Nanostructured titanium dioxide-based photocatalysts for self-cleaning concrete: assessment of effects of phase composition on photocatalytic activity of TiO2
Автор: Balykov A.S., Chugunov D.B., Kyashkin V.M., Davydova N.S.
Журнал: Nanotechnologies in Construction: A Scientific Internet-Journal @nanobuild-en
Рубрика: The results of the specialists’ and scientists’ researches
Статья в выпуске: 3 Vol.17, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Introduction. Currently, the development of photocatalytically active cement-based materials with self-cleaning properties is a promising area of building materials science. Self-cleaning concrete is obtained by using photocatalytic additives, of which titanium dioxide (TiO2) is the most common. It has been found that the functional properties of TiO2 depend largely on its phase composition. This study aimed to establish the patterns of influence of phase composition on the photocatalytic activity of titanium dioxide under the impact of artificial ultraviolet and natural solar radiation and to identify the most effective titanium oxide-based photocatalysts for subsequent use in the composition of self-cleaning concrete. Methods and materials. Four titanium dioxide samples, namely two industrial samples and two samples synthesized by hydrolysis of titanium alkoxide in acidified water-alcoholic medium followed by calcination at 500 °C, were the objects of the study. X-ray powder diffractometry was the method used to investigate the structure parameters of TiO2 samples. The model reaction of oxidative degradation of methylene blue under UV- and daylight exposure was the means for studying the photocatalytic activity of titanium dioxide samples. Results and discussion. It was found that polymorphic modifications of titanium dioxide had a multidirectional effect on its functional characteristics, in particular, a rise in the content of anatase and rutile led to an increase and decrease in the photoactivity of TiO2 samples, respectively. The single-phase sample with anatase structure was most effective under UV irradiation, while the three-phase sample with the anatase : brookite : rutile ratio of 67% : 13% : 20% had the highest activity under daylight exposure. The photocatalyst composition, including several polymorphs of TiO2 with a predominance of anatase form (more than 50%), allowed to achieve a synergistic effect of increasing the photocatalytic activity of titanium dioxide under conditions of solar radiation due to the formation of type-II semiconductor heterojunctions. Heterostructures made it possible to improve the spatial separation of charge carriers and to reduce the recombination rate of photogenerated electron-hole pairs. Conclusion. The obtained results indicated the possibility of improving the functional characteristics of titanium oxide-based additives for self-cleaning concrete due to the targeted regulation of their phase composition by optimizing the synthesis parameters of photocatalytic modifiers.
Self-cleaning concrete, photocatalyst, titanium dioxide, sol-gel method, photocatalytic activity, phase composition, crystallite size, nanostructures, heterojunction, polymorphism, anatase, brookite, rutile, X-ray diffraction
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142244834
IDR: 142244834 | DOI: 10.15828/2075-8545-2025-17-3-307-324
Текст научной статьи Nanostructured titanium dioxide-based photocatalysts for self-cleaning concrete: assessment of effects of phase composition on photocatalytic activity of TiO2
Original article
Балыков А.С., Чугунов Д.Б., Кяшкин В.М., Давыдова Н.С. Наноструктурированные фотокатализаторы на основе диоксида титана для самоочищающихся бетонов. Оценка влияния фазового состава на фотокаталитическую активность TiO2. Нанотехнологии в строительстве. 2025;17(3):307–324. – EDN: YVRFDW.
The development of cement-based materials with high performance characteristics is a priority area of building materials science [1, 2]. The range of modern modified concretes is quite diverse and includes different types, in
particular, high-strength concrete [3, 4], self-compacting concrete [5, 6], fiber reinforced concrete [7–9], reactive powder concrete [10, 11], self-prestressing concrete [5, 12, 13], etc.
It is known that individual or complex application of chemical and mineral additives with different com-
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES position, dispersity, and mechanism of action allows to create high performance concrete. Effective types of additives are superplasticizers [14], superabsorbent polymers [15], microsilica [16], opal-cristobalite rocks [17], fly ash [18], expanding sulfoaluminate modifiers [5], carbonate rocks and calcined polymineral clays [19, 20], carbon-based modifiers [2, 21], etc. A special group of modifiers includes nanoscale photocatalytic additives that allow to obtain photocatalytically active cementbased materials [22–24] having the ability to self-clean and decompose atmospheric pollutants, antibacterial effect, etc. [25–27].
Nanostructured titanium dioxide, characterized by non-toxicity, chemical stability, and high activity under ultraviolet radiation exposure, is one of the effective types of photocatalysts [28–31]. Nevertheless, the high recombination rate of photogenerated charge carriers, as well as the narrowed spectral range of action with the band gap of known titanium dioxide polymorphs equal to 3.0–3.5 eV, are the main disadvantages of TiO2. The wide band gap of titanium(IV) oxide requires solving the problem of its sensitization to visible light [32–34].
The photocatalytic properties of titanium(IV) oxide depend significantly on its phase composition. Currently, the compound polymorphism, which consists in the existence in nature of four main crystalline modifications of TiO2, such as anatase, brookite, rutile, and TiO2(B), is actively used to improve the functional characteristics of titanium oxide-based photocatalysts [35].
Anatase and rutile are the most studied polymorphs of titanium dioxide, these tetragonal phases are widely used in the obtaining of commercial photocatalysts. Brookite, characterized by an orthorhombic crystal lattice, is the least stable phase in the TiO2 isomorphic series, is relatively rare in nature and remains poorly understood. Nevertheless, the results of individual studies show that the photoactivity of brookite may exceed the characteristics of anatase and rutile due to the presence of traps preferred for photocatalytic reactions [36, 37]. The TiO2(B) phase, which is a mixture of monoclinic syngony crystals, was first synthesized in 1980 by hydrolysis of K2Ti4O9 followed by thermal treatment at 500 °C [38]. TiO2(B) is the least dense polymorph of titanium dioxide. In addition, TiO2(B) is a less stable phase compared to anatase and rutile [35].
It is known that the presence of two or three polymorphic modifications in the titanium dioxide composition, in particular, anatase/brookite [39–41], anatase/rutile [42–44], brookite/rutile [45, 46], anatase/TiO2(B) [47, 48], and rutile/TiO2(B) [49], anatase/brookite/rutile [50– 52], and anatase/rutile/TiO2(B) [53], makes it possible to form heterostructures with intercrystalline boundaries in multiphase composites. These heterojunctions contribute to an increase in the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 by improving the separation of charge carriers and reducing
the recombination rate of photoinduced electron-hole pairs [35, 37, 39, 40]. In particular, the works [37, 40] show that the combination of anatase and brookite in the nanocrystalline composite structure allows to increase the catalytic activity of the material in both oxidation and reduction reactions. The high functional efficiency of titanium dioxide polymorphism also manifests itself in the well-known commercial Degussa P25 photocatalyst, which is a mixture of anatase and rutile in the ratio of 3 : 1 or 4 : 1 [42, 44].
