Практическое применение языка Alloy для распознавания тактических ситуаций
Автор: Хельвас А.В., Галицкий А.С.
Журнал: Труды Московского физико-технического института @trudy-mipt
Рубрика: Информатика и управление
Статья в выпуске: 4 (40) т.10, 2018 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В статье рассматривается подход к обнаружению тактических ситуаций на осно- ве анализа формальных утверждений, формируемых путем обработки потока сообще- ний о событиях и угрозах в формализованном виде в информационной системе ситу- ационного центра. Для анализа используется язык Alloy и аналитическое приложение Alloy Analyzer. Рассмотрен пример анализа типичной ситуации обнаружения паводко- вой угрозы.
Тактическая ситуация
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142220463
IDR: 142220463 | УДК: 004.93.11,
Текст научной статьи Практическое применение языка Alloy для распознавания тактических ситуаций
Предметом исследования является создание подхода, к автоматизации процесса, распознавания тактических ситуаций на основе анализа потока структурированных описаний событий и угроз.
Примерами таких ситуаций могут быть как достаточно сложные ситуации (угрозы наводнений или техногенных катастроф, отказы сложных технических систем, сложные диспетчерские или логистические ситуации), так и достаточно простые ситуации (управление транспортными потоками на. парковке, управление лифтами с небоскребах).
В статье приведено формальное описание сущностей и отношений между ними для типового ситуационного центра, решающего задачу сбора, и анализа, информации об объекте критической инфраструктуры как сложной системе, методов обработки потока, информационных сообщений, описывающих события и угрозы с целью распознавания и предупреждения тактических ситуаций, а. также формирования и ввода, в действие оперативных планов действий сил и средств.
В качестве инструмента, анализа, потока, сообщений предложено использовать язык формального анализа, систем Alloy [1].
Alloy разработан группой исследователей из Массачусетского технологического института [1].
Анализ литературы показывает, что Alloy, в основном, используется для нахождения инцидентов в системах безопасности. В работе [3] строится модель веб-безопасности системы и рассматриваются основные виды угроз, которым система может подвергаться. В [1] приведен пример практического использования мониторинга ключей в гостинице. Существует ряд теоретических работ, где Alloy рассмотрен как инструмент для доказательства некоторых теорем и утверждений.
Помимо этого, Alloy применяется для анализа программного обеспечения. Например,он был использован для верификации кода установки протонной терапии рака. В [5] исследовалась система экстренной остановки, а в [4] были рассмотрены некоторые возможные проблемы, которые могут возникнуть при плохо разработанном дизайне программного обеспечения подобной установки, а также использование Alloy для их избежания.
В авиации также находят свое применение возможности языка Alloy. В регулировании авиапотоков используют специальные приложения, которые помогают избегать конфликтов между траекториями воздушных судов. В работе [6] была создана абстрактная Alloy-модель для проверки правильной работы подобного приложения на фундаментальном уровне.
Также Alloy-модели могут быть использованы для анализа алгоритмов проведения аукционов. Например, в [7] проверялась модель проведения аукционов Викри. В области электронной коммерции создание электронных кошельков требует хорошей и продуманной системы. В работе [8] исследовалась система безопасности кошельков Mondex, и были обнаружены некоторые ошибки в ее модели. Для конфигурирования сетей типа end-to-end Alloy-модель использовалась для создания проектировщика, на вход которому подаются набор сетевых компонент и требования по их конфигурации, а на выходе получается необходимая конфигурация, которая удовлетворяет этим требованиям [9].
Alloy также способен помочь моделировать и анализировать сложности, возникающие при создании файловых систем для хранения информации во флеш-памяти [10]. Для обеспечения безопасности движения поездов и предотвращения опасного движения поездов на железнодорожной станции применяется система блокировки. Для ее автоматической работы используется специальный язык Train Control Language (TCL). В работе [11] этот язык был формализован в виде Alloy-модели, что позволило упростить анализ и поиск ошибок на раннем этапе моделирования железнодорожной станции.
В [12] были проведены проверка и анализ модели библиотечной системы.
В [13] Alloy использовался для проверки безопасности криптографического протокола. В [14] был смоделирован и проанализирован один из протоколов (Pull-Based Asynchronous Rekeying Framework), который относится к проблеме управления ключами.
