Реологическое поведение смесей для строительной 3D-печати: экспериментальная оценка эффективности критериальных требований к наполнителям
Автор: Славчева Г.С., Солонина В.А., Разов И.О., Филипенко П.В., Орлов В.С.
Журнал: Нанотехнологии в строительстве: научный интернет-журнал @nanobuild
Рубрика: Строительное материаловедение
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.16, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Введение. Для решения задачи проектирования составов смесей для строительных аддитивных технологий в работе представлены результаты экспериментальных исследований реологического поведения и технологических характеристик (пластичности и формоустойчивости) цементных смесей на различных видах наполнителей, отличающихся размерно-геометрическими характеристиками. Методы и материалы. Исследования реологических характеристик цементных смесей проводились методами сдавливающей реометрии. Для оценки пластичности использовался режим нагружения с постоянной скоростью деформирования 5 мм/с, для оценки формоустойчивости режим постоянной нагрузки 5 Н/с. Для оценки характеристик размерно-геометрических частиц цемента и наполнителей использовали метод сканирующей электронной микроскопии (Phenom XL), обработка изображений для определения длины l и ширины b частиц производилась с помощью программного обеспечения «ParticleMetric». Дисперсность и гранулометрический состав наполнителей оценивали на лазерном анализаторе размера частиц «Анализетте 22». Результаты и обсуждения. Установлено, что необходимым условием обеспечения пластичности и устойчивости смесей является создание плотной пространственной упаковки частиц дисперсной фазы. Рациональные для экструзии значения предела пластичности обеспечиваются в том случае, если частицы наполнителя имеют сопоставимый с зернами цемента размер и полифракционную гранулометрию. Характеристики наполнителей не являются определяющими для обеспечения формоустойчивости смесей.
Аддитивные технологии, цементные смеси, наполнители, реология, технологические свойства
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142242417
IDR: 142242417 | УДК: 666.9.03 | DOI: 10.15828/2075-8545-2024-16-4-310-319
Текст научной статьи Реологическое поведение смесей для строительной 3D-печати: экспериментальная оценка эффективности критериальных требований к наполнителям
Славчева Г.С., Солонина В.А., Разов И.О., Филипенко П.В., Орлов В.С. Реологическое поведение смесей для строительной 3d-печати: экспериментальная оценка эффективности критериальных требований к наполнителям // Нанотехнологии в строительстве. 2024. Т. 16, № 4. С. 310–319. – EDN: ISMLKK.
Р азвитие строительной практики технологии
3D-печати создает потребность в наличии на рынке широкой номенклатуры смесей, удовлетворяющих требованиям данной технологии. Эффективность и технологичность строительной 3D-печати определяется совокупностью критериальных характеристик смесей: пластичности для реализации процесса экструзии (extrudability), формоустойчивости при укладке слоев (buildability), скорости структуро-образования и твердения (structural build up) [1–4].
В результате накопления массива экспериментальной информации, например [5–19], разработаны
СТРОИТЕЛЬНОЕ МАТЕРИАЛОВЕДЕНИЕ и успешно апробированы десятки разновидностей составов смесей, которые имеют необходимые для печати технологические характеристики. Полученные смеси характеризуются многокомпонентностью, в их составах одновременно используются суперпластификаторы, модификаторы вязкости, регуляторы структурообразования, наполнители и заполнители различного химико-минералогического состава и дисперсности. При проектировании составов смесей роли связующего, пластификаторов и модификаторов вязкости в регулировании технологических характеристик теоретически обоснованы и однозначно установлены экспериментально [6–8, 10–11]. При этом выбор наполнителей и регулирование их концентрации в составе смесей базируется на эмпирическом подходе [12–19]. При разработке составов производится подбор дозировок наполнителей какого-либо конкретного вида без определения общих требований к их характеристикам, необходимых для априорного (до опыта) определения применимости того или иного наполнителя в технологии 3D-печати, определения границ его рациональных дозировок.
