Preliminary experience with bioabsorbable intramedullary nails for paediatric forearm fractures: results of a mini-series
Автор: Jozsa G., Kassai T., Varga M.
Журнал: Гений ортопедии @geniy-ortopedii
Рубрика: Случай из практики
Статья в выпуске: 6 т.29, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Introduction Forearm fractures are common injuries in childhood. Completely displaced and unstable fractures require surgical intervention. Elastic Stable Intramedullary Nailing (ESIN) is widely used in treating these fractures. Although stainless steel and titanium implants are the most widely used, resorbable nails are becoming an option.Aim To present our initial experience in treating forearm fractures in children with Resorbable Stable Intramedullary Nailing (ReSIN).Methods The authors present several cases treated with ReSIN, their summarry and describe the techniqual steps. Results The series included 4 patients operated on with ReSIN. Bone union with anatomic and functional recovery was stated in all cases within the period of 5-7 months after surgery.Discussion More and more paediatric fractures can be treated with absorbable implants and result in good outcomes. It can be said that the new methods enabled similar stable fixation as with metal implants, which is considered the gold standard. A distinct advantage over metal implants is that there is no need to remove the implant, thus avoiding a second operation and reducing the risk of surgical complications. Another positive thing is that absorbable implants can be sunk the level of the cortical layer of the bone, they can easily be dropped under the skin. The only drawback of the method is the price of the implants.Conclusion The management of paediatric diaphyseal forearm fractures with bioabsorbable intramedullary nails is a promising emerging alternative to the gold standard ESIN technique.
Paediatric, forearm, fracture, bioabsorbable, resorbable, implant, plga
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142240035
IDR: 142240035 | УДК: 616.717.5/.6-001.5-089.227.84-053.2 | DOI: 10.18019/1028-4427-2023-29-6-640-644
Текст научной статьи Preliminary experience with bioabsorbable intramedullary nails for paediatric forearm fractures: results of a mini-series
The current gold standard method in the treatment of paediatric diaphyseal forearm fractures requiring operative treatment is the elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN). Such fractures include displaced and or unstable fractures, where conservative treatment with a cast would be insufficient to achieve satisfactory results after bone healing. The ESIN or flexible intramedullary nailing (FIN) is minimally invasive, in contrast to an open approach using plate and screw fixation, and leads to less soft tissue damage upon later implant removal. Standard nails are titanium elastic nails (ESIN) which are generally removed in a second surgery after sufficient bone healing has occurred [1-9].
However, in recent years bioabsorbable intramedullary nails have been developed for and used to manage paediatric diaphyseal forearm fractures. Using a bioabsorbable material presents multiple benefits, such as eliminating the need for a second surgery to remove the nail, thereby
reducing soft tissue damage. Moreover, it decreases anaesthesia-related risk, exposure to radiation, and potential irritation which is usually caused by a protruding titanium elastic nail tip [10-12].
The Activa IM-Nail™ developed by Bioretec Ltd. has shown promising results in Finnish pediatric forearm diaphyseal fracture treatment clinical studies. This implant material is a PLGA (poly-L-lactide-co-glycolide) polymer with a radiopaque tricalcium phosphate ( β -TCP) tip. The Pécs University Hospital Department of Paediatrics and Department of Pediatric Traumatology, Péterfy Hospital, Manninger Jenő National Trauma Center have been involved in an ongoing prospective multicentre clinical study analysing the treatment of paediatric diaphyseal forearm fractures with the Activa IM-Nail™ since 2021 [13].
The authors will explore the advantages of using bioabsorbable intramedullary nails in treating paediatric diaphyseal forearm fractures.
Epidemiology and Aetiology of Forearm Fractures
Fractures are prevalent in the paediatric population, accounting for approximately 25 % of all childhood injuries [1]. Radial and ulnar fractures have the highest incidence, making up 36 % of all childhood fractures [2, 3]. The mechanism of injury is mainly accidental trauma resulting from sports or leisure activities. A 1996 Welsh study found that 36.1 % of subjects sustained fractures while participating in sports or leisure activities [2]. Team ball and wheel sports such as cycling, rollerskating, and skateboarding were the most common, making up 42.4 % and 34.9 %, respectively. That study found distal radius fractures to have the highest incidence and soccer and rollerskating to be the most common sports and leisure activities causing the injury [3, 14-17]. The study also observed that of the fractures that occurred in schools, 45 % happened on the playground. Of these, three-quarters occurred while the child was running, and half resulted from falling on a hard surface [2, 5-7].
