Об условиях ветрового выноса частиц почвы
Автор: Малиновская Елена Александровна, Чхетиани Отто Гурамович
Журнал: Вычислительная механика сплошных сред @journal-icmm
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.13, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В рамках решения задачи о ветровом выносе частиц почвы средствами открытого пакета OpenFOAM исследовано обтекание воздушным потоком при скорости 2-3,1 м/с песчаных сферических частиц диаметром 200 мкм с регулярным расположением на плоскости на расстояниях друг от друга, близких или меньших их диаметра с зазорами 50-250, 300 и 700 мкм. Применена многоуровневая сетка с адаптацией под форму элементов микрорельефа и сглаживающая область контакта сферических частиц с нижней плоскостью цилиндрическими формами малого радиуса. В расчетах для ветрового выноса рассматривается k-тип неровностей с большими расстояниями (превышающими 300 мкм). Близость значений поверхностного сопротивления для зазоров между частицами 50 и 300-700 мкм говорит о важности учета движения потока в порах среды (внутри плотно уложенного слоя). На основе данных о порозности песка оценены средние расстояния между частицами, показано, что они соответствуют d-типу неровностей поверхности, случаю, когда в слое существенны процессы между частицами. При расстояниях 100-250 мкм для области между частицами характерно наличие зон рециркуляции, что определяет на порядок большие значения поверхностного сопротивления. Динамическая скорость максимальна при 200 мкм и минимальна при 100 мкм и с изменением расстояния между частицами становится близкой к критической, при которой возможен вылет частицы такого размера с поверхности (по данным экспериментов). Значения высоты вязкого приповерхностного слоя, которая связана с параметром шероховатости, для разных расстояний между частицами хорошо согласуются с эмпирическими данными. Выталкивающая сила, действующая на частицы поверхности, рассчитанная исходя из оценок разности давления на противоположные стороны частицы, максимальна для расстояний между их поверхностями 200 мкм, минимальна при 50 и 100 мкм, и дает обратное - прижимающее к поверхности - воздействие при 150 и 250 мкм.
Ветровой вынос частиц, приповерхностный слой, аэродинамическое сопротивление, выталкивающая сила
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143172488
IDR: 143172488 | УДК: 551.551, | DOI: 10.7242/1999-6691/2020.13.2.14
Текст научной статьи Об условиях ветрового выноса частиц почвы
Ветровое воздействие на частицы песчаной почвы [1–7] приводит к их выносу, который определяет интенсивность поверхностного источника пыльного аэрозоля в атмосфере. Процесс ветрового выноса возможен при превышении скорости ветра воздушного потока над подстилающей поверхностью критических (пороговых) значений [1–12]. Частицы почвы (песка), отрываемые ветром, движутся в приповерхностном слое скачкообразно, ударившись о поверхность, могут отскочить вновь, перекатиться или выбить другие частицы. Такой процесс ветрового выноса называется сальтацией. Сальтационный поток частиц в атмосферу связан нелинейной зависимостью с динамической скоростью трения: u = τ/ρ , где τ — напряжение сдвига, ρ — плотность воздуха [10].
Подстилающая поверхность образована песчаными частицами. Частицы в верхнем слое, контактирующем с ветровым потоком, могут быть подвижными, совершать колебательные движения [1].
Это приводит к изменению локальных характеристик приповерхностного слоя воздуха и формированию на микромасштабах вторичных течений типа струй и вихрей с вертикальной или горизонтальной осью [1, 3].
Ветровой вынос частиц с подстилающей поверхности происходит при совместном воздействии нескольких факторов:
-
- подъемной силы, возникающей при обтекании частицы за счет разности давлений над частицей и под ней [13-16];
-
- силы Магнуса, вызываемой поворотом относительно точки сцепления частицы с подстилающей поверхностью [13-16];
-
- вязких сил при микроциркуляциях [11, 12, 17];
-
- вследствие турбулентных течений [14, 15] и микровихрей вблизи приповерхностного слоя [3].
Каждое из приведенных воздействий имеет место при различных условиях, при этом невозможно полностью объяснить ветровой вынос частицы из слоя только за счет одного из них. Так, отрыв вследствие разности давления над частицей и под ней не позволяет соотносить с ним ветровой вынос при использовании мульчирующего покрытия (в частности слоя соломы [18]) или выдувание из узких перпендикулярных щелей [3]. Влияние силы Магнуса также ограничено, поскольку лишь некоторая доля частиц движется с вращением [19]. Остается открытым вопрос о влиянии возникающих в приповерхностном слое турбулентных течений при условии, что частицы размерами около 200 мкм находятся в ламинарном подслое [20] с малыми скоростями и линиями тока, приближенными к форме подстилающей поверхности. Высота ламинарного подслоя определяется масштабом 5V [21]:
3v = v/u*, где v — коэффициент кинематической вязкости воздуха. От расстояния между частицами зависит характер их обтекания и глубины погружения в ламинарный слой. Для плотно упакованных, почти сферических элементов, таких как частицы песка, высота шероховатости равняется 1/30 части их диаметра. Максимальная шероховатость в 1/8 диаметра возникает, когда расстояние между центрами элементов примерно в два раза больше их диаметра [2].
При скоростях воздушного потока, близких к пороговому значению, процесс ветрового выноса сопровождается периодами покоя и активизируется при наличии турбулентного режима [22]. Незначительные локальные изменения скорости обтекания частиц и характеристики подстилающей поверхности влияют на реализацию одного из типов движения частицы: или перекатывания, или смещения, или подъема [14]. Возникающие вследствие подвижности частиц возмущения воздушной среды в ламинарном подслое [23, 24] меняют сам режим обтекания и создают условия для зарождения микровихрей. Флуктации давления в приповерхностном слое связаны с напряжением сдвига [25]. Возникают вертикальные потоки и вихри, увеличивающие начальный импульс вылетающей с поверхности частицы, а, следовательно, высоту ее подъема. Следует отметить также наблюдаемое в полевых экспериментах квазипериодическое изменение со временем концентрации сальтирующих частиц [26, 27], связанное, по всей видимости, с неоднородностями эолова (созданного ветром) микрорельефа.
Подвижность частиц в слое и падение сальтирующих частиц [27] приводит к изменению режима обтекания поверхности слоя от ламинарного к турбулентному на расстояниях, соизмеримых с размерами частиц [7]. Источниками изменения режима обтекания песчаной поверхности являются особенности ее структуры, вызванные взаимным расположением частиц, их подвижностью и процессами теплового перемешивания в воздушной среде. В результате образования вертикальных потоков после первоначального воздействия на частицы улучшаются условия их ветрового выноса из граничного слоя подстилающей поверхности. Поэтому важно исследовать обтекание частиц в слое, условия появления восходящих потоков у его поверхности и причины возникновения пороговых скоростей выноса.
