Развитие трещин в роторной стали Р2М при повышенной температуре
Автор: Шлянников В.Н., Косов Д.А., Федоренков Д.И., Zhang X.C., Tu S.T.
Статья в выпуске: 3, 2021 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Проведено комплексное расчетно-экспериментальное исследование скорости развития трещин при взаимодействии усталости и ползучести на компактных образцах из стали Р2М при температуре 550°C. Теоретическая часть исследования состояла в формулировке параметров сопротивления разрушению через классические и новые конституционные уравнения состояния среды с учетом накопления повреждений. Численные расчеты включали определение полей параметров напряженно-деформированного состояния для условий упругости, пластичности и ползучести, а также распределений нелинейных коэффициентов интенсивности напряжений и С*-интеграла по длине и фронту трещины для каждого испытанного компактного образца. Интерпретация экспериментальных результатов для одинаковых по форме в плане, но различной толщины образцов, дана в терминах упругих и нелинейных коэффициентов интенсивности напряжений с учетом накопления повреждений при ползучести. Получено, что скорость роста трещины при совместном действии усталости и ползучести по мере увеличения размеров трещины монотонно возрастает по сравнению с гармонической усталостью на порядок и более на образцах одинаковой геометрии. Учет поврежденности через коэффициенты интенсивности напряжений ползучести обусловливает различия в диаграммах циклического разрушения. Суперпозиция вкладов усталости и ползучести в терминах времени выдержки под нагрузкой показывает увеличение суммарной скорости роста трещины на порядок по сравнению с интерпретацией экспериментальных данных в терминах чистой ползучести.
Скорость развития трещины, взаимодействие усталости и ползучести, повышенная температура, сталь р2м
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/146282365
IDR: 146282365 | УДК: 539.4 | DOI: 10.15593/perm.mech/2021.3.19
Текст научной статьи Развитие трещин в роторной стали Р2М при повышенной температуре
ВЕСТНИК ПНИПУ. МЕХАНИКА № 3, 2021PNRPU MECHANICS BULLETIN
В последние десять лет активно разрабатываются модели прогнозирования скорости развития трещин и остаточной долговечности при взаимодействии малоцикловой усталости и ползучести. Актуальность этих исследований обусловлена необходимостью обеспечения безопасной эксплуатации при соответствующей экономической эффективности ответственных элементов конструкций тепловой и ядерной энергетики, авиации и общего машиностроения. Условия эксплуатации подобных изделий относятся к одному из самых трудных в реализации теоретического, экспериментального и вычислительного плана вариантов термомеханического нагружения.
Рассмотрение стадии развития трещин при высокой температуре в условиях, моделирующих эксплуатационные, потребовало формулировки новых определяющих конституционных уравнений поведения среды с учетом образования, накопления и развития повреждений. Теоретические основы инженерных приложений при оценке несущей способности конструкции с учетом накопления и развития повреждений при высокой температуре заложены фундаментальными работами [15] и [16]. Дальнейшее развитие механики повреждений в основном состояло в обобщении и развитии введенных авторами функций сплошности и поврежденности с учетом многоосности исходного номинального напряженного состояния и доминирующих механизмов разрушения. При этом различают силовой (stress) и деформационный (ductile) доминирующие механизмы разрушения по телу зерна или по межзеренным границам. Наиболее развит в отечественной и зарубежной литературе механизм кавитации по границам зерен.
Дальнейшее развитие формулировок уравнений состояния на стадии формирования и роста пор в твердом теле с начальным макродефектом в виде трещины представлено в обобщающей работе [17]. В этой работе сформулированы конституционные уравнения для механизма кавитации по границам зерен с учетом плотности распределения повреждений в пористой среде и введены основы построения полей напряжений и скоростей деформаций в локальной области вершины трещины. Более детально вопрос учета многоосного напряженного состояния в вершине трещины на стадии развития повреждений при ползучести рассмотрен в работе [18]. Данная работа получила широкое распространение в вычислительных комплексах при анализе напряженно-деформированного состояния ряда модельных задач. Основополагающими работами по деформационному доминирующему механизму разрушения в поврежденной области вершины трещины при ползучести является статья [19]. Приложение деформационной и силовой трактовки поведения материала для оценки эффектов стеснения по стадиям накопления и развития повреждений при ползучести содержится в работе [20]. Совсем недавно опубликован наиболее обстоятельный обзор [21] по моделям накопления повреждений при ползучести.
Те или иные конституционные модели накопления и развития повреждений при ползучести в первую очередь используются для анализа полей напряжений и скоростей деформации в области вершины трещины. Наиболее простое представление в форме закона Бейли–Нортона относится к категории неповрежденных полей, когда кинетические процессы накопления и развития повреждений по стадиям ползучести не участвуют в системе разрешающих уравнений того или иного вычислительного комплекса. Большинство работ в открытой литературе по механике повреждений относится именно к этой категории постановки численных исследований. На рубеже 1990-х годов получили свое развитие основополагающие формулировки поведения поврежденной среды [17] при исследовании НДС в области вершины стационарных трещин. Обобщение работ данного направления, доведенных до соответствующих стандартов испытаний по определению скорости роста трещин при ползучести, представлено в монографии [22].
