерна, а структура дуги, используемой в течение 9 недель, является крупнозернистой (зернистость достигает размера 10 мкм).
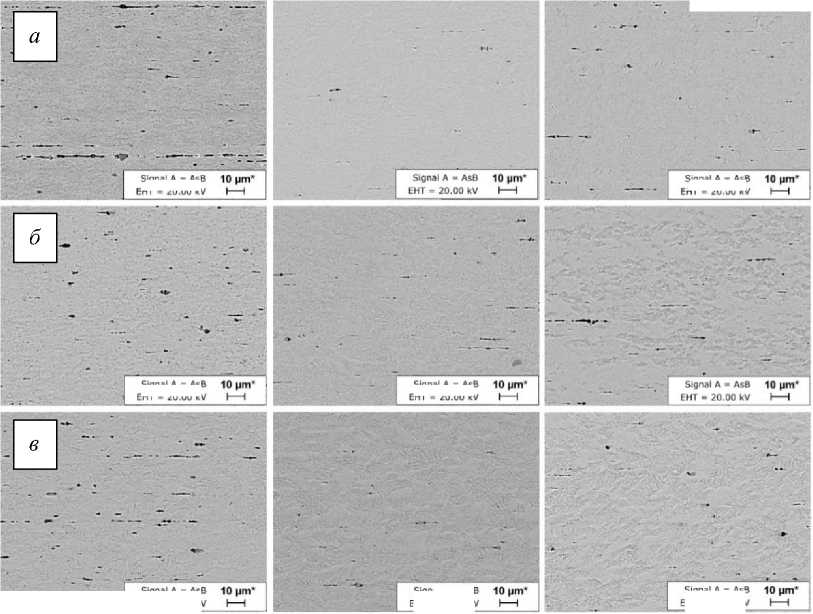
Микрофотографии поперечного сечения всех дуг показаны на рис. 2. Из изображений поперечного сечения можно увидеть, что передний сегмент является наиболее пористым, а в остальных сегментах дуги пористость уменьшается.
Элементарный состав в трех зонах эластичности дуг (новых и используемых в течение 6 и 9 недель) приведен в табл. 1 и 2.
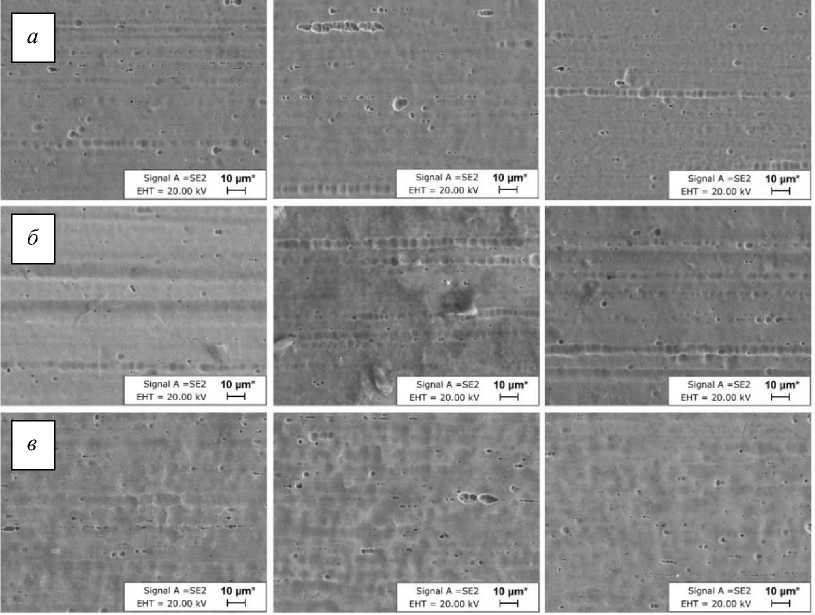
Рис. 1. Микрофотографии поверхности верхних дуг: а – неиспользованной; б – использованной в течение 6 недель; в – использованной в течение 9 недель. Слева направо: передняя, двустворчатая, задняя (увеличено в 2000 раз)
Signal A = asd
EHT = 20.00 kV
Signal A = AsB
EHT = 20.00 kV
Signal A = AsB EHT = 20.00 kV
Signal A = AsB EHT = 20.00 kV
Signal A = AsB EHT = 20.00 kV
Signal A = AsB EHT = 20.00 kV
Signal A = AsB EHT - 20-00 kV
Рис 2. Микрофотографии поперечного сечения дуг: а – неиспользованной; б – использованной в течение 6 недель; в – использованной в течение 9 недель. Слева направо: передняя, двустворчатая, задняя (увеличено в 2000 раз)
Таблица 1
Элементный состав поверхности дуги
|
Элемент, % |
Поверхность дуги |
Погрешность, % |
||||||||
|
неиспользованная |
использованная 6 недель |
использованная 9 недель |
||||||||
|
П |
Д |
З |
П |
Д |
З |
П |
Д |
З |
||
|
Ni |
54,40 |
54,72 |
54,40 |
54,68 |
53,03 |
54,29 |
54,13 |
54,42 |
54,09 |
+/- 0,8 |
|
Ti |
45,60 |
45,28 |
45,60 |
45,32 |
46,97 |
45,71 |
45,87 |
45,58 |
45,91 |
+/- 0,8 |
Обозначения: П – передний, Д – двустворчатый, З – задний сегменты.
Изображения с микроскопа поверхностей дуг, на которых проводился анализ, показаны на рис. 3–5, в соответственно. В табл. 1 показаны усредненные весовые доли для Ni и Ti, идентифицированные на поверхности дуги в трех зонах, а в табл. 2 показаны весовые доли для Ni и Ti из поперечного сечения передней области дуги. Как видим, существенной разницы в концентрации Ni и Ti в каждом типе дуг нет. С другой стороны, количество Ni и Ti из упаковки производителя ( American Orthodontics ) составляет соответственно 55 и 45% как среднее процентное соотношение для всей проволоки [21]. Минимальные отличия находятся в диапазоне погрешности.
