Predictors of residual coronary artery disease after PPCI in diabetic patients with STEMI
Автор: Zarif B.
Журнал: Cardiometry @cardiometry
Рубрика: Original research
Статья в выпуске: 21, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
To describe the patients’ characteristics and risk factors of diabetic and non-diabetic patients presenting with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) in relation to residual SYNTAX score after PPCI (primary PCI). Material and Method: Prospective observational study using data from all comers in NHI with STEMI and underwent PPCI over one month. Results: The present study consisted of 290 patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction over one month period. About 50% of the patients with diabetes were more often female, with a greater prevalence of hypertension and dyslipidemia. In the diabetic group, the eGFR
Stemi, diabetes, egfr, syntax
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148324185
IDR: 148324185
Текст научной статьи Predictors of residual coronary artery disease after PPCI in diabetic patients with STEMI
Imprint
Bassem Zarif. Predictors of residual coronary artery disease after PPCI in diabetic patients with STEMI. Cardiometry; Issue 21; February 2022; p. 85-89; DOI: 10.18137/cardiometry.2022.21.8589; Available from:
Background
Coronary artery disease is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in diabetes mellitus [1]. Pa- tients with diabetes who developed an acute coronary syndrome appeared to sustain worse outcomes than those without diabetes. The poor prognosis associated with diabetes after acute myocardial infarction has been observed in several studies [2] despite adjustment for age, sex, additional comorbidities, and coronary risk factors. These differences may be related to the severity and extent of coronary heart disease in diabetic patients.
According to the available literature, the prevalence of a significant multivessel coronary disease among patients with STEMI varies from 30% to 60% [3].
The natural history studies of STEMI that multiple plaque ruptures can occur distant from the site of the culprit lesion throughout the coronary tree, suggesting a dynamic process of plaque instability which would be associated with worse prognosis and a higher risk of ischemic recurrences [4].
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is the best overall index of kidney function. Normal GFR varies according to age, sex, and body size and declines with age. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects a substantial minority of people with type 2 diabetes (T2D). Analysis of US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) datasets from 2007 through 2012 showed Stage 3 or worse disease (estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] <60 mL/min per 1.73 m2) in nearly one in five patients [5].
More recently, the significant impact of chronic kidney disease (CKD) on cardiovascular risk has been increasingly recognized. Patients with CKD are far more likely to die, predominantly from CVD, than to progress to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) [6].
Residual SYNTAX Score (RSS) was derived from the SYNTAX score to quantify the burden of residual coronary artery disease after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) and has been validated as an independent predictor for clinical adverse events [7].
Aim of work
The purpose of the present study was to describe differences in presenting characteristics of diabetic and non-diabetic patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction and the relation with residual syntax score after PPCI using data from all comers to NHI over one month period.
Material and Method
Study design
This is a prospective observational study for all STEMI comers present to National Heart Institute for one month and underwent PPCI.
Study population
Our cohort recruited 290 patients who presented over 30 days to NHI with STEMI. Between 1-30 September 2021. Information about patients’ demographic, presenting symptoms, management practices coronary syndrome was recorded. The registry classified the patients into two groups, diabetics, and non-dia-betics
The present study included ST-elevation myocardial infarction, which is determined by chest pain and/or symptoms felt to be consistent with cardiac ischemia and elevated biochemical markers of myocardial necrosis, either total creatine phosphokinase or creatine kinase MB fraction > two times the upper limit of the hospital’s standard range and/ or positive troponin I or T results (if performed) with accompanying electrocardiographic changes fitting criteria for ST-segment elevation or new LBBB. Diabetes is diagnosed when the patient’s fasting plasma glucose is 126 mg/dL or higher at least two times or has a history of diabetes.
eGFR calculated using: The National Kidney Foundation recommends using the CKD-EPI Creatinine Equation (2021) to estimate GFR [8]. Residual SYNTAX Score (RSS) was used to estimate residual CAD after PPCI to the culprit lesion. It was calculated after the final angiogram using the online SYNTAX calculator [9] , excluding the culprit lesion.
Statistical analysis
Categorical data were summarized in frequencies and percentages. Continuous variables were reported as mean + SD or median and 25th and 75th percentiles. Differences in baseline characteristics, presentation, treatment practices among the comparison groups were examined using the Chi -Square test and t -test for categorical and continuous variables, respectively. Mann-Whitney U -test was used for comparing time to admission and length of stay between two groups. The significance of the difference was defined as a two-tailed p-value < 0.05. Logistic multivariable regression analysis by the SPSS program was used to 86 | Cardiometry | Issue 21. February 2022
examine differences in the residual SYNTAX for diabetes and other potentially confounding prognostic factors from baseline characteristics, clinical presentation.