Аналитические исследования влияния накопления и развития повреждений в формулировках конституционных уравнений состояния в области вершины трещины и, как следствие, кинетики полей напряжений и скоростей деформаций ползучести представлены в работах [23-25]. Существенным результатом работ этого направления явились установленные тренды изменения локальных поврежденных полей параметров НДС по возрастающим стадиям ползучести. Однако должного учета установленной кинетики повреждений в базовых параметрах, используемых при интерпретации экспериментальных данных по скорости развития трещин при ползучести и взаимодействии усталости и ползучести, не получилось. Это обстоятельство накладывает ограничение на использование традиционных моделей прогнозирования роста дефектов при высокой температуре в силу их консерватизма. Более того, известные модели прогнозирования скорости роста трещин при ползучести и усталости [5, 20, 6, 8] основаны исключительно на упрощенных полях напряжений и скоростей деформаций для неповрежденных состояний, в которых отсутствует учет влияния кинетики накопления и развития повреждений в локальной зоне процесса разрушения как функций времени выдержки под нагрузкой.
На основе приведенного выше обзора определены задачи настоящей работы, которые состояли в формулировке нелинейных параметров сопротивления разрушению, их численном определении и последующем приложении к интерпретации экспериментального исследования скорости роста трещин при взаимодействии усталости и ползучести. Объектом исследований при повышенной температуре выступали компактные образцы из роторной стали Р2М.
1. Модели состояния в вершине трещины
В настоящей работе интерпретация экспериментальных результатов по скорости развития трещин в компактных образцах из стали Р2М при повышенной температуре будет представлена в терминах сопротивления разрушению для условий упругости, пластичности и ползучести. В связи с этим кратко напомним конституционные уравнения состояния среды для соответствующих условий деформирования.
Упругие поля напряжений и перемещений в вершине трещины для плоской задачи описываются в соответствии с решением путем удержания первых двух членов разложения по степеням r ~12 в полярных координатах ( r , 0 ), центрированных на вершину трещины, следующим образом [26]:
°п ^ 121 K f 1 ( 0 ) ^ 21 ^ 22 J л/2 П Г L f 21 ( 0 )
f« ( 0 ) 1Г т о f 22 ( 0 ) J L 0 0,
u 1=к ГЕ Г h(0, к)Е т •£ Г h2(0,к,а) vJ G V^Ld (0, к)_| 8 G L d2 (0, к, а)
(к + 0 tan а ( к+ 1 )
, (2)
где v и а - коэффициент Пуассона и угол приложения нагрузки; к = 3 — 4 v и к = (3 —v )/(1 + v ) для плоской деформации и плоского напряженного состояния соответственно; T - несингулярный член и f (0), g^ (0), h ( 0 , к , а ), d ( 0 , к , а ) - известные безразмерные функции [27]; K 1 - упругий коэффициент интенсивности напряжений (КИН); G - модуль сдвига. Упругий КИН для компактного образца при внецентренном растяжении, который использован в экспериментальных исследованиях, определяется стандартной формулой
, _ P 2 + a/w
b-jw 1 — (a/w )1.5
х
2 34
л \ л \ л \ л \
0,866 + 4,64 1 a I — 13,32 1 a I + 14,72 1 a I — 5,6 | a I
^ w J ^ w J ^ w J ^ w J
, (3)
где P - приложенная нагрузка; b и w - толщина и ширина образца; a - длина трещины.
Поведение материала в упругопластической области при нелинейном деформировании описывалось по классической модели:
|
fc E |
c |
||
|
е = < |
c а ( |
n ^1 |
|
|
—+—c [ E E Y I |
1 , ic0 J |
c > c Y , |
|
где E и Су - модуль Юнга и предел текучести при простом одноосном растяжении; n и а - показатель и коэффициент деформационного упрочнения соответственно.
Поля напряжений, деформаций и перемещений в пластической области вершины трещины с сингулярностью, зависящей от пластических свойств материала 1/ (n+1)
r , представлены в соответствии с классическим решением [28–30]:
- 1
c p ( r , 0 ) = K p r n1 ф ( 0 ) ; - n
И Р ( r , 0 ) = а K^1 е р ( 0 ) ; (5)
u p ( r , 0 ) = а K n r n + i U p ( 0 ) ,
Qp ( 0 , n , ( a/w ) ) = —n -j-( c Р ) cos 0-
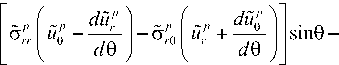
--1т ( c p u p + c p U p ) cos 0 . (8) n + 1х 7
Для состояния упруговязкопластичного материала в условиях ползучести поля напряженно-деформированного состояния в вершине трещины определяются с учетом безразмерного параметра повреждения го :
c j ( r , 0 , t , ro ) = c j ( r , 0 , t , ro)/c o = K . ( го ) rp c j ( 0 , n , t , го ) ;
c c. ( r , 0 , t , го ) = c cC ( r , 0 , t , ro )/ c 0 = Kcr ( го ) rp c er ( 0 , n , t , го ) ;
e Cr ( r , 0 , t , го ) =
= е j ( r , 0, t ,го )/ B = [ KC r ( го ) ] n r q 5 j ( 0, n , t , го ) ; (9)
Ucr ( r , 0 , t , го ) =
= U " ( r , 0 , t , го )/( BL ) = [ K r ( го ) ] n r q U ( 0 , n , t , го ) ;
где K – пластический коэффициент интенсивности напряжений [28]. В уравнениях (5) компоненты напряжений, деформаций и перемещений приведены к безразмерному виду за счет традиционной нормировки, принятой в нелинейном анализе: cij=cij/cY ,
U = uE^уL , r = .L , где c0 - предел текучести мате-
PP риала; L характерный размер тела с трещиной; cу, еу и UP - безразмерные функции полярного угла 0 и показателя упрочнения n; угловые распределения СP (0) нормализованы так, чтобы c тах (0) = (3/28Д• )12 = 1, где S – девиатор тензора напряжений. Амплитудный коэффициент или пластический КИН K в формулах (5) соответствует первоначальной формулировке [31]