Авторский подход к моделированию и управлению реологическим поведением вязко-пластичных смесей в процессах 3D-печати и оптимизации их составов основан на положениях структурной реологии дисперсных систем, приоритет теоретического обоснования которых принадлежит советской школе физико-химической механики [20–21]. Исходя из этого, нами в работе [22] обоснованы основные средства управления реологическим поведением вязкопластичных смесей, рассматриваемых как гетерогенные системы «дисперсная фаза + дисперсионная среда». В работе [23] теоретически обоснованы критериальные требования к характеристикам наполнителей, предложены численные критерии их оценки. К ним отнесены средний диаметр частиц dc , коэффициент формы частиц kф , гранулометрическая константа частиц Гкч , которые предложено применять для предварительной комплексной оценки наполнителей в задачах проектирования составов смесей.
Данная статья посвящена обсуждению результатов экспериментальной оценки эффективности влияния критериальных характеристик наполнителей на реологическое поведение и свойства смесей для 3D-печати.
МАТЕРИАЛЫ И МЕТОДЫ
Исследовались 5 типов смесей (табл. 1). В составах смесей соблюдалось постоянство массовых соотношений цемент : наполнитель (Ц : Н), концентрации добавок и вида добавок, фиброволокна, величины В/Ц, которые оптимизированы по результатам предыдущего этапа исследований [24–25].
Исследованы смеси на 4 видах наполнителей: алевропелите (Aл), золе уноса (ЗУ), молотом кварце (Кв), известняковой муке (ИМ). Варьируемым фактором являлись размерно-геометрические характеристики наполнителей. Характеристика исходных компонентов смесей представлена в табл. 2.
Методы оценки характеристик наполнителей. Для оценки формы частиц использовали метод сканирующей электронной микроскопии (СЭМ), съемка производилась на сканирующем электронном микроскопе марки Phenom XL ( vуск = 15 кВ, P = 0.10 Па). Обработка изображений для определения длины l и ширины b частиц производилась с помощью программного обеспечения «ParticleMetric». Дисперсность и гранулометрический состав наполнителей оценивали на лазерном анализаторе размера частиц «Анализетте 22» модели Nano Tec.
По полученным данным рассчитывались сле- дующие критериальные характеристики наполнителей:
-
1) средний диаметр частиц, dc
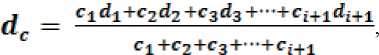
где ci – частные остатки на ситах, %; d 1 – диаметр, принимаемый за средний для данного интервала (фракции), мкм.
Таблица 1
Характеристика составов смесей
|
Система |
(ДМ), % от массы Ц |
СП, % от массы Ц |
Соотношение по массе Ц : Н |
Дозировка волокна (ВЛ), % от массы Ц |
|
|
КМ |
ЖС |
||||
|
Ц (эталон) |
0,2 |
0,2 |
0,2 |
1 : 1 |
0,3 |
|
Ц+Ал |
0,2 |
0,2 |
|||
|
Ц+ЗУ |
0,2 |
0,2 |
|||
|
Ц+Кв |
0,2 |
0,2 |
|||
|
Ц+ИМ |
0,2 |
0,2 |
|||
СТРОИТЕЛЬНОЕ МАТЕРИАЛОВЕДЕНИЕ
Таблица 2
Характеристика сырьевых компонентов
-
2) с постоянной скоростью действия нагрузки 5 Н/с, моделирующее поведение смеси в статических условиях послойной укладки (авторский метод [22]). В ходе проводимых сдавливающих тестов реологическое поведение смесей оценивалось по результатам анализа экспериментальных кривых:
– «нагрузка N – относительное изменение высоты образца hi/R» получаемых при испытаниях с постоянной скоростью деформирования;
– «нагрузка P – перемещение ∆» получаемых при испытаниях с постоянной скоростью нагружения образца.
Кривые « N – hi/R» интерпретировались в виде кривых «приведенная нагрузка F*– относительное изменение высоты образца hi/R» («F* – hi/R»). Приведенная нагрузка F* рассчитывалась по формуле:
Fi* = Nhi/πR2, (1)
где N – нагрузка, hi = (h0 –∆), h0 – начальная высота образца, ∆ – перемещение в i-тый момент времени, величина R принималась постоянной и равной радиусу образца в начале испытания.
По полученным экспериментальным кривым, «нагрузка σ – перемещение ∆» рассчитывались значения структурной (σ0) и пластической прочности (σpl) смесей в моменты, соответствующие началу
СТРОИТЕЛЬНОЕ МАТЕРИАЛОВЕДЕНИЕ деформирования (∆ = 0,1 мм) и началу трещиноо-бразования образцов по формуле:
σ = P/πR2.