Для численного изучения данной проблемы в настоящей работе рассматривается несколько идеализированная постановка эксперимента — обтекание воздушным потоком конфигурации частиц с последовательным расположением на плоскости. При этом учитывается влияние на изменение разности давлений с противоположных сторон частиц и поверхностного сопротивления, в частности, из-за изменений расстояния между частицами. Конкретно обтекаемая поверхность представляется как плоскость, на которой на коротких цилиндрических основаниях радиуса 60 мкм регулярно расположены сферические частицы с радиусом 100 мкм. Такая конфигурация принята для минимизации ошибок при построении сетки в области контакта сферической частицы с нижней плоскостью.
Эксперименты проводились для следующих значений параметров процесса обтекания:
- расстояния между поверхностями частиц составляли 50, 100, 150, 200 и 250 мкм;
- скорости воздушного потока на высоте 1 мм имели значения от 2,0 до 3,5 м/с и рассматривались с шагом 0,1 м/с в динамике по времени с шагом 5 -10-4с для интервала от 0 до 0,01 с, что вполне достаточно с учетом оценки времени прохождения потоком расчетной области (2- 10-3с) = (5^10-3м)/(2,5 м/с).
2. Численное моделирование ветрового выноса3. Исходные данные вычислительного эксперимента
3.1. Анализ параметров ветрового выноса частиц из плотноупакованного слоя
Сопротивление воздушному потоку подстилающей поверхности, составленной частицами при расстояниях между ними 50-300 и 700 мкм, вычислялось для скорости ветра 2,8 м/с над поверхностью слоя. При определении выталкивающей силы, динамической скорости и высоты приземного слоя выбирались значения скорости 2,0; 2,2; 2,5; 2,8 3,1 м/с при расстояниях между поверхностями частиц 50; 100; 150; 200; 250 мкм. Сравнивались данные экспериментов для двух конфигураций: из 9 частиц на поверхности при скорости воздушного потока 2,8 м/с и из 3 последовательно расположенных по направлению движения воздуха частиц. В силу близости полученных результатов для вертикального распределения давлений и скоростей при скорости потока 2,0–3,5 м/с использовалась конфигурация из 3 частиц. Размеры частиц и расстояния между ними в численных экспериментах характерны для процессов ветровой эрозии и сальтации [5, 28]. Скорости воздушного потока соответствуют значениям, известным по экспериментам в ветровых каналах и естественных условиях [12, 24].
Во втором разделе приведен обзор решаемых задач и методов численного моделирования, применяемых в задачах исследования ветрового выноса частиц с поверхности эоловых рельефов. В третьем разделе описываются характерные для природных условий расстояния между частицами при их различных ориентациях и рассматриваются детали численного моделирования, модели и методы. В четвертом разделе представлены результаты вычислительного эксперимента: определены характер обтекания и изменение разности давлений у поверхности частицы для различных расстояний между частицами; дается оценка сил, выталкивающих частицу с поверхности.
Возможности численного моделирования [15, 29–53] позволяют более детально исследовать структуру обтекающего потока при изменении формы элементов поверхности и рассматривать условия отрыва частиц на микроуровне. В численных экспериментах [29, 31, 34, 35, 36, 39, 40, 42–44] отмечается существенное влияние эоловых форм рельефа, структуры отдельных элементов [29, 38, 45] на характеристики воздушного потока [15, 41], на появление турбулентных структур [33, 34], на распределение концентраций эоловых частиц в приповерхностном слое [15, 46]. Оценивается сопротивление частиц [35, 38, 45], которое возрастает при увеличении плотности образуемого ими покрытия [35], при изменении формы обтекаемых объектов [38, 45]. В [15, 30, 41, 44, 46] с применением лагранжевой модели изучается взаимодействие воздушной среды со слоем плотноупакованных шарообразных частиц. Влияние потока на связанные частицы рассмотрено в [49, 50]. При анализе структуры воздушного потока, обтекающего небольшие дюны или рябь, используются к -е [39, 40, 41] и LES [15, 37] модели турбулентности. На больших масштабах моделирование пограничного слоя атмосферы осуществляется с учетом дополнительного уточнения к -е модели [42].
В описываемых здесь исследованиях применялся открытый пакет OpenFOAM [53]. Известны его приложения к решению задач моделирования структуры обтекающего потока вблизи эоловых форм рельефа [36, 38]. В [36] использовался решатель PimpleFOAM, а в [38] — PisoFOAM. В пакете OpenFOAM заложены различные реализации турбулентных моделей и возможности учета поверхностей сложной формы.
Для размеров частиц почв пустынь характерен логнормальный закон распределения [12, 54], согласно которому функция плотности вероятности имеет вид:
0,43429
f ( x ) =-----/т= exP
O lg x x v 2п
( lg x - lg x 0 ) 2
lg x
Здесь: x — размер песчинок, мкм; x0 — средний геометрический размер песчаной частицы, мкм; о — среднеквадратичное отклонение логарифмов размеров частиц. Для оценки характерных расстояний между частицами и их ориентации в слое песка с учетом распределения по размерам решалась задача, алгоритм которой был реализован в виде программы на языке С++.
В двумерном, сгенерированном случайным образом слое из n частиц круглой формы, размеры которых соответствуют распределению (1), определены координаты их центров при заполнении слоя снизу вверх при условии, что пары частиц соприкасаются между собой только в одной точке. Для случайной укладки в несколько слоев, начиная с первой цепочки частиц, выстроенных в линию, при перемещении снизу вверх найдено число взаимодействующих частиц (3, 4 или 5) вокруг каждой точки, не содержащей частицы (Рис. 1 а ). Доля таких групп соседей для пространственных структур из 5 частиц составляет т6 = 0,06 от общего числа, m5 = 0,6 — для групп из 4 частиц и m4 = 0,34 — для групп из 3 частиц (Рис. 1 б) .
