Роль маркеров острого повреждения почки в оценке функции почки при ее ишемии
Автор: Мирошкина И.В., Грицкевич аА., Байтман Т.П., Пьяникин С.С., Аревин А.Г., Калинин Д.В., Демидова В.С., Теплов А.А.
Журнал: Экспериментальная и клиническая урология @ecuro
Рубрика: Детская урология
Статья в выпуске: 4, 2018 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В настоящее время установлены различные биомаркеры острой почечной недостаточности (ОПН). Данные биомаркеры обнаруживаются в моче или крови и характеризуют структурное повреждение почки. В клинике они используются как дополнительные биомаркеры повреждения к креатинину, и используются для дифференциальной диагностики и прогностической оценки ОПН. Наиболее очевидными требованием к биомаркерам является отражение ими патофизиологии болезни. К сожалению, установленные функциональные биомаркеры скорости клубочковой фильтрации, такие как креатинин сыворотки крови, мочевина выявляются только через 24 - 48 часов. Новые биомаркеры повреждения почек указывают на почечную травму на начальном этапе развития ОПН. В статье приведен обзор современных биомаркеров повреждения почки - их патофизиологическая основа, клиническая эффективность и функциональная значимость. Основное внимание уделяется тем новым биомаркерам повреждения почек, которые обладают наиболее перспективными биологическими характеристиками и клиническими доказательствами прогноза развития ОПН, таким как: липокалин, связанный с нейтафильной желатиназой, молекула повреждения почек-1, интерлейкин 18, цистатин С, креатинин, мочевина...
Острая почечная травма, биомаркеры, молекула повреждения почек 1 (kim-1), липокалин, связанный с нейтафильной желатиназой (ngal), цистатин с, креатинин, мочевина
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142216901
IDR: 142216901
Текст научной статьи Роль маркеров острого повреждения почки в оценке функции почки при ее ишемии
уществуют различные методы способные оценить функцию почек и их повреждение при различных заболеваниях и стрессовых состояний органа. Проводимые в настоящее время исследования помогают определить место новых маркеров для диагностики острого повреждения почек (ОПП) интраоперационно или же в раннем послеоперационном периоде больным, после хирургической травмы почки. Эти маркеры могут дать оценку состояния почечной паренхимы во время ишемии почки, а также выявляют воздействие фармакологических препаратов на функцию почки.
Быстрое развитие научных исследований привело к внедрению стратегий, основанных на новых маркерах, которые позволяют оценить латентный период заболевания до выявления клинических симптомов фактической почечной недостаточности [1].
Ранняя диагностика острой почечной недостаточности (ОПН), связанной с хирургическим вмешательством, с помощью новых почечных биомаркеров дает пространство для терапевтического маневра. Хирургическое вмешательство приводит к травме внутри нефрона, которая в свою очередь, приводит к потере полярности клетки и последующей ее гибели. Вследствие чего нарушаются функциональные возможности почки (рис. 1). Современные биомаркеры способны выявить нарушение на этапе повреждения нефрона до появления первых функциональных нарушений [2].
Представление об остром повреждении почек (ОПП) в наши дни подверглось существенному пересмотру. Растет число данных, указывающих на то, что острое, относительно незначительное повреждение почек или нарушение почечной функции, проявляющееся изменениями объема выделяемой мо-
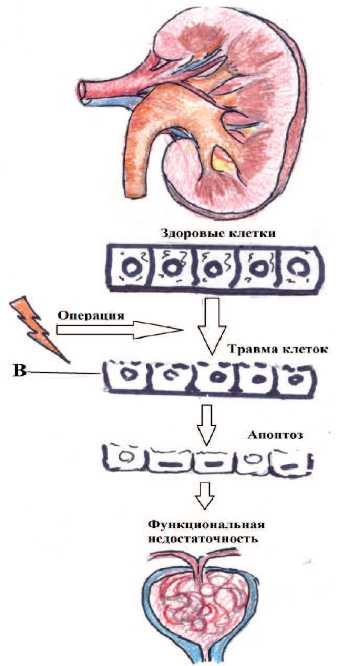
Рис. 1. Схема внутриклеточного повреждения почки, развившегося вследствие хирургического воздействия. (В - почечные биомаркеры).
чи и биохимического состава крови, имеет серьезные клинические последствия. Установлено, что у пациентов, имеющих в анамнезе ОПП, риск развития хронической почечной болезни является очень высоким.
