Применение технологии индуцированных плюрипотентных стволовых клеток для моделирования синдрома удлиненного интервала QT
Автор: Вялкова А.В., Дементьева Елена Вячеславовна, Медведев С.П., Покушалов Е.А., Закиян С.М.
Журнал: Патология кровообращения и кардиохирургия @journal-meshalkin
Рубрика: Обзоры
Статья в выпуске: 4-2 т.19, 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Синдром удлиненного интервала QT - аритмическое заболевание, связанное с повышенным риском развития желудочковой тахикардии и внезапной смерти. Несмотря на множество проводимых исследований, патология изучена недостаточно, а используемые методы лечения не всегда эффективны. Одна из ключевых проблем - отсутствие адекватной модели синдрома удлиненного интервала QT. Технология индуцированных плюрипотентных стволовых клеток открывает новый этап в моделировании генетических заболеваний человека, в частности наследственных сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний. Способность индуцированных плюрипотентных стволовых клеток дифференцироваться в функциональные кардиомиоциты позволяет использовать их для изучения молекулярных механизмов сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний и поиска новых лекарственных препаратов. В обзоре рассмотрены применение этой технологии для моделирования синдрома удлиненного интервала QT и достигнутые успехи.
Синдром удлиненного интервала qt, индуцированные плюрипотентные стволовые клетки, кардиомиоциты
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142140866
IDR: 142140866
Текст научной статьи Применение технологии индуцированных плюрипотентных стволовых клеток для моделирования синдрома удлиненного интервала QT
-
• Кардиомиоциты
Синдром удлиненного интервала QT – сердечнососудистое заболевание, которое диагностируют по увеличению продолжительности интервала QT на электрокардиограмме. Удлиненным считают корригированный интервал QT продолжительностью более 460 мс. Удлинение интервала QT обусловлено увеличением продолжительности фазы реполяризации потенциала действия (ПД) кардиомиоцитов желудочков. В результате возрастает риск развития полиморфной желудочковой тахикардии, как правило, желудочковой тахикардии типа «пируэт» (torsade de pointes), которая сопровождается потерей сознания. Основная опасность заключается в частой трансформации желудочковой тахикардии типа «пируэт» в фибрилляцию желудочков, которая может вызвать асистолию и внезапную смерть. Частота встречаемости заболевания составляет 1 : 2000 [1, 2].
Синдром удлиненного интервала QT – гетерогенное заболевание, имеющее врожденную и приобретенную формы. Причинами приобретенной формы могут быть другие сердечно-сосудистые заболевания, нарушения электролитного обмена, заболевания центральной нервной системы, эндокринные патологии, стресс, диеты и лекарственные препараты [3]. Врожденную форму могут вызывать более 700 мутаций в 15 генах, кодирующих белки, связанные со структурой и/или функционированием ионных каналов кардиомиоцитов. Выделяют 15 типов врожденного синдрома удлиненного интервала QT, среди которых наиболее распространены первый, второй и третий, достигающие 95% случаев [4, 5] (табл. 1).
Таблица 1 Типы врожденного синдрома удлиненного интервала QT
|
Функция белка |
Частота встмости мутаций, % |
||
|
1 |
KCNQ1 |
α-субъединица каналов медленного калиевого тока задержанного выпрямления |
45–55 |
|
2 |
KCNH2 |
α-субъединица каналов быстрого калиевого тока задержанного выпрямления |
35–45 |
|
3 |
SCN5A |
α-субъединица натриевых каналов |
2–8 |
|
4 |
ANK2 |
Анкирин B, участвующий в стабилизации ионных каналов и ионных обменников кардиомиоцитов |
<1 |
|
5 |
KCNE1 |
β-субъединица каналов медленного калиевого тока задержанного выпрямления |
<1 |
|
6 |
KCNE2 |
β-субъединица каналов быстрого калиевого тока задержанного выпрямления |
<1 |
|
7 |
KCNJ2 |
α-субъединица каналов тока входящего выпрямления |
<1 |
|
8 |
CACNA1C |
α-субъединица каналов кальциевого тока L-типа |
<1 |
|
9 |
CAV3 |
Кавеолин 3, мембранный белок, взаимодействующий с натриевыми каналами |
<1 |
|
10 |
SCN4B |
β-субъединица натриевых каналов |
<0,1 |
|
11 |
AKAP9 |
Yotiao, участвующий в фосфорилировании белка KCNQ1 |
<0,1 |
|
12 |
SNTA1 |
α1-синтропин, взаимодействующий с натриевыми каналами |
<0,1 |
|
13 |
KCNJ5 |
Субъединица ацетилхолин-чувствительных калиевых каналов |
? |
|
14 |
CALM1 |
Кальмодулин 1, участвующий в связывании ионов кальция |
? |
|
15 |
CALM2 |
Кальмодулин 2, участвующий в связывании ионов кальция |
? |
Основной метод лечения заболевания – прием бета-блокаторов. В более тяжелых случаях используют имплантацию кардиовертера-дефибриллятора и левостороннюю симпатическую денервацию сердца [1]. Однако не существует способа лечения, который бы исключил риск неблагоприятного исхода у больных с синдромом удлиненного интервала QT. Это во многом объясняется отсутствием модельной системы заболевания, которая позволяла бы изучать его механизмы, а также разрабатывать и тестировать более совершенные методы терапии. До недавнего времени для моделирования синдрома удлиненного интервала QT использовали животные модели и гетерологичные системы.
