Резистентная артериальная гипертония: новые возможности интервенционного лечения
Автор: Свешников А.В., Воробьев А.С.
Журнал: Вестник Национального медико-хирургического центра им. Н.И. Пирогова @vestnik-pirogov-center
Рубрика: Обзоры литературы
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.8, 2013 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140188145
IDR: 140188145 | УДК: 616.12-008.331.1-08
Текст обзорной статьи Резистентная артериальная гипертония: новые возможности интервенционного лечения
Артериальная гипертония (АГ) остается одной из наиболее актуальных проблем современного здравоохранения, что связано как с высокой распространенностью заболевания, так и с тем, что АГ является важнейшим фактором риска сердечно-сосудистых осложнений и смертности [1]. Впервые благоприятные эффекты антигипертензивных препаратов были продемонстрированы в исследовании Veteran Administration study [2, 3], и впоследствии подтверждены во многих клинических испытаниях. Фармакотерапия в течение длительного времени оставалась единственным видом лечения пациентов с артериальной гипертонией. Несмотря на эффективность и безопасность антигипертензивной терапии, оптимальный контроль АД представляет затруднения, которые могут быть обусловлены необходимостью длительного приема препаратов даже при полном отсутствии симптомов, побочными эффектами и стоимостью лечения, а также рядом других факторов. По данным центра контроля и профилактики заболеваний США, целевые уровни артериального давления регистрируются только у 50% пациентов с АГ [4]. Следует отметить, что данный показатель значительно ниже в других странах [5–8]. Представленная выше информация свидетельствуют о необходимости создания и изучения новых, в том числе интервенционных, методов лечения АГ.
Резистентная артериальная гипертония
Определение
В соответствии с определением Американской ассоциации сердца резистентной называют артериальную гипертонию с цифрами АД, превышающими целевые, несмотря на прием трех назначенных в оптимальных дозах, антигипертензивных препаратов, один из которых является диуретиком [9]. Резистентная АГ диагностируется также у пациентов с контролируемым течением артериальной гипертонии на фоне приема четырех антигипертензивных препаратов и с неконтролируемым течением артериальной гипертонии на фоне приема трех антигипертензивных препаратов при непереносимости диуретика.
Эпидемиология
Несмотря на отсутствие однозначных данных об истинной распространенности резистентной артериальной гипертонии, с учетом результатов клинических испытаний адекватный ответ на лечение может отсутствовать у 12–30% пациентов [10–12]. В исследовании ALLHAT (Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial) после 5 лет наблюдения субоптимальные цифры артериального давления регистрировались в среднем у 34% пациентов, несмотря на прием двух антигипертензивных препаратов. По окончании исследования для достижения целевых уровней АД прием трех и более антигипертензивных препаратов требовался у 27% испытуемых, 1–2 препаратов – у 49% испытуемых; таким образом, приблизительно 50% участников исследования получали три и более антигипертензивных препарата. Нельзя исключить, что полученные цифры являются заниженными, поскольку в исследование не включались пациенты с «трудно-контролируемой артериальной гипертонией» (АД не менее 160/100 мм рт. ст. на фоне приема двух и более препаратов). Представленные показатели отличаются от данных узкоспециализированных центров, в соответствии с которыми распространенность истинной резистентной артериальной гипертонии составляет 5% [13–15].
Характеристика пациентов
По данным фрамингемского исследования [16] и исследования ALLHAT [10] можно выделить следующие факторы риска резистентной АГ: значительное увеличение систолического АД, пожилой возраст, ожирение, гипертрофия левого желудочка, высокосолевая диета, хроническая болезнь почек, сахарный диабет и женский пол. Резистентная артериальная гипертония чаще возникает на фоне заболеваний, сопровождающихся вторичным повышением АД (симптоматические артериальные гипертонии) [9]. Также за маской резистентной АГ могут скрываться ошибки, связанные с назначением препаратов и низкая приверженность терапии.
Прогноз
В крупных исследованиях не изучалось влияние резистентной АГ на сердечно-сосудистую заболеваемость

и смертность. Среди факторов, свидетельствующих о неблагоприятном прогнозе следует отметить длительное и неконтролируемое течение АГ у пациентов с резистентной АГ, наличие дополнительных факторов риска (синдром обструктивного апноэ, гипертрофия левого желудочка, хроническая болезнь почек), линейную связь между уровнем АД и риском сердечно-сосудистых осложнений [9].
