Применение биомеханики в судебно-медицинской экспертизе дорожно-транспортных происшествий
Автор: Веселый В., Вилимек М., Равник Д.
Журнал: Российский журнал биомеханики @journal-biomech
Статья в выпуске: 1 (103) т.28, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
При дорожно-транспортных происшествиях с участием автомобилей и пешеходов травмы головы являются одним из наиболее распространенных повреждений. Известно, что самая распространенная причина смерти - удар пешехода головой о лобовое стекло автомобиля. В данной статье исследуются биомеханические аспекты при ударном взаимодействии автомобиля и пешехода, с целью анализа травм головного мозга и шейного отдела позвоночника. Для анализа нагрузок, при которых возникают переломы, использовались параметры прочности и жесткости костей лица и черепа, а также для определения скорости движения головы при ударе о лобовое стекло автомобиля применялся простой аналитический подход. Были проведены эксперименты для изучения дефектов на лобовом стекле, в результате столкновения с объектом, имитирующим голову человека с различной скоростью. Рассмотрены два варианта определения скорости удара головы пешехода при столкновении с автомобилем. Первый случай, предполагает, что центр тяжести манекена перемещается с той же скоростью, что и наезжающее транспортное средство, в результате чего скорость удара примерно вдвое превышает скорость автомобиля. Второй (более реалистичный сценарий) предусматривает перемещение тела с гораздо меньшей скоростью, что в результате дает большую в полтора раза угловую скорость головы, чем скорость автомобиля, при определенном угле наклона относительно оси x . Согласно расчетам, чем меньше угол наклона лобового стекла, тем меньше скорость удара головой при фиксированной скорости автомобиля. Признавая ограничения моделирования, в исследовании подчеркивается необходимость использования экспериментальных данных для более реалистичных результатов. Применение биомеханики в экспертизе дорожно-транспортных происшествий должно учитывать размеры повреждений лобового стекла в зависимости от скорости. Данное исследование способствует пониманию факторов, влияющих на травмы при дорожно-транспортных происшествиях, и подчеркивает важность эмпирических данных в судебно-медицинской экспертизе. Предлагаемый аналитический подход и результаты, полученные в ходе экспериментов, могут быть использованы для проверки корректности заключений при столкновении автомобиля с пешеходом.
Дорожно-транспортное происшествие, механизм травмы, травма головы, пешеход, лобовое стекло автомобиля, скорость удара головы
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/146282932
IDR: 146282932 | УДК: 531/534: | DOI: 10.15593/RZhBiomeh/2024.1.09
Текст научной статьи Применение биомеханики в судебно-медицинской экспертизе дорожно-транспортных происшествий
RUSSIAN JOURNAL OF BIOMECHANICS
Основной причиной гибели или инвалидности при столкновении пешехода с автомобилем является травма головы [19]. Во всех дорожно-транспортных происшествий с участием пешеходов 91 % людей получают травмы мягких тканей головы, а 39 % таких травм заканчиваются летальным исходом. В тоже время, повреждения других частей тела, также полученных в автомобильных авариях, смертельными совсем не являются. Самая распространенная причина смерти - удар пешехода головой о лобовое стекло автомобиля [4-7].
Виды наиболее распространенных травм головы уже неоднократно описывались ранее, но существует потребность в изучении момента столкновения головы пешехода с автомобилем (в частности, с лобовым стеклом). На основе таких исследований могут быть внесены конструктивные изменения в секцию кузова автомобиля таким образом, чтобы свести к минимуму последствия удара. Лю и его команда [13] использовали компьютерное моделирование удара головой о лобовое стекло автомобиля в соответствии с тестом Euro NCAP, чтобы определить деформацию лобового стекла и ее влияние на силу удара. Эта модель использовалась, в частности, для разработки состава отдельных слоев лобового стекла. Аналогичным образом Яо и соавт. [28] провели экспериментальное моделирование столкновения пешехода с автомобилем, чтобы найти критические области на лобовом стекле, где удар головой оказывает наихудший эффект. Ожидаемо, они обнаружили, что удар головой о края лобового стекла или о место его прилегания к кузову приводит к летальному исходу. В этих точках стекло подвергается наименьшей боковой деформации, поэтому удар головой подобен удару о неподвижное препятствие [11]. Почти идентичные результаты наблюдаются при столкновениях автомобилей с велосипедистами или мотоциклистами. Голова велосипедиста находится на большей высоте, чем у пешехода, и почти всегда при ударе о переднюю часть транспортного средства попадает в лобовое стекло. Травмы головы велосипедистов чаще всего не смертельны, так как они используют защитные шлемы.
Андерсон и соавт. [1], рассмотрели влияние средней скорости автомобиля на смертность пешеходов в дорожно-транспортных происшествиях, обнаружив, что снижение скорости с 60 до 50 км/ч снижает смертельные травмы на 48 %. Дальнейшее снижение числа травм с летальным исходом происходит при снижении скорости примерно до 35 км/ч, постепенное снижение скорости до нуля практически не влияет на снижение числа травм со смертельным исходом. При скорости столкновения 45 км/ч 6 из 10 травм пешеходов заканчиваются летально [26]. Пешеходы являются наиболее частыми участниками дорожного движения. Почти 35 % всех пешеходов в возрасте до 15 лет, попавших в аварию с автомобилем, получили какие-либо травмы.
