Robustness Assessment of Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Software for Data Leakage against Different Data Types and Sources
Автор: Ahmet Ali Suzen, Osman Ceylan
Журнал: International Journal of Education and Management Engineering @ijeme
Статья в выпуске: 2 vol.15, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Data leakage is the deliberate or accidental transfer of data of institutions or individuals to a different source. Especially, with the increasing use of IT assets after the pandemic, data leaks are more common. Firewalls, anti-virus software, Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS), or Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) products are preferred within the network to ensure the security of data sources. However, this type of security software works server-based and often protects the network from outside attacks. It is seen that the main source of data leaks experienced recently is internal vulnerabilities. Data Loss Prevention (DLP), which is the right choice for preventing data leaks, is a system developed to identify, monitor, and protect data in motion or stored in a database. DLPs are preferred to prevent unauthorized distribution of data at the source. DLP software is recommended for technical measures against data security, especially the Personal Data Protection Law (KVKK) in Turkey and General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. Test virtual machines were set up for implementation in real-world scenarios and using personal and corporate data, the behavior and durability of DLP software in cases of unauthorized data upload to USB, CD/DVD, cloud resources, office software, e-mail or ftp server were evaluated. It was observed that potential leaks and risks occur in data discovery, data masking, data hiding and data encryption according to the data density in data leakage prevention.
Data Leakage, Cyber Security, Cyber Resilience, Personal Data
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15019852
IDR: 15019852 | DOI: 10.5815/ijeme.2025.02.01
Текст научной статьи Robustness Assessment of Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Software for Data Leakage against Different Data Types and Sources
The necessity of internet usage and the increase in the number of users connected to the internet has led to a cumulative increase in data generation. These increases have also indirectly increased cyber threats and data leakage incidents. Data breaches jeopardize the privacy and security of individuals and organizations that access the internet or have data in digital environments. Cyber threat incidents cannot be effectively prevented by existing legal regulations, security standards and institutions. While more than 90% of the data published online has been created in the last two years, the size of data created in 2018 was 33 zettabytes (ZB), and this data size is expected to reach 175 ZB in 2025 [1]. While there were two and a half million internet users and three billion smartphone users worldwide in 2013, the number of internet users increased to five billion and smartphone users to six billion in 2023 [2].
A data leak/breach is a cyber threat carried out by unauthorized means that damages the confidentiality, security or integrity of information belonging to an individual or organization. In a published report, it is seen that approximately 197 million records were compromised in data leak incidents in 2017 and the number of data leaks recorded in 2020 increased to 37 billion. In addition, the report stated that the average cost of a data breach increased from 7.91 million dollars in 2018 to 8.64 million dollars in 2020 [4]. The cost of the damage experienced by organizations as a result of data breaches is 5.36 million dollars on average [5]. Today, the cost of cybercrimes is increasing day by day and is thought to be 10.5 trillion dollars by 2025 [6].
It is stated that organizations spend an average of 204 days in 2023 to detect data breaches [5]. According to the 2023 Data Breach Cost Report prepared by IBM Security, the most common attack methods in data breaches are phishing and compromised credentials. 40% of the data exposed to data breaches consists of data stored in multiple locations. On the other hand, data stored in only one location suffers data breaches less frequently, while data breach rates according to storage environments are 25% in public cloud environments, 20% in on-premises environments and 15% in private cloud environments. Leaks of data stored in cloud environments resulted in an average leakage cost of 5.17 million dollars. In addition, the report states that organizations using artificial intelligence-based security systems to prevent data leaks save an average of 2.22 million dollars. The loss of prestige and business of organizations after data leaks and the costs incurred to respond to data leaks are quite high for organizations [7].