Обычно доклинические исследования проводят на мышах и других мелких грызунах, однако грызуны отличаются от человека частотой сердечных сокращений и типами калиевых каналов, играющих главную роль при реполяризации кардиомиоцитов. В связи с этим грызунов затруднительно использовать для моделирования синдрома удлиненного интервала QT, вызванного нарушением калиевых токов задержанного выпрямления, в том числе наиболее распространенных его типов – первого и второго [6]. Гетерологичные системы – соматические клетки (например, клетки почечного эпителия человека, линия HEK293, или ооциты лягушки), в которых экспрессируeтся исследуемый белок ионного канала. Поскольку для наработки белка в клетках используют трансгены, это может привести к неконтролируемому и зачастую повышенному уровню его экспрессии. Кроме того, функционирование мутантного белка исследуется в некардиомиоцитарных клетках, то есть чужеродной среде, что, вероятно, приведет к некорректности результатов [7]. Из-за недостатков этих модельных систем потенциально эффективные лекарства могут быть отсеяны на доклинических стадиях, а лекарства, прошедшие доклинические стадии, могут вызвать в дальнейшем негативные побочные эффекты. Таким образом, для создания адекватных моделей синдрома удлиненного интервала QT предпочтительно использовать кардиомиоциты человека. Однако взятие биопсии сердечной мышцы – инвазивная процедура, которую выполняют не всем пациентам. Кроме того, кардиомиоциты выделяются из биопсии в небольшом количестве, а также не способны делиться и долговременно поддерживаться в культуре. До недавнего времени это значительно ограничивало возможности получения биологического материала для исследования механизмов синдрома удлиненного интервала QT. Решить проблему удалось благодаря недавнему прогрессу в области клеточных технологий.
Новый подход к созданию моделей врожденной формы синдрома удлиненного интервала QT
Соматические клетки можно репрограммировать к плюрипотентному состоянию с помощью индукции экспрессии определенного набора транскрипционных факторов [8, 9]. Получаемые в результате линии
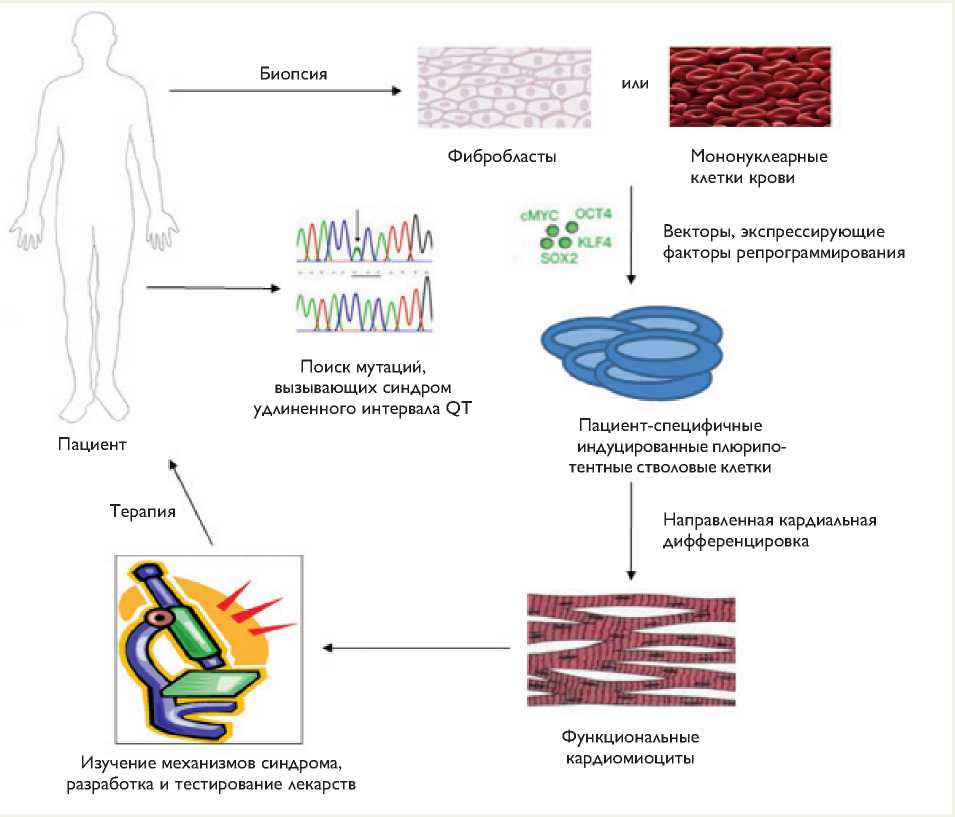
Схема использования пациент-специфичных индуцированных плюрипотентных стволовых клеток для моделирования синдрома удлиненного интервала QT
индуцированных плюрипотентных стволовых клеток (ИПСК) обладают свойствами плюрипотентных клеток, включая способность дифференцироваться в любой тип клеток организма. Следовательно, ИПСК могут служить источником получения функциональных кардиомиоцитов [10], что позволяет моделировать наследственные сердечно-сосудистые заболевания человека, в том числе врожденный синдром удлиненного интервала QT (рисунок). Подход к созданию моделей врожденного синдрома удлиненного интервала QT, основанный на применении новых клеточных технологий, включает: получение образца клеток (фибробластов из биопсии кожи или мононуклеарных клеток крови) от пациента, у которого выявлена вызывающая синдром мутация; репрограммирование этих клеток и получение линий пациент-специфичных индуцированных плюрипотентных стволовых клеток; их направленную дифференцировку в кардиомиоциты. Кардиомиоциты можно использовать для изучения механизмов синдрома, а также разработки и тестирования лекарственных препаратов для его терапии. ИПСК и кардиомиоциты можно получить в любой период жизни пациента без проведения значительных инвазивных процедур. Способность ИПСК к самообновлению позволяет получать пациент-специфичные кардиомиоциты в неограниченном количестве, что важно при проведении исследований и скрининге лекарственных препаратов. Пациент-специфичные кардиомиоциты
Таблица 2 Мутации, вызывающие синдром удлиненного интервала QT, для которых получены пациент-специфичные индуцированные плюрипотентные стволовые клетки
|
Тип синдрома |
Ген |
Мутация |
Ссылка |
|
R190Q |
[16] |
||
|
1 |
KCNQ1 |
P631fs/33 (1893delC) |
[17] |
|
Делеция 7-го экзона |
[24] |
||
|
R176W |
[19] |
||
|
A561T |
[25] |
||
|
2 |
KCNH2 |
A614V |
[18] |
|
G603D |
[50] |
||
|
N996I |
[27] |
||
|
3 |
SCN5A |
F1473C V1763M |
[21] [20] |
|
8 |
CACNA1C |
G406R |
[22] |
можно также использовать для проверки влияния лекарственных соединений на кардиотоксичность, удлинение интервала QT и способность вызывать аритмии. Кроме того, синдром удлиненного интервала QT различается по клиническим проявлениям у пациентов: продолжительности интервала, наличию кардиальных событий и синкопе, возрасту появления симптомов). Этот феномен наблюдается у носителей как различных [11, 12], так и одинаковых мутаций (даже в пределах одной семьи) [13–15]. Создание моделей синдрома удлиненного интервала QT с использованием ИПСК предполагает получение кардиомиоцитов конкретного пациента, что позволит разрабатывать методы терапии с учетом индивидуальных особенностей.