Наиболее распространенными травмами при столкновениях транспортных средств с людьми являются травмы нижних и верхних конечностей. Следующими по распространенности выступают травмы головы. Однако повреждения головы с гораздо большей вероятностью получат оценку по шкале AIS, равную или превышающую 3 (шкала тяжести AIS от 0 до 6 [3] для описания травм, полученных при столкновении с медицинской точки зрения: 0 - нет травм; 1 - незначительная травма; 2 - травма средней тяжести; 3 - серьезная травма; 4 - тяжелая травма; 5 -критическая травма; 6 - летальная травма (травма, при которой невозможно выжить). Чаще всего это очень серьезные травмы, приводящие к смерти (до 1/3 всех травм головы у пешеходов). И, напротив, наиболее распространенные травмы нижних и верхних конечностей всегда попадают в промежуток от 0 до 3 классификации AIS.
Большинство столкновений с пешеходами происходит, когда автомобиль движется вперед [10-12, 18, 27]. В таких авариях пешеход, стоящий или идущий пешком, получает удар, разгоняется до скорости транспортного средства и продолжает движение вперед, пока транспортное средство не затормозит до полной остановки. Пешеходы подвергаются сразу двум ударам - о транспортное средство и о землю, но большинство смертей происходит именно во время взаимодействия с транспортным средством [7]. Это взаимодействие характеризуется следующей последовательностью событий: бампер транспортного средства сначала соприкасается с нижними конечностями пешехода, передний край капота ударяется о бедра или таз, а затем о голову.
Первоначальное столкновение пешехода и транспортного средства
Легковой автомобиль классической конструкции (тип кузова - седан), движущийся со скоростью vc , наезжает на пешехода в точке A с силой FA на высоте h , как показано на рис. 1. Предполагается, что пешеход движется не в направлении движения автомобиля и имеет массу m . Для простоты человек рассматривается как твердое тело с высотой H , шириной W и длиной D . Тело имеет неоднородную плотность по вертикальной координате р ( у ) , центр тяжести C находится на высоте hc . Масса выражается уравнением:
WH D H
m = J р( У) dV = J dx J р( У) dyJ dz = WD J p( У) dy, (1) V 00 0 0
где dV = dxdydz и V = WHD .
Положение центра тяжести C определяется как
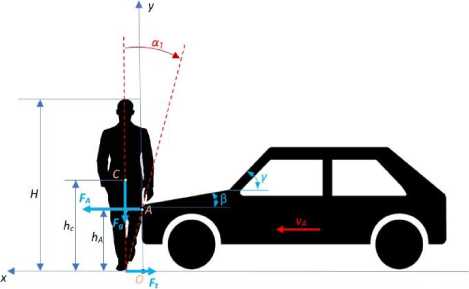
Рис. 1. Столкновение пешехода с транспортным средством – первоначальный контакт
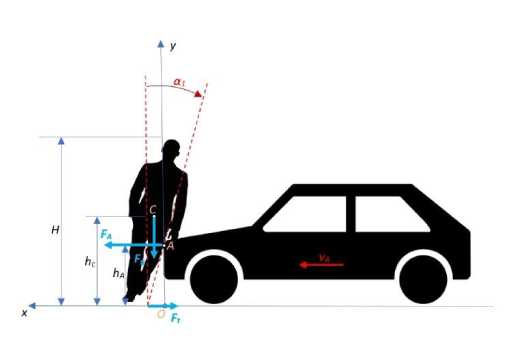
Рис. 2. Столкновение пешехода с транспортным средством – начало поворота пешехода
L C = V ---------= kH , где k e ( 0,55 v 0,57 ) . (2)
m
Центр тяжести обычно расположен в верхней части тела, немного выше середины величины H . Коэффициент k имеет меньшее значение для женщин и большее для мужчин. Для анализа движения предполагается, что масса тела сосредоточена в центре тяжести, который перемещается в плоскости движения транспортного средства, то есть в плоскости ( x , у ) , со скоростью v ( t ) = ( vx ( t ) , v y ( t ) ,0 ) . При ударе с неизвестной силой FA в точке контакта A тело начинает поворачиваться в плоскости ( x , у ) , и одновременно с этим будет перемещаться вверх по капоту, по направлении к лобовому стеклу. В то же время тело будет смещаться транспортным средством в направлении его движения. Сила FA , с которой машина сбивает тело, зависит от способности к деформации как тела, так и передней части автомобиля, которые очень трудно определить. Поэтому цель состоит в том, чтобы выяснить, при каких условиях тело перемещается вверх.
Величина скорости центра тяжести v (t) = (vx (t), vy (t) ,0) зависит от величины силы FA и силы трения Ft , а также от их положения относительно центра тяжести пешехода. В общем случае происходит поворот (наклон) тела, (рис. 2).
Динамика тела может быть описана с помощью кинетического момента. Пешеход представляет собой тело объемом V , которое находится в контакте с транспортным средством в точке A. В точке контакта возникает вращательный момент, как показано на рис. 1, 2.
Изменение кинетического момента пешехода во времени вызвано поверхностным и объемным моментами. Сила трения между обувью пешехода и землей в трехмерном случае Ff =(0, fEmg,0). Предполагаемый коэффициент трения пешехода о землю f (1 – 0,05), где низкие значения используются для очень скользких поверхностей, например, льда.
Момент инерции тела с учетом массы тела (1) и положение центра тяжести (2)
j x p ( у ) vydV - J ( у - hA ) p ( у ) vxdV =
VV
= vy J xdx J dz J p( у ) dy - mhCvx + mhAhvx = WDH
W
= —mvc v
2 C , y
- mhCvC , x + mhAvC , x .
Таким образом, скорость зависит только от времени.
После столкновения момент инерции пешехода изменяется с течением времени:
-
4 W mvC,у - mvC,x ( hC - hA ).
Сила тяжести равна
W x p( у) gdV = —mg(5)
V
Сила F t , как единственная поверхностная сила, создает момент:
hCfEmg .
