New check points of the region's foreign trade
Автор: Smirnova Tatyana Gennadevna, Gubanova Elena Sergeevna
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Development strategy
Статья в выпуске: 2 (14) т.4, 2011 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article considers the problems of the Russian regions’ foreign trade activity, which complicate qualitative transformations in the foreign commerce, are. In many respects these problems are caused by imperfection of the existing mechanism of state regulation. The necessity and the features of the foreign commerce’s regulation in a federative state are shown. The conceptual bases of the mechanism of the foreign commerce regulation at the regional level, which will promote a more full realization of the foreign commerce potential of a territory and transformation of the foreign commerce relations into the effective factor of the regional development, are formulated. The key directions of the foreign commerce policy of a region for the immediate prospects, which realization will allow diversifying export structure and expanding its geography, are proved. The means of regulating influence assisting to the activity’s coordination between the federal and the regional authorities, and to a region’s integration into the world economy’s space are argued. The opportunities of the mentioned means’ use in the Vologda Area are estimated.
Vologda oblast, foreign trade, mechanism of the foreign trade regulation
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147223251
IDR: 147223251 | УДК: 339.5(470.12)
Текст научной статьи New check points of the region's foreign trade
For many years among the countries there were various forms of economic relations, which in the productive forces’ development became complicated and improved. The global practice shows that for the majority of countries the basis for the external economic relations is international goods’ trade. Foreign commerce promotes overcoming of resources’ limitation and home market’s narrowness, creates the opportunities for the mass production’s and new workplaces’ organization, raises the amount of equipment at enterprises, promotes application of new technical equipment and technologies, increases economic growth opportunities, rationalization of the natural resources’ and labor use, that finally leads to the growth of labor productivity and population incomes. It allows approving that the foreign trade relations’ presence is the important condition of economic complex’s functioning not only in separate countries, but also in their regions.
The experience of many countries shows that the foreign commerce development requires the state regulating influence directed on trade volumes, commodity and geographical structure of export and import transactions. In a federative state such regulation is carried out at two levels (federal and regional).
At a federal level the national safety of a country is provided with the help of measures of obligatory or prohibitive character. It becomes apparent in the form of quantitative export and import limitation, licensing for carrying out foreign commerce operations, controlling the goods’ safety and quality. In our country to a regional level a rather wide spectrum of powers (which does not have analogues in any federative states in the world) in the sphere of support of the production export refers:
-
- negotiations with foreign legal and natural persons, foreign federative states’ subjects, administrative-territorial formations of the foreign states, and international financial organizations having economic interests in an area;
-
- information support of export-import and financial activity of legal and natural persons in an area;
-
- promotion of investments, goods and services to the countries being trade partners of a region; and also to the world markets;
-
- edition of reference materials, placing the information about a region in both foreign and Russian mass media on the foreign commerce issues;
-
- holding multimedia presentations in foreign languages about the socio-economic potential of a region;
-
- support of realization of the regional projects directed on the development of the foreign commerce relations of a region, with participation of the international financial organizations;
-
- monitoring of the economic potential of a region in the foreign states’ markets;
-
- data gathering, generalization and preliminary processing, the analysis of condition and development of the export and import activity of organizations and businessmen in
a region, foreign investments into the regional economy and the projects realized in its territory with bringing in foreign investments;
-
- coordination of the statutory acts’ projects prepared by the organization departments of the Regional Government, and by the executive power bodies of a region on the foreign commerce issues;
-
- methodical and consultative help to the executive power bodies of a region, to the local government’s institutions and to organizations on the foreign commerce issues;
-
- business, scientific, technical and other types of translation from and into foreign languages.
The analysis of the foreign commerce regulation in Russia showed that the specified powers’ realization is complicated by virtue of the following problems’ existence.
First, the majority of the regions in the Russian Federations increases export volumes without the change of their branch and geographical structure, and the goods’ nomenclature. At the same time the work on promoting goods’ separate kinds to foreign markets and on increasing the regional exporters’ quantity is not carried out. It leads to the fact that some of the powers mentioned above, especially the ones of economic character, are not used, and it complicates qualitative transformations in the foreign commerce.
