Нечеткие классификаторы в диагностике сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний. Обзор
Автор: Ходашинский И.А.
Журнал: Сибирский журнал клинической и экспериментальной медицины @cardiotomsk
Рубрика: Обзоры и лекции
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.35, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Сложность биологических объектов делает разработку компьютеризированных медицинских систем непростым алгоритмическим решением из-за естественной неопределенности, присущей указанным объектам. Человеческое мышление основано на неточных, приблизительных данных, анализ которых позволяет формировать четкие решения. На практике может не существовать точной математической модели биологических объектов, или такая модель может быть слишком сложной для реализации. В этом случае нечеткая логика является подходящим инструментом решения указанной проблемы. Проблема медицинской диагностики может рассматриваться как проблема классификации. В статье представлен литературный обзор применения нечетких классификаторов в области диагностики сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний. Основным достоинством нечетких классификаторов по сравнению с другими методами искусственного интеллекта является возможность интерпретации полученного результата классификации. Обзор направлен на расширение знаний различных исследователей, работающих в области медицинской диагностики.
Нечеткий классификатор, сердечно-сосудистые заболевания, медицинская диагностика
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/149126207
IDR: 149126207 | УДК: 616.1-07 | DOI: 10.29001/2073-8552-2020-35-4-22-31
Текст научной статьи Нечеткие классификаторы в диагностике сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний. Обзор
Для выявления заболеваний и мониторинга пациентов все чаще разрабатываются и внедряются компьютерные системы поддержки принятия клинических решений [1 – 4]. Такие системы способны предоставить клиницистам персонализированные оценки и/или рекомендации для оказания помощи в принятии медицинских решений. Однако если эти системы основаны на методах «черного ящика», то выданные рекомендации сложно интерпретировать в клиническом контексте, и, как следствие, врачи могут воспринимать их с недоверием [5].
Решить указанную проблему могут системы, основанные на правилах, и экспертные системы, в которых знания врача-специалиста представлены в виде множества явных, понятых, легко интерпретируемых, лингвистических «EСЛИ – ТО» правил. Указанные системы принятия решений ориентированы на человека. Используемые в процессе оценки принятия решений лингвистические термы, такие как «высокая» температура, «пожилой» возраст, «низкое» артериальное давление (АД), интуитивно понятны, с их помощью можно описать неопределенную и неточную информацию, они хорошо согласуются с мышлением и рассуждением врача. Перечисленные выше свойства привлекают большое внимание исследователей к разработке и использованию систем поддержки принятия решений на основе нечеткой логики [6–12].
Теория нечетких множеств обладает рядом свойств, которые делают ее пригодной для формализации неопределенной информации, на которой обычно основывается медицинская диагностика и лечение. Во-первых, эта теория определяет неточные медицинские объекты как нечеткие множества. Во-вторых, она обеспечивает снятие неопределенности, присутствующей в нечетких лингвистических выражениях пациентов при описании своих проблем. В-третьих, нечеткая логика предлагает методы рассуждения, способные делать приблизительные выводы. Эти факты свидетельствуют о том, что теория нечетких множеств может быть основой для разработки компьютерной системы диагностики [13–18].
Нечеткая логика – не единственное средство разработки эффективных систем медицинской диагностики. Наиболее часто используемые методы искусственного интеллекта, используемые для этих целей, помимо нечеткой логики, – это нейронные сети [19, 20], метод ближайших соседей [21, 22], приближенные множества [23, 24], машины опорных векторов [25, 26], генетические алгоритмы [27, 28]. Однако системы медицинской диагностики, построенные на основе перечисленных выше методов, для практикующего врача являются «черным ящиком», потому что в таких системах не предусмотрены подсистемы, объяснения сформированных рекомендаций, диагнозов и решений. Системы медицинской диагностики, основанные на клинически интерпретируемых правилах «EСЛИ – ТО», позволяют врачам получить доступ не только к клиническому решению, адаптированному к конкретному пациенту, но также к набору клинических правил, на основе которых это решение было получено [13].
Сердечно-сосудистые заболевания являются основной причиной смерти во многих странах мира. Многогранный характер заболеваний в сочетании с широким спектром методов лечения и сложными взаимосвязями с другими заболеваниями сделали диагностику сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний сложной проблемой даже для опытных кардиологов [29]. Одним из способов решения этой проблемы является создание интеллектуальных систем поддержки принятия решений. Классификация является проверенным инструментом поддержки принятия решений в медицинской диагностике [30]. Классификаторы, основанные на нечетких правилах, давно и успешно используются в системах поддержки принятия решений [31–34].
Цель данной работы: исследование применения нечетких классификаторов для диагностики и прогнозирования сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний.
Подходы к построению медицинских диагностических систем
Современная медицинская диагностика – это сложный процесс, требующий точных данных о пациенте, накопленных знаний и многолетнего клинического опыта. В условиях, когда информация от пациентов может содержать избыточные и взаимосвязанные симптомы, особенно если пациенты страдают от более чем одного типа заболевания, клинические решения часто принимаются на основе субъективного восприятия врача [34]. На помощь клиницистам могут прийти экспертные системы поддержки принятия клинических решений. Экспертные системы относятся к классу систем, основанных на правилах, базируются на знаниях эксперта, работают в узких предметных областях и способны объяснить свои действия и результаты. Центральным звеном экспертной системы является база знаний, которая разрабатывается как модель ограниченной части мира и позволяет, задав механизм вывода, рассуждать об этом мире. Знания представлены в явно сформулированном виде и организованы таким образом, чтобы облегчить процесс принятия решений. Процесс передачи знаний от эксперта в систему занимает много времени и зависит от субъективного мнения экспертов.