Table 1
Results
|
Group |
N |
Mean |
SD |
P-value |
|
|
Age(yrs) |
NonDiabetics |
176 |
58.420 |
10.970 |
< .001 |
|
Diabetics |
114 |
54.956 |
9.357 |
||
|
Female Sex |
NonDiabetics |
38/176 |
0.784 |
0.413 |
0.028 |
|
Diabetics |
38/114 |
0.664 |
0.475 |
||
|
BMI |
NonDiabetics |
176 |
28.055 |
3.876 |
0.009 |
|
Diabetics |
114 |
29.338 |
4.103 |
||
|
HTN |
NonDiabetics |
176 |
0.239 |
0.427 |
< .001 |
|
Diabetics |
114 |
0.673 |
0.471 |
||
|
Dyslipidemia |
NonDiabetics |
176 |
0.153 |
0.361 |
0.009 |
|
Diabetics |
114 |
0.372 |
0.485 |
||
|
Smoking |
NonDiabetics |
176 |
0.602 |
0.491 |
< .001 |
|
Diabetics |
114 |
0.389 |
0.490 |
||
|
eGFR (mL/min per 1.73 m2 |
NonDiabetics |
176 |
82.490 |
26.479 |
< .001 |
|
Diabetics |
114 |
68.040 |
26.228 |
||
|
Residual Syntax score >0 |
NonDiabetics |
33/176 |
6.045 |
9.302 |
0.015 |
|
Diabetics |
40/114 |
9.274 |
11.860 |
Baseline characteristics
The present study consisted of 290 patients with elevation myocardial infarction. 176 were non-di-abetics (60.6%), while 114 were diabetics. Diabetic patients were younger in average age (54 vs. 58 years) (figure 1). Patients with diabetes were more likely to be women (34% vs. 21%) (figure 2), and they were more likely to have a higher BMI (Figure 3), hypertension (figure 4), and dyslipidemia (Figure 5). They were less likely to be current cigarette smokers (figure 6). eGFR was less in diabetics (68 mL/min per 1.73 m2 vs 82 mL/min per 1.73 m2) (Figure 7). Both groups’ management strategies were similar, and the whole study population received PPCI to the culprit-only lesion.
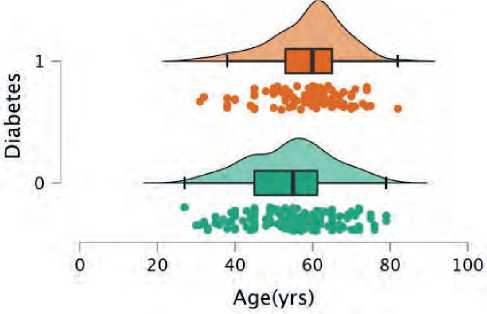
Figure 1. Mean age distribution between both groups; green plot represents non-diabetics and orange represent diabetics
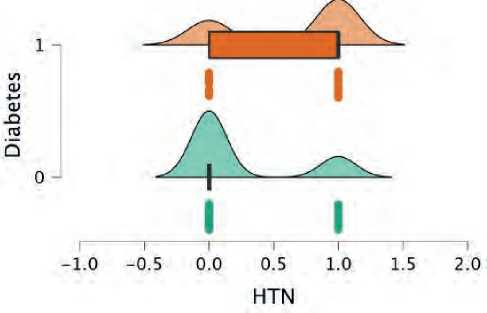
Figure 4. HTN distribution between both groups; green plot represents non-diabetics and orange represent diabetics
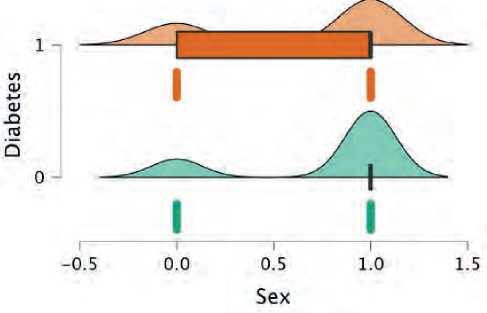
Figure 2. Gender distribution between both groups; green plot represents non-diabetics and orange represent diabetics
1.0 -0.5 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0
Dyslipidaemia
Figure 5. Dyslipidemia distribution between both groups; green plot represents non-diabetics and orange represent diabetics
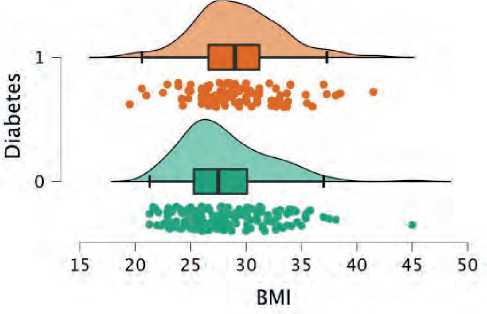
