Research of consumer properties of non-woven materials from wastes of wool-processing industries
Автор: Bugybay Zh.T., Jurinskaya I.M., Assanova A.N.
Журнал: Вестник Алматинского технологического университета @vestnik-atu
Рубрика: Техника и технологии
Статья в выпуске: 1 (126), 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Disposal of continuously accumulated household and industrial wastes of production and consumption is an acute environmental and economic problem. In this regard, scientific research in the field of waste recycling and analysis of its reuse in production are becoming highly topical. The article examines the consumer properties of needle-punched non-woven materials from waste processing fibers of wool and cotton, as well as to establish the optimal fibrous composition were developed experimental samples of non-woven fabrics with different percentage ratio of fibers. The studied samples of non-woven fabrics were developed by the method of needling of canvases produced from waste of wool and cotton spinning and processing industries.
Wool, wool waste, needle-punched non-woven materials, physico-mechanical properties, consumer properties, fibrous composition
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140250846
IDR: 140250846 | УДК: 677.1/.3
Текст научной статьи Research of consumer properties of non-woven materials from wastes of wool-processing industries
In Kazakhstan, there is an acute problem of recycling agricultural products, in particular -wool. As of recent years, about 30 thousand tons of wool is produced and recycled in Kazakhstan. The remaining wool waste of large-scale production is exported uncontrollably, unused waste of small production is not recycled, it is lost and transported to landfills. By entering the environment and accumulating in significant volumes (hundreds of tons), such wastes are sources of pollution of the soil, water and air.
One of the ways of processing such wastes is their use in the production of non-woven materials, as currently the use of non-woven materials are marked by high demand and competitiveness in the market compared to other materials of the textile industry. This is due to the fact that the production cycle of non-woven materials from obtaining of fibrous raw materials to the production of completed products is several times shorter than the technology for producing classical types of textiles and does not require large-scale funds, and the widest range of unique properties allows them to be used in various spheres of human activity. A variety of, sometimes unique properties of nonwoven materials admitted to apply in various fields, from medicine to construction of buildings, structures, motorways [1].
Today non-woven materials are produced both disposable and reusable. They can combine elasticity, softness and strength; serve as drainage, membrane and filter materials. They can be given the properties of water resistance (or conversely, increased absorbency capacity), incombustibility, bacteriostatism, etc. [2].
Objects and methods of research
The objects of the study are: wool waste and non-woven material from waste fibers of wool and cotton.
Wool fibre has a unique place in the fibre market despite stiff competition from man-made fibres because of its specific properties, such as softness and high thermal insulation. Because of the lack of demand, global wool production decreased by 50% over the past decade. However, it will increase in developing countries such as China and India and is expected achieve to a total of 1500 million kg at the end of 2030. The focus of sheep development was essentially on the improvement of quality and quantity of wool by using different types of breeding and management practices. Improvement of sheep through breeding strategies should involve decisions regarding objectives and approaches to bringing genetic improvements for quality wool used for carpets and apparel. There is a steady market and supply exists in the fine wool market owing to quality processing facilities and its use in apparels [3].
Wool fibers contain much higher levels of impurities than cotton fibers. Waxes, suint (perspiration salts), vegetable matter, and dirt can account for as much as 50% by weight of the wool fiber [4,5].
In order to establish the optimal fiber composition, experimental samples of nonwoven fabrics with different percentages of wool and cotton fibers were developed.
As result of the study of samples for physico-mechanical and consumer properties 3 options were selected with optimal mixing:
-
- homogeneous material produced from 100% wool;
-
- two-component non-woven material produced from cotton and wool in the ratio of 50% to 50%;
-
- two-component non-woven material produced from cotton and wool in the ratio of 30% to 70%.
Samples of non-woven fabrics were dеveloped by the method of needling of canvases, produced from waste wool and cotton spinning and processing industries.
In order to analyze the physical-mechanical and consumer properties of the produced non-woven materials were conducted laboratory studies.
The values of significant indicators of the studied samples of non-woven materials are presented in table 1.