Другим подходом к построению систем медицинской диагностики является применение методов машинного обучения для автоматического приобретения знаний из примеров или ретроспективных данных. Проблема медицинской диагностики формулируется как задача классификации и может быть решена путем нахождения подходящего классификатора или математической функции f , которая сопоставляет множество симптомов X с меткой класса cj :
f : X → cj .
Классификатором может быть искусственная нейронная сеть, машина опорных векторов, дерево решений или любой другой метод классификации.
Относительно хорошая точность классификации и наличие готовых программных реализаций являются причинами того, что искусственные нейронные сети и машины опорных векторов являются часто используемыми методами разработки систем медицинской диагностики. Однако отсутствие возможности интерпретировать полученный результат, а также учесть неопределенность и неточность медицинских данных является существенным недостатком названных методов. Нечеткие системы, основанные на экспертных знаниях, легко поддаются интерпретации, но не всегда обладают достаточной точностью классификации. На смену чисто экспертному подходу пришли методы нечеткого моделирования, основанного на наблюдаемых данных. При таком подходе удается соблюсти компромисс между точностью классификации и интерпретируемостью полученного результата [35, 36].
Нечеткие классификаторы. Общее описание
Теоретической основой построения нечетких классификаторов является нечеткая логика, оперирующая не точными, а приблизительными (нечеткими) утверждениями, формальным описанием которых является теория нечетких множеств, предложенная Л. Заде [37, 38]. Нечеткую логику можно рассматривать как попытку построения модели человеческого мышления. Нечеткая логика является многозначной логикой и служит для представления неопределенных или расплывчатых понятий. В классической теории множеств элемент множества либо принадлежит, либо не принадлежит множеству. В теории нечетких множеств элемент может принадлежать тому или иному множеству с некоторой степенью уверенности. Указанная степень уверенности задается функцией принадлежности, которая меняется в пределах от 0 (элемент не принадлежит множеству) до 1 (элемент полностью принадлежит данному множеству).
Нечеткое подмножество F множества элементов U определяется функцией принадлежности μ F ( u ). Эта функция отображает элементы u множества U на множество чисел в интервале [0,1], которые указывают степень принадлежности каждого элемента нечеткому подмножеству F .
На рисунке 1 приведены трапециевидные функции принадлежности традиционного четкого множества C и нечеткого множества F , заданных на универсуме U .
Пусть A = {x1, x2, …, xn} – множество входных признаков, C = {c1, c2, …, cm} – множество классов. Пусть X = x 1 x x2 x ... x xn e^n - n-мерное пространство признаков (симптомов, факторов риска, биологических маркеров). Объект (пациент) характеризуются своим вектором значений признаков. Задача классификации заключается в предсказании класса объекта по его вектору значений признаков [39, 40].
Рис. 1. Пример четкого и нечеткого множества Fig. 1. Crips and Fuzzy Set Example
Традиционный классификатор может быть определен как функция
-
f: ^ n ^ {0,1} m, _
где f ( x ; 9)=( c 1 , c 2, ..., c m ), причем c i = 1, a c j = 0, j = 1, m , i ≠ j , когда объект, заданный вектором x , принадлежит к классу ci ; θ – вектор параметров классификатора.
Нечеткий классификатор может быть представлен в виде функции, которая присваивает точке в пространстве входных признаков метку класса с вычисляемой степенью уверенности:
f : «n ^ [0,1]m .
Основой нечеткого классификатора является продукционное правило следующего вида:
Rij : ЕСЛИ x1= A1i И x2= A2i И x3= A3i И … И xn= = Ani ТО class = cj, где Aki – лингвистический терм (высокий, молодой), характеризующий k-й признак в i-м правиле и определяемый своей функцией принадлежности, i = , R – число правил.
Класс определяется правилом, ЕСЛИ-часть которого максимально соответствует описанию, заданному входным вектором X :
n class = cj*, j* = arg max ПMA (xk), J 1< j < m k =1 ki
μ Aki (xk) – значение функции принадлежности нечеткого терма Aki в точке xk .
Построение нечетких классификаторов предполагает решение следующих основных задач: отбор информативных признаков, формирование базы нечетких правил, оптимизация параметров функций принадлежности. Отбор информативных признаков относится к проблеме поиска таких входных атрибутов (симптомов, факторов риска) в наборе данных, которые обладают наибольшей обобщающей или прогностической способностью при решении задачи классификации. На этом этапе исключаются неинформативные и избыточные признаки, что приводит к снижению сложности классификатора и улучшению возможностей обобщения и понимания врачами полученного результата. Задача отбора признаков решается с помощью статистических методов, теоретико-информационных и метаэвристических методов [41]. База нечетких правил формируется либо с использованием экспертного метода, либо метода, основанного на дан- ных. В первом методе значения параметров нечеткого правила, такие как интервалы изменения и функции принадлежности, задаются экспертом вручную. Во втором методе указанные значения определяются автоматически из набора репрезентативных примеров с использованием машинных методов обучения. В последнее время методы формирования правил на основе данных преобладали в разработке нечетких систем диагностики отчасти из-за стоимости и сложности экспертного задания правил, а также из-за доступности ретроспективных данных о пациентах и доступности эффективных алгоритмов машинного обучения. Для оптимизации параметров функций принадлежности используются различные методы [42].