Спектр, показанный на рис. 3, представляет собой спектральные линии для Ni и Ti для каждого типа дуг, которые соответствуют значениям для линий рентгеновского излучения [26] этих элементов из литературных данных. Соответственно K α1 = 4,51 кэВ, K β1 = 4,93 кэВ и линии излучения L между 0,40–0,60 кэВ для Ti и K α1 = 7,48 кэВ, K α2 = 7,46, K β1 = 8,26 кэВ, линии L между 0,80–0,90 кэВ для Ni. Для использовавшихся в клинической практике дуг также имеются спектральные линии для C и O соответственно: при K α1 = 0,28 кэВ и K α1 = 0,52 кэВ. Для дуги TriTaniumTM , используемой в течение 6 недель, есть спектральные линии для K при K α1 и K α2 = 3,31 кэВ, K β1 = 3,59 кэВ и P при K α1 и K α2 = 2,01 кэВ, K β1 = 2,14 кэВ. Как видно на микрофотографиях (см. рис. 1), при длительном использовании дуг во рту их поверхность становится более шероховатой. Из-за этого становится сложнее тщательно очистить их от пищевых загрязнений перед исследованием пробы. Углерод является основным элементом всех органических соединений. Пока дуги находятся в полости рта, они постоянно контактируют с органическими материалами. После очистки перед испытанием они контактируют с атмосферным воздухом. Мы предполагаем, что присутствие C, O и других дополнительных элементов связано с едой и слюной, оставшимися после очистки, а также прямым контактом с воздухом до тестирования.
Таблица 2
Элементарный состав поперечного сечения переднего отдела дуги TriTanium™ , использованной в течение 9 недель
|
Элемент, % |
Поперечное сечение |
Погрешность, % |
||||
|
1 пора |
2 поры |
3 поры |
4 поры |
5 пор |
||
|
Ni |
36,27 |
36,66 |
54,33 |
54,72 |
54,13 |
+/- 0,8 |
|
Ti |
63,73 |
63,34 |
45,67 |
45,28 |
45,87 |
+/- 0,8 |
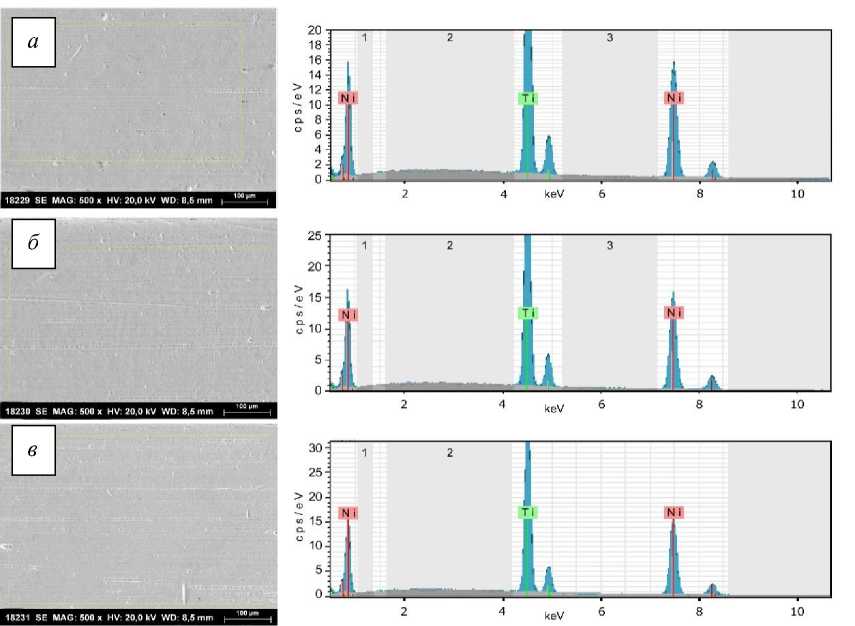
Рис. 3. Микрофотографии и спектры области неиспользованной дуги TriTaniumTM ; области: передняя ( а ); двустворчатая ( б ); задняя ( в )
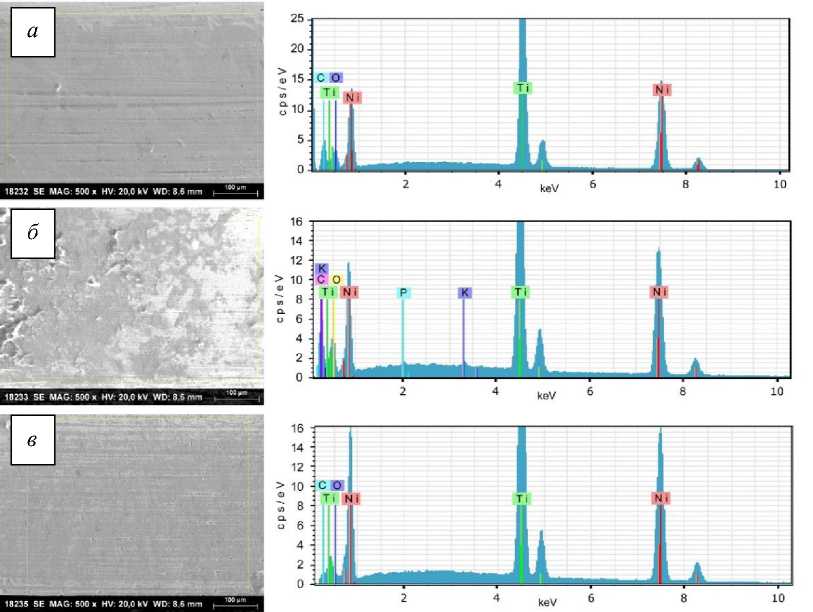
Рис. 4. Микрофотографии и спектры области использованной в течение 6 недель TriTaniumTM ; области: передняя ( а ); двустворчатая ( б ); задняя ( в )
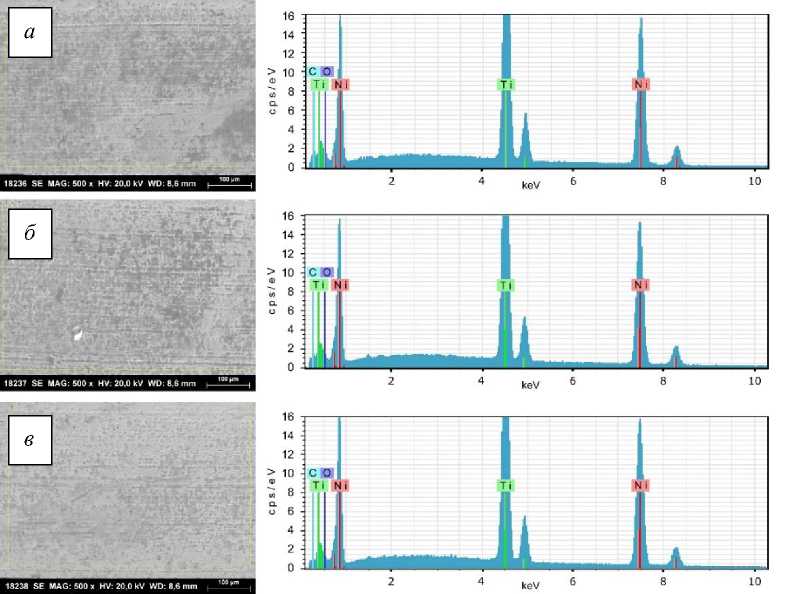
Рис. 5. Микрофотографии и спектры области использованной в течение 9 недель дуги TriTaniumTM ; области: передняя ( а ); двустворчатая ( б ); задняя ( в )
В исследовании 2019 года [11] использовался анализ электронной спектроскопии для исследования NiTi-дуг, который обнаружил сигнал от углерода, в основном происходящий от связей C – C при 280 эВ, что предполагает остаточное загрязнение, вероятно, из атмосферы.