По результатам испытаний определялись реотех-нологические свойства смесей, характеризующие их технологическую пригодность для 3D-печати строительных конструкций:
– предел пластичности Ki(I) , рассчитанный в первой точке перегиба (hi/R = 0,9) экспериментальных кривых «F* – hi/R»:
„(hl \ ^F'
K\/Rr~z ; (3)
– структурная прочность (σ0) – способность смеси воспринимать нагрузку без деформирования;
– пластическая прочность (σpl) и относительные пластические деформации (∆pl = ∆/h0), характеризующие способность смеси воспринимать нагрузку без трещинообразования.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ
Размерно-геометрические характеристики наполнителей. Все использованные виды наполнителей характеризуются полидисперсным составом (табл. 3, рис. 1), что, как ранее доказано [10,27], является необходимым условием обеспечения работоспособности смесей для 3D-печати по критериям пластичности и формоустойчивости. Гранулометрическая
Таблица 3
Гранулометрический состав материалов
|
Размер зерен, d, мкм |
ω частиц, % |
||||
|
Алевропелит |
Зола-уноса |
Кварц молотый |
Портландцемент |
Известняковая мука |
|
|
≤ 4 |
16,8 |
9,1 |
11,3 |
11,8 |
11,5 |
|
8 |
14,6 |
8,2 |
6,3 |
9,0 |
6,8 |
|
15 |
17,5 |
14,6 |
10,2 |
13,9 |
15,2 |
|
30 |
28,7 |
28,1 |
29,0 |
27,5 |
27,4 |
|
55 |
20,1 |
29,0 |
33,6 |
28,2 |
16,8 |
|
100 |
2,3 |
10,9 |
9,6 |
9,6 |
9,8 |
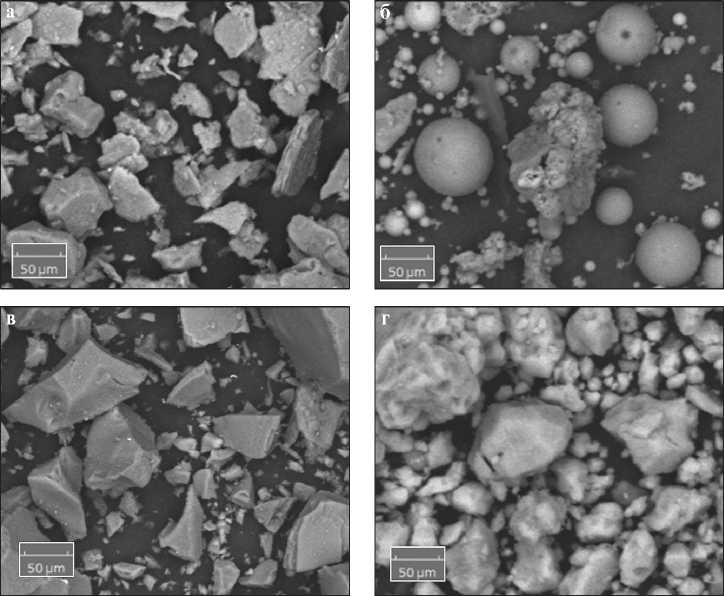
Рис. 1. Микрофотографии дисперсных материалов: а) алевропелит; б) зола-уноса; в) кварц молотый; г) известняковая мука
СТРОИТЕЛЬНОЕ МАТЕРИАЛОВЕДЕНИЕ
Таблица 4
Расчетные критериальные характеристики материалов
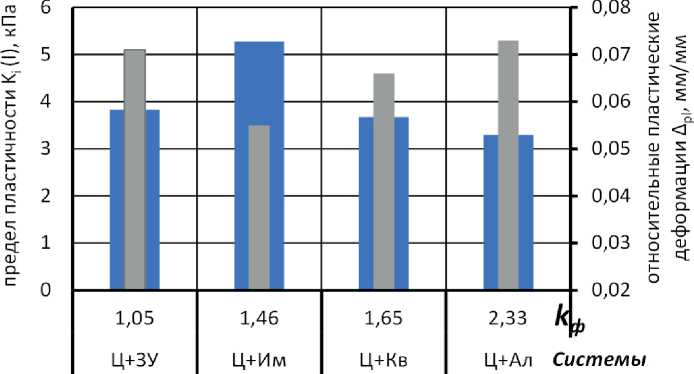
Наполнители существенно отличаются по форме и размеру. Плоские частицы алевропелита (рис. 1а) характеризуются коэффициентом формы kф = 2,33. Сферические частицы золы (рис. 1б) характеризуются коэффициентом формы kф = 1,05, близкие к кубическим частицы песка и известняковой муки (рис. 1в, г) – значением kф = 1,46 – 1,65, что близко к значению данного показателя для частиц портландцемента kф = 1,52.