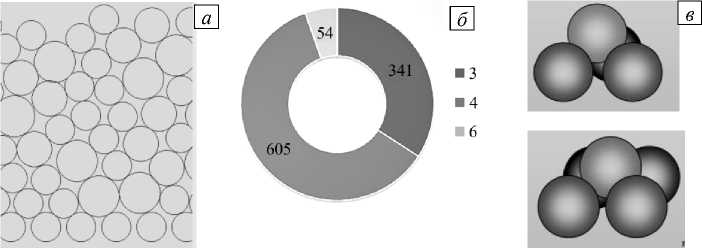
Рис. 1. Результат численной генерации случайно расположенных частиц, размеры которых соответствуют нормальному распределению ( а ); распределение по числу связанных частиц (3, 4 и 6 частиц) для тысячи случаев ( б ); структуры из 4 и 5 взаимодействующих частиц ( в ), модель частицы с использованием цилиндров в основании ( г )
Выяснено, что в плоском варианте число соседствующих частиц может равняться 3, 4 или 5, причем чаще 4 или 5. В объемном представлении более вероятны пирамидальные структуры из 4 взаимодействующих частиц (3 частицы в основании и 1 сверху) или из 5 частиц (4 частицы в основании, 1 сверху) (Рис. 1 в ). При этом система из 4 или 5 взаимодействующих частиц может быть развернута горизонтальной плоскостью (основанием) к направлению воздушного потока под различными углами, и, в зависимости от ориентации по отношению к потоку, будет меняться расстояние между устойчивыми верхними частицами.
Оценим характерные расстояния между частицами одинакового размера при 3 и 4 взаимодействующих частицах в основаниях. У 4 соседствующих частиц (1 частица лежит сверху на 3 других в пирамидальной структуре) при отсутствии зазоров между поверхностями межцентровое расстояние, в зависимости от ориентации структуры по направлению к движению воздушного потока, меняется от
( V3 ) r до 2 r ;
при максимальных зазорах между частицами расстояние колеблется от
2 (^)
r до 6 r . У 5 соседствующих
частиц (1 частица лежит на 4 других в пирамидальной структуре) при отсутствии зазоров расстояние
2 (V2)
между центрами меняется от 2 r до
r ; при этом максимально возможное расстояние укладывается в диапазон от
4 ( V2 ) r до 4 r .
Объемная доля пустот в слое определяет безразмерную величину порозности песка: е = 1 -т , где т — объемная концентрация твердой фазы. Так, для песков величина плотности твердой фазы (плотность частиц) есть рр = 2600 кг/м3, а плотность песка р5 = 1670 кг/м3, и реальная порозность песков равняется ек = 0,33 [28]. В пирамидальной структуре из 4 соседствующих частиц порозность минимальна: е4 = 0,28, при 5 частицах е5 = 0,21. Если принять, что в структуре имеется только два варианта укладки частиц, то с учетом процентного соотношения числа взаимодействующих 3 или 4 частиц в основании, полученных при численной генерации, получим приближенно заниженное значение порозности для случая, когда отсутствуют зазоры: е45 ® 0,24. Чтобы значение порозности стало выше, можно увеличить расстояние между поверхностями соседствующих частиц. Таким образом, подбирается величина параметра D — оптимального минимального расстояния между поверхностями частиц (наименьшего расстояния между поверхностями частиц, лежащих в одной плоскости), при котором порозность расчетная е4m4 +е5m5 соответствует порозности реальной ек . Приближенно D имеет значения:
-
- D ® 0,15 r при ориентации системы последовательно расположенных 4 и 5 взаимодействующих частиц
по направлению движения потока;
-
- D5 ~ 0,2 r при диагональном или угловом расположении системы из 4 соседствующих частиц;
-
- D4 ® 0,255 r при диагональном или угловом расположении системы из 5 соседствующих частиц.
-
3.2. Исходные данные
Так как средний размер частиц песка составляет 200 мкм [7], а их радиус приближен к 100 мкм, то наиболее характерные расстояния между поверхностями частиц будут заключены в пределах от 15 до 26 мкм. Если из такого плотно уложенного слоя убрать центральную частицу, расположенную между двумя другими при их последовательном расположении по направлению движения воздушного потока, то расстояние между оставшимися крайними частицами окажется равным 230–250 мкм.
Особенностями взаимного расположения частиц обуславливаются расстояния между их поверхностями. Расстояния варьируются в пределах от 0 до 200–280 мкм. При этом фактическое среднее наиболее характерное расстояние, рассчитанное для порозности песка, соответствует 15–26 мкм. Так как пески постоянно перевеиваются ветрами, а в зависимости от расстояний между частицами меняется вероятность отрыва частицы и, возможно, механизм ветрового выноса, то получается, что вследствие этого и формируется внутренняя структура песка. В частности, характерное расстояние между частицами предопределяет вероятность реализации того или иного типа первоначального перемещения в слое: будет это горизонтальное или вертикальное движение, или поворот относительно точки сцепления. В связи с этим в последующих разделах исследуется влияние расстояния между частицами на возможность ветрового выноса.
Множество комбинаций расположения частиц характеризуется сложной структурой взаимосвязей, дает многообразие состояний и типов реакции на ветровое воздействие, определяет локальные характеристики давления и скорости воздушного потока над микрорельефом.
Обтекание поверхности слоя частиц рассматривалось в рамках ламинарной модели из открытого пакета OpenFOAM. Использовался решатель RhoPisoCentralFOAM с итерационным методом Гаусса–Зейделя для решения системы линейных алгебраических уравнений. Для численного нахождения характеристик потоков в слое за основу принималось движение несжимаемой неизотермической среды с учетом теплового переноса [51]:
— + V-(u®u) = —1Vp + V-П, Vu = 0 , dt V P P рCI — + V • (uT) I = V ■ (XVT) + П : (Vu)T .
Здесь: t — время процесса; V — оператор Гамильтона; p — давление; T — температура; ц — динамическая вязкость; р — плотность воздуха; u — векторное поле скоростей воздушного потока; X — коэффициент теплопроводности; Π ˆ — тензор нормальных вязких напряжений; C — удельная изохорная теплоемкость.
