Оценка острого болевого синдрома у пациентов после септопластики при применении различных тактик анестезии
Автор: Калмыков И.К., Торшин В.И., Ермакова Н.В., Синельникова А.Н., Кастыро И.В.
Журнал: Ульяновский медико-биологический журнал @medbio-ulsu
Рубрика: Клиническая медицина
Статья в выпуске: 3, 2021 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Цель исследования заключалась в оценке острого болевого синдрома у пациентов после септопластики при применении различных тактик общей анестезии. Материалы и методы. Ко всем пациентам применяли местную инфильтрационную анестезию 2 % раствором прокаина. В 1-й группе (105 чел.) использовали премедикацию 2 % раствором промедола и 60 мг кеторолака вечером, во 2-й группе (108 чел.) - фентанил, пропофол, цисатракурия безилат, транексамовую кислоту, атропин и метоклопрамид, в 3-й группе (78 чел.) - атракурия безилат, тиопентал натрия, закись азота и галотан. Во 2-й и 3-й группах вечером в день операции внутримышечно вводили 100 мг кетопрофена. Переднюю тампонаду осуществляли поролоновыми тампонами в резиновой перчатке. В 1-й и 2-й группах тампонаду удаляли на 2-й день, а в 3-й группе - через сутки после операции. Болевой синдром оценивали через 1, 3 и 6 ч, 1 и 2 сут после операции с помощью визуально-аналоговой шкалы, вербальной шкалы-«молнии», цифровой рейтинговой шкалы. После удаления тампонов боль оценивали через 1 ч. Результаты. На всех этапах обследования, кроме 2-го дня, болевой синдром был менее выражен во 2-й группе. Через сутки у пациентов 3-й группы боль была выше, чем в остальных. Выводы. При проведении септопластики наименьшую болевую реакцию провоцирует схема общей анестезии, примененная в 3-й группе: фентанил, пропофол, цисатракурия безилат, транексамовая кислота, атропин и метоклопрамид. В условиях тампонады носа после септопластики тампоны необходимо удалять на 2-й день после операции.
Септопластика, анестезия, аналоговые шкалы, боль
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14122870
IDR: 14122870 | УДК: 612.822.81+616-001.41+616.211-089 | DOI: 10.34014/2227-1848-2021-3-97-110
Текст научной статьи Оценка острого болевого синдрома у пациентов после септопластики при применении различных тактик анестезии
Введение. Наиболее частой причиной затруднения носового дыхания является искривление перегородки носа (ИПН) [1, 2]. Анатомические исследования показали, что в той или иной степени ИПН присутствует у 19–80 % людей [3–8] в зависимости от критериев ее определения [9–11].
Наиболее распространенным хирургическим вмешательством по поводу ИПН до сих пор остается септопластика [11–14].
Часто возникающими осложнениями после септоплатики являются носовое кровотечение, плохая репарация слизистой, перфорация перегородки носа, синехии, атрофический ринит, повреждение носонебного нерва и др. [8, 15–18]. Среди них не последнее место отводится острому болевому синдрому [19]. Интенсивность острого послеоперационного болевого синдрома при различных ринологиче-ских хирургических вмешательствах различна
[20, 21]. Боль после септопластики остается одной из самых серьезных проблем, несмотря на прогресс в ринохирургии и периоперацион-ном обезболивании [22]. Хорошо известно, что адекватная анальгетическая терапия в послеоперационном периоде сокращает продолжительность пребывания в больнице, уменьшает количество осложнений, связанных с острым болевым синдромом. Комбинированные анальгетические методы являются наиболее часто используемыми методами повышения эффективности обезболивания и снижения побочных эффектов и доз применяемых препаратов для анестезии [23]. Передняя тампонада носа после септопластики дополнительно увеличивает интенсивность боли [24]. После септопластики невралгия лицевого нерва проявляется в тяжелой форме вследствие иссечения искривленных участков хряща, использования швов и/или носовых тампонов.
В послеоперационном периоде после септопластики интенсивность боли может быть от слабой до умеренной. Для облегчения боли, как правило, используются нестероидные противовоспалительные препараты (НПВП) и парацетамол [25]. Однако парацетамола недостаточно для обезболивания. Он имеет те же побочные эффекты, что и НПВП, и снижает комфорт пациента [26].
Цель исследования. Оценка острого болевого синдрома у пациентов после септопластики при применении различных тактик общей анестезии.
Материалы и методы. В период с 2018 по 2021 г. в исследовании принял участие 291 чел. с искривлением перегородки носа, им была проведена септопластика. Изучалась эффективность 3 наиболее популярных методов анестезиологического пособия при септопластике в лор-стационарах 4 клиник г. Москвы. Было прооперировано 164 мужчины и 127 женщин в возрасте от 18 до 45 лет. У женщин септопластика проводилась в периовуляторный период (фазу пролиферации эндометрия) менструального цикла, так как ранее было показано, что именно в это время минимален риск носового кровотечения при септопластике [27]. Септопластика проводилась и в хрящевом, и в костном отделах, так как в исследование включались пациенты с ИПН в обоих отделах.