Применение технологии пациент-специфичных индуцированных плюрипотентных стволовых клеток для моделирования и изучения синдрома удлиненного интервала QT
С использованием этой технологии получены ИПСК и кардиомиоциты пациентов с врожденным синдромом удлиненного интервала QT первого, второго, третьего и восьмого типов (табл. 2).
Впервые пациент-специфичные ИПСК и кардиомиоциты получены для мутации R190Q в гене KCNQ1 (врожденный синдром удлиненного интервала QT первого типа) [16]. По сравнению с контрольными кардиомиоцитами, полученными от здорового донора, паци-ент-специфичные кардиомиоциты имели увеличенную продолжительность ПД и фазы реполяризации. Добавление изопротеренола (бета-агониста) не приводило к уменьшению ПД по сравнению с контролем и вызывало раннюю постдеполяризацию. Эти эффекты компенсировали с помощью пропранолола (бета-блокатора). Следовательно, пациент-специфичные кардиомиоциты с мутацией R190Q способны адекватно воспроизводить ситуацию у пациентов с врожденным синдромом удлиненного интервала QT первого типа. Кроме того, установлена роль мутации R190Q в гене KCNQ1 в развитии синдрома. В кардиомиоцитах с мутацией, по сравнению с контрольными, уровень белка KCNQ1 снижен на мембране и повышен в эндоплазматическом ретикулуме. Это означает, что мутация R190Q приводит к нарушению транспорта белка KCNQ1, что снижает число каналов медленного калиевого тока задержанного выпрямления на мембране. Для врожденного синдрома удлиненного интервала QT первого типа также получены пациент-специфичные кардиомиоциты, несущие мутацию в гене KCNQ1 – P631fs/33 (1893delC) [17]. Мутация вызывала фибрилляцию предсердий и остановки сердца у пациента и была обнаружена впервые. Электрофизиологический анализ пациент-специфич-ных кардиомиоцитов показал значимое увеличение ПД по сравнению с контролем. Воздействие блокатором каналов быстрого калиевого тока задержанного выпрямления (Е4031) приводило к увеличению ПД как в пациент-специфичных, так и контрольных кардиомиоцитах, однако пациент-специфичные кардиомиоциты демонстрировали большую склонность к ранней постдеполяризации и аритмическим событиям. Блокатор каналов медленного калиевого тока задержанного выпрямления (хроманол 293В) увеличивал ПД в контрольных клетках, но не пациент-специфичных кардиомиоцитах. Следовательно, синдром вызван нарушением работы каналов медленного калиевого тока задержан- ного выпрямления, что характерно для пациентов с врожденным синдромом удлиненного интервала QT первого типа. Как и в предыдущем исследовании, установлено, что мутация 1893delC приводит к нарушению транспорта белка KCNQ1 из цитоплазмы на клеточную мембрану.
Пациент-специфичные ИПСК и кардиомиоциты получены и от пациентов, страдающих врожденным синдромом удлиненного интервала QT второго типа и имеющих мутации в гене KCNH2 [18, 19]. Пациент-спе-цифичные кардиомиоциты, несущие мутацию A614V, имели увеличенную продолжительность ПД по сравнению с контролем [18]. Увеличение продолжительности ПД обусловлено значительным (на 60%) снижением плотности быстрого калиевого тока задержанного выпрямления, что свойственно пациентам с врожденным синдромом удлиненного интервала QT второго типа. У 66% пациент-специфичных кардиомиоцитов наблюдалась склонность к ранней постдеполяризации, у 36% – преждевременные сокращения. Пациент-спе-цифичные кардиомиоциты с мутацией R176W также демонстрировали увеличение продолжительности ПД и снижение плотности быстрого калиевого тока задержанного выпрямления по сравнению с контролем [19]. Однако аритмические события в кардиомиоцитах с мутацией R176W возникали только в результате действия аритмогенных лекарств, например соталола. Этот результат согласуется с клинической картиной: у пациента, несмотря на удлинение интервала QT, не наблюдали аритмий. Таким образом, пациент-специфичные кардиомиоциты с вызывающими синдром удлиненного интервала QT мутациями способны воспроизводить не только основные свойства синдрома определенного типа, но и особенности его проявления у конкретного пациента.
Модели на основе пациент-специфичных ИПСК также созданы и для врожденного синдрома удлиненного интервала QT третьего типа. Так, получены кардиомиоциты от пациентов, имеющих мутации F1473C и V1763M в гене SCN5A [20, 21]. Пациент-специфич-ные кардиомиоциты демонстрировали увеличенную продолжительность ПД, нарушенную инактивацию натриевых каналов и увеличенную плотность позднего натриевого тока. Эффект ослаблялся при добавлении мексилитина (блокатора натриевых каналов) или увеличении частоты сокращений кардиомиоцитов. У пациента с мутацией F1473C также обнаружен полиморфизм K897T в гене KCNH2 , однако его участие в развитии синдрома не подтвердилось [21].
Пациент-специфичные ИПСК и кардиомиоциты получены также для врожденного синдрома удлиненного интервала QT восьмого типа, или синдрома Тимоти [22]. Это генетическое заболевание характеризуется не только удлинением интервала QT и аритмией, но и врожденными пороками сердца, синдактилией, ослаблением иммунной системы, аутизмом, отставанием в развитии и высоким риском внезапной смерти в раннем возрасте. Его вызывают мутации в гене CACNA1C [23]. Получены кардиомиоциты от пациентов с синдромом Тимоти, имеющих мутацию G406R. Пациент-специ-фичные кардиомиоциты демонстрировали нерегулярные сокращения, повышенный кальциевый ток и увеличенный ПД по сравнению с контролем. Добавление росковетина, увеличивающего потенциал-зависимую инактивацию кальциевых каналов L-типа, приводило к нормализации электрофизиологических показателей (кальциевый ток, ПД) кардиомиоцитов.
