Novel Hybrid Model: Integrating Scrum and XP
Автор: Zaigham Mushtaq, M. Rizwan Jameel Qureshi
Журнал: International Journal of Information Technology and Computer Science(IJITCS) @ijitcs
Статья в выпуске: 6 Vol. 4, 2012 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Scrum does not provide any direction about how to engineer a software product. The project team has to adopt suitable agile process model for the engineering of software. XP process model is mainly focused on engineering practices rather than management practices. The design of XP process makes it suitable for simple and small size projects and not appropriate for medium and large projects. A fine integration of management and engineering practices is desperately required to build quality product to make it valuable for customers. In this research a novel framework hybrid model is proposed to achieve this integration. The proposed hybrid model is actually an express version of Scrum model. It possesses features of engineering practices that are necessary to develop quality software as per customer requirements and company objectives. A case study is conducted to validate the proposal of hybrid model. The results of the case study reveal that proposed model is an improved version of XP and Scrum model.
XP model, Scrum Model, Software Engineering Practices, Quality
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15011703
IDR: 15011703
Текст научной статьи Novel Hybrid Model: Integrating Scrum and XP
Published Online June 2012 in MECS
Agile framework is based on iterative software development [1]. An independent working module is built and integrated after the completion of a release. According to Pressman [1], agile software development methodologies emphasize on delivering working software after iteration. Iteration must not consume more than two weeks. The main spirit of agile development is that software should be fully integrated and tested before the completion of iteration. The agile process models are light weight in nature and allow teams to develop software in rapidly changing requirements [2]. Agile development methodologies are based on such principles that facilitate a development team to build software in quick time.
The main agile process models are Extreme Programming (XP), Scrum, Feature Driven Development (FDD), Rational Unified Process (RUP), Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM), Adaptive Software Development (ASD) and Open Source Software development (OSSD) [1]. The term 'Scrum' originally derived from a game of rugby where it denotes "getting an out-of play ball back into the game" with teamwork [3]. Scrum is an adaptive, quick, self-organizing product development process [3]. It is one of popular and widely practiced agile models. Scrum is simple in nature and especially suitable for the environments where requirements are disordered and confusing. Scrum for software development teams began at Easel Corporation in 1993 and it was used to build the first object-oriented design and analysis (OOAD) tool that incorporated round-trip engineering. Code was auto-generated from a graphic designing tool and called as Smalltalk integrated development environment (IDE) [4].
Extreme programming (XP) process model was introduced to avoid lengthy development cycles of traditional development models [1]. The characteristics of XP process model include evolutionary design, incremental planning, small developmental cycles, continuous response and trust over communication [1]. XP model has the ability to respond well in changing environments. According to Williams [5], XP team members have successive sessions throughout a day to discuss programming, project management, design, feedback and team building. The word ‘extreme’ means bringing common sense practices and principles to extreme levels. The contents of XP practices include Planning, Small releases, Metaphor, Simple design, Refactoring, Pair programming, Collective ownership, 40-hour week, On-site customer and Coding Standards [1] .
In this research, Scrum is chosen to be the most effective methodology for managing projects along with XP practices due to their widespread usage, simplicity, flexibility and adaptability in changing environments.
XP practices help to enhance productivity and achieve quality. The improved proposed hybrid model contains both XP/engineering and Scrum/management practices. This integration will provide the ability within the proposed hybrid model to build high quality software to make happy to all of its stakeholders.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 covers the related work. Section 3 describes the problem definition. Section 4 illustrates the motivation for the model to be proposed. Section 5 presents the proposed hybrid methodology. Section 6 covers the experimental evaluation of the proposed work. Conclusion and future work are given in the final section.
-
II. Related Work
-
2.1 Weaknesses in Scrum and XP Models
Scrum is one of the most popular and practiced agile software development methodologies [6]. Agile project management with Scrum is derived from best business practices in terms of productivity and quality. Scrum is extremely beneficial for an organization because it improves existing engineering practices [6]. Scrum is a light weight framework and it has the ability to integrate with iterative incremental methodologies to mange and develop complex projects. This integration brings into high project quality and increase productivity extensively [4]. Scrum practices can also be successfully applied for distributed projects [7]. Sprint technique is suitable for distributed teams especially in the beginning of a project. Software can be built in short (26 week) time boxed steps or iterations using Sprint practices [4].
