Ontology Development and Query Retrieval using Protégé Tool
Автор: Vishal Jain, Mayank Singh
Журнал: International Journal of Intelligent Systems and Applications(IJISA) @ijisa
Статья в выпуске: 9 vol.5, 2013 года.
Бесплатный доступ
This paper highlights the explicit description about concept of ontology which is concerned with the development and methodology involved in building ontology. The concept of ontologies has contributed to the development of Semantic Web where Semantic Web is an extension of the current World Wide Web in which information is given in a well-defined meaning that translates the given unstructured data into knowledgeable representation data thus enabling computers and people to work in cooperation. Thus, we can say that Semantic Web is information in machine understandable form. It is also called as Global Information Mesh (GIM). Semantic Web technology can be used to deal with challenges including traditional search engines and retrieval techniques within given organizations or for e-commerce applications whose initial focus is on professional users. Ontology represents information in a manner so that this information can also be used by machines not only for displaying, but also for automating, integrating, and reusing the same information across various applications which may include Artificial Intelligence, Information Retrieval (IR) and many more. Ontology is defined as a collection of set of concepts, their definitions and the relationships among them represented in a hierarchical manner that is termed as Taxonomy. There are various tools available for developing ontologies like Hozo, DOML, and AltovaSemantic Works etc. We have used protégé which is one of the most widely used ontology development editor that defines ontology concepts (classes), properties, taxonomies, various restrictions and class instances. It also supports several ontology representation languages, including OWL. There are various versions of protégé available like WebProtege 2.0 beta, Protégé 3.4.8, Protégé 4.1 etc. In this paper, we have illustrated ontology development using protégé 3.1 by giving an example of Computer Science Department of University System. It may be useful for future researchers in making ontology on protégé version 3.1.
Semantic Web, Ontology Development, OWL, Protégé 3.1
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15010466
IDR: 15010466
Текст научной статьи Ontology Development and Query Retrieval using Protégé Tool
Published Online August 2013 in MECS
World Wide Web is the largest database in the Universe which is mostly understandable by human users and not by machines. WWW is human focused web. It discovers documents for the people. It lacks the existence of a semantic structure which maintains interdependency and scalability of its components. It returns results of given query with the help of hyperlinks between resources. It produces large number of results that may or may not satisfy user’s query. It results in the presentation of irrelevant information to the user. In the current web, resources are accessible through hyperlinks to web content spread throughout the world. The content of information is machine readable but not machine understandable. Use of current www does not support the concept of ontologies and users cannot make inferences due to unavailability of complete data. An enormous collection of unstructured data present on web leads to problems in extracting information about a particular domain. Hence information extraction is a logical step to retrieve relevant data and the extracted information. The word Information Retrieval is explicitly defined as process of extracting relevant results in context of given query. It is described as the task of identifying documents on the basis of properties assigned to the documents by various users requesting for retrieval. There are many Information Retrieval techniques for extracting keywords like NLP based extraction techniques. Content-based image retrieval system requires users to adopt new and challenges search strategies based on the visual pictures of images [1]. Multimedia information retrieval provides retrieval capabilities of text images and different dimensions like form, content and structure. When text annotation is nonexistent and incomplete content-based method must be used. Retrieval accuracy can be improved by content-based methods [2].
The remaining sections of paper are as follows. Section 2 makes readers aware of Semantic Web including its architecture and its importance as future web technology. In this section, we have also discussed about Ontology and its components. A list of differences is shown on Relational Database and Ontology. Section 3 defines development of ontology on “Computer Science Department” using Protégé tool via Case Study.
-
II. Semantic Web2.1 Importance
This futuristic concept of Semantic Web is needed to make our present web more precise and effective by increasing the structure and size of current web. Semantic Web (SW) uses Semantic Web documents (SWD’s) that must be combined with Web based Indexing. The idea of Semantic Web (SW) as envisioned by Tim Bermers Lee came into existence in 1996 with the aim to translate given information into machine understandable form.