где p и q – показатели сингулярности; Kcr – нелинейный КИН для ползучести, который нормализован напряжением второй устойчивой стадии ползучести c 0 и имеет смысл амплитудного коэффициента. Параметр повреждения го в уравнениях (9) изменяется от го = 0 для исходного бездефектного состояния материала до го = 1 в момент окончательного разрушения. Для ситуации ползучести в уравнениях (9) безразмерные функции напряжений и скоростей перемещений c cr ( 0 , n , t , го )
и U Cr ( 0 , n , t , го ) отличаются от таковых для условий пластичности (5). Авторы [32] ввели нелинейный КИН для ползучести, который определяется через С* -интеграл [33]:
K cr
1 f C ) n cr + 1
c o I BT nr Z J
Kp =
V \ 2
Г K 1
lc Y J а I n w
1 n + 1
Авторы [31] разработали основанный на МКЭ численный метод определения I – интеграла, входящего в выражение для пластического КИН K (6), для обще-
го трехмерного случая деформирования образцов и элементов конструкций путем учета углов девиации наклонной трещины 0 * :
п
I n ( 0 , n , ( a/w ) ) = j Q р ( 0 , n , ( a/w ) d 0 ; (7)
-п
где
+п
C * = J Br
-п
n cr C-^M" +1
n c: ^1( c ■ )
cos 0 d 0-
+п
- J
-п
. й f „8UC cr5Uccr sin 0 cCr —— + cCr —- l rr 80 r0 50
nf
„
E
C
u
c
cr
- r cos 0l c Cr -^- + c C 0-0- l d r d r
d 0 ;
п
I C ( 0 , t , Пс. , го ) = J q Cr ( 0 , t , n Cr , го ) d 0 ;
-п
Q cr ( 0, t , n cr ,го ) = -n c ^-( c er ) ncr +1 cos0- n„, + 1
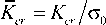
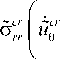
ducr d 6
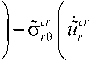
dU c " + " d 6" ,
sin 6-
--1-7 ( б V U C + 6 C 6 U C ) cos 6. (12) n cr + 1
В формулах (10)–(12) B и ncr – константы ползучести по конституционному уравнению Нортона. Скорость накопления деформаций ползучести в уравнении (9) авторами [15, 33] обобщена на состояние многоосного деформирования через J 2 -теорию течения следующим образом:
d S eqv dt
= —- ncr -1
2 B 6 eqv S ij
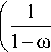
В работе [15] введен параметр сплошности, а в [16] предложено одно из первых уравнений накопления повреждений при ползучести и введено как функция приложенных номинальных напряжений 6 :
d to dt
( 1 -to)
где C и m – экспериментальные константы материала. Впоследствии это уравнение было модифицировано и введено несколько более сложных моделей накопления и развития повреждений [23–25], обзор которых представлен в работе [21]. На основе критерия Писаренко– Лебедева для сложного напряженного состояния авторы [34] ввели обобщенную деформационную модель накопления повреждений при ползучести для многоосного нагружения, которая использована в настоящей работе.
d to _ d^ [ ( 1 -x)/n-+%] n cr dt t

(1 -to ) g ,
где t f – время до разрушения; d и g – экспериментальные константы материала; b i и n i - функции вида напряженного состояния; % - отношение напряжений разрушения при одноосном сжатии и растяжении.
Результаты экспериментов, которые представлены в настоящей работе, относятся к гармоническому циклическому нагружению и сочетанию малоцикловой усталости и ползучести. Подобные ситуации предполагают учет каждой из составляющих общего процесса накопления и развития повреждений. В литературе известны несколько моделей для описания накопления и роста повреждений при взаимодействии ползучести и усталости. Ряд авторов предполагают, что помимо хорошо известного влияния повреждений при ползучести на усталостную выносливость существует возможность влияния усталостных повреждений на поведение при ползучести. В работе [3] предложены обобщенные диаграммы, включающие нелинейное взаимодействие ползучести и усталости в виде следующего комбинированного уравнения:
tor со to=— f— +-^-, (16)
1 -tocr 1 -tof где to - общее повреждение; tocr - повреждение при ползучести; tof - повреждение при усталости. При достижении равенства to = 1 соотношение между ними определяется выражением tof = 0,5[(2-toс,)-V4tocr -3to2. ]. (17)
Уравнения (13), (15)–(17) в дальнейшем будут использованы в численных МКЭ расчетах полей параметров напряженно-деформированного состояния в испытательных образцах при взаимодействии усталости и ползучести при повышенной температуре.
2. Определение параметров сопротивления разрушению
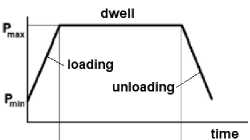
Объектом экспериментальных исследований в настоящей работе являлись цилиндрические и компактные образцы из роторной стали Р2М для испытаний при температуре 550 ° C. Цилиндрические образцы испытывались при одноосном статическом растяжении, малоцикловой усталости и длительном статическом нагружении в порядке определения констант уравнений Рам-берга–Осгуда, типа Мэнсона–Коффина и Нортона. Вторая основная часть экспериментальных работ состояла в исследовании скорости роста трещины в компактных образцах при гармоническом циклическом нагружении и совместном действии усталости и ползучести в трапециевидном цикле нагружения с временем выдержки под нагрузкой 60 с при повышенной температуре 550 ° C. Во всех случаях коэффициент асимметрии цикла нагружения R = 0,1. В таблице приведены основные свойства пластичности и ползучести стали Р2М при температуре 550 ° C, идентификация которых дана в пояснениях к соответствующим вышеприведенным формулам.