Нечеткие классификаторы риска ишемической болезни сердца
Ишемическая болезнь сердца (ИБС) является наиболее распространенным типом сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний и одной из основных причин смерти во всем мире [21, 29, 32]. Несмотря на достигнутый в последние годы прогресс в диагностике ИБС, проблемой остается раннее выявление этого заболевания. Диагностика ИБС является сложной задачей, поскольку это заболевание связано со многими факторами риска, и врач должен тщательно изучить комбинацию симптомов и признаков, которые могут совпадать с причинами других заболеваний. Для решения этой проблемы было предложено много подходов и методов. Инвазивная коронарная ангиография – наиболее точный метод диагностики ИБС, однако его повсеместное использование ограничено из-за высокой стоимости и высокого уровня технических знаний и технологий, необходимых для выполнения этой процедуры [8, 32]. В этой связи стали больше уделять внимания использованию и разработке относительно недорогих и надежных неинвазивных методов, чтобы как можно больше пациентов с подозрением на ИБС могли позволить себе пройти тестирование и могли быть идентифицированы на ранней стадии в случае наличия ИБС. Неинвазивные методы включают электрокардиографию, фотоплетизмографию, фонокардиографию. Данные, полученные с применением вышеупомянутых методов и других источников, таких как клинические данные, используются для создания компьютерных систем поддержки принятия решений. Одним из методов оценки риска ИБС является исследование факторов риска. Гипертония, высокий уровень холестерина липопротеинов низкой плотности (ЛПНП-Х), низкий уровень холестерина липопротеинов высокой плотности (ЛПВП-Х), высокий общий холестерин (ОХС), высокие триглицериды (ТГ), сахарный диабет, курение, ожирение, пол, отсутствие физической активности, возраст, социально-экономический и психологический стресс, наследственность и различные генетические факторы являются некоторыми из факторов риска ИБС [43].
P. Kora и соавт. описали нечеткий классификатор определения риска ИБС, который включает 44 правила [31]. Входными признаками являются холестерин, АД, физическая активность, возраст, индекс массы тела (ИМТ), курение и диабет (таблица). Классификатор определяет три класса риска заболевания: здоров (healthy), начальная стадия (early-stage) и прогрессирующая стадия (advanced-stage). Примеры функций принадлежности фактора риска «холестерин» и термов, определяющих риск, приведены на рисунке 2.
Таблица. Факторы риска сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний в Южной Азии [31]
Table. Cardiovascular disease risk factors in South Asian [31]
Факторы риска Параметры Значения
Risk factors Parameters Values
|
Холестерин, мг/дл Cholesterol, mg/dL |
Нормальный Normal Средний Moderate Высокий High Очень высокий Very High |
<200 190–250 230–320 280–500 |
|
Артериальное давление, мм рт. ст. Blood Pressure, mmHg |
Нормальное Normal Промежуточное Moderate Высокое High |
<135 120–159 150–200 |
|
Физическая активность Physical activity |
Нет No Да Yes |
<0,6 0,3–1,0 |
|
Возраст, лет Age, years |
Молодой Young Средний Middle age Старый Old Очень старый Very old |
<38 34–45 40–58 53–75 |
|
ИМТ, кг/м2 BMI, kg/m2 |
Нормальный Normal Избыточный вес Overweight Ожирение Obesity |
<25 24–32 30–50 |
|
Курение Smoking |
Нет No Да Yes |
<0,6 0,3–1,0 |
|
Диабет, мг/дл Diabetes, mg/dl |
Нормальный Normal Диабетик Diabetic |
<160 150–400 |
Ниже приведено несколько примеров правил, используемых в работе [31].
ЕСЛИ (возраст – старый) И (АД – нормальное) И (холестерин – средний) И (диабет – нормальный) И (ИМТ – нормальный) И (физическая активность – да) И (курение – нет) ТО (здоров).
ЕСЛИ (возраст – молодой) И (АД – высокое) И (холестерин – высокий) И (диабет – нормальный) И (ИМТ – ожирение) И (физическая активность – нет) И (курение – да) ТО (ранняя стадия).
ЕСЛИ (возраст – средний) И (АД – высокое) И (холестерин – высокий) И (диабет – нормальный) И (ИМТ – ожирение) И (физическая активность – нет) И (курение – да) ТО (ранняя стадия).
ЕСЛИ (возраст – старый) И (АД – высокое) И (холестерин – очень высокий) И (диабет – нормальный) И (ИМТ – ожирение) И (физическая активность – нет), И (курение – да) ТО (прогрессирующая стадия).
Нечеткий классификатор показал точность предсказания ИБС на уровне 99,3%.
D. Pal и соавт. разработали нечеткую экспертную систему стратификации риска ИБС с использованием клинической и первичной информации от пациентов [44].