This study aimed to establish the patterns of influence of phase composition on the photocatalytic activity of titanium dioxide under the impact of artificial ultraviolet and natural solar radiation and to identify the most effective titanium oxide-based photocatalysts for subsequent use in the composition of self-cleaning concrete.
We completed the following tasks in order to achieve the goal of this study:
-
1. The effects of synthesis conditions on the structure parameters of TiO2 precursors obtained by hydrolysis of titanium alkoxide in acidified water-alcoholic medium were studied.
-
2. The kinetics of photodecomposition process of methylene blue in solution was investigated under conditions of exposure to ultraviolet radiation and solar radiation in the absence and presence of titanium oxide-based photocatalysts.
-
3. The effects of phase composition on the photo-catalytic activity of titanium dioxide samples were researched under conditions of exposure to ultraviolet light and daylight.
-
4. The interrelations and regularities were established between the synthesis conditions, phase composition and photoactivity of TiO2, which made it possible to optimize the prescription and technological parameters for obtaining effective titanium oxide-based photocatalysts for self-cleaning concrete.
METHODS AND MATERIALS
Synthesis of TiO2 samples from hydrolyzed precursors
Titanium(IV) oxide samples were synthesized by solgel method, which involves hydrolysis of titanium alkoxide in acidified water-alcoholic medium followed by thermal treatment of the resulting precursor in the form of hydrated titanium oxide (TiО2·nH2О).
At the initial stage of the synthesis, titanium tetraiso-propoxide (TTIP, pure grade) was dissolved in anhydrous isopropyl alcohol (C3H7OH, pure grade), then 0.1 M HNO3 solution was added to the mixture in doses, after which the mixture was vigorously stirred for 2 hours. The ratio of the reaction mixture components by volume was VTTIP : VC3H7OH : VHNO30,1 M = 0.75 : 1.0 : 1.0. The sol-gel
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES synthesis product formed by hydrolysis aged at a given temperature for 5 hours. The final stages involved sequential filtration, washing, and drying of the precipitate to obtain TiO2 precursor powder.
During the experimental study, the variable parameters of synthesis were temperature at mixing of solutions ( Tmixing ) and temperature of gel aging ( Taging ). The variation levels of these parameters were 20 °C and 80 °C. The drying temperature ( Tdrying ) and drying time ( tdrying ) of samples were constant at 80 °C and 2 hours, respectively.
Table 1 shows the synthesis parameters and labeling of TiO2 precursor samples.
The P-TiO2-1 and P-TiO2-2 precursors were calcined at 500 °C for 4 hours to obtain titanium dioxide powders. The calcined samples were labeled according to the type of precursor used, namely TiO2-1 and TiO2-2. Two commercial (industrial) samples of titanium(IV) oxide, characterized by different phase composition and designated as TiO2-3 and TiO2-4, were control samples.
Table 2 shows the list of TiO2 samples, which were the object of experimental study, as well as information on the technology for their obtaining.
X-ray diffraction phase analysis of TiO2 samples and their precursors
The phase composition of TiO2 samples and their precursors was determined by X-ray powder diffractometry on the PANalytical Empyrean diffractometer (the
Netherlands). The shooting conditions included the use of CuKα radiation with wavelength λ = 1.5406 Å, θ-2θ scanning mode, shooting range 2θ = 5–75°, angle step of 0.0131°, and exposure time at point of 200 seconds. The phases were identified using the Crystallography Open Database (COD).
The sizes of coherent scattering regions (CSR) of the main phases such as anatase, rutile, and brookite, were calculated from the X-ray diffraction analysis results to assess the crystallinity degree of TiO2 samples. The average sizes of CSR (crystallites) of these phases were determined by the main diffraction peaks free from superposition, in particular, at 2θ = 25.3° and 2θ = 37.9° for anatase (in the absence and presence of brookite, respectively), at 2θ = 30.8° for brookite, and at 2θ = 27.4° for rutile. The classical Scherrer formula was used to calculate the crystallite size:
к-х
D = Lcr = ~ 29' (1)
p■cos there D (Lcr) is the average size of crystallites (CSR) of the analyzed phase, Å;
K is the particle shape coefficient (Scherrer constant), K ≈ 0.9–1.0;
λ is the wavelength of X-ray radiation, λ = 1.5406 Å;
β is the full width at half maximum (FWHM) for the analyzed diffraction peak of phase, radians;
θ is the X-ray diffraction angle, radians.
Table 1. Synthesis parameters and labeling of TiO2 precursor samples
|
* Ф О. Л E E Я 3 <л с |
Labeling of TiO2 precursor samples |
Synthesis parameters |
|||||
|
Solution mixing |
Gel aging |
Gel drying |
|||||
|
Temperature, T , оС mixing |
Time, t mixing , h |
Temperature, T aging , оС |
Time, aging , |
Temperature, T drying , оС |
Time, t , h drying |
||
|
1 |
P-TiO2-1 |
20 |
2 |
20 |
5 |
80 |
2 |
|
2 |
P-TiO2-2 |
80 |
2 |
80 |
5 |
80 |
2 |
Table 2. List of investigated TiO2 samples and conditions for their obtaining
|
Sample number |
Labeling of TiO2 samples |
Type of precursor used (Table 1) |
Calcination parameters of TiO2 precursors |
Note |
||
|
Temperature, calcination , |
Temperature rise rate, v calcination , оС/min |
Isothermal aging time, calcination , |
||||
|
1 |
TiO2-1 |
P-TiO2-1 |
500 |
5 |
4 |
samples synthesized by calcination of precursors |
|
2 |
TiO2-2 |
P-TiO2-2 |
||||
|
3 |
TiO2-3 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
commercial (industrial) samples |
|
4 |
TiO2-4 |
|||||
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES
Evaluation of photocatalytic activity of TiO2 samples
The photocatalytic activity of titanium dioxide samples was studied in a model photochemical reaction of oxidative destruction of methylene blue (MB), when aqueous suspensions of MB solution and TiO2 powder were exposed to artificial ultraviolet and natural solar radiations. Two identical series of solutions with photocatalysts were the objects of study.