Записав теорему о движении центра масс, получим.
-
v CP , у - g = —[ fE g + ( hC - hA ) vCP , x ] . (6)
Условие, при котором разница между ускорением в вертикальном направлении и ускорением силы тяжсти должна быть положительной:
vCF - 1 > 0 . (7)
g
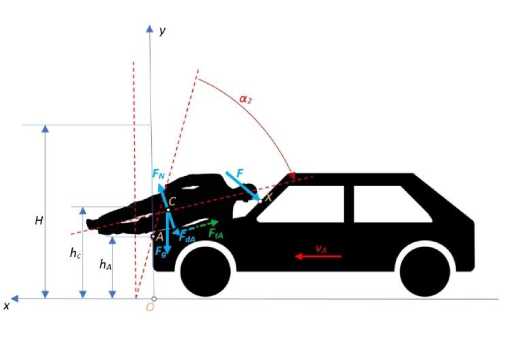
Рис. 3. Столкновение пешехода с транспортным средством – вращение пешехода с одновременным скольжением по капоту автомобиля
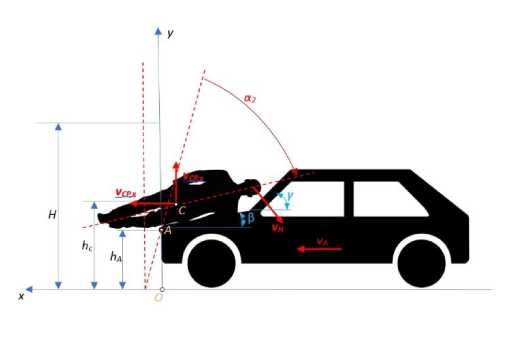
Рис. 4. Столкновение пешехода с транспортным средством – скорость центра тяжести и направление скорости головы при ударе
Это условие представляет собой ситуацию, когда пешеход при ударе перемещается вверх по капоту в сторону лобового стекла. Используя зависимость (2), условие можно упростить до соотношения:
kH > hA . (8)
В результате центр тяжести автомобиля всегда должен быть ниже центра тяжести пешехода, что справедливо для большинства автомобилей.
Также встает вопрос о том, при каких условиях пешеход соскальзывает с капота автомобиля обратно на землю. То есть, когда происходит диссипация энергии удара о капот автомобиля на которую влияют на следующие величины: угол наклона капота р и коэффициент трения между пешеходом и поверхностью капота ftA (см. рис. 3). Большее значение коэффициента применимо к шероховатым поверхностям. Значение, равное 0,6, применимо к контакту кожи с гладкой металлической поверхностью.
Сила трения на передней части автомобиля равна:
Fa = famS cos а.
Сила, притягивающая тело к земле, равна:
FdA = mg sin а .(10)
Из условия
Fa ^ Fd,(11)
можно определить подходящий угол наклона капота, чтобы предотвратить скольжение тела пешехода под колеса.
tg«^ 1- .(12)
fT
В этих условиях тело будет сверху автомобиля. Данная модель сильно упрощена, и конечный результат будет зависеть не только от трения, но и от механики удара тела, сопровождаемого последующим отскоком. На практике угол наклона капота близок к 10°.
Падение пешехода, сопровождаемое его вращением
Для
упрощения
человеческое
тело
рассматривается как массивный жесткий стержень с центром тяжести в точке C , расположенный на высоте
hC ,
(см. рис. 1). Момент инерции однородного длиной H относительно оси более длинной mH 2
стержня стороны
равен
.
Тело вращается вокруг своего центра
тяжести
после удара, следовательно, момент инерции равен:
J z = m ( hC — 0,5 H )2 —
= ( к — 0,5) 2 mH 2
mH
—
mH 2
- = 0,087 mH 2
Поскольку тело после удара вращается жесткому стержню, можно определить
подобно угловую
скорость записав выражение для кинетического момента тела
где i , j = x, y , z .
M i = J j Й j ,
Изменение кинетического момента во времени равно сумме моментов внешних сил:
J z ® z
— h C F f +( h C — h A ) F A .
Это уравнение описывает вращение стержня вокруг смещенного центра тяжести в системе ( x ', y ’) , которая
сама смещается со скоростью центра vC (t) =(vC,x(t), vC,У (t)). Подставляя (13)
получим выражение для углового ускорения
® z
—
h C F f + ( h e — h a ) F A
0, 087 mH 2
.
тяжести
в (15),
Таблица 1
Значения максимальной скорости удара головы человека о лобовое стекло автомобиля при равных скоростях движения автомобиля и человека
|
v A [км/ч] |
10 |
15 |
20 |
25 |
30 |
35 |
40 |
|
v H ( γ = 20◦) [км/ч] |
21 |
31 |
41 |
52 |
62 |
72 |
82 |
|
v H ( γ = 30◦) [км/ч] |
22 |
33 |
43 |
54 |
65 |
76 |
87 |
|
v H ( γ = 45◦) [км/ч] |
23 |
35 |
46 |
58 |
69 |
81 |
92 |
|
v H ( γ = 60◦) [км/ч] |
24 |
36 |
48 |
60 |
72 |
84 |
96 |
|
v H ( γ = 80◦) [км/ч] |
25 |
37 |
50 |
62 |
74 |
87 |
99 |
Таблица 2
Значения максимальной скорости удара головы человека о лобовое стекло автомобиля при разных скоростях движения человека и автомобиля
Скорость перемещения центра тяжести тела уменьшается на одну треть вследствие деформации передней части автомобиля и воздействия сил трения. Абсолютная скорость головы при ударе также уменьшится. В табл. 2 приведены значения скорости удара, при разных скоростях центра тяжести тела и транспортного средства. В данном случае угловая скорость фигуры была определена из соотношения (21). Эти скорости примерно в 1,5 раза превышают скорость движущегося транспортного средства.
