Прогностическое значение истинного кастрационного уровня тестостерона при гормоно-чувствительном раке предстательной железы
Автор: Грицкевич А.А., Мишугин С.В., Казанцева М.В., Теплов Александр Александрович, Медведев В.Л., Русаков И. г
Журнал: Экспериментальная и клиническая урология @ecuro
Рубрика: Онкоурология
Статья в выпуске: 2, 2016 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Современные руководства рекомендуют поддерживать целевой уровень тестостерона (Т) при проведении гормональной терапии рака предстательной железы (РПЖ)не выше 1,73 нмоль/л (50 нг/дл). Однако у большинства пациентов, которым проводится хирургическая кастрация (ХК), концентрации Т меньше 0,694 нмоль/л (
Андрогенная депривационная терапия, дегареликс, антагонисты лгрг, гормоночувствительный рак предстательной железы, фолликулостимулирующий гормон, тестостерон
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142188103
IDR: 142188103
Текст научной статьи Прогностическое значение истинного кастрационного уровня тестостерона при гормоно-чувствительном раке предстательной железы
Kazantseva MV – MD, PhD, professor, chief physician of clinical oncology center №1, Krasnodar
Медведев В.Л. – д.м.н., профессор, руководитель Краевого уронефрологического центра Краевой клинической больницы № 1 им. проф. С.В. Очаповского, заведующий кафедрой урологии
Кубанского государственного медицинского университета г. Краснодар
Medvedev VL – MD, PhD, professor, head of the Regional uronephrological center of Regional Clinical Hospital № 1 named after prof. SV Ochapovsky, head of the cathedra of Urology Medical University
Kuban in Krasnodar
Института хирургии им. А.В. Вишневского

Российской Федерации число мужчин, заболевших раком предстательной железы (РПЖ) в 2014 г. составило 37186, тогда как в 2004 г. было выявлено 15238 случаев. В структуре онколо гических заболеваемости РПЖ занимает второе место после опухолей легких и составляет 14,3%. Стандартизированный показатель заболеваемости в 2014 году составил 39,4 на 100 000 мужчин. При этом рост заболеваемости за 10 лет достиг 117%. При общем снижении смертности от всех онкозаболеваний, отмечается увеличение смертности от РПЖ (в 2004 г. – 9,52, а в 2014 г. – 11,86 случаев на 100 тыс. мужчин) [1]. Несмотря на значительное увеличение числа больных с ранними формами заболевания РПЖ, 45,5% пациентов на период выявления заболевания имеют местно-распространенные и метастатические формы, в лечении которых показана андрогенная депривационная терапия (АДТ) [2].
АДТ аналогами лютеинизирующего рилизинг гормона (ЛГРГ) или орхэктомия является основой терапии у пациентов с местно-распространенным или метастатическим РПЖ. Современные руководства рекомендуют поддерживать целевой уровень тестостерона (Т) во время AДТ на уровне 1,73 нмоль/л (50 нг/дл). У большинства пациентов, которым проводится орхэктомия, концентрации Т достигает уровня <0,694 нмоль/л (<20 нг/дл), однако эти уровни редко достижимы у пациентов, получающих аналоги ЛГРГ. В последнее время активно изучается прогностическая роль динамики уровня Т, но до сих пор остается неизвестным его оптимальный уровень. Вполне вероятно, что необходимо снижать уровень Т плазмы крови ниже, чем принято в настоящее время. Споры ведутся о том, какой же уровень Т в сыворотке крови принимать за верхний предел при лечении аналогами ЛГРГ – 1,73 нмоль/л или ниже, и как это влияет на прогноз лечения? Настоящее исследование было проведено для изучения прогностической роли сывороточного уровня Т при АДТ. При этом рассмотрена взаимосвязь между уровнем Т при АДТ и динамикой ПСА и возможность влияния на них антагонистами ЛГРГ и хирургической кастрацией (ХК) [2-9].
Цель исследования – оценить потенциальную терапевтическую значимость замены аналога ЛГРГ на антагонист ЛГРГ (АЛГРГ) или ХК при биохимическом прогрессировании гормоночувствительного РПЖ.
МАТЕРИАЛЫ И МЕТОДЫ
В исследование включено 47 пациентов гормоночувствительным РПЖ, проходивших лечение в Институте хирургии им. А. В. Вишневского, Городской клинической больнице № 57 г. Москвы и Клиническом онкологическом диспансере №1 г. Краснодара с 2012 по 2016 г. Пациенты получали медикаментозную АДТ аналогом ЛГРГ (бусерелин-депо 3,75 мг внутримышечно каждые 28 дней). Больные получали экспериментальная и клиническая урология №2 2 0 16 терапию до появления биохимического прогрессирования (БП), которое определяли при наличии двух последовательных подъемов ПСА больше 50% выше надира или повышение ПСА ≥ 2,5 нг/мл в двух последовательных измерениях за двухнедельный период.
Часть больных (n=26) при БП на фоне проводимой АДТ начали получать дегареликс в следующем режиме: в течение 1 месяца индукционная доза 240 мг подкожно с последующим ежемесячным введением в дозе 80 мг подкожно. Другой группе больных (n=21) проведена ХК. В таблице 1 приведена краткая характеристика пациентов обеих групп.
