Radio-diagnostic capabilities of the lung lesion during the Bekhchet's disease
Автор: Khukhareva N.M., Lukina O.V.
Журнал: Теория и практика современной науки @modern-j
Рубрика: Медицина и здоровье
Статья в выпуске: 7 (37), 2018 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The paper describes the features of changes in lungs with Bekhchet's disease. Recently more and more patients with Bekhchet's disease have been diagnosed in Russia, especially in the North Caucasus. Early detection of the disease will reduce probability of serious complications, including a lethal outcome. In the article on the example of a clinical case? The possibilities of radiodiagnosis of pulmonary lesions in this disease are. The obtained results prove that the main method of diagnosing lungs lesions for such patients is the computed tomography.
Vasculitis, bekhchet''s disease, radiodiagnosis, computer tomography, pulmonary lesion
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140273696
IDR: 140273696
Текст научной статьи Radio-diagnostic capabilities of the lung lesion during the Bekhchet's disease
Occurrence of Bekhchet's disease varies in different geographical zones and mostly coincides with the " Great Silk Road". It most often found in the countries of the Middle East (often Turkey) and the Far East (Japan). Young people aged 20-35 years are more likely to fall ill. Men suffer more often than women.
About 316 patients were registered in Russia in 2017 (cohorts of the Nasonova NGB FBBU), most of them living in the North Caucasus, mostly residents of Dagestan = 48.7%, Moscow and Moscow residents = 39.2% .
The etiology of Bekhchet’s disease is still unknow, a combination of causes, mainly genetic and infectious is suggested. The disease is associated with a carrier of HLA-B51- antigen and with a polymorphism in the gene controls the immune response.
At the heart of Behcet's disease is vascular damage (vasculitis) in combination with hyperfunction of neutrophils and autoimmune reactions. [2] Due to the defeat of vasa vasorum, large vessels are involved in the process, organ pathology develops. A typical symptom is thrombosis of the superficial and deep veins and arteries with the development of aneurysms, which causes the development of bleeding, heart attacks, organ failure; defeat of joints in the form of mono- or oligoarthritis of large joints; abdominal pain and diarrhea with possible development of intestinal bleeding and intestinal perforation; also described cases of hemiparesis and tetraplegia, increased intracranial pressure with edema of the optic nerve, the development of dementia; the incidence of lung involvement in Behçet's disease ranges from 1 to 7% (pulmonary arterial aneurysms (89%), arterial and venous thromboses, pulmonary infarctions, relapsing pneumonia, obliterating bronchiolitis, pleurisy, nodular formations in the lung parenchyma (76%), cavity formation 54%) and exudative pleurisy were noted (59%), renal and cardiac damage. [3]
Patient V., male, 68 years old, resident of Dagestan, is observed in the clinic of the Scientific Research Institute of Nephrology since 2008. The patient has granulomatosis with polyangiitis with damage to the kidneys, upper respiratory tract, lungs. Kidney damage led to the development of terminal renal failure, received replacement renal therapy by program hemodialysis since 2008 on the department of chronic hemodialysis of the Scientific Research Institute of Nephrology. The patient received immunosuppressive therapy for a long time, on the background of a prolonged remission, independently canceled preparations by the end of 2016. Received in connection with the deterioration of the state in midMarch 2017 - constant fever, shortness of breath, sleepless-cough, with the passage of viscous sputum with hemorrhagic inclusions, migratory arthritis, hemorrhagic rheum.
The results of the survey revealed: signs of active autoimmune process and acute inflammation. It is worth noting the presence of HLA-B51 antigen.
According to CT-scans data at admission it’s determined (Fig.1):
-
• un the middle lobes of both lungs and S6 of the right lung sites of central and peripheric amplification pulmonary interstition, with the formation of the areas of pneumonia reduction of lung tissue as "ground glass opacity".
-
• In the middle - lower parts of both lungs, multiple perivascularly located focal pockets of lung tissue, 0.3-1.0 cm in diameter, and a density of " ground glass opacity " type.