В табл. 1 представлены максимальные скорости удара головы человека о лобовое стекло, в случае, когда тело сначала контактирует с транспортным средством, а затем ударяется о лобовое стекло. Это получается в том случае, если вся кинетическая энергия идет на вращательное движение, а скорость перемещения центра тяжести тела совпадает со скоростью транспортного средства. Гораздо более реалистичными являются расчетные скорости удара головой о лобовое стекло автомобиля, которые приведены в табл. 2. Здесь принимается во внимание, что тело поворачивается после контакта с транспортным средством в направлении противоположном скорости автомобиля, поэтому скорость движения центра масс тела человека вперед составляет одну треть от скорости транспортного средства, а угловая скорость вращения тела рассчитывается из закона сохранения количества движения (25). Скорость удара головой о лобовое стекло уменьшается при меньшем наклоне стекла. Этот факт может показаться нелогичным, но, если учитывать направление угловой скорости головы, то есть угловую скорость по отношению к траектории, которую описывает голова фигуры при вращении, то вертикальная составляющая скорости (направление y ) доминирует над горизонтальной (направление x ) в случае контакта со стеклом с низким углом наклона.
Необходимо прояснить два аспекта. Из векторной суммы скорости фигуры в направлении движения автомобиля и угловой скорости ясно, что при некотором наклоне лобового стекла направление скорости при ударе не перпендикулярно лобовому стеклу автомобиля (что соответствует правилам испытаний Euro NCAP, когда известен угол удара). Второй аспект заключается в следующем. Скорость автомобиля и скорость вращения тела вряд ли будут постоянными в течение всего времени столкновения автомобиля с пешеходом. Транспортное средство может изменить свою скорость, затормозив во время столкновения. На скорость вращения сильно влияет движение тела относительно передней части автомобиля. Поэтому следует отметить, что скорости удара, рассчитанные в этой статье, являются приблизительными. Для получения более реалистичных данных необходимо применение соответствующего оборудования и большее количество экспериментов с манекенами.
Экспериментальное исследование
Для оценки относительного уровня защиты пешехода при наезде транспортного средства проводятся краш-тесты. Тестирование обычно проводится в рамках программ оценки новых автомобилей ( Euro NCAP, ANCAP ) на соответствие требуемым правилам. В одном из видов краш-теста манекен контактирует с передней частью автомобиля (обычно с капотом или лобовым стеклом). Ускорение головы манекена измеряется и используется для оценки относительного уровня защиты путем расчета критерия травмы головы ( HIC ).
В данной работе имитируется контакт пешехода с передней частью транспортного средства. Во время испытания автомобиль остается неподвижным, а ударный элемент сталкивается с транспортным средством при заданной скорости и угле. В качестве ударного элемента используется макет головы взрослого человека. Использование ударных испытаний только с одним макетом являлось ограничением исследования.
Лобовое стекло состоит из двух отдельных стекол, соединенных тонкой пленкой. Пластиковая пленка, изготавливаемая обычно из PVB, имеет отличную адгезию к стеклу и оптическую прозрачность. Толщина всего лобового стекла автомобиля, как правило около 4,5 мм, толщина стеклянных панелей 2,1 и 1,6 мм, и толщина пленки PVB между ними – 0,76 мм. Соединение слоев автомобильного лобового стекла происходит в автоклаве – специальной печи, в которой с помощью температурного воздействия и давления создается прочное и устойчивое к дефектам и повреждениям целое стекло.
Когда ламинированное стекло разбивается, его осколки остаются склеенными между собой и не разлетаются.
При испытаниях краш-тест удара головы о лобовое стекло начальный угол направления удара составляет 65° от горизонтальной плоскости.
Голова манекена (ударный элемент) была размещена на конце стержня, расположенного вертикально (рис. 7). К голове был прикреплен акселерометр для регистрации ускорения. Высота и длина стержня была выбрана так, чтобы соблюдались два условия: должны были соблюдаться стандартное направление удара и необходимая скорость удара, приблизительно равная 11–18 м/с (40–65 км/ч).
Теоретическая скорость удара головы человека была приблизительно определена из равенства кинетической и потенциальной энергии (26).
mv— = mgR ( sin a + sin p ) ,
Интегрируя (16) по времени, получим:
Ю z ( t ) = -
h C F f + ( h e - h A ) F A
0,087 mH 2
t = n t . (17)
Скорость некоторой точки тела на расстоянии r от центра тяжести в системе отсчета ( x ’, у ' ) равна:
Полная кинетическая энергия после столкновения определяется движением центра тяжести тела и его вращением вокруг него:
E kin = - mv cP , x + - J z O z . (22)
( v x ‘ ( t ) , v y' ( t ) ) = ( ю z ( t ) r sin a , co z ( t ) r cos a ) =
= (®z (t)(-у'), юz (t) x'), ^^
где r = J(- у ') 2 + x '2
Скорость перемещения центра тяжести тела в направлении движения автомобиля будет максимально приближенной к скорости автомобиля vc = vV , если высота точки удара равна высоте центра тяжести фигуры hc = hA .
Таким образом, тело вращается вокруг центра тяжести с угловой скоростью, которая для твердого тела может быть вычислена в соответствии с соотношением:
s \ 1 I d vy' d vx' ^ A
О (t) = - — ---x~ = O t.
z() 2 dx' dу 'J
Следовательно, диапазон возможной угловой скорости пешехода, который начинает вращение после столкновения с транспортным средством задается как
Скорость головы пешехода
Полная скорость головы пешехода относительно передней части автомобиля имеет определяющее значение для оценки последствий столкновения. Эта скорость определяется суммой скорости вращения пешехода и его поступательно скорости.