а
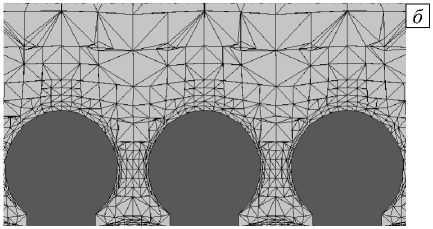
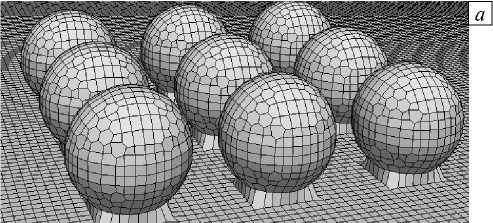
Рис. 2. Вид адаптированной 4-уровневой сетки для вычислительного эксперимента: на поверхности частиц ( а ), в вертикальном сечении, проходящем через центр расчетной области ( б )
Область 5000 x 5000 x 1000 мкм, занимаемая обтекающей средой, разбивалась на два слоя в связи с особенностями установления граничных условий в применяемом пакете. В верхнем слое задавался поток с характерным для этой высоты в условиях переноса частиц значением скорости [12, 24], в нижнем слое на левой и правой стенках — свободный поток со значением internalField, на нижней стенке и поверхности частиц выполнялось условие прилипания. Обтекаемый объем построен средствами 3D моделирования. Частицы имели форму сферы, были посажены на цилиндры меньшего радиуса (Рис. 1 г ). Этот технический прием выполнялся для устранения ошибок вычислений, связанных с разной величиной погрешности построения 3D-поверхностей и размером минимального звена сетки. Для послойного представления сетки с адаптацией под форму поверхности использовалась утилита SnappyHexMesh приблизительно с 10 6 узлами (их число различно при изменении геометрии взаимного расположения частиц) и минимальным шагом сетки 4 мкм (Рис. 2). В результате получен вид поверхности, покрытой сеткой (Рис. 2 а ), от которой строится 3D-сетка для всей вычислительной области (Рис. 2 б ). Частицы располагались на плоскости, параллельной направлению движения воздушного потока в центре области. Скорость воздушного потока на высоте 1 мм от поверхности соответствовала значениям 2,1 или 2,8–3,1 м/с [12, 24] над различными элементами эоловой ряби. В таблице 1 приведены ее экспериментально измеренные значения.
Для перегретой поверхности, характерной для песков пустынь, отмечается скачок температур у самой поверхности за счет процессов теплообмена воздуха с поверхностью, который по оценкам в [11] составляет от ~1 до 5 К на уровне z0 = 0,0001м. Для вычислительного эксперимента температура
Таблица 1. Значения скорости воздушного потока над различными элементами поверхности с формой эоловой ряби [12]
|
Z , мм |
Скорость ветра, м/с |
|||
|
над склоном |
над гребнем |
за гребнем |
на дне |
|
|
0,5 |
2,8 |
2,8 |
1,2 |
2,1 |
|
1,5 |
3,1 |
3,1 |
2,1 |
2,3 |
|
z 0 , см |
0,002 |
0,002 |
0,010 |
0,010 |
|
u , м/с |
0,24 |
0,25 |
0,32 |
0,31 |
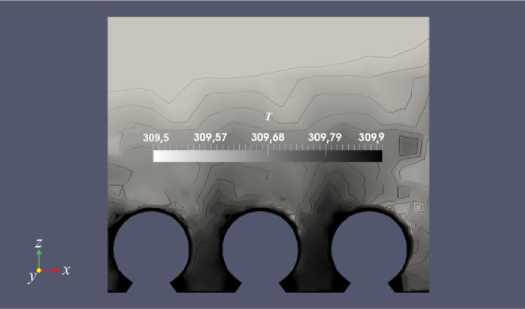
Рис 3. Мгновенное распределение температуры в момент времени 0,08 с в вертикальном сечении, проходящем через центр расчетной области, для умеренно разогретой поверхности
поверхности устанавливалась равной 312 K, а начальное значение температуры в расчетной области и на верхней границе — 310 K. При таких значениях вклад температуры в поле скорости между частицами на поверхности незначителен. Заметные эффекты возможны здесь при большем прогреве и штилевых условиях [17]. На рисунке 3 представлено температурное поле для случая преобладания ветрового воздействия при умеренном прогреве поверхности, когда не возникает конвективных потоков.
В следующем разделе приведены результаты серии вычислительных экспериментов, осуществленных при разных значениях скорости воздушного потока и расстояний между поверхностями частиц.
4. Результаты вычислительного эксперимента
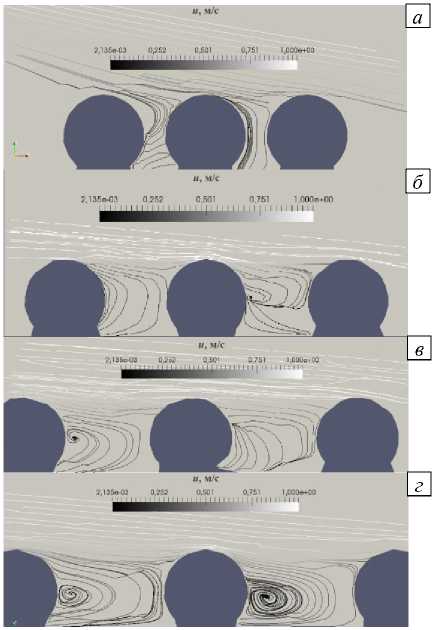
Рис. 4. Линии тока при обтекании слоя частиц при различных расстояниях D , мкм: 50 ( а ), 150 ( б ), 200 ( в ) и 250 ( г )
-
4.1. Влияние расстояния между частицами на характер обтекания и изменения скорости воздушного потока около частиц
Реализация того или иного типа первоначального перемещения в слое при ветровом выносе частиц зависит от структуры поверхности слоя, от расстояния между частицами и их подвижности в слое [22], а первоначальное перемещение влияет на особенности обтекания слоя частиц воздушным потоком (Рис. 4). В таблице 2 представлены вычисленные значения скорости потока у верхушек частиц, скорости потока в области между частицами, наличия (+) или отсутствия (–) микровихря после отрыва потока от
Таблица 2. Значения и параметры, полученные из вычислительных экспериментов при разных расстояниях между частицами
|
Расстояние между поверхностями частиц, D , мкм |
Скорость потока у поверхности слоя частиц uus , м/с |
Скорость потока в области между частицами, м/с |
Закручивание потока в области между частицами |
|
50 |
0,8–1,0 |
0,5–1·10–4 |
– |
|
100 |
1,1–1,4 |
7,4–7,6·10–4 |
– |
|
150 |
2,1–2,5·10–3 |
+ |
|
|
200 |
7–7,2·10–4 |
+ |
|
|
250 |
1,1–1,3·10–2 |
+ |
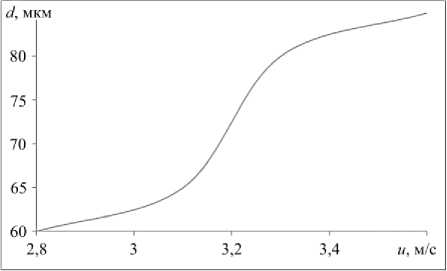
Рис. 5. Размер зоны рециркуляции d , мкм, в зависимости от скорости воздушного потока над подстилающей поверхностью
частицами на уровне их верхушек составляет
поверхности в области между частицами для расстояний между поверхностями частиц от 50 до 250 мкм.
При увеличении скорости воздушного потока над поверхностью слоя частиц относительное увеличение диаметра зоны рециркуляции изменяется в исследуемой области от 60 до 85 мкм (Рис. 5). В данной статье оно полагается равным длине отрезка d , соединяющего точки на крайнем витке линии тока, симметричные относительно центра частицы.