According to the Ponemon Institute in 2023, the total average cost after insider threat incidents was 8.3 million dollars in 2018, while this cost increased by approximately 95% to 16.2 million dollars in 2023. Regarding insider risks, it is stated that the highest cost is incurred in the expenses incurred for control and correction after the incident has occurred. It was also observed that the longer the time to respond to incidents, the higher the cost. Among the main causes of threatening incidents caused by non-malicious employees from the inside, negligence or incorrect operations are 55%, a deliberate attack from outside or inside is 20%, while threats by malicious employees are 25%. Although insider incidents by malicious employees are less common, they are reported to cause the highest costs with an average of 701,500 dollars after this data leak. In the report prepared by the Ponemon Institute, when the tools and practices used to prevent insider threats are analyzed, end-user trainings and awareness are in the first place with a rate of 72%, and the use of DLP tools is in the second place with a rate of 57%. Other applications and tools include Security incident and event management (SIEM) (56%), Privileged access management (PAM) (56%), User behavior analytics (UBA) (54%), Insider risk management (IRM) (43%), Strict third-party vetting procedures (39%), Employee monitoring and surveillance (38%), Risk intelligence sharing (36%) and Network traffic intelligence (27%) [8].
In digital environments, information belonging to individuals or institutions is characterized as digital data. Today, the speed of entry and exit of data in digital form into and out of systems is very high. Daily, an organization can save and transfer hundreds or even thousands of files and communicate with millions of emails through various channels. Typically, corporate data is generated or stored on media such as email, computers, mobile devices, Network, Cloud, USB Disk and CD/DVD (Fig. 1). Data owners (Customers, business partners, regulators and shareholders, etc.) expect the organizations they communicate with to protect this data. Data processed in organizations can lead to litigation, loss of competitive advantage, political crises or loss of customer loyalty and employee trust. Therefore, corporate data is one of the most important assets an organization has.

Fig. 1. Some words for data leakage channels
In information security, data leakage (or data loss) is referred to as unintended information disclosure. It is one of the most serious security issues that intentionally or unintentionally discloses private or sensitive data to an unauthorized entity. The unauthorized transfer of corporate sensitive data without the knowledge of the organizational authority is known as data leakage [10]. In organizations, an increase in data leakage incidents has been observed as a result of the intensive use of digital systems during and after the pandemic process. Personnel errors are among the main causes of recent data leaks. Especially in organizations with a high number of personnel, it becomes difficult to ensure data security control in cases where information technology (IT) departments are insufficient. For this reason, security systems should be used to eliminate the negativities caused by the human factor in the process of ensuring data security [11].
In many countries, data protection and data breaches are defined by special articles. Thus, countries operate legal processes with data protection regulations that specify the administrative and technical measures to be taken by organizations before/after data leaks. Table 1 shows the data protection regulations to which countries are bound. Although personal data is protected by regulations, it is very difficult to ensure this security in practice. After data leaks occur, it is necessary to announce how many people, and which data are affected within a certain period in legal processes [9].
Regulations mainly aim to protect personal data against risks such as unauthorized access, disclosure or loss. DLP software offers various functions such as data classification, data monitoring, encryption and access control to achieve these regulatory objectives. For example, DLP software enables automatic identification and protection of personal data by classifying the data within the organization according to the sensitivity level. This offers an approach in line with the principle of “privacy by design” in regulations. In addition, DLP software makes an important contribution to organizations to fulfill their obligations such as data breach notification obligation in regulations with its ability to detect data breaches in real time and prevent unauthorized data transfers.