Пренебрегая вертикальной составляющей скорости центра тяжести v Cy , которая очень мала из-за часто малого угла наклона капота в , приблизительную
скорость головы при ударе можно получить
О ( t )€ | 0, v A Vx z () I h e — h A
следующим образом:
Рассчитанные максимальные угловые скорости из уравнения (20) описывают механику движения тела в фазе столкновения.
Если вся кинетическая энергия удара преобразуется в энергию вращательного движения:
vH (vCx = 0) =
(VA+Оz (H - hc ) Sin Y)2 +
< + ( ° z ( H - hc ) cos y ) 2
22 mv _ Jz ю z 2 = 2
.
Разница между угловой скоростью, рассчитанной по формуле (20) и по формуле (21) составляет 5 %. Формулы могут применяться в случае, если столкновение автомобиля с телом человека произошло в точке , лежащей ниже центра масс тела человека. В противном случае человек оказывается перед транспортным средством или под ним.
vH ( vCx = 0,3 vA ) =
(vA - vCx+юz (H - hC ) Sin Y) +
^+(юz ( H - hC) cos y)2
Расчетные значения приведены в табл. 1 для
положения центра тяжести hC = 0,56 H и различных
значений наклона лобового стекла Y . Можно заметить,
что значения сильно зависят от угла наклона стекла и что по отношению к скорости автомобиля скорость удара примерно в 2 раза выше. Следует отметить, что
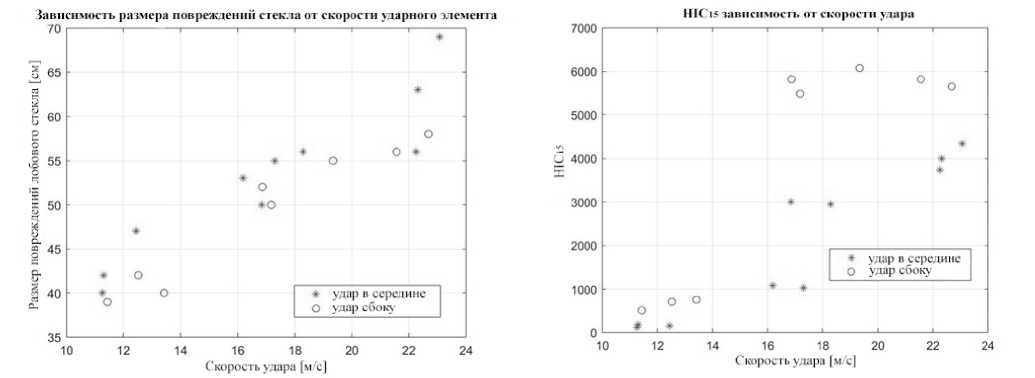
Рис. 6. Зависимость HIC 15 от скорости удара об лобовое стекло во время эксперимента
Рис. 5. Зависимость размера повреждений стекла от скорости ударного элемента
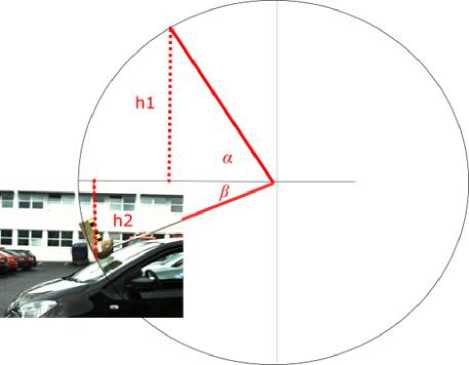
Рис. 7. Схема эксперимента удара модели головы о лобовое стекло автомобиля
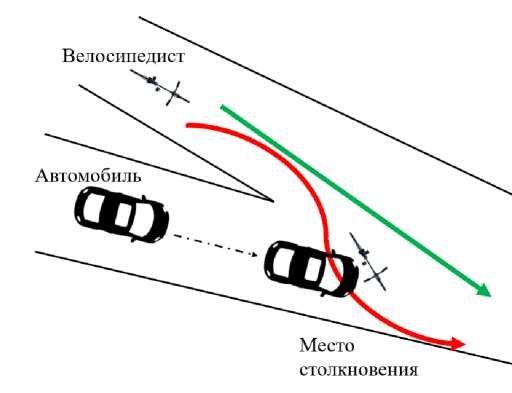
Рис. 8. Эскиз ситуации правильного (зеленого) и неправильного (красного) направления движения

Рис. 9. Повреждение передней части автомобиля при дорожно-транспортном происшествии относительно небольшого дефект лобового стекла
велосипедиста
v = 2 gR ( sin a + sin p ) . (27)
В эксперименте по столкновению с ударным элементом, представляющим собой голову взрослого человека, измерялись следующие параметры: скорость удара, ускорение, время контакта, диаметр и глубина повреждения на стекле транспортного средства. Также регистрировалось положение удара. Всего было проведено 18 испытаний: 10 с попаданием в центр лобового стекла, 8 – по краям, в пределах 1/3 ширины передних стоек автомобиля. Экспериментально подтверждено, что деформация по краям лобового стекла меньше. На высоких скоростях увеличивается значение ускорения при ударе, иногда даже превышающее значение 17 g . Увеличение ускорения на краях лобового стекла обусловлено увеличением. жесткости его крепления к металлической части корпуса. Значение HIC 15 = 700 представляет собой 50 %-ную вероятность серьезной травмы ( AIS 3) или 15 % -ную вероятность тяжелой травмы ( [ ) [6, 24], что является максимально допустимым уровнем воздействия при тестировании транспортного средства. Значения HIC 15, показанные на рис. 6, в большинстве случаев превышают допустимое значение, а в некоторых являются слишком высокими. Неудивительно, что измеренные скорости и ускорения при ударе также высоки, но тем не менее согласуются с предположениями о том, что значения ускорения выше при сопоставимых скоростях, когда удар наносится ближе к краям лобового стекла, где его боковая деформируемость ограничена.