Этот результат соответствует информации, полученной авторами из линий спектров для C ( K α1 = 0,28 кэВ) использованных дуг. Поэтому предполагается, что C в данном случае также может происходить из атмосферы.
В табл. 2 первые два значения для Ni и Ti показывают спектры в двух порах на поперечном сечении передней области проволоки, использованной в течение 9 недель. Соотношение Ni и Ti в них почти 1 к 2, и авторы предполагают, что происходит фаза Ti 2 Ni. В спектрах 3, 4 и 5 количество Ni и Ti соответствует количеству, определенному на поверхности. В работе [5] исследовано влияние частиц второй фазы, образующихся в процессе развития микроструктуры при переработке сплава в форму дуги. Их результаты показали, что в матрице сплава присутствовали частицы второй фазы типа Ti 2 Ni различных размеров (1–10 мкм) и формы. Наличие частиц второй фазы при обработке сплава играет значительную роль в уточнении микроструктуры. Деформация сплава может привести к локализованной аморфизации фазы матрицы вокруг данных частиц, как это наблюдается при интенсивной пластической деформации металлических материалов.
На рис. 6-8 показаны результаты статистического анализа динамики содержания Ni в зависимости от продолжительности использования для рассматриваемых сегментов: переднего, двустворчатого и заднего. Каждый рисунок содержит два графика: левый, показывающий результаты ANOVA , и правый, показывающий результаты множественных сравнений. Ось X на левом графике показывает три продолжительности использования. Ось Y на левом графике показывает содержание Ni в процентах.
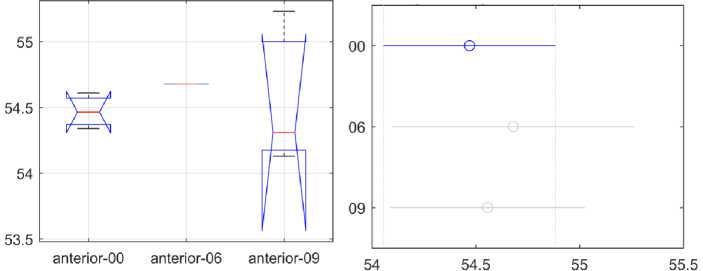
Рис. 6. Статистический анализ динамики различий между поверхностным содержанием Ni в переднем сегменте
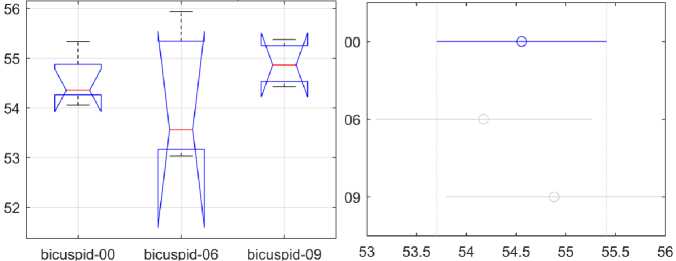
Рис. 7. Статистический анализ динамики различий между поверхностным содержанием Ni в двустворчатом сегменте
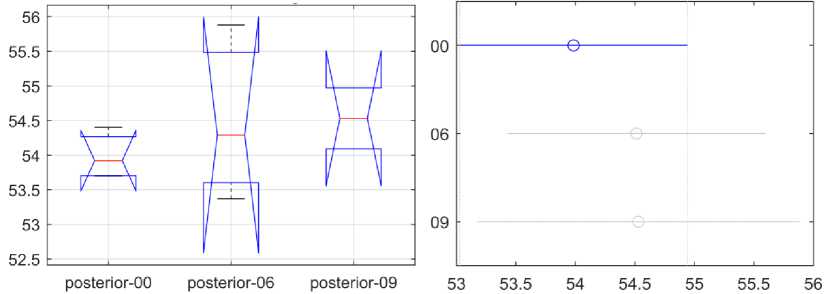
Рис. 8. Статистический анализ динамики различий между поверхностным содержанием Ni в заднем сегменте
Ось Y на правом графике показывает продолжительность использования для каждого типа дуги. На правом графике отражены результаты попарного сравнения из теста множественного сравнения, а также оценки и интервалы сравнения. Среднее групповое значение представлено символом, а интервал представлен линией, идущей от символа. Средние значения двух групп существенно различаются, если их интервалы не пересекаются, и наоборот. Содержание Ni в массовых процентах показано на оси X правого графика. Численные результаты непараметрического однофакторного дисперсионного анализа Краскела-Уоллиса приведены в отдельных таблицах дисперсионного анализа (табл. 3-5) для каждой области. Таблица ANOVA показывает вариацию между группами (столбцы) и вариацию внутри групп (погрешность). SS - это сумма квадратов, а df - степени свободы.