Second, functions’ duplication takes place; it results in the activity dissociation of the bodies carrying out regulation of the foreign commerce in a region. For example, for carrying out the function of the foreign commerce interaction of a region with foreign countries in the Russian Federation subjects government bodies, coordinating and regulating the foreign commerce activity, are formed (for example, the Ministry of economics and foreign relations of the Republic of Buryatiya, Committee on Foreign Commerce Activity of the Moscow Government, Ministry of foreign economic relations of the Moscow oblast, etc.). At the government bodies the consultative and advisory bodies on the issues of the foreign commerce relations can be created (for example, the Regional Advisory Council on working with the foreign commerce participants at the Governor of the Yaroslavl oblast). However in their authorized documents the mechanism of regulation in the sphere of a region’s Foreign Commerce Activity is not registered.
In the Vologda oblast all functions on regulating foreign economic relations, except the foreign commerce, are carried out by the Department of International, Inter-regional Relations and Tourism of the oblast. Concerning the foreign commerce this body carries out organizing residence in the Vologda oblast for delegations from other countries and regions.
At the same time coordination and determination of the basic directions in the sphere of the area’s foreign economic policy is given to the Department of Economy of the Vologda oblast Government. The Chief of the Department supervises the matters of priorities and coordination of the foreign commerce activity of the government bodies and managing subjects, and also the matters of international projects realized with the Vologda oblast’s participation. Thus, the powers in the field of the foreign commerce activity are dispersed between two authorities, at the same time in their authorized documents there is no mention of their corresponding activity coordination. In such conditions the functions’ duplication is inevitable.
Such difficulties became possible because of the fact that the mechanism of the foreign commerce regulation was formed in 1990-s without taking into account the requirements of structural economic reorganization and the necessity of the increase of the country’s and its regions’ international competitiveness. Making of the mentioned mechanism was passing in short terms at the experience absence not only in organization of the foreign commerce regulation in regions, but also at the experience absence of the experts, capable to direct the foreign commerce development to the decision of the major social and economic problems.
The analysis of the foreign commerce activity in the Vologda oblast showed that the exist- ing mechanism of the foreign commerce regulation does not allow realizing the foreign commerce potential of the region in full measure. It can be found in the following facts.
First, for the two decades of economic transformations the foreign commerce development has not promoted the improvement of the regional industrial structure in the direction of its equilibration1. The narrow export base, the basis of which is made by a small group of the goods with a low degree of processing, became the reason for the Vologda oblast economy’s vulnerability for external shocks.
Second, despite of the wide geography of the Vologda export, recently the Vologda oblast’s steady foreign commerce relations are observed only with few states in Europe and in the CIS; and a great quantity of agreements with foreign partners covenanted by the Area’s Government on continuing basis has not passed into quality. Many of them have exceptionally declarative character and only contain announcements about the general intentions to promote barter expansion. The mechanism and the steps of cooperation, taking into account the partners’ features and really being capable to support the regional exporters at their production realization in foreign markets, are not registered in them.
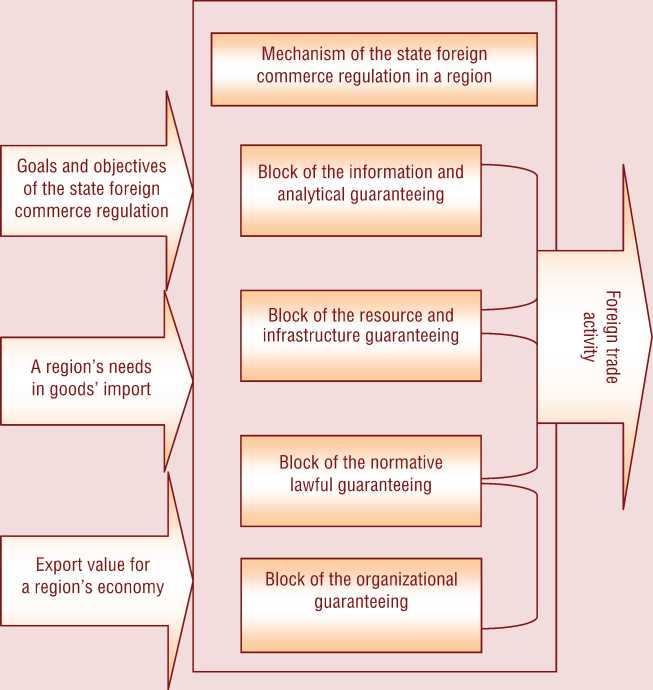
To change the situation in the sphere of the regional foreign trade and to transform the foreign trade relations into the effective factor of the regional development, capable to integrate a region into the world economy, the perfection of the existing mechanism of the foreign trade activity’s regulation is necessary. In our opinion, the structure of this mechanism can be represented in the given scheme (fig. 1) .