В ряде работ получение пациент-специфичных ИПСК и кардиомиоцитов успешно применили для тестирования потенциальных лекарственных соединений и их комбинаций. Например, пациент-специ-фичные кардиомиоциты, имеющие делецию седьмого экзона в гене KCNQ1 (врожденный синдром удлиненного интервала QT первого типа), использованы для оценки терапевтического эффекта активатора каналов медленного калиевого тока задержанного выпрямления – ML277 [24]. Обнаружено, что ML277 в 1,30–1,64 раза увеличивал плотность медленного калиевого тока задержанного выпрямления и на 20% уменьшал ПД в пациент-специфичных кардиомиоцитах. Исследования кардиомиоцитов пациента с мутацией A561T в гене KCNH2 (врожденный синдром удлиненного интервала QT второго типа) показали, что активаторы калиевых каналов, никорандил и/или PD-118057, эффективно снижают продолжительность ПД, не приводя к развитию ранней постдеполяризации [25]. Таким образом, данные соединения могут быть эффективны в лечении пациентов с врожденным синдромом удлиненного интервала QT первого и второго типов.
Пациент-специфичные кардиомиоциты могут применяться не только для поиска лекарств для терапии синдрома, но и проверки их кардиотоксичности и способности вызывать аритмии. В частности, были получены кардиомиоциты из ИПСК пациентов, страдающих синдромом удлиненного интервала QT, гипертрофической и дилатационной кардиомиопатиями. Пациент-специфичные кардиомиоциты сравнивали по чувствительности к препаратам с токсичным и/или аритмогенным эффектом (верапамил, альфузолин, ци- заприд, никорандил) с кардиомиоцитами, полученными из ИПСК здоровых доноров и эмбриональных стволовых клеток, а также гетерологичной системой (клетками линии HEK293, экспрессирующими белок KCNH2) [26]. Кардиомиоциты, полученные из ИПСК, более точно отвечали на воздействие данных соединений по сравнению с гетерологичной системой, которую стандартно используют в тестах на кардиотоксичность. Более того, у кардиомиоцитов, полученных от пациентов и здоровых доноров, значительно отличалась чувствительность к тестируемым препаратам. Таким образом, кардиомиоциты, получаемые из ИПСК человека, предпочтительнее для тестирования лекарственных препаратов, чем гетерологичные системы. Кроме того, для более точной оценки кардиотоксич-ного и/или аритмогенного эффекта нужно проверять лекарство на кардиомиоцитах пациента, страдающего тем заболеванием, для лечения которого его предполагают использовать.
Технология, основанная на пациент-специфичных ИПСК, также была использована для подтверждения роли одной из мутаций в гене KCNH2 в возникновении фенотипа синдрома удлиненного интервала QT [27]. Авторы получили две пары изогенных линий плюрипотентных клеток, которые имели общий генетический фон и различались лишь по наличию мутации N996I в гене KCNH2. Одна пара представляла собой ИПСК, полученные от пациентки с мутацией N996I, и те же самые ИПСК, но мутация в них была исправлена с помощью гомологичной рекомбинации. Вторую пару изогенных линий создали путем введения мутации N996I в линию эмбриональных стволовых клеток человека. Кардиомиоциты, полученные из ИПСК, несущих мутацию N996I, демонстрировали увеличенную продолжительность ПД и сниженную плотность быстрого калиевого тока задержанного выпрямления. Исправление мутации в ИПСК приводило к нормализации этих параметров в полученных из них кардиомиоцитах. Несмотря на другой общий генетический фон в кардиомиоцитах, полученных из эмбриональных стволовых клеток, введение мутации также вызывало увеличение ПД и снижение быстрого калиевого тока задержанного выпрямления. Таким образом, благодаря использованию двух пар изогенных линий плюрипотентных клеток человека доказано, что именно мутация N996I в гене KCNH2 является причиной развития синдрома удлиненного интервала QT у пациента. Аналогичную методику можно применять для выяснения роли некоторых однонуклеотидных полиморфизмов в увеличении продол- жительности интервала QT и возникновении аритмических событий [28–33].
Кардиомиоциты, полученные из пациент-специ-фичных ИПСК, могут также стать инструментом для разработки и тестирования новых методов терапии синдрома удлиненного интервала QT. В одном из исследований показана принципиальная возможность использовать аллель-специфичную РНК-интерференцию для коррекции фенотипа, вызванного мутацией A561T в гене KCNH2 [34]. Благодаря введению коротких интерферирующих РНК в пациент-специфичные кардиомиоциты уровень РНК, транскрибирующейся с мутантного аллеля, удалось снизить на 61,8%, что привело к увеличению вероятности формирования функционального канала быстрого калиевого тока задержанного выпрямления (тетрамера белка KCNH2) в 4,5 раза. Этого оказалось достаточно для нормализации продолжительности ПД и плотности быстрого калиевого тока задержанного выпрямления, а также снижения частоты аритмических событий. Аллель-специфич-ная РНК-интерференция может быть эффективным способом коррекции синдрома удлиненного интервала QT, вызванного аутосомно-доминантными мутациями. Однако для внедрения данной технологии в клиническую практику необходимо решить ряд задач, включая направленную доставку коротких интерферирующих РНК в кардиомиоциты.
Таким образом, кардиомиоциты, полученные из пациент-специфичных ИПСК, способны воспроизводить синдром удлиненного интервала QT in vitro : демонстрируют увеличение ПД, изменение плотности соответствующего ионного тока, склонность к ранней постдеполяризации и аритмическим событиям, а также адекватно отвечают на воздействие активаторами или блокаторами определенных ионных каналов. Более того, кардиомиоциты отражают индивидуальные особенности проявления синдрома у пациента, от которого их получили. Эти свойства позволяют использовать пациент-специфичные кардиомиоциты для решения биомедицинских задач, связанных с лечением синдрома удлиненного интервала QT.