Полные степени свободы - это общее количество наблюдений минус один (строка «Всего»). Межгрупповые степени свободы – это количество групп минус один (строка «Группы»). Степени свободы внутри групп – это общие степени свободы за вычетом степеней свободы между группами (строка «Погрешность»). MS – это среднеквадратичная ошибка, которая равна отношению SS и df для каждого источника вариации. F -статистика – это отношение среднеквадратических ошибок. P -значение – это вероятность того, что тестовая статистика может принять значение, большее, чем значение вычисленной тестовой статистики ( Prob > F ). Небольшое значение p ( p ≤ 0,05) указывает на то, что различия между средними значениями значительны.
Существенных различий в динамике содержания Ni в сравниваемых группах в рассматриваемых сегментах нет.
Таблица 3
Результаты ANOVA для переднего отдела (см. рис. 6)
|
Источник |
SS |
df |
MS |
F |
Prob > F |
|
Группы |
0,0594 |
2 |
0,0297 |
0,24 |
0,7937 |
|
Погрешность |
0,7413 |
6 |
0,1235 |
– |
– |
|
Всего |
0,8006 |
8 |
– |
– |
– |
Таблица 4
Результаты ANOVA для двустворчатого отдела (см. рис. 7)
|
Источник |
SS |
df |
MS |
F |
Prob > F |
|
Группы |
0,7582 |
2 |
0,3791 |
0,49 |
0,6302 |
|
Погрешность |
6,1969 |
8 |
0,7746 |
– |
– |
|
Всего |
6,9551 |
10 |
– |
– |
– |
Таблица 5
Результаты ANOVA для заднего отдела (см. рис. 8)
|
Источник |
SS |
df |
MS |
F |
Prob > F |
|
Группы |
0,6364 |
2 |
0,3182 |
0,48 |
0,6396 |
|
Погрешность |
3,9622 |
6 |
0,6604 |
— |
— |
|
Всего |
0,6604 |
8 |
– |
– |
– |
Результаты наноиндентирования
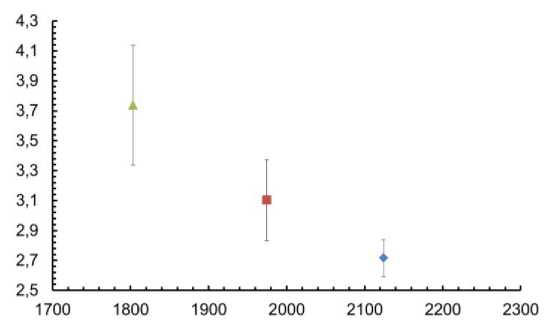
В результате экспериментов по наноиндентированию были получены кривые «нагрузка-смещение», а также рассчитаны твердость при вдавливании и модуль вдавливания для каждой области дуги с использованием аппроксимационного метода Оливера и Фарра [18]. Полученные результаты показали, что существует большая разница между механическими свойствами в различных областях исследуемых дуг TriTaniumTM в исходном состоянии. По сути, твердость вдавливания и модуль вдавливания в задней области самые высокие, а передняя область имеет самые низкие показатели (рис. 9–10).
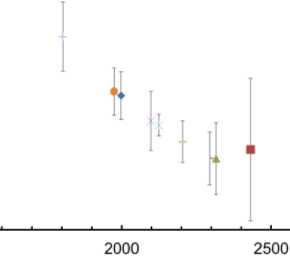
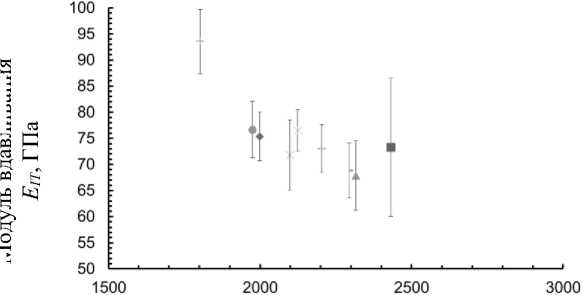
Возможная причина этого в том, что передняя область является наиболее пористой и пористость уменьшается в дальнейших областях дуги. Кроме того, сравнение механических свойств неиспользованных и использованных в течение 6 недель дуг TriTaniumTM на рис. 11–12 показали, что твердость при вдавливании и модуль упругости использованных в течение 6 недель проволок TriTaniumTM резко снижаются во всех трех областях (передней, двустворчатой и задней). Тем не менее наибольшее снижение наблюдается в двустворчатой области (твердость на вдавливание с 3,1 до 2,52 ГПа). Наблюдается небольшое снижение твердости при вдавливании и модуля упругости использованных дуг в течение 9 недель (с твердости вдавливания 2,52 ГПа в двустворчатой области дуги у использованных в течение 6 недель до 2,32 ГПа в той же области дуг, используемых в течение 9 недель). Возможной причиной снижения твердости вдавливания и модуля упругости с увеличением периода использования дуги во рту пациента является тот факт, что полученная дуга TriTaniumTM имеет мелкозернистую структуру, тогда как зернистая структура дуги, использованной в течение 6 недель, начинает рекристаллизоваться в более крупные зерна, а структура дуги, используемой в течение 9 недель, является крупнозернистой (размер зерна достигает 10 мкм), что можно увидеть на микрофотографии на рис. 1. Полученные механические свойства хорошо согласуются с данными других авторов [1, 14].
На рис. 13–15 и рис. 16–18 показаны результаты статистического анализа динамики «модуля вдавливания» и «твердости вдавливания» как функция продолжительности использования дуг с учетом переднего, двустворчатого и заднего сегментов.
