Review the Prospects and Obstacles of AI-Enhanced Learning Environments: The Role of ChatGPT in Education
Автор: Khalid Alshahrani, Rizwan Jameel Qureshi
Журнал: International Journal of Modern Education and Computer Science @ijmecs
Статья в выпуске: 4 vol.16, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
This paper delves into the transformative potential of artificial intelligence (AI), particularly focusing on ChatGPT, within educational realms. By conducting an exhaustive review across various scholarly publications and case studies, this research unveils ChatGPT’s multifaceted role in redefining educational landscapes–ranging from enhancing programming proficiency and fostering creativity in writing, to augmenting student engagement. Our findings illuminate the dual-edged influence of ChatGPT in education, showcasing not only its ability to tailor learning experiences and facilitate programming and creative writing but also its capacity to fortify student-teacher interactions. However, the study does not shy away from highlighting the intricate challenges that accompany the integration of AI in education, including concerns over academic integrity, ethical considerations, and the need for a balanced amalgamation with traditional pedagogical methods. Innovatively, this research proposes a forward-thinking, ethical framework for AI integration in educational settings, advocating for a harmonious blend of ChatGPT’s capabilities with human educators' insights to foster a more engaging, effective, and equitable learning environment. By introducing groundbreaking strategies for integrating interactive learning technologies with ChatGPT, and emphasizing the development of personalized educational trajectories, our study sets a new benchmark for future AI applications in education. The paper’s exploration into the innovative integration of ChatGPT with Virtual Reality (VR) offers a glimpse into the future of immersive learning experiences, opening new avenues for engaging and experiential learning. Through empirical validation and a nuanced discussion on the ethical deployment of AI tools in education, this study marks a significant contribution to the discourse on AI’s role in education, providing valuable insights for educators, policymakers, and technologists alike.
Artificial Intelligence (AI), ChatGPT, Education, Programming Instruction, AI Integration in Education, AI Impact on Education
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15019180
IDR: 15019180 | DOI: 10.5815/ijmecs.2024.04.06
Текст научной статьи Review the Prospects and Obstacles of AI-Enhanced Learning Environments: The Role of ChatGPT in Education
The introduction of artificial intelligence (AI) in the current education environment has brought about a new age of opportunities and difficulties. One of the most significant advancements in this domain is ChatGPT, an artificial intelligence system famous for its sophisticated skills in natural language processing and comprehension. This research review examines the diverse function of ChatGPT in educational environments, investigating its capacity to reinvent conventional teaching methods and improve the learning process. The review comprehensively analyzes a variety of research that specifically investigate the use of ChatGPT in different educational fields. These applications encompass programming education, where ChatGPT facilitates comprehension of intricate code and resolution of programming errors; creative writing, where it functions as a tool for generating ideas and developing narratives; and its wider influence on student learning achievements and teacher-student interactions. Every research offers valuable perspectives on the advantages, difficulties, and ethical implications of incorporating ChatGPT into educational systems. The evaluation seeks to provide a thorough comprehension of the abilities and constraints of ChatGPT as an educational tool by amalgamating these varied viewpoints. The system's capacity to customize learning experiences, simplify evaluation procedures, and cultivate creativity and innovation among students is emphasized. Simultaneously, it recognizes the ethical and practical obstacles associated with the incorporation of AI, including the need to uphold academic honesty, safeguard privacy, and regulate the dependability of AI-generated material.
The findings obtained from this research will play a crucial role in providing guidance to educators, policymakers, and technologists in using AI to enhance and revolutionize the learning process, as the field of education progresses in the digital era.
Further paper is arranged as: Section 2 focuses on the related work. Section 3 defines the problem in hand. Section 4 proposes the role of ChatGPT to enhance the quality of learning environment. Section 5 describes validation of the proposed research. Section 6 discusses the significant contributions of the proposed research regarding the integration of ChatGPT into educational systems . Implementation of ChatGPT for educators and policy makers are provided in section 7.
2. Literature Review
Yilmaz and Yilmaz[1] aim to examine student views on the use of ChatGPT for programming learning. The problem are covering is the use of generative artificial intelligence, specifically ChatGPT, in programming learning and its impact on student perspectives. They are proposing to conduct a case study to examine the opinions of students who use ChatGPT for programming learning purposes about the use of ChatGPT. One potential problem in the proposed research is the limited scope of the case study, which only examines the opinions of students in one specific programming course [1].
The paper [2] discusses Chat GPT's potential to fix code problems. The authors suggest using Chat GPT's natural language processing (NLP) to analyze code, as it can understand the purpose behind it and identify flaws based on language. However, they also discuss its limitations in identifying programming errors and the importance of using other debugging tools to verify its predictions and explanations. The research's challenge lies in its bug-fixing efficacy, which depends on the training data, system architecture, and programming flaws. The authors suggest that Chat GPT's effectiveness depends on these factors [2].
GPTutor is introduce a Tutoring System for Programming education that utilize ChatGPT technology, as a potential solution to mitigate the scarcity of programming education instructors [3]. The system utilizes ChatGPT to provide customized explanations for coding problems, facilitate learners' comprehension of sample code, and elucidate the underlying business justification behind each line of code. Nevertheless, the reliability and comprehensiveness of the study may be constrained, along with its capacity to grapple with intricate or domain-specific code. The system is an extension for Visual Studio Code that utilizes ChatGPT to provide explanations for source code [3].
Javaid et al. [4] In their study put forward the use of the ChatGPT Tool, an artificial intelligence (AI) powered technology, as a means to evaluate the writing competency of pupils. The tool exhibits the capability to generate replies that bear resemblance to those produced by humans, so showcasing its efficacy in accomplishing programming tasks and generating historical and philosophical papers of superior quality. Nevertheless, this research has several limitations that must be acknowledged. One such drawback is its inherent incapacity to comprehensively include the complexities inherent in human writing. Additionally, the evaluation of subjective elements such as creativity and originality may provide issues within the scope of this study. This research provides as a demonstration of the potential for future educational systems that include artificial intelligence [4].
Tian et al. [5] investigate the use of AI-driven software engineering and language models resembling ChatGPT as tools for programming assistance. The developers focus on various challenges such as program comprehension, code summary, and bug fixing by using the natural language processing capabilities of ChatGPT. This research presents an analysis of ChatGPT's proficiency in executing diverse programming tasks, including the generation of code of superior quality, elucidation of erroneous code, and identification of the intended objective behind defective code. Nonetheless, the investigation encounters some obstacles, including the limited attention span of ChatGPT, the quality and amount of the training data, and the intricacy of programming tasks [5].
The ethical, reference, reproducibility, and researcher issues of AI-supported scientific research systems are examined by Özcan et al. [6] They claim it is not enough to just use AI and submit results to a scientific journal in order to be recognized as the article's author. The authors claim that researchers who are up to the task should have skills that can be put to use in different phases of scientific inquiry. They claim that researchers are still necessary in the scientific investigation process and that AI is not enough. The article analyzes AI systems, including ChatGPT and Scite Assistant, evaluating their potential impact on scholarly work. Problems with recognizing AI-generated articles as distinct from human ones and with citing sources pose obstacles to scientific research that relies on AI [6].
