Перспективные направления развития информационно-коммуникационных систем и технологий в логистике
Автор: Пустынникова Е.В., Баклушинский В.В.
Журнал: Вестник Воронежского государственного университета инженерных технологий @vestnik-vsuet
Рубрика: Экономика и управление
Статья в выпуске: 3 (69), 2016 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В настоящее время высокий торговый оборот является типичным для российской экономики, которая, в свою очередь, активирует достаточную интенсивность движения товаров. Логистика, как путь движения товаров в контексте различных способов доставки (авто-, воздушный, водный, железнодорожный транспорт), в том числе через таможенную границу, остро страдают от всех видов экономической трансформации. Таким образом, создание стабильных условий для перемещения товаров в соответствии с условиями взаимовыгодного сотрудничества является одним из приоритетов для материально-технического обеспечения. Тенденции экономического развития характеризуются ростом интеграционных процессов, доказавшие свою экономическую состоятельность. Такие преобразования означают необходимость улучшения механизмов контроля, в том числе материально-технического обеспечения. В статье рассматривается фактический выпуск бизнес-процессов информационной поддержки в условиях логистической интеграции. Основа информационной системы состоит из информационно-коммуникационных ресурсов, инструментов и технологий, использование которых направлено на решение конкретных задач для формирования информационной инфраструктуры, реинжиниринга бизнес-процессов, поддержки экономической безопасности бизнеса. В процессе изучения этого вопроса становятся очевидными неоспоримые преимущества информационных и коммуникационных технологий использования в логистических операциях, применение которых возможно в результате согласования интересов интегрированной системы. В статье приводятся доказательства того, что рынок оказывает определенное влияние на улучшение информационно-коммуникационных систем и технологий для комплекса, осуществляющего логистические операции, которые, в свою очередь, оптимизирует длительность движения товаров и связанных с этим процессом расходов, таким образом, определяет улучшение материально-технических условий с точки зрения роста бизнеса и повышения конкурентоспособности. В статье приводятся доказательства того, что рынок оказывает определенное влияние на улучшение информационно-коммуникационных систем и технологий для комплекса, осуществляющего логистические операции, которые, в свою очередь, оптимизируют длительность движения товаров и связанных с этим процессом расходов, таким образом, улучшаются материально- технические условия с точки зрения роста бизнеса и повышается конкурентоспособность.
Информационные и коммуникационные ресурсы и технологии, программного обеспечения, информационная интеграция в области логистики
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140229611
IDR: 140229611 | DOI: 10.20914/2310-1202-2016-3-360-365
Текст научной статьи Перспективные направления развития информационно-коммуникационных систем и технологий в логистике
scheme, which are recommended for implementation to support logistics processes. It should be borne in mind that it is necessary to harmonize the methods, tools, and technologies of company’s information resources management.
The basis of the company's information sys- and communication resources, tools, and technologies of materials and related processes management. There is plenty of information resources used in business. The list of information and communication resources designed to support logistics processes is formed in table 1 on the basis
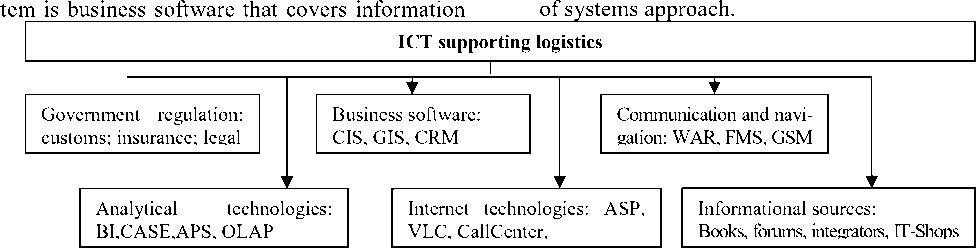
Figure 1. Modern ICT supporting logistics operations execution
Table 1.