Экспериментальное испытание на удар проводилось в том числе и для определения видимых повреждений лобового стекла. На стекле видны следы от ударов, представляющие собой трещины в форме концентрических кругов с плотными радиальными трещинами в центре, которые утончаются к краю дефекта. Размер диаметра повреждения зависит от скорости удара головы. На рис. 5 также показана разница, когда удар пришелся в середину лобового стекла и когда пришелся ближе к краю. Дефекты, расположенные ближе к краю, меньше.
Отклонение лобового стекла при ударе на высоких скоростях имело динамический характер. Начальная величина отклонения в месте удара составляла около 7–9 см, а после прекращения динамического воздействия ударника стабилизировалась до постоянного отклонения около 1–3 см.
Величину динамической деформации предварительно измеряли с помощью высокоскоростной камеры и прикреплённого к ней кронциркуля вдоль передней стойки, а максимальное боковое отклонение проверяли по уровню деформируемого элемента сжатия внутри автомобиля ниже точки удара. Измеренные величины динамической деформации лобового стекла согласуются с литературными данными [8, 9, 17].
Роль скорости в дорожно-транспортном происшествии
Правильное определение скорости столкновения при дорожно-транспортном происшествии важно особенно в случае столкновения автомобиля и незащищенного участника дорожного движения, то есть пешехода или велосипедиста [20, 21, 23]. Столкновение с незащищенным участником дорожного движения не может обойтись без травматизации, поэтому нельзя ошибиться с определением виновника происшествия! Ошибочное определение скорости удара может привести к неверному определению места столкновения, что может повлиять на результат судебно-медицинской экспертизы.
Имеет место следующая ситуация: велосипедист был сбит автомобилем в дорожно-транспортном происшествии. Он ехал по главной дороге: легковой автомобиль находился на второстепенной дороге, соединяющейся с главной под углом около 30°. После столкновения с легковым автомобилем велосипедист получил травму головы в результате удара о лобовое стекло. При поиске виновной стороны был неверно определен водитель автомобиля, а предполагаемой точкой столкновения считалась граница перекрестка.
Определение места столкновения и расположения травмы головы в зависимости от скорости транспортного средства связано с рядом сложностей [29, 30]. Во-первых, следует отметить, что автомобиль должен развивать определенную скорость, чтобы вообще иметь возможность сбить пешехода или велосипедиста так, чтобы голова ударилась о лобовое стекло. Если точка столкновения и точка остановки автомобиля почти идентичны, разумно предположить, голова вообще не соприкоснется с лобовым стеклом автомобиля.
В заключении эксперта было указано, что характер травмы велосипедиста при столкновении с транспортным средством показал, что происшествие произошло ранее на боковой дороге, по которой двигался автомобиль (рис. 8).
Во время самого столкновения велосипедист фактически упал на капот автомобиля, а затем его голова ударилась о лобовое стекло. В результате удара велосипед отбросило вперед в направлении движения автомобиля, а человека – по диагонали вперед через ограждение. Легковой автомобиль интенсивно тормозил перед и во время столкновения. Это описание события со слов участников. Повреждения легкового автомобиля представлены на рис. 9.
На автомобиле были явные признаки повреждения от велосипеда, и с уверенностью можно определить, каким частям велосипеда соответствуют те или иные дефекты: потертость от задней шины в нижней левой части бампера, повреждение передней части капота от седла и багажника, правый передний угол капота пострадал от руля и, конечно же, точка соприкосновения головы велосипедиста с лобовым стеклом в нижней его четверти справа.
Было предположено, что скорость автомобиля составляла от 35 до 50 км/ч, причем эксперты больше склонялись к нижней границе интервала, поскольку это больше соответствовало расстоянию, пройденному автомобилем до конечной точки – остановки. На основании повреждений и свидетельских показаний был предположен следующий сценарий несчастного случая. Столкновение транспортного средства произошло передней частью автомобиля с правой стороной велосипеда, причем положение транспортных средств было не совсем перпендикулярным, сначала произошел контакт с левой стороной носа автомобиля и задней частью велосипеда. Затем велосипед повернулся от удара перпендикулярно передней части автомобиля, в результате чего велосипедист переместился на капот автомобиля, ударившись головой о нижнюю правую часть ветрового стекла. Далее отскочил и велосипед, и велосипедист.
Далее дорожно-транспортное происшествие с учетом данных предположений было смоделировано экспертами при помощи программного обеспечения PC Crash , и было обнаружено, что столкновение произошло раньше . Критериями соответствия результатов моделирования, кроме финальных расположений участников, являются, прежде всего, скорости велосипедиста и велосипеда во время столкновения, согласование с реальным ущербом легкового автомобиля, а также сопоставление следов торможения легкового автомобиля с реальностью. Лучше всего для этой задачи подошла модель, в которой продольные оси транспортных средств находились под углом примерно 56°, скорость автомобиля составляла 42 км/ч, а скорость велосипедиста – 5 км/ч. Было достигнуто достаточно точное соответствие прогнозируемому движению, основанному на следах торможения и повреждениях. Так как авария произошла на развилке, где легковой автомобиль ехал по второстепенной дороге и врезался в зад/бок велосипедиста, едущего по главной дороге, но не так, как того предполагает продолжение движения по главной дороге, в какой-то момент он перестроился на правую сторону второстепенной дороги и пересекся с водителем легкового автомобиля с правой стороны. Здесь скорость автомобиля соответствует повреждению его лобового стекла от удара головой и последующего движения до точки конечной остановки.