В общей группе больных возраст
Таблица 1. Клиническая характеристика групп больных
|
Показатель |
Дегареликс (n=26) |
Хирургическая кастраци (n=21) |
|
Возраст, лет Средний возраст, лет |
51-84 68,54±9,24 |
56-79 66,76±7,18 |
|
ПСА, нг/мл ПСА (средний уровень) |
0,9-24 8,55±6,55 |
1,9-28,8 10,24±7,79 |
|
Общий тестостерон (N=12-33 нмоль/л) |
1,43±0,62 |
1,41±0,57 |
|
Индекс массы тела |
30,13±3,8 |
30,7±2,56 |
|
Время до прогрессирования, мес. |
37,5±35,6 |
34,57±31,36 |
|
ЛГ, мМЕ/мл |
0,16±0,29 |
0,19±0,25 |
|
ФСГ, мМЕ/мл |
4,78±3,32 |
4,68±3,01 |
|
Категория Т местной распространенности опухоли n (%) |
||
|
Т0/Х, n, % |
1 (3,8) |
— |
|
Т1/2, n, % |
4 (15,4) |
4 (19) |
|
Т3/Т4, n, % |
21 (80,8) |
17 (81) |
|
Категория N распространенности опухоли n (%) |
||
|
N0, n, % |
2 (7,7) |
^^^^^^в |
|
N+ , n, % |
13 (50) |
10 (47,6) |
|
NХ, n, % |
11 (42,3) |
11 (52,4) |
|
Категория М распространенности опухоли n (%) |
||
|
М0, n, % |
18 (69,2) |
14 (66,7) |
|
М1, n, % |
8 (30,8) |
7 (33,3) |
Таблица 2. Индекса массы тела у больных РПЖ, включенных в исследование
ИМТ Дегареликс (n) % Хирургическая кастрация (n) %
|
< 25 (норма) |
2 (7,7%) |
^^^^^^в |
|
25-30 (избыточный вес) |
11 (42,3%) |
8 (38,1%) |
|
30-35 (ожирение I ст.) |
9 (34,6%) |
12 (57,1%) |
|
> 35 (ожирение II-III ст.) |
4 (15,4%) |
1 (4,8%) |
Таблица 3. Уровень тестостерона у больных РПЖ на момент биохимического прогрессирования
|
Уровень тестостерона |
Дегареликс (n) % |
Хирургическая кастрация (n) % |
|
≤1,73 нмоль/л (50 нг/дл) |
16 (61,5%) |
13 (61,9%) |
|
0,69-1,73 нмоль/л (20-50 нг/дл) |
12 (46,1%) |
9 (42,9%) |
|
< 0,69 нмоль/л (20 нг/дл) |
4 (15,4%) |
4 (19%) |
|
>1,73 нмоль/л (50 нг/дл) |
10 (38,5%) |
8 (38,1%) |
|
>2,08 нмоль/л (60 нг/дл) |
2 (7,7%) |
1 (4,8%) |
больных колебался от 51 до 84 лет (средний возраст – 67,6 лет). У всех пациентов к началу лечения имелось морфологическое подтверждение диагноза РПЖ. Все случаи представлены различными вариантами аденокарцином. У 15 пациентов определялись костные метастазы, у 23 – метастазы в регионарные и отдаленные лимфатические узлы, у 11 – поражение лимфатических узлов и костей скелета, висцеральные метастазы (печень, легкие) присутствовали у двух пациентов. Общее количество больных с метастазами – 27 (57,4%).
В обеих группах средний уровень индекса массы тела (ИМТ) носил пограничный характер между избыточным весом и ожирением
1-й стадии. Более половины больных в обеих группах имели ожирение 1-й степени: 50% – в группе лекарственного лечения и 61,2% – в группе ХК. Характеристика ИМТ больных представлена в таблице 2.
Уровень ПСА до начала лечения колебался от 0,9 до 28,8 нг/мл и в среднем составил 9,4 нг/мл. Основная масса больных (68,1%) имела уровень ПСА 4 нг/мл и выше (69,2% пациентов в группе дегареликса и 66,7% пациентов в группе ХК).
Уровень лютеинизирующего гормона (ЛГ) в группе лечения АЛГРГ в среднем составлял 0,16±0,29 мМЕ/мл, и у 80,8% больных имел сотые значения. В группе ХК уровень ЛГ в среднем составил 0,19±0,25 мМЕЭ/мл и 57,1% больных имел сотые значения.
Уровень фолликулостимулирующего гормона (ФСГ) в группе ХК при БП составлял 4,68±3,01мМЕ/мл, против 4,78±3,32 мМЕ/ мл в группе дега-реликса.
У 29 (61,7%) из всех пациентов, включенных в исследование, уровень общего Т был в пределах общепринятого КУ (≤ 1,73 нмоль/л). В группе ХК у 8 (38%) больных уровень Т выше этого уровня, а у 1(5%) больного – превышал 2,08 нмоль/сл (>60 нг/дл). Уровень меньше 0,69 нмоль/л (<20 нг/дл) наблюдался в 4 (19%) случаях. У остальных 9 больных он был в пределах 0,69-1,73 нмоль/л. В группе АЛГРГ 16 (62%) больных имели общепринятый КУ Т меньше 1,73 нмоль/л. У 10 больных он превышал этот уровень, причем у 2 (8%) больных Т был больше 2,08 нмоль/л. Характеристика значений Т в 2-х группах больных представлена в таблице 3. На момент БП РПЖ у 38,3% больных обеих групп имели уровень Т больше общепринятого КУ (>1,73 нмоль/л).