Хирургическое лечение резистентной артериальной гипертонии
В настоящее время помимо лекарственной терапии для контроля резистентной АГ предложены два вида хирургического лечения: радиочастотная денервация почечных артерий и стимуляция барорецепторов каротидного синуса.
Радиочастотная денервация почечных артерий
Симпатическая иннервация почек
Симпатическая нервная система (СНС) почек представлена сетью эфферентных и афферентных нервных волокон, проходящих через адвентициальный слой почечных артерий.
Табл. 1. Факторы, характерные для пациентов с резистентной артериальной гипертонией*
Факторы, характерные для пациентов с резистентной артериальной гипертонией
Пожилой возраст
Высокий уровень артериального давления
Ожирение
Избыточное потребление соли
Хроническая болезнь почек
Сахарный диабет
Гипертрофия левого желудочка
Негроидная раса
Женский пол
Примечание : * – взято из Calhoun DA, Jones D, Textor S, et al. Resistant hypertension: diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment. A scientific statement from the American Heart Association Professional Education Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research. Hypertension. 2008;51: 1403-19.
Табл. 2. Причины симптоматических артериальных гипертоний
Причины симптоматических артериальных гипертоний
Первичный гиперальдостеронизм
Обструктивное ночное апноэ
Хроническая болезнь почек
Стеноз почечных артерий
Феохромоцитома
Коарктация аорты
Гиперкортицизм
Заболевания щитовидной железы
Сигналы от различных органов поступают в автономные центры ЦНС, откуда эфферентные нервные импульсы распространяются по направлению к симпатическим преганглионарным нейронам боковых рогов спинного мозга [17]. Аксоны преганглионарных нейронов достигают пре- и паравертебральных симпатических ганглиев, в которых расположены тела постганглионарных нейронов. Через ворота почки постганглионарные нервные волокна проникают в почечную ткань. Стимуляция симпатических нервов почки способствует выделению норадреналина в нервных окончаниях и активации адренорецепторов, что приводит к увеличению секреции ренина, реабсорбции натрия и воды и, как следствие, увеличению системного артериального давления [18, 19].
Окончания афферентных симпатических нервов почки преимущественно локализованы в области почечной лоханки, откуда восходящие сигналы распространяются к телам нейронов и далее в сердечно-сосудистые центры ЦНС. При активации афферентных нервов происходит выделение вазопрессина и окситоцина в нейрогипофизе. Данный механизм является одним из основных звеньев регуляции симпатического тонуса и системного сосудистого сопротивления [20, 21].
Следует отметить, что активность симпатической нервной системы не подчиняется принципу «все или ничего» [22]. Так, возможно изолированное увеличение активности СНС в отдельных органах (сердце, почки и.т.д.), не сопровождающееся системной симпатической активацией. Наряду с индивидуальной вариабельностью метаболизма катехоламинов данный фактор отчасти объясняет неоднородную эффективность антигипертензивной терапии у пациентов с АГ.
История метода
До появления современных средств фармакотерапии у больных с тяжелым течением АГ выполнялась хирургическая симпатэктомия, в большинстве случаев способствовавшая не только устойчивому снижению артериального давления, но и увеличению продолжительности жизни [23–25]. Так, в крупном обсервационном исследовании (2000 пациентов, у 1506 выполнялась симпатэктомия) было продемонстрировано двукратное увеличение выживаемости после вмешательства вне зависимости от стадии заболевания [26]. Удовлетворительный контроль артериального давления отмечался приблизительно у 50% пациентов, перенесших симпатэктомию. Применение процедуры было ограничено в связи с ее инвазивностью и неблагоприятным профилем безопасности.