Очевидно, что эксперты действовали правильно и логично, основываясь на опыте и инженерных знаниях при подготовке первоначального экспертного заключения. К сожалению, их выводы не были приняты и подлежали подтверждению только через пересмотр заключения. Применение биомеханики, при изучении автомобильных аварий с травмами уместно, когда механизм получения травмы неясен. В описанном выше случае органу, проводящему оценку, было бы достаточно получить информацию о том, с какой скоростью удар головы по лобовому стеклу автомобиля может привести к данной деформации, и было бы ясно, что указанный дефект на стекле соответствовал скорости движения транспортного средства, примерно равной 35 км/ч.
Применение биомеханического подхода, представленного в статье, позволяет приблизительно определить скорость удара головы о лобовое стекло на основании степени травмы головы пешехода/велосипедиста, степени повреждения самого лобового стекла автомобиля, а в сочетании с другими расчетами или моделированием движения автомобиля можно с уверенностью определить даже место, где произошел удар.
Обсуждение
Определение скорости удара головы пешехода о лобовое стекло автомобиля при столкновении производилось в двух вариантах. В первом, где не учитывались деформации передней части автомобиля, предполагалось, что центр тяжести фигуры после удара перемещается с той же скоростью, что и транспортное средство, и предполагалось, что энергия удара преобразуется в кинетическую энергию вращательного движения. Таким образом, скорость удара головы пешехода о лобовое стекло примерно в два раза превышает скорость автомобиля в момент столкновения с телом.
Во втором случае: после столкновения центр тяжести тела перемещается вперед медленнее, чем транспортное средство, что также может соответствовать реальной ситуации. Из-за трения и предполагаемой высоты точки соприкосновения с телом человека было выбрано снижение его скорости движения до 30 % от скорости транспортного средства, то есть центр тяжести тела глобально перемещается в направлении скорости автомобиля, но относительно автомобиля, он движется против него, то есть приближается к лобовому стеклу. Из-за этого угловая скорость также ниже, а результирующая скорость удара головы о лобовое стекло примерно в полтора раза превышает скорость транспортного средства по абсолютной величине. Скорость удара, направлена в противоположную сторону от лобового стекла [17]. Расчет приблизительный, потому что на скорость движения тела после того, как его подхватывает автомобиль, влияют, например, одежда, трение капот и т. д [2]. Скорости, определенные в этой статье, в любом случае и могут быть приняты за максимально достижимые в реальной ситуации.
Расчетным путем было определено, что скорость удара головой о лобовое стекло уменьшается с уменьшением наклона лобового стекла при той же скорости транспортного средства. Таким образом, при столкновении с автомобилем, имеющим более горизонтальное лобовое стекло, скорость удара головой будет меньше, чем при столкновении с автомобилем, чье лобовое стекло более вертикальное. Если учитывать направление линейной скорости головы, направленной по касательной к траектории, которую она описывает при вращении, то вертикальная составлявшая скорости (vy) доминирует над горизонтальной (vx), что согласуется с опубликованными моделями [14–16].
Как скорость автомобиля, так и скорость вращения тела вряд ли будут постоянными в течение всего времени столкновения. Транспортное средство может изменить свою скорость, затормозив во время столкновения. На вращение сильно влияет движение тела вокруг и вдоль передней части автомобиля.
Поэтому следует отметить, что по причинам, перечисленным выше, скорости удара, рассчитанные в этой статье, являются приблизительными. Более реалистичные данные могут быть получены только при помощи дополнительных экспериментов с манекенами и соответствующим измерительным оборудованием.
Скорость удара является одним из важнейших факторов, влияющих на травму головы. Другим, не менее важным фактором выступает время контакта и величина деформации стекла и черепа. Время контакта и величина поперечного прогиба стекла напрямую влияют на величину ускорения при ударе и, как следствие, на степень травмы [17].
При испытании лобового стекла автомобиля с помощью ударного элемента в виде головы взрослого человека контролировались скорость удара, ускорение, время контакта, диаметр и глубина повреждения на лобовом стекле автомобиля. Все измеренные данные приблизительно соответствуют опубликованным результатам, за исключением того, что опубликованные данные в основном ограничены скоростью удара около 11,11 м/с, что меньше, чем было измерено при тестировании в эксперименте. На краях лобового стекла деформации меньше, усадка жестче, а ускорение выше, следовательно, риск получения травм также выше [13, 22].
В судебной криминалистике для анализа дорожнотранспортного происшествия рассматриваются
Список литературы Применение биомеханики в судебно-медицинской экспертизе дорожно-транспортных происшествий
- Anderson R.W.G., McLean A.J., Farmer M.J.B., Lee B.H., Brooks C.G. Vehicle travel speeds and the incidence of fatal pedestrian crashes // Accident Analysis and Prevention. -1997. - no. 29. - P. 667-674.
- Berg A., Schmitt B., Weiss S. Pedestrian head impact on the windscreen of compact car a new test rig and first results // In IRCOBI Conference. - 2000. - P. 293-305.
- Committee on Injury Scaling. The abbreviated injury scale revision [Электронный ресурс] - URL: http://www.thaincd.com (дата обращения: 14.11.2023).
- Halari M.M., Stewart T.C., McClafferty K.J., Pellar A.C., Pickup M.J., Shkrum M.J. Injury patterns in motor vehicle collision-pediatric pedestrian deaths // Traffic Injury Prevention. - 2022. - No. 1. - P. 68-73.