-
2.2 Definition
Semantic Web is the new-generation Web that tries to represent information such that it can be used by machines not just for display purposes, but for automation, integration, and reuse across applications [3]. The emerging Semantic Web technology has revolutionized the way we use the Web to find and organize information. It is defined as framework of expressing information because we can develop various languages and approaches for increasing IR effectiveness. Semantic Web (SW) uses Semantic Web documents (SWD’s) that are written in SW languages like OWL, DAML+OIL. We can say that Semantic Web documents are means of information exchange in Semantic Web (SW).The Semantic Web (SW) is an extension of current www in which documents are filled by annotations in machine understandable markup language. Semantic Web technology can be used first to address efficiency, productivity and scalability challenges within Enterprises or for e-commerce applications and the initial focus is on professional users [4].
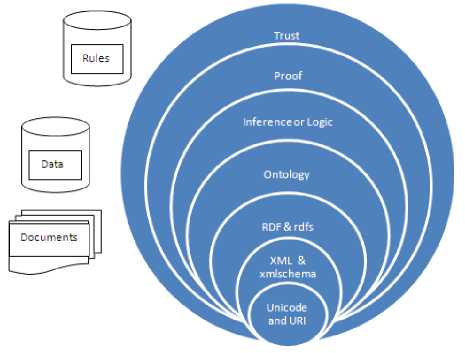
Fig. 1: “Semantic Web layered Architecture [5]”
Berners-lee outlined the architecture of the Semantic Web in the following 3 layers [15]:
The metadata layer: It contains the concepts of resource and properties and RDF (Resource Description Framework), most popular data model for the metadata layer.
The schema layer: Web ontology languages (OWL) are introduced here to define a hierarchical description of concepts (is-a hierarchy) and properties and RDFS (RDF Schema) is a popular schema layer language.
The logical layer: Set of web ontology languages are introduced at this layer to provide a richer set of modeling primitives in which Semantic Web plays a very important role to replace slow, ineffective, inefficient, & non intelligent web processes by fast, effective and inexpensive automatic processes. We can make our web more precise and increase retrieval capacity by adding annotations to documents. The
Semantic Web will allow both humans and machines to find and make use of data in modern ways that previously haven't been possible by www.
Both Semantic Web (SW) and World Wide Web (www) are different from each other in various aspects which are described in the form of table as shown
Table 1: “Comparison between Web and Semantic Web” [16]
|
Feature |
WWW |
Semantic Web |
|
Fundamental Component |
Unstructured Content |
Structured Content |
|
Primary Audience |
Humans |
Applications |
|
Links |
Indicate Location |
Indicate Location and Meaning |
|
Primary Vocabulary |
Formatting Instructions |
Semantics and Logics |
|
Logic |
Informal/Nonstandard |
Descriptive Logic |
|
Resources |
Web Pages, Photos, Videos etc. |
Web Pages, Photos, People |
|
Search Engines |
Google, Yahoo etc. |
Hakia, Sindise etc. |
|
Use of Ontology |
Not Applicable |
Applicable |
|
Inference |
WWW users cannot reach to conclusions. |
SW users can reach. |
The WWW consists primarily of content for human consumption. Content links to other content on the WWW via the universal Resource Locator (URL). The URL relies on surrounding context (if any) to communicate the purpose of the link that it represents; usually the user infers the semantics. Web content typically contains formatting instructions for a nice presentation, again for human consumption [17]. WWW content does not have any formal logical constructs. Correspondingly, the Semantic Web consists primarily of statements for application consumption. The statements link together via constructs that can form semantics, the meaning of the link. Thus, link semantics provide a defined meaningful path rather than a user-interpreted one. The statements may also contain logic that allows further interpretation and inference of the statements.
-
2.3 Ontology
The term ontology can be defined in many different ways. Genesereth and Nilsson defined Ontology as an explicit specification of a set of objects, concepts, and other entities that are presumed to exist in some area of interest and the relationships that hold them. It enables the Web for software components can be ideally supported through the use of Semantic Web technologies [18]. This helps in understanding the concepts of the domain as well as helps the machine to interpret the definitions of concepts in the domains and also the relations between them. Ontologies can be broadly divided into two main types: lightweight and heavyweight. Lightweight Ontologies involve taxonomy (or class hierarchy) that contains classes, subclasses, attributes and values. Heavy weight Ontologies model domains in a deeper way and include axioms and constraints [19]. Ontology layer consists of hierarchical distribution of important concepts in the domain and describing about the Ontology concepts, relationships and constraints. Fig. 2 displays the Ontology and its Constituents parts.