In his scholarly article, Firat [7] delves into the examination of ChatGPT's capacity to bring about transformational changes in autodidactic experiences and open education. The author discusses the constraints inherent in conventional educational institutions and emphasizes the need for tailored learning encounters. The suggested method involves the use of powerful artificial intelligence models, such as GPT-4, to provide interactive and dynamic learning environments. The research also examines the effective deployment of ChatGPT in many educational contexts, including language acquisition, exam readiness, and individualized instruction. Nevertheless, Firat encounters apprehensions about possible prejudice and mistakes inherent in the language model. Additionally, ethical considerations arise, including problems related to privacy and security, employment displacement, and societal inequity [7].
Table 1. Summary of Related Work
|
Paper Title |
Limitation |
|
“Augmented intelligence in programming learning: Examining student views on the use of ChatGPT for programming learning” [1] |
Programming tools may cause occupational anxiety, lead to laziness, and require additional knowledge. They may weaken students' thinking skills, lack a genuine training environment, and provide unsatisfactory answers. Table 2 |
|
“Use Chat GPT to Solve Programming Bugs” [2] |
The efficacy of ChatGPT in bug resolution is contingent upon the caliber of the training data, the system's architecture, and the particular programming problems under consideration. The research does not emphasize this aspect. |
|
“GPTutor: a ChatGPT-powered programming tool for code explanation” [3] |
Current NLG code explainers may offer superficial insights, overlook domain logics, and be outdated, especially for object-oriented design, and may not be suitable for new or private libraries. Figure 3 |
|
“Unlocking the opportunities through ChatGPT Tool towards ameliorating the education system” [4] |
ChatGPT's use in education raises academic integrity, ethical concerns, content control, privacy, security risks, job displacement, inconsistent responses, and wordiness issues, necessitating clearer rules and procedures. |
|
“Is ChatGPT the Ultimate Programming Assistant - How far is it? ”[5] |
The research on ChatGPT's efficacy faces limitations due to the intrinsic stochasticity of expansive language models, its reliance on specific programming problems, and potential obsolescence of trained models, limiting applicability to other domains or applications. |
|
“Artificial Intelligence and Chat Bots in Academic Research” [6] |
AI-supported platforms in academic research may lead to overreliance, bias, and cultural nuances, affecting research outcomes and highlighting the need for continued researcher involvement. |
|
“How Chat GPT Can Transform Autodidactic Experiences and Open Education?” [7] |
This study explores ChatGPT's potential benefits in autodidactic experiences and open education, but may not provide a comprehensive analysis of its limitations or challenges. Additionally, the paper may be limited by the scope of its research and the availability of data and resources at the time of publication. |
|
“the use of artificial intelligence-based chatgpt and its challenges for the world of education; from the viewpoint of the development of creative writing skills” [8] |
ChatGPT's limitations include insufficient direct teacher-learner interaction, inability to innovate, accommodate diverse learning styles, and potential negative effects on critical thinking, necessitating further research. |
|
“Can Chat GPT Replace the Role of the Teacher in the Classroom: A Fundamental Analysis” [9] |
there are some limitations that need to be considered. Firstly, ChatGPT can only generate text and cannot provide live explanations or examples as teachers can. Secondly, ChatGPT can only work with existing data and cannot provide a more in-depth assessment of students' abilities. |
|
“Chatting and cheating: Ensuring academic integrity in the era of ChatGPT” [10] |
limitations include insufficient direct teacher-learner interaction, inability to innovate, accommodate diverse learning styles, and potential negative effects on critical thinking, necessitating further research. |
Shidiq [8] uses ChatGPT, an AI-based chatbot, to teach students creative writing. The writers examine the pros and cons of AI in creative writing instruction. Shidiq discusses the challenges students encounter in developing creative writing abilities and how AI might help. Suggests to using ChatGPT to help students brainstorm and write better. He also suggests using ChatGPT as a writing tool in the classroom. And provides a creative writing class case study using ChatGPT to prove their point. The key issue with the proposed study is ChatGPT's potential to reduce students' writing originality. Shidiq advises utilizing ChatGPT for ideation rather than writing to address this problem [8].
The study investigates by Ausat et al. [9] investigated the implications of ChatGPT in the field of education, with a specific emphasis on its capacity to supplant traditional teachers. The authors engage in a discourse on the need to accommodate emerging technology and its possible impact on conventional pedagogical approaches. This research uses a qualitative analytical approach to examine the data, referencing reputable sources such as Emerald Insight, ResearchGate, and Elsevier. The authors discuss concerns pertaining to the dependability and precision of qualitative analysis findings, emphasizing the need for more investigation into the possible impact of ChatGPT on conventional pedagogical approaches [9].
Cotton et al. [10] investigate the difficulties that colleges have in the era of AI-generated material, with a specific focus on the issues of academic integrity and plagiarism. It is recommended that institutions of higher education engage in meticulous assessment design and adopt measures to mitigate instances of academic dishonesty. The use of AI-generated material for evaluation purposes necessitates a paramount emphasis on safeguarding the integrity and genuineness of student submissions. They provide a proof of concept whereby ChatGPT is used to produce material, with the specific focus on replacing fake references with authentic ones. The primary concern is in the potential of AI-generated material to compromise the integrity of academic pursuits, prompting the suggestion that colleges should adopt proactive measures to tackle this matter [10].
A study by Batra and Verma [11] explored the use of ChatGPT by students and teachers in higher education, highlighting its extensive use for various purposes, including academic learning. While students largely use it for academic purposes, teachers utilize ChatGPT for different objectives. The study also discusses the advantages, disadvantages, and ethical concerns of ChatGPT's usage in academic learning [11]. Wardat et al. [12] examined stakeholders' perspectives on using AI, specifically ChatGPT, in teaching mathematics. While ChatGPT shows promise in enhancing educational success in mathematics, there are concerns about its understanding of complex topics and its ability to correct misconceptions. Sánchez-Ruiz et al. [13] explored ChatGPT's potential impact on blended learning methodologies in engineering education, particularly mathematics. The study found positive student adoption and usage of ChatGPT, but raised concerns about its impact on developing competencies essential for engineers [13]. Rahman and Watanobe [14] discussed the opportunities and threats presented by ChatGPT in education, including its use in programming learning. They conducted experiments with coding-related tasks and surveyed students and teachers to evaluate how ChatGPT supports programming education [14]. Lo [15] conducted a rapid review of the literature to assess ChatGPT's capabilities across subject domains and its use in education. The review highlights ChatGPT's potential as an assistant for instructors and a virtual tutor for students but notes challenges such as generating incorrect information and bypassing plagiarism detectors [15].
3. Problem Statement
ChatGPT, being an AI model that relies on text-based communication, is confined to generating textual responses, lacking the capability to offer real-time explanations or practical examples, both of which play a vital role in facilitating effective teaching and learning experiences. Consequently, this limitation impedes its ability to replicate the dynamic and interactive nature of a physical classroom setting, where educators can promptly adapt their instructional strategies and course materials based on immediate student feedback and interaction. Unlike human teachers who possess the capacity to assess students' learning progression and tailor their pedagogical approaches accordingly, ChatGPT's responses are constrained by the information it has been trained on. Consequently, this constraint restricts its capacity to provide a more comprehensive and individualized evaluation of students' abilities. Consequently, it might result in a less nuanced comprehension of the unique requirements of each student and a more generalized approach to education, potentially neglecting the distinctive challenges and strengths that each student possesses.