Основные механические свойства стали Р2М при температуре 550 ° С
Main mechanical properties of P2M steel at the temperature of 550 ° C
|
E ГПа |
V |
6 y МПa |
а |
n p |
B 1/(MHa)n - hr) |
n cr |
C 1/(MHa) m - hr) |
m |
|
180 |
0,3 |
460 |
1,20 |
6,67 |
1,41 х 10-12 |
5,07 |
2 х 10-11 |
2,48 |
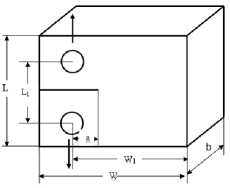
Испытания на скорость роста трещин проведены при температуре 550 ° C на компактных образцах одинаковой формы в плане шириной w = 50 мм. Эксперименты при гармоническом нагружении выполнены на образцах толщиной b = 6,2 мм и 12,5 мм, а при взаимодействии усталости и ползучести на образцах трех толщин b = 6,2, 12,5 и 25 мм (рис. 1, а , б ).
Каждый цикл нагружения при взаимодействии усталости и ползучести составлял 70 с, в котором по 5 с занимали периоды нагрузки и разгрузки и время выдержки под нагрузкой составляло 60 с (рис. 1, в). Испытания по определению скорости роста трещин выполнены на специализированной установке УТС-10 с непрерывной атоматизированной фиксацией длины трещины методом разности электрических потенциалов и раскрытия берегов трещины керамическим датчиком перемещений (рис. 2).

а
б
в
Рис. 1. Компактный образец ( a , б ) и профиль его нагружения ( в ) при усталости +ползучесть
Fig. 1. C(T) specimen ( a , b ) and its loading profile ( c ) under fatigue+creep

Рис. 2. Установка для экспериментов при взаимодействии усталости и ползучести
Fig. 2. Creep-fatigue test equipment
а

б
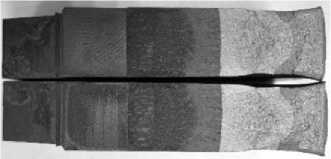
Рис. 3. Изломы образцов для усталости ( а ) и усталости+ползучесть ( б )
Fig. 3. Fracture surfaces for fatigue ( a ) and creep+fatigue ( b )
В результате испытаний серии образцов из стали Р2М были получены поверхности разрушения каждого образца, типовые примеры которых показаны на рис. 3, а и б для гармонической усталости и взаимодействия усталости и ползучести соответственно. В процессе испытаний каждого образца при высокой температуре формировались три маркера текущего положения фронта развивающейся трещины на изломе образца за счет изменения асимметрии цикла нагружения с R = 0,1 до R = 0,5 в течение одной минуты. При этом максимальные напряжения цикла оставались неизменными, а повышалось значение минимального номинального напряжения. Таким способом обеспечивалось отсутствие эффектов торможения роста трещины из-за возможной перегрузки в цикле нагружения. Типовые экспериментальные фронты трещин показаны на рис. 4.
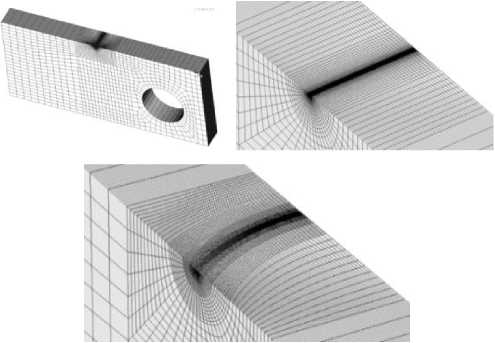
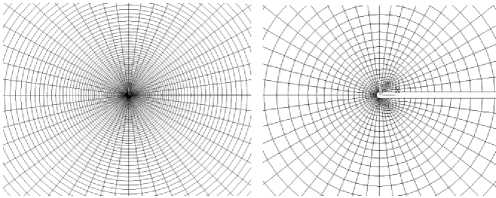
Информация об экспериментально полученных положениях фронтов трещин положена в основу численных расчетов для определения упругих и нелинейных параметров трещиностойкости по уравнениям (3), (6), (10), (11) в компактных образцах с использованием метода конечных элементов. Для каждого испытанного образца формировалось по три расчетных схемы МКЭ для моделирования положения прямолинейных и криволинейных фронтов трещин (рис. 4, а ) для соответствующих условий нагружения. Сетки конечных элементов строились с использованием объемных 20-узловых конечных элементов второго порядка. Вершина трещины моделировалась надрезом с конечным малым радиусом кривизны ρ / a = 1,3 ⋅ 10–4 (рис. 4, б , в ), где ρ – радиус кривизны; а – длина трещины. Минимальный размер элемента составлял 3 мкм, а общее количество узлов расчетной схемы МКЭ превышало 3 млн. Сетка конечных элементов сгущалась по направлению к вершине трещины и по мере выхода фронта трещины на свободную поверхность образца.