Перемещение, нм
Рис. 9. Сравнение твердости вдавливания дуг TriTaniumTM в исходном состоянии в различных участках: синий – передний, красный – двустворчатый, зеленый -задний
105 :
К 100;
М 95■ и G 90;
« £5 85■
80 ■
70 ..............................
1700 1800 1900 2000 2100 22002300
Перемещение, нм
Рис. 10. Сравнение твердости вдавливания дуг TriTaniumTM в исходном состоянии в различных участках: синий – передний, красный – двустворчатый, зеленый -задний
Численные результаты ANOVA показаны в соответствующих таблицах (табл. 6–11). Все используемые символы и пояснения такие же, как для рис. 6–8 и соответствующих таблиц (см. табл. 3–5). Ось X на левом графике на рис. 13–15 показывает три продолжительности использования (неиспользованные, использованные в течение 6 и 9 недель). Ось Y на левом графике на тех же рисунках показывает модуль вдавливания в ГПа.
4 ;
3,5 •
3 •
2,5 ■
2 ■
1,5 — 1500
Перемещение, нм
Рис. 11. Сравнение твердости при вдавливании в неиспользованных и использованных в течение 6 и 9 недель дугах TriTaniumTM
s s is
/
Перемещение, нм
Рис. 12. Сравнение модуля вдавливания в неиспользованных и использованных в течение 6 и 9 недель дугах TriTaniumTM
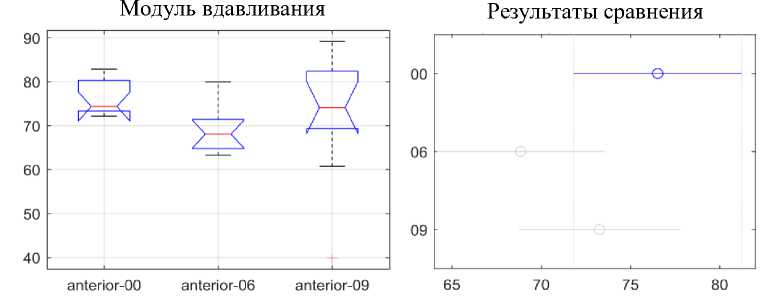
Рис. 13. Статистический анализ динамики различий модуля вдавливания передних сегментов
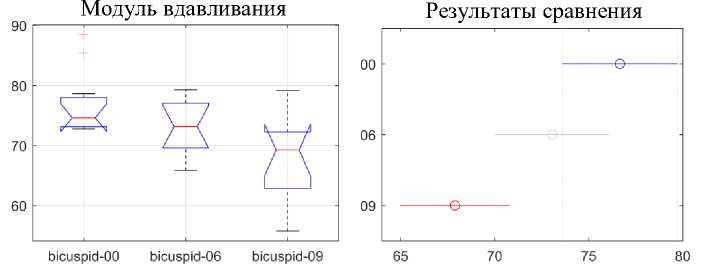
Рис. 14. Статистический анализ динамики различий модуля вдавливания двустворчатых сегментов
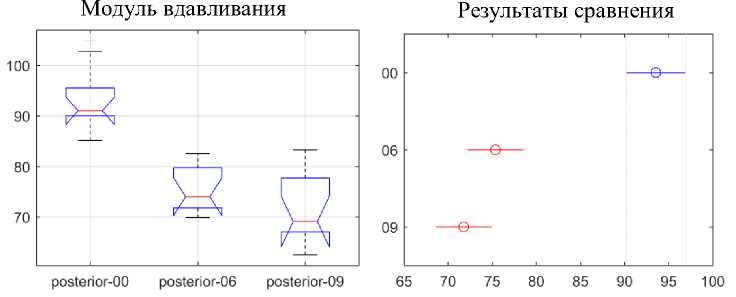
Рис. 15. Статистический анализ динамики различий модуля вдавливания задних сегментов
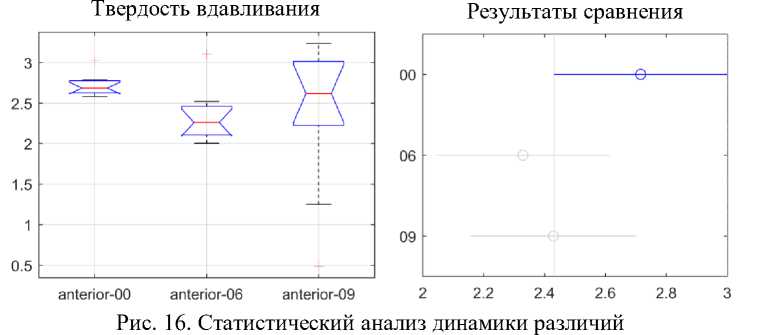
твердости вдавливания передних сегментов
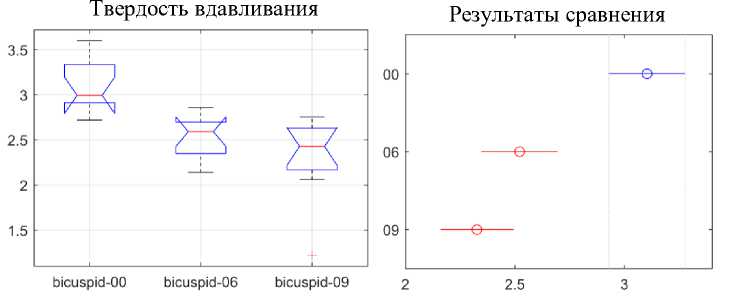
Рис. 17. Статистический анализ динамики различий твердости вдавливания двустворчатых сегментов
Ось X правого графика на рис. 13-15 показывает модуль вдавливания в ГПа, тогда как ось Y на правом графике на тех же рисунках показывает три продолжительности использования.
На рис. 13-15 видно, что модуль вдавливания в передней области не показывает каких-либо статистически значимых различий в зависимости от продолжительности использования. Напротив, модуль вдавливания для двустворчатого и для заднего сегментов, действительно, показывает статистически значимое снижение значений модуля вдавливания между неиспользованными и использованными в течение 9 недель дугами. Однако можно упомянуть, что снижение значений модуля вдавливания присутствует в течение всего периода использования и ускоряется почти вдвое после 6-й недели использования.