Исторически сложилось, что мочевина стала первым маркером, который использовался для оценки функции почек. В 1827 году Richard Bright первым связал накопление мочевины в крови и ее снижение в моче у больных с заболеванием почек. В клиническую практику, как диагностический тест, в начале 1900-х было введено количественное определение азота мочевины. Несмотря на то, что оценка азота мочевины остается широко применяемым тестом при оценке функции почек, в настоящее время признается, что данный тест является субоптимальным маркером для данной цели [3].
Следующим маркером, пришедшим на смену азоту мочевины, стал креатинин. В середине 1900-х он стал широко применяться в лабораторных тестах при оценке скорости клубочковой фильтрации (СКФ) и применяется в повседневной практике по сей день. Креатинин свободно фильтруется клубочками и не реабсорбируется почечными канальцами, но он секретируется с разной скоростью. Такие лекарства, как циметадин и триметоприм, тормозят канальцевую секрецию. Также сомнительно утверждение о том, что канальцевая секреция относительно пропорциональна его клубочковой фильтрации, так как функция почки снижена, что приводит к неправильной оценке СКФ и, как следствие, увеличение креатинина сыворотки может не наблюдаться до того момента, когда СКФ существенно снизится. Еще один фактор, создающий трудности в диагностике при использовании креатинина сыворотки – это внут-рииндивидуальная и межиндивидуальная вариабельность образования креатинина. Исторически значи- тельная вариабельность, связанная с изменением креатинина в сыворотке, обычно приводит к менее точной оценке СКФ в случаях, когда концентрация креатинина в сыворотке была в пределах референсного значения или несколько ниже [4].
В наши дни ведется поиск диагностических критериев, которые могли бы на ранних этапах указать на формирование ОПП. В качестве диагностических критериев предложены биомаркеры ОПП, которые не зависят от фильтрационной функции почек.
Липокалин, связанный с ней-тафильной желатиназой (NGAL) – этот белок принадлежит к суперсемейству липокалина, которые являются секретируемыми или цитозольными белками, переносящими гидрофобные лиганды (такие как жирные кислоты, ретиноиды и феромоны) [5]. Человеческий NGAL существует как мономер или как гомодимер, а также он может существует как гетеродимер, где он конъюгирован с желатиназой и специфичен к нейтрофилам. Мономер представляет собой продукт гена, который очень быстро выделяется из поврежденных эпителиальных клеток [6]. Функции NGAL обусловлены его способностью связывать железо-сидерофорные комплексы. Он формирует бактериостатическую функцию врожденной иммунной системы путем секвестрации железо-сидерофорных комплексов и тем самым предотвращает поглощение железа бактериями [7]. Эта функция также может быть кооптирована для транспортировки железа в цитоплазму через комплексы «кате-холат-железо», где данный комплекс активирует или репрессирует гены, чувствительные к железу. После поглощения сидерофора, связанный NGAL перемещается в эндосому, от комплекса отщепляется железо. Это приводит к регуляции генов, чувствительных к железу (рис. 2А). Не связанный NGAL захватывает сиде-рофорсвязанное железо и переносит его во внеклеточное пространст- во. NGAL связывает бактериальные сидерофоры и, тем самым, ограничивает потребление железа бактериями и регулирует потребление железа клетками организма (рис. 2Б) [8].
Данный белок (NGAL) был открыт в 1993 году и вскоре получил признание у нефрологов в качестве маркера ОПП. Причиной повышенного интереса к данному белку явилось то обстоятельство, что при остром повреждении в моче преобладает «ренальный» пул NGAL, синтезируемый в почках, и не поступающий в систему кровообращения. Повышение синтеза NGAL в клетках проксимальных канальцев связано с ишемией почечной паренхимы и ее поражениями нефротоксическими соединениями. Плазменный NGAL свободно фильтруется гломерулами, большая его часть эффективно реабсорбируется в проксимальных канальцах мегалинза-висимым эндоцитозом, возвращая
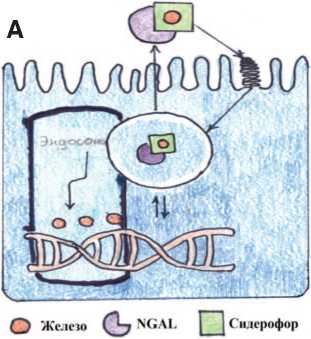
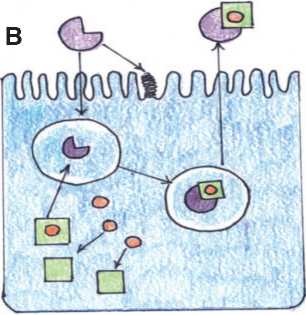
Рис. 2. Схематическая модель транспортной функций NGAL
A - регуляции генов, чувствительных к железу. В - регуляция потребления железа клетками организма.