После внедрения в клиническую практику антигипертензивных препаратов, обладающих значительно меньшим количеством побочных эффектов, хирургическая симпатэктомия в значительной степени утратила свою актуальность. Основанная на тех же принципах эндоваскулярная денервация почечных артерий была предложена в середине 2000-х годов в качестве одного из
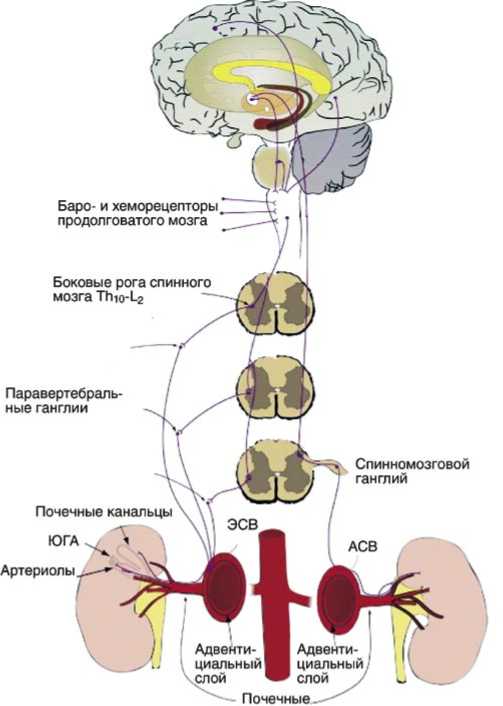
Рис. 1. Схема симпатической иннервации почек. ЮГА – юкстагломерулярный аппарат, ЭСВ – эфферентные симпатические волокна, АСВ – афферентные симпатические волокна. Взято из SC Bertog, PA Sobotka, H. Sievert. Renal Denervation for Hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol Intv. 2012; 5(3): 249–258
новых малоинвазивных подходов к лечению АГ. Данная процедура обладает рядом потенциальных преимуществ, среди которых следует отметить отсутствие системных побочных эффектов, короткую продолжительность вмешательства и восстановительного периода.
Описание метода
В настоящее время для клинического применения зарегистрирована одна система радиочастотной катетерной денервации почечных артерий. Также изучаются другие системы с использованием радиочастотной энергии и ультразвука.
Под рентгеноконтролем через бедренную артерию абляционный катетер проводят в дистальный сегмент почечной артерии [27–29]. Воздействие радиочастотной энергии (максимальная мощность: 8 Ватт; продолжительность: 2 минуты) приводит к нагреванию стенки сосуда до 50–70 º C и разрушению симпатических нервных волокон, расположенных в адвентициальном слое. Далее
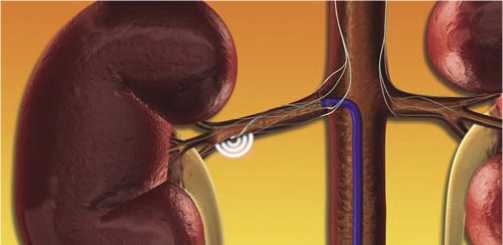
Рис. 2. Схематическое изображение радиочастотной денервации почечных артерий. Взято из http://www.medtronicrdn.com катетер проводится проксимально с последующим нанесением 4–6 аппликаций, расположенных по спирали, с интервалами не менее 5 мм. Медиана продолжительности процедуры составляет 38 минут. Для контроля болевых ощущений во время операции требуется введение наркотических аналгетиков и седативных препаратов.
Клинические исследования эндоваскулярной денервации почечных артерий
Среди программ изучения катетерной денервации почечных артерий у пациентов с резистентной АГ наибольшего внимания заслуживают исследования Symplicity HTN-1 [27, 30], и Symplicity HTN-2 [29].
В многоцентровом открытом нерандомизированном исследовании Symplicity HTN-1 [27, 30] приняли участие 153 пациента с резистентной артериальной гипертонией (систолическое артериальное давление не менее 160 мм рт. ст. на фоне комбинации не менее трех антигипертензивных препаратов в целевых или максимально переносимых дозировках, включающей диуретик). Критериями исключения являлись вторичные АГ (за исключением синдрома обструктивного ночного апноэ и хронической болезни почек), снижение СКФ менее 45 мл/мин/1,73 м2 (по формуле MDRD), сахарный диабет первого типа и аномалии развития почечных артерий.
Перед вмешательством исходный уровень артериального давления составил 176/98 мм рт. ст, среднее количество антигипертензивных препаратов – 5,1. Первичной конечной точкой данного исследования являлась величина снижения артериального давления. Через 1, 3, 6, 12, 18 и 24 месяцев наблюдалось снижение АД на 20/10, 24/11, 25/11, 23/11, 26/14 и 32/14 мм рт. ст., соответственно (P < 0,0001 для систолического и диастолического АД за исключением P = 0,002 для диастолического АД через 24 месяца наблюдения). На протяжении всего периода наблюдения не отмечалось увеличения цифр артериального давления. Уменьшение активности симпатической нервной системы (n = 10) сопровождалось значительным снижением выброса норадреналина и коррелировало со степенью изменения артериального давления через 6 месяцев.