Таким образом, группы больных до лечения по совокупности рассмотренных показателей были однородными ( р <0,05).
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ
Группа хирургической кастрации
После трех месяцев лечения в группе ХК снижение уровня Т произошло у 10 (47,6%) больных. Величина снижения уровня Т варьировала от 0,46 до 1,56 нмоль/л. Значение Т после лечения составило 0,93± 0,37 нмоль/л.
Снижение уровня ПСА в этой группе произошло у 3 (14,3%) больных. Продолженный рост ПСА был у 71,4% больных. Стабилизация уровня ПСА отмечена у 3 (14,3%) больных. Среднее значение ПСА всей группы возросло до 14,5±13,73 нг/мл.
В группе ХК у всех больных отмечен резкий рост уровня ФСГ. Среднее значение ФСГ составило 15,76± 2,8 мМЕ/мл. Данные Т, ПСА, ФСГ в динамике приведены в таблице 4.
Отличие показателей Т, ПСА и ФСГ до и после лечения в группе ХК статистически значимо ( р <0,05).
В группе ХК из 10 больных, у которых наблюдалось снижение уровня Т в трех случаях отмечено снижение уровня ПСА. Этих больных характеризует наличие ожирения I степени (среднее значение ИМТ 31,2±1,73), отсутствие костных метастазов. Определен длительный период до прогрессиро- вания: 95,7±19,03 мес., а также наличие высокодифференцированных форм РПЖ (среднее значение индекса Глисона (ИГ) – 4,67±0,58). Интересно, что у всех этих больных уровень Т исходно был больше 1,73 нмоль/л (2,02±0,24 нмоль/л). Через 3 месяца лечения уровень Т составил 0,68±0,05 нмоль/л.
При анализе результатов лечения остальных 7 больных со снижением уровня Т выявлено, что в трех случаях зафиксирована стабилизация уровня ПСА, в то время, как у остальных больных отмечался рост ПСА. Больных со стабилизацией ПСА характеризует наличие ожирения I степени (среднее значение ИМТ 31,87±2,22), в двух из трех случаев – отсутствие костных метастазов. Период до прогрессирования составлял 26,3±14,74 мес., а также отмечено наличие более агрессивных форм рака (среднее значение ИГ 6,7±1,15). Среднее значение Т больных имело пограничные значения с кастрационным и составило 1,7±0,31 нмоль/л. Через 3 месяца лечения уровень Т составил 0,99±0,02 нмоль/л. У всех больных без изменений уровня Т, наблюдался рост ПСА.
Таким образом, в группе ХК через 3 месяца лечения у больных с уровнем Т, превышающим 2,08 нмоль/л
(60 нг/дл), наряду со снижением Т отмечено и снижение уровня ПСА. У больных с пограничным кастрацион-ным уровнем Т при его снижении отмечена стабилизация ПСА. Этих больных характеризует наличие ожирения I степени, и высоко- и умереннодифференцированных форм РПЖ.
Группа применения АЛГРГ
После 3-х месяцев лечения в группе применения АЛГРГ снижение уровня Т произошло у 10 (38,5%) больных. Величина снижения уровня Т варьировала от 0,34 до 1,41нмоль/л. Значение Т после лечения составило 1,06±0,42 нмоль/л.
Снижение уровня ПСА в группе АЛГРГ произошло у 5(19,2%) больных. Продолженный рост ПСА был в 65,4% случаев. Стабилизация уровня ПСА отмечена у 4(15,4%) больных. Среднее значение ПСА во всей группе увеличилось до 11,83±10,31 нг/мл.
В группе АЛГРГ снижение уровня ФСГ отмечено в 80,8% случаев. Величина снижения уровня ФСГ варьировала от 0,1 до 14,81 мМЕ/мл. Уровень ФСГ не изменилось у 5 больных. Значение ФСГ составило 1,62±0,88 мМЕ/мл. Сывороточная концентрация ФСГ снизилась на 33,9% (3,16 мМЕ/мл). Данные Т, ПСА, ФСГ в динамике приведены в таблице 5.
Таблица 4. Значения Т, ПСА, ФСГ до и после лечения в группе ХК
|
T-критерий для зависимых выборок (группа кастрации) Отмечены разности, значимые на уровне p <0,05000 |
||||||||
|
Переменная |
Среднее |
Ст. откл. |
N |
Разн. |
Ст. откл. разн. |
T |
с |
p |
|
Тестостерон |
1,408571 |
0,565387 |
||||||
|
Л-Тестостерон* |
0,927143 |
0,372883 |
21 |
0,481429 |
0,560699 |
3,934704 |
20 |
0,000820 |
|
ПСА |
10,23810 |
7,78880 |
||||||
|
Л-ПСА* |
14,49524 |
13,73526 |
21 |
-4,25714 |
7,709058 |
-2,53062 |
20 |
0,019887 |
|
ФСГ |
4,67810 |
3,014841 |
||||||
|
Л-ФСГ* |
15,75524 |
2,794082 |
21 |
-11,0771 |
4,108082 |
-12,3566 |
20 |
0,000000 |
* Л-Тестостерон, Л-ПСА, Л-ФСГ — значения после 3-х месяцев лечения
Таблица 5. Значения Т, ПСА, ФСГ до и после лечения в группе АЛГРГ
|
T-критерий для зависимых выборок (группа лечения дегареликсом) Отмечены разности, значимые на уровне p <0,05000 |
||||||||
|
Переменная |
Среднее |
Ст. откл |
N |
Разн. |
Ст. откл. разн. |
Т |
с |
p |
|
Тестостерон |
1,427692 |
0,618083 |
||||||
|
Л-Тестостерон* |
1,056538 |
0,415056 |
26 |
0,371154 |
0,541112 |
3,497463 |
25 |
0,001777 |
|
ПСА |
8,54615 |
6,54909 |
||||||
|
Л-ПСА* |
11,83462 |
10,31373 |
26 |
-3,28846 |
6,904531 |
-2,42854 |
25 |
0,022687 |
|
ФСГ |
4,779615 |
3,323694 |
||||||
|
Л-ФСГ* |
1,619231 |
0,882315 |
26 |
3,160385 |
3,496670 |
4,608632 |
25 |
0,000103 |
* Л-Тестостерон, Л-ПСА, Л-ФСГ — значения после 3-х месяцев лечения экспериментальная и клиническая урология №2 2 0 16
Отличие показателей Т, ПСА и ФСГ до и после лечения в группе АЛГРГ статистически значимо ( р <0,05).