таким путем железо клеткам. В моче NGAL появляется только при повреждении проксимальных канальцев за счет роста синтеза NGAL de novo в дистальных отделах нефрона, что и происходит при ОПП. В ответ на повреждение ренальных канальцев уровень NGAL возрастает в плазме крови в 7-16 раз (уровень сывороточного NGAL (s-NGAL)) и в моче в 25-1000 раз (уровень NGAL в моче (u-NGAL)). Экскреция NGAL с мочой на 24-48 часов опережает повышение концентрации креатинина в сыворотке крови. Рост концентрации NGAL в моче наблюдается при ОПП, остром тубулярном некрозе или тубулоинтерстициальной нефропатии [9-11].
В 2011 году было проведено исследование, которое поставило своей целью проверить гипотезу о том, что без изменения креатинина сыворотки крови у пациентов с субклинической ОПН повышается уровень NGAL, что может определить дальнейший прогноз таких больных. В исследовании были проанализированы данные 2 322 пациентов с кардиоренальным синдромом из 10 проспективных независимых исследований. В исследовании использовались NGAL (-) и NGAL (+), для оптимального прогнозирования ОПП и термины Креатинин (-) или Креатинин (+). Априорные исходы включали необходимость применения заместительной почечной терапии, летальные исходы, их сочетание и продолжительность пребывания в реанимации и стационаре. На основе проведенных исследований ученые пришли к выводу, что при отсутствии диагностического повышения уровня креатинина в сыворотке крови повышение уровня NGAL выявляется у пациентов с вероятной субклинической ОПП [12].
В 2015 году в Мельбурне проведено исследование, которое оценивало способность NGAL прогнозировать у кардиохирургических больных ОПН, а также влияние искусственного кровообращения на уровень NGAL. В исследование бы- ло включено 288 кардиохирургических больных старше 18 лет. NGAL измерялся в начале исследования, сразу после операции и в 1, 2 дни послеоперационного периода. Было установлено, что NGAL может использоваться как маркер повреждения при развитии ОПП и его уровень тесно связан с продолжительностью искусственного кровообращения [13].
Таким образом, был сделан вывод о пограничных уровнях NGAL, позволяющих с оптимальной чувствительностью и специфичностью предсказывать ОПП. Установленные в разных исследованиях и у пациентов с ОПП разных этиологий, значения NGAL находятся в диапазоне 100 – 270 нг/мл. Для рутинного измерения NGAL с целью диагностики и прогнозирования ОПП рекомендуется пограничный уровень NGAL, разный 150 нг/мл [14].
Цистатин С – хорошо изученный современный маркер ОПП. В качестве маркера повреждения почек цистатин С оценивают в двух средах: сыворотке крови и в моче. Сывороточный цистатин С – белок, принадлежащий ко 2-й группе генетического семейства цистатинов. Цистатин С содержится в плазме крови человека, функцию выведения белка из организма осуществляют почки [10-11]. Цистатин С представляет собой негликозилиро-ванный белок с молекулярной массой 13,4 кДа и изоэлектрической точкой при рН 9,3. Относится к семейству ингибиторов цистеиновых протеиназ, идентичен пост-гамма-глобулину; впервые идентифицирован у пациентов с почечной недостаточностью как белок спинномозговой жидкости и мочи [15]. Сывороточная концентрация цистатина С, в отличие от креатинина, не зависит от питания, массы тела, пола, возраста. Поэтому как эндогенный биомаркер почечной функции он близок к идеальному и показывает лучшие результаты по сравнению с креатинином [10,11]. Исходно высокие при рождении уровни циста- тина С в первый год жизни снижаются и остаются стабильными до 50 лет, а затем повышаются. В большинстве исследований обнаружено, что референтный интервал значений концентрации цистатина С в сыворотке составляет для женщин 0,52 – 0,90 мг/л со средним значением 0,71 мг/л и 0,56 – 0,98 мг/л – для мужчин, среднее значение – 0,77 мг/л [16]. Цистатин С мочи в настоящее время являться индикатором количественной оценки тяжести канальцевых нарушений [11].