Пациенты случайным образом распределялись по трем группам. В первой группе (105 чел.) септопластика проводилась под местной анестезией. Местная инфильтрационная анестезия была использована также в обеих других группах с применением 2 % раствора прокаина, а для снижения риска интраоперационного носового кровотечения использовался 0,1 % раствор эпинефрина. В качестве обезболивающего препарата у пациентов этой группы внутримышечно применялся кеторо-лак (60 мг) в вечернее время (табл. 1).
Во второй группе (108 пациентов), кроме местной анестезии, использовался фентанил, пропофол, цисатракурия безилат (нимбекс), транексамовая кислота (транексам), атропин и метоклопрамид (церукал).
В 3-й группе (78 пациентов) в качестве общей анестезии применялись атракурия бези- лат, тиопентал натрия, закись азота и галотан (фторотан).
В качестве НПВП пациентам 2-й и 3-й групп в вечерние часы в день операции внутримышечно вводился кетопрофен 100 мг (табл. 1).
Всем пациентам для передней тампонады носа использовались поролоновые тампоны в резиновой перчатке. В 1-й и 2-й группах тампоны удалялись через двое суток после операции, а в 3-й – через сутки.
Степень выраженности острой боли после септопластики оценивалась с помощью визуально-аналоговой шкалы (ВАШ), вербальной шкалы-«молнии» (ВШМ) и цифровой рейтинговой шкалы (ЦРШ) (рис. 1). Пациентам предлагалось отметить вертикальной линией то место шкалы, которое, по их представлению, соответствовало испытываемой боли. Длина каждой из шкал равнялась 100 мм, боль оценивалась по 100-балльной системе. Градация интенсивности боли была следующей: при 0–25 мм боль оценивалась как слабая, либо она отсутствовала; при 26–50 мм боль считали средней силы; сильная боль соответствовала диапазону 56–75 мм; очень сильная и нестерпимая боль – 76–100 мм. Аналоговые шкалы в последовательности ВАШ – ЦРШ – ВШМ предлагались пациентам раздельно через 1, 3, 6 ч после операции. Через сутки и два дня после операции интенсивность боли оценивалась через 1 ч после удаления передних тампонов носа.
Статистическая обработка полученного материала осуществлялась в пакетах программ Exel 2019, JASP 0.14.0.0. При равномерном распределении выборки данных для определения достоверности различий использовался критерий Стьюдента, при неравномерном – критерий Манна – Уитни.
Результаты. Интенсивность болевого синдрома. ВАШ. Болевой синдром в течение первых 3 ч после септопластики был достоверно ниже во второй группе по сравнению с остальными (p<0,001) (табл. 1, рис. 2а). В это же время интенсивность острой боли в первой группе была достоверно выше, чем в третьей (p<0,01). Через 6 ч после операции интенсивность боли в группах с общей анестезией была достоверно ниже, чем в группе с местной анестезией и премедикацией (p<0,01), и не разли- чалась внутри второй и третьей групп. Через сутки после септопластики выраженность болевого синдрома в первых двух группах была статистически одинаковой и менее интенсив- ной, чем в третьей группе (p<0,01) (табл. 1, рис. 2а). Через двое суток во всех группах интенсивность болевого синдрома была низкой либо боли не было вообще (p>0,05).
a
сильная боль / с severe pain
b
боль средней
нет боли / no pain
Ч_____________________>z_—
100 мм / mm
Рис. 1. Аналоговые шкалы для оценки боли: а – ВАШ, b – ЦРШ, c – ВШМ Fig. 1 . Analogue scales for pain assessment: a – VAS, b – NRS, c – VLS
Динамика выраженности острой боли внутри групп была следующей. В первой группе было отмечено достоверное снижение болевого синдрома как на 3-й (p<0,01) и 6-й (p<0,05) ч после операции, так и в последующий период (p<0,001) (табл. 1, рис. 2а). Наблюдалось постепенное снижение остроты боли в 1-й группе через 1 и 3 ч (p<0,05), а также на 1-е и 2-е сут после септопластики (p<0,001). У пациентов 3-й группы снижение болевого синдрома было отмечено лишь через 6 ч после операции (p<0,05) с постепенным ее регрессом.
ВШМ. Вербальная шкала-«молния» показала практически те же результаты, что и ви- зуально-аналоговая шкала. Во 2-й группе интенсивность боли была достоверно ниже, чем в 1-й и 3-й группах, через 1, 3 и 6 ч после септопластики (p<0,001) (табл. 1, рис. 2b). Также боль была значимо ниже в 3-й группе, по сравнению с 1-й группой, на 1-й (p<0,05), 3-й (p<0,05) и 6-й ч (p<0,01) после септопластики. Через сутки пациенты 1-й и 2-й групп имели болевой синдром низкой интенсивности, в то время как в 3-й группе пациенты оценивали боль как среднюю (p<0,001). На второй день после операции у всех пациентов боли не было или она оценивалась как минимальная (табл. 1, рис. 2b).