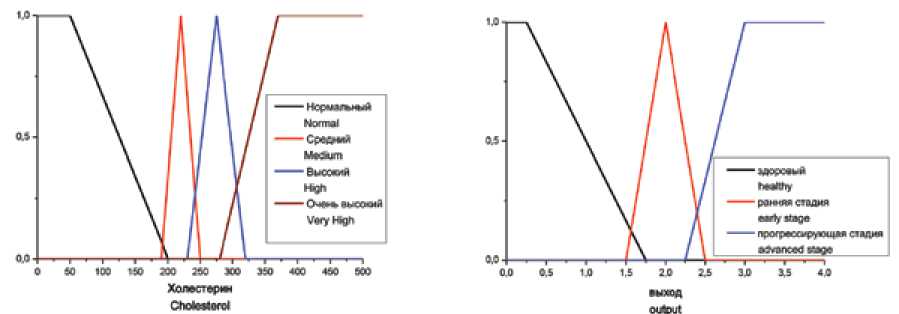
Рис. 2. Входная лингвистическая переменная «холестерин» и выходная переменная Fig. 2. Input linguistic variable "cholesterol" and output variable
Нечеткие правила и факторы риска сформированы методом многоэтапного структурированного интервью с врачами-кардиологами. Выявлены следующие факторы риска: возраст, курение, ожирение (ИМТ), гипертония (систолическое артериальное давление – САД, диастолическое артериальное давление – ДАД), диабет (уровень сахара в крови натощак – УСК), липидный профиль (ОХС, ЛПНП, ЛПВП, ТГ), боль в груди. Факторы риска являются входными переменными для нечеткой системы. Каждая переменная принимает три нечетких значения, которые описываются трапециевидными функциями принадлежности. Выходной переменной является нечеткая переменная «риск», которая принимает нечеткие значения: низкий, средний и высокий. Эти нечеткие значения определяются также трапециевидной функцией принадлежности, соответствующей четкому значению процента риска. Диапазоны каждой переменной риска определяются как низкий риск [0–30%], средний риск [30–55%] и высокий риск [55–100%].
Диагностические нечеткие правила [44]:
R1: ЕСЛИ (возраст – молодой) И (курение – низкий) ТО (риск – низкий).
R2: ЕСЛИ (возраст – средний) И (курение – высокий) И (ИМТ – средний) ТО (риск – средний).
R3: ЕСЛИ (возраст – старый) И (курение – высокий) И (ИМТ – высокий) И (САД – высокий) И (ДАД – высокий) И (УСК – средний) И (ОХС – низкий) И (ЛПНП – низкий) И (ЛПВП – высокий) ТО (риск – низкий).
R4: ЕСЛИ (возраст – старый) И (курение – высокий) (ИМТ – высокий) И (САД – высокий) И (ДАД – высокий) И (УСК – средний) И (ОХС – средний) И (ЛПНП – средний) И (ЛПВП – высокий) ТО (риск – высокий).
R5: ЕСЛИ (возраст – старый) И (курение – высокий) И (ИМТ – высокий) И (САД – высокий) И (ДАД – высокий) И (УСК – высокий) И (ОХС – высокий) И (ЛПНП – средний) И (ТГ – высокий) И (ЛПВП – низкий) ТО (риск – высокий)
R6: ЕСЛИ (возраст – средний) И (курение – низкий) И (ИМТ – высокий) И (САД – высокий) И (ДАД – высокий) И (УСК – высокий) И (ОХС – высокий) И (ЛПНП – средний) И (ТГ – высокий) И (ЛПВП – средний) И (боль в груди – средний) ТО (риск – высокий).
R7: ЕСЛИ (возраст – низкий) И (ИМТ – средний) И (САД – средний), (ДАД – средний) И (УСК – средний) И (ОХС – средний), (ЛПНП – средний) И (ЛПНП – средний) И (ЛПВП – высокий) И (боль в груди – низкий) ТО (риск – средний).
R8: ЕСЛИ (возраст – старый) И (ИМТ – высокий) И (САД – высокий) И (ДАД – высокий) И (УСК – высокий) И (ОХС – высокий) И (ЛПНП – высокий) И (ТГ – высокий) И (ЛПВП – низкий) И (боль в груди – высокий) ТО (риск – высокий).
R9: ЕСЛИ (возраст – старый) И (ИМТ – средний) И (САД – средний) И (ДАД – средний) И (ДАД – средний) И (УСК – средний) И (ОХС – средний) И (ЛПНП – средний) И (ТГ – низкий) И (ЛПВП – низкий) И (боль в груди – низкий) ТО (риск – средний).
R10: ЕСЛИ (возраст – молодой) И (ИМТ – средний) И (САД – немного увеличен И (ДАД – средний) И (УСК – средний) И (ОХС – средний) И (ЛПНП – средний) И (ТГ – средний) И (ЛПВП – низкий) И (боль в груди – низкий) ТО (риск – низкий).
Точность классификации нечеткой экспертной системы – 84,2%.
A. Lahsasna и соавт. разработали нечеткую систему поддержки принятия решений для диагностики ИБС, которая учитывает не только точность принятия решений, но и их интерпретируемость [32]. В системе принята стратегия вывода «победитель получает все», когда решение принимается на основании одного правила, ЕСЛИ-часть которого наиболее подходит под описание конкретных факторов риска. Авторы расширили структуру нечетких правил, добавив в ТО-часть правила степень их важности и определенности, чтобы врач мог проверить обоснованность каждого правила и определить, следует ли принимать во внимание это правило в процессе принятия решения. Кроме того, точность принимаемого решения повышается за счет использования ансамбля классификаторов в случае, когда степень уверенности в решении правила победителя является низкой. Эти особенности позволяют врачу не только точно определить наличие ИБС, но и понять взаимосвязь между факторами и диагнозом ИБС.