Цистатин С является одним из самых точный эндогенных маркеров и по своим диагностическим возможностям значительно превосходит креатинин, также высокочувствительный маркер при кардиохи-рургичеких вмешательствах, независимый от каких-либо кардиомаркеров (кардиальные тропонины, натрийуретические пептиды, С-ре-активный белок) [17-22]. Впервые уровень цистатина C мочи был определен в 1979 г. и составил 0,095± 0,057 мг/л [23]. На данный момент установлена связь между уровнем цистатина C мочи и концентрацией креатинина в моче, что было выявлено у пациентов с персистирующей протеинурией. Установлена также связь уровня креатинина с возрастом и количеством мышечной массы (средний уровень креатинина мочи возрастает с возрастом и увеличением мышечной массы). В то же время уровень цистатина С не зависит ни от одного из этих факторов. Уровень цистатина С мочи четко отражает эффективность реабсорбции цистатина С в проксимальных канальцах. В том случае, если соотношение цистатина С мочи и креатинина мочи находится в нормальном диапазоне, то цистатин С более точно отражает фильтрационную способность клубочков [24].
Молекула-1 поражения почек (KIM-1) – трансмембранный гликопротеин 1-го типа, который в норме присутствует в почечной ткани в минимальном количестве. В результате ишемического или нефротоксического ОПП происходит его значительное увеличение в клетках проксимальных почечных канальцев. KIM-1 является ранним неинвазивным биомаркером для ОПП, связанного с повреждением проксимальных почечных канальцев [9-11]. KIM-1 действует как фосфатидилсериновый рецептор, связывающий апоптотические тельца. KIM-1 связывается с альфа-субъединицей ге-теротримерного белка G12, тем самым опосредуя фагоцитоз апоп-тотических телец (рис. 3). Внеклеточный домен KIM-1 выводится с поверхности клетки металлопротеиназой [8].
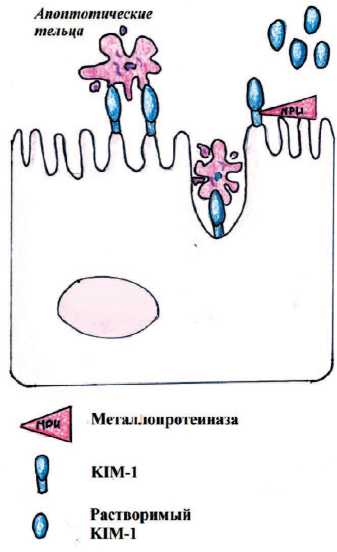
Рис. 3. Схема действия KIM-1 при фагоцитозе апоптотических телец
Имеются исследования, подтверждающие экспрессию KIM-1 в клубочках, в ходе очагового клубочкового некроза почек, нефропатии IgA или мембранно-пролиферативной гломерулопатии. У пациентов с высокой степенью протеинурии в результате хронического повреждения клубочков чаще развивается ОПП. На этом основании можно утверждать, что KIM-1 может является маркером повреждения почек [25- 26].
Особая значимость KIM-1 была обнаружена при остром повреждении канальцев, которые могут быть следствием гипоксии (шок, обширное хирургическое вмешательство, трансплантация почки), септического или токсического повреждения почек, повреждения индуцированного контрастными, антибактериальными, противогрибковыми и цитотоксическими препаратами. Появляется KIM-1 в моче в первый день после токсического или ишемического повреждения канальцев почек, в то время как креатинин плазмы увеличивается только на третий день. Более того, было отмечено увеличение концентрации KIМ-1 через час после хирургического вмешательства [27-28].
Экспериментальные испытания, проведенные на животных и генетическом материале, полученном из проксимального канальца, позволили обнаружить гены, которые индуцируются в начале и после повреждения почки. Белковые продукты этих генов можно рассматривать как полезные маркеры для диагностики почечной недостаточности. Индукция гена KIM-1 (называемая молекулярной патологией почек-1) приводит к образованию белка, который можно рассматривать как диагностический маркер. Также КИМ-1 является еще и маркером почечно-клеточного рака (ПКР) до проявления клинических признаков. Группой ученых нескольких европейских стран было проведено исследование, в ходе которого удалось доказать значимость КИМ-1 при ранней диагностике ПКР. Так, повышение концентрации в плазме крови КИМ-1 может предсказать развитие ПКР за 5 лет до установления диагноза и, как следствие этого, может повлиять на выживаемость больных [29].