Each of the mechanism’s blocks is aimed at the decision of certain problems which in aggregate will allow to overcome the obstacles, impeding the advancing foreign trade development in a region and to balance the activity of all the participants of this process.
Figure 1. Structure of the foreign trade regulation mechanism in the region
Results of the foreign trade activity of a region
High position of the foreign trade turnover in gross regional product
A great share of products with the high processing degree in export
Successful financial and economic activity of the regional exporters
Saturation of the home market with necessary import goods
Regional economy embedding into the world economy
To make the decisions, particularly accepted at the level of the regional government, meeting the requirements on validity and timeliness, first of all it is necessary to support the process of the decisions’ preparation by the sufficient, reliable and actual information. From here it follows, that in the structure of mechanism of the foreign commerce regulation the block of the information and analytical guaranteeing should be chosen; to the primary goals of this block the following ones can be referred: monitoring the commodity markets where there is the demand for the production made in a region; revealing the problems arising during the foreign commerce realization; searching the forms and the ways of the problems’ solution; monitoring export and import operations in a region.
The block of the resource and infrastructure guaranteeing includes studying all kinds of resources which can be involved into the foreign commerce, conditions, preconditions; the analysis of probable directions of their use, and also infrastructural objects, capable to provide promoting goods to foreign markets.
The block of the normative lawful guaranteeing is called to form institutional frameworks for foreign commerce realization. Its basis is formed by the federal legislation, corresponding statutory acts accepted by the Russian Federation subjects, and methodical regulations and recommendations, according to which the foreign commerce is organized.
All mentioned above blocks of the mechanism of the foreign commerce regulation can function continuously only under the condition of the organized guaranteeing including necessary organizational structures’ creation for providing initiation actions, for developing and controlling the objects’ achievement in the field of the foreign commerce policy in a region.
While researching the condition and the features of the foreign commerce realization in the region, and also considering the interests of all the participants of this process, we can draw a conclusion that the key directions of the foreign trade policy in the nearest prospects should be the following ones: improvement of export structure and expansion of its (export’s) geographical structure. Let’s consider them in detail.
-
1 . The export basis of the Vologda oblast is made by ferrous and non-ferrous metals (56.2%) and by chemical production (36.1%); the share of equipment is 1.4%-2%. The Vologda oblast international specialization which has not varied for many years cannot be considered a progressive one that is represented by the prevalence of raw material and products of a low processing degree in export. Therefore it is possible to tell that the region plays a passive role in the international division of labor and shows comparative backwardness in the international specialization.
The economic instability of the Vologda oblast was stressed by the world economic crisis which burst at the end of the year of 2008 and negatively influenced both the foreign commerce activity in the Vologda oblast and the regional economy as a whole. The great drop in prices for some goods, which are the Vologda export’s basis, appeared enough for that.
The similar situation was observed in the Russian export-directed regions which end production are the goods with the low processing degree (metals, chemical products, wood materials, etc.). Not only the Vologda oblast, but the Tatarstan, Nizhniy Novgorod, Sverdlovsk, Lipetsk, Omsk, Kemerovo, Chelyabinsk oblasts and also some other regions of Russia experienced abrupt drop in such branches, as metallurgy, chemical production, oil production and processing because of the reduction in demand for their production in foreign markets. At the crisis period in the mentioned regions a considerable reduction of the investment activity was observed, there was an abrupt drop in industrial production (for more than 10%), everywhere organizations’ and enterprises’ financial position distinctly has worsened, and the share of the retarded bill payable rose sharply. The same thing occurred in the export-directed regions of other countries, particularly in coal-mining and metallurgical areas in Ukraine (the Mariupol, Donetsk, Lugansk, Dnepropetrovsk and Zaporozhye oblasts), in Brazil states, etc. As a result of the industrial production reduction serious problems with providing the effective population employment arose.
For export structure changing the subjects of the foreign commerce regulation should choose the priorities of the foreign commerce development and single out the means of influence which will allow carrying out the transition to a more balanced export structure in a region. The necessity of these measures is also emphasized by the direct participants of the foreign trade activity in a region who have permanently to face with difficulties of its realization. Let’s note that regional exporters expect the support from all levels’ authorities.