• How might we incorporate ChatGPT with interactive and adaptable educational technologies in order to augment its capacity for delivering dynamic, instantaneous feedback and illustrations within the context of a classroom environment?
• What methodologies can be utilized to integrate the capabilities of ChatGPT with the proficiency of human educators in order to establish a comprehensive and efficient educational encounter?
• How can we improve the algorithm of ChatGPT in order to enhance its comprehension and responsiveness towards the distinct learning difficulties and strengths of each student, particularly in terms of evaluating and tackling their specific individualized needs?
4. The Proposed Solution4.1 Goal 1:Intermingling with Interactive Learning Technologies
The objective of this research endeavor is to establish a seamless integration between ChatGPT, a state-of-the-art conversational AI model, and interactive educational platforms, thereby fostering a highly immersive and engaging learning environment. This integration will be facilitated through the utilization of advanced technological tools such as virtual classrooms and augmented reality (AR) environments, which are specifically designed to support live feedback, interactive examples, and real-time student-teacher interactions. By incorporating ChatGPT into these educational platforms, students will be able to benefit from its ability to provide contextual information and instant responses, thereby enhancing their overall learning experience. This groundbreaking integration holds immense potential in revolutionizing the field of education and redefining the way in which knowledge is disseminated and acquired.
By developing a system that seamlessly integrates ChatGPT with interactive educational platforms, we aim to bridge the gap between cutting-edge AI technology and the realm of education. This integration will enable students to engage in a dynamic and interactive learning process, where they can receive live feedback, explore interactive examples, and engage in real-time student-teacher interactions. Through the utilization of virtual classrooms, interactive simulations, and augmented reality (AR) environments, ChatGPT will serve as a valuable educational tool, assisting students by providing contextual information and delivering instant responses to their queries. This innovative integration has the potential to revolutionize traditional educational practices, as it opens up new avenues for knowledge acquisition and promotes a more personalized and immersive learning experience.
The successful integration of ChatGPT with interactive educational platforms represents a significant milestone in the field of education. By harnessing the power of advanced technological tools, such as virtual classrooms, interactive simulations, and augmented reality (AR) environments, this integration aims to provide students with a highly interactive learning experience. With ChatGPT's ability to offer contextual information and instant responses, students can access valuable resources and receive immediate feedback, thereby enhancing their understanding and retention of the subject matter. Moreover, the integration of ChatGPT promotes real-time student-teacher interactions, fostering a collaborative learning environment that encourages active participation and engagement. This groundbreaking integration has the potential to transform the landscape of education, empowering students with the necessary tools and resources to thrive in an increasingly digital world.
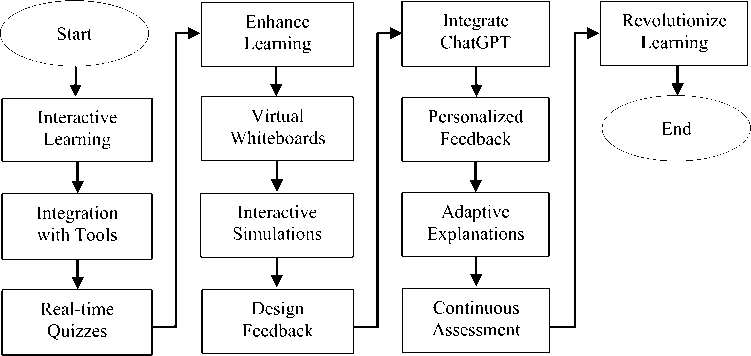
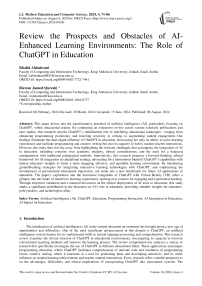
Fig. 1. Goal 1: Intermingling with Interactive Learning Technologies
To augment the capacity of ChatGPT in delivering dynamic and real-time feedback as well as providing illustrative instances, it is possible to integrate it with interactive learning technologies, thereby expanding its versatility as shown in figure 1. Such integration may encompass a range of interactive tools, including virtual whiteboards, realtime quizzes, and interactive simulations, all of which contribute to fostering a more captivating and interactive learning environment. Consequently, ChatGPT is empowered to furnish practical examples and offer live explanations, thereby greatly enhancing the overall learning experience for users. In order to achieve this goal, it is imperative to design and implement real-time feedback systems within the interactive platform. These systems should be meticulously developed to ensure their seamless integration with ChatGPT, enabling the platform to effectively analyze student responses and promptly provide personalized feedback. This dynamic feedback mechanism is vital in facilitating a tailored learning experience for each individual student, ensuring that their unique needs and understanding levels are adequately addressed.
-
4.2 Goal 2: Collaboration with Human Educators
-
4.3 Goal 3: Customized Educational Trajectories
Figure 2 depicts the formulated strategies to amalgamate the strengths of ChatGPT with the profound expertise possessed by human educators. A potential solution to this could be the adoption of a hybrid teaching model, wherein ChatGPT is utilized to provide preliminary responses and explanations, while human educators supplement these with further clarification, personal anecdotes, and real-world examples. By adopting such an approach, we are able to harness the inherent strengths of both AI and human educators, thereby culminating in a more comprehensive and efficacious educational experience. One potential avenue for exploration is the development of a content generation system that engenders collaboration between ChatGPT and educators, with the aim of creating dynamic and interactive lessons. This system would harness the capabilities of ChatGPT's linguistic prowess to generate a plethora of diverse examples and explanations, which can then be tailored to cater to the distinct learning styles and individual needs of students. Through this collaborative effort, a more personalized and engaging learning experience can be fostered, ensuring that educational content resonates with students on a deeper level.
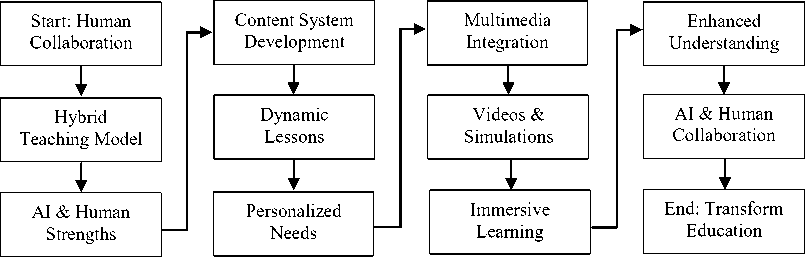
Fig. 2. Goal 2: Collaboration with Human Educators
To further augment the educational process, the integration of multimedia elements such as videos, simulations, and augmented reality (AR) experiences can prove to be immensely beneficial. By incorporating these elements, the learning process becomes more immersive and interactive, enabling students to grasp concepts and ideas in a more tangible and experiential manner. Visual aids can help to elucidate complex topics, while simulations and AR experiences can provide students with an opportunity to actively engage with the subject matter, thereby enhancing their understanding and retention. The collaboration between ChatGPT and human educators holds immense potential in revolutionizing the field of education. Through the development of a content generation system that fosters collaboration, and the integration of multimedia elements to enhance the learning process, we can create a more holistic and effective educational experience. By leveraging the strengths of both AI and human educators, we can pave the way for a future where education is tailored to individual needs, and students are empowered to reach their full educational experience. One potential avenue for exploration is the development of a content generation system that engenders collaboration between ChatGPT and educators, with the aim of creating dynamic and interactive lessons. This system would harness the capabilities of ChatGPT's linguistic prowess to generate a plethora of diverse examples and explanations, which can then be tailored to cater to the distinct learning styles and individual needs of students. Through this collaborative effort, a more personalized and engaging learning experience can be fostered, ensuring that educational content resonates with students on a deeper level.