The mechanism of distal radial fractures is typically a fall on an outstretched arm (FOOSH). Forearm shaft fractures often occur this way or due to a direct blow to the forearm. Studies show that protective equipment such as wrist guards can effectively prevent distal radius fractures during activities such as rollerskating. These guards prevent the hyperextension motion, which can occur in a FOOSH, absorb shock, and facilitate sliding of the guard along a surface to divert the direction of the kinetic force [14-16].
Diagnosis and Classification of Paediatric Forearm Fractures
The gold standard approach to diagnosing a forearm fracture is X-ray imaging. Patient’s history and physical examination consistent with the clinical picture of a fracture can be sufficient for diagnosis. However, X-ray imaging will confirm the diagnosis and provide information influencing the treatment plan. Both anterior-posterior and lateral view images should be ordered. Orthogonal films enable the clinician to examine for pathologies that may not be visible at certain angles. The clinician should also consider imaging the elbow or wrist joint to check for Monteggia or Galeazzi injuries.
Treating a multi-fragmentary fracture includes careful analysis of X-ray images in preoperative planning. In the case of highly complex fractures, CT may be indicated to provide a more detailed image of the fracture morphology and soft tissue involvement. The clinical approach to the diagnosis of fractures in children, however, differs slightly from that in adult patients.
If a clinician were to be confident in their professional opinion that a paediatric forearm fracture was, for example, a minimally or non-angulated radial greenstick fracture, an X-ray could be omitted and opted for conservative therapy. Furthermore, examining fracture crepitation and excessive palpation should be avoided to minimise the child’s pain and negative psychological response.
Paediatric diaphyseal forearm fractures are classified by the AO (Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Osteosynthesefragen) Paediatric Comprehensive Classification of Long-Bone Fractures. They are classified according to the fracture morphology, complexity, and involvement of one or both forearm bones. The classification code comprises two main parts describing the fracture location and morphology. Paired forearm bones are collectively defined as ‘2’. Fracture locations are further labelled as proximal ‘1’, diaphyseal ‘2’, or distal ‘3’. A lowercase letter specifies which bone is broken in fractures affecting only one bone belonging to a set of paired bones. For example, the code for an isolated radius fracture would include an ‘r’. The fractured subsegment, i.e. epiphysis, metaphysis, and diaphysis, is labelled ‘E’, ‘M’, or ‘D’, respectively. The second part of the code describes the fracture morphology. Fracture pattern and severity are described with numbers.
Finally, a degree of displacement can be described with roman numerals. A simple transverse nondisplaced fracture of the radial diaphysis, when no ulnar fracture is present, is therefore described with the code 22r-D/4.1. A both-bone forearm fracture, e.g. a simple transverse nondisplaced fracture of the radial and ulnar diaphysis, is described with the code 22-D/4.1. This classification system helps to describe fractures clearly and concisely and is used internationally [4].
Aim To present our initial experience in treating forearm fractures in children with Resorbable Stable Intramedullary Nailing (ReSIN).
METHODS
Bioabsorbable Intramedullary Nailing Technique
Bioabsorbable intramedullary nails such as the Activa IM-Nail™ from Bioretec Ltd. are introduced similarly to the aforementioned traditional ESIN technique, with some differences due to the different material of the nail. Intraoperative imaging with C-arm fluoroscopy is also used in bioabsorbable intramedullary nail insertion. However, only the radiopaque tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP) tip is visible on the film, not the entire nail as with TENs. The PLGA material is radiolucent. Also, unlike the ESIN procedure, the medullary canal should be prepared with an implant-specific dilator tool when using a bioabsorbable intramedullary nail. This is done to decrease the risk of implant breakage upon insertion against resistance.
The dilator tool prepares a space for the implant within the canal. Furthermore, surgeons often bend titanium elastic nails prior to insertion to create a curvature of the nail. It should not be performed with the Activa IM-Nail™, as the current PLGA material is too brittle and could be damaged if bent with force [8-10].