В исследовании R.A. Mohammadpour и соавт. описана нечеткая система прогнозирования ИБС [45]. Основой для построения системы являются результаты перфузионного сканирования миокарда и ангиографии коронарной артерии 115 пациентов. Исходные данные разделены на четыре класса: отсутствие стеноза (39 пациентов), стеноз в одном сосуде (35 пациентов), стеноз в двух сосудах (17 пациентов), стеноз в трех сосудах (24 пациента). Нечеткая система оперирует десятью факторами риска, которые являются входными переменными: возраст, пол, диабет, уровни холестерина, ТГ, ЛПНП, САД, суммарный показатель стресса, курение и генетический фактор. Выходом нечеткой системы является метка класса. Точность классификации составила 92,8%.
Микроальбуминурия (МА) является независимым предиктором сердечно-сосудистых и почечных заболеваний, развития явной нефропатии и сердечно-сосудистой смертности у пациентов с диабетом 2-го типа. Определение МА является важным инструментом для выявления людей с высоким риском сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний и заболеваний почек. H.R. Marateb и соавт. предложили новый метод диагностики МА, в котором используются клинические параметры, которые обычно контролируются у пациентов с диабетом 2-го типа без необходимости дополнительного измерения альбумина в моче [46]. В качестве входных использовались следующие данные: возраст, пол, ИМТ, продолжительность диабета, САД, УСК, средний процентный уровень глюкозы в крови за предыдущие 3 мес., глюкоза в крови через 2 ч после приема пищи, ОХС, ЛПНП, ЛПВП и ТГ.
Результат классифицировался как нормоальбумину-рия (альбумин в моче менее 30 мг/день) или МА (альбумин в моче от 30 до 300 мг/день). Нечеткий классификатор протестирован на выборке из 200 пациентов с диабетом 2-го типа. Точность нечеткого классификатора составила 92%, что превысило значения точности других протестированных классификаторов: линейный и квадратичный дискриминантный анализ, метод опорных векторов, наивный байесовский классификатор.
T.P. Exarchos и соавт. в своей работе описали две нечеткие системы диагностики [29]. Нечеткая система определения риска ИБС была создана с использованием 11-часовых двухканальных записей ЭКГ базы данных ESC ST-T [47]. Три медицинских эксперта независимо друг от друга определяли биение как нормальное, ишемическое или артефакт. В случае разногласий эксперты принимали окончательное решение на основе консенсуса. После удаления артефактов и неверно обнаруженных ударов окончательный набор данных содержал 76 989 сердечных сокращений, диагностированных как нормальные или ишемические. Для классификации использованы следующие признаки: отклонение сегмента ST, наклон сегмента ST, область сегмента ST, амплитуда зубца Т, интервал QT, возраст пациента. База содержит 53 нечетких правила, 27 из которых ответственны за предсказание нормальных сердечных сокращений, остальные 26 – за классификацию ишемических сердечных сокращений. Вторая нечеткая система создана для классификации аритмии на основе данных тахограмм базы MIT-BIH [48]. T.P. Exarchos и соавт. определяют четыре класса ритма: 1) фибрилляция желудочков; 2) преждевременное сокращение желудочков; 3) блокада сердца II степени; 4) нормальный [29]. Объем базы – 109 880 ударов. База содержит 17 правил, два из которых ответственны за предсказание класса 1, семь – за предсказание класса 2, семь – за предсказание класса 4, и одно правило предсказывает класс 3. Точность классификации составляет 92 и 96% для ишемической и аритмической нечетких систем соответственно.
Нечеткие классификаторы риска гипертонической болезни
Гипертонию называют тихим убийцей, потому что она не имеет ярко выраженных симптомов, но может вызвать серьезные проблемы, если ее долго не лечить. Именно поэтому так важны разработки систем диагностики и лечения пациентов с гипертонией [49].
В исследовании P. Melin и соавт. для диагностики риска гипертонии предложена гибридная модель с использованием нейронных сетей и нечеткой логики [33]. Модель учитывает возраст, факторы риска и поведение АД в течение 24 ч. Авторы используют два нечетких классификатора, первый – для оценки сердечного ритма и второй – для мониторинга ночного АД. Нечеткий классификатор для мониторинга АД содержит 25 нечетких правил, которые разработаны на основе знаний эксперта и Европейских рекомендациях по гипертонии. Указанный классификатор имеет два входа, соответствующих САД и ДАД, и один выход, который соответствует уровню АД. Лингвистические переменные «систолическое» и «диастолическое артериальное давление» определены семью нечеткими термами треугольного типа, которые соответствуют следующим значениям: «низкий», «несколько ниже нормального», «нормальный», «несколько выше нормального», «высокий», «очень высокий» и «слишком высокий». Выходная переменная представлена следующими термами треугольного типа: Hipotension, Optimal, Normal, HighNormal, Grade1, ISHGrade1, Grade2, ISHGrade2, Grade3 и ISHGrade3. Нечеткий классификатор уровня сердечного ритма содержит 20 нечетких правил, имеет два входа, соответствующих возрасту и частоте сердечных сокращений, и один выход, который соответствует уровню сердечного ритма. Лингвистические переменные «возраст» и «частота сердечных сокращений» определены четырьмя и пятью нечеткими трапециевидными термами соответственно. Выходная переменная представлена пятью трапециевидными нечеткими термами. Классификатор правильно определил сердечный ритм у 100% протестированных пациентов. Кроме того, разработан нечеткий классификатор ночного профиля АД с двумя входными переменными, которые соответствуют уровням САД и ДАД соответственно. Классификатор содержит четыре нечетких правила, которые разработаны и проанализированы совместно с врачом-кардиологом. Точность классификации – 93,3%.