Figure 3 explains goal 3 to enhance the efficacy of ChatGPT's algorithm in comprehending and catering to the specific requirements of individual students, there is a need to embark upon a journey of development and improvement. This journey entails the creation of personalized learning paths that are tailored to the progress, strengths, and weaknesses of every student. By meticulously scrutinizing the interactions and performance of students, ChatGPT can adapt its instructional techniques and educational content in a manner that aligns harmoniously with the distinctive learning style each student possesses. To achieve this ambitious goal, it is imperative to implement cutting-edge machine learning algorithms that possess the capability to comprehend and adapt to the diverse array of student profiles. These algorithms will serve as the bedrock upon which ChatGPT will be able to acquire knowledge and adjust its functionality accordingly, thereby catering to the idiosyncratic requirements of each student. Additionally, it is crucial to develop robust methodologies that enable ChatGPT to accurately assess and effectively address the unique learning challenges, strengths, and preferences of students. This will enable the system to provide tailored support, thereby maximizing the potential for academic growth and success.
Furthermore, the continuous enhancement of the model's performance is of paramount importance. This can be achieved through the establishment of feedback loops and meticulous data analysis. By scrutinizing the feedback provided by students and educators alike, and analyzing the data generated through their interactions with ChatGPT, it becomes possible to gain profound insights into the diverse educational needs that exist within the student population. This knowledge serves as the foundation upon which improvements can be made to the model, thereby ensuring that it consistently evolves and responds adeptly to the ever-changing educational landscape. The aspiration to develop personalized learning paths within ChatGPT represents a significant advancement in the field of education technology. The implementation of advanced machine learning algorithms, coupled with the development of methodologies for accurately assessing and addressing unique learning challenges, will pave the way for a more tailored and effective educational experience. Moreover, the commitment to continuous improvement through feedback loops and data analysis will enable ChatGPT to remain at the forefront of catering to the diverse educational needs of students, ultimately fostering a more inclusive and equitable learning environment.
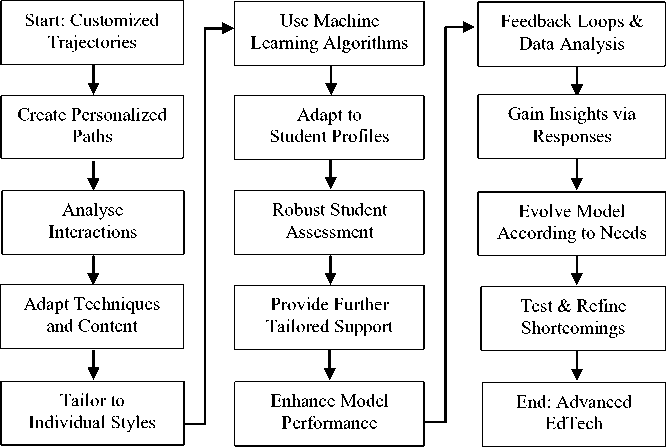
Fig. 3. Goal 3: Customized Educational Trajectories
-
4.4 Goal 4: Perpetual Acquisition and Enhancement
-
4.5 Goal 5: Innovative Integration of ChatGPT with Virtual Reality (VR) in Education
Figure 4 reveals continuous learning and improvement that is centered around the idea of designing ChatGPT. It allows for a perpetual process of acquiring knowledge and enhancing its performance based on the feedback and interactions it receives. This can be achieved by incorporating advanced machine learning techniques that enable the analysis of student feedback and performance, subsequently leading to adjustments in ChatGPT's responses. Through this continuous learning process, ChatGPT can develop a profound understanding of the individualized challenges and strengths encountered by each student, thereby facilitating a more personalized and efficacious learning experience. To achieve this goal, it is crucial to establish a collaborative framework wherein human educators and ChatGPT can work harmoniously together. This framework would entail a seamless integration of the expertise and guidance provided by human educators with the capabilities and insights offered by ChatGPT. By fostering such collaboration, educators can be trained to leverage the unique strengths of ChatGPT to augment their teaching methods, thereby enhancing the overall educational experience.
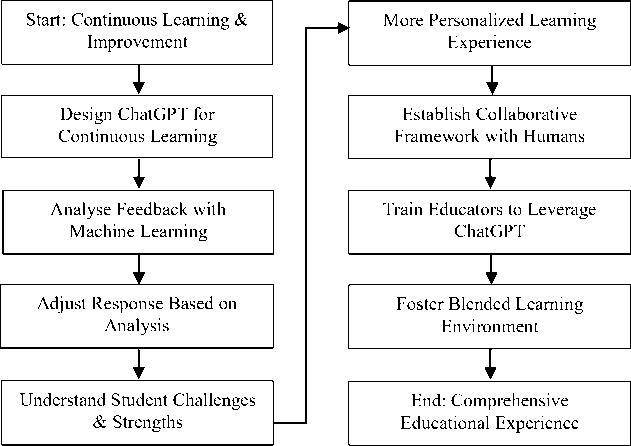
Fig. 4. Goal 4: Perpetual Acquisition and Enhancement
To cultivate an environment conducive to continuous learning and improvement, it is imperative to create a blended learning environment wherein the intuitive skills possessed by human educators seamlessly coalesce with the AI-powered insights of ChatGPT. This amalgamation of human intuition and artificial intelligence can yield a comprehensive educational experience that encompasses the best of both worlds. By harnessing the power of both human expertise and AI capabilities, students can benefit from a holistic approach to learning that effectively addresses their individual needs and optimizes their educational journey. Goal 4 emphasizes the importance of continuous learning and improvement for ChatGPT. By utilizing machine learning techniques, analyzing student feedback and performance, and adapting responses accordingly, ChatGPT can gain a profound understanding of each student's unique challenges and strengths. Additionally, by establishing a collaborative framework between human educators and ChatGPT, educators can leverage the capabilities of ChatGPT to enhance their teaching methods. Furthermore, by fostering a blended learning environment that combines human intuition with AI-powered insights, a comprehensive educational experience can be provided to students. augment the capacity of ChatGPT in delivering dynamic and realtime feedback as well as providing illustrative instances, it is possible to integrate it with interactive learning technologies, thereby expanding its versatility. Such integration may encompass a range of interactive tools, including virtual whiteboards, real-time quizzes, and interactive simulations, all of which contribute to fostering a more captivating and interactive learning environment. Consequently, ChatGPT is empowered to furnish practical examples and offer live explanations, thereby greatly enhancing the overall learning experience for users. In order to achieve this goal, it is imperative to design and implement real-time feedback systems within the interactive platform. These systems should be meticulously developed to ensure their seamless integration with ChatGPT, enabling the platform to effectively analyze student responses and promptly provide personalized feedback. This dynamic feedback mechanism is vital in facilitating a tailored learning experience for each individual student, ensuring that their unique needs and understanding levels are adequately addressed.