Через 1 год после операции клинически значимый ответ на вмешательство (снижение систолического АД не менее чем на 10 мм рт. ст.) отсутствовал у 13% пациентов. Однако в марте 2012 года на ежегодном научном симпозиуме Американской коллегии кардиологов были представлены данные трехлетнего наблюдения за популяцией пациентов, включенных в исследование Symplicity HTN-1, в соответствии с которыми снижение систолического АД отмечалось у всех пациентов.
В течение первого года наблюдения скорость клубочковой фильтрации оставалась стабильной. Изменения СКФ через 1, 3, 6 и 12 месяцев составили +0,1 мл/мин (95% доверительный интервал [ДИ]: -2,8–3,0; N = 112), -1,6 мл/мин (95% ДИ: -4,3–1,1; N = 102), -0,1 мл/мин (95% ДИ: -2,9–2,8; N = 87) и -2,9 мл/мин (95% ДИ: -6,2–+0,3; N = 64), соответственно. Через два года наблюдения данные о СКФ были получены у 10 пациентов (изменение СКФ -16,0 мл/мин 1,73 м2).
Среди осложнений процедуры были зарегистрированы диссекция почечной артерии после установки катетера до нанесения РЧ-аппликаций (n = 1) и псевдоаневризма бедренной артерии (n = 3). Во время ангиографии, которая выполнялась у 20 испытуемых на 14–18 сутки после вмешательства, не было зафиксировано признаков стеноза почечных артерий. По данным МР-, КТ-ангиографии или УЗДГ почечных артерий через 6 месяцев после вмешательства (n = 81) стеноз почечной артерии с локализацией вне зоны вмешательства был выявлен у одного пациента.
В рандомизированноe контролируемое исследование Symplicity HTN-2 [29] были включены 106 пациентов с резистентной артериальной гипертонией (систолическое артериальное давление ≥ 160 мм рт. ст.; ≥ 150 мм рт. ст. у пациентов с сахарным диабетом второго типа). После периода наблюдения продолжительностью 2 недели проводилась рандомизация (1:1) в группу лечения (n = 52) и контрольную группу (продолжение лекарственной терапии (n = 52)). Средняя величина артериального давления при включении в исследование несмотря на прием 5,3 антигипертензивных препаратов составила 178/96 мм рт. ст. Через 6 месяцев после процедуры отмечалось снижение артериального давления на 32/12 мм рт. ст. (p < 0,0001) при отсутствии изменений в группе контроля. При самостоятельном измерении в амбулаторных условиях в группе активного вмешательства было продемонстрировано снижение артериального давления на 20/12 мм рт. ст. (p < 0,0001, n = 32), при небольшом увеличении цифр артериального давления на 2/0 мм рт. ст. в группе контроля (n = 40). В 20% случаев снижение цифр артериального давления позволило уменьшить дозировки или отменить некоторые антигипертензивные препараты. Имеются данные о долгосрочном контроле артериального давления у 20 пациентов, перенесших денервацию почечных артерий. Через 6 месяцев сохранялось снижение цифр артериального давления на 11/7 мм рт. ст. (p = 0,007/0,014). В контрольной группе статистически значимых изменений артериального давления зарегистрировано не было.
В ходе исследования не было зарегистрировано серьезных осложнений, связанных с процедурой. Среди малых осложнений, были идентифицированы один случай псевдоаневризмы бедренной артерии, устраненной посредством мануальной компрессии, один случай выраженного снижения артериального давления, потребовавший снижения дозы антигипертензивных препаратов, один случай инфекции мочевых путей, один случай возникновения парестезий, потребовавших прологации пребывания в стационаре и один случай боли в спине, регрессировавшей в течение 1 месяца на фоне терапии аналгетическими препаратами. У семи (13%) из 52 пациентов отмечалась брадикардия во время процедуры, потребовавшая введения атропина.