Alloy используется для непосредственного анализа программного кода. Для этого необходимо ограничить задачу некоторыми конечными рамками, например, лимитировать количество итераций в цикле, число рекурсивных вызовов процедуры и т. д. Используя этот подход, который по-другому называется проверкой по ограниченной области (bounded verification), в [15] были найдены ошибки программного обеспечения, которое использовалось для проведения публичных выборов в Голландии. А раннее в работе [16] было представлено приложение Jalloy для анализа JAVA-методов. Основываясь на этом приложении, в [17] был представлен фреймворк Forge.
Таким образом, Alloy — это язык описания структур и в то же время инструмент для их исследования и анализа. Он используется для широкого спектра приложений: от задач нахождения недостатков систем безопасности до проектирования телефонных сетей. Модель Alloy представляет собой набор ограничений, задающих (хотя и неявно) структуру объектов рассматриваемой предметной области.
Целью данной работы является показать, что множество событий формирует тактическую ситуацию (формальное определение события и тактической ситуации будет введено в соответствующем разделе). Показывается, что любую ситуацию можно представить в виде набора переменных, которые принимают значения «истина-ложь». На основании этих значений делается вывод о реакции на данную ситуацию.
1.1. Формальная постановка задачи
Схематическое изображение предметной области приведено на рисунке 1.
Рассмотрим некоторое множество объектов критической инфраструктуры О = {oi,...,Oj}, каждый из которых описывается некоторым набором состояний Sij.
Поведение множества объектов описывается массивом (потоком) событий Е = {еі,...,е^}. Под каждым событием е^ будем понимать набор информации, источником которой могут быть необслуживаемые датчики различного типа (включая датчики систем экологического мониторинга, контроля периметров, охранной и пожарной сигнализации и т.д.), интеллектуальные камеры наблюдения, сообщения дежурных диспетчерских служб, сообщения граждан.
Все сообщения типизированы, Каждому типу сообщений ставится в соответствие некоторое множество описывающих его параметров xj Обязательными параметрами является информация о месте и времени события.
Поток сообщений анализируется с целью обнаружения тактических ситуаций или их угроз.
Тактическая ситуация — одно или множество событий, объединенных по территориальному, временному и причинно-следственному признаку, для которых система на основе анализа предлагает типовой план действий.
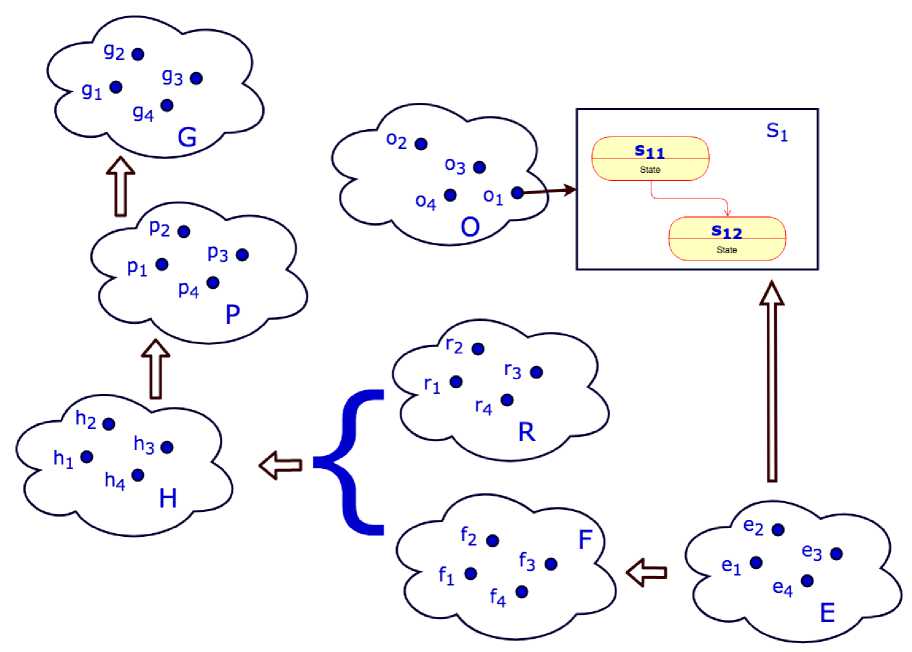
Рис. 1. Модель №1
Жизненный цикл системы и каждого объекта критической инфраструктуры Ог представляет собой множество состояний
S г = {^...Л }.