В нечеткой экспертной системе диагностики гипертонии [50] в качестве входных переменных используются следующие факторы: возраст, ИМТ, АД и частота сердечных сокращений. Процесс диагностики, лингвистические переменные и их значения были сформированы на основе знаний эксперта.
Среднее АД человека является наиболее значимым гемодинамическим параметром, который необходимо удерживать в стабильных пределах в условиях анестезии, хирургии и интенсивной терапии. Ручное управление инфузией лекарственного средства пациенту является простым и традиционным способом регулирования, однако такое управление не является предпочтительным, поскольку оно отнимает много времени и сопряжено с риском для пациентов из-за недостаточной точности контроля дозировки [51]. Для решения указанной проблемы R. Sharma и соавт. разработали контроллер на основе нечеткой логики, регулирующий скорость инфузии лекарственного средства (sodium nitroprusside) в соответствии со скоростью изменения давления [52].
Интерпретация ЭКГ является важной составляющей своевременной медицинской диагностики, однако просмотр информации объемом более 24 ч становится трудоемкой задачей для врачей. В статье E. Ramirez и соавт.
описан подход к формированию гибридной модели в качестве метода классификации аритмий сердца [53]. Гибридная модель основана на искусственных нейронных сетях и нечеткой логике. Обучение и тестирование модели проводились с использованием базы данных аритмии Массачусетского технологического института и больницы Бет-Исраэль (MIT-BIH). Гибридная модель состоит из двух базовых модульных блоков для выполнения классификации сигналов от каждого отведения. Каждый базовый модуль состоит из трех различных классификаторов: нечеткий KNN, многослойный персептрон с градиентным спуском и многослойный персептрон с масштабированным сопряженным градиентным обратным распространением. Выходы каждого из базовых модулей объединяются с использованием двух различных нечетких классификаторов. Точность первого классификатора – 93,8%, второго – 94,2%.
В работе A. Minutolo и соавт. рассмотрена проблема формализации клинических руководящих указаний в контексте внедрения доказательной медицины в клиническую практику [13]. Большинство руководящих указаний представлено в форме текстовых документов (бумажных или электронных), которые содержат описательные разделы, касающиеся исходных клинических проблем, методологии разработки рекомендаций и подтверждающих данных, а также резюме стандартных рекомендаций. Авторы сводят клинические руководства к набору рекомендаций, выраженных в форме «ЕСЛИ – условие, ТО – действие» и представленных в виде группы из одного или нескольких нечетких правил. Пример трех руководящих указаний и рекомендаций, взятых из клинического руководства NICE 127 , приведен ниже [13].
Руководящее указание 1
Рекомендация 1. ЕСЛИ клиническое САД равно 180 мм рт. ст. или выше, ТО стадия гипертонии является тяжелой.
Рекомендация 2. ЕСЛИ клиническое ДАД равно 110 мм рт. ст. или выше, ТО стадия гипертонии является тяжелой.
Руководящее указание 2
Рекомендация 1. ЕСЛИ стадия гипертонии является тяжелой, ТО немедленно начните лечение гипотензивным лекарственным средством с высокой дозой ингибитора АПФ.
Руководящее указание 3
Рекомендация 1. ЕСЛИ стадия гипертонии тяжелая, ТО немедленно начните антигипертензивную медикаментозную терапию высокой дозой селективного блокатора бета-1.
Отличительными особенностями предлагаемой нечеткой системы являются 1) разбиение всей нечеткой системы на подсистемы; 2) многоуровневая схема логического вывода, основанная на иерархическом подходе к
Список литературы Нечеткие классификаторы в диагностике сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний. Обзор
- Fernandes M., Vieira S.M., Leite F., Palos C., Finkelstein S., Sousa J.M.C. Clinical Decision Support Systems for Triage in the Emergency Department using Intelligent Systems: a Review. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020;102:101762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2019.101762.
- Mustaqeem A., Anwar S.M., Majid M. A modular cluster based collaborative recommender system for cardiac patients. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020;102:101761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2019.101761.
- Souza-Pereira L., Pombo N., Ouhbi S., Felizardo V., Garcia N. Clinical decision support systems for chronic diseases: A systematic literature review. Comput. Methods Program Biomed. 2020;195:105565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105565.
- Olakotan O.O., Yusof M.M. Evaluating the alert appropriateness of clinical decision support systems in supporting clinical workfl ow. Journal Biomedical Informatics. 2020;106:103453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2020.103453.