Таблица 1
Table 1
Средние значения интенсивности острого болевого синдрома после септопластики
Average values of the acute pain syndrome intensity after septoplasty
|
Шкала Scale |
ВАШ, мм VAS, mm |
ВШМ, мм VLS, mm |
ЦРШ, мм NRS, mm |
Среднее по шкалам, мм Average value according to scales, mm |
|
1 ч после операции 1 hour after septoplasty |
||||
|
1-я группа Group 1 |
44,65±3,37 |
46,65±3,84 |
48,75±3,85 |
46,68±3,85 |
|
2-я группа Group 2 |
17,15±2,47 |
20,68±2,55 |
22,47±2,36 |
20,1±2,4 |
|
3-я группа Group 3 |
30,75±2,21 |
42,38±2,68 |
44,3±3,03 |
39,17±2,64 |
|
3 ч после операции 3 hours after septoplasty |
||||
|
1-я группа Group 1 |
40,1±3,03 |
46,75±3,4 |
43,5±3,33 |
43,45±3,38 |
|
2-я группа Group 2 |
21,82±2,83 |
27,05±2,69 |
27,47±2,74 |
25,45±2,7 |
|
3-я группа Group 3 |
31,21±2,5 |
43±3,26 |
46,25±3,32 |
40,15±2,03 |
|
6 ч после операции 6 hours after septoplasty |
||||
|
1-я группа Group 1 |
34,95±2,74 |
42,25±3,48 |
42,5±3,04 |
39,9±2,94 |
|
2-я группа Group 2 |
25±3,02 |
28,34±2,74 |
29,12±2,68 |
27,51±2,75 |
|
3-я группа Group 3 |
27,67±3,35 |
38,79±2,07 |
40,42±2,15 |
35,63±2,19 |
|
1 сут после операции 1 day after septoplasty |
||||
|
1-я группа Group 1 |
16,65±3,01 |
21±2,61 |
26±3,55 |
21,22±2,32 |
|
2-я группа Group 2 |
16,64±2,36 |
19,96±2,27 |
22,71±1,9 |
19,77±2,06 |
|
3-я группа Group 3 |
22,71±3,67 |
33,08±2,92 |
37,5±2,32 |
31,1±2,3 |
|
2 сут после операции 2 days after septoplasty |
||||
|
1-я группа Group 1 |
3,75±2 |
4,45±2,1 |
12,5±1,26 |
6,9±1,76 |
|
2-я группа Group 2 |
3,68±1,01 |
5,68±1,27 |
12,53±1,04 |
7,3±1,03 |
|
3-я группа Group 3 |
3,45±2,5 |
4,75±2,7 |
12,5±1,9 |
6,9±2,37 |
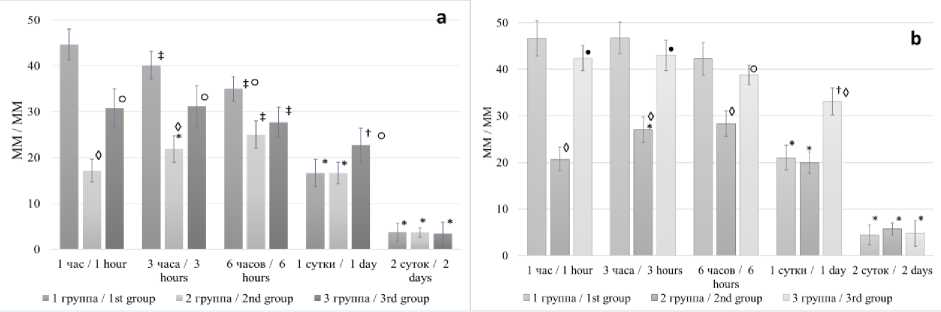
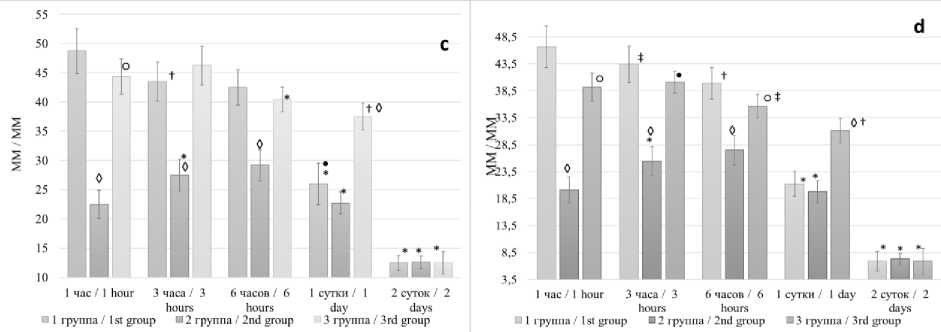
Рис. 2. Сравнение болевого синдрома в группах пациентов с различной анестезиологической тактикой: а – средние показатели болевого синдрома в группах по ВАШ;
b – средние показатели болевого синдрома в группах по ВШМ;
c – средние показатели болевого синдрома в группах по ЦРШ;
d – средние показатели болевого синдрома в группах по трем шкалам
(* – достоверные различия между сроками после операции внутри группы при p<0,001;
† – достоверные различия между сроками после операции внутри группы при p<0,01;
‡ – достоверные различия между сроками после операции внутри группы при p<0,05;
◊ – достоверные различия между группами при p<0,001;
○ – достоверные различия между группами при p<0,01;
• – достоверные различия между группами при p<0,05)
Fig. 2 . Comparison of pain syndrome in groups of patients with different anesthetic strategies:
a – average indicators of pain syndrome in groups according to VAS;
b – average indicators of pain syndrome in the groups according to VLS;
c – average indicators of pain syndrome in groups according to NRS; d – average indicators of pain syndrome in groups according to three scales. Note: * – the differences between the terms after surgery are significant within the group (p<0.001);
-
† – the differences between the terms after surgery are significant within the group (p<0.01);
-
‡ – the differences between the terms after surgery are significant within the group (p<0.05);
-