Через 6 месяцев не было выявлено изменений концентраций сывороточного креатинина и цистатина С, а также скорости клубочковой фильтрации, рассчитанной по формуле MDRD. В течение 6 месяцев не наблюдалось снижения скорости клубочковой фильтрации более чем на 50%. Снижение СКФ более чем на 25% отмечалось у двух пациентов в группе активного вмешательства и трех пациентов в группе контроля.
В октябре 2011 года компания Medtronic Inc. сообщила о начале рандомизированного плацебо-контро-лируемого исследования Symplicity-HTN-3, в котором будут изучаться эффективность и безопасность денервации почечных артерий у пациентов с резистентной артериальной гипертонией [31]. В исследование будут включены приблизительно 530 пациентов из 60 медицинских центров США. С целью минимизации системной ошибки будет проведено «ослепление» всех пациентов и исследователей относительно схемы рандомизации. В качестве первичных конечных точек будут использоваться изменение артериального давления через 6 месяцев по сравнению с исходным уровнем и частота больших побочных эффектов, зарегистрированных в течение 6 месяцев с момента рандомизации.
Ограничения исследований Symplicity
Несмотря на значимость полученных данных, для исследований Symplicity HTN-1 и Symplicity HTN-2 был характерен ряд представленных ниже ограничений.
Поскольку в исследовании Symplicity HTN-1 отсутствовала контрольная группа и не проводилось ослепление пациентов и исследователей, нельзя исключить влияние эффектов Готорна и плацебо на конечный результат. Также перед проведением процедуры не выполнялись мероприятия, направленные на выявление пациентов с гипертонией белого халата, низкой приверженностью к терапии и вторичными формами артериальной гипертонии. Одним из критериев исключения являлось наличие добавочных почечных ар-
терий, что препятствует экстраполяции результатов на всех пациентов с АГ. Среди ограничений исследования Symplicity HTN-2 следует отметить открытый дизайн и отсутствие плацебо-контроля.
Поскольку воздействие радиочастотного тока при других вмешательствах (радиочастотная абляция левого предсердия, РЧА злокачественных новообразований и.т.д.) приводит к локальному повреждению и фиброзу тканей, стеноз почечных артерий рассматривается в качестве одного из потенциальных осложнений процедуры. Низкая мощность энергии, используемая при радиочастотной денервации почечных артерий, теоретически препятствует их стенозированию, что подтверждается результатами исследований Symplicity. Однако для получения достоверных результатов необходимы дополнительные исследования с большим количеством испытуемых и продолжительностью наблюдения.
Среди вопросов, связанных с безопасностью вмешательства, следует отметить, что в обоих исследованиях принимали участие пациенты с анатомией почечных артерий, «приемлемой» для катетерной абляции; однако выполнение процедуры у других категорий больных может быть сопряжено с более высоким периоперационным риском.
Противопоказания
В настоящее время противопоказаниями к проведению процедуры являются анатомическая непригодность почечных артерий (диаметр < 4 мм; длина < 20 мм; фибромышечная дисплазия; гемодинамически значимый стеноз почечных артерий) и скорость клубочковой фильтрации менее 45 мл/мин/1,73 м2 (по формуле MDRD). Относительным противопоказанием является наличие некоторых анатомических вариантов отхождения почечных артерий (множественные и добавочные почечные артерии) [27, 29].
Альтернативные сферы применения процедуры
Сахарный диабет второго типа . В пилотном исследовании у 50 пациентов (n = 37 – группа активного вмешательства; n = 13 – группа контроля) с резистентной АГ помимо снижения АД было продемонстрировано статистически значимое уменьшение концентраций глюкозы, инсулина и С-пептида [32].
Фибрилляция предсердий . В небольшом исследовании (n = 27) продемонстрировано увеличение эффективности контроля ритма при выполнении симультанной радиочастотной катетерной денервации почечных артерий и изоляции устьев легочных вен по сравнению с группой контроля (изоляция легочных вен) [33].
Также в настоящее время изучаются возможности применения денервации почечных артерий у пациентов с резистентной артериальной гипертонией и синдромом обструктивного ночного апноэ [34], диабетической нефропатией [35] и хронической сердечной недостаточ-ностью[36, 37].