-
• In S6 of the right lung, paravertebral against fibrotic deformed pulmonary tissue, the focus of compaction of lung tissue, ovoid form, measuring 2.0 to 1.0 cm is determined.
-
• Moderately enlarged (up to 1.5 cm in diameter) lymph nodes of the lower paratracheal, bifurcation group and aortopulmonary window group are visualized.
-
• Pulmonary artery (3.5 cm) and its branches dilated.
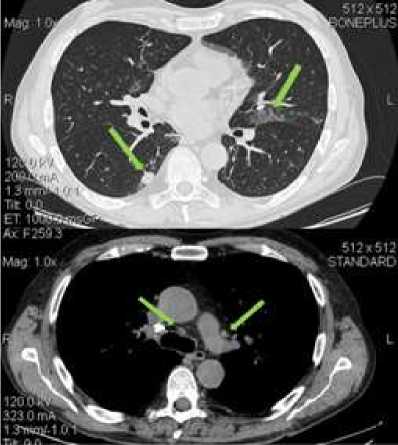
Fig.1: СT-scans from 25.04.2017
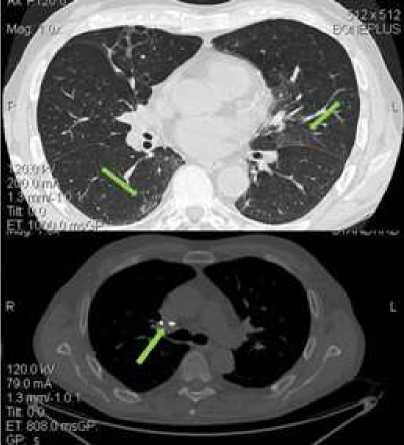
Fig.2: СT-scans from 24.05.2017
On the background of therapy, a significant positive effect was observed with a decrease in the inflammatory parameters (normalization of the level of C- reactive protein and the number of eosinophils of blood and sputum), and positive clinical and radiological dynamics were also determined.
According to CT of 24.05.2017 in comparison with the previous positive dynamics (Fig.2):
-
• The focus of lung tissue compaction, previously visualized in S6 of the right lung, is not detected, in its place is visualized the "matt glass" seal area.
-
• In the middle lobes of both the lungs and in the S6 of the right lung, areas of amplification of the central and peripheral pulmonary interstitium.
-
• In the middle and lower parts of both lungs, multiple perivascularly located focal pads of pulmonary tissue of the same type as "frosted glass" are preserved, with a decrease in the magnitude of changes in their number and size.
-
• In S3 of the upper lobe of the right lung, S7 n / d of the right lung retains the areas of linear compaction of the lung tissue according to the type of fibrous changes.
-
• The visualized intrathoracic lymph nodes are not enlarged in size, they are calcified in the lymph nodes of the right bronchopulmonary group (10mm). Axillary lymph nodes in size are not enlarged.
-
• Pulmonary artery (2.8 cm) and its branches are not dilated.
Results and conclusions: The clinical picture of the patient's illness was largely due to the severity of lung damage. Since Behcet's disease is a rare disease and causes complexity in the diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a full examination of the patient as soon as possible. The main method of diagnosing lung injury for such patients is CT, which allows timely detection of aneurysms of pulmonary arteries, pulmonary infarction, thrombosis of large vessels and prevent the occurrence of fatal consequences.
Список литературы Radio-diagnostic capabilities of the lung lesion during the Bekhchet's disease
- Галански М. Лучевая диагностика. Грудная клетка: пер. с англ. / М. Галански [и др.]. - М.: МЕДпресс-информ, 2013 - 265 с.
- Семенкова Е.Н. Системные васкулиты. М.: Медицина, 1988. - 129 с.
- Труфанов Г.Е. Конспект интерстициальных заболеваний легких./ Труфанов Г.Е., Рязанов В.В., Сигина О.А. - СПб.: Элби-СПб, 2011 - 92с.
- Тюрин И.Е. Компьютерная томография органов грудной полости: монография /И.Е. Тюрин - СПб.: Элби-СПб, 2003 - 372 с.