В группе АЛГРГ из 10 больных, у которых наблюдалось снижение уровня Т, в 5 случаях отмечено снижение уровня ПСА. Этих больных характеризует наличие ожирения I степени (среднее значение ИМТ 32,76±4,95), отсутствие костных метастазов. Определен длительный период до прогрессирования: 57,6±50,39 мес., а также наличие высокодифференцированных форм РПЖ (среднее значение ИГ 5,8±1,3). Интересно, что у всех этих больных уровень Т был больше 1,73 нмоль/л (2,17±0,46 нмоль/л). Через 3 месяца лечения уровень Т этих больных составил 1,06±0,61 нмоль/л.
При анализе остальных 5 больных со снижением уровня Т выявлено, что в 4 случаях зафиксирована стабилизация уровня ПСА и у одного больного отмечен рост ПСА. Больных со стабилизацией ПСА характеризует наличие ожирения I стадии (среднее значение ИМТ 30,35±0,71), в трех из 4 случаев – отсутствие костных метастазов, а также наличие более агрессивных форм рака (среднее значение ИГ 6,75±0,5). Период до прогрессирования составлял 39,75±37,56 мес. Среднее значение Т больных было выше общепринятой кастрационной нормы и составляло 1,94±0,15 нмоль/л. Через 3 месяца лечения уровень Т составил 0,99±0,27 нмоль/л. У всех больных без изменений уровня Т, наблюдался рост ПСА.
В группе АЛГРГ наблюдалось резкое снижение уровня ФСГ с 4,78±3,32 до 1,62±0,88 мМЕ/мл. При детальном рассмотрении больных после лечения выявлено два пациента, у которых на фоне нормальных значений ФСГ до лечения (12,3± 3,78 мМЕ/мл), и его резкого снижения до 0,17±0,007 мМЕ/мл после лечения, наблюдалось снижение ПСА с 13,25±13,79 до 4,9±4,81 нг/мл. У обоих больных были низкодифференцированные формы РПЖ (ИГ – 7 баллов), ИМТ составил 28,4±5,8. Этих больных характеризует непродолжительный период гормональной терапии (ГТ) до биохимического прогрессирования 17,5±2,12 мес.
Таким образом, в группе АЛГРГ через 3 месяца лечения у больных с уровнем Т превышающим 2,08 нмоль/л (60 нг/дц), отмечено наряду со снижением Т, и снижение уровня ПСА. У больных с пограничным кастрацион-ным уровнем Т при его снижении отмечена стабилизация ПСА. Больных с положительным ответом по ПСА, характеризует наличие ожирения I степени, и присутствие высоко- и умереннодифференцированных форм РПЖ. Также у двух больных с ИГ равным 7 и избыточным весом (ИТМ 2530) был выявлен ответ со стороны ПСА при значительном снижении уровня ФСГ. Этих больных также отличает непродолжительный период ГТ до прогрессирования.
Таким образом, в результате лечения в обеих группах произошли статистически значимые изменения показателей Т, ПСА, ФСГ. Происшедшие изменения в обеих группах по совокупности рассмотренных показателей не имели статистически достоверных отличий.
При однофакторном дисперсионном анализе в обеих группах при сравнении уровня ПСА до и после лечения с ИМТ определяется статистически незначимая зависимость: у больных с более высоким ИМТ средние значения ПСА до и после лечения были выше, но различия не достигли статистически достоверной значимости ( p >0,05). Возможно, что статистическая значимость не достигнута из-за малого количества больных в группах.
При исследовании корреляционных связей возраста с исследуемыми прогностическими параметрами в обеих группах выявлено, что с увеличением возраста наблюдается более низкий уровень ПСА как до, так и после лечения (р<0,05). В группе ХК с увеличением возраста имелась тенденция к более низкому индексу Глисона и увеличению длительности лечения до начала БП. В группе дегареликса эта тенденция приобрела статистическую значимость (р<0,05).
При исследовании корреляционных связей ИМТ с исследуемыми прогностическими параметрами выявлено, что в группе ХК с увеличением ИМТ происходит статистически значимое увеличение исходного уровня ПСА ( р <0,05), а также имеется тенденция к более высоким значениям исходного и конечного уровня Т, исходного уровня ФСГ и конечного уровня ПСА. В группе дегареликса с увеличением ИМТ происходит статистически значимое увеличение уровня ЛГ ( р <0,05) и тенденция к уменьшению уровня Т после лечения.
