Research work in training programs for future masters of pedagogical education
Автор: Vernidub R.M.
Журнал: Science, Education and Innovations in the Context of Modern Problems @imcra
Статья в выпуске: 7 vol.8, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Improvement of professional and pedagogical training of future masters of pedagogical education is considered in the context of inclusion of research work directly into the structure of the educational process. Development of integration processes on the European continent is accompanied by the formation of a single educational and scientific space within the framework of the implementation of the principles of the Bologna Declaration. Development of a multi-stage system of higher education in Ukraine has long been hampered by the slow improvement of the regulatory framework for higher education. After May 2005, when Ukraine officially joined the Bologna process, the issue of introducing a higher education system based on two key levels: bachelor - master, which assumes the orientation of the second level to promote further research, remains unresolved.
Education, research activities, master's degree training, research skills
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/16010877
IDR: 16010877 | DOI: 10.56334/sei/8.7.54
Текст научной статьи Research work in training programs for future masters of pedagogical education
ч RESEARCH ч ARTICLE Research work in training programs for future masters of pedagogical education / Vernidub Roman Prof. Dr. ч Mikhailovich \ \ / / / Dragomanov Ukrainian State University Ukraine, Kyiv Email: Doi Serial Keywords Education, research activities, master's degree training, research skills. Abstract
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by Science, Education and Innovations in the context of modern problems (SEI) by IMCRA - International Meetings and Journals Research Association (Azerbaijan). This is an open access article under the CC BY license .
A study of the development of modern foreign educational systems [1; 2] and scientific developments of domestic researchers [3; 4; 5] shows that the improvement of the system of higher professional education requires constant updating of it content, development of information technologies, transformation of science into the most priority sphere, which fills the content of modern education, creates new knowledge, transfers it to the student, each person and society as a whole.
The purpose of this article is to develop ways to improve pedagogical programs for master's degree training by strengthening the research component of the educational process.
The problem of improving master's training, despite its active development and discussion, remains acute due to the need to reform the activities of universities in new socio - economic conditions. "A modern university needs a teacher with a different typological personality structure. This should be a labile subject, capable of self-development and selfdetermination in a situation that is constantly changing, open to the social order of education (a subject who understands his professional purpose, who perceives pedagogical activity as an important priority, who is capable and ready for constant retraining and updating of knowledge, skills and abilities in organizing students' educational activities)" [ 2,168 ]. Many researchers note that the theoretical development of the problem of master's degree training is insufficient from the point of view of the needs of training a modern teacher [3; 6 ].
The state of organization of scientific research work in the training of specialists at the master's level in various universities of Ukraine and neighboring countries received a general analytical assessment in the work of G.M. Sombamania [ 7 ]. The author characterizes the uncertainty of the functioning of the master's program in the normative-legislative and organizational-pedagogical aspects, points out the need to specify issues that, first of all, concern the target tasks and the content of professional and scientific research training of future masters.
To achieve this goal, we will conduct a comparative review of master's degree programs. To do this, we will analyze several typical structures of master's programs at different universities.
Organization of research work of master's students of Luhansk National University named after T. Shevchenko is carried out on the basis of the Regulation on the Master's program of LNU named after T. Shevchenko [ 8 ]. During the year of study, students carry out research work during their internship and in the process of preparing their master's thesis on a topic that corresponds to the direction of the scientific work of the departments. The report on the results of the work done is provided in the following forms:
o modular works;
o reports at scientific and methodological seminars;
o preparation and defense of abstracts;
o preparation and publication of research materials;
o preparation and defense of a master's thesis.
Masters who have significant scientific achievements, after successful completion of training and state certification, are recommended by the Academic Council of the faculty (institute) for postgraduate studies.
A similar structure of master's programs is available at Donetsk National University [ 9 ]. Master's training in the vast majority of specialties lasts one year. Theoretical training is conducted during the first semester (30 credits). During the second semester, in addition to theoretical training (up to 12 weeks), a 4-6-week industrial practice is provided; the preparation of the master's thesis lasts the same amount of time ( 4-6 weeks) (6-9 credits).
More than half of the master's programs (in chemistry, political science, history, law, finance, accounting) do not provide theoretical training during the second semester, which begins with industrial practice (6-8 weeks) and ends with the completion of the master's thesis (10 weeks). Thus, the volume of research work provided for by the curriculum is 27 credits.