Проблемы, связанные с применением технологии пациент-специфичных индуцированных плюрипотентных стволовых клеток
Несмотря на достижения в создании клеточных моделей синдрома удлиненного интервала QT с использованием пациент-специфичных ИПСК, остается ряд методических проблем. Прежде всего, это качес- тво получаемых линий пациент-специфичных ИПСК. Индуцированные плюрипотентные стволовые клетки должны экспрессировать основные маркеры плюрипотентного состояния (щелочную фосфатазу, ряд транскрипционных факторов и поверхностных антигенов), дифференцироваться в производные трех зародышевых листков, сохранять нормальный кариотип и мутацию, вызывающую синдром удлиненного интервала QT [35, 36]. Для получения ИПСК часто используется трансдукция соматических клеток ретро- или ленти-вирусными векторами, экспрессирующими факторы репрограммирования [16–19]. Однако данный тип векторов встраивается в геном клетки случайным образом, что может нарушить транскрипцию некоторых генов. В настоящее время все больше используются не интегрирующиеся в геном клеток векторы: плазмидные [37], эписомные [38], аденовирусные [39]. Кроме того, получение ИПСК не всегда сопровождается полным репрограммированием на уровне эпигенома. ИПСК могут сохранять эпигенетические метки, характерные для соматических клеток, из которых они были получены («эпигенетическая память»), что может повлиять на способность ИПСК дифференцироваться в желаемый тип клеток [40–42]. Это может отразиться на свойствах пациент-специфичных ИПСК и получаемых из них кардиомиоцитов и повлиять на результаты исследований.
Получаемые из пациент-специфичных ИПСК кардиомиоциты имеют характерную саркомерную структуру, экспрессируют специфические кардиальные маркеры, а также обладают способностью генерировать ПД [16–21, 25], однако, как правило, имеют незрелый фенотип, соответствующий эмбриональным кардиомиоцитам [7]. Для изучения сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний, проявляющихся в постнатальный период, необходимы кардиомиоциты со зрелым фенотипом. Работы в данном направлении уже ведутся. Показано, что длительное культивирование, культивирование в условиях 3D, а также механическая и электрическая стимуляции способствуют созреванию кардиомиоцитов [43–45]. Кроме того, в результате кардиальной дифференцировки ИПСК получают смешанную популяцию клеток, состоящую из вентрикулярных, атриальных и нодальных кардиомиоцитов [16–19, 25]. Сердечно-сосудистые заболевания могут затрагивать различные типы кардиомиоцитов, что приводит к необходимости получения чистых популяций определенных типов кардиомиоцитов для их моделирования. Таким образом, актуальной задачей является разработка эффективных протоколов получения трех типов кардиомиоцитов [7].
Кроме того, открытым остается вопрос об оптимальном контроле при моделировании синдрома удлиненного интервала QT с помощью пациент-специфичных ИПСК. В большинстве исследований контролем являются кардиомиоциты, полученные из ИПСК здоровых добровольцев, в частности здоровых родственников пациента. Однако данные клетки имеют иной, по сравнению с пациентом, общий генетический фон. Даже ближайшие родственники могут отличаться от пациента по набору однонуклеотидных полиморфизмов в геноме, что, вероятно, повлияет на результаты проводимых исследований. В последнее время широкое распространение получили методы геномной инженерии, основанные на нуклеазах TALENs (Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases) и системе CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats)/Cas9 и позволяющие вносить мутации в любую точку генома или исправлять их [46, 47]. Технология не только дает возможность создавать «идеальный» контроль с идентичным генетическим фоном, но также позволяет проверить участие мутаций в развитии синдрома удлиненного интервала QT [27] или получить линии ИПСК, несущие редкие генетические мутации.
Использование кардиомиоцитов, полученных в результате направленной дифференцировки пациент-специфичных ИПСК, в значительной степени ограничивается врожденной формой синдрома удлиненного интервала QT, когда заболевание обусловлено конкретной мутацией. Однако даже в случае врожденного синдрома удлиненного интервала QT исследования, проведенные на уровне одиночных пациент-специфич-ных кардиомиоцитов, не могут в полной мере отражать поведение сердечной ткани. В недавно опубликованной работе показана способность кардиомиоцитов, полученных при дифференцировке плюрипотентных клеток человека, формировать синцитии, обладающие электрической активностью [48]. Регулируя плотность клеток и частоту их стимуляции, авторы индуцировали вращающиеся спиральные волны (re-entry), которые напоминают развитие аритмии в миокарде и могут быть остановлены применением нифекаланта, E-4031, соталола или хинидина. Исследование доказало возможность создания с использованием пациент-специ-фичных ИПСК клеточных 3D-моделей заболеваний, связанных с нарушением сердечного ритма, и тестирования с их помощью потенциальных лекарственных препаратов.
Заключение
Развитие клеточных технологий, в частности открытие феномена индуцированной плюрипотентности, привело к прогрессу в создании моделей наследственных заболеваний, включая синдром удлиненного интервала QT. С использованием технологии ИПСК получены кардиомиоциты пациентов с врожденным синдромом удлиненного интервала QT первого, второго, третьего и восьмого типов. Пациент-специфич-ные кардиомиоциты адекватно воспроизводили in vitro характерные черты соответствующих типов синдрома, а также отражали клиническую картину проявления синдрома у конкретных пациентов. Пациент-специфичные кардиомиоциты могут использоваться для изучения молекулярных механизмов синдрома удлиненного интервала QT, разработки и тестирования лекарственных препаратов и методов коррекции синдрома. Кроме того, перспективность данного подхода подтверждена на кардиомиоцитах, полученных из ИПСК пациентов, страдающих другими сердечнососудистыми заболеваниями, такими как катехолами-нергическая полиморфная желудочковая тахикардия, наследственные кардиомиопатии, надклапанный аортальный стеноз и другие.