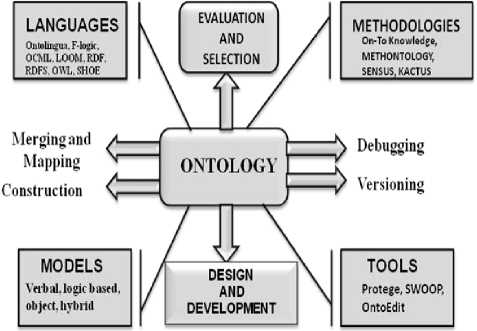
Fig. 2: “Ontology and its components [20]”
Advantages
There are many advantages of using ontology in the Semantic Web technology. Some of them are as follows [21, 22]:
-
• Sharing common understanding of the structure of information among people or software agents is one of the more common goals in developing Ontologies [23].
-
• Ontology enables reusability of domain knowledge in representing concepts and their relationships.
-
• Making explicit domain assumptions underlying an implementation makes it possible to change these assumptions easily if our knowledge about the domain changes [24].
-
• Separating the domain knowledge from the
operational knowledge is another common use of ontologies. We can describe a task of configuring a product from its components according to a required specification and implement a program that does this configuration independent of the products and components themselves [25].
-
• Use of ontology enables to analyze domain knowledge on basis of declared terms in a document.
-
• Each user has its defined attributes and relationships between other users.
-
• Ontology is considered as backbone of Software. Since SW translates the given data into machine understandable language using concept of ontologies [26].
-
• Ontology development is a cooperative process; it allows different peoples to express their views on given domain.
-
• Ontology language editors helps to build SW.
-
2.4 Ontology Languages and Editors
It is defined as formal language used to encode ontology. Various languages are listed below:
-
• DAML+OIL: - DAML stands for DARPA Agent Markup Language. DARPA stands for Defense Advanced Research project Agency. OIL stands for Ontology Interchange Language. This language uses Description Logic (DL) to express this language.
-
• SWRL: - It stands for Semantic Web Rule Language. It adds rules to OWL+DL.
-
• OWL: - It stands for Web Ontology Language. It is used to represent relations between entities by using formal semantics and vocabulary.
Ontology Editors : - They are applications designed to assist modifications of ontology. Various editors are listed below:
-
• Protégé: - It is free, open source and knowledge requisition system. It is written in Java and uses Swings to create the complex user interface.
-
• DOME: - It stands for DERI Ontology Management Environment. It is designed to create effective management of ontologies.
-
• Onto Lingua: - It is an ontology developed by OnTO Knowledge Project. It implements Ontology construction process.
-
• Altova SemanticWorks: - It is an RDF document editor and ontology development IDE. It creates and edits RDF documents, RDF Schema and OWL ontologies.
Table 2: “Comparison between RDBMS and Ontology”
|
Feature |
Relational Database |
Knowledgebase |
|
Structure |
Schema |
Ontology Statements |
|
Data |
Rows |
Instance Statements |
|
Administration Language |
DDL |
Ontology Statements |
|
Query Language |
SQL |
SPARQL |
|
Relationships |
Foreign Keys |
Multidimensional |
|
Logic |
External of Database/Triggers |
Formal Logic Statements |
|
Uniqueness |
Keys of Table |
URI |
-
III. Case Study
-
3.1 Ontology Development
The Computer Science Department Ontology describes various terms used in a computer science department. It shows the terms and their inheritance but not the relationships. For example, A Professor inherits from a Teaching which inherits from the Staff which is a generalization of a Person. Similarly Assistant inherits from Non Teaching which in turn inherits from Staff which in turn Person. The Screen Shot of Computer Science Department is shown in Fig. 3.
Tool: Protégé is an open-source tool for editing and managing Ontologies. It is the most widely used domain-independent, freely available, platformindependent technology for developing and managing terminologies, Ontologies, and knowledge bases in a broad range of application domains. There are various versions of protégé available out of which the frequently used ones are: protégé 2000, protégé 3.1, protégé 3.4 beta, protégé 3.4(released recently) and protégé 4.0 beta.