- MsRae M.P., Bozkurt B., Ballantyne C.M., Sanchez X., Christodoulides N., Simmons G. et al. Cardiac ScoreCard: A diagnostic multivariate index assay system for predicting a spectrum of cardiovascular disease. Expert Systems with Applications: An International Journal. 2016;54:136-147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2016.01.029.
- Thukral S., Rana V. Versatility of fuzzy logic in chronic diseases: A review. Medical Hypotheses. 2019;122:150-156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2018.11.017.
- Gadaras I., Mikhailov L. An interpretable fuzzy rule-based classification methodology for medical diagnosis. Artif. Intell. Med. 2009;47(1):25-41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2009.05.003.
- Mokeddem S.A. A fuzzy classification model for myocardial infarction risk assessment. Applied Intelligens. 2018;48:1233-1250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-017-1102-1.
- Nauck D., Kruse R. Obtaining interpretable fuzzy classification rules from medical data. Artif. Intell. Med. 1999;16(2):149-169. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0933-3657(98)00070-0.
- Kalantari A., Kamsin A., Shamshirband S., Gani A., Alinejad-Rokny H., Chronopoulos A.T. Computational intelligence approaches for classification of medical data: State-of-the-art, future challenges and research directions. Neurocomputing. 2018;276:2-22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2017.01.126.
- Jemal H., Kechaou Z., Ayed M.B. Enhanced decision support systems in intensive care unit based on intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Advances in Fuzzy Systems. 2017;(5b):1-8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7371634.
- Pota M., Esposito M., Pietro G. Designing rule-based fuzzy systems for classification in medicine. Knowl-Based Systems. 2017;124(C):105-132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2017.03.006.
- Minutolo A., Esposito M., Pietro G. A fuzzy framework for encoding uncertainty in clinical decision-making. Knowl-Based Systems. 2016;98:95-116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2016.01.020.
- Ahmadi H., Gholamzadeh M., Shahmoradi L., Nilashi M., Rashvand P. Diseases diagnosis using fuzzy logic methods: A systematic and meta-analysis review. Comput. Methods Program Biomed. 2018;161:145-172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.04.013.
- Kour H., Manhas J., Sharma V. Usage and implementation of neuro-fuzzy systems for classification and prediction in the diagnosis of different types of medical disorders: a decade review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2020;53:4651-4706. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-020-09804-x.
- Sajadi N.A., Borzouei S., Mahjub H., Farhadian M. Diagnosis of hypothyroidism using a fuzzy rule-based expert system. Cliical Epidemiology and Global Health. 2019;7(4):519-524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cegh.2018.11.007.
- Arji G., Ahmadi H., Nilashi M., Rashid T.A., Ahmed O.H., Aljojo N. et al. Fuzzy logic approach for infectious disease diagnosis: A methodical evaluation, literature and classification. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering. 2019;39(4):937-955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbe.2019.09.004.
- Кобринский Б.А. Нечеткость в клинической медицине и необходимость ее отражения в экспертных системах. Врач и информационные технологии. 2016;5:6-14.
- Amato F., Lopez A., Pena-Mendez E.M., Vanhara P., Hampl A., Havel J. Artificial neural networks in medical diagnosis. J. Appl. Biomed. 2013;11(2):47-58. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10136-012-0031-x.
- Jiang J., Wang H., Xie J., Guo X., Guan Y., Yu Q. Medical knowledge embedding based on recursive neural network for multi-disease diagnosis. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020;103:101772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2019.101772.
- Alizadehsani R. Machine learning-based coronary artery disease diagnosis: A comprehensive review. Computers in Biology and Medicine. 2019;111:103346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2019.103346.
- Acharya U.R., Fujita H., Sudarshan V.K., Oh S.L., Adam M., Tan J.H. et al. Automated characterization of coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, and congestive heart failure using contourlet and shearlet transforms of electrocardiogram signal. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2017;132(15):156-166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2017.06.026.
- Yang H.-H., Wu C.-L. Rough sets to help medical diagnosis - Evidence from a Taiwan’s clinic. Expert System with Applications. 2009;36(5):9293-9298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2008.12.003.
- Zhang Z., Shi Y., Gao G. A rough set-based multiple criteria linear programming approach for the medical diagnosis and prognosis. Expert System with Applications. 2009;36(5):8932-8937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2008.11.007.
- Wang M., Chen H. Chaotic multi-swarm whale optimizer boosted support vector machine for medical diagnosis. Applied Soft Computing. 2020;88:105946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105946.
- Chen H.L., Yang B., Wang G., Wang S.-J., Liu J., Liu D.-Y. Support vector machine based diagnostic system for breast Cancer using swarm intelligence. J. Med. Syst. 2012;36(4):2505-2519. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-011-9723-0.
- Tan K.C., Yu Q., Heng C.M., Lee T.H. Evolutionary computing for knowledge discovery in medical diagnosis. Artif. Intell. Med. 2003;27(2):129-154. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0933-3657(03)00002-2.
- Park Y.-J., Chun S.-H., Kim B.-C. Cost-sensitive case-based reasoning using a genetic algorithm: Application to medical diagnosis. Artif. Intell. Med. 2011;51(2):133-145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2010.12.001.