Goal 5 is narrated to integrate ChatGPT with VR to grasp the benefits of both technologies to enrich the quality of education as shown in figure 5. The intersection of artificial intelligence (AI) and educational technologies is rapidly evolving, offering new avenues to enrich learning environments. Among these advancements, ChatGPT stands out as a pivotal tool capable of revolutionizing educational methodologies through personalized learning experiences. However, to fully unlock the potential of AI in education, there's a compelling need to explore beyond conventional boundaries. This leads us to the innovative integration of ChatGPT with Virtual Reality (VR), a frontier that promises to redefine immersive learning experiences. Integrating ChatGPT with VR presents a groundbreaking approach to education, merging the interactive and personalized capabilities of ChatGPT with the immersive and experiential nature of VR. This combination creates a symbiotic relationship where ChatGPT's adaptive learning paths and instant feedback mechanisms are enhanced by VR's ability to simulate real-world scenarios, providing a rich, multi-sensory learning environment.
By situating learners in virtually simulated environments, this integration facilitates a contextual learning experience where theoretical knowledge is applied in practical, real-world scenarios. ChatGPT can guide, instruct, and provide feedback in real-time within the VR environment, making learning more relevant and impactful. The immersive nature of VR, combined with the conversational interface of ChatGPT, significantly enhances student engagement. This interaction not only makes learning more enjoyable but also improves retention rates by providing experiences that are closer to real-life than traditional classroom settings or e-learning modules. While VR offers immersive experiences, integrating ChatGPT allows for these experiences to be tailored to the individual learner’s needs, interests, and learning pace. This personalization at scale ensures that each learner receives the most relevant and effective instruction, optimizing their learning outcomes. Implementing this innovative integration requires careful consideration of both technological infrastructure and pedagogical methodologies:
• Curriculum Design: Curriculum developers must envision lessons that leverage the strengths of both VR and ChatGPT, ensuring that learning objectives are aligned with the capabilities of these technologies.
• Technology Infrastructure: Institutions must invest in the necessary VR hardware and software, ensuring compatibility with ChatGPT and other AI tools. This also includes training for educators to effectively utilize these technologies in their teaching practices.
• Assessment and Feedback: Leveraging ChatGPT within the VR environment for continuous assessment and personalized feedback can significantly enhance learning outcomes. Designing these assessments to match the immersive experiences will be key to their effectiveness.
 5. Validation of the Proposed Solution
5. Validation of the Proposed Solution
|
Innovative Integration Approach |
Personalized Learning Experiences |
Enhanced Student Engagement & Retention |
Contextual Learning Experiences |
Curriculum Design & Lesson Development |
Technology Infrastructure & Implementati on |
Continuous Assessment & Personalized Feedback Design |
Fig. 5. Goal 5: Integration of ChatGPT with VR in Education
In the realm of Literature research, the process of validation emerges as an eminent and crucial approach to gauge the efficacy of proposed methodologies, models, or approaches, and further assess the very essence of the concepts expounded within research papers. Within the confines of this particular paper, the proposed method has been subjected to the rigorous process of validation through the utilization of a survey approach. The underlying objective behind the employment of this particular approach lies in its ability to attain the required sample size, whilst simultaneously collecting data from a multitude of geographic areas, all without the encumbrance of time and cost constraints. The survey, in this specific context, assumes the role of a potent research tool employed to diligently test the efficacy and viability of the proposed method. However, it is important to acknowledge that the utilization of a survey technique does present certain challenges and issues. One such challenge entails the observation that a substantial number of participants failed to accurately and comprehensively complete the provided form, thereby compromising the integrity and veracity of the information they submitted. Furthermore, it is worth noting that a significant proportion of the information furnished by the participants is riddled with ambiguity, thereby necessitating a more nuanced approach to data analysis. It is essential to underscore that the aforementioned survey was administered to a sample size of thirty participants in order to arrive at conclusive results that can be deemed reliable and representative of the broader population.
The results of the survey that was conducted are visually represented using a bar chart, which provides a graphical depiction of the findings. The survey was administered to a total of 30 individuals who possess expertise in the relevant field, thus ensuring a diverse and knowledgeable sample size. In order to gather the necessary data, an electronic form was utilized as a means of distributing the questionnaires to the participants. This method allowed for a convenient and efficient dissemination of the survey, as it was shared across a variety of social media platforms, including popular applications such as WhatsApp, Telegram, and Twitter. The use of these platforms facilitated a broad reach and ensured that a wide range of individuals had the opportunity to participate in the survey. To ensure consistency and ease of analysis, the participants were instructed to utilize a likert scale when responding to the survey questions. This scale, which is comprised of five distinct numbers, enables the participants to express their opinions and attitudes towards the survey statements. Specifically, number 1 signifies a response indicating very low agreement or satisfaction, while number 2 denotes a low level of agreement or satisfaction. Number 3 corresponds to an average level of agreement or satisfaction, number 4 signifies a high level of agreement or satisfaction, and finally, number 5 indicates a very high level of agreement or satisfaction. The survey itself consists of a total of 20 questions, which have been thoughtfully divided into four distinct categories or goals. This categorization allows for a comprehensive exploration of the research objectives and ensures that each aspect is adequately addressed and analyzed. Overall, the utilization of a bar chart, the inclusion of expertise participants, and the use of an electronic form and likert scale contribute to the robustness and validity of the survey results.
-
• Goal 1 aims to enhance the interactivity and responsiveness of ChatGPT by integrating it with educational tools like virtual whiteboards, quizzes, and simulations, thereby enriching the learning environment.
-
• Goal 2 aims to leverage the synergy between ChatGPT's AI capabilities and the expertise of human educators to create dynamic, personalized, and more effective learning experiences.
-
• Goal 3 aims to refine ChatGPT's algorithms to provide tailored educational paths that adapt to the individual learning styles, strengths, and challenges of each student.
-
• Goal 4 aims to establish a continuous cycle of learning and improvement for ChatGPT, utilizing feedback and interaction data to perpetually enhance its educational performance and relevance.
-
• Goal 5 aims to find the relationship between innovative integration of ChatGPT with virtual reality (VR) in education. The integration of Goal 5 represents a significant advancement in leveraging cutting-edge technology to enhance educational experiences, allowing for the occurrence of Goals 1-4.
The relationship of Goal 5 with Goals 1 to 4 is explained as follows.
-
• Goal 1 - Intermingling with Interactive Learning Technologies: Goal 1 focuses on enhancing interactivity and engagement in learning. The integration of ChatGPT with VR (Goal 5) complements this by adding a new layer of immersion, making learning experiences more dynamic and real-time. VR technology supports interactive tools like virtual whiteboards and simulations, enhancing the interactive capabilities outlined in Goal 1.