В качестве подхода к описанию событий жизненного цикла ОКИ предложено использовать Common Alerting Protocol [20].
Этот протокол использует XML семантику для описания информации о событии или угрозе.
Важными для нашей задачи атрибутами являются время события t^ и место события. Отметим, что используемая нами в дальнейшем модель позволяет работать как с точно локализованными событиями, так и с событиями, имеющими неточечную пространственную локализацию. Событие может быть привязано, например, к пространственной области, которая может быть даже неодносвязной.
Что касается момента времени t^ , описывающего событие, то мы будем требовать, чтобы событие носило мгновенный характер и описывалось точкой на временной оси. Для описания продолжительных во времени процессов мы можем использовать два события, описывающие начало и конец процесса, соответственно.
Таким образом, множество событий может быть упорядочено по времени. Будем считать, что индекс к всегда больше у того события, которое произошло позже.
На основе анализа упорядоченного множества событий мы можем сформулировать некоторые логические утверждения, принимающие значения «true» или «false». Множество таких логических утверждений будем обозначать
F = {/1,...,/т}.
Также может быть сформулировано некоторое количество логических утверждений -правил, не связанных с динамикой системы и задаваемых на основе некоторых фактов, находящихся вне рассматриваемой предметной области R = {ri,..., rj }.
Наша задача состоит в том, чтобы на основании анализа поступающего потока сообщений о событиях и формируемых на их основе логических утверждений обнаружить тактические ситуации и обеспечить задействование типовых планов действий Р = {pi,... ,pj } реагирования сил и средств G = {gi,... ,дп} с учетом сложившейся ситуации. Под планом реагирования мы понимаем шаблон, представляющий собой упорядоченную последовательность действий сил и средств в случае возникновения ситуации.
Множество тактических ситуаций будем обозначать:
н = {hi,...,M.
Множество тактических ситуаций всегда можно дополнить ситуацией «Не обнаружена ни одна из заданных тактических ситуаций».
Множество планов реагирования будем обозначать:
Р = {pi,... ,pm}.
Каждый план реагирования включает некоторое количество типовых действий, упорядоченных некоторым образом.
При обнаружении тактической ситуации на основе типового плана реагирования порождается процесс, включающий набор действий.
В связи с тем, что задача управления силами и средствами, как правило, решается некоторыми уже существующими решениями, мы будем считать, что процесс может описываться в рамках одной из нотаций:
• Live State Chart [18];
• BPMN [19].
2. Пример анализа тактической ситуации
Поясним приведенные выше формальные описания на примере анализа паводковой ситуации, образующей угрозу для гидротехнического узла (РТУ).
Множество Е представляет собой набор событий следующих типов:
-
• сообщения, полученные с датчиков метеорологического наблюдения, находящихся в пределах территории водосбора верхнего бьефа РТУ. Каждое событие содержит ситуацию об объеме выпавших осадков и о средней температуре в точке наблюдения за последний час;
-
• сообщения, полученные с датчиков уровня верхнего и нижнего бьефа;
-
• сообщения о прогнозе погоды (ожидаемое количество осадков и температура), привязанные к всей территории верхнего водосбора РТУ.
В рамках приведенной простейшей модели мы не будем рассматривать каскады РТУ.
С помощью приведенного набора сообщений о событиях мы сможем сформировать следующие логические утверждения:
-
1) fi - за сутки зарегистрировано выпадение не менее I мм осадков не менее, чем в т точках наблюдения на территории водосбора верхнего бьефа РТУ;
-
2) f2 - среднесуточная температура превысила п градусов по Цельсию не менее, чем в к точках наблюдения на территории водосбора верхнего бьефа РТУ;
-
3) fa _ количество выпавших, но не растаявших осадков выше критического уровня не менее, чем в к точках:
-
4) f4 - есть условие для массового таяния не менее, чем в к точках;
-
5) f5 - уровень воды в верхнем бьефе вырос более чем на XL за последний час.
Для формирования логических утверждений используется информация из получаемых сообщений. Анализ исходных сообщений с целью формирования логических утверждений не представляет какой либо сложности и нами, в рамках данной статьи, рассматриваться не будет.