Средний диаметр зерен песка и золы уноса соотносим с его значением для портландцемента ( dc = 22,6 мкм), для алевропелита средний размер зерен в 1,3 меньше, а для известняковой муки в 2 раза больше, чем для портландцемента.
Реологическое поведение смесей при сдавливании. Пластическое поведение смесей характеризуется экспериментальными кривыми «F* – hi/R» (рис. 2). Полученные экспериментальные кривые можно разделить на два типа. Первый тип имеет участок пластического деформирования между двумя точками перегиба в диапазоне относительных деформаций
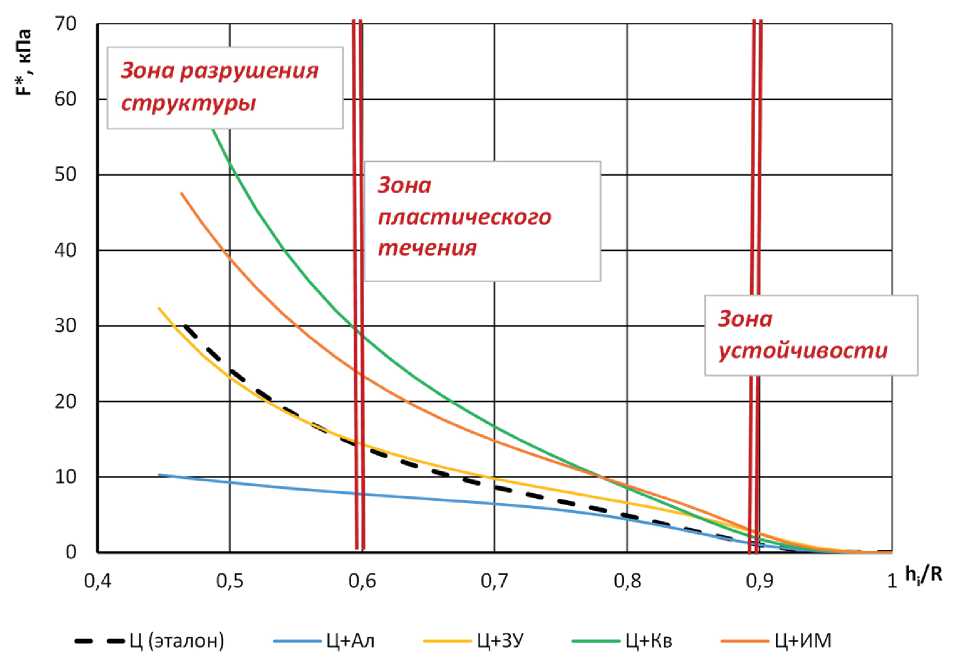
Рис. 2. Экспериментальные кривые «F* – hi/R» для цементных смесей
СТРОИТЕЛЬНОЕ МАТЕРИАЛОВЕДЕНИЕ образца 0.6 ≤ hi/R ≤ 0.9, но не фиксируются ярко выраженные переходы между участками кривой. При действии низких сжимающих напряжений структура вязкопластичных смесей сохраняет устойчивость («placing phase» [26]) – первый участок экспериментальных кривых «F* – hi/R» (0,9 ≤ hi/R ≤ 1,0). При возрастании напряжений на втором участке 0,6 ≤ hi/R ≤ 0.9 система пластически деформируется («per-fect plaste response phase» [26]). Резкое возрастание нагрузки и интенсификация течения на третьем участке связаны с полным разрушением структуры вязко-пластичной смеси (0.6 ≥ hi/R). Кривые «F* – hi/R» данного типа характерны для всех исследованных смесей, кроме смеси с алевропелитом. Наличие горизонтального участка на кривых свидетельствует о способности вязкопластичных систем к пластическому деформированию без разрушения структуры в широком диапазоне сдавливающих напряжений F* = 2,5 – 15 кПа. Значение оценки предела пластичности для данных систем составляет Ki(I) = 2,14–5,27 кПа (табл. 5).