◊ – the differences are significant if compared with all study groups (p<0.001);
○ – the differences are significant if compared with all study groups (p<0.01);
-
• – the differences are significant if compared with all study groups (p<0.05)
По ВШМ динамика болевого синдрома была аналогична таковой по ВАШ. Однако в 1-й группе боль начала снижаться только на 6-й ч после операции (табл. 1, рис. 2b).
ЦРШ. Цифровая рейтинговая шкала показала, что в первые 1–6 ч боль была достоверно меньше у пациентов 2-й группы по сравнению с пациентами 1-й и 3-й групп (p<0,001). При этом в первый час боль была меньше в 3-й группе по сравнению с 1-й (p<0,01), на 3-й и 6-й ч различий между этими группами выявлено не было. Через сутки после опера- ции пациенты 3-й группы оценили болевой синдром как средней силы, что было выше, чем в двух других (p<0,001). Кроме того, в 1-й группе болевой синдром был достоверно выше, чем во 2-й группе (p<0,05), хотя боль была либо минимальная, либо средней интенсивности. Через двое суток пациенты практически не отмечали боли (табл. 1, рис. 2c).
ЦРШ показала практически ту же динамику боли, что и ВШМ.
Средняя оценка по шкалам . Средние значения болевого синдрома по всем трем шкалам для каждого пациента в частности и для групп в целом показали, что интенсивность боли с 1-го по 6-й ч после септопластики была достоверно выше в 1-й и 3-й группах (p<0,001). При этом боль была ниже в 3-й группе по сравнению с 1-й (p<0,05) (табл. 1, рис. 2d). Через день болевой синдром был ниже в 1-й и 2-й группах по сравнению с 3-й (p<0,001), а на 2-й день пациенты практически не ощущали боли.
Пик болевого синдрома у пациентов первой группы пришелся на день хирургического вмешательства. Максимум интенсивности боли во 2-й группе был выявлен через 6 ч после операции, в 3-й группе – в день операции и через сутки после нее.
Обсуждение. Большая эффективность использования наркотических анальгетиков, общей анестезии, по сравнению с местной анестезией, была показана во многих работах [22, 23], данные которых совпадают или очень схожи с данными, полученными в настоящем исследовании. Исследуя эффективность ведения пациентов в первые 48 ч после септопластики под местной анестезий 2 % раствором лидокаина и эпинефрина с тампонадой носа и без нее, M.T. Bernardo et al. показали, что степень болевого синдрома у пациентов с тампонадой была равна 4 баллам. Причем авторы использовали ВАШ и измеряли выраженность боли от 0 до 10 [28].
В нашем исследовании первые сутки пациенты 1-й группы испытывали боль, интенсивность которой, согласно аналоговым шкалам, оценивалась в среднем как 21,22±2,32 мм, а через 48 ч после операции – 6,9±1,76 мм, что существенно ниже, чем в работе M.T. Bernardo et al. Это можно объяснить тем, что авторы из- меряли боль при помощь цифровой рейтинговой шкалы, а не ВАШ [28]. При этом результаты можно считать достаточно сопоставимыми между собой.
Показано, что использование опиоидных анальгетиков в периоперационном периоде при проведении септопластики снижает интенсивность болевого синдрома и улучшает качество жизни пациентов [29]. Этим можно объяснить самый низкий показатель интенсивности боли по всем трем шкалам во 2-й группе.