Стимуляция барорецепторов каротидного синуса
Каротидный синус участвует в модуляции активности вегетативной нервной системы и регуляции артериального давления. Сигналы от барорецепторов каротидного синуса поступают в головной мозг по афферентным нервным волокнам с последующим уменьшением активности симпатической нервной системы, снижением артериального давления и частоты сердечных сокращений. По данным экспериментальных и клинических исследований электростимуляция в области сонных артерий способствует снижению артериального давления [38–42]. Для стимуляции барорецепторов каротидного синуса разработано два поколения имплантируемых устройств. Электроды имплантируются в области сонных артерий с одной (второе поколение) или двух (первое поколение) сторон и присоединяются к устройству, установленному подкожно в подключичной области.
В нерандомизированном проспективном исследовании DEBuT-HT (Device Based Therapy in Hypertension Trial) безопасность и эффективность устройства изучалась у 45 пациентов с резистентной артериальной гипертонией (исходное значение артериального давления 179/105 мм рт. ст., медиана количества антигипертензивных препаратов: 5) [43]. Имплантация устройства была выполнена у 42 пациентов. Наблюдение в течение 3 месяцев, 1 года и 2 лет осуществлялось за 37, 26 и 17 пациентами, соответственно. В указанные временные интервалы было зарегистрировано снижение офисного артериального давления на 21/12 мм рт. ст., 30/20 мм рт. ст. и 33/22 мм рт. ст., соответственно. Среднесуточная величина артериального давления снизилась на 6/4 мм рт. ст., 13/8 мм рт. ст. и 24/13 мм рт. ст. Следует отметить значительную вариабельность степени снижения артериального давления с полным отсутствием эффекта у некоторых пациентов. У 8 (19%) из 42 пациентов процедура сопровождалась серьезными осложнениями. Через 6 суток после вмешательства один пациент скончался от ангионевротического отека до активации устройства. Также были зарегистрированы один случай инсульта, инфекционные осложнения, смещение генератора, парез языка, наиболее вероятно связанный с повреждением подъязычного нерва и отек легких.
В двойном-слепом плацебо-контролируемом исследовании 265 пациентов с резистентной артериальной гипертонией после имплантации устройства Rheos были рандомизированы в группы немедленной (группа А) и отсроченной на 6 месяцев (группа B) терапии [44]. Через 6 месяцев среднее снижение артериального давления составило 16 ± 29 мм рт. ст. в группе A и 9 ± 29 мм рт. ст. в группе B (p = 0,08). Осложнения, связанные с процедурой, были зарегистрированы в 25,5% случаев.
В недавно опубликованном открытом нерандомизированном исследовании изучалась эффективность и безопасность второго поколения устройств для стимуляции барорецепторов каротидного синуса [45]. В исследовании приняли участие 30 пациентов с резистентной

артериальной гипертонией. Через 6 месяцев наблюдения отмечалось снижение систолического артериального давления на 26,0 ± 4,4 мм рт. ст. Частота осложнений в раннем послеоперационном периоде (30 дней) составила 10%.
Несмотря на эффективный контроль АД при стимуляции барорецепторов каротидного синуса применение процедуры ограничено в связи с инвазивностью метода, необходимостью частых замен устройства (средняя продолжительность работы 2,8 ± 1,4 года) [45], относительно высоким риском периоперационных осложнений. Таким образом, барорефлекторная стимуляция каротидных синусов является экспериментальной терапевтической опцией у ограниченной популяции пациентов с резистентной артериальной гипертонией.
Заключение
Резистентная артериальная гипертония является распространенным состоянием с высоким риском сердечно-сосудистых осложнений. Лечение резистентной АГ требует мультимодальной стратегии с необходимостью привлечения специалистов из смежных областей медицины. Помимо оценки приверженности пациентов лечению и необходимости индивидуализации фармакотерапии большое значение имеет идентификация вторичных форм АГ. Однако у большинства пациентов выявление причины повышения артериального давления не представляется возможным даже после проведения всеобъемлющего диагностического поиска. Для данной категории больных разрабатываются новые альтернативные терапевтические опции, в том числе минимально инвазивная денервация почечных артерий и стимуляция барорецепторов каротидного синуса. Симпатическая денервация почечных артерий является интервенционной процедурой с низким риском осложнений, позволяющей достичь клинически-значимого и долгосрочного снижения артериального давления. Возможность применения метода у пациентов с нерезистентным течением АГ и некоторыми заболеваниями, сопровождающимися повышением активности симпатической нервной системы (хроническая почечная недостаточность, хроническая сердечная недостаточность, фибрилляция предсердий), также влияние метода на твердые конечные точки требуют дальнейшего изучения.