Рассмотрим аэродинамическое сопротивление
G f , определяемое как G, = Дт , где т = П — [35]. pu 9z
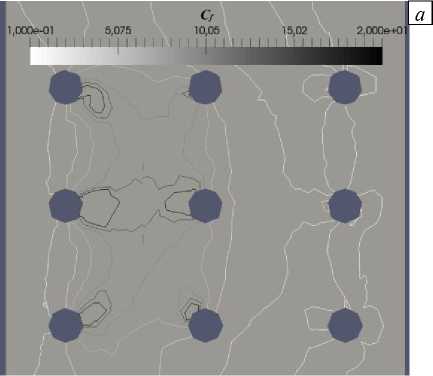
Его среднее значение для области между 1,9r при расстояниях между поверхностями частиц на линии их центров 50, 150, 200, 250, 300 и 700 мкм и оказывается максимальным для 250 мкм (Рис. 6). Это соответствует значению плотности покрытия поверхности Хр = 0,2 (Хр = 4r2nJS , n — число частиц, S — площадь подстилающей поверхности [58]). Для меньших или больших значений Хр сопротивление падает [35] (Рис. 7).
1,0006-01
5,075
15,02
2,000е- а
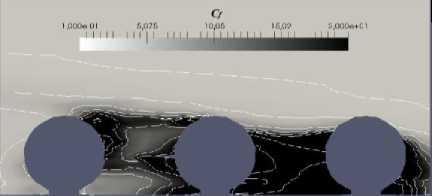
Рис. 6. Изменение сопротивления на горизонтальной плоскости вблизи частиц на высоте их верхушек ( а ) и на вертикальной плоскости ( б )
— CV по данным [57] по формуле (10)
А Су по данным [35] для кубиков на плоскости х С, из вычислительного эксперимента
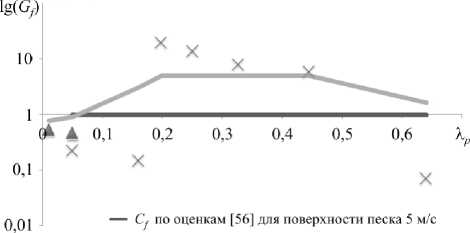
Рис. 7. Зависимость величины сопротивления G для области около частиц от плотности покрытия
Полученные для расстояний D = 700 мкм между поверхностями шариков (когда Хр = 0,05) значения
G в целом
весьма близки к оценкам
коэффициента сопротивления для песчаной поверхности при скорости потока 5 м/с [56]. Они оказались также близкими к значениям коэффициента сопротивления для частиц в форме кубиков, распределенных на плоскости [35].
Имеет место хорошее согласование найденных значений с рассчитанными по формуле (10) из [57]: С = 24 ( 1 + 0,15 Re 0 ’ 687 ) /Re, с учетом изменения
скорости потока в зависимости от
(здесь Re
подстилающей поверхности
соответствуют расстояниям
Х (значения Х pp между поверхностями
частиц D , мкм: 50, 100, 150, 200, 250, 300, 700)
у поверхности частиц расстояния между ними
число Рейнольдса). Величина
сопротивления для расстояний от 100 до 250 мкм между поверхностями частиц на порядок выше, чем для расстояний от 50 и 300–700 мкм. Границы разных больших значений сопротивлений
при условиях Хр < 0,2 и Хр > 0,6 соответствуют расстояниям между частицами D < 5 г /2 и D > г /2,
для которых отмечается появление зоны рециркуляции в области между частицами.
C увеличением расстояния между частицами от 100 до 250 мкм уменьшается коэффициент сопротивления. Менее резкое изменение сопротивления для 150–250 мкм связано, вероятно, с появлением микровихря в области между частицами, за счет чего коэффициент сопротивления оказался в 1,5 раза меньше, чем максимальное значение.
-
4.2. Оценка сил, выталкивающих частицу с поверхности,
на основе данных вычислительных экспериментов
Расстояние D = 200 мкм между поверхностями частиц является особым случаем d-типа неровностей (близких к кубической форме углублений между элементами шероховатости) [52]. Для них постоянно напряжение сдвига над подстилающей поверхностью, которое обуславливается влиянием на движение потока циркуляций между препятствиями. Изменение расстояний относительно величины 200 мкм приводит к увеличению эффективной шероховатости как для случая плотноупакованного слоя, так и в 4 раза для случая D > 2 r , который используется в расчетах при исследованиях ветрового выноса частиц. Увеличение эффективной шероховатости приводит к увеличению потока сальтации [27] и уменьшению значения динамической скорости [11, 55]. При D > 2 r рассматриваются неровности k-типа (для плоских углублений прямоугольной формы между элементами шероховатости), где не учитываются процессы в порах [11]. Однако сама поверхность близка в большей степени по структуре к d-типу.
Для расстояния D = 2 r , соответствующего 200 мкм наблюдаются, наибольшие возможные значения динамической скорости и, = ^ ( ц/р )( 5 и /5 z ) при различных скоростях ветра (Рис. 8). Вероятно, это связано с тем, что минимально расходуется энергия потока при взаимодействии с поверхностью. Для расстояний | D - 2 r | = 50 мкм (150 и 250 мкм) зависимости похожи на u , близкие к пороговым значениям [2] и [5]. Кроме этого, наблюдается резкое увеличение u при значениях скорости над поверхностью слоя частиц, больших 2,9 м/с.
Для расстояний D = r =100 мкм и D = г /2 = 50 мкм динамические скорости минимальны. При этом самые низкие значения соотносятся с D = r =100 мкм. Энергия потока над поверхностью слоя частиц расходуется на процессы взаимодействия с частицами, вследствие которых происходит относительное возрастание динамического давления на нижней поверхности частиц.
Эффективная шероховатость линейно связана с величиной Хр [58], что определяет высоту вязкого приповерхностного слоя 5V, где отмечается линейный профиль скорости. Вычислены значения 5V при скоростях 2,0; 2,8; 3,1 м/с воздушного потока над поверхностью. В целом она уменьшается в зависимости от расстояния между частицами, что соответствует расчетным значениям [58] (Рис. 9).