- Han Y., Yang J., Mizuno K., Matsui Ya. Effects of vehicle impact velocity, vehicle front-end shapes on pedestrian injury risk // Traffic Injury Prevention. - 2012. - No. 5. - P. 507-518.
- Henn H.W. Crash tests and the head injury criterion. Teaching Mathematics and its Applications // An International Journal of the IMA. - 2007. - No. 17. - P. 162-170.
- Hoyt T.A., MacLaughlin T.F., Kessler J.W. Experimental pedestrian accident reconstructions-head impacts. // Engineering, Medicine. - 1988.
- Huang Z., Liu X., Song X., He Y. Probabilistic risk assessment for pedestrian-vehicle collision considering uncertainties of pedestrian mobility // Traffic Injury Prevention. - 2017. -no. 6. - P. 650-656.
- Jayaraman A., Soni J, Baladaniya S., Rajaraman R., Patel M., Padmanaban J. Characteristics of pedestrian injuries caused due to impacts with powered 2-wheelers in India // Traffic Injury Prevention. - 2020. - no. 1. - P. 107-111.
- Jermakian J., Edwards M., Fein S., Maltese M.R. Factors contributing to serious and fatal injuries in belted rear seat occupants in frontal crashes // Traffic Injury Prevention. -2019. - no. 1. - P. 84-91.
- Kleiven S. Predictors for traumatic brain injuries evaluated through accident reconstructions // Stapp Car Crash Journal. -2007. - No. 51. - P. 81-114.
- Li G., Yang J., Simms C. A virtual test system representing the distribution of pedestrian impact configurations for future vehicle front-end optimization // Traffic Injury Prevention. -2016. - No. 5. - P. 515-523.
- Liu Q., Liu J., Miao Q., Wang D., Tang X. Severity and mechanism of head impact in car to pedestrian accidents. In Proceedings of the 12th International LS-DYNA Users Conference // SAE Society of Automotive Engineers. - 2012. - No. 720960. - P. 78-104.
- Lyons M., Simms C. Predicting the influence of windscreen design on pedestrian head injuries // Engineering, Environmental Science. - 2012.
- Matsui Ya., Oikawa S., Ando K. Risks of pedestrian serious injuries and fatalities associated with impact velocities of cars in car-versus-pedestrian accidents in Japan // Stapp Car Crash Journal. - 2013. - No. 57. - P. 201-217.
- Miao Q., Zhang Y.L., Yang X.A., Miao Q.F., Zhao W.D., Tong F., Lan F.C., Li D.R. Analysis of pedestrian fractures in collisions between small cars and pedestrians based on surveillance videos // The American Journal of Forensic Medicine and Pathology. - 2022. - No. 43. - P. 11-17.
- Mizuno K., Yonezawa H., Kajzer J. Pedestrian headform impact tests for various vehicle locations // In International Technical Conference on Enhanced Safety of Vehicles. -2001. - No. 278. - P. 1-10.
- Nogayeva S., Gooch J., Frascione N. The forensic investigation of vehicle-pedestrian collisions: A review // Science and Justice. - 2021. - P. 112-118.
- Otte D. Severity and mechanism of head impact in car to pedestrian accidents. In Proceedings of the 1998 international IRCOBI conference of the biomechanics of impact // International Research Council on the Biokinetics of Impacts. - 1999. - P. 324-341.
- Schubert A., Babisch S., Scanlon J.M., Campolettano E.T., Roessler R., Unger T., McMurry T.L. Passenger and heavy vehicle collisions with pedestrians: assessment of injury mechanisms and risk // Accident Analysis and Prevention. -2023. -No. 190. - P. 1-14.
- Spicka J., Cermak M. Forensic analysis and a new investigation into the death of the czechoslovak minister of foreign affairs in 1948 // Journal of Forensic Identification. -2022. - no. 72. - P. 245-286.
- Stammen J.A., Saut R.A., Ko B. Pedestrian head impact testing and PDS reconstruction // In International Technical Conference on Enhanced Safety of Vehicles. - 2001. - No. 326. - P. 1-9.
- Tian J., Zhang C., Wang Q. Analysis of craniocerebral injury in facial collision accidents // Plos One. - 2020. - No. 15. -P. 1-16.
- Versace J. A review of the severity index // SAE Technical. -1971. - No. 710881. - P. 1-26. DOI: doi.org/10.4271/710881
- Vesely V., Vilimek M. Head injury biomechanics I - head and neck injury // Bulletin of Applied Mechanics. - 2012. - no. 8. - P. 5-76.
- Walz F.H., Hoefliger M., Fehlmann W. Speed limit reduction from 60 to 50 km/h and pedestrian injuries // SAE Society of Automotive Engineers. - 1983. - P. 311318.
- Wang F., Yu C., Wang B., Li G., Miller K., Wittek A. Prediction of pedestrian brain injury due to vehicle impact using computational biomechanics models: Are head-only models sufficient? // Traffic Injury Prevention. - 2019. -P. 1-6.
- Yao J., Yang J., Otte D. Investigation of head injuries by reconstructions of real-world vehicle-versus-adult-pedestrian accidents // Safety Science. - 2008. - No. 46. - P. 1103-1114.
- Yoshida H., Tsutsumi S. Experimental and numerical analyses of whiplash motions in low-speed rear-end collisions // Russian Journal of Biomechanics. - 2000. - Vol. 4, no. 3. -P. 1-9.
- Zhang G., Cao L., Hu J., Yang K.H. A field data analysis of risk factors affecting the injury risks in vehicle-to-pedestrian crashes // Annals of Advances in Automotive Medicine. -2008. - No. 52. - P. 199-214.