Применение НПВП в постоперационном периоде после септопластики является золотым стандартом и важным компонентом мультимодальной аналгезии [30–32]. Так, в работе S.K. Kar et al. в качестве НПВП использовали лорноксикам внутривенно за 30 мин до начала септопластики, которая проводилась под местной анестезией 2 % раствором лидокаина с раствором эпинефрина. Интенсивность болевого синдрома в первые 8 ч после хирургического вмешательства колебалась от 36,95±9,2 мм (0 мин) до 37,24±6,9 мм (4 ч). Через 24 ч средняя интенсивность болевого синдрома в группе пациентов, которым вводился лорнокси-кам, составила 27,85±5,04 мм [30].
В группе пациентов, к которым применялась местная анестезия, согласно нашим данным, интенсивность боли в день операции была максимальна в первый час и составила в среднем 46,68±3,85 мм, но через 24 ч она была даже ниже, чем в работе S.K. Kar et al. Данное сравнение позволяет сделать вывод о том, что введение НПВП необходимо не после, а до хирургического вмешательства, что играет важную роль для предотвращения развития острого болевого синдрома именно в первые 24 ч после септопластики.
В нашем исследовании было отдано предпочтение передней тампонаде носа поролоновыми тампонами в резиновой перчатке из-за того, что другие методы профилактики носового кровотечения после септопластики, такие как сплинты, могут вызвать значительное усиление боли и дискомфорт, особенно спустя неделю [17]. Было показано, что применение сплинтов не предотвращает образования спаек, а также провоцирует послеоперацион- ную боль и дискомфорт, как и обычные носовые тампоны [33, 34]. В результате применения сплинтов наблюдается усиление работы желез слизистой оболочки полости носа с последующим увеличением отделяемого из полости носа как вперед, так и в носоглотку, что связанно с усилением кровотока в полости носа и частыми эпизодами рвоты, потенциально свидетельствующими об увеличении заднего дренажа и вызывающими дискомфорт у пациента [35–37]. Кроме того, всегда есть большой риск возникновения спаек в полости носа при применении шин [35, 36, 38]. Тем не менее существует противоположное мнение S.J. Kim et al., основанное на метаанализе литературы. Так, авторы заявляют о минимальном риске образования спаек в полости носа и болевого синдрома [39].
Применение передней тампонады носа может провоцировать болевой синдром в 47,2 % случаев [40, 41]. По нашему мнению, увеличение интенсивности болевого синдрома в 3-й группе связано именно с более ранним сроком удаления тампонов (1-е сут после операции), чем в 1-й и 2-й группах.
В исследовании E. Eşki et al. были показаны противоположные полученным в настоящем исследовании результаты [42]. Авторы исследовали послеоперационную боль у пациентов после септопластики с передней тампонадой носа и без нее. Результаты показали, что интенсивность боли через 4 ч после операции у пациентов с тампонами оценивалась как 6,12±2,78, без тампонады – 2,34±1,76 с последующим снижением боли. Известно, что степень болевого синдрома может зависеть от ряда факторов, например от площади операционного поля [43], фазы овариально-менструального цикла [44], возраста [45] др. С учетом малой выборки (38 пациентов на обе группы), широкого возрастного диапазона пациентов (18–61 год), отсутствия подробно описанного протокола общей анестезии и указания на то, в какую фазу менструального цикла были прооперированы женщины [42], результаты исследования E. Eşki et al. представляются сомнительными. В других исследованиях вовсе не указываются сроки оценки боли в день проведения септопластики [46], при этом не учитывается фазность развития хирургического стресс-ответа [47, 48]. Данные, более близкие нашим, получены в исследовании M.T. Bernardo et al. [28]. Также мы обратили внимание на тот факт, что в других исследованиях на второй постоперационный день данные по болевому синдрому [28] заметно не отличались от наших результатов. Это подтверждает мнение о том, что интенсивность воспалительных процессов (нейтрофильная инфильтрация, отек) [49–51] в полости носа после септопластики снижается на второй день. Кроме того, существуют клинические исследования, в которых было показано, что во избежание осложнений после сеп-топлатики (кровотечение, гематома перегородки носа, боль и др.) необходимо удалять тампоны через 48 ч [52]. Также известно, что преждевременное удаление носового тампона после септопластики может спровоцировать и носовое кровотечение, и острую боль [53], что совпадает с результатами, полученными нами в 3-й группе пациентов. Кроме того, длительная тампонада (от 48 до 72 ч) также не желательна. Она провоцирует повышение температуры тела, острый бактериальный синусит и болевой синдром, обусловленный вторичными факторами, а не только самой септопластикой [54, 55], что требует дополнительной системной антибактериальной терапии [56].