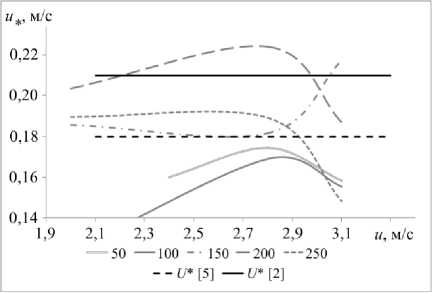
Рис. 8. Зависимость динамической скорости u от скорости воздушного потока u в верхнем слое расчетной области над частицами для расстояний D , мкм: 50, 100, 150, 200, 250; для сравнения приведены кривые пороговых скоростей U*
из работ [2] и [5]
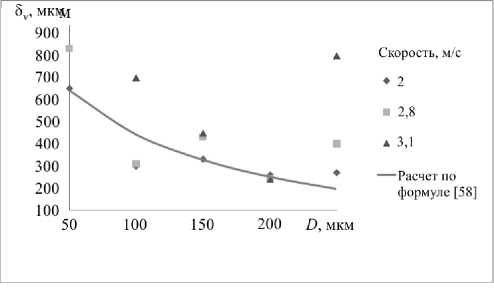
Рис. 9. Изменение величины эффективной шероховатости поверхности слоя частиц в зависимости от расстояний D , мкм: 50, 100, 150, 200, 250 при различных значениях скорости воздушного потока
На основе оценок разности давлений над и под частицей в зависимости от расстояния D между их поверхностями можно получить значения сил, выталкивающих частицы из слоя (Рис. 10) .
Согласно вычислительным экспериментам, сила, возникающая за счет разности давления на противоположные стороны частиц (выталкивающая сила F ), сопоставима с силой сцепления
Ван-дер-Ваальса [57]: Fa = Car , где Ca = 0,0024 Н/м. Сила Fc максимальна для расстояний между
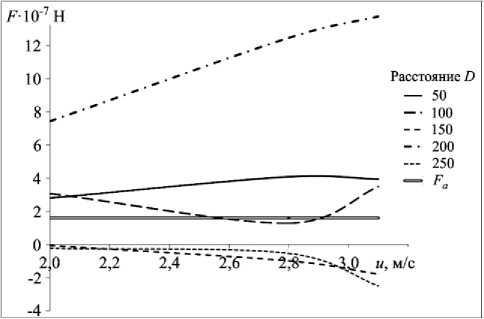
Рис. 10. Выталкивающая сила F - 10 7 Н, действующая на частицы в слое, в зависимости от значений скорости воздушного потока над его поверхностью при различных расстояниях между поверхностями частиц; для сравнения приведена кривая сил Ван-дер-Ваальса F
поверхностями частиц D около 200 мкм. Для расстояний 100–150 и более 250 мкм отрыв частицы от поверхности слоя маловероятен, так как по оценкам величина выталкивающей силы соизмерима с силой сцепления или отрицательна. Для плотно уложенного слоя, когда расстояние между поверхностями частиц около 50 мкм, отрыв частицы возможен, а вылет на большую высоту маловероятен, так как выталкивающая сила давления близка по величине к силе сцепления.
Силы, выталкивающие частицы из слоя, максимальны при расстояниях между поверхностями частиц, близких к их диаметру. При расстояниях между поверхностями частиц, меньших их диаметра, отмечается тенденция к закручиванию потока, обтекающего частицы, в области между ними так же, как и при движении потока над прямоугольной каверной. За счет этого давление в нижней области частиц уменьшается. Для расстояний, близких к диаметру, разность давлений максимальна. Отмечаются относительно большие значения выталкивающей силы. При расстояниях между поверхностями, близких к 100 мкм, частицы не могут вылетать с поверхности. Расстояние между частицами влияет на механизм начального выталкивания из слоя и создает особенности движения потока у поверхности слоя частиц (Рис. 9).
Сопоставляя все оценки (см. Рис. 6–10), можно заключить, что выталкивающая сила определяется изменением динамической скорости u и величиной эффективной шероховатости для разных расстояний между частицами, образующими регулярную структуру поверхности. Условно можно выделить два сценария поведения потока около частиц: с преобладанием горизонтального и с преобладанием вертикального движений. Первый сценарий применим для расстояний D от 150 до 250 мкм, а второй — для D < 50 мкм. Инициировать начальный процесс ветрового выноса частиц достаточно трудно.
При возникновении в слое неоднородностей в виде отсутствующих (унесенных) частиц и увеличении расстояний между их поверхностями от 50 мкм до 250 мкм (для радиуса частицы 100 мкм) получаются условия, при которых маловероятен отрыв частиц. Следует отметить, что для больших расстояний увеличивается горизонтальная разность давлений на боковых поверхностях частицы, происходит ее перекатывание или горизонтальное смещение в граничном слое подстилающей поверхности без отрыва.
5. Заключение
По данным о порозности песка определено, что наиболее характерные расстояния между поверхностями частиц в слое соответствуют 15–26 мкм, при этом из геометрических соображений они могут увеличиваться до 280 мкм. В серии вычислительных экспериментов средствами открытого пакета OpenFOAM частицы сферической формы радиусом 100 мкм располагались последовательно с разными расстояниями друг от друга 50, 100, 150, 200, 250 мкм под воздействием горизонтально направленного воздушного потока.
Для случая d-типа неровностей поверхности, когда существенны процессы в слое между частицами, оценивались следующие параметры:
– выталкивающая сила, возникающая за счет разности давлений на противоположных сторонах частицы;
– размеры зон рециркуляции в области между частицами, скорости над частицами u ;
– поверхностное сопротивление потоку;
– установление динамической скорости u около частиц при заданных расстояниях и различных скоростях воздушного потока u .
Рассматривалась идеализированная ситуация с регулярными частицами одного размера, при этом предполагалось, что удается уловить некоторые основные черты происходящих процессов при изменении расположения частиц относительно друг друга.
Вертикальный градиент давления, возникающий при взаимодействии потока с частицами и определяющий возможность отрыва частицы от поверхности, зависит от расстояния между ними и максимален для его значения 200 мкм. Для расстояний между поверхностями частиц около 50 мкм выталкивающая сила близка к величине силы сцепления Ван-дер-Ваальса, ветровой вынос частиц отсутствует, а для D , равных 100, 150 мкм он маловероятен.
Скорость движения потока u у верхней кромки рельефа возрастает при увеличении расстояния между частицами. Так, скорость потока uus в области между частицами при D = 250 мкм на порядок выше скоростей при расстояниях 150–200 мкм. Отмечается локальный максимум скорости обтекания при D = 150 мкм, минимум при D = 50 мкм.
На порядок отличаются значения поверхностного сопротивления для зазоров между частицами 50 и 300–700 мкм от наибольших для 100–250 мкм, что определяется наличием в области между частицами зоны рециркуляции. При увеличении расстояний между частицами возникает закручивание потока в области между частицами, которое наиболее интенсивно для D = 250 мкм. Полученные близкие значения для сопротивлений при малых зазорах 50 мкм и больших расстояниях, которые соответствуют k-типу шероховатости обтекаемой поверхности, положенные в основу теоретических расчетов в моделях ветрового выноса, говорят о важности учета движения потока в порах среды (внутри плотно уложенного слоя).