Figure 3. BMI distribution between both groups; green plot represents non-diabetics and orange represent diabetics
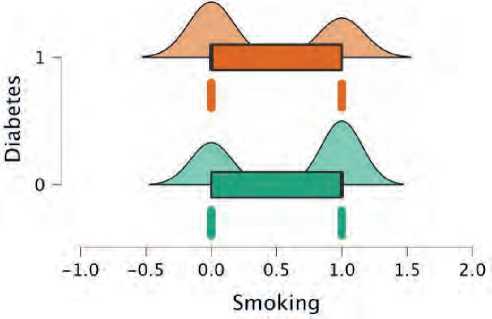
Figure 6. Smoking distribution between both groups; green plot represents non-diabetics and orange represent diabetics
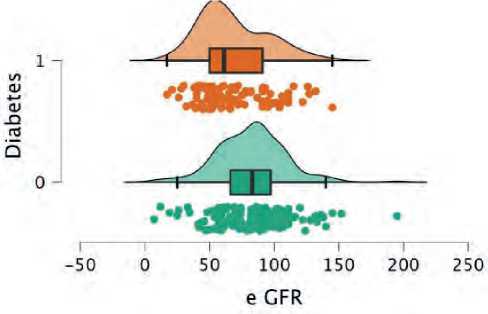
Figure 7. eGFR distribution between both groups; green plot represents non-diabetics and orange represent diabetics
Predictors of residual SYNTAX score
217 patients have a residual SYNTAX score of zero (75%), while 73 (25%) have residual syntax more than zero, which is considered a multivessel disease (MVD). Diabetic subgroup 35% (40 patients) have MVD while 18% (33 patients) of the non-diabetic subgroup have MVD.
Then the association between residual syntax score groups and every other measured variable was tested (Univariate analysis). Diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia showed no significant correlation with residual SYNTAX (p=0.7).
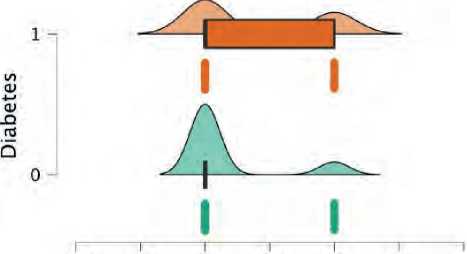
Correlation between eGFR and residual SYNTAX (Figure 8):
-
• Diabetic patients with eGFR<60 mL/min per 1.73 m2 was found in 54 patient of the diabetic subgroup. Multivessel disease 30 (57%) patients average residual syntax above zero with average residual SYNTAX of 25. While 60 diabetic patients have an eGFR >60 mL/min per 1.73 m2; of them, 17 (28%) has MVD, average syntax 22
-
• Non-diabetic with eGFR<60 mL/min per 1.73 m2: 35 patient; of them (17%) has residual syntax above zero with an average of 18.
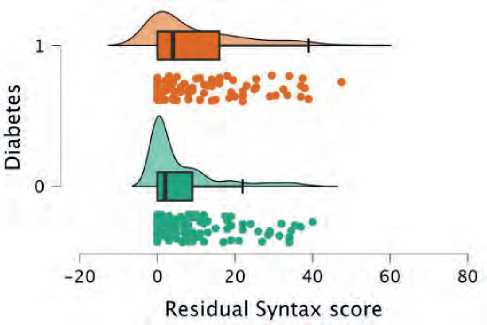
Figure 8. Residual Syntax score distribution between both groups; green plot represents non-diabetics and orange represent diabetics
Discussion
The presented study found that 40% of ST-eleva-tion myocardial infarctions were diabetes, while approximately one-quarter of patients with ACS had diabetes from the GRACE registry. Diabetic patients in the present study were more often female, more likely to have hypertension and dyslipidemia, less likely to be a smoker, which is consistent with the data available from the GRACE registry. 25% of all study cohort showed MVD, which is less than observed in worldwide registries, which showed an average of 40-60% of all patients with STEMI that showed MVD [10].