Однако для успешного применения технологии, основанной на пациент-специфичных ИПСК, дальнейшего изучения и разработки методов терапии сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний необходимо разработать и стандартизировать протоколы получения пациент-специфичных ИПСК требуемого качества, кардиомиоцитов различных типов со зрелым фенотипом и методов 3D-культивирования. Усовершенствованию данной технологии будут также способствовать методы геномного редактирования, такие как TALENs и CRISPR/Cas9, позволяющие создавать контрольные линии клеток, ИПСК и кардиомиоциты, несущие редкие мутации, а также проверять участие мутаций и/или однонуклеотидных полиморфизмов в развитии сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний.
Еще одно направление в области получения клеточных моделей синдрома удлиненного интервала QT – создание биобанка линий пациент-специфич-ных ИПСК. Мутации, вызывающие синдром удлиненного интервала QT, могут проявляться по-разному: от значительного увеличения интервала QT и раннего начала кардиальных событий до нормальной длины интервала и отсутствия симптомов. Такая гетерогенность в клиническом проявлении характерна даже для мутаций, вызывающих врожденный синдром одного типа, то есть локализующихся в одном гене. По- видимому, это обусловлено тем, что мутации имеют разный механизм действия: изменяют биофизические свойства ионного канала, влияют на регуляцию его активности, транспорт белков ионного канала на мембрану и т. д. [49]. Механизм действия мутации, в свою очередь, будет определять стратегию терапии синдрома. Таким образом, для полного изучения синдрома удлиненного интервала QT требуются пациент-спе-цифичные ИПСК с мутациями, которые не только вызывают различные типы врожденного удлинения интервала QT, но и имеют различный механизм действия.
Работа поддержана бюджетным проектом VI.60.1.2 Института цитологии и генетики СО РАН и грантом РФФИ № 14-04-31906.
Список литературы Применение технологии индуцированных плюрипотентных стволовых клеток для моделирования синдрома удлиненного интервала QT
- Crotti L., Celano G., Dagradi F., Schwartz P.J. Congenital long QT syndrome//Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2008. Vol. 3. P. 18.
- Schwartz P.J., Stramba-Badiale M., Crotti L., Pedrazzini M., Besana A., Bosi G., Gabbarini F., Goulene K., Insolia R., Mannarino S., Mosca F., Nespoli L., Rimini A., Rosati E., Salice P., Spazzolini C. Prevalence of the congenital long-QT syndrome//Circulation. 2009. Vol. 120. № 18. P. 1761-7.
- Roden D.M. Acquired long QT syndromes and the risk of proarrhythmia//J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2000. Vol. 11. № 8. P. 938-40.
- Hedley P.L., Jorgensen P., Schlamowitz S., Wangari R., Moolman-Smook J., Brink P.A., Kanters J.K., Corfield V.A., Christiansen M. The genetic basis of long QT and short QT syndromes: a mutation update//Hum. Mutat. 2009. Vol. 30. № 11. P. 1486-511.
- Boczek N.J., Best J.M., Tester D.J., Giudicessi J.R., Middha S., Evans J.M., Kamp T.J., Ackerman M.J. Exome sequencing and systems biology converge to identify novel mutations in the L-type calcium channel, CACNA1C, linked to autosomal dominant long QT syndrome//Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2013. Vol. 6. № 3. P. 279-89.
- Salama G., London B. Mouse models of long QT syndrome//J. Physiol. 2007. Vol. 578. Pt. 1. P. 43-53.
- Hoekstra M., Mummery C.L., Wilde A.A., Bezzina C.R., Verkerk A.O. Induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes as models for cardiac arrhythmias//Front. Physiol. 2012. Vol. 3. P. 346.
- Takahashi K., Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem Cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors//Cell. 2006. Vol. 126. № 4. P. 663-76.
- Yu J., Vodyanik M.A., Smuga-Otto K., Antosiewicz-Bourget J., Frane J.L., Tian S., Nie J., Jonsdottir G.A., Ruotti V., Stewart R., Slukvin I.I., Thomson J.A. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells//Science. 2007. Vol. 318. № 5858. P. 1917-20.
- Mordwinkin N.M., Burridge P.W., Wu J.C. A review of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes for high-throughput drug discovery, cardiotoxicity screening, and publication standards//J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2013. Vol. 6. № 1. P. 22-30.
- Shimizu W., Horie M., Ohno S., Takenaka K., Yamaguchi M., Shimizu M., Washizuka T., Aizawa Y., Nakamura K., Ohe T., Aiba T., Miyamoto Y., Yoshimasa Y., Towbin J.A., Priori S.G., Kamakura S. Mutation site-specific differences in arrhythmic risk and sensitivity to sympathetic stimulation in the LQT1 form of congenital long QT syndrome: multicenter study in Japan//J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004. Vol. 44. № 1. P. 117-25.
- Moss A.J., Shimizu W., Wilde A.A., Towbin J.A., Zareba W., Robinson J.L., Qi M., Vincent G.M., Ackerman M.J., Kaufman E.S., Hofman N., Seth R., Kamakura S., Miyamoto Y., Goldenberg I., Andrews M.L., McNitt S. Clinical aspects of type-1 long-QT syndrome by location, coding type, and biophysical function of mutations involving the KCNQ1 gene//Circulation. 2007. Vol. 115. № 19. P. 2481-9.
- Priori S.G., Napolitano C., Schwartz P.J. Low penetrance in the long-QT syndrome: clinical impact//Circulation. 1999. Vol. 99. № 4. P. 529-33.
- Moss A.J., Zareba W., Kaufman E.S., Gartman E., Peterson D.R., Benhorin J., Towbin J.A., Keating M.T., Priori S.G., Schwartz P.J., Vincent G.M., Robinson J.L., Andrews M.L., Feng C., Hall W.J., Medina A., Zhang L., Wang Z. Increased risk of arrhythmic events in long-QT syndrome with mutations in the pore region of the human ether-a-go-go-related gene potassium channel//Circulation. 2002. Vol. 105. № 7. P. 794-9.
- Scicluna B.P., Wilde A.A., Bezzina C.R. The primary arrhythmia syndromes: same mutation, different manifestations. Are we starting to understand why?//J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2008. Vol. 19. № 4. P. 445-52.