The structure of master's programs at the National Pedagogical University named after M.P. Dragomanov is typical for pedagogical universities and was developed in accordance with the requirements of the Ministry of Education for the preparation of educational and professional training programs.
For the annual period of training of full-time master's students, the basic structure of the programs is set as follows:
|
> Theoretical training - |
> 26 weeks (39 credits): - 1st semester – 14 weeks , > - 2nd semester - 12 weeks . |
|
> Practical training - > -industrial practice > -pre-graduate practice |
> 10 weeks (15 credits): > 6 weeks in the 1st semester , > 4 weeks in the second semester . |
|
> Preparation of a master's thesis |
> - 4 weeks (6 credits ) - 2nd semester. |
When preparing for correspondence courses form term training in such educational programs as master's degree level is 1.5 years . In this case theoretical education calculated for the first year training , and during the third semester students pass pre-graduation practice and complete preparation Master's works .
For the organization research works are used mainly forms extracurricular works :
S individual scientific research Job students - participation students in development specific problems under management scientific manager ;
S student scientific circles, problematic groups and others associations ;
S independent scientific research during the period production or pre-graduation practice;
S participation in scientific events various level : scientific seminars , conferences , symposiums , competitions , exhibitions scientific works , students Olympiads in areas and specialties , etc.
Within the framework of specialized educational courses included in the curriculum , such as " Methodology and Methods scientific research » studied theoretical Basics organization and implementation scientific research , planning and implementation scientific experiment , processing scientific data . However , not always teaching such courses is carried out taking into account relationships with research student work on the topic Master's works . Analysis graphics educational process ( see Table 1) shows that theoretical classes continue eight months , in time which students daily should attend 2-3 pairs of classroom classes. In addition, elective courses educational institutions for training in specialization or additional pedagogical specialties in the majority programs not related to the topic research works .
Table 1 . Graph ofthe scientific process
|
Period |
Content educational activities |
|
1st semester |
|
|
1-2 weeks September |
Theoretical classes . Introductory lectures on educational disciplines . Approval of topics and scientific managers , practice bases. Definition individual practice assignments . |
|
From 2-3 weeks September to October |
Industrial ( pedagogical ) practice. Start of preparation first section Master's works . Protection report on pedagogical practice . |
|
November - December |
Theoretical preparation for the first semester curriculum . Preparation of Section I Master's works . |
|
December 28 – January 10 |
Holidays . |
|
January 11-25 |
Winter examination session . |
|
January 26 – January 5 |
Holidays . |
|
2nd semester |
|
|
February – March |
Theoretical Curriculum II classes semesters . Independent Job students ( consultations with scientific (head ). Preparation of Section II Master's works . Pre-graduation practice. Preparation of Section III Master's works . Protection practice report . |
|
March - April |
|
|
April 18 – 30 |
Examination session . |
|
May – beginning of June |
Completions Master's works . Pre-defense at the meeting departments . Admission of work to defense . |
|
Reviewing Master's works . |
|
|
June |
State certification . |
|
Protection Master's works . |
The main disadvantage considered programs preparations Masters pedagogical education the term turned out to be short training that determines next problems :
o Overload students theoretical classes . In many programs the formation of the content of training is based on the list of theoretical courses of the training programs of the educational level "specialist" and does not provide sufficient time for conducting research. A large volume of classroom studies does not provide an opportunity to develop the abilities and scientific interests of students, reduces responsibility, independence and initiative in developing the topic of the master's thesis, and ultimately the quality of professional training suffers;
o Lack of sufficient time for practical training of master's students, for preparation and completion of writing of the master's thesis. Very often pre-graduation practice of master's students is conducted without interruption from theoretical training, sometimes formally linked with solving research problems and issues of preparation of the master's thesis;
o The absence in the training structure of organizational and educational elements that are directly aimed at the formation of scientific research competence, the preparation of master's students for independent scientific research work, as one of the basic components of the professional activity of a future scientific and pedagogical worker.
o To solve these problems, improve the quality of professional training of future masters, implement competitive training programs that can increase the volume and dynamics of scientific research at the university, there is an objective need to introduce a model of professional training of masters that ensures the implementation of the principle of "learning through research" by improving the organization of scientific research activities of students to form creative, professional and social-personal qualities that allow them to fully realize their intellectual potential, be competent in solving any problems of professional activity and everyday life.