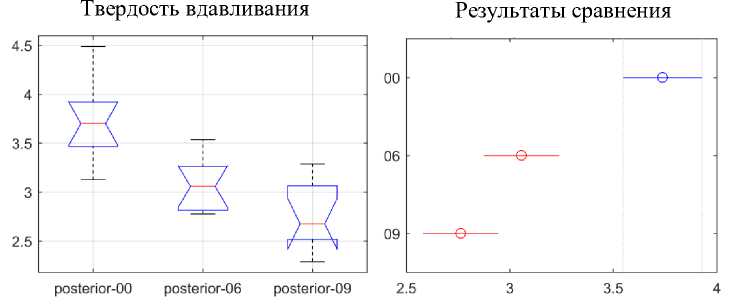
Рис. 18. Статистический анализ динамики разницы между задними сегментами твердости вдавливания
Таблица 6
Результаты ANOVA для переднего сегмента (см. рис. 11)
|
Источник |
SS |
df |
MS |
F |
Prob > F |
|
Группы |
326,85 |
2 |
163,427 |
2,14 |
0,1347 |
|
Погрешность |
2367,55 |
31 |
76,373 |
— |
— |
|
Всего |
2694,41 |
33 |
— |
— |
— |
Таблица 7
Результаты ANOVA для двустворчатого сегмента (см. рис. 12)
|
Источник |
SS |
df |
MS |
F |
Prob > F |
|
Группы |
448,64 |
2 |
224,32 |
7 |
0,0031 |
|
Погрешность |
994,11 |
31 |
32,068 |
– |
– |
|
Всего |
1442,75 |
33 |
– |
– |
– |
Таблица 8
Результаты ANOVA для заднего сегмента (см. рис. 13)
|
Источник |
SS |
df |
MS |
F |
Prob > F |
|
Группы |
2814,32 |
2 |
1407,16 |
40,9 |
3,62166e-09 |
|
Погрешность |
997,73 |
29 |
34,4 |
||
|
Всего |
3812,06 |
31 |
На рис. 16-18, отражены три продолжительности использования. Ось Y на левом графике на этих рисунках показывает твердость при вдавливании в ГПа. Ось X на правом графике показывает твердость вдавливания в ГПа, а ось Y на правом графике показывает три продолжительности использования. Твердость вдавливания для передней области не показывает каких-либо статистически значимых различий в зависимости от продолжительности использования. Напротив, твердость вдавливания в двустворчатом и заднем сегментах действительно показывает статистически значимое снижение значений твердости вдавливания между неиспользованными и использованными дугами от 6 до 9 недель. Снижение значений твердости при вдавливании практически линейно в течение всего периода использования и становится статистически различным на 6-й неделе использования.
Таблица 9
Результаты ANOVA для переднего сегмента (см. рис. 14)
|
Источник |
SS |
df |
MS |
F |
Prob > F |
|
Группы |
0,88815 |
2 |
0,44408 |
1,6 |
0,2172 |
|
Погрешность |
8,5781 |
31 |
0,27671 |
– |
– |
|
Всего |
9,46616 |
33 |
– |
– |
– |
Таблица 10
Результаты ANOVA для двустворчатого сегмента (см. рис. 15)
|
Источник |
SS |
df |
MS |
F |
Prob > F |
|
Группы |
3,6841 |
2 |
1,8427 |
17,73 |
7,35787e-06 |
|
Погрешность |
3,22217 |
31 |
0,10394 |
||
|
Всего |
6,90758 |
33 |
Таблица 11
Результаты ANOVA для заднего сегмента (см. рис. 16)
|
Источник |
SS |
df |
MS |
F |
Prob>F |
|
Группы |
5,18032 |
2 |
2,59016 |
22,99 |
1,04304e-06 |
|
Погрешность |
3,26747 |
29 |
0,11267 |
||
|
Всего |
8,44779 |
31 |
Выводы
Для оценки поведения дуг TriTaniumTM после клинического использования было проведено сравнение механических свойств и характеристик поверхности дуг в неиспользованном виде и использованных в течение 6 и 9 недель. Спектральный анализ характеристик поверхности дуги TriTaniumTM в неиспользованном виде выявил гладкую пористую поверхность в трех областях, причем передняя часть является наиболее пористой. При длительном клиническом использовании шероховатость увеличивается. Элементарный анализ неиспользованных и использованных дуг TriTaniumTM показал, что Ni и Ti являются основными составляющими сплава. Нет существенной разницы в концентрации Ni и Ti во всех сегментах дуг, соотношение элементов сохраняется примерно 1:1. В спектрах проявлялись спектральные линии для небольшого количества C, O и других дополнительных элементов. Предполагается, что присутствие C, O и других неорганических элементов связано с пищей и слюной, оставшимися после очистки, а также прямым контактом с воздухом до тестирования. Возможное присутствие фазы Ti2Ni в порах дуги может повлиять на окружающую микроструктуру и привести к локальной аморфизации матрицы во время деформации сплава. Полученные результаты экспериментов по наноиндентированию показали, что модуль упругости при вдавливании и твердость при вдавливании для передней области не имеют статистически значимых различий в зависимости от продолжительности использования. Модуль вдавливания для двустворчатой дуги и для задней части действительно, показывает статистически значимое разрушение между исходными и использованными в течение 9 недель дугами. Однако можно упомянуть, что снижение значений модуля вдавливания присутствует в течение всего периода использования и ускоряется почти вдвое после 6-й недели использования. Твердость вдавливания для двустворчатой дуги и для задних отделов, действительно, показывает статистически значимое снижение значений твердости вдавливания между полученными и использованными дугами 6 и 9 недель. Снижение значений твердости при вдавливании практически линейно в течение всего периода использования и становится статистически различным на 6-й неделе использования. Отсутствует негативное влияние на здоровье пациентов из-за снижения твердости вдавливания и модуля вдавливания извлеченных многосиловых дуг TriTaniumTM. Во время клинического применения уровень дезактивирующих сил падает, что может привести к задержке лечения. По этой причине для ортодонтов важно выбрать правильное время для замены дуги на следующую. Использование дуг с разными уровнями силы внутри проволоки может быть безопаснее для пораженных зубов и использоваться у пациентов с заболеваниями пародонта и потерей костной массы.