Table 1. Data protection regulations in countries
|
Country |
Regulation |
|
European Union |
GDPR-General Data Protection Regulation |
|
Türkiye |
KVKK- Personal Data Protection Law |
|
ABD |
CCPA- California Consumer Privacy Act |
|
Australia |
Austrian Data Protection Law |
|
India |
The Personal Data Protection |
|
China |
China Personal Information Protection Law |
The most basic task of information security systems is to ensure that data is not accessed by unauthorized persons. There are many traditional solutions such as firewalls, virtual private networks (VPN), intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to prevent data leaks. Today, there are various systems that work alone or in a hybrid way to ensure data security. Firewalls are used to provide data security in the networks of organizations [12]. Firewalls generate alerts by analyzing anomalous behavior in incoming and outgoing requests. Some firewalls have intrusion detection systems (IDS) or intrusion prevention systems (IPS) in their capabilities. Such systems generally protect the network in the event of an attack. Although firewalls, IPS and IDS systems prevent suspicious behaviors related to process and transaction, they are insufficient in detecting and preventing data leaks in different leakage channels and forms. One of the most effective methods to prevent data leaks is the Data Leakage Prevention System (DLP). DLPs can analyze the source of data in use, at rest or in motion. It generates effective alarms for monitoring, unauthorized use and protection of sensitive data in organizations [13].
In this study, the durability of sensitive data in Data in Motion, Data at Rest, Data in Use situations for seventeen different commercially available DLP software is comparatively analyzed. In the comparison, parameters such as their behavior and durability in cases of unauthorized data upload to USB, CD/DVD, cloud resources, office software, e-mail or ftp server were taken into account.
2. Data Leakage Prevention System
Today, a vast amount of data is generated in digital form, and the rate at which this data flows in and out of organizations is very high. Daily, a typical organization may send and receive millions of e-mail messages and downloads through various channels, saving and transferring hundreds or even thousands of files. This data is among the most important assets of the organization and organizations need to take special measures to protect this sensitive and private data. One of the main measures to be taken is to determine which types of data are used, shared and stored by the organizations and to plan how these data are managed and how to protect them from unauthorized access [14].
DLP detects and prevents unauthorized access to confidential data using deep analysis of confidential data. In addition, DLP systems have the ability to identify, monitor and protect data at rest, in motion and in use with deep content analysis method. Thus, DLP helps organizations monitor and protect their important and sensitive data by identifying leakage risks [16]. DLP is used to prevent unauthorized access to confidential data as well as to prevent accidental sharing of important and sensitive data for organizations. Unlike systems such as firewalls, IPS and IDS, which are used to protect data against external threats, DLP systems perform protection and blocking tasks from the inside. Thanks to this feature of DLP, with the use of DLP, organizations have the opportunity to prevent data breaches before they are connected to the outside world. Unlike firewall or antivirus software, DLP software has the ability to receive updates automatically, while DLP software, which has a living system feature, needs to be updated manually as new sensitive data is added [16].
-
2.1 DLP Types
-
2.2 . Data Types in DLP
DLP is a technology developed to prevent data leaks and ensure the secure protection, sharing and processing of private and sensitive data in organizations. DLP systems are used in four environments: Network, Endpoint, Storage and Cloud. The data in these environments are protected against data breaches by providing monitoring and protection in every environment of storage, processing, transmission by using DLP technology [17]. The solutions offered by DLP systems in four different environments and which data sources these environments provide monitoring and protection strategies are shown in Fig. 2.
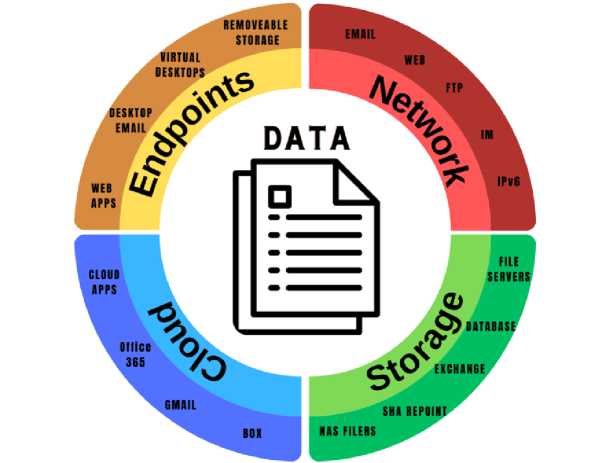
Fig. 2. DLP types and protection areas
DLP types provide protection of sensitive and private data in network, endpoint, cloud and storage environments at network and device level. Each DLP type has advantages and disadvantages specific to these environments while providing protection for data transmitted to different environments [18]. The features, advantages and disadvantages of DLP types are given comparatively in Table 2.