- Moretti A., Bellin M., Welling A., Jung C.B., Lam J.T., Bott-Flügel L., Dorn T., Goedel A., Höhnke C., Hofmann F., Seyfarth M., Sinnecker D., Schömig A., Laugwitz K.L. Patient-specific induced pluripotent stem-cell models for long-QT syndrome//N. Engl. J. Med. 2010. Vol. 363. № 15. P. 139709.
- Egashira T., Yuasa S., Suzuki T., Yae K., Aizawa Y., Yamakawa H., Murata M., Miyoshi S., Kamiya K., Fukuda K. Disease characterization using LQTS-specific induced pluripotent stem cells//Cardiovasc. Res. 2012. Vol. 95. № 4. P. 419-29.
- Itzhaki I., Maizels L., Huber I., Zwi-Dantsis L., Caspi O., Winterstern A., Feldman O., Gepstein A., Arbel G., Hammerman H., Boulos M., Gepstein L. Modelling the long QT syndrome with induced pluripotent stem cells//Nature. 2011. Vol. 471. № 7337. P. 225-9.
- Lahti A.L., Kujala V.J., Chapman H., Koivisto A.P., Pekkanen-Mattila M., Kerkelä E., Hyttinen J., Kontula K., Swan H., Conklin B.R., Yamanaka S., Silvennoinen O., Aalto-Setälä K. Model for long QT syndrome type 2 using human iPS cells demonstrates arrhythmogenic characteristics in cell culture//Dis. Model. Mech. 2012. Vol. 5. № 2. P. 220-30.
- Ma D., Wei H., Zhao Y., Lu J., Li G., Sahib N.B., Tan T.H., Wong K.Y., Shim W., Wong P., Cook S.A., Liew R. Modeling type 3 long QT syndrome with cardiomyocytes derived from patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells//Int. J. Cardiol. 2013. Vol. 168. № 6. P. 5277-86.
- Terrenoire C., Wang K., Tung K.W., Chung W.K., Pass R.H., Lu J.T., Jean J.C., Omari A., Sampson K.J., Kotton D.N., Keller G., Kass R.S. Induced pluripotent stem cells used to reveal drug actions in a long QT syndrome family with complex genetics//J. Gen. Physiol. 2013. Vol. 141. № 1. P. 61-72.
- Yazawa M., Hsueh B., Jia X., Pasca A.M., Bernstein J.A., Hallmayer J., Dolmetsch R.E. Using induced pluripotent stem cells to investigate cardiac phenotypes in Timothy syndrome//Nature. 2011. Vol. 471. № 7337. P. 230-4.
- Splawski I., Timothy K.W., Sharpe L.M., Decher N., Kumar P., Bloise R., Napolitano C., Schwartz P.J., Joseph R.M., Condouris K., Tager-Flusberg H., Priori S.G., Sanguinetti M.C., Keating M.T. Ca(V)1.2 calcium channel dysfunction causes a multisystem disorder including arrhythmia and autism//Cell. 2004. Vol. 119. № 1. P. 19-31.
- Ma D., Wei H., Lu J., Huang D., Liu Z., Loh L.J., Islam O., Liew R., Shim W., Cook S.A. Characterization of a novel KCNQ1 mutation for type 1 long QT syndrome and assessment of the therapeutic potential of a novel IKs activator using patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocyte//Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015. Vol. 6. P. 39.
- Matsa E., Rajamohan D., Dick E., Young L., Mellor I., Staniforth A., Denning C. Drug evaluation in cardiomyocytes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells carrying a long QT syndrome type 2 mutation//Eur. Heart J. 2011. Vol. 32. № 8. P. 952-62.
- Liang P., Lan F., Lee A.S., Gong T., Sanchez-Freire V., Wang Y., Diecke S., Sallam K., Knowles J.W., Wang P.J., Nguyen P.K., Bers D.M., Robbins R.C., Wu J.C. Drug screening using a library of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes reveals disease-specific patterns of cardiotoxicity//Circulation. 2013. Vol. 127. № 16. P. 1677-91.
- Bellin M., Casini S., Davis R.P., D'Aniello C., Haas J., Ward-van Oostwaard D., Tertoolen L.G., Jung C.B., Elliott D.A., Welling A., Laugwitz K.L., Moretti A., Mummery C.L. Isogenic human pluripotent stem cell pairs reveal the role of a KCNH2 mutation in long-QT syndrome//EMBO J. 2013. Vol. 32. № 24. P. 3161-75.
- Gouas L., Nicaud V., Berthet M., Forhan A., Tiret L., Balkau B., Guicheney P. Association of KCNQ1, KCNE1, KCNH2 and SCN5A polymorphisms with QTc interval length in a healthy population//Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2005. Vol. 13. № 11. P. 1213-22.
- Pfeufer A., Jalilzadeh S., Perz S., Mueller J.C., Hinterseer M., Illig T., Akyol M., Huth C., Schöpfer-Wendels A., Kuch B., Steinbeck G., Holle R., Näbauer M., Wichmann H.E., Meitinger T., Kääb S. Common variants in myocardial ion channel genes modify the QT interval in the general population: results from the KORA study//Circ. Res. 2005. Vol. 96. № 6. P. 693-701.
- Mank-Seymour A.R., Richmond J.L., Wood L.S., Reynolds J.M., Fan Y.T., Warnes G.R., Milos P.M., Thompson J.F. Association of torsades de pointes with novel and known single nucleotide polymorphisms in long QT syndrome genes//Am. Heart J. 2006. P. 152. № 6. P. 1116-22.
- Newton-Cheh C., Guo C.Y., Larson M.G., Musone S.L., Surti A., Camargo A.L., Drake J.A., Benjamin E.J., Levy D., D'Agostino R.B.Sr, Hirschhorn J.N., O'donnell C.J. Common genetic variation in KCNH2 is associated with QT interval duration: the Framingham Heart Study//Circulation. 2007. Vol. 116. № 10. P. 1128-36.
- Marjamaa A., Newton-Cheh C., Porthan K., Reunanen A., Lahermo P., Väänänen H., Jula A., Karanko H., Swan H., Toivonen L., Nieminen M.S., Viitasalo M., Peltonen L., Oikarinen L., Palotie A., Kontula K, Salomaa V. Common candidate gene variants are associated with QT interval duration in the general population//J. Intern. Med. 2009. Vol. 265. № 4. P. 448-58.