The weight ratio of TiO2 and methylene blue in the suspensions was 50 : 1. The dye concentration in the solution was 10 mg/l. To destroy large agglomerates and evenly distribute the dispersed phase particles in the solution, ultrasonic dispersion of samples was performed for 10 min on the Bandelin Sonorex ultrasonic bath.
Ultraviolet light irradiated the first series of dye solutions with TiO2 for 2 hours under constant stirring of suspensions on a magnetic stirrer. The radiation sources were two 25 W 254 nm UV lamps.
Solar radiation affected the second series of solutions with photocatalysts. Exposure of samples took place in the summer on the windowsill under natural daylight without using additional artificial light sources. The exposure time was 75 hours, namely 15 hours per day for 5 days.
During the study, aliquots of the solution were taken at certain intervals of exposure time to perform spectrophotometric measurements of the residual dye concentration. The sampling and measurement intervals were 15–30 minutes and 15 hours (1 day) for the first and sec-
ond series of samples, which were exposed to ultraviolet and solar radiation, respectively.
The selected samples were centrifuged for 15 min at 4000 rpm to separate the photocatalyst powder from the solution. The optical density of the solution (i.e. concentration of methylene blue) was measured at 664 nm relative to distilled water using the Shimadzu UV-1800 spectrophotometer. The measured absorption spectrum of aqueous solution of methylene blue, shown in Figure 1, led to the use of the above wavelength. The absorption spectrum of this dye had four characteristic peaks, including two peaks in the UV region at 246 nm and 292 nm, as well as two peaks in the visible region at 614 nm and 664 nm (the main maximum).
The formulas for calculating the residual relative concentration (∆ Ct , rel. units) and the photocatalytic decomposition degree (φ∆C ), %) of methylene blue were:
Ct
^l — c’ (2)
Lo
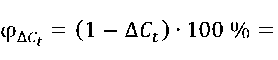
= (1 - ^) ■ 100 % = (C° Ct\ ■ 100 %, (3)
there Ct is the optical density of MB solution after exposure to UV radiation or solar radiation during time ( t ), rel. units (it characterizes the current dye concentration at time ( t ), mmol/L);
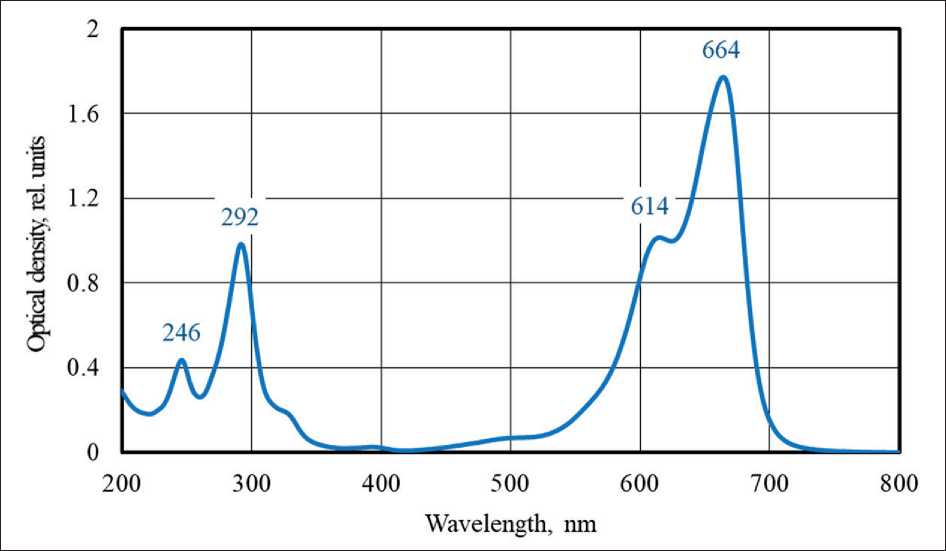
Fig. 1. Absorption spectrum of aqueous solution of methylene blue
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES
C 0 is the initial optical density of MB solution, rel. units (it characterizes the initial dye concentration before exposure to UV light or sunlight ( t 0 = 0 minutes or t 0 = 0 hours), mmol/L).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Effects of synthesis conditions on structure parameters of TiO2 precursors
Figure 2 shows the diffraction patterns of P-TiO2-1 and P-TiO2-2 samples of titanium dioxide precursors obtained under different synthesis conditions (see Table 1).
The study results showed that hydrated forms of titanium dioxide (TiО2·nH2О), which have an X-ray amorphous structure, represented the phase composition of the P-TiO2-1 precursor synthesized at room temperature. The characteristic features of the diffraction pattern of this precursor, in particular, the complete absence of diffraction peaks and the presence of halos at 2θ = 20–40° and 2θ = 40–55° (Fig. 2), testified to this.
Compared with P-TiO2-1, increasing the synthesis temperature of the P-TiO2-2 sample from 20 °C to 80 °C led to the formation of crystalline phases of titanium(IV) oxide in the form of two polymorphic modifications, such as anatase and brookite. The diffraction peaks at 2θ of 25.3°, 37.9°, 47.9°, 54.5°, 62.9°, and 69.5° characterized the anatase phase with a tetragonal crystal lattice. The diffraction peaks located at 2θ of 25.3°, 30.8°, 36.2°, 42.4°, 47.9°, and 54.5° (Fig. 2) corresponded to the brookite phase related to orthorhombic syngony. The low intensity
and noticeable broadening of these peaks indicated the insignificant presence of X-ray amorphous component represented by titanium hydroxoforms in the P-TiO2-2 sample. By the nature of diffraction pattern profile, the X-ray amorphous phase content in this precursor was no more than 3–5%.
It is important to note that the most intense peaks at 2θ of 25.3°, 47.9°, and 54.5° in the diffraction pattern of the P-TiO2-2 sample were a superposition of peaks from anatase and brookite. For this reason, the parameters of superposition-free diffraction peaks of these crystalline phases, in particular, those located at 2θ = 37.9° for anatase and at 2θ = 30.8° for brookite, acted as data for the quantitative phase analysis and evaluation of the crystallite (CSR) sizes using the Scherrer method.
According to the results of quantitative X-ray phase analysis, the crystallinity degree of the P-TiO2-2 sample structure was 97 % with the content of anatase and brookite in the phase composition equal to 81 wt. % and 16 wt. %, respectively, i.e. the ratio of anatase : brookite = 83.5 % : 16.5 % ≈ 5 : 1. The average size of coherent scattering regions (CSR) of anatase and brookite, calculated using formula (1), was 5.4 and 6.4 nm, respectively (Table 3).