При исследовании корреляционных связей возраста и ИМТ с изменением показателей в динамике в процентах были выявлены статистически значимые изменения в группе дегареликса. При ИМТ больше 24 наблюдается тенденция к более выраженному снижению уровня Т ( p <0,05) (рис 1).
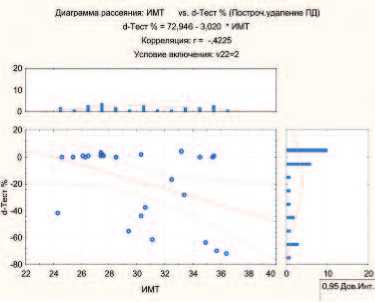
Рис 1. Взаимосвязь между ИМТ и степенью снижения уровня Т (d-T, %) в группе дегареликса
Из рисунка 2 видно, что у больных с ИМТ от 22 до 32 происходит меньший рост ПСА вплоть до отсутствия изменений этого показателя. У больных с ИМТ от 32 до 40 на фоне лечения происходит более выраженное снижение уровня ПСА (р<0,05).
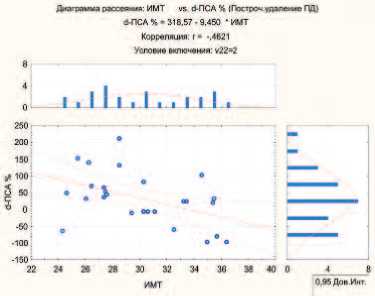
Рис 2. Взаимосвязь между ИМТ и изменением уровня ПСА (d-ПСА, %) в группе дегареликса
Непараметрический корреляционный анализ подгрупп по уровню Т с исследуемыми критериями (гамма корреляция и корреляции Спирмена) проводился согласно референсным значениям Т: <0,694нмоль/л (<20нг/дл), от 0,694 до 1,736 нмоль/л (20- 50 нг/дл), > 1,736 нмоль/л (> 50 нг/дл). В группе ХК на момент роста ПСА определена умеренная, но статистически не значимая связь местнораспространенной формы РПЖ (Т3) и уровнем Т от 0,694 до 1,736 нмоль/л (20- 50 нг/дл) ( р =0,09). В группе больных, получавших дегареликс, на момент БП имевших уровень Т > 0,69 нмоль/л, в подавляющем количестве отсутствовали отдаленные метастазы ( р =0,021). Можно предположить, что в группе дегаре-ликса отсутствует связь роста ПСА и наличия генерализованных форм РПЖ.
В группе ХК у 7 больных с уровнем Т>1,736 нмоль/л после операции произошло статистически значимое снижение Т до уровня 0,694-1,736 нмоль/л (20-50 нг/дл) и стабилизация уровня Т при исходном значении < 0,694 нмоль/л ( р =0,00088). У больных с уровнем Т от 0,694 до 1,736 нмоль/л (20-50 нг/дл) в трех случаях произошло снижение Т ( р >0,05). В группе дегареликса у 9 больных с уровнем Т > 1,736 нмоль/л произошло статистически значимое снижение Т до уровня 0,694 – 1,736 нмоль/л (2050 нг/дл) и в 11 случаях стабилизация
Т с исходным уровнем Т 0,694 – 1,736 нмоль/л ( р =0,00002). У больных с уровнем Т от 0,694 до 1,736 нмоль/л (20-50 нг/дл) в одном случае также произошло снижение Т ( р >0,05).
В группе ХК у больных с уровнем Т > 1,736 нмоль/л в трех случаях произошло статистически незначимое снижение уровня ПСА и в одном – его стабилизация ( р >0,05). У больных с уровнем Т от 0,694 до 1,736 нмоль/л (20-50 нг/дл) в двух случаях наблюдалась стабилизация ПСА. У остальных пациентов определялся прогрессивный его рост ( р =0,039). В группе дега-реликса у больных с уровнем Т > 1,736 нмоль/л (> 50 нг/дл) в 5 случаях произошло статистически незначимое снижение уровня ПСА и в 4 – стабилизация ( р >0,05). У остальных больных определялся прогрессивный рост ПСА ( р =0,00002). На рис. 3 представлена гистограмма распределения уровней Т с динамикой ПСА после лечения в группе дегареликса.
Категарю. гиски рампа Tect диш. х іру г ma d ПСА
Условие а<гкмвіия v23=2
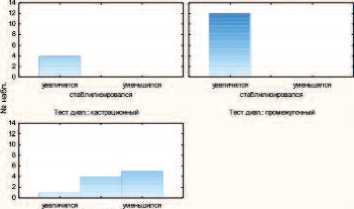
спвкжмнрсаехя leer »en: hsmumwO группа d ПСА
Рис 3. Гистограмма распределения уровней Т с динамикой ПСА после лечения в группе дегареликса.
В группе ХК статистически достоверной зависимости между ИМТ и динамикой ПСА получено не было ( р =0,28). В группе больных, получавших дегареликс, при ИМТ от 25 до 30 средние значения уровня ПСА прогрессивно возрастали, несмотря на проводимую терапию ( р =0,019), тогда как у больных, у которых наблюдали снижение ПСА, это не зависело от ИМТ ( р >0,05).
При анализе взаимосвязи изменений уровней Т и ПСА в обеих группах получена статистически значимая связь уровня стабилизированного Т с прогрессивным увеличением ПСА (р<0,05). Статистической связи снижения и стабилизации ПСА со снижением Т не получено (р>0,05).