a
б в
Рис. 4. Моделирование фронтов в компактном образце ( а ) и вершины трещины ( б , в ) с минимальным размером элемента 3 мкм
Fig. 4. Finite element mesh for the C(T) specimen crack-tip problem ( a ); Near-tip mesh with the initial crack-tip radius ( b ); the characteristic element size is on the order of 3 µ m ( c )
Программа численных расчетов состояла в определении полей параметров напряженно-деформированн-ного состояния и дальнейшем определении упругих и пластических коэффициентов интенсивности напряжений (3), (6), а также C *-интеграла и КИН при ползучести (10), (11) в каждом испытанном образце из стали Р2М. Для учета свойств поврежденности при ползучести в программный комплекс ANSYS [35] через пользовательскую процедуру USERMAT введены новые конституционные уравнения (13)–(15) состояния среды в соответствии с силовой моделью накопления и развития повреждений при сложном напряженном состоянии. Постпроцессорная обработка результатов расчетов осуществлялась по компьютерному коду, разработанному авторами [35, 36], который включает численное определение контурных интегралов (7), (12) и собственно расчет упругих и нелинейных параметров сопротивления разрушению в условиях пластичности и ползучести с учетом накопления и развития повреждений. В порядке интерпретации экспериментальных результатов по развитию трещин необходимо располагать зависимостями параметров сопротивления разрушению от длины трещины в испытательном образце. В результате выполненных численных расчетов подобные зависимости найдены для различных точек фронта в каждом испытанном компактном образце.
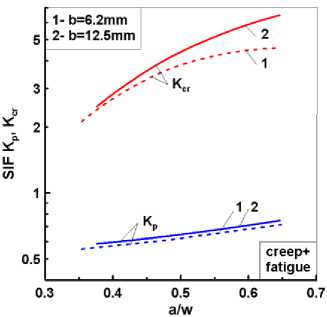
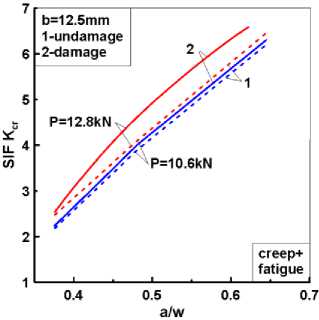
На рис. 5, а приведены расчетные зависимости пластического КИН КР и КИН при ползучести Kcr от относительной длины трещины a / w в компактных образцах различной толщины при совместном нагружении усталостью и ползучестью.
б
Рис. 5. Зависимости нелинейных КИН от длины трещины в образцах различной толщины ( а ) и условий деформирования ( б )
Fig. 5. Nonlinear SIF dependencies on crack length in specimens of different thicknesses ( a ) and loading conditions ( b )
На этом рисунке КИН Kcr соответствует классическому (без учета повреждений) конституционному уравнению ползучести типа Norton. Различия в нелинейных КИН КР и Kcr от вкладов пластичности при малоцикловом деформировании и ползучести при выдержке под нагрузкой составляют почти половину порядка с доминированием коэффициента интенсивности напряжений при ползучести Kcr . Из рис. 5, б , следует, что эффект поврежденности через соответствующие конституционные уравнения ползучести (13), (15) приводит к увеличению значений КИН Kcr , который зависит от уровня приложенной к образцу нагрузки.
Изломы компактных образцов на рис. 3 после испытаний демонстрируют существенное изменение кривизны фронта трещины по толщине образца. Следуя подобным экспериментальным фронтам трещин, на рис. 6
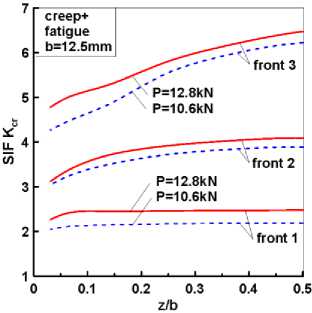
и 7 приведены распределения С*-интеграла и КИН при ползучести Kcr в зависимости от приложенной нагрузки и выбора уравнений состояния среды. Видно, что различия в значениях этих параметров в середине толщины образца z / t = 0,5 и на свободной поверхности z / t = 0,0 могут достигать более 20 %.
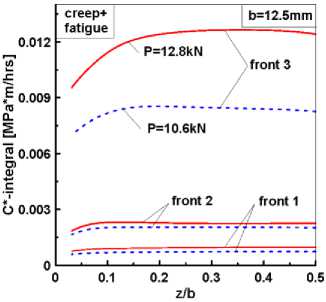
Рис. 6. Распределения С*-интеграла вдоль фронта трещины по толщине образца
Fig. 6. C*-integral distributions along the crack front along the specimen thickness
б
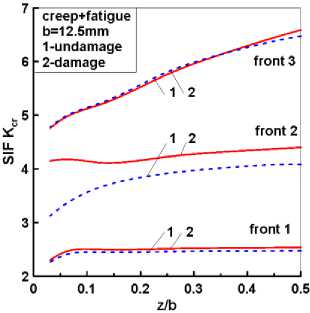
Рис. 7. Распределения КИН Kcr вдоль фронта трещины по толщине образца
Fig. 7. SIF Kcr distributions along the crack front along the specimen thickness
На рис. 7, б представлено сравнение распределений КИН при ползучести для классического закона Norton и силовой модели накопления повреждений (13), (15). Очевидно, что на начальной стадии развития трещины (фронт 1 ) при взаимодействии усталости и ползучести, как и ожидалось, различий в поведении КИН Kcr почти не наблюдается. Однако на стадии устойчивого развития трещины (фронт 2 ) различия в распределениях КИН по фронту трещины из-за учета накопления повреждений становятся уже существенными. На стадии окончательного разрушения образца (фронт 3 ) эффекты повреждений от ползучести становятся менее значимыми из-за общей текучести образца.