Scrum development methodology is suitable for projects where requirements are vague and ambiguous. Scrum increases speed of development, align individual and corporate objectives, creates a culture based on performance, supports share-holder value, achieve constant and reliable communication of performance at all levels, and improve individual development and quality of life. It helps to a software development company to overcome competitors and achieve industry dominance [4]. The main focus is to deliver high quality software by managing the system development process in Scrum development [6]. Scrum software development is an empirical process. It insists on self-organizing teams and helps to provide flexibility and adaptability of systems [4].
According to Pressman [1], the Scrum is an iterative and incremental process for product development. Each iteration phase in Scrum is called a Sprint. At the end of each Sprint cycle, Sprint review meeting is conducted which provide a closer look at the final outcome of the Sprint development cycle. Sprint retrospective meeting aids the Scrum team to be more successful in the next Sprint. In Scrum process, the Project manager is called
Scrum Master; the development team is called Scrum team. The Product owner (usually from client side) is responsible for the product. Main Scrum techniques e.g. about product backlog, sprints and daily Scrums are described in the [2].
Torgeir Dingsoyr [8] has discussed Scrum software development methodologies in small organizations. Project estimation can be challenging due to the customer involvement in the project. This is due to the fact that rapidly changing requirements increases over all cost of the project. Scrum methodology boosts the development time and it also welcomes change at any phase of development. It is challenging for an organization to estimate development time because change request comes at any stage of the development. Michele Marchesi [9] implements Scrum model for distributed project. The most important factor in Scrum is the communication and regular feedback of the customer to the Scrum team. The success of the project depends upon proper communication between the product owner and scrum team. For a quality product the distributed project requires continuous unit testing.
Scrum is an incremental process model that requires frequent meetings [1]. The duration of a sprint is up to four weeks. It helps to conclude the whole project within few months. Scrum is suitable for those projects where requirements are changed frequently. The main purpose, of conducting Scrum meetings, is to highlight overlapping areas, integration and data readiness. Scrum can also be used to develop large projects. [10] describes the concept of multi product Scrum using multi teams. Weekly MetaScrum meeting also takes place once a week to start and change a sprint by the mutual understandings of customer and team.
Scrum and XP has been adopted in software industry from last many years. Several benefits of Scrum and XP have been explored but they have some limitations.
-
• The main focus of Scrum is on project management and remained silent about to engineer software.
-
• Scrum demands highly qualified professionals to build Scrum team.
-
• XP lacks in project management practices.
-
• XP fully depends upon customer that may become a risk to fail a project.
-
• XP is not suitable for medium and large scale projects.
-
III. Problem Definition
Scrum model concentrates on software project management practices and it does not describe how to engineer a software product. Whereas XP process model focuses more on software engineering practices and little on software project management. The design of XP process makes it suitable for simple and small projects and not appropriate for medium and large scale projects. Therefore, there is a desperate need of fine integration of management and engineering practices to achieve high quality software from the prospective of all stakeholders.
-
IV. Motivation Of The Model To Be Proposed
The proposed hybrid model is an extended version of Scrum methodology. The idea, behind the proposal of hybrid process model, is that the Scrum provides a very effective project management framework. If it is enriched with the project engineering abilities then the outcome will be an efficient model. The proposed hybrid model is a project management paradigm that is enriched with complete project engineering practices. In this way, the hybrid model is modified from a Scrum framework to a complete process model.
The existing Scrum does not provide any clear guidelines or steps about sprint zero to follow. The whole process is leftover to an organization to adjust according to their needs. Scrum starts from product backlog activity. The proposed hybrid process provides complete steps to perform sprint zero. The process starts with the creation of product attributes and is further divided in further sub processes that involve estimation and prioritization. The resultant of sprint zero activity is product backlog. Sprint development cycle of hybrid model in enriched with engineering capabilities by using XP practices during planning, designing, coding, testing and integration phases. All these process are observed though daily scrum. The hybrid model ensures the availability of product owner to watch the development process parallel on daily basis. In this way, the product can provide feedback and can rest assure that the whole development process is proceeding in a right direction. This exercise can dramatically improve the rate of customer satisfaction.
The beauty of the hybrid process model is that it is a full flavor of product engineering capabilities along with product management potential. The product development capabilities are fully composed with product management framework. All the steps of product development cycle are fully aligned with the Scrum framework.