Computer Science Department Ontology Computer Science Person
Staff
Teaching (faculty)
Professor
Reader
Lecturer Non-Teaching Assistant Technician Student
Post Graduate
Graduate
Publication Books Journals
It provides a rich set of knowledge modeling structures. We have used the protégé version 3.1 to develop my Ontology on Computer Science Department. It provides the facility to support for multi user system, class trees on different tabs are synchronized by default, standard max memory allocation is 100 MB, RDF backend validates frame names, improved handling of sub slots and database backend correctly identifies MSSQL server and optimizes table creation accordingly.
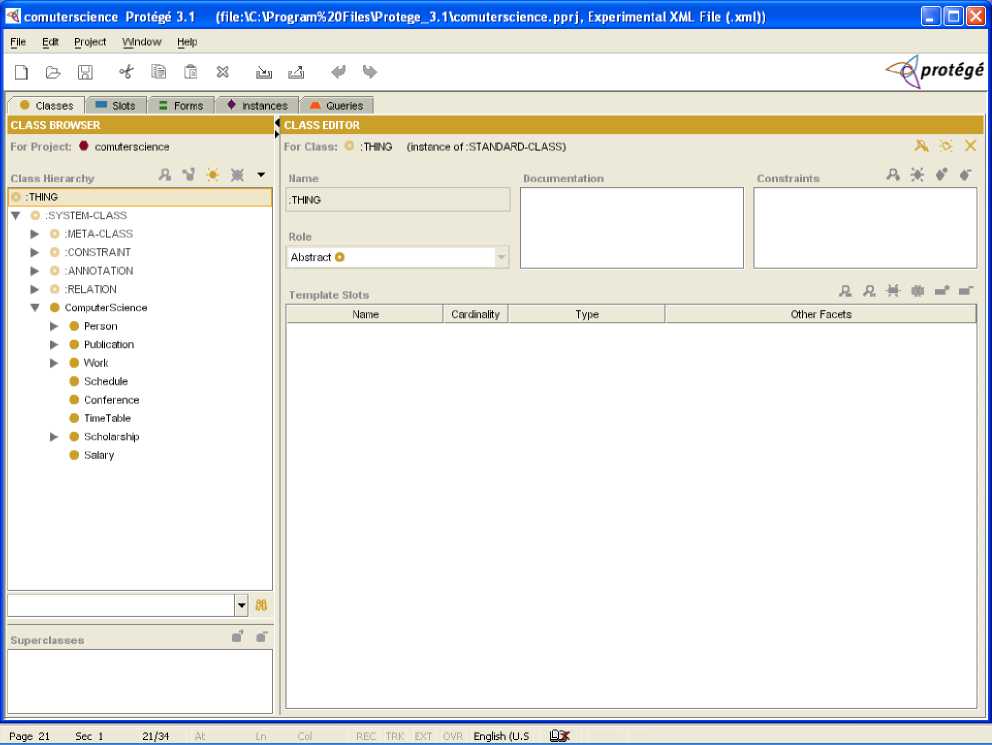
Fig. 3:“Computer Science Department Ontology”
Fig.3, shows the Ontology on “Computer Science Department with the help of Protégé tool.