При этом для эталонной системы без наполнителей характерно наиболее низкое значение предела пластичности Ki(I) = 2,14 кПа, при введении наполнителей значение данного показателя повышается, следовательно, пластичность смесей, напротив, снижается. Система на известняковой муке (Ц+ИМ) характеризуется значением Ki(I) = 5,27 кПа, то есть является наиболее жесткой.
Для системы с алевропелитовым наполнителем (Ц+Ал) второй перегиб на кривой «F* – hi/R» при hi/R ≈ 0,6 не фиксируется. Это значит, что структура вязко-пластичной смеси необратимо разрушается в начальный момент нагружения. В результате она теряет устойчивость, приобретает текучесть. Такие системы не обладают необходимыми упруго-вязкопластическими свойствами и устойчивостью для экструзии.
Показатели формоустойчивости смесей оценены по результатам анализа кривых «нагрузка σ – перемещение ∆» (рис. 3), который показывает, что все исследованные системы демонстрируют сходные значения структурной Σ0 = 0,32–0,45 кПа и пластической Σpl = 19,6–23,1 кПа прочности (см. табл. 5). Для всех систем характерны минимальные пластические деформации (∆пл < 0,07 мм/мм) при действии нагрузки.
Система (Ц+ИМ) проявляет наименьшие значения структурной и Σ0 и пластической Σpl прочности и наименьшие пластические деформации ∆pl (см. табл. 3, рис. 3). В результате сокращается промежуток между моментом появления первых трещин и разрушением, что говорит о снижении устойчивости системы к действию нагрузки.
ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Оценка эффективности влияния критериальных размерно-геометрических характеристик наполнителей на реологическое поведение и свойства смесей для 3D-печати позволила установить следующее.
В условиях эксперимента моделирующих вязкопластическое течение смесей при экструзии (в динамических условиях) основным фактором обеспечения их необходимой пластичности и агрегативной устойчивости является кинетический фактор, связанный со способностью дисперсной фазы находиться во взвешенном состоянии в дисперсионной среде и противодействовать кинетической энергии внешних сил и силам тяжести. Для этого необходимы сохранение определенного критического размера частиц дисперсной фазы, их высокая плотность упаковки.