Perhaps of most clinical significance and in contrast to traditional treatment with ESINs, postoperative immobilisation with a cast is recommended for bioabsorbable intramedullary nails such as the Activa
IM-Nail™. Cast options include a long arm cast for two weeks followed by a short arm cast for two to four weeks or a long semicircular arm cast with volar support for 4-6 weeks. Unfortunately, cast immobilisation typically leads to joint stiffness and decreased range of motion after cast removal. This is a primary cause of hesitation for surgeons considering the bioabsorbable intramedullary nailing method when comparatively, the standard TEN technique does not require plaster casting and therefore avoids such complications entirely [10-13].
RESULTS
Case 1 An eight-year-old female patient with a displaced both-bone diaphyseal forearm fracture was treated using the Activa IM-Nail™. Preoperatively the fracture underwent closed reduction. The patient experienced no surgical or postoperative complications. A long arm cast was applied for three weeks, followed by a short arm cast for the subsequent two weeks. The clinical outcome was highly satisfactory; the patient did not experience functional impairment or decreased range of motion. X-rays taken pre-, intra-, and postoperatively illustrate the success of the treatment (Fig. 1). Unlike children treated with titanium elastic nails, this patient does not require a second surgery for hardware removal. The outcome of this patient is representative of the vast majority of the preliminary outcomes recorded in this study.
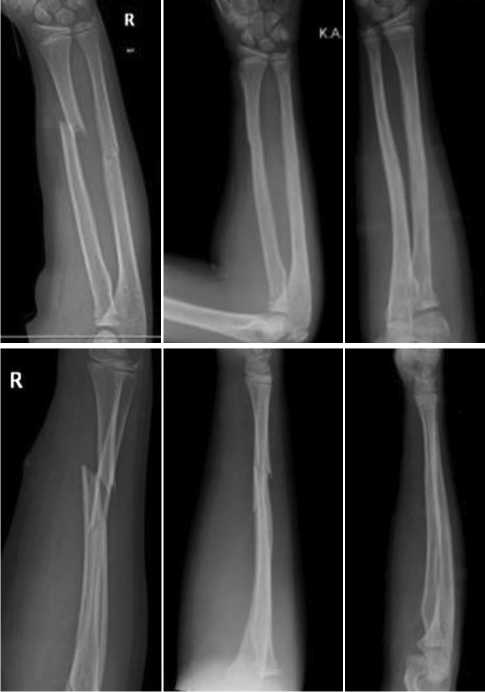
Fig. 1. Case 1. From left to right: рreoperative, same-day postoperative control, six months postoperative control X-rays
Case 2 The 11-year-old girl fell while playing; her right forearm was injured and deformed, and she reported pain when moving the wrist and elbow joints. During her physical examination, we noticed a deformity of the left forearm and a dorsal deviation proximal to the middle third. However, sensation, circulation and movement were preserved in the fingers. The X-ray confirmed the right radius and ulna’s incomplete (subperiosteal) fracture with axis deviation (Fig. 2, a). The patient was admitted to the pediatric surgery department for surgical treatment.
Closed reduction was performed under general anaesthesia, after which the fracture of the radius and ulna were stabilised with absorbable 3.2 mm diameter medullary nails. After the operation, an additional long arm cast was applied. The postoperative control X-ray showed the fracture in a good position; the tricalcium-phosphate marking is visible in the metaphysis of the proximal radius and distal ulna (Fig. 2, b).
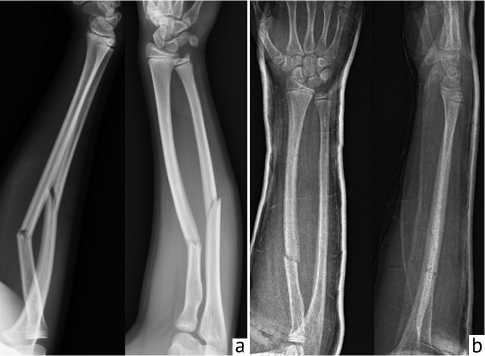
Fig. 2. Case 2: a – рreoperative subperiosteal right forearm fracture; b – IM nails stabilise forearm postoperatively
Case 3 An 8-year-old boy was playing in the yard, running, and then fell on his left forearm. According to him, he heard a crack. During his physical examination, the child reported tolerable pain under the effect of the Fentanyl given in the ambulance, and there were no neurovascular abnormalities in the fingers. However, significant swelling and deformity were observed in the middle third of the right forearm. The X-ray confirmed a middle-third forearm fracture with displacement (Fig. 3, a).