Thus, in the experimental study, the nanocrystalline sample of titanium dioxide (P-TiO2-2), having the anatase/brookite structure, was obtained at low synthesis temperature ( T = 80 °C) and atmospheric pressure as a result of course of colloidal chemical processes in solutions. This low-temperature sol-gel method consisted of hydrolysis of titanium alkoxide in acidified water-alcoholic
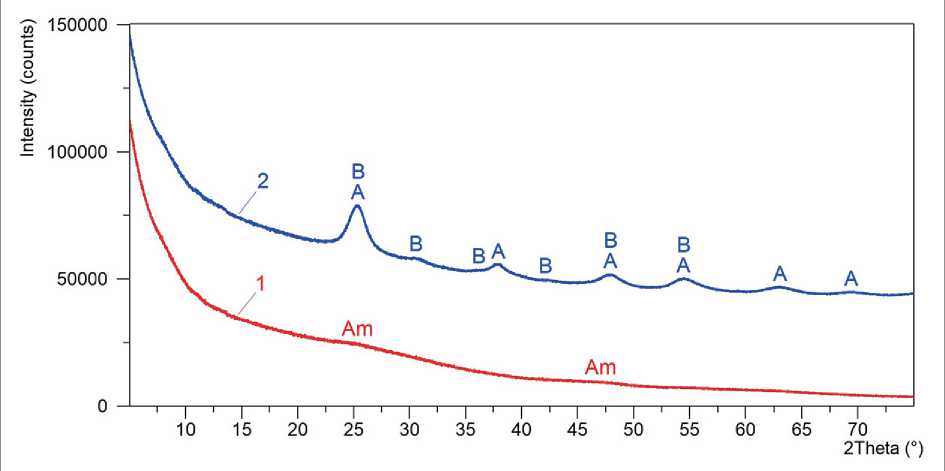
Fig. 2. Diffraction patterns of P-TiO2-1 (1) and P-TiO2-2 (2) samples of titanium dioxide precursors (see Table 1) with designated peaks of X-ray amorphous TiO2 (Am), anatase (A), and brookite (B)
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES
Table 3. Results of quantitative X-ray diffraction analysis of TiO2 precursor samples (Table 1, Fig. 2)
Phase composition of TiO2 samples
Figure 3 shows the diffraction patterns of TiO2-1 and TiO2-2 titanium dioxide samples synthesized by calcination of the P-TiO2-1 and P-TiO2-2 precursors (see Table 1 and Fig. 2), as well as the diffraction patterns of TiO2-3 and TiO2-4 control industrial samples (see Table 2).
It was found that the phase composition of the studied samples included from one to three polymorphic modifications of TiO2, namely anatase, brookite, and rutile. The diffraction peaks located at 2θ of 25.3°, 37.8°, 48.1°, 53.9°, 55.1°, 62.7°, 68.8°, 70.3°, and 2θ of 27.4°, 36.1°, 39.2°, 41.2°, 44.0°, 54.3°, 56.6°, 62.7°, 64.0°, 69.0°, 69.8° (Table 4) in the diffraction patterns (Fig. 3) respectively characterized the anatase and rutile phases with tetragonal crystal lattices. The diffraction peaks situated at 2θ of 25.3°, 30.8°, 36.1°, 48.1°, 53.9°, and 55.1° cor- responded to the brookite phase related to orthorhombic syngony.
It was determined that the TiO2-1 and TiO2-3 samples contained only one crystalline phase in the form of anatase and rutile, respectively. The structure of the TiO2-4 sample was two-phase and consisted predominantly of rutile (97 wt. %) with inclusion of anatase (3 wt. %). The TiO2-2 sample included three phases as a mixture of anatase, brookite, and rutile with the weight component ratio of 67 % : 13 % : 20 % ≈ 5.2 : 1 : 1.5 (Table 4).
The effects of the synthesis temperature of TiO2 precursors on the phase composition of their calcination products were analyzed. It is known that thermal treatment leads to the ordering of the precursor structure due to the occurrence of olation-oxolation processes that promote the substance transition from X-ray amorphous to crystalline state. It was found that calcination of the P-TiO2-1 precursor at 500 °C resulted to the formation of the anatase phase from X-ray amorphous TiO2 (see Figs. 2 and 3). At the same time, such thermal treatment of the P-TiO2-2 precursor contributed to the occurrence of three parallel crystallization processes, which gave rise to the phase transitions from X-ray amorphous TiO2 to anatase, from anatase to rutile, and from brookite to rutile.
Thus, the obtained experimental data showed that the increase in the precursor synthesis temperature from
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES
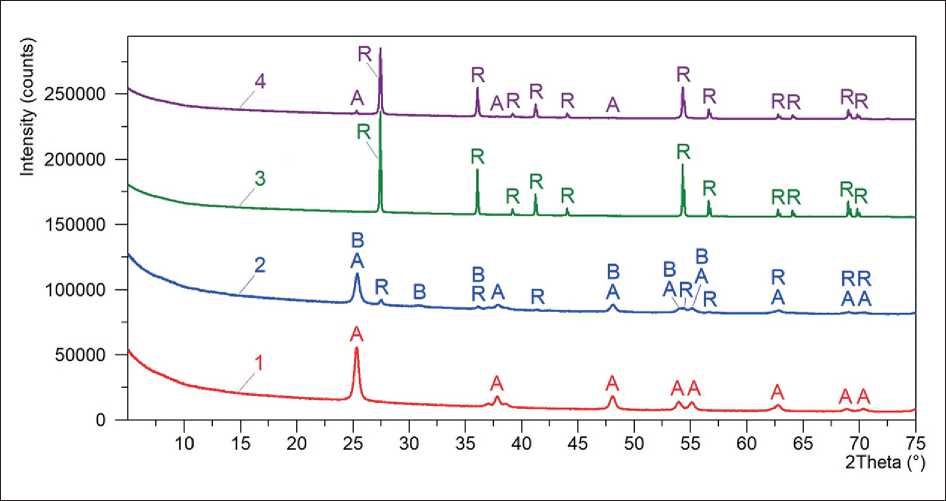
Fig. 3. Diffraction patterns of TiO2-1 (1), TiO2-2 (2), TiO2-3 (3), and TiO2-4 (4) samples of titanium dioxide (see Table 2) with designated peaks of anatase (A), brookite (B) , and rutile (R)
20 °C (for P-TiO2-1) to 80 °C (for P-TiO2-2) led to a decrease in the initial crystallization temperature of rutile. At the same time, the differences in the phase composition of the TiO2-2 and P-TiO2-2 samples indicated that the crystallization of rutile occurred primarily due to anatase and to a lesser extent due to brookite.