В группе дегареликса статистически значимых изменений ПСА при общем снижении ФСГ получено не было ( р =0,246).
При попытке провести раздельный корреляционный анализ влияния ИТМ на уровень Т до и после лечения в обеих группах из-за малой выборки больных статистически значимой взаимосвязи выявить не удалось. Однако, в обеих группах при ИМТ 30-35 и больше 35 наблюдалась тенденция к увеличению уровня Т и его изменения на фоне лечения ( р >0,05).
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Оптимальный уровень тестостерона при лечении РПЖ.
Нормальный диапазон уровня Т в сыворотке крови (который может незначительно отличаться в зависимости от лаборатории) колеблется от 10,434,7 нмоль/л для мужчин в возрасте 17 лет и старше. Неточность анализа (отклонение около 7%) должна учитываться при интерпретации значения Т. Уровень общего Т (свободный + связанный с белком) ниже 6,9 нмоль/л (200 нг/дл) – 10 нмоль/л (300 нг/дл) согласно рекомендациям AACE (Американская ассоциация клинических эндокринологов) и FDA (Управление по контролю качества пищевых продуктов и лекарственных препаратов) свидетельствует о наличии гипогонадизма и требует дальнейшего обследования этих больных. Свободный Т (8,8-27 пг/мл) иногда используется в оценке гипогонадизма при повышении или снижении глобулина, связывающего половые стероиды (ГСПГ), что изменяет соответственно биодо-ступную (метаболически активную) фракцию Т. Например, ожирение характеризуется понижением общего Т экспериментальная и клиническая урология №2 2 0 16 с нормальным уровнем свободного Т в связи с сокращением связывания с белками. Концентрация ГСПГ в сыворотке увеличиваются с возрастом. С увеличением возраста, меньше общего Т находится в свободном, биологически активном состоянии, т.к. ГСПГ связывает Т с высокой афинностью. Пока нет однозначного ответа об оптимальном уровне Т, который должен быть достигнут при АДТ РПЖ. Традиционно используется определение так называемого КУ Т. Однако, этот уровень фактически зависит от вида вмешательства: менее 0,69 нмоль/л (20 нг/дл) при ХК и менее 1,735 нмоль/л (50 нг/дл) – при терапии аналогами ЛГРГ [10, 11].
На совещании экспертов в 2005 году в г. Сан-Антонио (США) и аналогичном заседании во время Шестой Международной Консультации о новых разработках при раке и других заболеваниях предстательной железы в г. Париже в 2005 г. обсудили дефиниции, касающиеся оптимального контроля уровня Т при РПЖ. Было определено, что термин кастрация вводит в заблуждение в случае назначения агонистов ЛГРГ, поскольку кастрация означает хирургическое удаление яичек (двусторонняя орхэктомия). Было отмечено, что уровень Т после двусторонней орхэктомией следует использовать в качестве ориентира для достижения соответствующего уровня Т при назначении агонистов ЛГРГ. Поскольку большинству пациентов удается достичь и поддерживать сывороточный уровень Т ниже 20 нг/дл после ХК, эксперты согласились, что этот уровень следует использовать и для медикаментозной кастрации. Кроме того, было решено, что клинически значимый уровень Т при терапии аналогами ЛГРГ более 50 нг/дл может иметь негативные последствия для результатов лечения [12].
Совещание экспертов ВОЗ пришло к выводу, что «оценка состояния пациентов, получающих агонисты
ЛГРГ должна проводиться на основании уровня ПСА, а не уровня Т, хотя уровень Т, аналогичный полученному после орхэктомии должен быть достигнут» [13].
Некоторые авторы полагают, что необходимо пересмотреть КУ Т на основе современных методов лабораторной диагностики. В современной литературе КУ Т определяется на уровне ниже 1,735 нмоль/л. Ранее существующая техника анализа для определения Т сыворотки – двойной изотопный метод разбавления – мог давать ошибку при низком уровне Т. Современный хемилюминисцентный анализ более надежен при низких уровнях Т. Принята концепция, что при применении агонистов ЛГРГ необходимо поддерживать уровень Т эквивалентный таковому при ХК [14-20].
В настоящее время неизвестно, является ли минимальный уровень Т необходимым для того, чтобы эффективно предотвращать рост и прогрессирование РПЖ. Вопрос оптимального уровня Т и «ускользание» андрогенов были оценены J. Morote и соавт. В исследование были изучены результаты лечения 73 мужчин с неметастатическим РПЖ, получавших аналоги ЛГРГ. Им проводился контроль уровней ПСА и Т. Больные были разделены на три группы (Т <20, 20-50, >50 нг/дл). Лучшие результаты в отсрочке андроген-независимого прогрессирования РПЖ продемонстрированы при уровне Т ниже 32 нг/дл. – 137 мес. по сравнению с 88 мес. при более высоких значениях. У мужчин, которые поддерживали уровень Т ниже 20 нг/дл безрецидивная выживаемость была 106 мес. против 90 мес. с уровнями между 20 и 50 нг/мл, и только 72 месяца, если Т был выше, чем 50 нг/дл. Это исследование также подтверждает предположение, что максимальная андрогенная блокада может принести пользу при медикаментозной кастрации в случае роста ПСА и при увеличении Т выше 50 нг/дл [16].