Table 2. Comparison of DLP types and their characteristics
|
DLP Type |
Features |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Network DLP |
|
Controls all data flow on the network |
It cannot monitor in-device movements that do not take place over the network. |
|
Endpoint DLP |
|
Prevents user-induced data loss on devices. |
Since it only works on a device-by-device basis, it cannot monitor data movements in network traffic. |
|
Storage DLP |
|
It detects confidential data in systems that store large amounts of data and prevents unauthorized access to this data. |
It cannot track dynamic data movements or user-based actions. |
|
Cloud DLP |
|
Ensures data security by restricting unauthorized access to data in cloud environments. |
It is ineffective for data where cloud systems are not used. Also, the presence of encryption requirements can affect the performance of the system. |
DLP systems provide solutions for unauthorized use, monitoring and protection of sensitive data. DLP systems have three main features. First, they can analyze the content of the data and the surrounding context. Second, they can be used to protect sensitive data in different situations such as use and rest [19]. The third is the ability to protect data through actions such as informing, inspecting, blocking, encrypting and quarantining. Traditional security systems are less dependent on the actual content of the data. In these systems, security breaches cannot be tracked in real time. The fact that DLP systems depend on the content of the data and have the ability to track data breaches in real time makes the use of DLP mandatory in organizations [20].
DLP systems prevent data leaks by providing protection for both structured and unstructured data. Structured data is data that is created according to a specific format and layout and can be easily searched and analyzed. This data is stored in software with a specific format, such as databases, word or pdf files, spreadsheets, etc. Unstructured data is data that does not have a specific layout or format structure. These free-format data such as text, images, videos, etc. can be found in file systems, e-mail, social media content, documents and presentation files. Unstructured data is more difficult to search, analyze and preserve than structured data because it can come in a wide variety of formats. If DLP systems are used to protect both structured and unstructured data, data classified as sensitive can be defined in three different states: at rest, in use and in motion [21].
2.2.1. Data at Rest
2.2.2 Data in Use
2.2.3. Data in Motion
3. Comparison And Evaluation of DLP Software3.1. Preparation of Test Environment
Data at rest is defined as all data contained in a computer or storage device. Security measures such as data encryption and access control are widely used to prevent unauthorized access, theft or modification of data at rest [22]. With DLP systems, a scanning process is performed to access the data at rest, which is defined as sensitive. This scanning process is performed according to a predefined, special content, file name or a specially defined rule to view the data.
A DLP data type that is frequently accessed and updated by multiple users on a network. This data type is linked to sensitive and confidential data and is therefore categorized as an active data type. Data that is being worked on by an end user at a network endpoint, such as a computer, is defined as in use. DLP systems apply a rule defined by the policies created by the user to perform update operations on sensitive data in use. In addition to the transfer of this sensitive data in use, the system has the ability to take action in copy-paste operations. This data is usually monitored on the endpoint device while being transported to peripheral devices via different transmission channels and is blocked or restricted if data breach is detected [20-21].
It is the type of data that is in constant motion within the network and is transmitted through many communication devices, such as email, instant messaging, cloud and portable devices or other outlets. Sensitive data in motion is likely to be exposed to various threats such as user error, network errors, malicious file sharing, illegal actions. DLP systems scan network traffic for sensitive data in motion for end-user or other potentially dangerous situations and do not allow this data to experience a data breach [23]. The protection here involves implementing solutions at gateways to monitor, encrypt, filter and intercept sensitive data in the outbound direction without restricting the flow of non-sensitive communications. Furthermore, this system provides solutions at gateways to track, encrypt, filter and intercept sensitive data with no restrictions defined on the transmission of non-sensitive data.