The structure crystallinity of TiO2 samples was evaluated during the study. The synthesized TiO2-1 and TiO2-2 samples had a nanocrystalline structure, as evidenced by the reduced intensity and noticeable broadening of the diffraction peaks of the crystalline phases in the diffraction patterns. The average CSR size of the anatase, brookite, and rutile phases, calculated using the Scherrer formula (1), for the TiO2-1 and TiO2-2 samples was 13.0–17.3 nm, 13.4 nm, and 31.3 nm, respectively. Thus, the P-TiO2-2 precursor calcination at 500 °C resulted in the increase of the anatase crystallite size, estimated by the peak at 2θ = 37.8–37.9°, from 5.4 nm to 13.0 nm, i.e. by 2.4 times (see Tables 3 and 4).
The industrial TiO2-3 and TiO2-4 samples had larger crystallite sizes. The average CSR sizes of the anatase and rutile phases for these control samples were 38.0–50.6 nm and 53.8–86.1 nm, respectively, which was 2.2–3.9 times and 1.7–2.8 times higher than the similar parameters of the synthesized TiO2-1 and TiO2-2 samples (Table 4).
Photocatalytic activity of TiO2 samples
It is known [55] that the rate of a dye solution discoloration during photocatalysis is determined by the combined action of several basic processes, such as:
-
1. Dye photodegradation in the liquid phase.
-
2. Dye adsorption on the photocatalyst surface.
-
3. Photocatalytic decomposition of dye molecules adsorbed on the surface of photocatalyst particles.
Processes 2 and 3 are sequential, while the dye photodegradation in the liquid phase proceeds independently and simultaneously with processes 2 and 3.
Figure 4 shows the kinetic curves of methylene blue (MB) photodegradation in solution under exposure conditions of ultraviolet radiation (a) and solar radiation (b) in the absence and presence of titanium oxidebased photocatalysts such as TiO2-1, TiO2-2, TiO2-3, and TiO2-4. The kinetic curves show the change in relative dye concentration in solution (∆ Ct ), calculated using the formula (2), during ultraviolet irradiation for 120 minutes (Fig. 4(a)), as well as under exposure conditions to sunlight (natural daylight) for 75 hours (Fig. 4(b)).
The study results showed that the concentration of methylene blue in the solution decreased exponentially under ultraviolet radiation. The rate of the photochemical reaction of dye decomposition was highest in the first 15– 30 minutes of UV light irradiation (Fig. 4(a)). The degree of MB degradation in the solution (φ∆ C ), see formula (3)) in the absence of photocatalyst was φ∆ C 120 = 11.0 % after 120 minutes of UV exposure. When using control TiO2-3 and TiO2-4 samples, the dye photodecomposed to the specified degree (11%) in less than 30 minutes of UV exposure, while the φ∆ C 120 parameter increased by 3.8 times and 5.2 times to the level of 42.2 % and 57.1 %, respectively.
The presence of photocatalysts based on synthesized TiO2-1 and TiO2-2 samples in the solution resulted in
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES a significant increase in the efficiency of dye photodegradation under UV radiation. In particular, when using these photocatalysts, the time to achieve the destruction level of methylene blue φ∆C = 11 %, corresponding to 120-minute photolysis of the dye, was 3–5 minutes. At the same time, the decomposition degree of methylene blue after t = 120 minutes of UV irradiation was 99.7 % and 97.3 % in solutions with TiO2-1 and TiO2-2, respectively (Fig. 4(a)). It was 8.8–9.1 times and 1.7–2.4 times higher than the φ∆C 120 values recorded (1) during the MB photolysis in solution without photocatalysts and (2) during the dye photocatalytic decomposition in the presence of TiO2-3 and TiO2-4 control samples.
The efficiency of titanium oxide-based photocatalysts decreased significantly under conditions of sunlight exposure. It was revealed that the degradation rate of methylene blue was highest in the first 15 hours of natural light (first day of exposure) (Fig. 4 (b)). The decomposition degree of the dye in the solution without photocatalysts after t = 75 hours of exposure to daylight was φ∆ C = 88.2 %. The presence of TiO2-3 and TiO2-4 powders in the solution only slightly increased the φ∆ C75 value, to the level of 91.0 % and 92.2 %, respectively. The photodestruction degree of methylene blue after t = 75 hours of exposure to solar radiation was 99.5 % and 99.7 % when using the synthesized TiO2-1 and TiO2-2 photocatalysts, respectively (Fig. 4(b)). In addition, the time to achieve the level of MB degradation φ∆ C = 88 %, characteristic of 75-hour photolysis of the dye, for solutions with TiO2-1 and TiO2-2
was reduced to 50–55 hours, which was 15–22 hours less than for the TiO2-3 and TiO2-4 control samples.
It is known that the Langmuir–Hinshelwood model often describes the kinetics of photolysis and photocata-lytic degradation of dye molecules in an aqueous medium, while the linearized integral forms of pseudo-first (4) or pseudo-second (5) order reaction equations usually approximate experimental data [56, 57]:
-1пД = к^, (4)
Lo
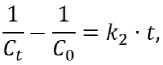
there C 0 and Ct are the initial and current concentrations of the dye in aqueous solution (the same as in formulas (2) and (3)), mmol/L;
t is the time of photochemical reaction, such as photolysis or photocatalytic decomposition of the dye, corresponding to the duration of exposure to UV radiation or solar radiation, min or h;
k 1 is the rate constant of photochemical reaction, such as photolysis or photocatalytic decomposition of the dye, in the linearized pseudo-first order kinetic equation (4), min–1 or h–1;
k 2 is the rate constant of photochemical reaction, such as photolysis or photocatalytic decomposition of the dye, in the linearized pseudo-second order kinetic equation (5), L/(mmol•min) or L/(mmol•h).