Список литературы Резистентная артериальная гипертония: новые возможности интервенционного лечения
- Lawes CM, Vander Hoorn S, Rodgers A. Global burden of blood-pressure-related disease. 2001. Lancet 2008; 371: 1513-1518.
- Veterans Administration Cooperative Study Group on Antihypertensive Agents, «Effects of treatment on morbidity in hypertension. Results in patients with diastolic blood pressures averaging 115 through 129 mm Hg», Journal of the American Medical Association, 1967, Vol. 202, N. 11, P. 1028-1034.
- Veterans Administration Cooperative Study Group on Antihypertensive Agents, «Effects of treatment on morbidity in hypertension. Results in patients with diastolic blood pressures averaging 90 through 114 mm Hg», Journal of the American Medical Association, 1970, Vol. 202, P. 1143-1152.
- CDC. Vital signs: prevalence, treatment, and control of hypertension-United States, 1999-2002 and 2005-2008. MMWR. 2011; 60(4): 103-8.
- Kotseva K, Wood D, De Backer G et al. EUROASPIRE Study Group. EUROASPIRE III: a survey on the lifestyle, risk factors and use of cardioprotective drug therapies in coronary patients from 22 European countries. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil 2009; 16: 121-137.
- Mancia G, Pessina AC, Trimarco B, Grassi G. SILVIA (Studio Italiano Longitudinale sulla Valutazione della Ipertensione Arteriosa nel 2000) Study Group. Blood pressure control according to new guidelines targets in low-to high-risk hypertensives managed in specialist practice. J Hypertens 2004; 22: 2387-2396.
- Mancia G, Volpe R, Boos S, Ilardi M, Giannattasio C. Cardiovascular risk profile and blood pressure control in Italian hypertensive patients under specialist care. J Hypertens 2004; 22: 51-57.
- Guido Grassi, Renata Cifkova, Stephane Laurent et al. Blood pressure control and cardiovascular risk profile in hypertensive patients from central and eastern European countries: results of the BP-CARE study. Eur Heart J (2011) 32 (2): 218-225.
- Calhoun DA, Jones D, Textor S, et al. Resistant hypertension: diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment. A scientific statement from the American Heart Association Professional Education Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research. Hypertension. 2008; 51: 1403-19.
- Cushman WC, Ford CE, Cutler JA, et al. Success and predictors of blood pressure control in diverse North American settings: the antihypertensive and lipid-lowering treatment to prevent heart attack trial (ALLHAT). J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2002; 4: 393-404.
- Hajjar I, Kotchen TA. Trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in the United States, 1988-2000. JAMA. 2003; 290: 199-206.
- de la Sierra A, Segura J, Banegas JR, et al. Clinical features of 8295 patients with resistant hypertension classified on the basis of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. Hypertension. 2011; 57: 898-902.
- P. A. Sarafidis and G. L. Bakris, «Resistant hypertension. An overview of evaluation and treatment,» Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 2008, Vol. 52, N. 22, P. 1749-1757.
- M. Moser and J. F. Setaro, «Resistant or difficult-to-control hypertension,» The New England Journal of Medicine, 2006, Vol. 355, N. 4, P. 385-392.
- D. Wojciechowski, V. Papademetriou, C. Faselis, and R. Fletcher, «Evaluation and treatment of resistant or difficult to control hypertension,» Journal of Clinical Hypertension, 2008, Vol. 10, N. 11, P. 837-843.
- Lloyd-Jones DM, Evans JC, Larson MG, O’Donnell CJ, Rocella EJ, Levy D. Differential control of systolic and diastolic blood pressure: factors associated with lack of blood pressure control in the community. Hypertension. 2000; 36: 594-599.
- L. Barajas, L. Liu, and K. Powers, «Anatomy of the renal innervation: intrarenal aspects and ganglia of origin», Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology, 1992, Vol. 70, N. 5, P. 735-749.
- G. F. DiBona and U. C. Kopp, «Neural control of renal function», Physiological Reviews, 1997, Vol. 77, N. 1, P. 75-197.
- U. C. Kopp and G. F. DiBona, «The neural control of renal function» in The Kidney: Physiology and Pathophysiology, G. Seldin and G. Giebisch, Eds., pp. 981-1006, Raven Press, New York, NY, USA, 3rd edition, 2006.