Closed reduction was performed under general anaesthesia; the ulna reposition was done with a wire inserted percutaneously into the fracture gap. Stabilisation of the forearm bones was done with absorbable IM nails. A long arm cast immobilised the left upper limb for four weeks. The postoperative control radiogram showed the fracture in a good position (Fig. 3, b).
Case 4 A 7-year-old girl fell while riding a horse; her right forearm was injured and deformed, and she complained of severe pain. X-rays confirmed the patient had a both-bone diaphyseal forearm fracture (Fig. 4, a) of the right arm. The fractures were reduced, and both bones were fixed with Activa IM-Nail™. Postoperative imaging showed good alignment (Fig. 4, b).
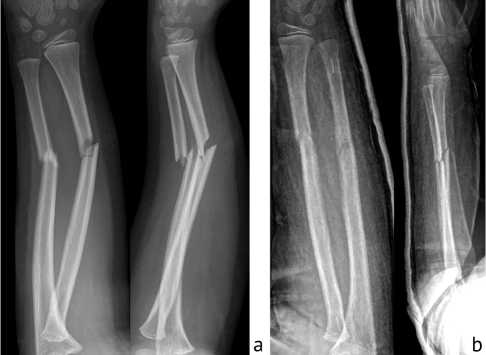
Fig. 3. Case 3: a – preoperative X-rays; b – postoperative control X-rays
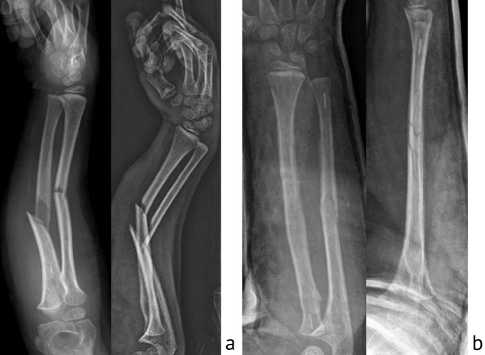
Fig. 4. Case 4: a – preoperative radiograms; b – postoperative excellent alignment
DISCUSSION
More and more paediatric fractures can be treated with absorbable implants and result in good outcomes. The authors described the most frequently occurring types of forearm fractures, in which the same results can be achieved with absorbable implants as with metal and titanium implants, which are currently considered the gold standard. Based on the clinical results so far (short- and medium-term follow-up of the patients), it can be said that the new methods enabled similarly stable fixation as the fixation with metal implants, which is considered the gold standard. A distinct advantage over the procedures with metal implants is that there is no need to remove the implant, thus avoiding a second operation and reducing the risk of surgical complications [10, 11, 12, 13, 18]. It is also a positive thing that absorbable implants can be sunk the level of the cortical layer of the bone, they can easily be dropped under the skin, so they do not cause soft tissue irritation. The health care system is also not burdened by the second operation (metal removal) and the associated hospital care costs [19, 20]. The only drawback of the method is the price of the implants.
CONCLUSION
The management of paediatric diaphyseal forearm fractures with bioabsorbable intramedullary nails is a promising emerging alternative to the gold standard ESIN technique. Research suggests that patient outcomes are comparable to those treated with traditional ESIN. However, large-scale and long-term studies are still needed, as well as further research into bioabsorbable polymers and other potential alternative biomaterials.
Conflict of interest Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement Clinical application of the technique was accepted and permitted in 2010 by our medical review board, the Hungarian Pediatric Trauma Committee, and the Hungarian Pediatric Surgery Committee.
The work was performed in Pécs and Budapest. Surgical Division, Department of Paediatrics, Medical School, University of Pécs, 7 József Attila Street, Pécs, H7623, Hungary and Department of Paediatric Traumatology, Péterfy Hospital, Manninger Jenő National Trauma Center, 1081, 17 Fiumei Street, Budapest, Hungary.
Funding This research received no specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Disclosure The authors report no conflict of interest.