Для расстояний между поверхностями частиц 200 мкм устанавливается такой профиль движения потока у поверхности слоя из них, для которого динамическая скорость u максимальна в сравнении с другими вариантами расположения, и превышает критическое значение, при котором возможен отрыв. Для величин зазора, относительно близких к 200 мкм (150 и 250 мкм), динамическая скорость демонстрирует похожее поведение для всех значений вплоть до ~ 2,9 м/с, затем она начинает сильно отклоняться. Для 100 мкм динамические скорости u минимальны, при уменьшении расстояния между частицами они увеличиваются до величины, близкой к критической. Оценки высоты вязкого приповерхностного слоя 5V для разных расстояний между частицами показали хорошее соответствие эмпирической линейной связи этой величины параметру шероховатости. Вследствие нелинейной связи динамической скорости u со скоростью потока над поверхностью u процесс ветрового выноса имеет пороговый характер.
Так как при расстояниях 100–150 и 250 мкм между поверхностями частиц их ветровой вынос маловероятен, а при 200 мкм выталкивающая сила максимальна, отдельные частицы выносятся из плотно уложенного слоя с расстояниями D < 50 мкм. На месте вынесенной частицы появляется область с D от 200 до 250 мкм. Поэтому на динамику дальнейшего процесса ветрового выноса влияют перемещения частиц внутри слоя при изменении расстояний между оставшимися частицами. Критическая скорость ветрового выноса определяется особенностями структуры плотно уложенного слоя и возможностью начальной инициации ветрового выноса частиц.
Исследование выполнено при поддержке Российского научного фонда (грант 20-17-00214).
Список литературы Об условиях ветрового выноса частиц почвы
- Chou Y.J., Fringer O.B. A model for the simulation of coupled flow bed form evolution in turbulent flows // J. Geophys. Res. 2010. Vol. 115. C10041.
- Greeley R., Iversen D.J. Wind as geological process of Earth, Mars, Venus and Titan. New York: Cambridge University press, 1985. 333 p.
- Гендугов В.М., Глазунов Г.П. Ветровая эрозия почвы и запыление воздуха. М.: Физматлит, 2007. 238 с.
- Baas J.H., Best J.L., Peakall J. Depositional processes, bedform development and hybrid bed formation in rapidly decelerated cohesive (mud-sand) sediment flows // Sedimentology. 2011. Vol. 58. P. 1953-1987.
- Shao Y. Physics and modeling of wind erosion. Springer, 2008. 452 p.
- Lu H. An integrated wind erosion modeling system with emphasis on dust emission and transport / PhDoctor Dissertarion in Mathematical Science, Sydney: School of Mathematics The University of New South Wales, 1999. 185 p.
- Pye K., Tsoar H. Aeolian sand and sand dunes. Springer, 2009. 458 p.
- Nikuradse J. Laws of flow in rough pipes. Washington: NACA, 1950. 61 p.
- Горчаков Г.И., Карпов А.В., Копейкин В.М., Злобин И.А., Бунтов Д.В., Соколов А.В. Исследование динамики сальтирующих песчинок на опустыненных территориях // ДАН. 2013. Т. 452, № 6. С. 669-676.
- Bagnold R.A. The physics of blown sand and desert dunes. Springer, 1973. 265 p.
- Бютнер Э.К. Динамика приповерхностного слоя воздуха. Л.: Гидрометиздат, 1978. 156 с.
- Семенов О.Е. Введение в экспериментальную метеорологию и климатологию песчаных бурь. Алматы, 2011. 580 с.
- Anderson R.S., Hallet B. Sediment transport by wind: toward a general model // GSA Bulletin. 1986. Vol. 97(5). P. 523-535.
- Dey S., Ali S.Z. Advances in modeling of bed particle entrainment sheared by turbulent flow // Phys. Fluid. 2018. Vol. 30. 061301.
- Huang G., Le Ribault C., Vinkovic I., Simoëns S. Large-eddy simulation of erosion and deposition over multiple two-dimensional gaussian hills in a turbulent boundary layer // Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 2019. Vol. 173. P. 193-222.
- Малиновская Е.А. Модель отрыва песчаной частицы ветром // Изв. РАН. Физика атмосферы и океана. 2017. Т. 53, № 5. С. 588-596.
- Чхетиани О.Г., Калашник М.В., Ингель Л.Х. Генерация "теплового ветра" над неоднородно нагретой волнистой поверхностью // Изв. РАН. Физика атмосферы и океана. 2013. Т. 49, № 2. С. 137-143.
- Ильин А.Н., Васильев О.А., Ильина Т.А., Никитин К.П. Влияние ресурсосберегающей технологии на плодородие серой лесной почвы // Аграрный научный журнал. 2015. № 7. С.18-22.
- Xie L., Ling Y., Zheng X. Laboratory measurement of saltating sand particles' angular velocities and simulation of its effect on saltation trajectory // J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007. Vol. 112. D12116.
- Zheng X. Mechanics of wind-blown sand movements. Springer, 2009. 309 p.
- Lorenz R.D., Zimbelman J.R. Dune worlds: How windblown sand shapes planetary landscapes. Springer, 2014. 308 p.
- Williams J.J., Butterfield G.R., Clark D.G. Aerodynamic entrainment threshold: effects of boundary layer flow conditions // Sedimentology. 1994. Vol. 41. P. 309-328.
- Pähtz T., Valyrakis M., Zhao X.-H., Li Z.-S. The critical role of the boundary layer thickness for the initiation of aeolian sediment transport // Geosciences. 2018. Vol. 8. 314.
- Lämmel M., Rings D., Kroy K. A two-species continuum model for aeolian sand transport // New J. Phys. 2012. Vol. 14. 093037.
- Emmerling R. The instantaneous structure of the wall pressure under a turbulent boundary layer flow // Mitteilun-gen aus dem Max-Planck Institut für Strömungsforschung. 1973. B. 9. P. 1-25.
- Горчаков Г.И., Карпов А.В., Кузнецов Г.А., Бунтов Д.В. Квазипериодическая сальтация в ветропесчаном потоке на опустыненной территории // Оптика атмосферы и океана. 2016. Т. 29, № 6. С. 472-477.
- Martin R.L., Kok J.F. Distinct thresholds for the initiation and cessation of aeolian saltation from field measurements // J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surface. 2018. Vol. 123. P. 1546-1565.