Применение передних носовых тампонов после септопластики во многом зависит от опыта врача и предназначено, как правило, для профилактики носового кровотечения и образования гематом перегородки носа [53]. Однако тампонада носа служит также дополнительным источником повреждения слизистой оболочки и может усилить боль сама по себе [57]. В настоящее исследование не включались пациенты с такими осложнениями, как носовое кровотечение и гематома перегородки носа, которые могли бы внести дополнительный вклад в развитие болевого синдрома в послеоперационном периоде [58]. При этом, на наш взгляд, в дальнейшем необходимо изучить взаимосвязь развития осложнений после септопластики в раннем постоперационном периоде со степенью стрессовой реакции [59], а также изучить причинно-следственные связи болевого синдрома и объема ринохирургических вмешательств [60].
Заключение. Таким образом, при рутинном проведении септопластики наименьшую болевую реакцию провоцирует схема общей анестезии, примененная во 2-й группе: фентанил, пропофол, цисатракурия безилат, транек-самовая кислота, атропин и метоклопрамид. Исключительно местная анестезия не является методом выбора, однако в случае ее ис- пользования рекомендуется применять предоперационно нестероидные противовоспалительные средства для снижения болевого синдрома в первые 24 ч. При проведении профилактической передней тампонады носа после септопластики тампоны необходимо удалять через 48 ч после операции.
Список литературы Оценка острого болевого синдрома у пациентов после септопластики при применении различных тактик анестезии
- Orhan I., Aydin S., Ormeci T., Yilmaz F. A radiological analysis of inferior turbinate in patients with deviated nasal septum by using computed tomography. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy. 2014; 28: 68-72.
- Andrades P., Cuevas P., Danilla S., Bernales J., Longton C., Borel C., Rodrigo Hernández, VillalobosR. The accuracy of different methods for diagnosing septal deviation in patients undergoing septorhino-plasty: a prospective study. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2016; 69: 848-855.
- Thomas A., Alt J., Gale C., Vijayakumar S., Padia R., Peters M., Champagne T., Meier J.D. Surgeon and hospital cost variability for septoplasty and inferior turbinate reduction. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016; 6: 1069-1074.
- Rotenberg B. W., Pang K.P. The impact of sinus surgery on sleep outcomes. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015; 5: 329-332.
- LoSavio P.S., O'Toole T.R. Surgery of the nasal septum and turbinates. In: Batra P.S., Han J.K. (eds.). Practical medical and surgical management of chronic rhinosinusitis. Cham: Springer; 2015: 483-507.
- Gillman G. Septoplasty. In: Myers E., Kennedy D. (eds.). Rhinology. Netherlands: Wolters Kluwer, Al-phen aan den Rijn; 2016: 7-21.
- Ketcham A.S., Han J.K. Complications and management of septoplasty. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2010; 43: 897-904.
- Dqbrowska-Bien J., Skarzynski P.H., Gwizdalska I., Laz^cka K., Skarzynsk H. Complications in septoplasty based on a large group of 5639 patients. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology. 2018; 275: 1789-1794.
- Stallman J.S., Lobo J.N., Som P.M. The incidence of concha bullosa and its relationship to nasal septal deviation and paranasal sinus disease. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2004; 25 (9): 1613-1618.
- Smith K.D., Edwards P.C., Saini T.S., Norton N.S. The prevalence of concha bullosa and nasal septal deviation and their relationship to maxillary sinusitis by volumetric tomography. Int. J. Dent. 2010; 2010.
- Bugten V., Nilsen A.H., Thorstensen W.M., MoxnessM.H.S., Amundsen M.F., Nordgard S. Quality of life and symptoms before and after nasal septoplasty compared with healthy individuals. BMC Ear, Nose and Throat Disorders. 2016; 16 (1): 13.
- Bhattacharyya N. Ambulatory sinus and nasal surgery in the United States: demographics and perioperative outcomes. Laryngoscope. 2010; 120: 635-638.
- Пустовит О.М., Наседкин А.Н., Егоров В.И., Исаев В.М., Исаев Э.В., Морозов И.И. Воздействие ультразвуковой кавитации и фотохромотерапии на процесс репарации слизистой оболочки носа после септопластики и подслизистой вазотомии нижних носовых раковин. Голова и шея. 2018; 6 (2): 20-26.
- Sommer F., Hoffmann T.K. Septoplasty - a surgical or political challenge? The Lancet. 2019; 394: 276-277. DOI: 10.1016/s0140-6736(19)31241-3.
- Van EgmondM.M.H.T., RoversM.M., Hannink G., Hendriks C.T.M., van HeerbeekN. Septoplasty with or without concurrent turbinate surgery versus non-surgical management for nasal obstruction in adults with a deviated septum: a pragmatic, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2019; 394 (10195): 314-321.
- Siegel N.S., Gliklich R.E., Taghizadeh F., Chang Y. Outcomes of septoplasty. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2000; 122 (2): 228-232.
- Bloom J.D., Kaplan S.E., Bleier B.S., Goldstein S.A. Septoplasty Complications: Avoidance and Management. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2009; 42: 463-481.
- Shah J., Roxbury C.R., Sindwani R. Techniques in Septoplasty. Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2018; 51: 909-917.