The results of the survey 2, where the regional enterprises’ heads, carrying out the foreign commerce activity, speak about the necessity of the regional industrial enterprises’ support in foreign markets, confirms it. In the respondents’ opinions, the governmental bodies both in the country and in a region can support exporters by realizing such measures as:
-
- supporting producers in joining the world markets (37.5%);
-
- formation of an area’s favorable image for potential investors and foreign trade partners (35.9%);
-
- privileged credit conditions for some exporters’ categories (34.4%);
-
- presence of the strategy of the region foreign trade development (31.3%);
-
- training experts in the foreign commerce field (25%);
-
- creation of the program of providing production’s quality and certification (17.2%);
-
- constant monitoring of the world market’s economic situation (12.5%).
Thus, the basis of the export structure’s change in a region can be made by the corresponding program of the foreign trade development, containing both the substantiation of its priorities and the methods of influencing the commodity composition in the structure of which there can be the following steps:
-
- export stimulation of the enterprises making deep processing production, by preferential crediting export production, and also providing them with preferential export channels;
-
- use of tax remissions for exporters by decreasing payments to the regional budget;
-
- supporting commodity producers in searching foreign markets;
-
- informational and consulting services concerning potential foreign partners, the markets’ conjuncture on the basic nomenclature of a region’s export goods.
-
- providing insurance mechanisms’ functioning for the export goods with the local executive authorities’ participation;
-
- providing consulting services to regional exporters;
-
- providing types of financial support as forfeiting 3, export leasing, dealings on the basis of counter trade;
-
- creation of the system of the goods’ promoting for foreign markets 4 (advertising increase and fair and exhibition activity, especially in the sphere of services’ export; organizing of the network of trade missions, foreign trade firms and specialized firms engaged in production’s export and import in view of a region’s intere sts);
-
- development of the foreign trade infrastructure in a region;
-
- training skilled personnel in the field of foreign commerce for working at the enterprises of all patterns of ownership within the framework of the foreign trade cooperation.
-
2. If the commodity export diversity can be achieved with the help of the regional authorities’ economic means of exporters’ stimulation, then the export geography expansion is mainly possible with the help of means of organizational character which only can be realized within the framework of the coordinated efforts between the Federation and its regions. Among such means there is a region’s representation abroad.
Declaration of the export diversity and work in this direction as paramount tasks of the foreign trade development in a region will promote economic growth stimulation and transition to the innovational type of the economy in an export-directed region. On the contrary, continuation by regional authorities supporting export of the products with a low processing degree to the prejudice of more technological goods complicates qualitative economic growth of a region, cements the structure of its industrial production, deprives a region of stability during global economic cruises, sharply reducing total product volumes, budget filling and a population’s standard of living in a region. The declared policy on the Russian economy’s enhancement cannot be realized in case of preservation of the existing export structure both in the country as a whole and in its export-directed regions.
While choosing the measures of influence it is necessary to take into account that in many respects the use of the organizational measures of the foreign trade activity regulation in a region depends on the features of the administrative-territorial system of a country and its other features; and while choosing the most effective means of economic character it is necessary to use extensive world experience. One of the main market means in this sphere in advanced countries is export crediting. Through the banking system it is possible to stimulate the development of regional export by granting lax credits for the signed contracts to exporters. Thus it is expedient that the financial support is given not only as short-term (as it is widespread in Russia), but also as middle-term and long-term credits.
Besides lax credits it is necessary to provide attracting private commercial credits under the state guarantees. For this purpose it is necessary to develop cooperation between the regional authorities and credit organizations. For considerable expansion of the financial support to regional exporters the corresponding governmental body of a region can sign the agreement with a commercial or a state bank about joint exporters’ financing on the basis of joining up a bank’s and a region’s financial resources.
Opening and keeping economic and commercial representation abroad is a very expensive procedure for any region, even for an advanced region, and this problem’s solution, as the world experience shows, is only possible within the framework of the effective cooperation between the regional and the federal authorities. For this purpose a country’s representations abroad are used, where a representative from a region can operate as an employee. In case of opening a region’s representations abroad for means’ saving their personnel is mainly completed with the citizens of a host country. For instance, more than half of the American states’ representations abroad are completed with private persons employed under the contract while the rest share represents one of the service divisions of a concrete state.
Some big Russian regions which are actively carrying out foreign commerce are capable to keep representatives in the trade missions of those countries which markets are of interest for regional exporters.