In order to expand the scientific and research activities of higher education institutions and establish research-type universities, the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine adopted the State Targeted Scientific, Technical and Social Program "Science in Universities". The program envisaged the activation of student scientific and scientific and technical activities, ensuring the participation of students in scientific research at universities and their internships in leading scientific institutions of the National and industry academies of sciences, supporting the participation of students and young scientists in international conferences, seminars and symposia, deepening the relationship between scientific activity and the educational process by training masters on the basis of independent scientific research.
In pursuance of the State Program "Science in Universities", research universities have been created (Kyiv National University named after T.G. Shevchenko , National Technical University of Ukraine "Kyiv Polytechnic Institute", etc.). Innovative projects to expand scientific activity are being developed in such universities, including the introduction of master's programs with a two-year term of study, taking into account the requirements of the Bologna process for improving the scientific research work of students.
The main forms of educational work in the master's program of NTUU "KPI" [1 0 ], which are associated with the conduct of scientific research work are:
-
> scientific and educational seminars on individual topics, sections of academic disciplines and research conducted by master's students;
-
> Independent work, including conducting research on an approved topic and preparing a master's thesis.
-
> During their studies, master's students carry out the following types of research work: preparation and presentation of reports at scientific and educational seminars;
-
> preparation and defense of abstracts and reports on completed scientific research;
-
> preparation and presentation of articles in print, methodological developments, etc.;
-
> Preparation and defense of a master's thesis, which should include conducting scientific research on problems in the relevant field.
A typical example of the combination of scientific research and teaching is the American research universities, which make up about 7% of the total number of higher educational institutions in the country [1 1 ]. In research universities, the scientific work of the faculty is considered an obligatory component of the activity. Scientific research continuously feeds the educational process, maintaining its relevance with the latest developments and a high level of teaching by the professor - researcher. But the teaching process itself has another side - a deep and comprehensive understanding of scientific issues by the professor, which has a positive effect on the effectiveness of research.
At the university, "teacher and student must serve together in the common cause of acquiring knowledge. The maturity and competence of the one, the youth and inspiration of the other, are the most fruitful combination for the conduct of scientific research" [1 2,447 ].
The creation of a pan-European framework for higher education has led to the harmonization of degrees in all European universities. A three-level system of training was introduced in the French higher education system, which was called the "LMD reform" ( Licence - Master - Doctorate ). According to the LMD system (diagram 1), the second level corresponds to a master's degree (2 years of training - 120 credits). Educational programs have two levels of master's training - Master 1 and Master 2, with a total duration of 2 years [1 3 ].
In order to improve the quality and needs of training, the Grenoble Academy strengthens the role of scientific centres of excellence and innovation in teaching and research in the field of education, promotes the development of academic exchange programmes, the creation of transnational teaching modules and pedagogical approaches, as well as research partnership programmes.
According to the Department of Science and Education ( Le department Sciences de education de L'UPMF ) University Pierre - Mende s - France during the first year of preparation for the Master 1 program, students acquire knowledge and methods in the field of scientific research of education (educational processes), prepare a research project within the framework of official research programs. Graduates of Master 1 have the opportunity to continue their studies in the programs Master 2 in Education or Science, or pursue a professional career as a Senior Education Advisor [1 4 ].
To provide pedagogical training at Master 2 level at the Grenoble Academy (IUFM Academia de Grenoble ) a joint project of Joseph Fourier University ( Grenoble 1 ), Pierre - Mende s - France University ( Grenoble 2 ), Stendhal University ( Grenoble 3 ) and Savoie - Chambéry University was developed . Each of the project participants proposed 5-7 master's programs for training teachers - researchers of various specialties in the natural, humanities and social fields. Laboratory of pedagogical sciences for training under the program Master 2 offers three separate specialties.
the Master 2 specialties - "Teaching, training and personnel training" includes theoretical training in the 3rd semester in the form of lectures and classes in the amount of approximately 300 classroom hours (30 credits). During the 4th semester, a 4-month internship ( 360 hours - 10 credits) and writing of a dissertation (20 credits) are conducted.