In today's digital world, preventing data breaches plays a critical role in organizations' efforts to ensure information security, availability and integrity. DLP solutions are one of the powerful security measures used to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. In order to be effective in data loss prevention policies, organizations should examine the features of DLP solutions available in the market and choose accordingly.
The 17 DLP software selected for evaluation were chosen based on their high usage rate in industry reports, compatibility with different operating systems and compliance with globally accepted security standards. This selection was made in order to minimize possible biases by including products that are widely accepted in the industry.
Windows server, Ubuntu server and Windows 10 operating systems at the end-user level were installed on the virtual machine to use the demo versions of the 17 different DLP products and to test the features on the web pages. These three operating systems were configured according to the technical requirements of each DLP application and installed on the relevant operating system. Moving and static data were tested on the test machines and on the end-user machine with data stored in word, pdf, jpg, png files. In addition, the basic personal and corporate data given in Table 3 were preferred for data classification in order to address many end users and organizations.
Table 3. Preferred personal and organizational data
|
Personal Data |
Phone, E-mail, ID No, IBAN, Address, Credit Card information, Password, Username. |
|
Organizational Data |
Phone, E-mail, Tax, IBAN, Health No, Check / Bill image, Database backup file information. |
In the performance evaluation of DLP software, User Behavior Analytics (UBA), Data Classification Device Control, File Fingerprinting and OCR/ICR Support were tested. The Unique Features section given in Table 3 was taken from the technical documentation of the relevant DLP software and evaluated. The reasons for choosing the features used in performance comparison and their importance levels are explained as follows:
-
• User Behavior Analytics: A criterion that aims to detect abnormal or suspicious activity by analyzing users' normal behavior patterns. In DLP software, this feature is used to identify and prevent insider threats (for example, intentional or unintentional data leaks by employees).
-
• Data Classification: It is a criterion that allows the data within the organization to be categorized according to the sensitivity level. This criterion in particular allows DLP software to understand which data needs to be protected and implement policies accordingly.
-
• Device Control: A criterion that controls the use of devices such as USB drives, external disks and other removable storage devices. DLP software using this criterion prevents data leaks by preventing data from being copied or moved to unauthorized devices.
-
• File Fingerprinting: This criterion, which allows files to be uniquely identified, is especially important for monitoring and protecting sensitive documents. With this feature, DLP software can prevent certain files from being shared or moved by unauthorized persons or track whether files have been modified.
-
• OCR/ICR Support: By identifying text in image files and allowing DLP software to scan such files, this criterion ensures the protection of sensitive information, especially in images containing text, such as scanned documents or photos. This reduces the risk of data leakage and extends security coverage.
-
• Unique Features: Every DLP software offers unique features to differentiate itself from the competition. These features reveal the advantages and differences of the software compared to others. This heading is used to evaluate the innovative aspects of the software.
-
3.2. Evaluation of DLP Software’s
In the evaluation of DLP software, a test was performed manually on real-world scenarios. The test analyzed the DLP behavior of personal and corporate data in virtual machines by causing leakage through different processes such as USB, CD/DVD, cloud resources, office software, e-mail or ftp server.
The comprehensive features of 17 different DLP solutions used today are given comparatively in Table 4. The 17 DLP software selected for evaluation were chosen based on their high usage rate in industry reports, compatibility with different operating systems and compliance with globally accepted security standards. This selection was made in order to minimize possible biases by covering products that are widely accepted in the industry.
The main purpose of the table is to analyze the level of protection provided by the DLP solution in terms of ensuring data security for specific data types and sources of organizations and to reveal which solutions are more effective. Each DLP solution has many different features unique to itself. However, in the table, features such as User Behavior Analytics (UBA), Data Classification, Device Control, File Fingerprinting and OCR/ICR Support, which are considered necessary and important to prevent data breaches, are used for comparison. The superior features of each solution are also shown in the table. As can be seen in the table, most of the DLP solutions of different brands are similar in the criteria used for comparison. This comparison will show the resilience of DLP solutions against different attack scenarios and data sources, making it easier for organizations to choose which solution is most suitable for their organization. It will also provide guidance in determining which features in a DLP solution minimize which security risks.