-
3.2 Code Snippets
Following are different various Code snippet of Computer Science Department Ontology, developed in
Protégé 3.1
XML Code Snippet
xmlns:xsi="" xsi:schemaLocation=" ">
RDF Code Snippet
]>
xmlns:rdf_="&rdf_;" xmlns:a="&a;" xmlns:rdfs="&rdfs;">
rdfs:label="Academic">
OWL Code Snippet
xmlns:swrlb= xmlns:swrl="" xmlns:protege=" wl/protege#" xmlns:rdf="" xmlns:xsd=""
In this paper, we have described the use of Semantic Web in Information Retrieval with the help of Ontology. Information Retrieval over collection of those documents offers new challenges and opportunities. The paper shows that Semantic Web (SW) is better than current World Wide Web (www) by defining various differences between them. It gives brief overview on Ontology and its role in Semantic Web (SW). 3.3 Class-Subclass
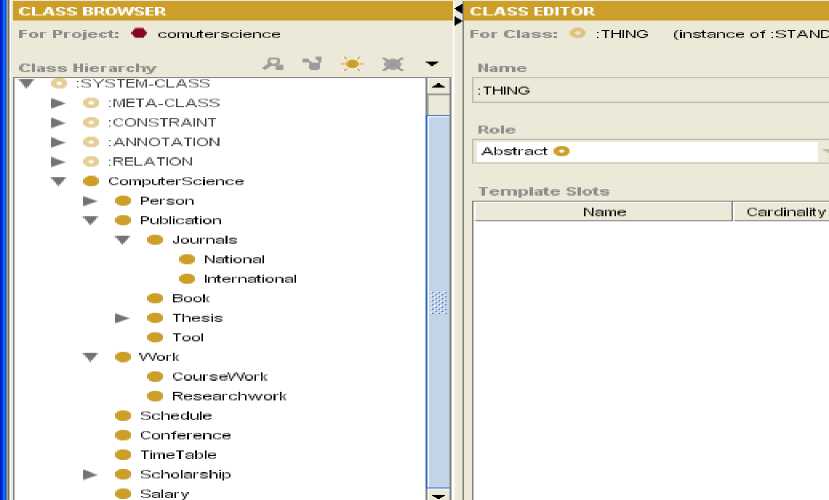
Fig. 4: ” Ontology on Computer Science Department in Protégé 3.1 (Sub Class)”
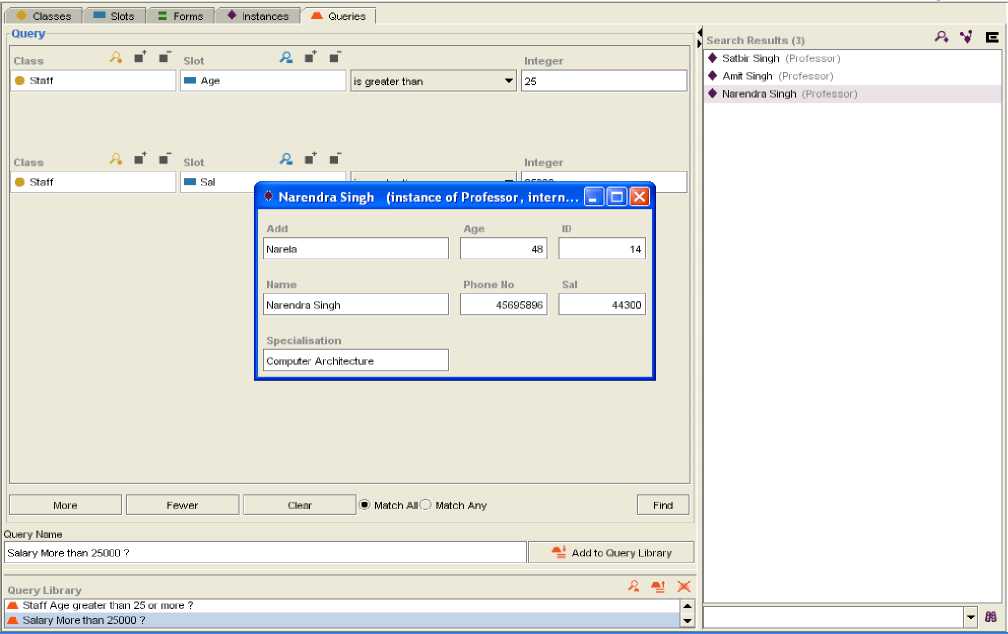
3.4 Query Retrieval
Fig. 5: “Query retrieval “Staff Salary Greater than 25000”
Fig. 5, shows the result of query given to the Ontology based system. IV. Conclusion
Ontology represents information in a manner so that this information can also be used by machines not only for displaying, but also for automating, integrating, and reusing the same information across various applications
.
We have developed ontology on Computer Science and Engineering Department using one of famous ontology editor named as Protégé 3.1. Protégé is an open-source tool for editing and managing Ontologies. It is the most widely used domainindependent, freely available, platform-independent technology for developing and managing ontologies. This paper will help upcoming researchers to develop an ontology using the protégé 3.1 in the semantic web. This ontology can also be used by any university system to make relevant search on the web. The developed ontology can be extended further to improve the performance of the Internet Technology.
Acknowledgement I ,Vishal Jain would like to give my sincere thanks to Prof. M. N. Hoda, Director, Bharati Vidyapeeth’s Institute of Computer Applications and Management (BVICAM), New Delhi for giving me opportunity to do P.hD from Lingaya’s University, Faridabad.