Благодарность
Эта работа была поддержана Операционной программой ЕС «Наука и образование для умного роста» [№ BG05M2OP001-1.001-0008]; Болгарский национальный научный фонд [№ H27 / 29 и D-139 / 23.04.2019] и двусторонний проект между Болгарской академией наук и Эстонской академией наук, Таллиннским технологическим университетом [№ TAR16016, IUT-T4].
-
1. Alcock J.P., Barbour M.E., Sandy J.R., Ireland A.J. Nanoindentation of orthodontic archwires: the effect of decontamination and clinical use on hardness, elastic modulus and surface roughness // Dental Materials. -2009. – Vol. 25, no. 8. – P. 1039-1043.
-
2. American orthodontics. - URL: http://www.americanortho.com/catalog/mobile/index.html (accessed 5 May 2020).
-
3. Andreasen G.F., Morrow R.E. Laboratory and clinical analyses of nitinol wire // American Journal of Orthodontics. – 1978. – Vol. 73, no. 2. - P. 142-151.
-
4. Bench R.W., Gugino C.F., Hilgers J.J. Bio-progressive therapy. - Denver: Rocky Mountain Orthodontics, 1977/78.
-
5. Bhagyaraj J., Ramaiah K.V., Saikrishna C.N., Bhaumik S.K., Gouthama. Behavior and effect of Ti 2 Ni phase during processing of NiTi shape memory alloy wire from cast ingot // Journal of Alloys and Compounds. -2013. - Vol. 581. - P. 344–351.
-
6. Dimberg L., Arnrup K., Bondemark, L. The impact of maloclusion on the quality of life among children and adolescents: a systematic review of quantitive studies // European Journal of Orthododontics. - 2015. -Vol. 37, no. 3. - P. 238-247.
-
7. Gravina M.A., Brunharo I. H.V.P., Canavarro C., Elias C. N., Quintao C.C.A. Mechanical properties of NiTi and CuNiTi shape-memory wires used in orthodontic treatment. Part 1: Stress-strain tests // Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics. – 2013. – Vol. 18, no. 4. – P. 35–42.
-
8. Ibe D.M., Segner D. Superelastic materials displaying different force levels within one archwire // Journal of Orofacial Orthopedics / Fortschritte der Kieferorthopädie. - 1998. - Vol. 59, no. 1. - P. 29–38.
-
9. Iijima M., Ohno H., Kawashima I., Endo K., Mizoguchi, I. Mechanical behavior at different temperatures and stresses for super-elastic nickel-titanium orthodontic wires having different transformation temperatures // Dental. Materials. - 2002. - Vol.18, no. 1. - P. 88-93.
-
10. Kroll reagent. - URL: https://etchantstore.com/?s=Kroll+reagent (accessed 5 May 2020).
-
11. Lepojević N., Šćepan I., Glišić B., Jenko M., Godec M., Hočevar S., Rudolf R. Characterisation of NiTi orthodontic archwires surface after the simulation of mechanical loading in CACO2-2 cell culture // Coatings. - 2019. - Vol. 9, no. 7. - P. 1-12.
-
12. Lombardo L., Ceci M., Mollica F., Mazzanti V., Palone M., Siccliani G. Mechanical properties of multi-force vs. conventional NiTi archwires // Journal of Orofacial Orthopedics. - 2019. - Vol. 80. -P. 57-67.
-
13. Lombardo L., Toni G., Mazzanti V., Mollica F., Spedicato G., Siciliani G. The mechanical behavior of as received and retrieved nickel titanium orthodontic archwires // Progress in Orthodontics. - 2019. - Vol. 20, no. 1. – P. 1–8.
-
14. Mehta A. S. K. Thermomechanical characterization of variable force NiTi orthodontic archwires. Master's thesis. - Milwaukee, 2015. – 50 p.
-
15. Miura F. Orthodontic Archwire. Patent U.S. No. 5,017,133. – 1991.
-
16. Miura F., Mogi M., Ohura Y., Hamanaka H. The super-elastic property of the Japanese NiTi alloy wire for use in orthodontics // American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics. - 1986. - Vol. 90, no. 1. - P. 1-10.
-
17. Oguienko O. Mechanical properties of graded thermodynamic nickel titanium archwires in bending and torsion. Master's Thesis. - University of Toronto, 2017.
-
18. Oliver W., Pharr G. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments // Journal of Materials Research. - 1992. - Vol. 7, no. 6. -P. 1564-1583.
-
19. Oral Health. - URL: http://www.who.int/oral_health/en/ (accessed 5 May 2020).
-
20. Proffit W., Fields H., Sarver D. Contemporary Orthodontics. - St. Louis: Elsevier/Mosby, 2013. – 768 p.
-
21. Sarul M., Kawala B., Antoszewska J. Comparison of Elastic Properties of Nickel-Titanium Orthodontic Archwires // Advances in Clinical and Experimental Medicine. - 2013. - Vol. 22, no. 2. - P. 253–260.
-
22. Sarul M., Rutkowska-Gorczyca M., Detyna J., Ziety A., Kawala M., Antoszewska-Smith J. Do mechanical and physicochemical properties of orthodontic NiTi wires remain stable in vivo? // BioMed Research International. - 2016. - Vol. 2016. – Article ID 5268629. - P.1-5.
-
23. Schwarz A.M. Tissue changes incidental to orthodontic tooth movement // International Journal of Orthodontia, Oral Surgery and Radiography. -1932. - Vol. 18, no. 4. - P. 331-352.
-
24. Sevilla P., Martorell F., Libenson C., Planell A. J., Gil, F.J. Laser welding of NiTi orthodontic archwires for selective force application // Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine. - 2008. - Vol. 19, no. 2. -P. 525-529.