3. Скорость развития трещин при повышенной температуре
Одним из основных вопросов исследований развития трещин при повышенной температуре является оценка влияния вида нагружения. На рис. 8 приведены диаграммы скорости развития трещин в стали Р2М при температуре 550 ° C в терминах традиционных упругих коэффициентов интенсивности напряжений К 1 (3). На рис. 8, а представлено сравнение диаграмм для гармонического малоциклового нагружения с частотой 7 Гц и программного трапецевидного нагружения (см. рис. 1, в ) при взаимодействии усталости и ползучести. Сравнение проведено для образцов толщиной 6,2 и 12,5 мм. Из этих данных следует, что наложение времени выдержки ползучести при максимальной нагрузке цикла приводит к ускорению роста трещины по мере увеличения ее длины. Для ситуации взаимодействия усталости и ползучести скорость развития трещин может быть интерпретирована в терминах количества циклов нагружения N или времени выдержки под нагрузкой t . На рис. 8, б , приведены диаграммы циклического разрушения для совместного действия усталости и ползучести в координатах скорости роста трещин по времени и упругого коэффициента интенсивности напряжений для компактных образцов трех разных толщин, но одинаковой формы в плане. Как и ожидалось, в терминах упругих КИН, которые имеют одинаковые значения для условий плоского напряженного состояния и плоской деформации, толщина образцов не оказывает существенного влияния на скорость роста трещин.
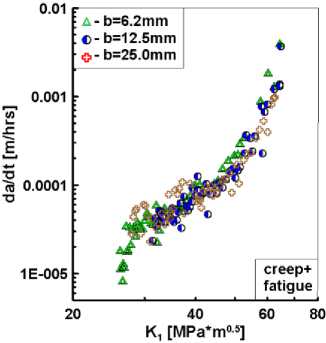
Солгласно стандарту ASTM E2760–10 [37], скорость роста трещин при взаимодействии усталости и ползучести должна быть интерпретирована в терминах С *-интеграла. Для этих целей в предыдущем разделе по уравнению (11) численно на основе МКЭ были рассчитаны распределения С *-интеграла по фронтам трещин в каждом испытанном образце. На рис. 9, а , показаны диаграммы циклического разрушения с использованием этих данных для компактных образцов различной толщины. Можно заметить, что изменение толщины несколько увеличивает полосу разброса экспериментальных данных с сохранением общего тренда результатов.
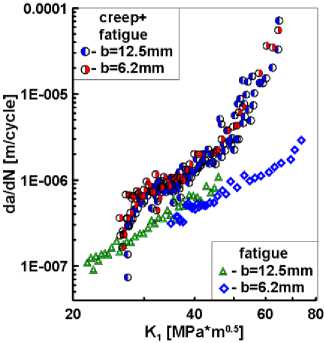
ния циклического разрушения элементов конструкций приведет к различным несовпадающим между собой оценкам остаточной долговечности при одном и том же виде нагружения. В связи с этим при определении скорости роста трещин целесообразно использовать комбинированные модели взаимодействия ползучести и усталости, которые учитывают эффекты времени выдержки и накопленное количество циклов нагружения.
б
Рис. 8. Влияние вида нагружения ( a ) и толщины образца ( б ) на скорость роста трещин
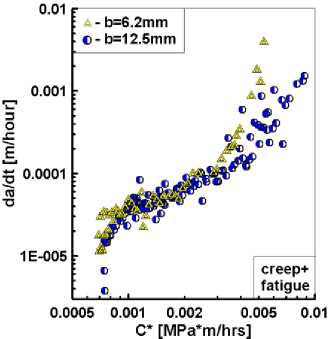
Fig. 8. Influence of loading conditions (a) and specimen thickness (b) on the crack growth rate
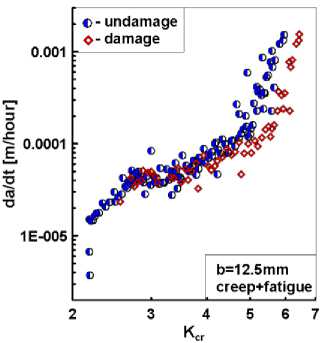
На рис. 9, б , представлено сравнение диаграмм скорости роста трещин при совместном действии усталости и ползучести в терминах КИН K cr (10) для двух типов конституционных уравнений состояния среды. В отличие от традиционных подходов на основе упругого КИН и С *-интеграла, интерпретация экспериментальных данных посредством КИН при ползучести K cr позволяет выявить эффект влияния накопления и развития повреждений, который возрастает по мере увеличения размеров трещины и длительности времени приложения нагрузки.
Особенностью интерпретации результатов испытаний при совместном действии малоцикловой усталости и ползучести является необходимость построения диаграмм циклического разрушения в терминах количества накопленных циклов нагружения или времени ползучести, которые соответствуют трапецевидному профилю программного нагружения. Выбор той или иной формы представления данных в итоге приведет к определению собственных для данного вида нагружения констант трещиностойкости материала. Однако последующее использование этих констант в задачах прогнозирова-
б
Рис. 9. Влияние толщины образца ( a ) и накопления повреждений ( б ) на скорость роста трещин
Fig. 9. The influence of the specimen thickness ( a ) and damage accumulation ( b ) on the crack growth rate
В этом плане наиболее простыми являются модели линейного суммирования повреждений, которые широко используются в оценках развития трещин при взаимодействии ползучести и усталости для прогнозирования срока службы элементов конструкций. Авторы [3] предложили простое правило суперпозиции для определения скорости роста трещин при совместном действии усталости и ползучести:
da dN
da dt
f da )
l dN J fatigue
Г da )
+ 1 I l dN J creep
f da )
l dN J fatigue
1 ( da ^
+ ;
3600 f l dt J creep
da ) (da ) (da ) (da )
I +1 I = 3600f I I +1 I dt), ■ к dt) I dN), ■ к dt)
fatigue creep fatigue creep
где da/dN – скорость роста трещины по циклам нагружения (m/cycle); da/dt – скорость роста трещины по времени выдержки под нагрузкой (m/hour) и f – частота нагружени в Гц. На рис. 10 в качестве примера приведены диаграммы циклического разрушения при расчете суммарной скорости роста трещин в терминах количества циклов нагружения по уравнению (20) и времени ползучести по уравнению (21).