Список литературы Preliminary experience with bioabsorbable intramedullary nails for paediatric forearm fractures: results of a mini-series
- Kosuge D, Barry M. Changing trends in the management of children's fractures. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B(4):442-448. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.97 B4.34723
- Lyons RA, Delahunty AM, Kraus D, et al. Children's fractures: a population based study. Inj Prev. 1999;5(2):129-132. doi: 10.1136/ip.5.2.129
- Schieber RA, Branche-Dorsey CM, Ryan GW, et al. Risk factors for injuries from in-line skating and the effectiveness of safety gear. N Engl J Med. 1996;335(22):1630-1635. doi: 10.1056/NEIM199611283352202
- Audige L, Slongo T, Lutz N, et al. The AO Pediatric Comprehensive Classification of Long Bone Fractures (PCCF). Acta Orthop. 2017;88(2):133-139. doi: 10.1080/17453674.2016.1258534
- Alzen G, Benz-Bohm G. Radiation protection in pediatric radiology. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2011;108(24):407-414. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2011.0407
- Noonan KJ, Price CT. Forearm and distal radius fractures in children. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1998;6(3):146-156. doi: 10.5435/00124635199805000-00002
- Caruso G, Caldari E, Sturla FD, et al. Management of pediatric forearm fractures: what is the best therapeutic choice? A narrative review of the literature. Musculoskelet Surg. 2021;105(3):225-234. doi: 10.1007/s12306-020-00684-6
- Navarro M, Michiardi A, Castaño O, Planell JA. Biomaterials in orthopaedics. J R Soc Interface. 2008;5(27):1137-58. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2008.0151
- Kulkarni RK, Pani KC, Neuman C, Leonard F. Polylactic acid for surgical implants. Arch Surg. 1966;93(5):839-843. doi: 10.1001/ archsurg.1966.01330050143023
- Heye P, Matissek C, Seidl C, et al. Making Hardware Removal Unnecessary by Using Resorbable Implants for Osteosynthesis in Children. Children (Basel). 2022;9(4):471. doi: 10.3390/children9040471
- Perhomaa M, Pokka T, Korhonen L, et al. Randomized Controlled Trial of the Clinical Recovery and Biodegradation of Polylactide-co-glycolide Implants Used in the Intramedullary Nailing of Children's Forearm Shaft Fractures with at Least Four Years of Follow-Up. J Clin Med. 2021;10(5):995. doi: 10.3390/jcm10050995
- Sinikumpu JJ, Keranen J, Haltia AM, wt al. A new mini-invasive technique in treating pediatric diaphyseal forearm fractures by bioabsorbable elastic stable intramedullary nailing: a preliminary technical report. Scand J Surg. 2013;102(4):258-264. doi: 10.1177/1457496913490459
- Roeder C, Alves C, Balslev-Clausen A, et al. Pilot Study and Preliminary Results of Biodegradable Intramedullary Nailing of Forearm Fractures in Children. Children (Basel). 2022;9(5):754. doi: 10.3390/children9050754
- Ryan LM, Teach sJ, Searcy K, et al. Epidemiology of pediatric forearm fractures in Washington, DC. J Trauma. 2010;69(4 Suppl):S200-S205. doi: 10.1097/TA.0b013e3181f1e837
- Grabala P. Epidemiology of forearm fractures in the population of children and adolescents: Current data from the typical polish city. Orthop Muscular Syst. 2015;5(203). doi: 10.4172/2161-0533.1000203
- Landin LA. Fracture patterns in children. Analysis of 8,682 fractures with special reference to incidence, etiology and secular changes in a Swedish urban population 1950-1979. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 1983;202:1-109.
- Hassan FO. Hand dominance and gender in forearm fractures in children. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2008;3(3):101-103. doi: 10.1007/ s11751-008-0048-6
- On SW, Cho SW, Byun SH, Yang BE. Bioabsorbable Osteofixation Materials for Maxillofacial Bone Surgery: A Review on Polymers and Magnesium-Based Materials. Biomedicines. 2020;8(9):300. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8090300
- Juutilainen T, Patiala H, Ruuskanen M, Rokkanen P. Comparison of costs in ankle fractures treated with absorbable or metallic fixation devices. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1997;116(4):204-8. doi: 10.1007/BF00393710
- Bostman O. Economic considerations on avoiding implant removals after fracture fixation by using absorbable devices. Scand J Soc Med. 1994;22(1):41-5. doi: 10.1177/140349489402200107