- Exarchos T.P., Tsipouras M.G., Exarchos C.P., Papaloukas C., Fotiadis D.I., Michalis L.K. A methodology for the automated creation of fuzzy expert systems for ischaemic and arrhythmic beat classification based on a set of rules obtained by a decision tree. Artif. Intell. Med. 2007;40(3):187-200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2007.04.001.
- Mastoi Q., Wah T.Y., Raj R.G., Iqbal U. Automated diagnosis of coronary artery disease: A review and workflow. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2018;2016282. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2016282.
- Kora P., Meenakshi K., Swaraja K., Rajani A., Islam K.M. Detection of cardiac arrhythmia using fuzzy logic. Inform. Med. Unlocked. 2019;17:100257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2019.100257.
- Lahsasna A., Ainon R.N., Zainuddin R., Bulgiba A. Design of a fuzzybased decision support system for coronary heart disease diagnosis. J. Med. Syst. 2012;36(5):3293-3306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-012-9821-7.
- Melin P., Miramontes I., Prado-Arechiga G. A hybrid model based on modular neural networks and fuzzy systems for classification of blood pressure and hypertension risk diagnosis. Expert System with Applications. 2018;107:146-164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2018.04.023.
- Anooj P.K. Clinical decision support system: Risk level prediction of heart disease using weighted fuzzy rules. Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences. 2012;24(1):27-40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2011.09.002.
- Горбунов И.В., Ходашинский И.А. Методы построения трехкритериальных Парето-оптимальных нечетких классификаторов. Искусственный интеллект и принятие решений. 2015;(2):75-87.
- Yankovskaya A.E., Gorbunov I.V., Hodashinsky I.A. Tradeoff search methods between interpretability and accuracy of the identification fuzzy systems based on rules. Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis. 2017;27(2):243-265. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1054661817020134.
- Zadeh L. Fuzzy sets. Information and Control. 1965;8(3):338-353. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0019-9958(65)90241-X.
- Zadeh L. Knowledge representation in fuzzy logic. IEEE Transaction and Knowledge and Data Engeneering. 1989;1(1):89-100. https://doi.org/10.1109/69.43406.
- Мех М.А., Ходашинский И.А. Сравнительный анализ применения методов дифференциальной эволюции для оптимизации параметров нечетких классификаторов. Известия Российской академии наук. Теория и системы управления. 2017;4:65-75.
- Ходашинский И.А., Горбунов И.В. Оптимизация параметров нечетких систем на основе модифицированного алгоритма пчелиной колонии. Мехатроника, автоматизация, управление. 2012;(10): 15-20.
- Ходашинский И.А., Сарин К.С. Отбор классифицирующих признаков: сравнительный анализ бинарных метаэвристик и популяционного алгоритма с адаптивной памятью. Программирование. 2019;(5):3-9. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0132347419050030.
- Ходашинский И.А. Идентификация нечетких систем на базе алгоритма имитации отжига и методов, основанных на производных. Информационные технологии. 2012;(3):14-20.
- Marateb H.R., Goudarzi S. A noninvasive method for coronary artery diseases diagnosis using a clinically-interpretable fuzzy rule-based system. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2015;20(3):214-223.
- Pal D., Mandana K.M., Pal S., Sarkar D., Chakraborty C. Fuzzy expert system approach for coronary artery disease screening using clinical parameters. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2012;36:162-174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2012.06.013.
- Mohammadpour R.A., Abedi S.M., Bagheri S., Ghaemian A. Fuzzy rule-based classification system for assessing coronary artery disease. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2015;2015:564867. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/564867.
- Marateb H.R., Mansourian M., Faghihimani E., Amini M., Farina D. A hybrid intelligent system for diagnosing microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes patients without having to measure urinary albumin. Comput. Biol. Med. 2014;45:34-42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2013.11.006.
- European ST-T database directory. URL: https://physionet.org/content/edb/1.0.0.
- MIT-BIH arrhythmia database. URL: https://physionet.org/content/mitdb/1.0.0.
- Wang A., An N., Chen G., Li L., Alterovitz G. Predicting hypertension without measurement: A non-invasive, questionnaire-based approach. Expert System with Applications. 2015;42(21):7601-7609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2015.06.012.
- Das S., Ghosh P.K., Kar S. Hypertension diagnosis: A comparative study using fuzzy expert system and neuro fuzzy system. In: IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems. Hyderabad: IEEE; 2013. https://doi.org/10.1109/FUZZ-IEEE.2013.6622434.
- Su T.-J., Wang S.-M., Vu H.-Q., Jou J.-J., Sun C.-K. Mean arterial pressure control system using model predicative control and particle swarm optimization. Microsystem Technologies. 2018;24:147-153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-3212-9.
- Sharma R., Deepak K.K., Gaur P., Joshi D. An optimal interval type2 fuzzy logic control based closed-loop drug administration to regulate the mean arterial blood pressure. Computer Methods and Programs Biomedicine. 2020;185:105167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.105167.
- Ramirez E., Melin P., Prado-Arechiga G. Hybrid model based on neural networks, type-1 and type-2 fuzzy systems for 2-lead cardiac arrhythmia classifi cation. Expert System with Applications. 2019;126:295-307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2019.02.035.
- Wolpert D., Macready W. No free lunch theorems for optimization. IEEE Transaction Evolutionary Computation. 1997;1(1):67-82. https://doi.org/10.1109/4235.585893.