Table 4. Results of quantitative X-ray diffraction analysis of TiO2 samples (Table 2, Fig. 3)
|
Description of phases |
Position of the main peaks d , Å (2θ, °) |
Samples |
||||
|
Type |
Name |
TiO2-1 |
TiO2-2 |
TiO2-3 |
TiO2-4 |
|
|
Phase composition, wt. % |
||||||
|
<л ф <л 03 -С о. ф _С 0 |
anatase |
3.52 Å, 2.38 Å, 1.89 Å, 1.70 Å, 1.67 Å, 1.48 Å, 1.36 Å, 1.34 Å (25.3°, 37.8°, 48.1°, 53.9°, 55.1°, 62.7°, 68.8°, 70.3°) |
100 |
67 |
– |
3 |
|
brookite |
3.52 Å, 2.90 Å, 2.49 Å, 1.89 Å, 1.70 Å, 1.67 Å (25.3°, 30.8°, 36.1°, 48.1°, 53.9°, 55.1°) |
– |
13 |
– |
– |
|
|
rutile |
3.25 Å, 2.49 Å, 2.30 Å, 2.19 Å, 2.06 Å, 1.69 Å, 1.63 Å, 1.48 Å, 1.45 Å, 1.36 Å, 1.35 Å (27.4°, 36.1°, 39.2°, 41.2°, 44.0°, 54.3°, 56.6°, 62.7°, 64.0°, 69.0°, 69.8°) |
– |
20 |
100 |
97 |
|
|
Average CSR size of the crystalline phases, nm |
||||||
|
anatase |
peak at 2θ = 25.3° |
17.3 |
13.0 |
– |
50.6 |
|
|
peak at 2θ = 37.8° |
17.2 |
13.0 |
– |
38.0 |
||
|
brookite |
peak at 2θ = 30.8° |
– |
13.4 |
– |
– |
|
|
rutile |
peak at 2θ = 27.4° |
– |
31.3 |
86.1 |
53.8 |
|
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES
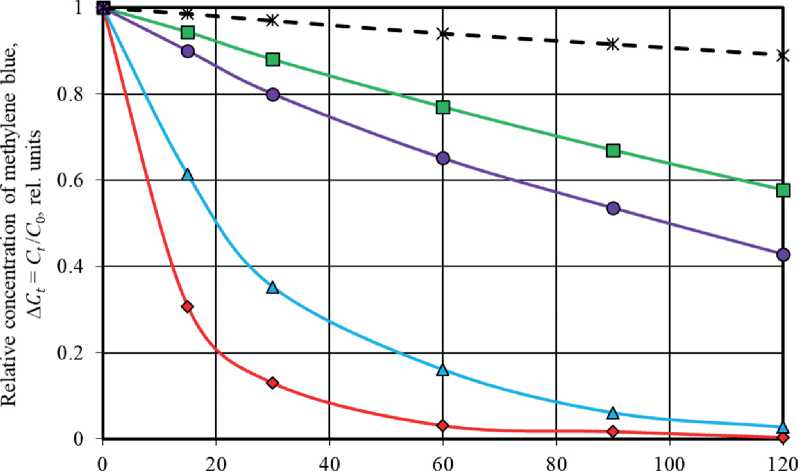
Exposure time to UV radiation, min Samples under study:
-
♦ T102-I △ T1O2-2 —■—TiO2-3 ♦ -TiO2-4 —Ж—Dye photolysis
b
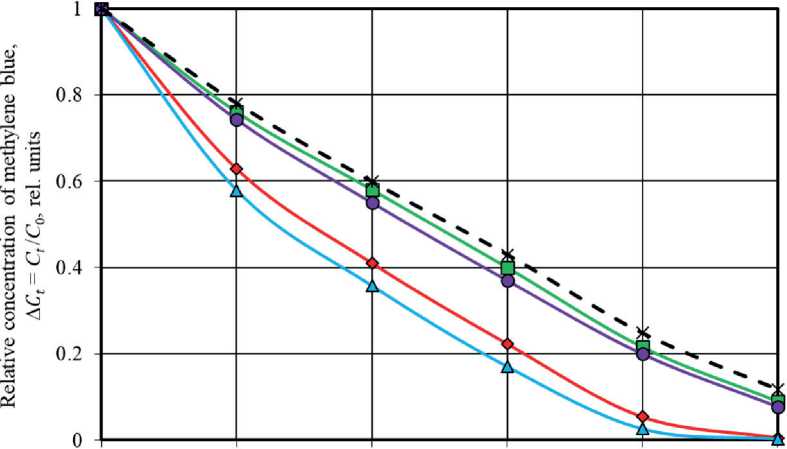
0 15 30 45 60 75
Exposure time to solar radiation, h Samples under study:
-
—♦—ТЮ2-1 —Д—TiO2-2 □ T1O2-3 —О—T1O2-4 —X—Dye photolysis
Fig. 4. Kinetic curves of methylene blue photodegradation in solution under UV radiation (a) and solar radiation (b) in the absence of photocatalysts (black dotted curve characterizes to MB photolysis) and in the presence of TiO2 samples (colored solid curves characterize to MB photocatalytic decomposition processes)
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES
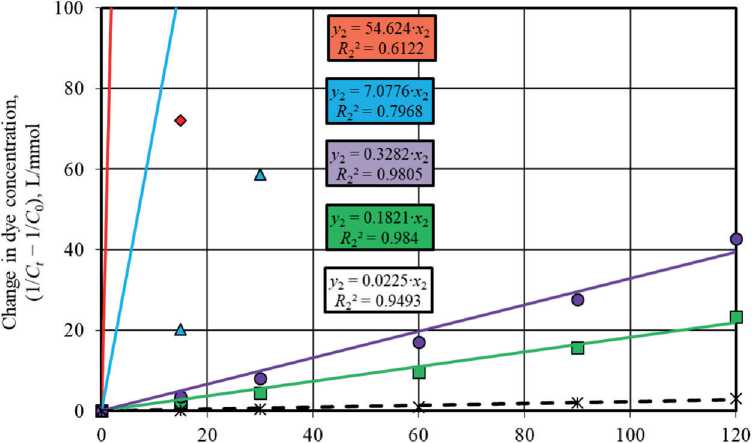
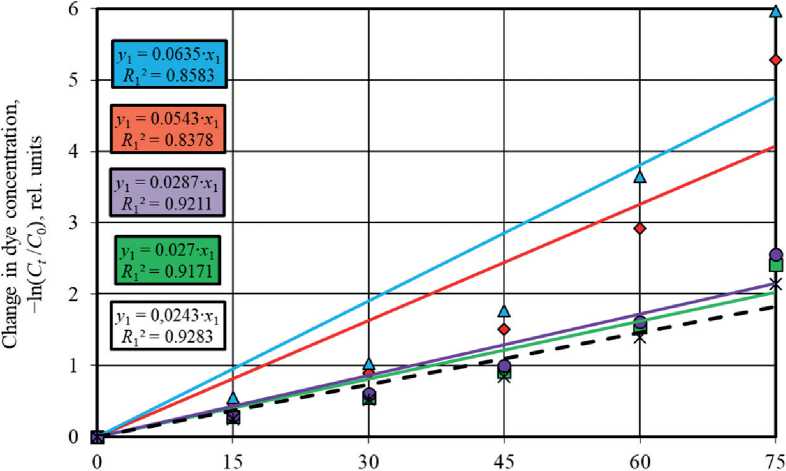
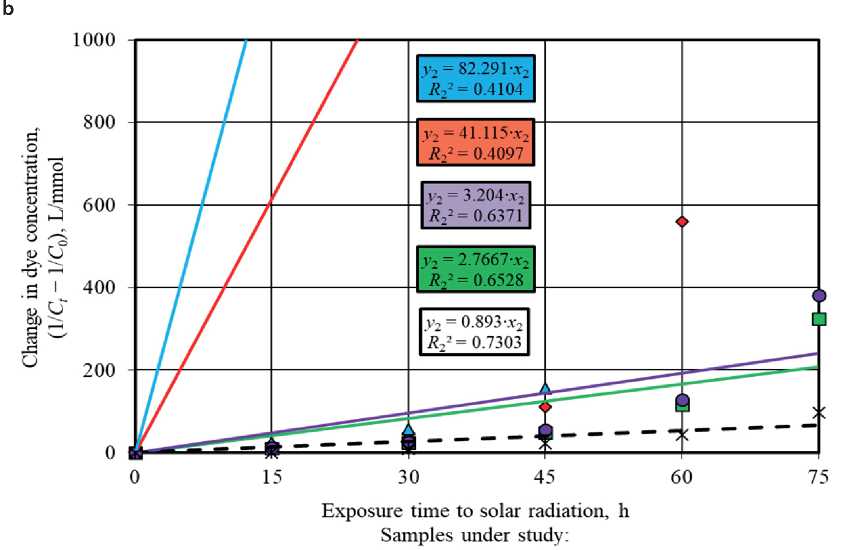
Figures 5 and 6 show graphs describing the kinetics of photolysis and photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue in solution under UV light irradiation and sunlight irradiation using pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order
reaction equations. The angle of inclination of the linear dependences allowed to identify the rate constant values of the corresponding photochemical reactions occurring in the absence and in the presence of photocatalysts.