Аналогичная результаты получил M. Perachino и соавт. В исследование были включены данные о 162 мужчинах с метастатическим РПЖ. Целью исследования было выявить лучшую модель терапии гозерелином в плане прогноза выживаемости на основе 6-месячного мониторинга уровня Т. Кастрационный порог ниже 50 нг/дл был достигнут у 119 (73,5%) пациентов после 6 месяцев терапии гозерелином; порог Т менее 20 нг/дл был только у 46 (28,4%) пациентов. Было выявлено, что уровень Т через 6 месяцев коррелирует с выживаемостью. Чем ниже был уровень Т через 6 месяцев, тем больше увеличивалась выживаемость ( р =0,0286) [21].
Высокая экспрессия рецепторов ФСГ на поверхности кровеносных сосудов была продемонстрирована при различных опухолях, в том числе и при РПЖ. Гормононезависимые клетки РПЖ экспрессируют ФСГ и биологически активные рецепторы ФСГ [22-24]. E Ben-Josef и соавт. предположили, что рецепторы ФСГ и их лиганды могут играть определенную роль в регуляции роста гормонорефрактерного РПЖ. В исследовании III фазы показано, что лечение дегаре-ликсом привело к более быстрому и длительному, чем при лечении леупро-лидом, подавлению уровня ФСГ. Кроме того, отмечено начальное увеличение ЛГ и ФСГ в группе леупро-лида, а ФСГ никогда не снижался в той же степени, как в группе дегареликса. Кроме того, у тех пациентов, которые были переведены с леупролида на де-гареликс, уровень ФСГ дополнительно снижался на 30%. Была выдвинута гипотеза, что рецепторы ФСГ могут быть вовлечены в индукцию фактора роста эндотелия сосудов (VEGF) и VEGF-2 сигналов и, следовательно, могут способствовать ангиогенезу. Хотя эта гипотеза не доказана, снижение уровня ФСГ при применении де-гареликса может способствовать ингибированию роста опухоли [25].
ВЫВОДЫ
-
1. При длительной терапии гормоночувствительного РПЖ аналогами ЛГРГ на момент биохимического прогрессирования (36,04± 33,48 мес.) у больных наблюдался уровень Т выше кастрационного (>1,73 нмоль/л) в 39% случаев, а в 8% случаев – больше 2,08 нмоль/л, и только 19% имели истинно кастра-ционный уровень (<0,69 нмоль/л) ( р <0,05).
-
2. В группе лечения дегарелик-сом и ХК при сравнении уровня ПСА до и после лечения с ИМТ имеется статистически не значимая зависимость: чем больше ИМТ, тем больше среднее значение ПСА ( р >0,05).
-
3. При БП замена аналога ЛГРГ
на ХК или антагонист ЛГРГ приводит к снижению уровня Т у 47,6% и 38,5% больных соответственно ( р <0,05) и к снижению уровня ПСА у 14,3% и 19,2% больных, соответственно ( р <0,05). При БП замена аналога ЛГРГ на антагонист ЛГРГ приводит к снижению уровня ФСГ у 80,8% больных на 33,9% ( р =0,0001). В группе дегареликса статистически значимых изменений ПСА при общем снижении ФСГ получено не было ( р =0,246).
-
4. В группе лечения дегарелик-сом при ИМТ больше 24 наблюдалось более выраженное снижение уровня Т ( p <0,05) и более выраженное снижение уровня ПСА, особенно при ИМТ 32 и более ( р <0,05).
-
5. Выявлено, что с увеличением
-
6. У больных обеих групп с уровнем Т >1,736 нмоль/л произошло статистически значимое снижение уровня Т до диапазона 0,694 – 1,736 нмоль/л (20-50 нг/дл) и стабилизация уровня Т при исходных значениях меньше 0,694 нмоль/л ( р <0,05). При Т от 0,694 до 1,736 нмоль/л (20-50 нг/дл) произошло снижение Т в группе ХК в трех случаях и у одного больного в группе дегареликса ( р >0,05).
Резюме:
Современные руководства рекомендуют поддерживать целевой уровень тестостерона (Т) при проведении гормональной терапии рака предстательной железы (РПЖ)не выше 1,73 нмоль/л (50 нг/дл). Однако у большинства пациентов, которым проводится хирургическая кастрация (ХК), концентрации Т меньше 0,694 нмоль/л (<20 нг/дл), но эти уровни редко достижимы у пациентов, получающих аналоги лютеинизирующего рилизинг гормона (ЛГРГ). Вполне вероятно, что при гормональной терапии необходимо снижать уровень Т плазмы ниже, чем принято в настоящее время. Исследование проведено для изучения прогностической роли уровня сывороточного Т при андрогенной депривационной терапии (АДТ). Изучено влияние подъема уровня Т («всплески») при длительном лечении аналогами ЛГРГ на биохимическое прогрессирование (БП) гормоночувствительного РПЖ. Может ли являться кастрационный уровень (КУ) Т ниже 1,73 нмоль/л параметром эффективности лекарственных препаратов в лечении РПЖ. Рассматривалась взаимосвязь между уровнем Т при АДТ и динамикой простатспецифического антигена (ПСА). В работе проведена сравнительная оценка клинических эффектов терапии дегареликсом и хирургической кастрации (ХК), проводимой во второй линии гормональной терапии (ГТ) при возникновении БП гормоночувствительного
Список литературы Прогностическое значение истинного кастрационного уровня тестостерона при гормоно-чувствительном раке предстательной железы
- Каприн А.Д., Старинский В.В., Петрова Г.В. Злокачественные новообразования в России в 2014 году. М., 2016.-С.9-145.