Интерлейкин-18 (ИЛ-18) – провоспалительный цитокин, принадлежащий к семейству интерлейкина 1. Синтезируется макрофагами и другими клетками организма. Был впервые открыт в 1995 году в каче- стве интерферон-гамма-индуциру-ющего фактора, который увеличивал активность клеток естественных киллеров в селезенке, причем его активность выше, чем у интерлейкина 12 [30]. ИЛ-18 является про-воспалительным цитокином, продуцируемым в проксимальных канальцах, и определятся в моче у больных с ишемическим ОПП. Кроме того, было обнаружено, что увеличение концентрации ИЛ-18 мочи в раннем послеоперационном периоде позволяет предсказать развитие ОПП в течение ближайших 24 часов с вероятностью 73%. Установлено, что повышение концентрации ИЛ-18 опережает повышение концентрации креатинина сыворотки крови на 4872 часа. Повышение концентрации ИЛ-18 в моче более 100 пг/мл указывает на ОПП [10-11]. ИЛ-18 играет активную роль в различных процессах почечных заболеваний, включая апоптоз, ишемию/реперфузию, отторжение аллотрансплантата, инфекцию, аутоиммунные состояния и злокачественность.
Белок, связывающий печеночные жирные кислоты (L-FABP) представляет собой протеин, который в норме проявляется в проксимальных извитых и прямых канальцах почек. В случае ОПП повышение L-FABP определяется в первые 24 часа, в то время как повышение креатинина отмечается только через 72 часа [9-11]. L-FABP представляет собой белок из большого надсемейства липидсвязывающих белков [31]. Общей функцией всех членов этого семейства является внутриклеточный транспорт. L-FABP переносит альбумин в митохондрии и пероксисомы, в которых белок метаболизируется. В почках L-FABP преимущественно располагается в проксимальных канальцах и выводится вместе со связанными токсичными продуктами окисления, в случае травмы почек данные продукты накапливаются в клетках почки [32].
L-FABP является новым потенциальным биомаркером почечной дисфункции. В Дании провели диагностическое исследование, представлявшее собой анализ информативности экскреторного мочевого L-FABP в отношении установленных маркеров риска, таких как артериальное давление, экскреция альбумина и СКФ, относительно прогрессирования хронической почечной недостаточности (ХПН). Было установлено, что уровень экскреторного мочевого L-FABР постоянно повышается у пациентов с ХПН, но коррелирует только со снижением СКФ у пациентов без альбуминурии [33].
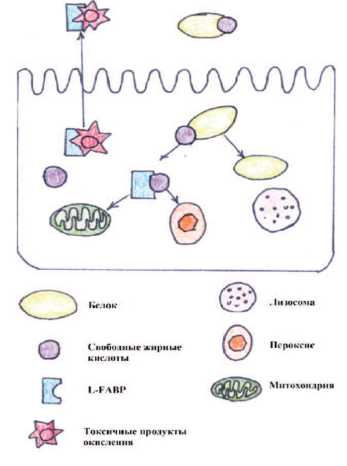
Рис. 4. Схематическая модель транспортной функции L-FABP. L-FABP транспортирует свободные жирные кислоты в митохондрии и пероксисомы, а затем L-FABP выводится из клетки вместе с токсичными продуктами окисления.
Резюме:
В настоящее время установлены различные биомаркеры острой почечной недостаточности (ОПН). Данные биомаркеры обнаруживаются в моче или крови и характеризуют структурное повреждение почки. В клинике они используются как дополнительные биомаркеры повреждения к креатинину, и используются для дифференциальной диагностики и прогностической оценки ОПН. Наиболее очевидными требованием к биомаркерам является отражение ими патофизиологии болезни. К сожалению, установленные функциональные биомаркеры скорости клубочковой фильтрации, такие как креатинин сыворотки крови, мочевина выявляются только через 24 – 48 часов. Новые биомаркеры повреждения почек указывают на почечную травму на начальном этапе развития ОПН. В статье приведен обзор современных биомаркеров повреждения почки – их патофизиологическая основа, клиническая эффективность и функциональная значимость. Основное внимание уделяется тем новым биомаркерам повреждения почек, которые обладают наиболее перспективными биологическими характеристиками и клиническими доказательствами прогноза развития ОПН, таким как: липокалин, связанный с нейтафильной желатиназой, молекула повреждения почек-1, интерлейкин 18, цистатин С, креатинин, мочевина. Данные биомаркеры расширяют терапевтическое окно, с помощью которого становится возможной индивидуальная терапия для каждого отдельно взятого пациента. Применение данных биомаркеров в клинической практике помогает своевременно выявлять ОПН, что в свою очередь способствует снижению частоты серьезных осложнений.