At the absence of such an opportunity there is also another decision of the problem. The Russian legislation provides support to exporters only at the level of direct interaction between the Russian Federation trade mis- sion and a company-exporter 5. Regions are completely excluded from this circuit. As each of the Russian regions is a component of a certain district, and also of an economic area, it is expedient, that such representation was carried out at meso-level. Its powers should include carrying out corresponding marketing researches, distributing information about region’s (federal district’s/economic region’s) enterprises which they represent, and also rendering assistance into organizing business visits and trips of representatives of the host country’s companies to a region.
For regional exporters could get real support from the regional authorities, it is necessary to mention in authorized documents the authorities’ duty to form corresponding inquiries from regional exporters to the trade missions of the Russian Federation. These inquiries should be based both on the regional commodity producers’ interest in production export and on studying available opportunities of goods’ production and transportation demanded in the market.
Thus, in case of the trade mission’s or embassy’s presence in a country at which trade and economic representatives of Russia function, it is possible to offer the algorithm of interaction between exporters and regional and federal authorities for goods’ advancement to a foreign market (fig. 2) .
Rendering further services on searching potential contractors (selection of several most suitable business partners being given brief characteristics), organizing visits to the country and negotiations’ organizing should be envisaged, on the compensational basis, in the obliging form for a representation. In this case successful goods’ advancement to foreign markets by the Russian exporters become real since participation of staff at trade missions, embassies, consulates (not diplomats) will favorably affect contractors’ attitude towards Russian
Figure 2. Algorithm of interaction between exporters and regional and federal authorities for goods’ advancement to a foreign market
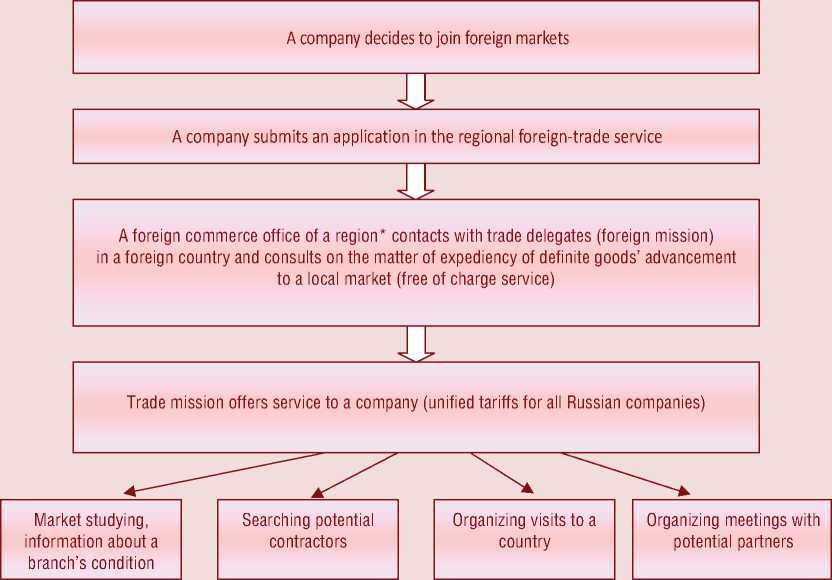
* As a foreign trade service of a region both the specialized body of foreign commerce regulation in a region and Department of economy (or other department which competence is foreign trade regulation in a region) can act.
businessmen; the latter will be informed about the business dealing’s specificities in the given country from the persons, obliged to trace the economic situation in a state of stay and to give corresponding data to the interested Russian exporters.
The considerable problem of the Russian exporters is the circumstance that the overwhelming majority of available representations are concentrated in European and other advanced markets, which are extremely difficult to join. At the same time in the countries which are potentially interested in products made in the Russian regions, such establishments are either absent or they are not enough6. So, Russia only has trade missions in 42 of more than 200 countries (including in South
America – 2 representations, in Africa – 3, the others – in the largest economies of the world)7. Thus the embassies working in these countries have the purpose of diplomatic representation, instead of economic interests of Russia and its producers. This problem is only possible to solve at the federal level.
It is also necessary to note that regions should constantly improve their marketing activity. More often international trading exhibitions and fairs are organized in those countries which markets are difficult to join because of their raised appeal to exporters. On the contrary, the countries where regions could deliver their products, as a rule, give insufficient information for decision-making on business relations’ establishment and signing contracts on products’ deliveries that complicates the Russian regions’ marketing activity. Choosing the countries and the regions, where the regional bodies’ efforts on the export geography expansion should be directed, in the program of the foreign trade development would promote concentration of a region’s efforts in corresponding directions.