- Chen L., Zhang W., Fang C., et al. Polymorphism H558R in the human cardiac sodium channel SCN5A gene is associated with atrial fibrillation//J. Int. Med. Res. 2011. Vol. 39. № 5. P. 1908-16.
- Matsa E., Dixon J.E., Medway C., Georgiou O., Patel M.J., Morgan K., Kemp P.J., Staniforth A., Mellor I., Denning C. Allele-specific RNA interference rescues the long-QT syndrome phenotype in human-induced pluripotency stem cell cardiomyocytes//Eur. Heart J. 2014. Vol. 35. № 16. P. 1078-87.
- Maherali N., Hochedlinger K. Guidelines and techniques for the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells//Cell Stem Cell. 2008. Vol. 3. № 6. P. 595-605.
- Gore A., Li Z., Fung H.L., Young J.E., Agarwal S., Antosiewicz-Bourget J., Canto I., Giorgetti A., Israel M. A., Kiskinis E., Lee J.H., Loh Y.H., Manos P.D., Montserrat N., Panopoulos A.D., Ruiz S., Wilbert M.L., Yu J., Kirkness E.F., Belmonte J.C.I., Rossi D.J., Thomson J.A., Eggan K., Daley G.Q., Goldstein L.S.B., Zhang K. Somatic coding mutations in human induced pluripotent stem cells//Nature. 2011. Vol. 471. № 7336. P. 63-7.
- Medvedev S.P., Grigor'eva E.V., Shevchenko A.I., Malakhova A.A., Dementyeva E.V., Shilov A.A., Pokushalov E.A., Zaidman A.M., Aleksandrova M.A., Plotnikov E.Y., Sukhikh G.T., Zakian S.M. Human induced pluripotent stem cells derived from fetal neural stem cells successfully undergo directed differentiation into cartilage//Stem Cells Dev. 2011. Vol. 20. № 6. P. 1099-112.
- Yu J., Hu K., Smuga-Otto K., Tian S., Stewart R., Slukvin I.I., Thomson J.A. Human induced pluripotent stem cells free of vector and transgene sequences//Science. 2009. Vol. 324. № 5928. P. 797-801.
- Zhou W., Freed C.R. Adenoviral gene delivery can reprogram human fibroblasts to induced pluripotent Stem Cells//Stem Cells. 2009. Vol. 27. № 11. P. 2667-74.
- Kim K., Doi A., Wen B., Ng K., Zhao R., Cahan P., Kim J., Aryee M.J., Ji H., Ehrlich L., Yabuuchi A., Takeuchi A., Cunniff K.C., Hongguang H., Mckinney-Freeman S., Naveiras O., Yoon T.J., Irizarry R.A., Jung N., Seita J., Hanna J., Murakami P., Jaenisch R., Weissleder R., Orkin S.H., Weissman I.L., Feinberg A.P., Daley G.Q. Epigenetic memory in induced pluripotent stem cells//Nature. 2010. Vol. 467. № 7313. P. 285-90.
- Polo J.M., Liu S., Figueroa M.E., Kulalert W., Eminli S., Tan K.Y., Apostolou E., Stadtfeld M., Li Y., Shioda T., Natesan S., Wagers A.J., Melnick A., Evans T., Hochedlinger K. Cell type of origin influences the molecular and functional properties of mouse induced pluripotent stem cells//Nat. Biotechnol. 2010. Vol. 28. № 8. P. 848-55.
- Kim K., Zhao R., Doi A., Ng K., Unternaehrer J., Cahan P., Huo H., Loh Y.H., Aryee M.J., Lensch M.W., Li H., Collins J.J., Feinberg A.P., Daley G.Q. Donor cell type can influence the epigenome and differentiation potential of human induced pluripotent stem cells//Nat. Biotechnol. 2011. Vol. 29. № 12. P. 1117-9.
- Chan Y.C., Ting S., Lee Y.K., Ng K.M., Zhang J., Chen Z., Siu C.W., Oh S.K., Tse H.F. Electrical stimulation promotes maturation of cardiomyocytes derived from human embryonic stem cells//J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2013. Vol. 6. № 6. P. 989-99.
- Ivashchenko C.Y., Pipes G.C., Lozinskaya I.M., Lin Z., Xiaoping X., Needle S., Grygielko E.T., Hu E., Toomey J.R., Lepore J.J., Willette R.N. Human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes exhibit temporal changes in phenotype//Am. J. Physiol. Heart. Circ. Physiol. 2013. Vol. 305. № 6. P. H913-22.
- Mihic A., Li J., Miyagi Y., Gagliardi M., Li S.H., Zu J., Weisel R.D., Keller G., Li R.K. The effect of cyclic stretch on maturation and 3D tissue formation of human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes//Biomaterials. 2014. Vol. 35. № 9. P. 2798-808.
- Ding Q., Lee Y.K., Schaefer E.A., et al. A TALEN genome-editing system for generating human stem cell-based disease models//Cell Stem Cell. 2013. Vol. 12. № 2. P. 238-51.
- Ding Q., Regan S.N., Xia Y., Oostrom L.A., Cowan C.A., Musunuru K. Enhanced efficiency of human pluripotent stem cell genome editing through replacing TALENs with CRISPRs//Cell Stem Cell. 2013. Vol. 12. № 4. P. 393-4.
- Kadota S., Minami I., Morone N., Heuser J.E., Agladze K., Nakatsuji N. Development of a reentrant arrhythmia model in human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiac cell sheets//Eur. Heart J. 2013. Vol. 34. № 15. P. 1147-56.
- Sinnecker D., Goedel A., Dorn T., Dirschinger R.J., Moretti A., Laugwitz K.L. Modeling long-QT syndromes with iPS cells//J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2013. Vol. 6. № 1. P. 31-6.
- Okata S., Yuasa S., Yamane T., Furukawa T., Fukuda K. The generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from a patient with KCNH2 G603D, without LQT2 disease associated symptom//J. Med. Dent. Sci. 2013. Vol. 60. № 1. P. 17-22.