Table 1 - Physico-mechanical indexes of samples of non-woven materials produced by needle-punched method
|
Physical and mechanical properties |
Mix options |
||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
Surface density, g m2 |
131,6 |
316,0 |
245,2 |
|
Thickness, mm |
2,4 |
2,1 |
2,7 |
|
Breaking load, N - longitudinal direction - transverse direction |
198 110,2 |
179,5 91 |
210,1 143 |
|
Explosive elongation,% - longitudinal direction - transverse direction |
8 12 |
4 9 |
6 8 |
|
Electrostatic tension fields, sq/m |
0,42 |
0,36 |
0,35 |
|
Sorption properties: - hygroscopicity, % - capillarity, % |
7,47 11,3 |
6 7 |
8,5 9,5 |
|
Permeability: - air permeability, dm3/ m2s |
115 |
121 |
126,2 |
Results and their discussion
According to the results of determining the breaking load, it was shown that the most durable in both the longitudinal and transverse directions are samples of non-woven materials, which produced from the mixture No. 3 (70% wool and 30% cotton). The magnitude of the breaking load of non-woven materials is higher in the longitudinal direction, since in this direction non-woven materials have better strength properties. Also, the physical properties of this non-woven material (3-option) do not exceed the standard and have good performance. All experimentally produced non-woven materials meet the requirements of the technical regulations of the Customs Union TR TS 017/2011 "On the safety of light industry products" and comply with the significance of regulatory documentation, and can be used as nonwoven materials for the manufacture of quilted blankets.
A quilt was made from the obtained nonwoven material in the recommended ratio of the mixture (No. 3) of wool and cotton fiber waste.
■ Option 1 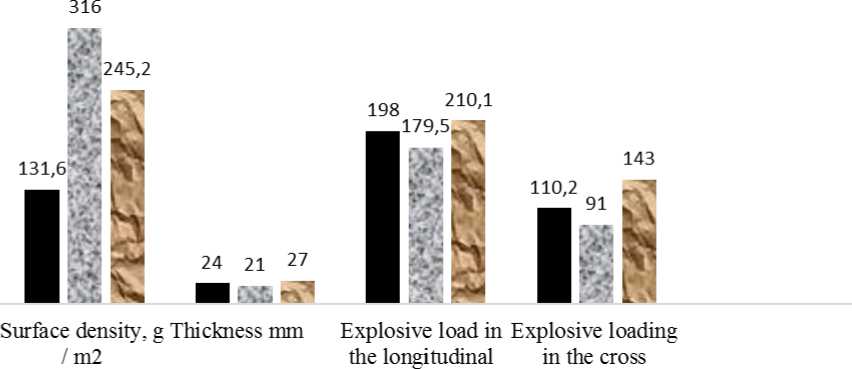
direction, N direction, N
Figure 1 - Physico-mechanical properties of the samples of non-woven materials
A quilt was made from the obtained nonwoven material in the recommended ratio of the mixture (No. 3) of wool and cotton fiber waste.

Figure 2 - nonwoven fabric

Figure 3 - quilt blanket
In order to analyze the physical and mechanical properties of the quilted blanket, were conducted laboratory studies. The values of significant indicators of the studied samples are presented in table 2.
Table 2 - Physical and mechanical properties of quilted blankets
|
№ |
Physical and mechanical properties |
Test methods |
Requirements |
Actual result |
|
1 |
Shrinkage after washing and drying |
ISO 6330-2011 |
+2/-4% |
-1,5% |
|
2 |
Thermal resistance level |
BS 5335 |
4.6 to 6.5 m2 • ° С / W |
5,06 m2 • ° С / W |
As a result of the research, it was established that the physico-mechanical properties of the received quilted blankets do not exceed the standard and have good indicators.
Conclusion
The study found that the production of two-component non-woven materials from waste wool and cotton in the recommended mix ratio (No. 3) is appropriate, since:
-
- they have sufficient strength, good physico-mechanical and consumer properties and can be used as non-wovens for household purposes;
-
- the production cycle is shortened with a decrease in the number of technological transitions, which allows to increase labor productivity and obtain a sufficiently low cost product due to a reduction in production space;
-
- increases economy of high-quality raw materials from natural and chemical fibers, due to wide use of industrial wastes and secondary raw materials;
-
- allows to expand the range of textiles due to the effective replacement of the range of wool blend and blended fabrics developed by non-woven fabrics.
Список литературы Research of consumer properties of non-woven materials from wastes of wool-processing industries
- Gorchakova V.M. Non-woven materials, development prospects and training // Non-woven materials, 2014.- №1. - P.16-17.
- Ajay Kumar Lesile, L.Prince Seiko Jose, Sustainable fibres and textile // The textile Institute book series. 2017. - №4. - P. 87-112.
- H.Kuffner, C.Popescu. Handbook of natural fibres // The textile institute book series. 2012. - №8. - P. 171-195.
- Baktybaeva G.K., Dzhurinskaya I.M., Kurochkin V.V. Giving flame retardant finishing to nonwoven materials from hemp fibers / Materials of the Int. Scientific practice. Conference. Innovative development of textile and light industry. Moscow, Inteks, 2018. - P.167.
- Stanton J., Improving comfort in clothing // The textile institute book series. 2011, - №3. - P. 79-96.