Список литературы Ontology Development and Query Retrieval using Protégé Tool
- Carlo Meghini_ Fabrizio Sebastiani and Umberto Straccia, “A Model of Multimedia Information Retrieval”.
- Henning Muller, Nicolas Michoux, David Bandon and Antoine Geissbuhler, “A Review of Content Based Image Retrieval Systems in Medical Applications - Clinical Benefits and Future Directions”.
- http://lpt.fri.uni-lj.si/research/15-semantic-web-and-ontologies/6-semantic-web-and-ontologies.
- Harold Boley, Said Tabet and Gerd Wagner, “Design Rationale of RuleML: A Markup Language for Semantic Web Rules, http://ruleml.org/papers/DesignRationaleRuleML-SWWS01paper20.pdf.
- Gagandeep Singh, Vishal Jain, “Information Retrieval (IR) through Semantic Web (SW): An Overview”, In Proceedings of CONFLUENCE 2012- The Next Generation Information Technology Summit, September 2012, 23-27.
- Christoph Bussler, Dieter Fensel, Alexander Maedche, “A Conceptual Architecture for Semantic Web Enabled Web Services”, NSF-EU Workshop on Database and Information Systems Research for Semantic Web and Enterprises, April 3 - 5, 2002 Amicalola Falls and State Park, Georgia.
- P. Lambrix, “Towards a Semantic Web for Bioinformatics using Ontology-based Annotation”, in: proceedings of the 14th IEEE international workshops on Enabling Technologies: Infrastructures for Collaborative Enterprises, 2005, pp.3-7.
- Semantic Web Education by Vladan Devedzic, Springer, springer.com ,2006, Pages 33-50.
- http://www.comp.rgu.ac.uk/staff/fh/CM3028/index.php
- Dario Bonino, “Architectures and Algorithms for Intelligent Web Applications”, December 2005.
- Zhaohui Wu, Huajun Chen, “Semantic Grid – Model, Methodology and Applications”, Springer, 2008, Page 26-32.
- Junhua Qu, Chao Wei, Wenjuan Wang, Fei Liu, “Research on a Retrieval System Based on Semantic Web”, 2011 IEEE International Conference on Internet Computing and Information Services. http://doi.ieeecomputersociety.org/10.1109/ICICIS.2011.142.
- Grigoris Antoniou and Frank van Harmelen, “Web Ontology Language: OWL”.
- Thomas B. Passin, “Explorer's Guide to the Semantic Web”, Manning Publications Co., 2004.
- Grigoris Antoniou and Frank Von Hormelen, “A Semantic Web primer”, The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England.
- www.dime-co.com/column/uploads/1/article_4.txt.
- Ee-Peng Lim and Aixin Sun, “Web Mining- The Ontology Approach”.
- http://www.sciam.com/article.cfm?id=the-semantic-web.
- Sergey Sosnovsky, Darina Dicheva, “Ontological technologies for user modeling”, Int. J. Metadata, Semantics and Ontologies, Vol. 5, No. 1, 2010.
- http://semanticweb.org/wiki/Semantic_Web.
- Noy and McGuinness ,“Ontology Development 101: A Guide to Creating Your First Ontology”, Stanford University.
- Sugumaran and Storey, “The Role of Domain Ontologies in Database Design : An Ontology Management and Conceptual Modeling Environment”, ACM Transactions on Database Systems, Vol. 31, No. 3, September 2006, Pages 1064–1094.
- Chandrasekaran, Josephson, Benjamins. "What are Ontologies and why do we need them". IEEE Intelligent Systems, Jan/Feb 1999.
- Time Berners-Lee, The Semantic Web Revisited, IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2006.
- Lina Tankelevičienė, Ontology and Ontology Engineering: Analysis of Concepts, Classifications and Potential Use in E-Learning Context, Technical Report MII-SED-08-01, February 2008.
- Daniel L. Rubin, Natalya F. Noy and Mark A. Musen, “Protégé: A Tool for Managing and Using Terminology in Radiology Applications”, Journal of Digital Imaging. 2007 Nov; 20(Suppl 1)34-46.