-
• Goal 2 - Combining AI Capabilities with Human Educators: Goal 2 aims at leveraging AI and human expertise together. In Goal 5, ChatGPT within VR environments can provide AI-driven assistance while allowing educators to offer real-time feedback and context, thus enhancing collaborative teaching models. This combination creates a rich educational experience that benefits from both AI and human input.
-
• Goal 3 - Customized Educational Trajectories: Goal 3 is about personalizing learning paths. With VR, ChatGPT can create highly personalized and adaptive learning environments that respond to the individual needs of students, offering tailored educational experiences. The immersive nature of VR helps in delivering content that matches the learning pace and style of each student, aligning with the customization goals.
-
• Goal 4 - Perpetual Acquisition and Enhancement: Goal 4 involves continuous learning and improvement of ChatGPT. Integrating it with VR environments allows for constant updates and feedback loops, refining both the AI and the immersive educational content continuously. VR can provide rich data on student interactions, aiding in the perpetual enhancement of educational tools and methods.
-
5.1 Cumulative Analysis of Goal 1
-
5.2 Cumulative Analysis of Goal 2
The findings of the comprehensive examination of goal 1 are illustrated in figure 6. It is evident from figure 6 that a significant portion of the participants, namely 22%, hold a strong consensus regarding the applicability and efficiency of the suggested approach. In addition, 18% express agreement, 16% remain neutral, 15% voice disagreement, and a substantial 28% strongly oppose the proposed methodology as shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Cumulative Analysis of Goal 1
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
|
Q1 |
36.67 |
10.00 |
16.67 |
10.00 |
26.67 |
|
Q2 |
40.00 |
16.67 |
3.33 |
20.00 |
20.00 |
|
Q3 |
33.33 |
10.00 |
20.00 |
20.00 |
16.67 |
|
Q4 |
20.00 |
23.33 |
6.67 |
26.67 |
23.33 |
|
Q5 |
10.00 |
16.67 |
36.67 |
13.33 |
23.33 |
|
Total |
140.00 |
76.67 |
83.34 |
90.00 |
110.00 |
|
Avg. |
28.00% |
15.33% |
16.67% |
18.00% |
22.00% |
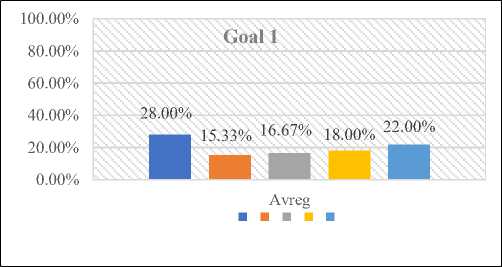
Fig. 6. Graphical Representation of Goal 1
The results of the comprehensive examination of goal 2 can be observed in figure 7 illustrates that a significant proportion, specifically 23%, of the individuals who took part in the study expressed a strong level of agreement regarding the benefits associated with the implementation of the proposed approach during the planning stage. In contrast, 24% of participants indicated agreement, while 10% neither agreed nor disagreed, 19% disagreed, and 22% strongly disagreed as shown in Table 3.
Table 3. Cumulative Analysis of Goal 2
|
Very Low |
Low |
Nominal |
High |
Very High |
|
|
Q6 |
20.00 |
23.33 |
3.33 |
30.00 |
23.33 |
|
Q7 |
23.33 |
20.00 |
13.33 |
16.67 |
26.67 |
|
Q8 |
20.00 |
26.67 |
6.67 |
23.33 |
23.33 |
|
Q9 |
16.67 |
23.33 |
13.33 |
23.33 |
23.33 |
|
Q10 |
33.33 |
3.33 |
13.33 |
30.00 |
20.00 |
|
Total |
113.33 |
96.66 |
49.99 |
123.33 |
116.66 |
|
Avg. |
22.67% |
19.33% |
10.00% |
24.67% |
23.33% |
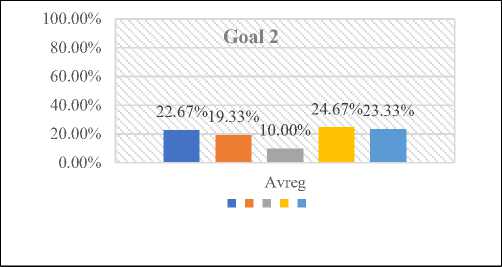
Fig. 7. Graphical Representation of Goal 2
-
5.3 Cumulative Analysis of Goal 3
-
5.4 Cumulative Analysis of Goal 4
The findings of the comprehensive examination of objective 3 are depicted in figure 8. It can be deduced from figure 7 that a significant proportion of respondents, specifically 24%, expressed a strong inclination towards the benefits associated with the utilization of the suggested approach during the implementation stage. Furthermore, 20% of participants indicated their agreement, while 11% remained neutral in their stance. Conversely, 16% voiced their disagreement, and 21% strongly opposed the proposed method as shown in Table 4.
Table 4. Cumulative Analysis of Goal 3
|
Very Low |
Low |
Nominal |
High |
Very High |
|
|
Q11 |
40.00 |
10.00 |
10.00 |
13.33 |
26.67 |
|
Q12 |
16.67 |
16.67 |
10.00 |
26.67 |
30.00 |
|
Q13 |
26.67 |
23.33 |
3.33 |
20.00 |
26.67 |
|
Q14 |
9.52 |
14.29 |
14.29 |
16.67 |
16.67 |
|
Q15 |
13.33 |
20.00 |
20.00 |
23.33 |
23.33 |
|
Total |
106.19 |
84.29 |
57.62 |
100.00 |
123.34 |
|
Avg. |
21.24% |
16.86% |
11.52% |
20.00% |
24.67% |
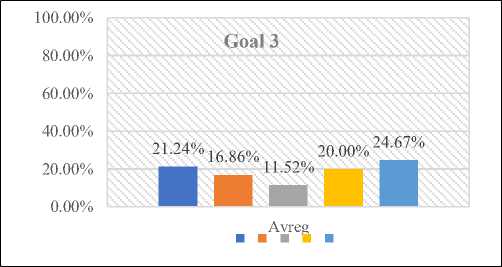
Fig. 8. Cumulative Analysis of Goal 3
The findings of the comprehensive examination of objective 4 can be observed in figure 9. Figure 9 illustrates that a significant portion, namely 24%, of the respondents strongly agreed with the benefits associated with incorporating the suggested approach into the system of change management. Conversely, Table 5 shows that 20% of the participants are agreed, whilst 11% neither agreed nor disagreed, 16% disagreed, and 21% strongly disagreed.