Within the scope of the comparison given in Table 4, the notable advantages of DLP software are evaluated as follows.
Acronis Advanced DLP and CoSoSys Endpoint Protector DLP appear to have versatile features and robust security infrastructure.
-
• CoSoSys provides high-level data security with multi-OS support, advanced device control and AES-256 encryption. CoSoSys seems to be an ideal option for organizations that attach importance to international security standards with its feature compatible with global regulations. With its flexible structure, it is a solution that can be preferred by sectors that require precision in data classification.
-
• Acronis Advanced DLP, on the other hand, is seen to have the feature of automatic policy creation according to user behavior with too many control channels. It also has various integrated security features such as centralized cyber protection console, backup and malware protection. Offering a multi-layered security solution with these features, Acronis can provide protection against other cyber threats as well as preventing data breaches.
-
• Microsoft DLP solutions, which have the Microsoft ecosystem, offer easy-to-use features for organizations with their own operating system infrastructure. Thanks to its customized data classification support, it is preferred to ensure data security of institutions.
-
• Forcepoint DLP stands out with its user risk scoring feature and has the ability to effectively track users' security risks.
-
• Proofpoint Enterprise DLP is known for its fast and detailed security audit feature with real-time alert notification and advanced features in analyzing content.
-
• Safetica DLP solution, which has a cloud-based structure, complies with international regulations such as GDPR, Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS), and detects data leaks caused by user errors thanks to the machine learning feature in its systems.
-
• Symantec DLP, on the other hand, offers rapid response for organizations in ensuring data security with its one-click response and fine-tuning features.
-
• Trellix DLP solution, which belongs to Trellix, which was established in 2022 with the merger of FireEye and McAfee Enterprise, offers the opportunity to integrate different security systems with the ePolicy Orchestrator feature. This provides a centralized and comprehensive security solution from a single console.
-
• Vatos offers a versatile and effective protection service thanks to its features such as real-time event monitoring, offline usage feature, artificial intelligence-based classification to protect the data of organizations.
Within the scope of the comparison given in Table 4, the critical shortcomings of DLP software are evaluated as follows.
-
• The fact that Code 42 DLP and Code 42 DLP do not support File Fingerprinting and OCR/ICR has resulted in many critical sensitive data not being detected.
-
• Code 42 DLP's lack of device control indicates that data leakage may occur from external sources such as USB.
-
• Cyberhaven DLP does not support File Fingerprinting, which results in the omission of Special Format or Unstructured Data.
4. Conclusion
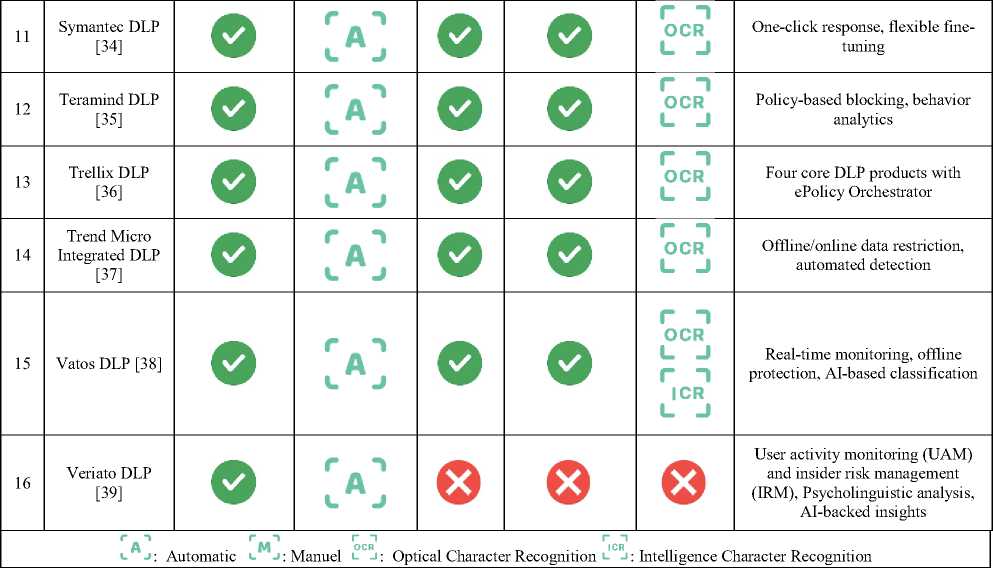
Table 4. Comparison table of commonly used DLP software.