Terminological review of information and communication resources
|
Resource name |
Abbreviation expansion |
|
MES |
Manufacturing execution system |
|
MRP |
Material requirements planning |
|
MRP II |
Manufacturing resource planning |
|
ERP |
Enterprise resource planning |
|
CSRP |
Customer synchronized resources planning |
|
SCM |
Supply chain management |
|
GIS |
Geographic information system |
|
CRM |
Customer relations management |
|
SRM |
Supplier relations management |
|
BRM |
Business Performance Management |
|
WMS |
Warehouse management system |
|
EDI |
Electronic data interchange |
|
FMS |
Fleet management system |
|
GSM |
Global System for Mobile connections |
|
WAP |
Wireless Application Protocol |
|
ASP |
Application service providing (technology outsourcing various programs with user access via the Internet) |
|
RFID |
Radio frequency identification |
|
VLC |
Virtual logistics center |
|
APS |
Advanced planning & scheduling |
|
GPS |
Global positioning system |
|
OLAP |
Online analytical processing |
|
BI |
Business Intelligence |
|
e-SCOR |
Supply Chain Operation Reference model |
|
CASE |
Computer Aided System Engineering |
Selection of a specific software is aimed at solving specific problems for the formation of information infrastructure, the choice of hardware and software, business process reengineering based on information systems, information outsourcing, ensuring the information security of business. When creating information space for support of logistics operations in the supply chain it is important to coordinate decisions on the selection of a particular set of information and communication resources, otherwise, lack of harmonization does not allow participants of product distribution to recognize the information. It should be noted that the market of information and communication technologies is very diverse, which in turn determines the high demands of the abilities and skills of IT-managers, both in design and development of information solutions, as well as when they are used in business practice.
Figure 2. Market trends of logistics services development
Table 2.
The main types of information systems applied in a comprehensive logistics automation
|
IS type |
Purpose |
|
MRP |
Material requirements planning. These systems are used in planning of parts demand for production of certain products quantity. Thus MRPs allow enterprise to determine optimal stocks for manufacturing goods according to forecasted sales. Nowadays MRP concept is outdated and usually isn’t used singly, but it forms part of current information systems [11] |
|
MRP II |
Manufacturing resource planning. MRP II systems have the capabilities of MRPs and provide additional functions of planning and controlling of cost calculation, procurement, sales and production data acquisition. Main idea of MRP II systems is to take into account all relevant resources for company’s success in planning. However, these systems include only manufacturing resources. |
|
ERP |
Enterprise resource planning. ERP systems include MRP II functionality and provide general functions of accounting, controlling, financial planning and HR. |
|
CSRP |
Customer synchronized resource planning. This type of systems has abilities of ERP and CRM. Concept of CSRP is inclusion of customer in the production process. It allows customer to order manufacturing of product and control it’s implementation and deadline. |
|
CALS |
Continuous acquisitions and life cycle support. CALS is an approach to designing and production of highly technological products. CALS technologies provide information support at all stages of lifecycle of the merchandise. This approach is based on creation of unified information space implemented according requirements of international standards system. |
These concepts reflect the importance of managing both of the internal resources of the company and external, such as consumer behavior, the means of distribution of goods and service maintenance, which are fundamentally important aspects under the conditions of modern integration processes.
A typical response to the needs of companies in the information integration can be seen in the evolution of information systems, and this process is accompanied by not only expanding their functionality, but also increasing compatibility with other systems, such as CRM, SCM, BPM (Figure 3).
Information integration in logistics and management at the global level is currently being implemented in the framework of international programs. One of these programs, which Russia has ratified, is TEDIM – Telematics in Foreign
Trade Logistics and Delivery Management. The development of program is going in the direction of the integrated logistics and SCM network formation with the appropriate information support based on the concept of a unified information technology environment “Northern Dimension”.
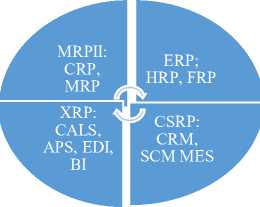
Figure 3. The evolution of corporate information system in the direction of information resources integration
Among the promising, emerging logistics trends in domestic practice there are several ones that require the use of ICT and should be noticed first and foremost:
-
• Automation of supply planning and re-planning with minimal losses;
-
• Client-oriented supply management
using CRM and SRM integrated automation technologies based on personified accounting of demand, ranging customers and suppliers;
-
• Automation of supplies on the basis of electronic planning (e-commerce).