- Pagliarulo V, Bracarda S, Eisenberger MA, Mottet N, Schröder FH, Sternberg CN, et al. Contemporary role of androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer./Eur Uro. 2012; 61 (1): 11-25.
- Sharifi N, Gulley JL, Dahut WL. Androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer. JAMA 2005; 294: 238-244.
- Mottet N, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Joniau S, Mason M, Matveev V, et al. EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part II: Treatment of advanced, relapsing, and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur Urol 2011; 59 (4): 572-583.
- Wheeler MJ, D’Souza A, Matadeen J, et al. Wheeler MJ1, D'Souza A, Matadeen J, Croos P. Ciba Corning ACS:180 testosterone assay evaluated. Clin Chem 1996; 42 (9): 1445-1449.
- Oefelein MG, Feng A, Scolieri MJ, Ricchiutti D, Resnick MI. Reassessment of the definition of castrate levels of testosterone: implications for clinical decision making. Urology 2000; 56 (6): 1021-1024.
- Perachino M, Cavalli V, Bravi F. Testosterone levels in patients with metastatic prostate cancer treated with luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone therapy: prognostic significance? Br J Urol 2010; 105 (5): 648-651.
- Morote J, Planas J, Ramirez C, Gomez E, Raventos CX, Placer J, et al. Evaluation of the serum testosterone to prostate-specific antigen ratio as a predictor of prostate cancer risk. BJU Int 2010; 105 (4): 481-484.
- Tombal B. The importance of testosterone control in prostate cancer. Eur Urol 2007; (6): 834-839.
- Testosterone levels. In: Gomella LG, ed. 5-Minute Urology Consult. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. In press.
- Miner MM, Sadovsky R. Evolving issues in male hypogonadism: evaluation, management, and related comorbidities. Cleve Clin J Med 2007; 74 (suppl 3): 38-46.
- Zlotta A, Debruyne FMJ. Expert opinion on optimal testosterone control in prostate cancer. Eur Urol Suppl 2005; 4 (8): 37-41.
- de Jong IJ, Eaton A, Bladou F. LHRH agonists in prostate cancer: frequency of treatment, serum testosterone measurement and castrate level: consensus opinion from a roundtable discussion. Curr Med Res Opin 2007; 23 (5): 1077-1080.
- Tombal B, Berges R. How good do current LHRH agonists control testosterone? Can this be improved with Eligard®? Eur Urol Suppl 2005; 4 (8): 30-36.
- R0hl HF, Beuke HP. Effect of orchidectomy on serum concentrations of testos terone and dihydrotestosterone in patients with prostatic cancer. Scand J Urol 1992; 26 (1): 11-14.
- Morote J, Orsola A, Planas J, Trilla E, Raventos CX, Cecchini L, et al. Redefining clinically significant castration levels in patients with prostate cancer receiving continuous androgen deprivation therapy. J Urol 2007; 178 (4, Pt1): 1290-1295.
- Veldhuis JD, Liem AY, South S, Weltman A, Weltman J, Clemmons DA, et al. Differential impact of age, sex steroid hormones, and obesity on basal versus pulsatile growth hormone secretion in men as assessed in an ultrasensitive chemiluminescence assay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1995; 80 (11): 3209-3222.
- Oefelein MG, Cornum R. Failure to achieve castrate levels of testosterone during luteinizing hormone releasing hormone agonist therapy: the case for monitoring serum testosterone and a treatment decision algorithm. J Urol 2000; 164: 726-729.
- Leonard G. Gomella. Effective Testosterone Suppression for Prostate Cancer: Is There a Best Castration Therapy? Reviews in urology 2009; 11 (2): 52-60.
- Грицкевич А.А., Медведев В.Л., А.А.Теплов, Мишугин С.В., Шахнович Е.Б., Пьяникин С.С., Русаков И.Г. Cовременные возможности антагонистов лютеинизирующего гормона-рилизинг-гормона третьего поколения в лечении гормоночувствительного рака предстательной железы. Онкология. Журнал им. П.А. Герцена. 2014; 3(6): 63-71.
- Perachino M, Cavalli V, Monferrato C. Testosterone (T) level correlates with survival in pts with advanced prostate cancer (APC): the lower is really the better. J Urol 2008; 179: 179-180. Abstract 512.
- Klotz L, Boccon-Gibod L, Shore ND, Andreou C, Persson BE, Cantor P, et al.The efficacy and safety of degarelix: a 12-month, comparative, randomized, open-label, parallel-group phase III study in patients with prostate cancer. BJU Int 2008; 102 (11): 1531-1538.
- de la Rosette J, Davis R 3rd, Frankel D, Kold Olesen T. Efficacy and safety of androgen deprivation therapy after switching from monthly leuprolide to monthly degarelix in patients with prostate cancer. Int J Clin Pract 2011; 65(5): 559-566.
- Radu A, Pichon C, Camparo P, Antoine M, Allory Y, Couvelard A, et al. Expression of follicle-stimulating hormone receptor in tumor blood vessels. N Engl J Med 2010; 363(17): 1621-1630.
- Ben-Josef E, Yang SY, Ji TH, Bidart JM, Garde SV, Chopra DP et al. Hormone-refractory prostate cancer cells express functional follicle-stimulating hormone receptor (FSHR). J Urol 1999; 161 (3): 970-976.