Таким образом, нами получен набор логических переменных F = {fi,..., f5}, где каждое fj принимает одно из двух значений:
• 0, если утверждение ложно;
• 1, если оно истинно.
3. Язык моделирования Alloy3.1. Общие принципы языка Alloy
Заметим, что количество таких высказываний может быть достаточно большим. В реальной ситуации учет разного рода факторов позволяет получать сотни и тысячи утверждений. При этом на основании этих утверждений должно быть принято решение о наличии опасной ситуации (выбор некоторого 8г из множества типовых тактических ситуаций 5).
Для анализа логических утверждений предложено использовать язык анализа формальных утверждений Alloy.
Alloy — это язык моделирования на основании логики первого порядка [2].
В модели используется конструкция языка sig Name {}, представляющая собой некоторый эквивалент класса в объектно-ориентированных языках программирования, таких, например, как Java. Она содержит все объекты класса и отношения между этими объектами.
Инструментом для работы в рамках формализма Alloy является Alloy Analyzer, представляющий собой программу, которая по заданным для структуры ограничениям находит те конфигурации структуры, которые будут им удовлетворять. Она работает по принципу перевода выражений, используемых в Alloy в булевы выражения, которые затем анализируются. Такой подход удобен как для того, чтобы рассматривать сгенерированные примеры всевозможных конфигураций структуры, так и для генерации контрпримеров конфигураций. Структуры отображаются графически. Вид схематичного отображения может быть настроен пользователем.
Для удобства код на Alloy предложено разбивать на два файла.
Первый файл FirstCode формируется автоматически программой, осуществляющей анализ потока событий.
Второй файл SecondCode содержит набор статических правил, описывающих тактические ситуации.
Вначале, с помощью конструкций языка sig Name {}, создается множество булевых переменных Bool. Оно состоит из двух подмножеств True и False, которые являются истиной и ложью соответственно.
Принадлежность к множеству Bool описывается ключевым словом extends. Чтобы показать, что Bool состоит только из этих подмножеств и никаких других, используется ключевое слово abstract. Множества True и False, в свою очередь, состоят из одного элемента (их мощность равна единице), что отражено в ключевом слове one.
Затем, используя ключевое слово in, создаются два подмножества множества истинных утверждений. Фактически, они являются просто копиями множества True. Первое подмножество fi соответствует утверждению «За. сутки зарегистрировано выпадение не менее I мм осадков не менее, чем в m точках наблюдения», а второе подмножество f2 соответствует утверждению «Среднесуточная температура превысила п градусов по Цельсию не менее, чем в к точках = истина».
// Создаем множество булевых переменных:
// Делим его на два типа: Истина и Ложь:
one sig True, False extends Bool {}
// Fl - за сутки зарегистрировано выпадение не менее $1$ мм
// осадков не менее, чем в $т$ точках наблюдения sig Fl in False {}
// F2 - среднесуточная температура превысила $п$ градусов по
// Цельсию не менее, чем в $к$ точках sig F2 in True {}
// ҒЗ - кол-во выпавших, но не растаявших осадков
// выше критического уровня не менее, чем в $к$ точках sig F3 in False {}
-
// F4 - есть условие для массового таяния не менее, чем в $к$ точках
sig F4 in False {}
-
// F5 -уровень воды в верхнем бьефе вырос более чем на $\Delta L$
// за последний час
sig F5 in False {}
Во втором файле задаются множества результатов Results и тактических ситуаций Situations, которые связаны между собой отношением is. Отношением (по англ, relation) в языке Alloy описывается отображение одного множества на другое. То есть, некоторому элементу а множества Results ставится в соответствие некоторый элемент b множества S Situations по следующему правилу a.is = b. Множество тактических ситуаций S Situations состоит из двух подмножеств: si «Есть угроза наводнения» и S2 «Нет угрозы наводнения».
Наглядно отношения множеств изображены на рисунке 2.