Table 5. Cumulative Analysis of Goal 4
|
Very Low |
Low |
Nominal |
High |
Very High |
|
|
Q16 |
26.67 |
10.00 |
16.67 |
16.67 |
30.00 |
|
Q17 |
23.33 |
6.67 |
30.00 |
16.67 |
23.33 |
|
Q18 |
16.67 |
13.33 |
23.33 |
30.00 |
16.67 |
|
Q19 |
16.67 |
16.67 |
20.00 |
26.67 |
20.00 |
|
Q20 |
23.33 |
16.67 |
23.33 |
20.00 |
16.67 |
|
Total |
106.67 |
63.34 |
113.33 |
110.01 |
106.67 |
|
Avg. |
21.33% |
12.67% |
22.67% |
22.00% |
21.33% |
|
100.00% |
Goal 4 |
80.00%
60.00%
|
40.00% |
21.33% 22.67% 22.00% 21.33% |
|
20.00% 0.00% |
12.67% Avreg |
Fig. 9. Cumulative Analysis of Goal 4
-
5.5 Cumulative Analysis of Goal 5
-
5.6 Final Cumulative Analysis of Five Goals
47.65%
40.00%
30.00%
19.41%22.35%
90 00%
8.23%
10.00% 2.35%
0.00%
The findings of the comprehensive examination of goal 5 can be observed in figure 10. Figure 10 illustrates that a significant portion, namely 22%, of the respondents strongly agreed with the benefits associated with incorporating the suggested approach into the system of change management. Conversely, Table 6 shows that 22% of the participants are agreed, whilst 23% neither agreed nor disagreed, 13% disagreed, and 22% strongly disagreed.
Table 6. Cumulative Analysis of Goal 5
|
Very Low |
Low |
Nominal |
High |
Very High |
|
|
Q21 |
2.94 |
11.76 |
11.76 |
20.59 |
52.94 |
|
Q22 |
0.00 |
2.94 |
14.71 |
20.59 |
61.76 |
|
Q23 |
2.94 |
17.65 |
50.00 |
20.59 |
8.82 |
|
Q24 |
2.94 |
0.00 |
14.71 |
23.53 |
58.82 |
|
Q25 |
2.94 |
8.82 |
5.88 |
26.47 |
55.88 |
|
Total |
11.76 |
41.17 |
97.06 |
111.77 |
238.22 |
|
Avg. |
2.35% |
8.23% |
19.41% |
22.35% |
47.65% |
Fig. 10. Cumulative Analysis of Goal 5
The final cumulative analysis of five goals is depicted in figure 11. Table 7 illustrates that 49% of the participants are of the opinion i.e., agreed and strongly agreed whereas 20% have neither concurred nor dissented, 14% have dissented, and 17% have strongly dissented.
Table 7. Final Cumulative Analysis of Five Goals
|
Scale Five Goals 1 |
Very Low |
Low |
Nominal |
High |
Very High |
|
Goal 1 |
28.00% |
15.33% |
16.67% |
18.00% |
22.00% |
|
Goal 2 |
22.67% |
19.33% |
10.00% |
24.67% |
23.33% |
|
Goal 3 |
21.24% |
16.86% |
11.52% |
20.00% |
24.67% |
|
Goal 4 |
21.33% |
12.67% |
22.67% |
22.00% |
21.33% |
|
Goal 5 |
2.35% |
8.23% |
19.41% |
22.35% |
47.65% |
|
Total |
95.59% |
72.42% |
80.27% |
107.02% |
138.98%% |
|
Avg. |
17% |
14% |
20% |
21% |
28% |
|
30% |
28% |
|
17% 20% 14% 10% 0% |
20% 21% III |
■ Goal 1 ■ Goal 2 ■ Goal 3 ■ Goal 4 ■ Goal 5
Fig. 11. Final Cumulative Analysis of Five Goals
6. Significant Contributions of the Proposed Research
Section 6 is incorporated in this paper highlighting unique contributions of ChatGPT integration into educational systems. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI), particularly ChatGPT, into educational systems marks a paradigm shift in pedagogical approaches. This paper has delved into the multifaceted role of ChatGPT, exploring its potential to enhance learning environments through personalized instruction, interactive learning technologies, and its symbiosis with virtual reality (VR) for immersive education. The unique contributions of this integration are underscored by its capacity to address existing educational challenges, provide innovative learning pathways, and prepare students for a rapidly evolving digital landscape. Following contributions make this paper a significant addition to the existing body of research on AI in education, setting the stage for future investigations and implementations of ChatGPT in learning environments.
• Comprehensive Analysis of ChatGPT's Educational Applications: Unlike previous works that focus on narrow applications of AI in education, this paper provides a thorough examination of ChatGPT across various educational settings, including programming, creative writing, and personalized learning experiences. This holistic approach offers a more complete understanding of the potential impacts and applications of ChatGPT in the educational sector.
• Innovative Integration of ChatGPT with Virtual Reality (VR): This study pioneers the discussion on combining ChatGPT with VR technology to create immersive and interactive learning environments. This novel integration proposes a future where learning is not only personalized through AI but also deeply engaging and experiential, thanks to VR's immersive capabilities.
• Empirical Validation of Proposed Methodologies: By conducting a survey to validate the proposed integration models and methodologies, this paper goes beyond theoretical speculation, offering empirical evidence to support the effectiveness of ChatGPT in enhancing the quality of education. This adds a layer of credibility and practical relevance to our research, highlighting its applicability in real-world educational settings.
• Focus on Personalized Learning Paths: The emphasis on creating customized educational trajectories through ChatGPT's advanced algorithms stands out as a unique contribution. This study details how AI can adapt to individual learning styles and needs, ensuring a more personalized and effective learning experience for students, a significant advancement over one-size-fits-all educational approaches.
• Addressing Educational Accessibility and Equity: The proposed research uniquely addresses how ChatGPT can bridge educational gaps, offering quality learning opportunities to underserved and remote communities. This contribution is particularly pertinent in the context of global educational disparities, showcasing the potential of AI to democratize access to education.
• Holistic Educational Experience: By discussing the integration of ChatGPT not just as a technological tool but as part of a blended approach that includes human educators, this paper contributes a nuanced perspective on how AI and human expertise can complement each other to enrich the learning process. This balanced view on technology-human collaboration in education provides a roadmap for implementing AI in a way that enhances, rather than replaces, traditional teaching methodologies.
• Ethical Considerations and Future Directions: This study uniquely contributes to the discourse on the ethical use of AI in education, raising important questions about academic integrity, data privacy, and the long-term implications of AI integration. By offering guidelines and considerations for future research and policymaking, this paper serves as a foundational text for responsibly navigating the integration of ChatGPT and other AI technologies in educational contexts.
7. Strategies and Recommendations to Implement ChatGPT7.1 Implementation of ChatGPT for Educators
Integrating ChatGPT into educational systems while addressing ethical concerns and ensuring academic integrity is a nuanced process that requires comprehensive strategies for educators and policymakers alike. This study provides an in-depth analysis of ChatGPT's role in education, touching upon its potential benefits and the challenges it presents, especially in terms of ethical considerations and maintaining academic integrity. Building upon this foundation, here are detailed strategies and recommendations to navigate these concerns effectively:
-
• Educators should leverage ChatGPT alongside interactive learning technologies such as virtual classrooms, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR) to create more dynamic, engaging, and personalized learning experiences. This integration can help in delivering real-time feedback and practical examples, making the learning process more interactive and less reliant on rote memorization.
-
• Develop a Hybrid Teaching Model i.e., a blend of AI capabilities and human educators' expertise can produce a more comprehensive and effective educational experience. ChatGPT can serve as a preliminary tool for providing responses and explanations, while educators can add depth with personal insights, real-world examples, and critical thinking exercises. This model ensures that the technology complements rather than replaces traditional teaching methodologies.