-
• Transportation outsourcing in coordination of logistics operations, including interactive kind, that operate through virtual centers;
-
• Design of supply chain on the basis of automation principles (e-SCOR).
Information integration should be carried out comprehensively and in the combination of different organizational and technological forms. In the modern economic practice there are the most demanded ones:
-
• network integration associated with the construction of the physical topology of computer
networks and data networks driven by network operating systems;
-
• integration of business processes (business integration), focused on the office integration through e-mail and document management systems;
-
• intraindustrial integration, related to the automation of planning and management of manufacturing processes on the basis of MRP, ERP, MES systems;
-
• cross-enterprise integration based on Internet network, expandable up to the level of integration with customers;
-
• integration of business applications and resources sharing enterprise-level data, providing a comprehensive, interlinked solution of organization’s tasks, tactical production management, longterm planning and business process reengineering.
The main instruments of information integration are unified protocols, documentation languages and data communication systems, OpenSource and Internet/Intranet technologies, remote access to data and mobile management systems, shown in Table 3.
Table 3.
Terminology of information resources integration system
|
Definition |
Matter (functions) |
|
Internet |
Open global information system based on WEB technology; it is used for creation of a local network of a company, intercorporate associations (integration of Intranet) and regional networks (Extranet integration) |
|
Integration |
Technology and tools of integration of IS developed by various implementators (IBM WebSphere, AquaLogisBEASystems) |
|
SOA |
Service Oriented Architecture is a process technology of applications integration to the unified company’s information system |
|
XML/XSL |
Extensible Markup Language and Extensible Style Language are languages that simplify the interaction between different information systems on the document flow and data exchange. It serves as an environment for application integration |
|
SCADA |
Supervisory Control And Acquisition can be described as an automated process control system (APCS). These systems are quiet suitable for control over technological and business processes of industrial enterprise. |
Integration of information resources is related to the tactical tasks of information support of management in modern logistics, and therefore it’s implementation should be formed comprehensively by joined tools and technologies at all levels of the supply chain as follows:
-
• workplace should be automated to work with a local information system, e-mail, office applications and Internet access;
-
• department, service or unit should be equipped with a network information system of narrow functional orientation to work in groups, conduct electronic meetings management automation;
-
• at the level of the organization (corporation) a comprehensive management automation with a guide to the relevant sectoral, national and international projects and programs should be carried out.
One of main principles of describing the future development of logistics is the safety of product distribution and data transmission. In this connection there should be noted feasibility of important management tools to ensure security in the supply chain:
-
• Automatic tracking of the shipment (GPS);
-
• Generation of warnings about the dangers of electronic communication;
-
• Electronic seals;
-
• Audio and video identification when paying invoices by using special credit cards;
-
• Electronic flow of document, providing outrunning information support;
-
• The virtual inspection of the goods packaging.
Table 4 provides a list of tools and technologies for monitoring the supply chain that are recommended for use in business practice.
Since logistical services market capacity is continuously growing, it causes the expansion of the logistics abilities of subjects (senders, recipients, freight forwarders, brokers, carriers, etc.) in the management of material and associated flows.
A promising direction in terms of this trend of market changes is the formation of logistical structures managed by operators of logistics and transport and logistics centers. An example of the logistics subjects’ interaction for transport of cargo is the multi-modal transportation of goods (Figure 4).
Table 4.