- Doumas M, Faselis C, Papademetriou V. Renal sympathetic denervation and systemic hypertension. Am J Cardiol, 2010; 15: 570-576.
- L. Liu and L. Barajas, «The rat renal nerves during development,» Anatomy and Embryology, vol. 188, no. 4, pp. 345-361, 1993.
- Esler M., Jennings G., Lambert G., Meredith I., Horne M., Eisenhofer G.; Overflow of catecholamine neurotransmitters to the circulation: source, fate, and functions, Physiol Rev 70 1990 963-985
- Harris SH. Renal sympathectomy: its scope and limitations. Proc R Soc Med. 1935;28:1497-1510.
- Smithwick RH, Thompson JE. Splanchnicectomy for essential hypertension; results in 1,266 cases. J Am Med Assoc. 1953; 152: 1501-1504.
- Hoobler SW, Manning JT, Paine WG, et al. The effects of splanchnicectomy on the blood pressure in hypertension; a controlled study. Circulation. 1951; 4: 173-183.
- R. H. Smithwick, «Hypertensive vascular disease. Results of and indications for splanchnicectomy,» Journal of Chronic Diseases,1955, Vol. 1, N. 5, P. 477-496.
- Krum H, Schlaich M, Whitbourn R, et al.: Catheter-based renal sympathetic denervation for resistant hypertension: a multicentre safety and proof-of-principle cohort study. Lancet 2009; 373: 1275-81.
- Schlaich MP, Sobotka PA, Krum H, Lambert E, Esler MD: Renal sympathetic-nerve ablation for uncontrolled hypertension. N Engl J Med 2009; 361: 932-4.
- Esler MD, Krum H, Sobotka PA, Schlaich MP, Schmieder RE, Böhm M. Renal sympathetic denervation in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension (The Symplicity HTN-2 Trial): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet, 2010; 376: 1903-1909.
- H. Krum, N. Barman, M. Schlaich, P. Sobotka et al. Catheter-Based Renal Sympathetic Denervation for Resistant Hypertension. Hypertension. 2011; 57: 911-917.
- http://www.symplifybptrial.com/.
- Mahfoud F, Schlaich M, Kindermann I, et al.: Effect of renal sympathetic denervation on glucose metabolism in patients with resistant hypertension: a pilot study. Circulation 2011; 123: 1940-6.
- Pokushalov E, Romanov A, Corbucci G, et al. A randomized comparison of pulmonary vein isolation with versus without concomitant renal artery denervation in patients with refractory symptomatic atrial fibrillation and resistant hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 2012.
- http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01366625.
- http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01588795.
- http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01538992.
- http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01392196.
- Warner HR. The frequency-dependent nature of blood pressure regulation by the carotid sinus studied with an electric analog. Circ Res. 1958; 6: 35-40.
- Carlsten A, Folkow B, Grimby G, Hamberger CA, Thulesius O. Cardiovascular effects of direct stimulation of the carotid sinus nerve in man. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958; 44: 138-45.
- Schwartz SI, Griffith LS, Neistadt A, Hagfors N. Chronic carotid sinus nerve stimulation in the treatment of essential hypertension. Am J Surg. 1967; 114: 5-15.
- Bilgutay AM, Lillehei CW. Treatment of Hypertension with an Implantable Electronic Device. JAMA. 1965; 191: 649-53.
- Bilgutay AM, Lillehei CW. Surgical treatment of hypertension with reference to baropacing. Am J Cardiol. 1966; 17: 663-7.
- Scheffers IJ, Kroon AA, Schmidli J, et al.: Novel baroreflex activation therapy in resistant hypertension: results of a European multi-center feasibility study. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2010; 56: 1254-8.
- Bisognano JD, Bakris G, Nadim MK et al.: Baroreflex activation therapy lowers blood pressure in patients with resistant hypertension results from the double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled rheos pivotal trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011; 58(7): 765-73.
- Hoppe UC, Brandt MC, Wachter R, Beige J, Rump LC, Kroon AA, Cates AW, Lovett EG, Haller H. Minimally invasive system for baroreflex activation therapy chronically lowers blood pressure with pacemaker-like safety profile: results from the Barostim neo trial. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2012 Jul-Aug;6(4): 270-6.