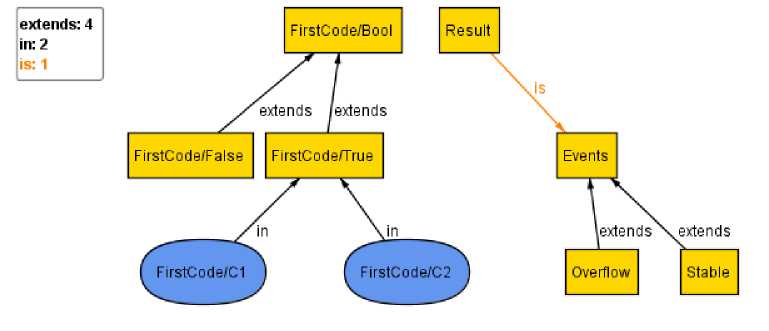
Рис. 2. Отношение множеств
На элементы множеств наложены некоторые ограничения. Ограничения задаются в виде некоторых утверждений (фактов) с помощью ключевого слова fact.
Записанный ниже факт имеет следующий смысл — если утверждения fi и /2 являются истинными, то имеется угроза наводнения.
Приведем листинг файла SecondCode.
open FirstCode //загрузка первой программы
// создание множества результатов с отношением is, которое связывает
// его с множеством Situations: one sig Result {is: Situations} // создание множества ситуаций: abstract sig Situations {}
// ситуации двух типов - угроза наводнения или отсутствие угрозы наводнения one sig Fl extends Events {} one sig F2 extends Events {}
// Задается факт, что при наличии двух истин возникает наводнение: fact { all t:True, fl:Fl, f2:F2, r:Result, el:Sl| fl = t and f2 = t implies r.is = el }
Для проверки некоторого утверждения используется конструкция assert. Данная конструкция представляет собой некоторый набор ограничений и свойств.
3.2. Проверка корректности набора правил
Предложенный подход обеспечивает возможность контроля множества правил и фактов на непротиворечивость.
Зададим в приведенном выше примере дополнительное утверждение, которое является неверным.
«Если выражения С1 и Сй истинны, то угрозы наводнения нет».
При проверке система предложит контрпример к этому утверждению. Наглядно это можно увидеть на рисунке 3.
Проверка гипотез производится с помощью команды check. Эта команда является инструкцией для Alloy Analyzer проверить конкретное утверждение. Если утверждение противоречит заданному набору правил, то Alloy Analyzer найдет контрпример, т. е. такую конфигурацию модели, которая не удовлетворяет условиям, содержащимся внутри проверяемого утверждения. Если утверждение не противоречит заданному набору правил, то анализатор контрпримеров не находит.
Механизмом, лежащим в основе Alloy Analyzer и позволяющим достаточно быстро находить контрпримеры, является SAT-решатель (по англ. SAT solver, от слова satisfiability). Он представляет из себя специальную программу. На вход SAT-решателя подается некоторое булевское выражение, т.е. набор именованных логических переменных, скобок, операций конъюнкции, дизъюнкции и логического отрицания. В некоторых таких выражениях имеется возможность задать каждой логической переменной значения 1 или 0 таким образом, чтобы выражение в итоге приняло значение истина, т.е. "1". И задачей SAT-решателя является именно поиск такого набора логических переменных, при которых булевское выражение является истинным. SAT-решатель способен справляться с задачами, в которых могут быть миллионы утверждений.
Важно, что существуют решатели с открытым исходным кодом. Так, например, MiniSAT и некоторые другие решатели используются в Alloy Analyzer.
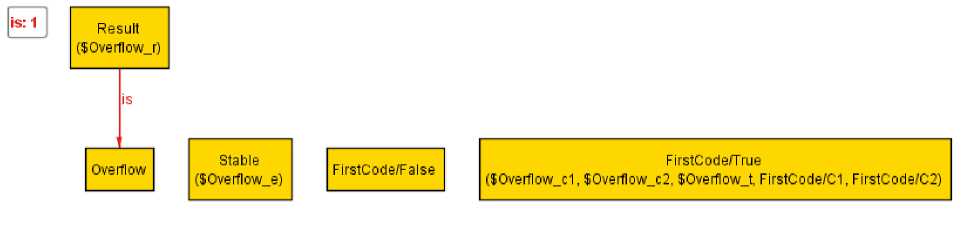
Рис. 3. Контрпример
// Для наглядности проверка модели простым утверждением, // которое противоречит заданному набору фактов.