Means and technologies for monitoring the supply chain
|
Monitoring tool |
Available functions |
|
Satellite system |
Ensuring global communication, navigation (GPS); global dispatching management of transport operations. |
|
Mobile communications |
Providing local level of the mobile voice communication; roaming in the global communication systems. |
|
Internet |
Video monitoring; notifications in real time. |
|
Individual display |
Special stickers for single use to control the object's state. |
|
Board units |
On-board computer; digital tachograph for control of work and rest of the crew; authorization of routing information record from the sensors. |
|
Radio-electronic and optical equipment and technologies of identification |
Passive and active RFID tags and devices designed for reading and processing information in warehousing management systems and the movement of goods. |
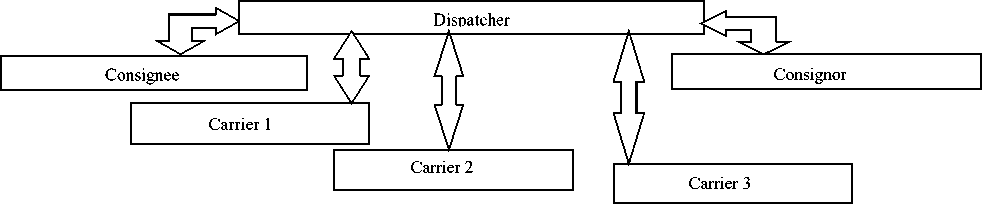
Figure 4. Information interaction of the subjects of delivery through the control center on the basis of requests for information
Conclusion
The integration of information flows and communication chains ensuring the supply of goods on the basis of open client-server technologies and unified data delivery technology are going to become the key areas in the development of logistics services. Thus, information integration is needed to build a unified information space of the chain, which helps to secure the necessary speed, completeness and accuracy of obtaining the information useful for the provision of services at a particular time.
It should be noted that currently virtual technology in logistics are actively developing, because competition in this sector is quite high.
Список литературы Перспективные направления развития информационно-коммуникационных систем и технологий в логистике
- Каширина М.Л., Загуменная Ю.С. Применение инновационных технологий в развитии логистики в кризисный период. Вестник ВГУИТ. 2016. № 2 (68). С. 346-349.
- Министерство связи и массовых коммуникаций Российской Федерации. URL: http://minsvyaz.ru/ru/
- Стратегия развития отрасли информационных технологий в Российской Федерации на 2014-2020 гг. и на перспективу до 2025 г. Утверждена распоряжением Правительства Российской Федерации от 1 ноября 2013 г. № 2036-р
- Прогноз научно-технологического развития Российской Федерации на период до 2030 года (утв. Правительством РФ 3 января 2014 г.). URL: http://www.garant.ru/products/ipo/prime/doc/70484380/#ixzz4GeNdE6FpП
- Пустынникова Е.В., Романова М.М. Совершенствование интеграционного подхода управления как условие реализации политики импортозамещения//Актуальные проблемы развития социально-экономических систем I Международная научно-практическая конференция (18-22 апреля 2016 года Россия, г. Ульяновск). C. 127-132.
- Пустынникова Е.В. Современные подходы управления производственными потоками промышленного предприятия в условиях корпоративной интеграции//Научно-технические ведомости Санкт-Петербургского государственного политехнического университета. Экономические науки. 2015. № 3 (221). С. 254-262.
- Пустынникова Е.В., Подгорнов В.В. Развитие единого информационного пространства как фактор формирования устойчивых региональных интегрированных систем//Симбирский научный вестник. 2012. № 3 (9). С. 145-151.
- Пустынникова Е.В. Обоснование целесообразности внедрения автоматизированной системы управления производством//Симбирский научный вестник. 2014. № 1. С. 123-129.
- Crumbly J., Fryling M. Rocky Relationships: Enterprise Resource Planning and Supply Chain Management//Journal of Information Systems Applied Research. 2013. №6(2). P. 31-39.
- Хан Д.В. Перспективные направления развития информационно-коммуникационных технологий в России и за рубежом: вопросы, проблемы, классификации. Материалы XIV Всероссийской объединенной конференции «Интернет и современное общество». URL: http://foresight.ifmo.ru/shared/files/201110/1_5.pdf
- Хорев А.И., Лутченко Т.В. Модель работы корпоративного центра интегрированной структуры в современных условиях Вестник ВГУИТ. 2016. № 2 (68). С. 356-360.
- Kurbel K.E. Enterprise Resource Planning and Supply Chain Management Functions//Business Processes and Software for Manufacturing Companies. 2013.
- Ягузинская И.Ю., Бирюков Е.О. Перспективы внедрения и развития информационных систем в транспортной логистике//Научно-методический электронный журнал Концепт. 2015. Т. 35. С. 151-155.