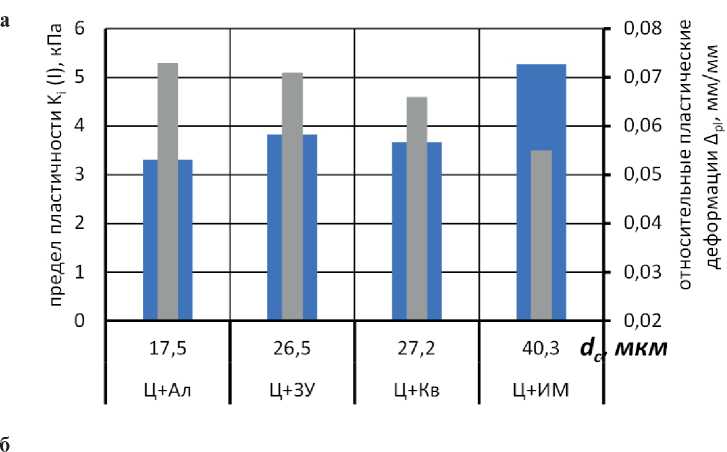
Данное теоретическое положение подтверждается результатами эксперимента. Установлено, что наиболее значимым фактором регулирования реологического поведения и показателей пластичности смесей является размер частиц наполнителя (рис. 4). Предел пластичности Ki(I) повышается в 1,7 раза, а пластические деформации снижаются в 1,4 раза при увеличении среднего размера зерен наполнителя в диапазоне dc = 17,5–40,3 мкм. Иными словами,
Таблица 5
Реологические характеристики смесей для 3D-печати
|
Система |
Предел пластичности Ki(I), кПа |
Прочность, кПа |
Относительные пластические деформации ∆pl, мм/мм |
|
|
структурная σ0 |
пластическая σ pl |
|||
|
Ц (эталон) |
2,14 |
0,45 |
21,1 |
0,07 |
|
Ц+Ал |
3,30 |
0,38 |
20,8 |
0,07 |
|
Ц+ЗУ |
3,83 |
0,44 |
23,1 |
0,07 |
|
Ц+Кв |
3,67 |
0,33 |
20,5 |
0,07 |
|
Ц+ИМ |
5,27 |
0,32 |
19,6 |
0,05 |
СТРОИТЕЛЬНОЕ МАТЕРИАЛОВЕДЕНИЕ
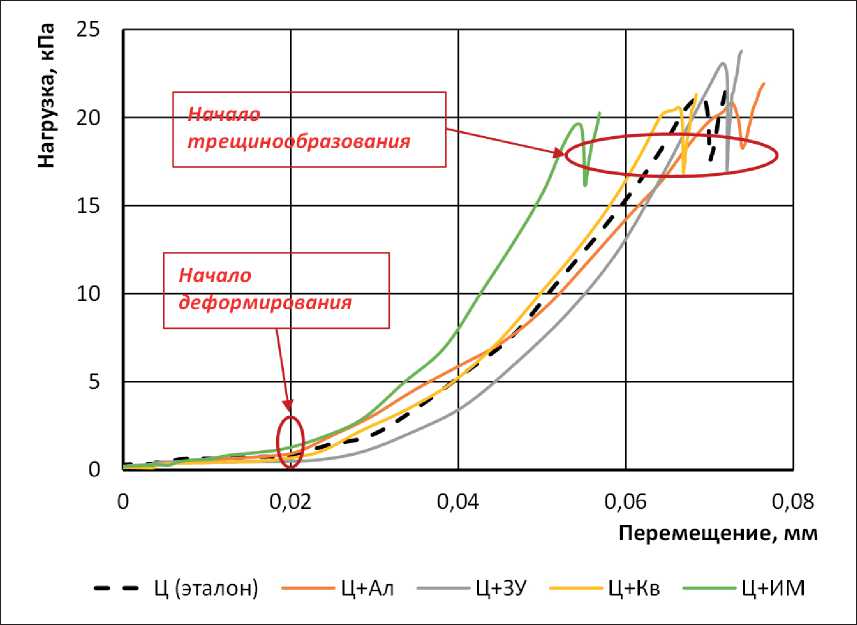
Рис. 3. Экспериментальные кривые «нагрузка σ – перемещение ∆» для цементных смесей
наблюдается прямо пропорциональная зависимость снижения пластичности системы при увеличении размера зерна наполнителя. Важно подчеркнуть, что определяющим является соотношение размера зерен вяжущего (цемента) и наполнителя. Для систем Ц+Ал, Ц+ЗУ, Ц+Кв, средний диаметр зерен наполнителей в которых меньше или примерно равен среднему диаметру зерен цемента ( dc = 22,6 мкм), повышение предела пластичности по отношению к эталонной системе без наполнителей составило 1,5–1,7 раза, а для системы Ц+ИМ ( dc = 40,3 мкм) – 2,6 раза.
Однозначных закономерностей влияния формы зерен наполнителя на реологическое поведение и пластичность смесей не выявлено (см. рис. 4а).
На основании этого можно заключить, что реологическое поведение смесей, их пластичность и устойчивость структуры в динамических условиях экструзии определяется главным образом размером и морфологией частиц дисперсной фазы. Необходимым условием обеспечения пластичности и агрегативной устойчивости смесей является создание плотной пространственной упаковки частиц дисперсной фазы. Это обеспечивается в том случае, если частицы наполнителя имеют сопоставимый с зернами цемента размер и полифракционную гранулометрию.