а
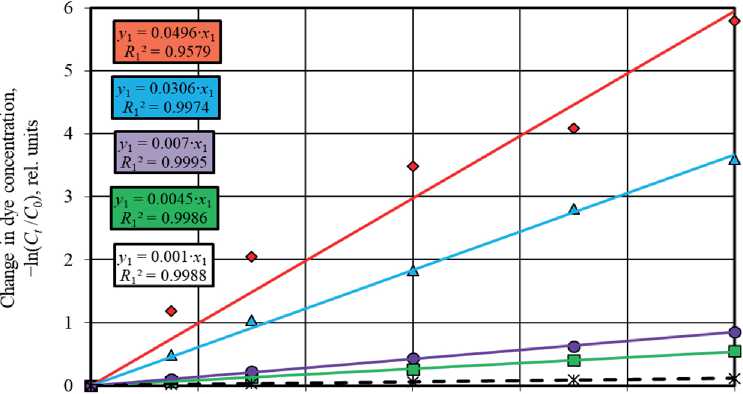
О 20 40 60 80 100 120
Exposure time to UV radiation, min Samples under study
b
0ТЮ2-1 ДТ1О2-2 □ ТЮ2-3 ®TiO2-4 Ж Dye photolysis
Exposure time to UV radiation, min Samples under study:
ОТЮ2-1 ATiO2-2 □ТЮ2-3 ®TiO2-4 ж Dye photolysis
-
Fig. 5. Description ofthe methylene blue photodecomposition kinetics in solution under UV radiation in the absence (black dotted lines) and in the presence of photocatalysts based on TiO2 (colored solid lines) in the coordinates of pseudo-first order (a) and pseudo-second order (b) kinetic models
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES

а
Exposure time to solar radiation, h Samples under study:
oTiO2-l ДТЮ2-2 DTiO2-3 OTiO2-4 Ж Dye photolysis
OT1O2-1 ДТЮ2-2 □TiO2-3 OTiO2-4 Ж Dye photolysis
-
Fig. 6. Description of the methylene blue photodecomposition kinetics in solution under solar radiation in the absence (black dotted lines) and in the presence of photocatalysts based on TiO2 (colored solid lines) in the coordinates of pseudo-first order (a) and pseudo-second order (b) kinetic models
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES
It was established that the pseudo-first order equations most adequately approximate the experimental data obtained during the study of photochemical reactions under UV radiation and solar radiation. Higher values of the determination coefficients in models (4) compared to pseudo-second order models (5), namely R 1 = 0.9579– 0.9995 > R 2 = 0.6122–0.984 (UV light, Fig. 5) and R 1 = 0.8378–0.9283 > R 2 = 0.4097–0.7303 (sunlight, Fig. 6), testify to this.
It is known [57, 58] that heterogeneous reactions have two possible modes of course depending on the limiting stage, in particular, kinetic mode and diffusion mode characterized by the limiting contribution of chemical reaction or diffusion, respectively. A more accurate description of the experimental data by the pseudo-second order kinetic model indicates the limiting contribution of the chemical reaction to the heterogeneous process. The conformity of the process kinetics to the pseudo-first order model suggests that the diffusion stage limits the heterogeneous reaction. Thus, the obtained experimental data showed that the photodegradation of methylene blue in solution under UV radiation and solar radiation with the participation of TiO2-1, TiO2-2, TiO2-3, and TiO2-4 samples proceeded in the diffusion mode due to the correspondence to the pseudo-first order model (4). Dye adsorption on the surface of titanium oxide-based photocatalysts limited these photocatalytic processes.
The study results showed that the presence of titanium dioxide powders in the solution significantly intensified the process of methylene blue decomposition under UV light irradiation. The values of the rate constants of pseudo-first order reactions for photocatalytic processes were k 1 = 0.0045–0.0496 min–1, which was 4.5–49.6 times higher than in the dye photolysis without titanium oxidebased photocatalysts ( k 1 = 0.001 min–1) (Fig. 5(a)).
The photoactivity of the studied TiO2 samples markedly decreased under the conditions of solar radiation exposure (Fig. 6(a)), which was evidenced by the convergence of the values of the rate constants of photocatalytic reactions ( k 1 = 0.027–0.0635 h–1) and dye photolysis ( k 1 = 0.0243 h–1).
According to Fig. 4, 5, and 6, the synthesized TiO2-1 and TiO2-2 samples had higher photocatalytic activity compared to the TiO2-3 and TiO2-4 control industrial samples, regardless of the exposure conditions, namely UV radiation or solar radiation.