|
Id |
DLP Solution |
User Behavior Analytics (UBA) |
Data Classification |
Device Control |
File Fingerprinting |
OCR/ICR Support |
Unique Features |
|
1 |
Acronis Advanced DLP [24] |
о |
X |
о |
© |
и°€ |
70+ controlled channels; behaviorbased automatic policy creation; centralized cyber protection console integrating DLP, backup, malware protection, and more. |
|
2 |
CleverControl DLP [25] |
о |
UMJ |
о |
© |
Real-time employee monitoring, user-friendly interface, for small to medium-sized businesses |
|
|
3 |
Code 42 DLP [26] |
о |
UMJ |
© |
© |
© |
Insider threat focused, file activity monitoring |
|
4 |
CoSoSys Endpoint Protector DLP [27] |
о |
с< |
© |
© |
и°€ |
Offers multi-OS support, advanced device control, military-grade AES-256 encryption, and compliance with global regulations. |
|
5 |
Cyberhaven DLP [28] |
о |
© |
и°€ |
Real-time activity monitoring, browser data leverage |
||
|
6 |
Digital Guardian DLP [29] |
о |
© |
© |
и°€ |
Automatically classifying data |
|
|
7 |
Forcepoint DLP [30] |
о |
© |
© |
и°€ |
Unified console, user risk scoring |
|
|
8 |
Microsoft DLP [31] |
о |
© |
© |
и°€ |
Microsoft ecosystem integration, specialized classification |
|
|
9 |
Proofpoint Enterprise DLP [32] |
о |
© |
© |
и°€ |
Real-time alert review, advanced content analysis |
|
|
10 |
Safetica DLP [33] |
о |
X |
© |
© |
и°€ |
Cloud-based, easy setup, supports compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS; behavior-based risk assessment, automatic event detection, and machine learning for identifying real data leaks from user errors. |
A comparative examination of the features of DLP solutions against different data types and sources is thought to be an important guide for future research in these areas and strategies to be determined to prevent data loss. This comparison will not only facilitate the security teams of organizations to determine which DLP solutions are more suitable for their organizations, but also to determine which features of a DLP solution minimize which security risks, and thus to determine the most suitable solution for them according to their own security risk assessment strategies. In the future, companies that will work on DLP solutions and researchers who will research these solutions should focus on the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning to detect data leaks faster and more accurately. In particular, DLP solutions developed with deep learning algorithms will provide more successful results in analyzing user behavior, automatic classification of data types and sources, and content-based scans. Most of the DLP solutions given as a comparison in the study widely use cloud-based data loss prevention solutions. Ensuring the full integration of DLP solutions into these systems to prevent data leaks in cloud storage and IoT devices, which are components of Industry 4.0, is another area that needs to be worked on. As a result, this comparative analysis, in addition to being a guide in determining the DLP solutions of organizations, sets an important framework in determining which features should be included with artificial intelligence integration in DLP solutions that need to be developed to prevent data leaks more effectively. Thus, in a rapidly developing and increasing digital threat environment, organizations will increase their ability to protect their sensitive data against malicious people and attacks, and the security strategies offered by DLP solutions to organizations will become more powerful, flexible, reliable and efficient.