-
V. The Proposed Hybrid Methodology
-
5.1 Planning Phase
-
5.2 Design Phase
The proposed hybrid model is shown in figure 1.
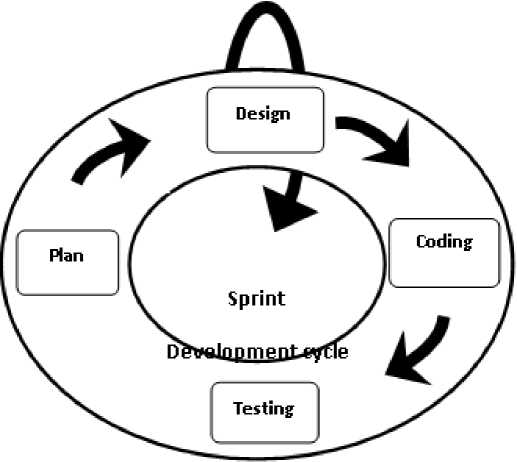
Fig 1: The Proposed Hybrid Model
The main phases of XP model are implemented by integrating Scrum activities. The details, of the proposed hybrid model, are as follows.
The process of planning is the first step of sprint development cycle. Planning involves the definition of the system being developed. The tasks defined in the sprint backlog are planned for development. The tasks are sequenced on the basis of priorities and dependencies and assigned to the concerned developers. Furthermore, the classes identified in the "developing of an overall model" process are assigned to individual developers. The planning phase requires close interaction among scrum master, product owner and scrum team. The effort required to implement a task, of a sprint backlog, are estimated in this phase. This process is carried by the collaboration of scrum master and development team. The scope and timing is decided by mutual collaboration of product owner and scrum master.
The design focuses on current requirements items. The format of the design should follow keep it simple (KIS) principle that is easy and understandable to a team and customer. In the designing phase, two types of diagrams are developed from tasks of sprint backlog. These diagram includes class diagrams and object diagram. For testing purpose, test classes are also designed.
-
5.3 Coding Phase
-
5.4 Testing Phase
The real development of the product is done during this phase. The process of coding requires coding standards, code ownership, pair programming and continuous integration. Coding process needs continuous testing and refactoring. It is necessary by the programmers to follow the coding standards in order to make the source code readable and understandable for others. Test code should be written first before writing source code. Code of the whole application is written using pair programmer technique. Although the research shows that pair programming takes more effort than a solo programming but optimized code is written using this technique that leads to high quality [5]. The purpose of code refactoring is to improve source code. The code refactoring technique helps to restructure a code without changing the functionality of program. The refactoring technique includes removing duplicates, simplifying code, adding flexibility in the system and communication improvement. Every person is responsible for individual code segments and he/she is allowed to change any part of a code at any time.
As long as the code is written it is tested frequently through unit tests. The part or feature of the application is successfully accepted only when it is passed through testing. The process of testing is started in early phases even before writing code. This process aids the programmers to understand problem. Each feature of the product is designed, implemented and tested individually within the sprint development cycle. A new code is integrated into existing code as soon as it is passed through testing. This process continues till the completion of software. The process of continuous integration helps in reducing implementation risks. Continuous integration ensures that working module is available to use with new features.
Daily Scrum Meeting is conducted on regular basis. The duration of this meeting is 15 minutes. The main participants are Scrum master, product owner and development team. The main benefits of daily scrum meeting are as follows.
-
• It allows development team to solve their
problems and shows good progress [1] .
-
• Helps to watch the tone and pace of
development.
-
• Helps to remove impediments in the development process as soon as possible.
Working set of the product is released after the completion of a release. This part of the product is presented in sprint review meeting. All stake holders are invited in the sprint review meeting. Whole product is launched with its full features after the successful completion of all releases.
-
VI. Experiment And Analysis
A controlled case study is conducted to validate the proposed model. The basic purpose of conducting case study is to build a system following the proposed model. For this purpose, a team of 6 members was selected. The duration of case study was five weeks. The project assigned to development team was Payroll Management System. The team worked under the guidelines and directions of proposed model and it took four iterations to complete the project. A training program was conducted to educate the team about the proposed model at the beginning of Payroll system case study. The team members have developed their term projects and they have good experiences of software development. However, the team did not have any experience of agile development. The team was first introduced agile practices required to build a software product. The proposed model has flavors of management and engineering practices.