- Ocalan R., Akin C., Disli Z.K., Kilinc T., Ozlugedik S. Preoperative anxiety and postoperative pain in patients undergoing septoplasty. B-ENT. 2015; 11: 19-23.
- Кастыро И.В., Попадюк В.И., Зализко А.В., Ключникова О.С., Стефанова М.В. Сравнение интенсивности послеоперационной боли после септопластики и полипотомии носа. Бюллетень ВСНЦ СО РАМН. 2012; 4 (86): 61.
- Попадюк В.И., Кастыро И.В., Зализко А.В. Определение тенденций в исследовании болевого синдрома после тонзиллэктомии (пилотное исследование). Бюллетень ВСНЦ СО РАМН. 2012; 4 (86): 106-109.
- Simsek T., Coskun Musaoglu I., UluatA. The effect of lidocaine and tramadol in nasal packs on pain after septoplasty. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology. 2019; 276 (6): 1663-1669.
- Altunkaya H., Ozer Y., Kargi E., OzkocakI., Mubin Hosnuter, Demirel C.B., Babuccu O. The postoperative analgesic effect of tramadol when used as subcutaneous local anesthetic. Anesth. Analg. 2004; 99 (5): 1461-1464.
- Pang W., Huang P. Y., Chang D.P., Huang M.H. The peripheral analgesic effect of tramadol in reducing propofol injection pain: a comparison with lidocaine. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 1999; 24 (3): 246-249.
- Sener M., Yilmazer C., Yilmaz I., Ozer C., Donmez A., Arslan G. Efficacy of lornoxicam for acute postoperative pain relief after septoplasty: a comparison with diclofenac, ketoprofen, and dipyrone. J. Clin. Anesth. Pain Manag. 2008; 20 (2): 103-108.
- White P.F. The changing role of non-opioid analgesic techniques in the management of postoperative pain. Anesth. Analg. 2005; 101 (5S): S5-S22.
- Findikcioglu K., Findikcioglu F., Demirtas Y., Yavuzer R., Ayhan S., Atabay K. Effect of the menstrual cycle on intraoperative bleeding in rhinoplasty patients. Eur. J. Plast. Surg. 2009; 32: 77-81.
- BernardoM.T., AlvesS., LimaN.B., HelenaD., CondeA. Septoplasty with or without postoperative nasal packing? Prospective study. Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2013; 79 (4): 471-474.
- Rock A.N., Akakpo K., Cheresnick C., Zmistowksi B.M., Essig G.F., Chio E., Nogan S. Postoperative Prescriptions and Corresponding Opioid Consumption After Septoplasty or Rhinoplasty. Ear, Nose & Throat Journal. 2019; 15.
- Kar S.K., Das D., Mondal A.K. The Analgesic Efficacy of Preoperative Lornoxicam in Prevention of Postoperative Pain after Septoplasty. J. Neurol. Neurophysiol. 2016; 7: 353-358.
- Brown E.N., Pavone K.J., Naranjo M. Multimodal General Anesthesia. Anesthesia & Analgesia. 2018; 127 (5): 1246-1258.
- Sherman M., Sethi S., Hindle A.K. Chanza T. Multimodal Pain Management in the Perioperative Setting. Open Journal of Anesthesiology. 2020; 10: 47-71.
- Gaia R., Coelho J., Brandao F.H., Carvalho M.R.M.S., Aquino J.E.P., Paula S.H.P., Fabi R.P., Eiras B. Frequencia de Sinequia Nasal apos Cirurgia de Septoplastia com Turbinectomia com e sem Uso de Splint Nasal. Arq. Int. Otorrinolaringol. 2008; 12 (1): 24-27.
- Baptistella E., Rispoli D.Z., de Brito Malucelli D.A., de Carvalho Fonseca V.R.D., de Trotta F., Costa A.F.C.B., Rispoli L., Watanabe S.S., da Silva T.P. Degree of the Patient Satisfaction and Post-operative Complications for Septoplasty Surgery With and Without the Use of Nasal Buffer. Int. Arch. Otorhino-laryngol. 2008; 12 (3): 334-341.
- Malki D., Quine S.M., Pfleiderer A.G. Nasal splints, revisited. J. Laryngol. Otol. 1999; 113 (8): 725-727.
- Guyuron B., Vaughan C. Evaluation of stents following septoplasty. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 1995; 19 (1): 75-77.
- Cook J.A., Murrant N.J., Evans K.L., Lavelle R.J. Intranasal splints and their effects on intranasal adhesions and septal stability. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 1992; 17 (1): 24-27
- Wdnman A., MarklundS. Treatment outcome of supervised exercise, home exercise and bite splint therapy, respectively, in patients with symptomatic disc displacement with reduction: a randomised clinical trial. Journal of oral rehabilitation. 2020; 47 (2): 143-149.