The phase composition noticeably influenced the efficiency of titanium oxide-based photocatalysts. It was revealed that polymorphic modifications of TiO2 had multidirectional effects on the functional characteristics of the material, in particular, an increase in the content of anatase and rutile led to an increase and decrease in the photoactivity of TiO2 samples, respectively (Fig. 7). The single-phase TiO2-1 sample of anatase modification was the most effective under UV irradiation, while the three-
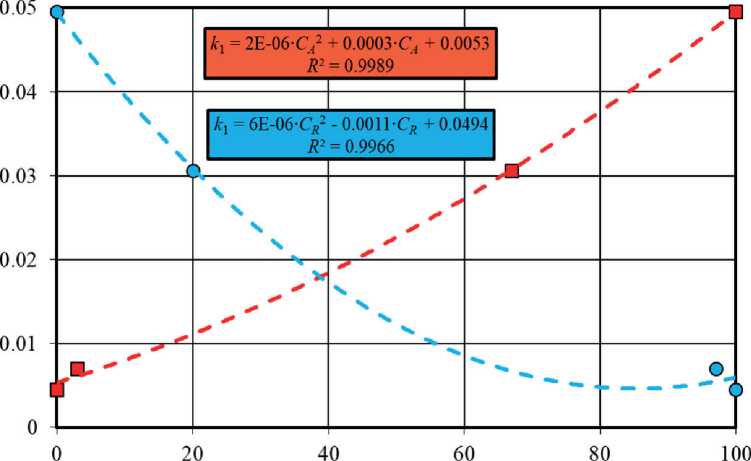
Phase content (C,) in sample, wt. % Phases under study:
■ Anatase О Rutile
-
Fig. 7. Effects of anatase and rutile content in phase composition on photocatalytic activity of titanium dioxide in methylene blue solution under ultraviolet radiation (a) and solar radiation (b)
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES
b
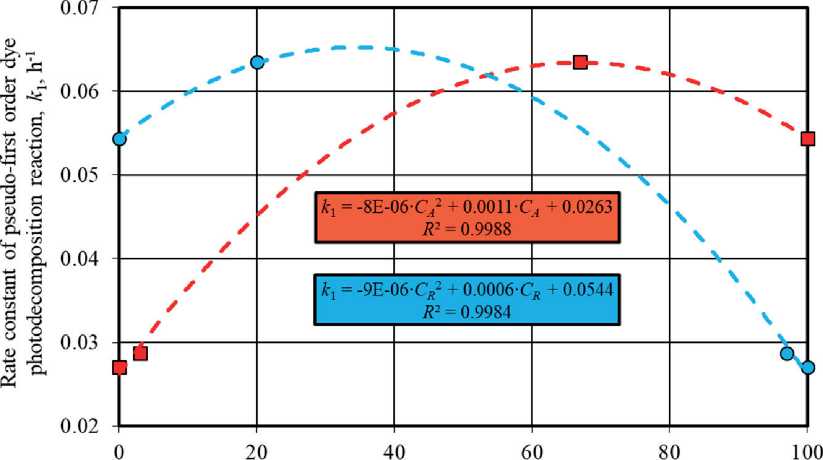
Phase content (C;) in sample, wt. % Phases under study:
□ Anatase О Rutile
Fig. 7. The End phase TiO2-2 sample with the ratio of anatase : brookite : rutile = 67% : 13% : 20% ≈ 5,2 : 1 : 1,5 (Table 4) had the highest activity under daylight exposure. At the same time, according to Fig. 7, the photoactivity of heterophase samples under solar was higher in comparison with the TiO2-1 sample when the content of anatase in the mixture of crystalline phases was at least 40–50%, i.e. when this phase prevailed in the material composition.
The obtained experimental data were consistent with the results of studies by other authors. In particular, the papers [35, 39, 40] showed that the combination of two or three polymorphic modifications of TiO2 in the structure, in particular, anatase/rutile, anatase/brookite, anatase/ brookite/rutile with anatase predominating, made it possible to increase the photocatalytic activity of the material compared to single-phase titanium oxide photocatalysts by reducing the recombination rate of photoinduced charge carriers.
CONCLUSION
The following scientific results were obtained in the paper:
-
1. The effects of synthesis conditions on the structure parameters of TiO2 precursors obtained by hydrolysis of titanium alkoxide in acidified water-alcoholic medium were established.
-
2. The phase composition features were determined for four titanium(IV) oxide samples, namely two industrial samples and two samples synthesized by calcination of TiO2 precursors at 500 °C.
-
3. The kinetics of photodecomposition process of methylene blue in solution was disclosed under conditions of exposure to ultraviolet radiation and solar radiation in the absence and presence of titanium oxide-based photocatalysts. The most effective TiO2 samples under the specified exposure conditions were determined.
-
4. The effects of phase composition on the photocata-lytic activity of titanium dioxide samples were revealed under conditions of exposure to artificial ultraviolet light and natural daylight.
-
5. The interrelations and regularities were established between the synthesis conditions, phase composition and photoactivity of TiO2, which made it possible to optimize the prescription and technological parameters for obtaining effective titanium oxide-based photocatalysts for self-cleaning concrete.
The results of the experimental study showed the possibility of obtaining the nanocrystalline sample of titanium(IV) oxide with anatase/brookite structure at low synthesis temperature ( T = 80 °C) and atmospheric pressure as a result of course of colloidal-chemical processes in solutions. It was revealed that a decrease in the synthesis temperature, including the gel aging tempera-
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES ture, from 80 to 20 °C led to the transition of TiO2 from the nanocrystalline to X-ray amorphous state.
The phase composition noticeably influenced the efficiency of titanium oxide-based photocatalysts. It was found that polymorphic modifications of TiO2 had multidirectional effects on its functional characteristics, in particular, an increase in the content of anatase and rutile led to an increase and decrease in the photoactivity of titanium dioxide samples, respectively. The single-phase sample with anatase structure was the most effective under UV irradiation, while the three-phase sample with the ratio of anatase : brookite : rutile = 67% : 13% : 20% ≈ 5,2 : 1 : 1,5 had the highest activity under daylight exposure.
The photocatalyst composition, including several polymorphs of TiO2 with a predominance of anatase form (more than 50%), allowed to achieve a synergistic effect of increasing the photocatalytic activity of titanium dioxide under conditions of solar radiation due to the formation of type-II semiconductor heterojunctions in multiphase composite. Heterostructures made it possible to improve the spatial separation of charge carriers and to reduce the recombination rate of photogenerated electron-hole pairs. Thus, the obtained results indicated the possibility of improving the functional characteristics of titanium oxide-based additives for self-cleaning concrete due to the targeted regulation of their phase composition by optimizing the synthesis parameters of photocatalytic modifiers.