Список литературы Роль маркеров острого повреждения почки в оценке функции почки при ее ишемии
- Gaiäo SM, Paiva JAOC. Biomarkers of renal recovery after acute kidney injury. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva 2017;29(3):373-381 DOI: 10.5935/0103-507X.20170051
- Ronco C, McCullough P, Anker SD, Anand I, Aspromonte N, Bagshaw SM, et al. Cardio-renal syndromes: report from the consensus conference of the аcute dialysis quality initiative. Eur Heart J 2010;31 (6):703-11 DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehp507
- Steensma DP, Kyle RA. A history of the kidney in plasma cell disorders. Contrib Nephrol 2007;153:5-24 DOI: 10.1159/000096757
- Pasala S, Carmody JB. How to use.. serum creatinine, cystatin C and GFR. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed 2017; 102(1):37-43. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2016-311062.
- Schiefner A, Skerra A. The menagerie of human lipocalins: a natural protein scaffold for molecular recognition of physiological compounds Acc Chem Res 2015;48(4):976-85 DOI: 10.1021/ar5003973
- Cai L, Rubin J, Han W, Venge P, Xu S. The origin of multiple molecular forms in urine of HNL/NGAL. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2010;5(12):2229-35 DOI: 10.2215/CJN.00980110
- Bao GH, Ho CT, Barasch J. The Ligands of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin. RSC Adv 2015;5(126):104363-104374.
- Schrezenmeier EV, Barasch J, Budde K, Westhoff T, Schmidt-Ott KM. Biomarkers in acute kidney injury -pathophysiological basis and clinical performance. Acta Physiol 2017;219(3):556-574. doi: 10.1111/apha.12764.
- Смирнов А.В., Каюков И.Г., Добронравов В.А., Кучер А.Г.: Острое повреждение почек -новое понятие в нефрологии. Клиническая нефрология 2009;(1):11 -15;
- Смирнов А.В., Добронравов В.А., Румянцев А.Ш., Шилов Е.М., Ватазин А.В., Каюков Ю.Г. и др. Национальные рекомендации. Острое повреждение почек: основные принципы диагностики, профилактики и терапии. Часть I. Нефрология 2016;20(1):79 -104;
- Уразаева Л.И., Максудова А.Н. Биомаркеры раннего повреждения почек: обзор литературы. Практическая медицина 2014;1 (4):125 -130;
- Haase М, Devarajan Р, Haase-Fielitz А, Pharm D, Bellomo R, Wagener G, et al. The Outcome of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL)-positive subclinical acute kidney injury: a multicenter pooled analysis of prospective studies. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011;7(17):1752-1761 DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.11.051
- Garcia-Alvarez M, Glassford NJ, Betbese AJ, Ordonez J, Banos V, Argilaga M, et al. Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as predictor of short or long-term outcomes in cardiac surgery patients. Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 2015;29(6):1480-8. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2015.05.060
- Haase M, Bellomo R, Devarajan P. Accuracy of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in diagnosis and prognosis in acute kidney injure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis 2009;54(6):1012-1024.
- Zhai JL, Ge N, Zhen Y, Zhao Q, Liu C. Corticosteroids Significantly Increase Serum Cystatin C Concentration without Affecting Renal Function in Symptomatic Heart Failure. Clin Lab 2016;62(1-2):203-7.
- Iversen E, Bodilsen AC, Klausen H, Treldal C, Andersen O, Houlind M, Petersen J. Kidney function estimates using cystatin C versus creatinine: Impact on medication prescribing in acutely hospitalized elderly patients. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2018 Oct DOI: 10.1111/bcpt.13156
- Jalalonmuhali M, Elagel SMA, Tan MP, Lim SK, Ng KP. Estimating Renal Function in the Elderly Malaysian Patients Attending Medical Outpatient Clinic: A Comparison between Creatinine Based and Cystatin-C Based Equations. Int J Nephrol 2018;2018:3081518 DOI: 10.1155/2018/3081518
- Khosravi N, Zadkarami M, Chobdar F, Hoseini R, Khalesi N, Panahi P, Karimi A. The value of urinary cystatin C level to predict neonatal kidney injury. Curr Pharm Des 2018 Sep 17 DOI: 10.2174/1381612824666180918100819
- Herget-Rosenthal S, Bökenkamp A. Hofmann W. How to estimate GFR-serum creatinine, serum cystatin C or equations? Clin Biochem 2007;40(3-4):153-61.