-
• Utilize ChatGPT's algorithms to tailor educational content to the individual learning styles, strengths, and weaknesses of each student. This approach requires a continuous refinement of ChatGPT's understanding of student profiles and performance, enabling it to adjust its instructional techniques accordingly. Such personalized learning paths can significantly enhance student engagement and achievement.
-
7.2 Implementation of ChatGPT for Policy Makers
• Policymakers must develop and enforce clear guidelines that address the ethical use of AI tools like ChatGPT in educational settings. These guidelines should cover issues such as data privacy, academic integrity, content reliability, and the prevention of bias in AI-generated materials.
• Ensure that the integration of AI tools into education is done transparently, with mechanisms in place for accountability. This includes disclosing the extent of AI's involvement in the learning and assessment processes, as well as ensuring that educators and students are aware of the capabilities and limitations of these tools.
• Encourage ongoing research into the impacts of AI in education, focusing on long-term effects, scalability, and implications across diverse learning environments and demographics. Policymakers should support initiatives that explore innovative uses of AI in education while addressing potential drawbacks and ethical concerns.
• Collaborate with technologists and researchers to promote the development of ethical AI systems that are designed with educational equity and integrity in mind. This includes investing in AI that can adapt to diverse educational needs and that is trained on unbiased data sets.
• Implement professional development programs that equip educators with the skills to effectively integrate AI tools into their teaching practices. This includes training on the ethical use of AI, understanding AI's capabilities and limitations, and strategies for combining AI with traditional teaching methods.
8. Conclusion
By adopting these detailed strategies, educators and policymakers can work together to ensure that the integration of ChatGPT and similar AI tools into education enhances learning outcomes without compromising ethical standards or academic integrity. The goal should be to create a balanced and effective educational ecosystem where AI supports personalized learning, fosters innovation, and prepares students for the digital future, all while maintaining the core values of education.
In this research, the comprehensive and extensive analysis of ChatGPT's utilization in educational settings reveals a multifaceted and intricate landscape that encompasses various dimensions. ChatGPT, as an advanced and cutting-edge artificial intelligence tool, has demonstrated immense potential in completely transforming numerous aspects of education, ranging from augmenting programming skills to nurturing and stimulating creativity in the realm of writing. One of its most remarkable attributes is its capability to customize and individualize learning experiences based on the unique needs and preferences of each student, thereby presenting a distinct advantage that fosters a more personalized and captivating educational journey. Nevertheless, this critical evaluation also brings to the forefront the myriad of challenges and ethical considerations that are inherently intertwined with the integration of AI tools like ChatGPT into educational practices. Issues concerning academic integrity, safeguarding data privacy, and ensuring the reliability of AI-generated content emerge as crucial matters that educators and policymakers must confront and address with utmost importance. Striking the right balance between harnessing the benefits derived from AI and upholding the traditional values that underpin education necessitates a meticulous and thoughtful approach that must be taken into account.
Moreover, the comprehensive review underscores the paramount significance of ongoing research endeavors and the development of policies in this particular field. As AI technology continues to advance and progress at an unprecedented rate, it becomes increasingly imperative that our comprehension of its role and impact within the educational sphere evolves in tandem. Future studies should concentrate their efforts on examining the long-term effects of AI implementation, scalability in various educational contexts, and the diverse implications that it may have on different demographics. In summary, ChatGPT epitomizes both an exceptional opportunity and a formidable challenge for the education sector. Its integration into educational practices holds the promise of delivering a more streamlined, captivating, and customized learning experience. Nonetheless, this must be approached with a heightened awareness of the potential pitfalls and obstacles that may arise. It is therefore incumbent upon educators, technologists, and policymakers to collaborate effectively to ensure that the deployment of AI tools such as ChatGPT is executed responsibly, ethically, and in a manner that augments the educational experience without compromising the core values and principles that form the foundation of education. Case studies or primary research data will be incorporated to demonstrate the direct impact of ChatGPT on learning outcomes or educational practices in the future work.
Список литературы Review the Prospects and Obstacles of AI-Enhanced Learning Environments: The Role of ChatGPT in Education
- R. Yilmaz and F. G. Karaoglan Yilmaz, Augmented intelligence in programming learning: Examining student views on the use of ChatGPT for programming learning. Computers in Human Behavior: Artificial Humans, 2023, 1(2), 1-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chbah.2023.100005.
- N. M. S. Surameery and M. Y. Shakor, Use chat GPT to solve programming bugs. International Journal of Information Technology & Computer Engineering (IJITC). 2023, 3(1), 17-22.
- E. Chen, R. Huang, H.-S. Chen, Y.-H. Tseng, and L.-Y. Li, GPTutor: a ChatGPT-powered programming tool for code explanation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.01863 (2023).
- P M. Javaid, A. Haleem, R. P. Singh, S. Khan, and I. H. Khan, Unlocking the opportunities through ChatGPT Tool towards ameliorating the education system. BenchCouncil Transactions on Benchmarks, Standards and Evaluations, 2023, 3(2), p. 1-12, https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TBENCH.2023.100115.
- WH. Tian et al., Is ChatGPT the Ultimate Programming Assistant -- How far is it?. 2023, https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.11938v2.
- A. Özcan, and Polat, S. Artificial Intelligence and Chat Bots in Academic Research. Journal of Research in Social Sciences and Language, 2023, 3(1), 81-90, https://doi.org/10.20375/0000-000f-ff1e-2.
- M. Firat, How chat GPT can transform autodidactic experiences and open education. Department of Distance Education, Open Education Faculty, Anadolu Unive, 2023.
- M. Shidiq, The use of artificial intelligence-based chat-gpt and its challenges for the world of education; from the viewpoint of the development of creative writing skills, Proceeding of International Conference on Education, Society and Humanity, 353-357.
- A. M. A. Ausat, B. Massang, M. Efendi, N. Nofirman, and Y. Riady, Can chat GPT replace the role of the teacher in the classroom: A fundamental analysis. Journal on Education, 2023, 5(4), 16100-16106.
- D. R. E. Cotton, P. A. Cotton, and J. R. Shipway, Chatting and cheating: Ensuring academic integrity in the era of ChatGPT. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 1-12.
- S. Batra and S. Verma, To Study the Impact of ChatGPT Tool on Academic Learning: Perspective of Students and Teachers in Higher Education. Journal of Informatics Education and Research. 20,23, 3(2), 1969-1977.
- Y. Wardat et al., A revolutionary tool for teaching and learning mathematics. EURASIA J Math Sci Tech Ed. 2023,19(7), 1-18.
- Sánchez-Ruiz et al., ChatGPT Challenges Blended Learning Methodologies in Engineering Education: A Case Study in Mathematics. Applied Sciences. 2023,13(10), 1-22.
- M. M. Rahman an Y. Watanobe, ChatGPT for Education and Research: Opportunities, Threats, and Strategies. Applied Sciences. 2023, 13(9), 1-21.
- C. K. Lo. What Is the Impact of ChatGPT on Education? A Rapid Review of the Literature. Education Sciences. 2023; 13(4), 1-15.