- Kim S.J., Chang D.S., Choi M.S., Lee H. Y., Pyo J.-S. Efficacy of nasal septal splints for preventing complications after septoplasty: A meta-analysis. American Journal of Otolaryngology. 2021; 42 (3): 102389.
- Vaiman M., Sarfaty S., Shlamkovich N., Segal S., Eviatar E. Fibrin sealant: alternative to nasal packing in endonasal operations. A prospective randomized study. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2005; 7 (9): 571-574.
- Vaiman M., Eviatar E., Segal S. The use of fibrin glue as hemostatic in endonasal operations: a prospective, randomized study. Rhinology. 2002; 40 (4): 185-188.
- E§ki E., Guveng I.A., Hizal E., Yilmaz 1. Effects of nasal pack use on surgical success in septoplasty. Kulak. Burun. Bogaz. Ihtis. Derg. 2014; 24 (4): 206-210.
- Кастыро И.В., Медянцева Д.А. Интенсивность болевого синдрома после резекции перегородки носа в зависимости от площади операционного поля. Российская оториноларингология. 2014; 1 (68): 86-88.
- ChinM.L., Fillingim R.B., Ness T.J. Pain in Women. 1st Edn. Oxford University Press; 2013. 335.
- Gagliese L. Pain and Aging: The Emergence of a New Subfield of Pain Research. The Journal of Pain. 2009; 10 (4): 343-353.
- BistaM. A Comparative Study of Pain and Discomfort in Septoplasty with Quilting of Nasal Septum and Nasal Packing. Glob. J. Oto. 2018; 13 (4): 555866.
- Burton D., Nicholson G., Hall G. Endocrine and metabolic response to surgery. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia Critical Care & Pain. 2004; 4 (5): 144-147. DOI: 10.1093/bjaceaccp/mkh040.
- Giannoudis P.V., Dinopoulos H., Chalidis B., Hall G.M. Surgical stress response. Injury. 2006; 37: S3-S9.
- Khalmuratova R., Jeon S.-Y., Kim D. W., Kim J.-P., Ahn S.-K., Park J.-J., Hur D.-G. Wound healing of nasal mucosa in a rat. American Journal of Rhinology and Allergy. 2009; 23 (6): 33-37.
- Khalmuratova R., Kim D. W., Jeon S.-Y. Effect of Dexamethasone on Wound Healing of the Septal Mucosa in the Rat. American Journal of Rhinology & Allergy. 2011; 25 (3): e112-e116.
- Choi K.Y., Cho S.W., Choi J.-J., Zhang Y.-L., Kim D.W., Han D.H., Kim H.J., Kim D.-Y., Rhee C.-S., Won T.-B. Healing of the nasal septal mucosa in an experimental rabbit model of mucosal injury. World Journal of Otorhinolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery. 2017; 3 (1): 17-23.
- Wang W.W., Dong B.C. Comparison on effectiveness of trans-septal suturing versus nasal packing after septoplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017; 274 (11): 3915-3925.
- Liao Z., Liao W., Tan K.S., Sun Y., Peng A., Zhu Y., He H., Yang S., Xu G., Su R., Yao J., Fan Y., Yang Q., Hong H. Decreased hospital charges and postoperative pain in septoplasty by application of enhanced recovery after surgery. Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management. 2018; 14: 1871-1877.
- Canty P.A., Berkowitz R.G. Hematoma and abscess of the nasal septum in children. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 1996; 122 (12): 1373-1376.
- Mooney C.P., Rimmer J. Spontaneous nasal septal haematoma and abscess: a case report and literature review. Rhinology Online. 2018; 1: 122-126.
- Salam B., Camilleri A. Non-traumatic nasal septal abscess in an immunocompetent patient. Rhinology. 2009; 47 (4): 476-477.
- DadgarniaM., MeybodianM., Karbasi A., Baradaranfar M., Atighechi S., Zand V., Vaziribozorg S. Comparing nasal packing with trans-septal suturing following septoplasty: a randomized clinical trial. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017; 274 (9): 3513-3518.
- Karaman E., Gungor G., Alimoglu Y., Kilic E., Tarakci E., Bozkurt P., Enver O. The effect of lidocaine, bupivacaine and ropivacaine in nasal packs on pain and hemorrhage after septoplasty. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology. 2010; 268 (5): 685-689.
- Kastyro I.V., Inozemtsev A.N., Shmaevsky P.E., Khamidullin G.V., Torshin V.I., Kovalenko A.N., Pryani-kov P.D., Guseinov I.I. The impact of trauma of the mucous membrane of the nasal septum in rats on behavioral responses and changes in the balance of the autonomic nervous system (pilot study). J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 2020; 1611: 012054.
- ПопадюкВ.И., Кастыро И.В., Ермакова Н.В., Торшин В.И. Септопластика и тонзиллэктомия: сравнение эффективности местных анестетиков с позиций острого стресс-ответа. Вестник оториноларингологии. 2016; 81 (3): 7-11.