Another Master 2 program - "Modeling the process of education and professional training" provides theoretical training only in the 3rd semester, when 5 disciplines are studied (6 ECTS credits each). The entire 4th semester ( 30 credits) is allocated for completing the master's thesis.
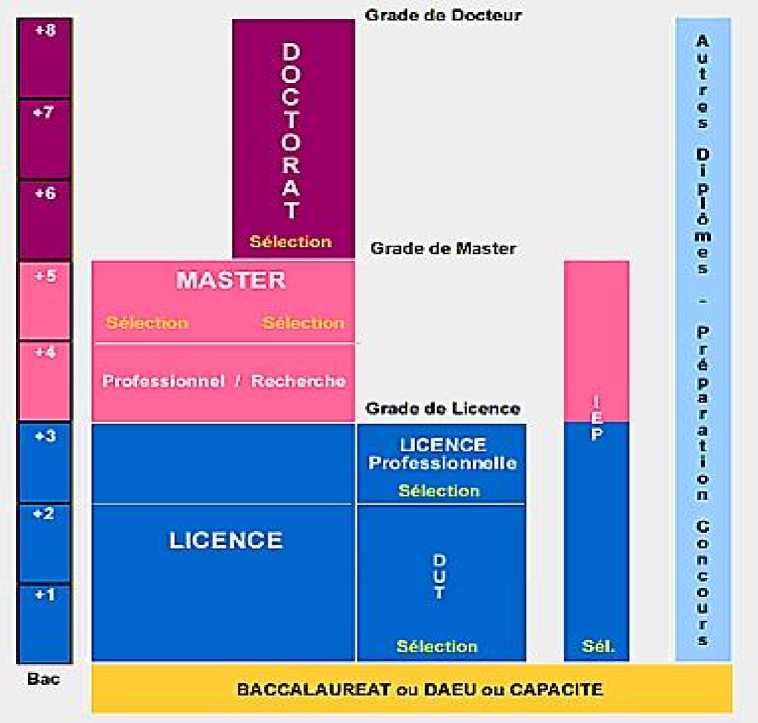
Diagram 1. The structure of the levels of higher education in France, introduced within the framework of the "LMD reform"[1 3 ].
The reform of higher professional education in the Russian Federation is associated with the introduction of the third-generation federal state educational standards ( FSES-3), which provide for the transition of master's programs to new curricula [1 5 ]. Master's educational programs are designed for a two-year training period and include two academic cycles: general scientific and professional, and a separate section for practice and research work. Each cycle includes a normative and an optional ( specialized, which is determined by the university) part. The curriculum for training a master of sociology at Lomonosov Moscow State University ( MSU) provides for three components of research work: work in a semester - 1200 hours, research and research and pedagogical practice - 400 hours (7 weeks) each. At the end of the preparation of the master's dissertation, 300 hours are allocated over 6 weeks. Other master's programs at MSU and other universities in Russia have a similar structure [1 6-18 ].
In the context of increasing competition for the distribution of resources, the importance of integrating science and the educational sector is growing due to the mutual reinforcement and complementarity of their competitive advantages. The high level of training of young specialists who are engaged in scientific research ensures the same high level of results in subsequent scientific research with high transfer potential. This, in turn, allows us to expand the list of educational and professional programs, update educational, laboratory and research equipment that meets the current state of science. Integration processes, along with the active research activities of university teachers, make it possible to involve students in the implementation of scientific projects and topics. In close cooperation, future scientists not only acquire solid knowledge in the process of conducting research, but also adopt the techniques and methods of scientific knowledge, ensuring the development and reproduction of scientific and pedagogical schools.
“It is extremely important for science to be in a good university, one where cutting-edge research is being conducted by the most renowned scientists in laboratories equipped with the latest technology... it is like a snowball process, when one outstanding scientist receives funding for his breakthrough research, attracts his colleagues to it, then his best students -until such a critical mass is formed, rapidly attracting to itself any young scientist who is just starting a scientific career” [ 19 , 20 ].
An analysis of master's degree programs in leading universities in different countries, as well as in domestic research universities, indicates the need to introduce various forms of organizing students' research activities into the structure of master's degree programs. To do this, it is necessary to change curricula and curricula in order to allocate academic hours for conducting research work , and to expand creative tasks of a research and project nature.