В условиях эксперимента, моделирующего поведение смеси в статических условиях послойной укладки, выявлено, что реологическое поведение и показатели формоустойчивости смесей практически не зависят от размера и формы частиц наполнителя. В статических условиях поведение гетерогенных микродисперсных систем (размер частиц d ~ 1 100 мкм [21]), к которым относятся исследованные смеси, определяется действием сил тяжести (фактор седиментации) и силами внутренних взаимодействий (поверхностных явлений, контактных взаимодействий). Частицы объединяются в пространственные структуры, если поле действия данных сил соизмеримо с силой тяжести. В этих условиях основным фактором устойчивости вязко-пластичной структуры к внешним воздействиям относится гидродинамический, определяющий ее зависимость от плотности и вязкости дисперсионной среды. При их увеличении снижается подвижность частиц дисперсной фазы в дисперсионной среде и возрастает устойчивость системы. Для исследованных систем данные показатели были оптимизированы на основании ранее проведенных исследований путем введения комплексного модификатора вязкости «камедь + жидкое стекло» в оптимальной дозировке. При этом жидкое стекло в силу своей химической природы способствует изменению ионного состава и вязкости дисперсионной
СТРОИТЕЛЬНОЕ МАТЕРИАЛОВЕДЕНИЕ
■ предел пластичности
-
■ относительные пластические деформации
Рис. 4. Влияние размера (а) и формы зерен наполнителя (б) на показатели пластичности цементных смесей среды, а частицы камеди – повышению ее вязкости и плотности. В результате, приоритетным фактором, определяющим реологическое поведение смесей и их формоустойчивость в статических условиях послойной укладки, являются свойства дисперсионной среды, регулируемые видом и концентрацией модификаторов вязкости.
Таким образом, при проектировании составов смесей для строительной 3D-печати приоритетными критериальными характеристиками наполнителей являются гранулометрическая константа Гкч, характеризующая характер распределения частиц по размерам, и средний диаметр частиц, dc .
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Работоспособность смесей в процессе 3D-печати при экструзии и послойной укладке определяется их пластичностью и агрегативной устойчивостью к внешним воздействиям.
Установлено, что в динамических условиях экструзии необходимым условием обеспечения пластичности и агрегативной устойчивости смесей является создание плотной пространственной упаковки частиц дисперсной фазы. При проектировании составов смесей приоритетными критериальными характеристиками наполнителей являются:
СТРОИТЕЛЬНОЕ МАТЕРИАЛОВЕДЕНИЕ средний диаметр частиц наполнителей dc не должен превышать средний диаметр зерен цемента; гранулометрическая константа, характеризующая характер распределения частиц по размерам. Рациональный диапазон ее значений Гкч = 7,5–10 соответствует полифракционному составу наполнителей.
В статических условиях послойной укладки характеристики наполнителей не являются определяющими для обеспечения формоустойчивости смесей. Приоритетным фактором ее обеспечения являются свойства жидкой фазы (дисперсионной среды), регулируемые видом и концентрацией модификаторов вязкости.
Список литературы Реологическое поведение смесей для строительной 3D-печати: экспериментальная оценка эффективности критериальных требований к наполнителям
- Perrot A. et al. From analytical methods to numerical simulations: A process engineering toolbox for 3D concrete printing. Cement and Concrete Composites. 2021; 122: 104164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2021.104164
- Rehman A.U., Kim J. H.3d concrete printing: A systematic review of rheology. mix designs. mechanical. microstructural. and durability characteristics. Materials. 2021; 14(14): 3800. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143800
- Lu B., Weng Y., Li M., Qian Y. Leong K.F., Tan M. J. Qian S. A systematical review of 3D printable cementitious materials. Construction and Building Materials. 2019; 207: 477–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.02.1441
- Ngo T.D., Kashani A., Imbalzano G., et al. Additive manufacturing (3D printing): A review of materials. methods. applications and challenges. Composites Part B: Engineering. 2018; 143:103 – 110.
- Park C., Noh M., Park T. Rheological properties of cementitious materials containing mineral admixtures. Cement and Concrete Research. 2005; 35: 842 – 849.
- S.C., Tay Y.W.D., Panda.B., Tan M.J. Fresh and hardened properties of 3D printable cementitious materials for building and construction. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering. 2018; 18(1): 311 – 319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acme.2017.02.008
- Varela H., Barluenga G., Palomar I. Rheology Evaluation of Cement Paste with Nanoclays. Nanosilica and Polymeric Admixtures for Digital Fabrication. RILEM Bookseries. 2020; 28: 144 – 152. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-49916-7_15
- Varela H., Barluenga G., Palomar I. Influence of nanoclays on flowability and rheology of SCC pastes. Construction and Building Materials. 2020; 243: 118285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118285
- Kawashima S., Chaouche M., Corr D.J., Shah S.P. Rate of thixotropic rebuilding of cement pastes modified with highly purified attapulgite clays. Cement and Concrete Research. 2013; 53: 112 – 118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2013.05.019
- Liu Z., Li M., Weng Y., Wong T.N., Tan M.J. Mixture Design Approach to optimize the rheological properties of the material used in 3D cementitious material printing. Construction and Building Materials. 2019; 198: 245 – 255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.11.252
- Jiao D., Shi C., Yuan Q., An X., Liu Y., Li H. Effect of constituents on rheological properties of fresh concrete-A review. Construction and Building Materials. 2017; 83: 146–159.