- Tidman M, Sjöström P, Jones I. A Comparison of GFR estimating formulae based upon s-cystatin C and screatinine and a combination of the two. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2008;23(1):154-60.
- Stevens LA, Coresh J, Schmid CH. Estimating GFR using serum cystatin C alone and in combination with serum creatinine: a pooled analysis of 3,418 individuals with CKD. Am J Kidney Dis 2008;51(3):395-406.
- Sterner G, Björk J, Carlson J. Validation of a new plasma cystatin C-based formula and the modification of diet in renal disease creatinine-based formula for determination of glomerular filtration rate. Scand J Urol Nephrol 2009;43(3):242-249.
- Lofberg H, Grubb A. Quantitation of gamma-trace in human biological fluids: indications for production in the central nervous system. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 1979; 39: 619-626;
- Herget-Rosenthal S, Feldkamp T, Volbracht L. Measurement of urinary cystain C by particle enhanced nephelometric immunoassay: precision, interferences, stability, and reference range. Ann Clin Biochem 2004;41 (Part 2):111-118.
- Comnick M, Ishani A. Renal biomarkers of kidney injury in cardiorenal syndrome. Curr Heart Fail Rep 2011;8(2):99-105 DOI: 10.1007/s11897-011-0052-x
- Nijboer WN, Schuurs TA, Damman J, van Goor H., Vaidya VS, van der Heide JJ, et al. Kidney injury molecule-1 is an early noninvasive indicator for donor brain death-induced injury prior to kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant 2009;9(8):1752-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2009.02713.x.
- Liang XL, Liu SX, Chen YH, Yan LJ, Li H, Xuan HJ, et al. Combination of urinary kidney injury molecule-1 and interleukin-18 as early biomarker for the diagnosis and progressive assessment of acute kidney injury following cardiopulmonary bypass surgery: a prospective nested case-control study. Biomarkers 2010;15(4):332-9 DOI: 10.3109/13547501003706558
- Liang XL, Shi W. Beyond early diagnosis: prognostic biomarkers for monitoring acute kidney injury. Hong Kong J Nephrol. 2010;12(2):45-49.;
- Bagshaw SM. Novel biomarkers for early diagnosis of acute kidney injury. Expert Opin Med Diagn 2008;2(9):1041-54 DOI: 10.1517/17530059.2.9.1041
- Appenrodt B, Lammert F. Renal Failure in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: Novel Classifications, Biomarkers, Treatment. Visc Med 2018;34(4):246-252 DOI: 10.1159/000492587
- Gohda T, Nishizaki Y, Murakoshi M, Nojiri S, Yanagisawa N, Shibata T, et al. Clinical predictive biomarkers for normoalbuminuric diabetic kidney disease. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2018;141:62-68. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2018.04.026.
- Moriyama T, Hagihara S, Shiramomo T, Nagaoka M, Iwakawa S, Kanmura Y. The protective effect of human atrial natriuretic peptide on renal damage during cardiac surgery. J Anesth 2017;31(2):163-169. | DOI: 10.1007/s00540-016-2284-0
- Khatir DS, Bendtsen MD, Birn H, N0rregaard R, Ivarsen P, Jespersen B, et al. Urine liver fatty acid binding protein and chronic kidney disease progression. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 2017;77(7):549-554. ; DOI: 10.1080/00365513.2017.1355561
- De Loor J, Ingrid H, Francois K, Van Wesemael A, Nuytinck L, Meyer E, et al. Diagnosis of cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury: differential roles of creatinine, chitinase 3-like protein 1 and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: a prospective cohort study. Ann Intensive Care 2017; 7(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s 13613-017-0251 -z.
- Кит О.И., Франциянц Е.М., Розенко Д. А., Ушакова Н.Д., Димитриади С.Н., Погорелова Ю.А., и др. Динамика маркеров острого повреждения почек при использовании эпидуральной блокад во время резекции в условиях тепловой ишемии. Онкоурология 2017;13(4): 2533 DOI: 10.17650/1726-9776-2017-13-4-25-33