The scientific research work of students outside of class time has a certain systematic orderliness - it is carried out under the guidance of the councils of scientific research activity ( scientific and technical creativity) of students and scientific departments of universities and is organized in the following forms: joint work of students with leading scientists in scientific societies, schools and circles, scientific research work of students on state budget and business contract topics, involvement of students in the performance of work on international grants, participation of students in inventive activity; presentations of students at scientific conferences, seminars, symposia, the results of which are reflected in scientific publications, participation of students in exhibitions, competitions, olympiads.
In order to organize the research work of master's students, which is included in the structure of academic time, it is advisable to introduce scientific seminars as a form of systematic interaction between students and the supervisor, performing laboratory, practical and independent assignments on the topic of scientific research, writing and defending abstracts and term papers, performing collective and individual scientific projects, solving problematic, search and experimental tasks during industrial and pre-graduation practices . The introduction of diversified master's degree programs with a training period of 1.5-2 years in accordance with pan-European requirements allows us to foresee time for research work and to allocate in the master's program:
-
- Research programs that are focused on subsequent continuation of education and conducting in-depth research after entering graduate school;
-
- Professional programs, graduates of which enter the labor market - find employment in their specialty or specialization.
When creating such master's degree programs, it is important to ensure dynamic conditions their development , focusing on a significant share of variability their content , which is provided with the appropriate structure of the total preparation time (see Table 2).
Taking into account the proposed distribution of hours in the structure of educational programs for the preparation of a master's degree, in addition to theoretical training in general professional the disciplines of the first cycle (professionally oriented humanitarian and socio-economic training) and the special disciplines of the second cycle (natural science and professional training) can be separately divided into section III - scientific research work that , according to the forms of organization is divided on :
-
> scientific- research work throughout semesters ;
-
> scientific research practice ;
-
> scientific and pedagogical practice.
Table 2. Structure ofprograms training ofmasters
|
Standard volume of study / number of credits |
|||
|
professional programs |
research programs |
||
|
Duration of study |
1.5 years |
2 years |
2 years |
|
Program volume, total |
3240 h./ 90 cr. |
4320 h./ 120 cr . |
4320 h./ 120 cr . |
|
Theoretical training, |
2160 h. / 60 cr . |
2700 h./ 75 cr . |
3240 h./ 90 cr . |
|
including: |
|||
|
normative disciplines |
864 h./ 24 cr . |
1080 h./ 30 cr . |
1080 h./ 30 cr . |
|
elective courses |
1296 h./ 36 cr . |
1620 h./ 45 cr. |
2160 h./ 60 cr . |
|
Practical training |
14 weeks / 21 cr . |
20 weeks / 30 cr . |
20 weeks / 30 cr . |
|
Master's thesis |
6 weeks / 9 cr . |
10 weeks/ 15 cr . |
|
The students' research work during the semester requires organization and systematic control, maintaining a high level of motivation in order to achieve high efficiency and a certain quality of formation of research skills . For this purpose, a research seminar is organized .
At the seminars under scientific management manager Master's works is happening students discuss current research issues work : setting tasks , listening and discussion performance reports current tasks of the experimental works , presentation reports on the theoretical part of the research . Based on the results of participation students at work scientific seminar , successful execution plan research work in the semester scientific leader is exhibited credit to everyone to a master's student .
During the practice , the following issues are resolved: software tasks related to the topic Master's dissertations . Students in close collaboration with scientific leader are working off experimental and practical aspects scientific research , conduct approbation theoretical models and analysis results their implementation . Introduction to the structure of professional programs modules (block of disciplines ) by specialization gives opportunity deepening and individualization preparation taking into account needs students and the labor market .
Systematic implementation of research components work in the educational process increases interest students to deepen and systematize their knowledge, strengthens motivation for independent educational and cognitive activities that is reflected in the expansion their professional competencies , develops ability to professional mobility and growth. At the same time, results research contribute permanent update contents educational disciplines . As a result is being formed scientific and educational field of creation and dissemination new knowledge.
Thus, effective organization scientific research works Master's students , inclusion in the program structure preparations research activities students promotes improvement educational process and development university science through mechanisms implementations scientific research in progress professional preparation , creates united educational space that provides purposeful formation research and special skills graduate students to complete professional tasks of innovation character .