The training involves the main Scrum practices were introduced to the team including sprint zero, product backlog, sprint backlog, sprint planning meetings, daily scrum meeting, sprint review meeting, and sprint retrospective. The main XP practices were also introduced to team including simple design, collective, pair programming, following coding standards, continuous testing, continuous integration and refactoring. The proposed model was also introduced to the development team during training. The team worked under a Scrum master. The team divided into three designers plus developers and two testers plus developers. Each task was assigned to two persons as a pair. The team developed the case study system using Rational Rose, Net Beans, My SQL, J-Unit, and Ireport tools. It was kept in mind that the team was balanced from all aspects such as designing, coding and testing. Table 1 shows the basic data gathered to validate the proposed model. The evaluation of case study becomes point of evidence for the authors that the proposal of hybrid model is suitable for industrial projects by eliminating the weaknesses of XP and Scrum models.
Table 1: The Data Obtained of Controlled Case Study
|
Items |
Releases _______________► |
||||
|
No of Releases |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
Average |
|
Calendar Time (weeks) |
2 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
5 |
|
Items in Sprint backlog |
8 |
4 |
5 |
3 |
20 |
|
Total Tasks defined |
50 |
12 |
14 |
6 |
82 |
|
Total work effort (h) |
400 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
1000 |
|
Team Productivity |
59.59 |
25.05 |
25.68 |
66.36 |
46.81 |
|
Post release defects |
7 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
16 |
|
Sprint Retrospective |
7 |
5 |
4 |
1 |
17 |
|
Pair programming % |
80% |
80% |
80% |
80% |
3.2 |
|
Customer Satisfaction |
80% |
80% |
90% |
90% |
85% |
-
VII. Conclusion And Future Work
Agile development methodologies are popular in the software industry due to efficient delivery of quality software. These methodologies focused on customer requirements and company objectives. Scrum and XP are one of the widely practiced agile development methodologies. XP and Scrum contain good features but they also have some limitations. Scrum does not provide much more about how to engineer a product while XP lacks in management practices.
The purpose of this research is to enhance the quality of successful products by proposing a novel hybrid model. This model is enriched with the good features of both XP and Scrum by removing their limitations. The proposed model is a project management paradigm and it has the ability to produce quality software product that is aligned with customer requirements and company objectives. The results of case study shows that productivity and retrospective are increasing from sprint to sprint due to learning of the authors and team. The future work is to test the proposed model using industrial environments.
Список литературы Novel Hybrid Model: Integrating Scrum and XP
- Pressman R. S. Software Engineering. McGraw Hill, USA, 2010.
- Li Jiang, Armin Eberlein. Towards a framework for understanding the relationships between classical software engineering and agile methodologies. In: Proceedings of the 2008 international workshop on Scrutinizing agile practices or shoot-out at the agile corral, Germany, May 2008, 9-14.
- Schwaber K, Beedle M. Agile Software Development with Scrum. Prentice Hall, USA, 2001.
- Jeff S, Anton V, Jack B, Nikolai P. Distributed Scrum: Agile Project Management with Outsourced Development Teams. In: Proceedings of the 40th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Hawaii, 2007, 274a-274a, 2007.
- Williams L, Cockburn A. Agile software development: it's about feedback and change. 2003, Computer, 36(6), 39-43.
- Abrahamson P, Salo O, Ron K. Agile Software Development Methods: Reviews and Analysis. VTT Electronics, 2002.
- Maria P. Sadra D., Casper L. Distributed Agile Development: Using Scrum in Large Projects. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Global Software Engineering, Bangalore, India, August 2008, 87-95.
- Torgeir Dingsoyr, Geir Kjetil Hanssen, Tore Dybal Geir Anker, Jens Olav Nygaard. Developing Software with Scrum in a Small Cross-Organizational Project. In: Proceedings of the 13th European conference on Software Process Improvement, Springer-Verlag Berlin, 2006, 5-15.
- Michele Marchesi, Katiuscia Mannaro, Selene Uras, Mario Locci. Distributed Scrum in Research Project Management. Springer Berlin/Heidelberg, 2007, 240–244.
- Brent Barton, Evan Campbel, Ken. Implementing a Professional Services Organization Using Type C Scrum. In: Proceedings of the 40th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Hawaii, 2007, 275 a-275 a..