assert Overflow { all t:True, fl:Fl, f2:F2, r:Result, e:S2| fl = t and f2 = t implies r.is = e }
// Анализатор выдаст контрпример после запуска команды: check si
4. Выводы
Модель, описанная выше, достаточно примитивна, но тем не менее показательна. Несмотря на ее учебно-демонстрационный характер сохраняется возможность добавлять данные об уровне осадков и температуре не в одной, а в нескольких точках. Также возможно скорректировать условие возникновения наводнения, усложнив набор анализируемых фактов. Таким образом, добавляя новые граничные условия, новые факты, новые переменные, усложняется модель. Alloy Analyzer переводит эту модель в булеву формулу, с которой работает SAT-решатель. Такой решатель способен справляться с моделями, имеющими большое число ограничений достаточно эффективно. Таким образом, мы продемонстрировали возможность анализировать тактическую ситуацию, извлекая из данных логические переменные и используя возможности языка Alloy.
Работа выполнена на кафедре твердотельной электроники, радиофизики и прикладных информационных технологий МФТИ.
Список литературы Практическое применение языка Alloy для распознавания тактических ситуаций
- Jackson D. Logic, language and analysis. The MIT Press, 2006. 369 p.
- Jackson D. Depandable Software by Design//Scientific American, 2006. V. 294, N 6. P. 69-75.
- Akhawe, Devdatta and Barth, Adam and Lam, Peifung E. and Mitchell, John and Song, Dawn. Towards a Formal Foundation of Web Security//Proceedings of the 2010 23rd IEEE Computer Security Foundations Symposium. Edinburgh. 2010. P. 290-304.
- D.Jackson and M.Jackson. Separating Concerns in Requirements Analysis: An Example//Rigorous Development of Complex Fault-Tolerant Systems. 2006. P. 210-225.
- Andrew Rae, Daniel Jackson, Prasad Ramanan, Jay Flanz and Didier Leyman. Critical Feature Analysis of a Radiotherapy Machine//Reliability Engineering and System Safety. 2004.
- Dennis G. TSAFE: Building a trusted computing base for air traffic control software. Master’s thesis. MIT. 2003.
- Tadjouddine E.M., Guerin F. Verifying Dominant Strategy Equilibria in Auctions//Multi-Agent Systems and Applications. V. 2007. P. 288-297.
- Tahina Ramananandro. Mondex, an electronic purse: specification and refinement checks with the Alloy model-finding method//Formal Aspects of Computing. 2008. P. 21-39.
- Sanjai Narain. Network Configuration Management via Model Finding//LISA ’05 Proceedings of the 19th conference on Large Installation System Administration Conference. 2005. P. 155-168.
- Eunsuk Kang, Daniel Jackson. Formal Modeling and Analysis of a Flash Filesystem in Alloy//Abstract State Machines, B and Z. 2008. P. 294-308.
- Svendsen A., Moller-Pedersen B., Haugen O., Endresen J., Carlson E. Formalizing Train Control Language: Automating Analysis Of Train Stations//Computers in Railways XII. 2010. P. 245-256.
- Frappier M.//Comparison of Model Checking Tools for Information Systems. 2010.
- Gassend B., Dijk M.V., Clarke D., Torlak E., Devadas S., Tuyls P. Controlled Physical Random Functions and Applications//ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. Secur. 2008. P. 245-256.
- Mana Taghdiri and Daniel Jackson. A Lightweight Formal Analysis of a Multicast Key Management Scheme//In Proceedings of Formal Techniques of Networked and Distributed Systems -FORTE 2003, LNCS. 2003. P. 240-256.
- Dennis G., Yessenov K., Jackson D. Bounded Verification of Voting Software//Verified Software: Theories, Tools, Experiments. 2008. P. 130-145.
- Vaziri M. Finding Bugs in Software with a Constraint Solver//PhD thesis. MIT. 2004.
- Dennis G. A relational framework for bounded program verification//PhD thesis. MIT. 2009.
- Harel D., Kugler H., Pnueli A. Synthesis Revisited: Generating Statechart Models from Scenario-Based Requirements, H.-J. Kreowski et al. (Eds.): Formal Methods (Ehrig Festschrift), 2006.
- Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN). OMG Specification, 2.0. 2011. http://www.omg.org/spec/BPMN/2.0
- Common Alerting Protocol Version 1.2. 2010. OASIS Standard http://docs.oasis-open.org/emergency/cap/v1.2/CAP-v1.2-os.pdf]