- Куликов А.И., Цыдыпов Б.З., Хамнаева Г.Г., Содномов Б.В. О количественных параметрах загрязнения урбанизированных территорий в контексте процессов опустынивания (на примере г. Закаменска, Республики Бурятия) // Вестник ИрГТУ. 2014. № 12(95). С.75-82.
- Dupont S., Bergametti G., Simoëns S. Modeling aeolian erosion in presence of vegetation // J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surface. 2014. Vol. 119. P. 168-187.
- Biegert E., Vowinckel B., Meiburg E. A collision model for grain-resolving simulations of flows over dense, mobile, polydisperse granular sediment beds // J. Comput. Phys. 2017. Vol. 340. P. 105-127.
- Liu Y., Fang H., Huang L., He G. Numerical simulation of the production of three-dimensional sediment dunes // Phys. Fluid. 2019. Vol. 31. 096603.
- Wang P., Feng S., Zheng X., Sung H.J. The scale characteristics and formation mechanism of aeolian sand streamers based on large eddy simulation // J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019. Vol. 124. P. 11372-11388.
- Wang C., Anderson W. Turbulence coherence within canonical and realistic aeolian dune-field roughness sublayers // Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 2019. Vol. 173. P. 409-434.
- Siminovich A., Elperin T., Katra I., Kok J.F., Sullivan R., Silvestro S., Yizhaq H. Numerical study of shear stress distribution over sand ripples under terrestrial and Martian conditions // J. Geophys. Res. Planets. 2019. Vol. 124. P. 175-185.
- Yang X.I.A., Xu H.H.A., Huang X.L.D., Ge M.-W. Drag forces on sparsely packed cube arrays // J. Fluid Mech. 2019. Vol. 880. P. 992-1019.
- Michelsen B., Strobl S., Parteli E.J.R., Pöschel T. Two-dimensional airflow modeling underpredicts the wind velocity over dunes // Scientific reports. 2015. Vol. 5. 16572.
- Lignarolo L., Gorlé C., Parente A., Benocci C. Large eddy simulation of the atmospheric boundary layer using OpenFOAM // Proc. of the13th Int. Conf. on Wind Engineering. ICWE13, Amsterdam, Netherlands, July 10-15, 2011. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/247778744_Large_eddy_simulation_of_the_atmospheric_boundary_layer_using_OpenFOAM
- Ali M.S.M., Salim S.A.Z.S., Ismail M.H., Muhamad S., Mahzan M.I. Aeolian tones radiated from flow over bluff bodies // Open Mech. Eng. J. 2013. Vol. 7. P. 48-57.
- Araújo A.D., Parteli E.J.R., Pöschel T., Andrade J.S., Herrmann H.J. Numerical modeling of the wind flow over a transverse dune // Scientific reports. 2013. Vol. 3. 2858.
- Faria R., Ferreira A.D., Sismeiro J.L., Mendes J.C.F., Sousa A.C.M. Wind tunnel and computational study of the stoss slope effect on the aeolian erosion of transverse sand dunes // Aeolian Research. 2011. Vol. 3. P. 303-314.
- Kang L., Guo L. Eulerian-Lagrangian simulation of aeolian sand transport // Powder tech. 2006. Vol. 162. P. 111-120.
- Parsons D.R., Wiggs G.F.S., Walker I.J., Ferguson R.I., Garvey B.G. Numerical modelling of airflow over an idealised transverse dune // Environ. Model. Software. 2004. Vol. 19. P. 153-162.
- Schatz V., Herrmann H.J. Flow separation in the lee side of transverse dunes: A numerical investigation // Geomorphology. 2006. Vol. 81. P. 207-216.
- Tong D., Huang N. Numerical simulation of saltating particles in atmospheric boundary layer over flat bed and sand ripples // J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012. Vol. 117. D16205.
- Turpin C., Badr T., Harion J.-L. Numerical modelling of aeolian erosion over rough surfaces // Earth Surface Processes and Landforms. 2010. Vol. 35. P. 1418-1429.
- Zheng X.J., Bo T.L., Xie L. DPTM simulation of aeolian sand ripple // Sci. China Ser. G-Phys. Mech. As. 2008. Vol. 51. P. 328-336.
- Li Y., Guo Y. Numerical simulation of aeolian dusty sand transport in a marginal desert region at the early entrainment stage // Geomorphology. 2008. Vol. 100. P. 335-344.
- Ji S.B., Gerber A.G., Sousa A.C.M. A convection-diffusion CFD model for aeolian particle transport // Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluid. 2004. Vol. 45. P. 797-817.
- Дерябина М.С., Мартынов С.И. Моделирование течения вязкой жидкости с частицами через ячейки пористой среды // Вычисл. мех. сплош. сред. 2016. Т. 9, № 4. С. 420-429.
- Мартынов С.И., Ткач Л.Ю. Динамика цепочечных агрегатов частиц в потоке вязкой жидкости // Ж. вычисл. матем. и матем. физ. 2016. Т. 56, № 5. С. 840-855.
- Гарбарук А.В., Стрелец М.Х., Шур М.Л. Моделирование турбулентности в расчетах сложных течений. СПб: Изд-во Политех. ун-та, 2012. 88 с.
- Perry A.E., Schofield W.H., Joubert P.N. Rough wall turbulent boundary layers // J. Fluid Mech. 1969. Vol. 37. P. 383-413.
- The OpenFOAM® Foundation. http://www.openfoam.org/index.php
- Krumbein W.C. Size frequency distributions of sediments and the normal phi curve // J. Sediment. Res. 1938. Vol. 8(3). P. 84-90.
- Bauer B.O., Houser C.A., Nickling W.G. Analysis of velocity profile measurements from wind-tunnel experiments with saltation // Geomorphology. 2004. Vol. 59. P. 81-98.
- Gu Z., Zhao Y., Li Y., Yu Y., Feng X. Numerical simulation of dust lifting within dust devils-simulation of an intense vortex // J. Atmos. Sci. 2006. Vol. 63(10). P. 2630-2641.
- Roney J.A., White B.R. Definition and measurement of dust aeolian thresholds // J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surface. 2004. Vol. 109. F01013.
- Minvielle F., Marticorena B., Gillette D.A., Lawson R.E., Thompson R., Bergametti G. Relationship between the aerodynamic roughness length and the roughness density in cases of low roughness density // Environ. Fluid Mech. 2003. Vol. 3. P. 249-267.
- Durst F., Miloievic D., Schönung B. Eulerian and Lagrangian predictions of particulate two-phase flows: a numerical study // Appl. Math. Model. 1984. Vol. 8. P. 101-115.
- Krupp H. Particle adhesion: theory and experiment // Advan. Colloid Interface Sci. 1967. Vol. 1. P. 111-239.