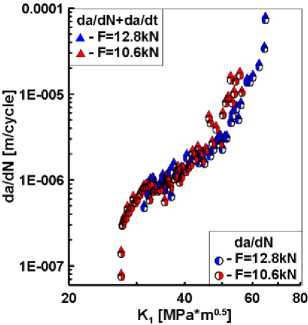
а
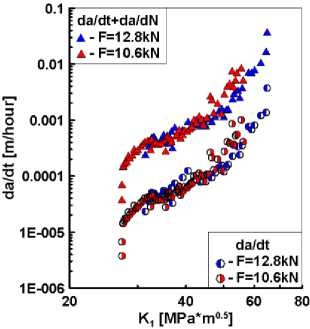
б
Рис. 10. Скорость роста трещин в терминах циклов нагружения ( a ) и времени ползучести ( б )
Fig. 10. Crack growth rate in terms of number of loading cycles ( a ) and creep time ( b )
Из рис. 10, а, следует, что добавление к скорости роста трещин усталости составляющей от ползучести не приводит к существенному изменению суммарных значений da/dN. В отличие от этого наложение на ползучесть циклического деформирования (рис. 10, в) приводит к увеличению суммарной скорости роста трещин почти на порядок. Подобный эффект влияния коррелирует с результатами численного расчета нелинейных коэффициентов интенсивности напряжений, представленных на рис. 5, а, где КИН ползучести Kcr существенно превышает КИН пластичности КР. На рис. 10 диаграммы циклического разрушения представлены как функции упругого коэффициента интенсивности напряжений К1. Тем не менее установленные различия в скоростях роста трещин при взаимодействии усталости и ползучести сохранятся и при интерпретации экспериментальных данных через нелинейные параметры сопротивления разрушению в форме С*-интеграла и КИН при ползучести Kcr.
Выводы
Проведено комплексное расчетно-экспериментальное исследование скорости развития трещин при взаимодействии усталости и ползучести на компактных образцах из стали Р2М при температуре 550 ° C. Формулировка параметров сопротивления разрушению представлена через классические и новые конституционные уравнения состояния среды с учетом накопления повреждений. Интерпретация экспериментальных результатов дана в терминах упругих, пластических коэффициентов интенсивности напряжений и КИН при ползучести. Получено, что скорость роста трещины при совместном действии усталости и ползучести по мере увеличения размеров трещины монотонно возрастает по сравнению с гармонической усталостью на порядок и более на образцах одинаковой геометрии. Учет повреж-денности через КИН ползучести обусловливает различия в диаграммах циклического разрушения. Суперпозиция вкладов усталости и ползучести в терминах времени выдержки под нагрузкой показывает увеличение суммарной скорости роста трещины на порядок по сравнению с интерпретацией экспериментальных данных в терминах чистой ползучести.
Работа выполнена при финансовой поддержке РФФИ (грант №20-58-53018\20_ГФЕН).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (Grant No. 20-58-53018 \ 20_GFEN).
Список литературы Развитие трещин в роторной стали Р2М при повышенной температуре
- Lagneborg R., Attermo R. The effect of combined low-cycle fatigue and creep of the life of austenitic stainless steels // Metal. Trans. - 1971. - Vol. 2. - Р. 1821-1827.
- Lemaitre J., Plumtree A. Application of damage concepts to predict creep-fatigue failures // Trans. ASME. - 1979. - Vol. 101. - Р. 284-292.
- Skelton R.P., Gandy D. Creep-fatigue damage accumulation and interaction diagram based on metallographic interpretation of mechanisms // Mater. High Temp. - 2008. - Vol. 25. - Р. 27-54.
- Ellyin F. Crack growth rate under cyclic loading and effect of different singularity fields // Engineering Fracture Mechanics. - 1986. - Vol. 25. - P. 463-473. doi: 10.1016/0013-7944(86)90260-2
- Nikbin K.M., Smith D.J., Webster G.A. An engineering approach to the prediction of creep crack growth // Trans. ASME. - 1986. - Vol. 108. - P. 186-191.
- Wasmer K., Nikbin K.M., Webster G.A. Creep crack initiation and growth in thick section steel pipes under internal pressure // International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping. - 2003. - Vol. 80. - P. 489-498. doi: 10.1016/S0308-0161(03)00103-0
- Yatomi M., Nikbin K.M., O’Dowd N.P. Creep crack growth prediction using a damage based approach // International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping. - 2003. - Vol. 80. - P. 573-583. doi: 10.1016/S0308-0161(03)00110-8
- Theoretical and numerical modelling of creep crack growth in a carbon-manganese steel / M. Yatomi, N.P. O'Dowd, K.M. Nikbin, G.A. Webster // Engineering Fracture Mechanics. - 2006. - Vol. 73. - P. 1158-1175. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2005.12.012
- Fookes A.J., Smith D.J. The in uence of plasticity in creep crack growth in steels // International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping. - 2003. - Vol. 80. - P. 453-463. doi: 10.1016/S0308-0161(03)00100-5
- Djavanroodi F. Creep-fatigue crack growth interaction in nickel base super alloy // American Journal of Applied Sciences. - 2008. - Vol. 5. - P. 454-460. doi: 10.3844/ajassp.2008.454.460
- Narasimhachary S.B., Saxena A. Crack growth behavior of 9Cr-1Mo (P91) steel under creep-fatigue conditions // International Journal of Fatigue. - 2013. - Vol. 56. - P. 106-113. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2013.07.006
- A novel creep-fatigue interaction damage model with the stress effect to simulate the creep-fatigue crack growth behavior / L. Xu, L. Zhao, Z. Gao, Y. Han // International Journal of Mechanical Sciences. - 2017. - Vol. 130. - P. 143-153. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2017.05.036
- Zhao L., Xu L., Nikbin K. Predicting failure modes in creep and creep-fatigue crack growth using a random grain/grain boundary idealised microstructure meshing system // Materials Science and Engineering: A. - 2017. - Vol. 704. - P. 274-286. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2017.08.035
- Finite element simulation of creep-fatigue crack growth behavior for P91 steel at 625 °C considering creep-fatigue interaction / H. Jing, D. Su, L. Xu, L. Zhao, Y. Han, R. Sun // International Journal of Fatigue. - 2017. - Vol. 98. - P. 41-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2017.01.004
- Качанов Л.М. Основы механики разрушения. - М.: Наука, 1974. - 312 с.