As the world experience shows, organizing specialized body coordinating the foreign trade activity of a region, in many respects promotes the expansion of export geographical structure. For example, in the export-directed states of the USA the international trade departments are formed. The basic information for realizing these bodies’ activity is given by the management service of international trade of the USA Ministry of Trade which promotes as much as possible American producers have the opportunity to get to foreign markets. Similar structures also operate in Belgium, Germany, Mexico and other countries with the federal form of a state system.
The regional export services (bureau), independent departments of international trade at the regional government, etc. are no doubt economically expedient. Thus trade missions and trade and economic departments, regional foreign trade services should be connected in a united information network with organized information exchange (for example, about unprincipled contractors, about interests of local authorities and businessmen in purchasing certain products made in Russia, etc.).
However, now the process of trade missions’ transformation into trade and economic departments of embassies is being carried out with the purpose of optimization of charges for their keeping instead of the increase of their activity efficiency from the point of view of the Russian exporters’ assistance. In such conditions domestic producers cannot make a worthy competition to other countries’ producers which interests are lobbied, both at state and at the regional levels.
For changing the situation, first of all, it is necessary to designate assistance to the Russian exporters as one of the primary goals of the specified establishments’ activity in corresponding statutory acts, with giving to them corresponding powers and duties. To coordinate the work of trade missions and trade and economic departments of embassies with regional export services, it is necessary to develop the unified list of free-of-charge and chargeable information services which they will be obliged to give to the Russian exporters on onerous and gratuitous basis. At the present moment it is happening on onerous but illegal basis, under the personal arrangement between the interested potential Russian exporters and the staff of corresponding representations having the necessary information. This list should be a component of statutory acts (charters, positions) on the basis of which the given establishments can carry out their activity.
Thus, the changes in the export structure of a region in many respects are determined by the actions’ coordination between federal and regional authorities. Potential and operating exporters should have clear idea about what authorities are responsible for assistance to the Russian exporters in each country. It is very important, that the system of the foreign trade activity’s support worked as a single whole: trade missions, regions’ representatives at embassies’ and consulates’ departments, foreign trade services in regions should work as elements of the unified mechanism. Thus these efforts’ coordination, which should be shown in mutual argumentability of regional programs on exporters’ support by means both regional and federal budgets, is necessary. Realizing general intent to involve in international economic relations plenty of participants, and also open to the limit territories’ export potential and its successful achievement by interaction between the subjects of the foreign trade activity’s regulation is a summand of successful interaction between the regions and the federation as a whole.
Presence of the target programs of the foreign trade activity’s development in regions should reduce the danger of the regional eco- nomic policy’s mistakes as a result of lobbying political and economic interests of a group of private persons to the prejudice of economic safety of a region. At the same time the pro- gram’s framework should not be absolutely motionless so as to give the opportunity of efficient and effective reaction to changes both of global and domestic character.
Список литературы New check points of the region's foreign trade
- Mikusheva, T.U. Theory and practice of the region’s foreign trade (Komi Republic experience)/T.U. Mikusheva. -Syktyvkar: Komi scientific centre of the Ural branch of the RAS, 2002. -148 p.
- The official site of the Vologda oblast Government . -Access mode: http://www.vologda-oblast.ru
- The official site of International Commerce Office of the USA Department of Commerce . -Access mode: http://www.trade.gov
- The official site of the Federal service of the state statistics . -Access mode: http://www.gks.ru
- Regulations about the Russian Federation trade delegates in a foreign state (resolution of the Russian Federation Government, 25.09.2007 № 609)//The Russian Federation legislation collection. -04.07.2005. -№ 27. -Item 2761.
- Smirnova T.G. Problems of the industrial development of an export-directed region (on the data of the industrial enterprises’ survey in the Vologda oblast)/T.G. Smirnova, L.V. Dubinicheva//Economy and business. -2010. -№ 4. -Pp. 56-65.
- Socio-economic position of the Vologda area from January to December of the year of 2009: report/VologdaStat. -Vologda, January 2010. -30 p.
- Statistical year-book of the Vologda oblast/VologdaStat. -Vologda, 2009. -410 p.