-
25. Thompson A., Attwood D., Gullikson E., Howells M., Kim K., Kirz J., Kortright J., Lindau I., Liu Y., Pianetta P., Robinson A., Scofield J., Underwood J., Williams G., Winick H. X-ray data booklet. Center for X-ray optics and advanced light source. – Berkeley, 2009.
-
26. Tritanium TM. - URL: https://damerica.com.br/produto/TriTanium®®-american-orthodontics/ (accessed 5 May 2020).
Список литературы Наноиндентация и характеристика поверхности клинических мультисиловых ортодонтических дуг из сплава NiTi
- Alcock J.P., Barbour M.E., Sandy J.R., Ireland A.J. Nanoindentation of orthodontic archwires: the effect of decontamination and clinical use on hardness, elastic modulus and surface roughness // Dental Materials. -2009. - Vol. 25, no. 8. - P. 1039-1043.
- American orthodontics. - URL: http://www.americanortho.com/catalog/mobile/index.html (accessed 5 May 2020).
- Andreasen G.F., Morrow R.E. Laboratory and clinical analyses of nitinol wire // American Journal of Orthodontics. - 1978. - Vol. 73, no. 2. - P. 142-151.
- Bench R.W., Gugino C.F., Hilgers J.J. Bio-progressive therapy. - Denver: Rocky Mountain Orthodontics, 1977/78.
- Bhagyaraj J., Ramaiah K.V., Saikrishna C.N., Bhaumik S.K., Gouthama. Behavior and effect of Ti2Ni phase during processing of NiTi shape memory alloy wire from cast ingot // Journal of Alloys and Compounds. -2013. - Vol. 581. - P. 344-351.
- Dimberg L., Arnrup K., Bondemark, L. The impact of maloclusion on the quality of life among children and adolescents: a systematic review of quantitive studies // European Journal of Orthododontics. - 2015. -Vol. 37, no. 3. - P. 238-247.
- Gravina M.A., Brunharo I. H.V.P., Canavarro C., Elias C. N., Quintao C.C.A. Mechanical properties of NiTi and CuNiTi shape-memory wires used in orthodontic treatment. Part 1: Stress-strain tests // Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics. - 2013. - Vol. 18, no. 4. - P. 35-42.
- Ibe D.M., Segner D. Superelastic materials displaying different force levels within one archwire // Journal of Orofacial Orthopedics / Fortschritte der Kieferorthopadie. - 1998. - Vol. 59, no. 1. - P. 29-38.
- Iijima M., Ohno H., Kawashima I., Endo K., Mizoguchi, I. Mechanical behavior at different temperatures and stresses for super-elastic nickel-titanium orthodontic wires having different transformation temperatures // Dental. Materials. - 2002. - Vol.18, no. 1. - P. 88-93.
- Kroll reagent. - URL: https://etchantstore.com/?s=Kroll+reagent (accessed 5 May 2020).
- Lepojevic N., Scepan I., Glisic B., Jenko M., Godec M., Hocevar S., Rudolf R. Characterisation of NiTi orthodontic archwires surface after the simulation of mechanical loading in CACO2-2 cell culture // Coatings. - 2019. - Vol. 9, no. 7. - P. 1-12.
- Lombardo L., Ceci M., Mollica F., Mazzanti V., Palone M., Siccliani G. Mechanical properties of multi-force vs. conventional NiTi archwires // Journal of Orofacial Orthopedics. - 2019. - Vol. 80. -P. 57-67.
- Lombardo L., Toni G., Mazzanti V., Mollica F., Spedicato G., Siciliani G. The mechanical behavior of as received and retrieved nickel titanium orthodontic archwires // Progress in Orthodontics. - 2019. - Vol. 20, no. 1. - P. 1-8.
- Mehta A. S. K. Thermomechanical characterization of variable force NiTi orthodontic archwires. Master's thesis. - Milwaukee, 2015. - 50 p.
- Miura F. Orthodontic Archwire. Patent U.S. No. 5,017,133. - 1991.
- Miura F., Mogi M., Ohura Y., Hamanaka H. The super-elastic property of the Japanese NiTi alloy wire for use in orthodontics // American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics. - 1986. - Vol. 90, no. 1. - P. 1-10.
- Oguienko O. Mechanical properties of graded thermodynamic nickel titanium archwires in bending and torsion. Master's Thesis. - University of Toronto, 2017.
- Oliver W., Pharr G. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments // Journal of Materials Research. - 1992. - Vol. 7, no. 6. -P. 1564-1583.
- Oral Health. - URL: http://www.who.int/oral_health/en/ (accessed 5 May 2020).
- Proffit W., Fields H., Sarver D. Contemporary Orthodontics. - St. Louis: Elsevier/Mosby, 2013. - 768 p.
- Sarul M., Kawala B., Antoszewska J. Comparison of Elastic Properties of Nickel-Titanium Orthodontic Archwires // Advances in Clinical and Experimental Medicine. - 2013. - Vol. 22, no. 2. - P. 253-260.
- Sarul M., Rutkowska-Gorczyca M., Detyna J., Ziety A., Kawala M., Antoszewska-Smith J. Do mechanical and physicochemical properties of orthodontic NiTi wires remain stable in vivo? // BioMed Research International. - 2016. - Vol. 2016. - Article ID 5268629. - P.1-5.
- Schwarz A.M. Tissue changes incidental to orthodontic tooth movement // International Journal of Orthodontia, Oral Surgery and Radiography. -1932. - Vol. 18, no. 4. - P. 331-352.
- Sevilla P., Martorell F., Libenson C., Planell A. J., Gil, F.J. Laser welding of NiTi orthodontic archwires for selective force application // Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine. - 2008. - Vol. 19, no. 2. -P. 525-529.
- Thompson A., Attwood D., Gullikson E., Howells M., Kim K., Kirz J., Kortright J., Lindau I., Liu Y., Pianetta P., Robinson A., Scofield J., Underwood J., Williams G., Winick H. X-ray data booklet. Center for X-ray optics and advanced light source. - Berkeley, 2009.
- Tritanium TM. - URL: https://damerica.com.br/produto/TriTanium®®-american-orthodontics/ (accessed 5 May 2020).