Diabetics have a higher possibility to have MVD than non-diabetics which is consistent with the available data [11].
However, the presence of diabetes was not independently correlated with the residual disease after treating the culprit lesion with PPCI. Other baseline characteristics showed no significant correlation with the residual SYNTAX, including gender, hypertension, smoking, and dyslipidemia.
We observed in our study that diabetic patients with eGFR < 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2 have a higher residual SYNTAX score than diabetics with normal GFR as well as non-diabetic with normal or reduced eGFR, which might represent a link between Cardiovascular and renal outcomes in diabetic patients.
Before our work, the residual SYNTAX score after PPCI was not tested on randomized data as a potential predictor of recurrent events. However, the patients with MVD presented with STEMI have a worse outcome and a higher rate of recurrent events [12]. More research is needed to evaluate the outcome of this group of patients.
Conclusion eGFR is correlated with the presence of MVD and with higher residual syntax score in diabetic patients presented with STEMI, which reflect the relation between the severity of CAD and nephropathy in diabetic. That observation was not existing in a diabetic with normal eGFR or in non-diabetics with normal or reduced eGFR.
Calculation of eGFR in all diabetic patients with STEMI should be encouraged and included in the baseline assessment of the patient’s risk profile.
Our observation generates a hypothesis about the missing link between micro and macrovascular complications in diabetes.
Further research is needed regarding cardiovascular outcomes and possible interventions that may improve renal and vascular outcomes in diabetic patients with nephropathy after STEMI.
Acknowledgment
We thank the CCU team at NHI for their help in data collection.
Statement of ethics
We declare that the research complies with the guidelines for human studies following the World
Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki. The ethics committee approved the study protocol of the general organization for teaching hospitals and institutes (GOTHI). Number IHC00019, date 14/7/2021. A written Informed Consent was obtained from all participants to participate in the study.
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
No funding
Список литературы Predictors of residual coronary artery disease after PPCI in diabetic patients with STEMI
- Goldberg RB. Cardiovascular disease in diabetic patients. Med Clin North Am. 2000; 84: 81-93.
- Chun BY, Dobson AJ, Heller RF. The impact of diabetes on survival among patients with first myocardial infarction. Diabetes Care. 1997; 20: 704-8.
- Goldstein JA, Demetriou D, Grines CL, et al. Multiple complex coronary plaques in patients with acute myocardial infarction The New England Journal of Medicine. 2000;343:915-22.
- Collet JP, Zeitouni M, Procopi N, et al. Long-term evolution of premature coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74:1868.
- Bloomgarden Z. The kidney and cardiovascular outcome trials. J Diabetes. 2018 Feb;10(2):88-89. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12616. PMID: 29031006.
- Keith DS, Nichols G a, Gullion CM, Brown JB, Smith DH. Longitudinal follow-up and outcomes among a population with chronic kidney disease in a large managed care organization. Arch. Intern. Med. 2004;164(6):659–63.
- Genereux P, et al. Quantification and impact of untreated coronary artery disease after percutaneous coronary intervention: the residual SYNTAX (synergy between PCI with Taxus and cardiac surgery) score. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012; 59:2165–74
- Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF 3rd, Feldman HI, Kusek JW, Eggers P, Van Lente F, Greene T, Coresh J; CKD-EPI (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration). A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. 2009 May 5;150(9):604-12. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-150-9-200905050-00006.
- Wang Y, et al., Residual SYNTAX score in relation to culprit-plaque characteristics and cardiovascular risk in acute myocardial infarction: an optical coherence tomography study. European Heart Journal. October 2021; Volume 42, Issue Supplement 1, 724-1459. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehab724.1459
- Lekston A, et al. Impact of multivessel coronary disease on one-year clinical outcomes and five-year mortality in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Kardiol Pol. 2011;69(4):336-43. PMID: 21523666.
- Cardiac mortality, diabetes mellitus, and multivessel disease in ST elevation myocardial infarction Sonya Burgesset al, August 14, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.08.021
- van der Schaaf RJ, et al. Impact of multivessel coronary disease on long-term mortality in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction is due to the presence of a chronic total occlusion. Am J Cardiol. 2006 Nov 1;98(9):1165-9. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard. 2006.06.010. Epub 2006 Aug 31. PMID: 17056319.