- Ma G., Li Z., Wang L. Printable properties of cementitious material containing copper tailings for extrusion based 3D printing. Construction and Building Materials. 2018. 16: 613 – 627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.12.051
- Kazemian A., Yuan X., Cochran E. et al. Cementitious materials for construction-scale 3D printing: Laboratory testing of fresh printing mixture. Construction and Building Materials. 2017;145: 639–647.
- Chen Y., Zhang Y., Pang B., Liu Z., Liu G. Extrusion-based 3D printing concrete with coarse aggregate: Printability and direction-dependent mechanical performance. Construction and Building Materials. 2021; 296: 123624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123624
- Bai G., Wang L., Ma G., Sanjayan J., Bai M. 3D printing eco-friendly concrete containing under-utilised and waste solids as aggregates. Cement and Concrete Composites. 2021; 120: 104037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2021.104037
- Álvarez-Fernández M.I., Prendes-Gero M.B., González-Nicieza C., Guerrero-Miguel D.J., Martínez-Martínez J.E. Optimum mix design for 3D concrete printing using mining tailings: A case study in Spain. Sustainability. 2021; 13(3): 1 – 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031568
- Ting G.H.A., Tay Y.W.D., Qian Y., Tan M.J. Utilization of recycled glass for 3D concrete printing: rheological and mechanical properties. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management. 2019; 29: 00857. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-019-00857-x
- Panda B., Ruan S., Unluer C., Tan M.J. Improving the 3D printability of high-volume fly ash mixtures via the use of nano attapulgite clay. Composites Part B Engineering. 2019; 165: 75 – 83.
- Kruglitsky N.N. Essays on physical and chemical mechanics. Naukova Dumka: Kyiv; 1988.
- Круглицкий Н.Н. Очерки по физико-химической механике. Киев: Изд. Наукова думка, 1988. 224 с.
- Урьев Н.Б. Физико-химическая динамика структурированных нанодисперсных систем и нанодисперсных композиционных материалов. Часть 1 // Физикохимия поверхности и защита материалов. 2010. Т. 46, № 1. С. 3 – 23.
- Slavcheva G.S., Razov I.O., Solonina V.A., Panchenko Y.F. Justification of the criteria requirements for fillers in mixtures for 3D construction printing. Nanotechnologies in construction. 2023; 15(4): 310–318. https://doi.org/10.15828/2075-8545-2023-15-4-310-318. – EDN: IFTQOV.
- Slavcheva G.S., Solonina V.A., Panchenko Yu.F., Orlov V.S., Filipenko P.V. Filler type influence on 3d-printable. mixtures fresh properties. Izvestiya vuzov. Stroitel’stvo [News of Higher Educational Institutions. Construction]. 2023; (12): 37–51. (In Russian).
- Slavcheva G.S., Solonina V.A., Panchenko Yu.F., Orlov V.S., Filipenko P.V. Effect of aleuropelite content on fresh and hardened properties of 3D-printable multi-binder composites. Construction of Unique Buildings and Structures. 2023; (109): 10909.
- Toutou Z., Roussel N., Lanos C. The squeezing test: A tool to identify firm cement-based material’s rheological behavior and evaluate their extrusion ability. Cement and Concrete Research. 2005: 35(10): 1891–1899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2004.09.007
- Slavcheva G., Artamonova O., Babenko D., Ibryaeva A. Effect of Limestone Filler Dosage and Granulometry on the 3D printable Mixture Rheology. IOP Conf. Series: Materials Science and Engineering. V International Conference Safety Problems of Civil Engineering Critical Infrastructures. 2020; 972: 012042. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/972/1/012042