- Работнов Ю.Н. Ползучесть элементов конструкций. - М.: Наука, 1966. - 752 с.
- Hutchinson J.W. Constitutive behavior and crack tip fields for materials undergoing creep-constrained grain boundary cavitation // Acta Metall. - 1983. - Vol. 31. - P. 1079-1088.
- Hayhurst D.R. Creep rupture under multi-axial states of stress // J. Mech. Phys. Solids. - 1972. - Vol. 20(6). - P. 381-390.
- Cocks A.C.F., Ashby M.F. Intergranular fracture during power-law creep under multiaxial stresses // Metal Science. - 1980. - Vol. 14, no. 8-9. - P. 395-402. doi: 10.1179/030634580790441187
- Budden P.J., Ainsworth R.A. The effect of constraint on creep fracture assessments // International Journal of Fracture. - 1997. - Vol. 87. - P. 139-149. doi: 10.1023/A:1007416926604
- Meng Q., Wang Z. Creep damage models and applications for crack growth analysis in pipes: a review // Engineering Fracture Mechanics. - 2019. - Vol. 205. - P. 547- doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2015.09.055
- Saxena A. Nonlinear fracture mechanics for engineers. - CRC Press LCC, 1998. - 472 p.
- Bassani J.L., Hawk D.E. Influence of damage on crack-tip fields under small-scale-creep conditions // International Journal of Fracture. - 1990. - Vol. 42. - P. 157-172. doi: 10.1007/BF00018384
- Meng Q., Wang Z. Asymptotic solutions of mode I steady growth crack in materials under creep conditions // Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica. - 2015. - Vol. 28(5). - P. 578-591. doi: 10.1016/S0894-9166(15)30051-3
- Murakami S., Hirano T., Liu Y. Asymptotic fields of stress and damage of a mode I creep crack in steady-state growth // International Journal of Solids and Structures. - 2000. - Vol. 37 (43). - P. 6203-6220. doi: 10.1016/S0020-7683(99)00267-X
- Williams M.L. On the stress distribution at the base of a stationary crack // J. Appl. Mech. - 1957. - Vol. 24. - P. 109-114.
- Eftis J., Subramonian N. The inclined crack under biaxial load // Engineering Fracture Mechanics. - 1978. - Vol. 10. - P. 43-67. doi: 10.1016/0013-7944(78)90049-8
- Hutchinson J.W. Singular behaviour at the end of a tensile crack in a hardening material // Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids. - 1968. - Vol. 16. - P. 13-31. doi: 10.1016/0022-5096(68)90014-8
- Hutchinson J.W. Plastic stress and strain fields at a crack tip // Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids. - 1968. - Vol. 16. - P. 337-347. doi: 10.1016/0022-5096(68)90021-5
- Rice J.R, Rosengren G.F. Plane strain deformation near a crack tip in a power-law hardening material // Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids. - 1968. - Vol. 16. - P. 1-12. doi: 10.1016/0022-5096(68)90013-6
- Shlyannikov V.N, Tumanov A.V. Characterization of crack tip stress fields in test specimens using mode mixity parameters // International Journal of Fracture. - 2014. - Vol. 185. - P. 49-76. doi: 10.1007/s10704-013-9898-0
- Shlyannikov V.N., Tumanov A.V., Boychenko N.V. A creep stress intensity factor approach to creep-fatigue crack growth // Engineering Fracture Mechanics. - 2015. - Vol. 142. - P. 201-219. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2015.05.056
- Riedel H., Rice J.R. Tensile crack in creeping solids // ASTM STP 700, Fracture Mechanics. - 1980. - P. 112-130.
- Shlyannikov V.N., Tumanov A.V. Creep damage and stress intensity factor assessment for plane multi-axial and three-dimensional problems // International Journal of Solids and Structures. - 2018. - Vol. 150. - P. 166-183. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2018.06.009
- ANSYS Mechanical APDL Theory Reference Release 14.5. - ANSYS, Inc. Southpointe, 2012 - 275 Technology Drive, CanonBurg, PA.
- Shlyannikov V.N., Tumanov A.V. Creep-fracture resistance parameters determination based on stress and ductility damage models // Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures. - 2018. - Vol. 41. - P. 2110-2129. doi: 10.1111/ffe.12766
- ASTM E2760-10. Standard test method for creep-fatigue crack growth testing. Annual book of ASTM standards. Philadelphia (PA): American Society for Testing and Materials, 2010.


